Dynamic Generation of Airy Beam Utilizing the Full-Space Programmable Metasurface
Abstract
1. Introduction
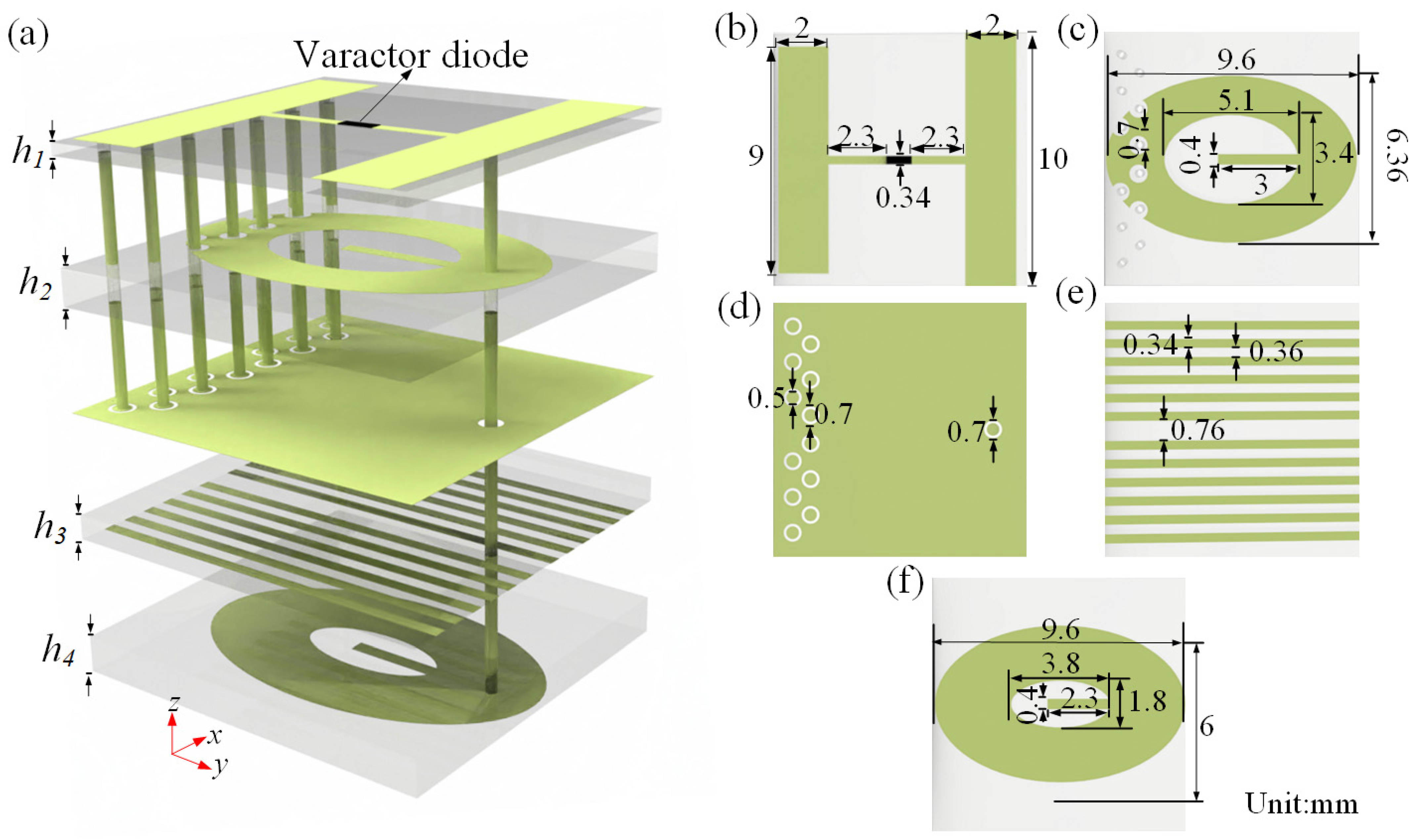
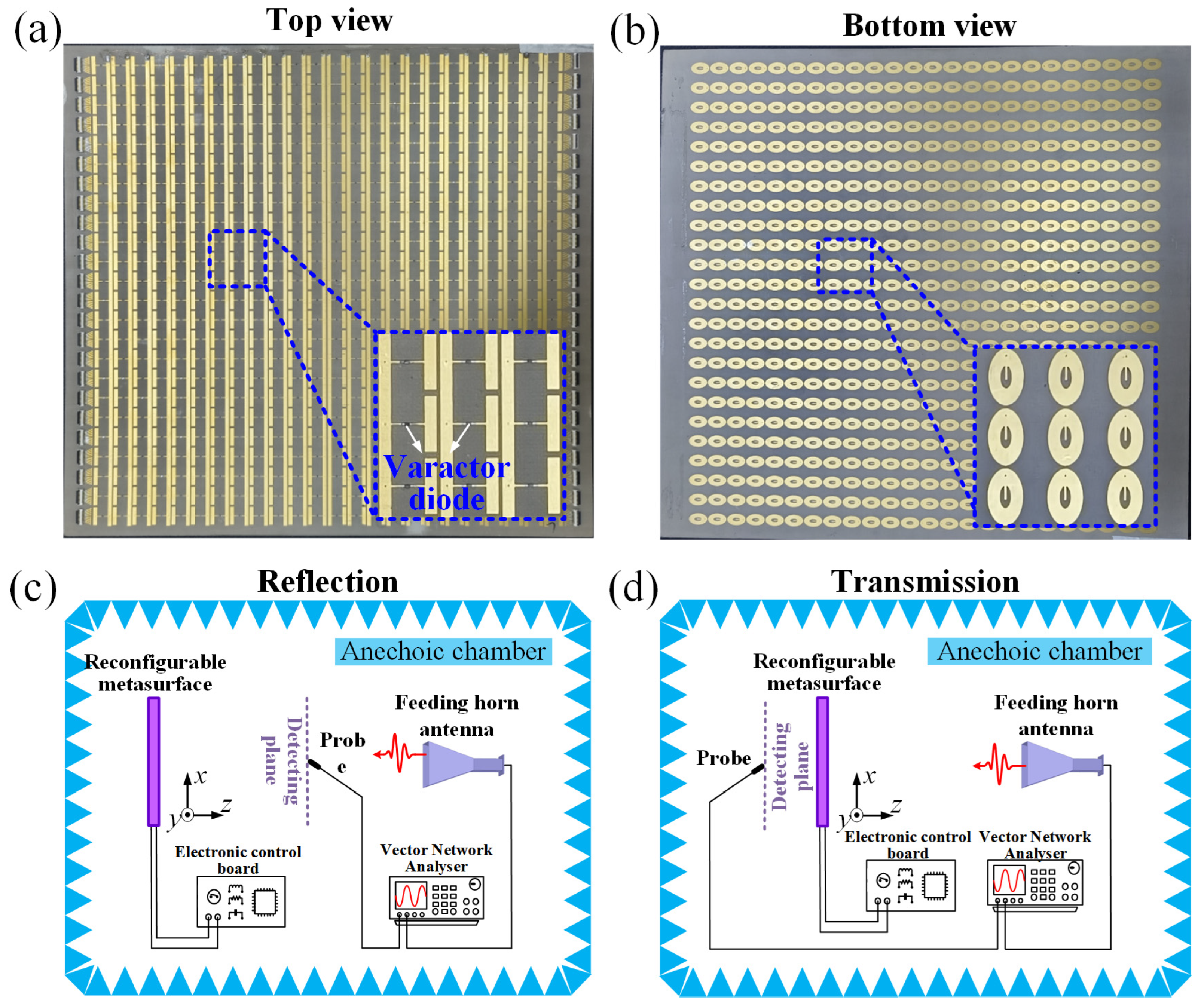
2. Programmable Metasurface Design
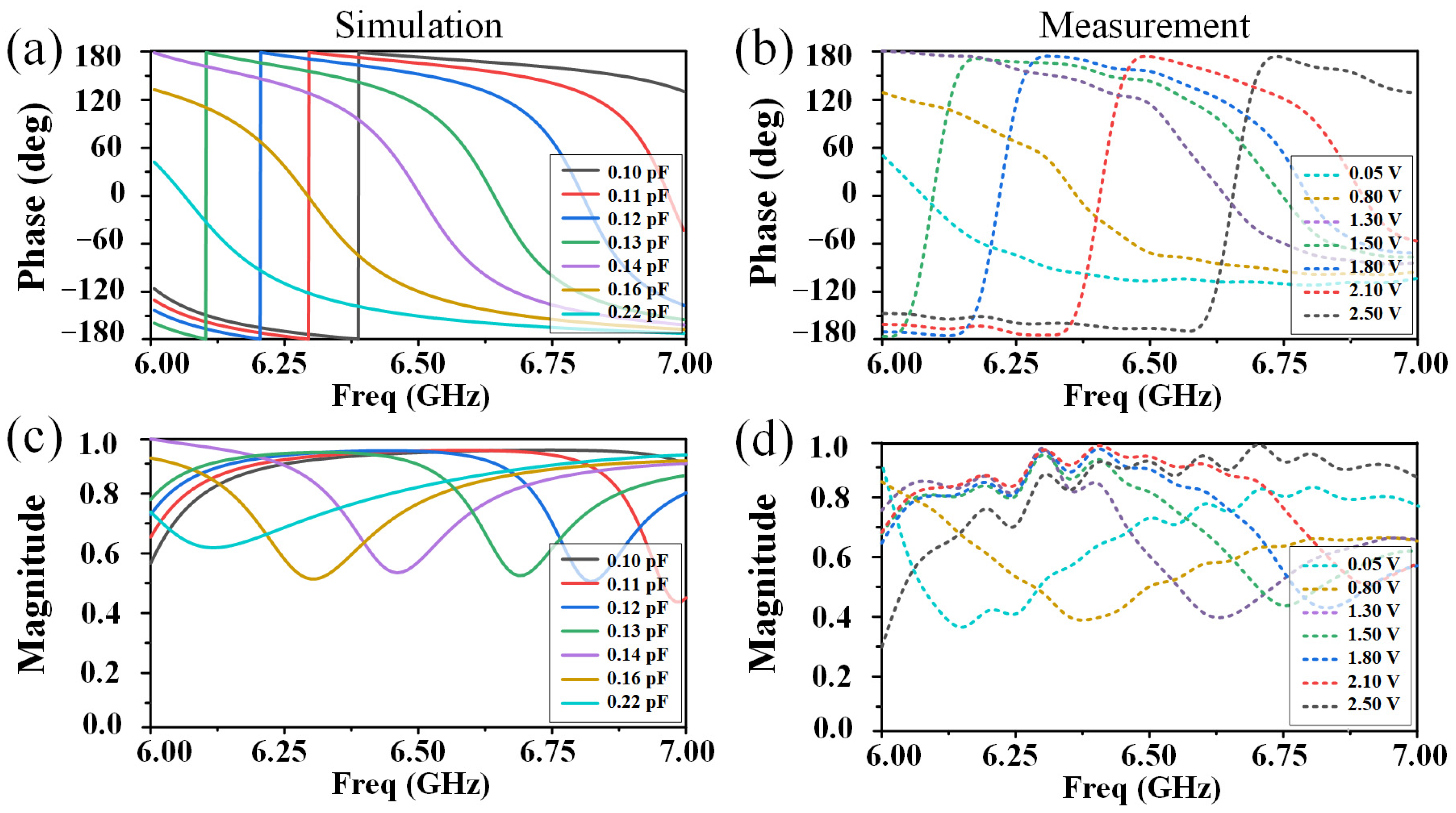
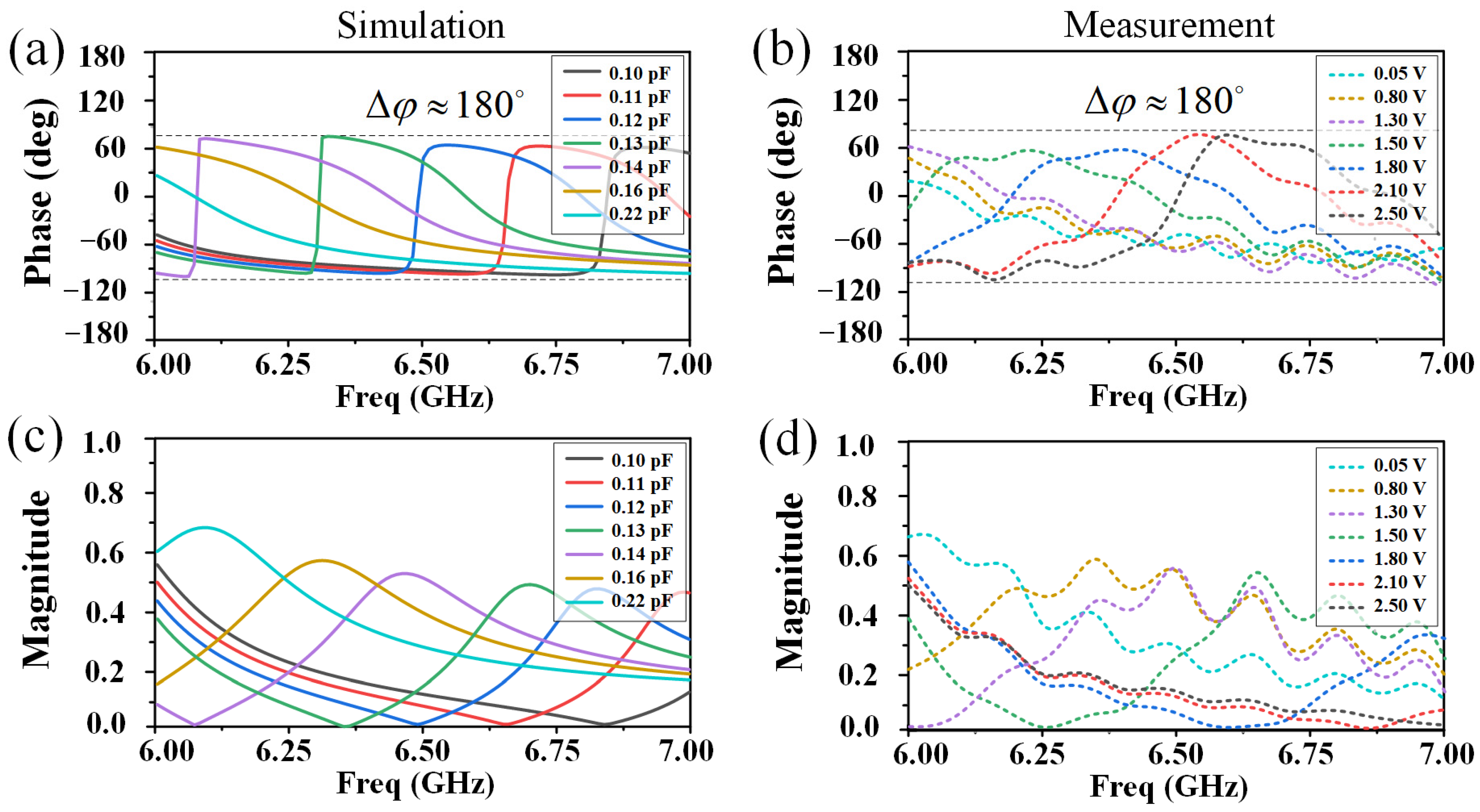
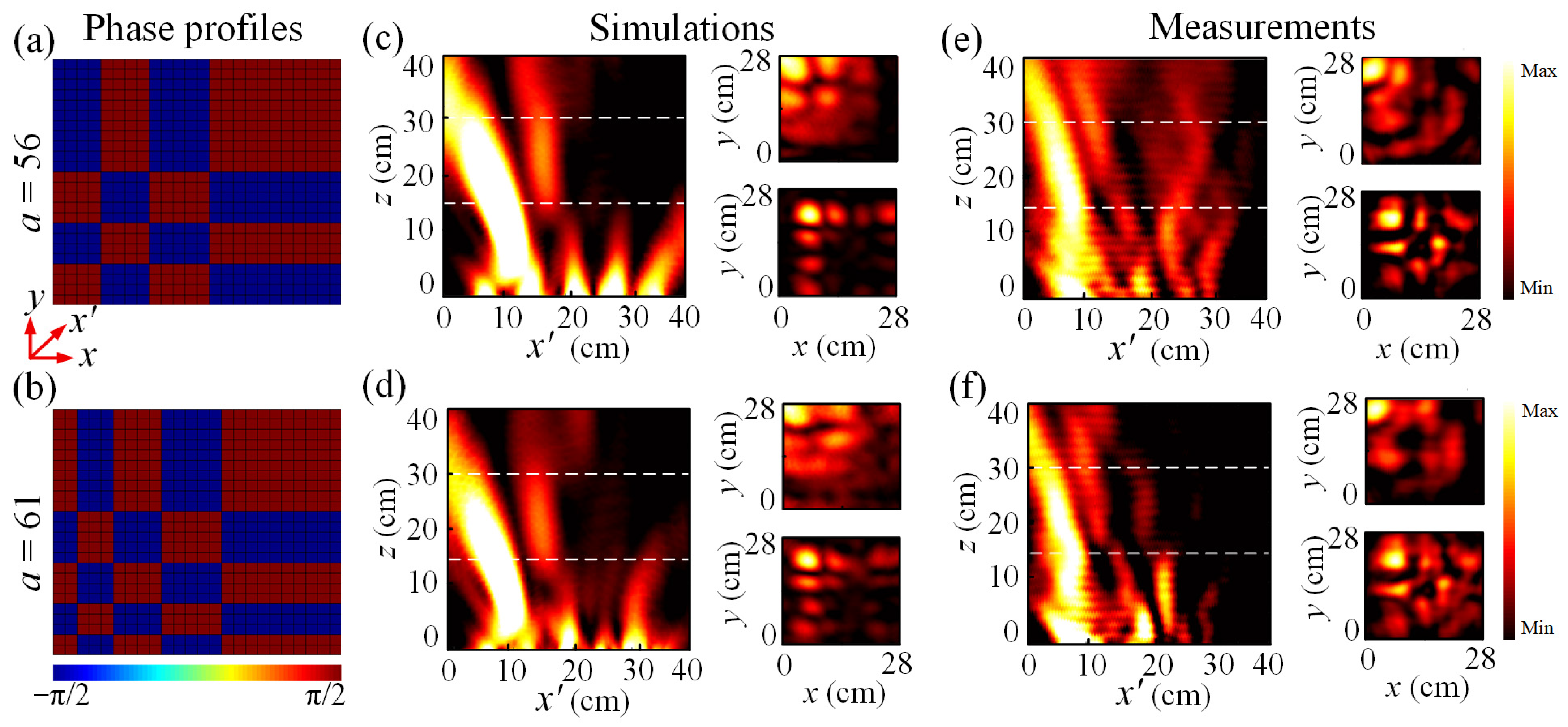
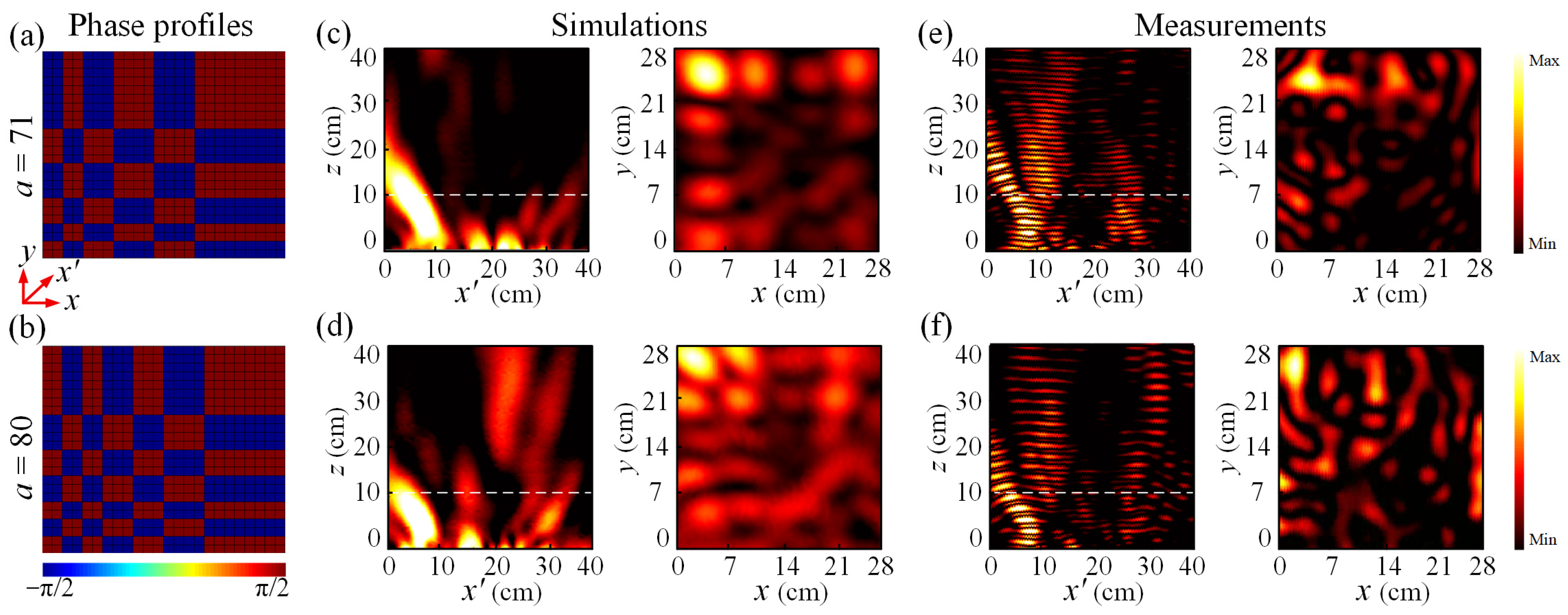
3. Principles and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DC | Direct current |
| SLMs | Spatial light modulators |
| LC | Liquid crystal |
| PCB | Printed circuit board |
| 2D | Two-dimensional |
| FEM | Finite-element method |
| SMT | Surface mount technology |
References
- Besieris, I.M.; Shaarawi, A.M. A note on an accelerating finite energy Airy beam. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 2447–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márkus, F.; Gambár, K. Quantized Approach to Damped Transversal Mechanical Waves. Quantum Rep. 2024, 6, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Mills, M.; Chen, Z.; Christodoulides, D.; Liu, J. Trapping aerosols with optical bottle arrays generated through a superposition of multiple Airy beams. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2013, 11, 033502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, X.; Christodoulides, D.N.; Siviloglou, G.A.; Chen, J.F. Spatiotemporal single-photon Airy bullets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2024, 132, 143601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Călin, B.Ş.; Preda, F.; Jipa, F.; Zamfirescu, M. Laser fabrication of diffractive optical elements based on detour-phase computer-generated holograms for two-dimensional Airy beams. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, M.V.; Balazs, N.L. Nonspreading wave packets. Am. J. Phys. 1979, 47, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviloglou, G.A.; Christodoulides, D.N. Accelerating finite energy Airy beams. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 979–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Dai, H.T.; Sun, X.W.; Demir, H.V. Electrically switchable finite energy Airy beams generated by a liquid crystal cell with patterned electrode. Opt. Commun. 2010, 283, 3846–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Vaughan, J.C.; Zhuang, X. Isotropic three-dimensional super resolution imaging with a self-bending point spread function. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettenburg, T.; Dalgarno, H.I.C.; Nylk, J.; Coll-Llado, C.; Ferrier, D.E.K.; Cizmar, T.; Gunn-Moore, F.J.; Dholakia, K. Light-sheet microscopy using an Airy beam. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Koulouklidis, A.D.; Papazoglou, D.G.; Tzortzakis, S.; Zhang, X. Enhanced terahertz wave emission from air-plasma tailored by abruptly autofocusing laser beams. Optica 2016, 3, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siviloglou, G.A.; Broky, J.; Dogariu, A.; Christodoulides, D.N. Ballistic dynamics of Airy beams. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, H. Production of accelerating quad Airy beams and their optical characteristics. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 15154–15164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, D.M.; Davis, J.A.; Hazard, T.M. Direct generation of accelerating Airy beams using a 3/2 phase-only pattern. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2634–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salandrino, A.; Christodoulides, D.N. Airy Plasmon: A Non-Diffracting Surface Wave. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 2082–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.G.; Bu, J.; Wang, M.W.; Yuan, X.C. Microfabricated continuous cubic phase plate induced Airy beams for optical manipulation with high power efficiency. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 261106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acebal, P.; Carretero, L.; Blaya, S.; Murciano, A. Generation of High-Quality Tunable One-Dimensional Airy Beams Using the Aberrations of a Single Lens. IEEE Photonics J. 2012, 4, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Liu, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, K.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J. Generation of One Dimensional Terahertz Airy Beam by Three-Dimensional Printed Cubic Phase Plate. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Ji, S.; Ni, J.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Wu, D.; Chu, J. Continuous cubic phase microplates for generating high-quality Airy beams with strong deflection. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 2483–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Chen, P.; Hu, W.; Ji, W.; Zheng, L.; Ge, S.; Ming, Y.; Chigrinov, V.; Lu, Y. Polarization-controllable Airy beams generated via a photoaligned director-variant liquid crystal mask. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalizay, B.; Soylu, B.; Akturk, S. Optical element for generation of accelerating Airy beams. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2010, 27, 2344–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, D.G.; Suntsov, S.; Abdollahpour, D.; Tzortzakis, S. Tunable intense Airy beams and tailored femtosecond laser filaments. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 061807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, A.; Merkel, A.; Wang, Y.; Assouar, B. Broadband tunable lossy metasurface with independent amplitude and phase modulations for acoustic holography. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 105038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.F.; Capasso, F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.T.; Taylor, A.J.; Yu, N.F. A review of metasurfaces: Physics and applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 076401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Genevet, P.; Kats, M.A.; Aieta, F.; Tetienne, J.-P.; Capasso, F.; Gaburro, Z. Light Propagation with Phase Discontinuities: Generalized Laws of Reflection and Refraction. Science 2011, 334, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoch, S.; Tayeb, G.; Sabouroux, P.; Guerin, N.; Vincent, P. A metamaterial for directive emission. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 213902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Islam, M.; Faruque, M. A Near-Zero Refractive Index Meta-Surface Structure for Antenna Performance Improvement. Materials 2013, 6, 5058–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.; Kang, S.B.; Shin, J.; Kwak, M.H.; Kang, K.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, N.; Min, B. A terahertz metamaterial with unnaturally high refractive index. Nature 2011, 470, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Cheng, Q.; Hand, T.; Mock, J.J.; Cui, T.J.; Cummer, S.A.; Smith, D.R. Experimental Demonstration of Electromagnetic Tunneling Through an Epsilon-Near-Zero Metamaterial at Microwave Frequencies. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 023903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fung, K.H.; Xu, J.; Ma, H.; Jin, Y. Ultra-broadband Light Absorption by a Sawtooth Anisotropic Metamaterial Slab. Nano Lett. 2011, 12, 1443–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.R.; Ma, Q.; Gao, X.X.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Q.; Iqbal, S.; Cui, T.J. Programmable Amplitude-Coding Metasurface with Multifrequency Modulations. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratni, B.; Merzouk, W.A.; de Lustrac, A.; Villers, S.; Piau, G.P.; Burokur, S.N. Design of Phase-Modulated Metasurfaces for Beam Steering in Fabry-Perot Cavity Antennas. IEEE. Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.H.; Cao, X.Y.; Yang, F.; Gao, J.; Xu, S.H.; Li, M.K.; Chen, X.B.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.J.; Li, S.J. A programmable metasurface with dynamic polarization, scattering and focusing control. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, D.; Seetharamdoo, D.; Burokur, S.N.; de Lustrac, A. Phase-compensated metasurface for a conformal microwave antenna. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 124102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Ratni, B.; Yi, J.; Zhang, H.; de Lustrac, A.; Burokur, S.N. Versatile metasurface platform for electromagnetic wave tailoring. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tsakmakidis, K.L.; Jiang, T.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Sun, S.; Shen, L. Unidirectional guided-wave-driven metasurfaces for arbitrary wavefront control. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Mosallaei, H.; Afshari, E. Radiation-efficient 60 GHz on-chip dipole antenna realised by reactive impedance metasurface. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.; Al-Naib, I.A.I.; Born, N.; Koch, M. Terahertz metasurfaces with high Q-factors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 051109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmahini-Farahani, M.; Mosallaei, H. Birefringent reflectarray metasurface for beam engineering in infrared. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; He, S.M.; Liu, Q.F.; Wang, W. Visible light metasurfaces based on gallium nitride high contrast gratings. Opt. Commun. 2016, 367, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Deng, H.; Xiong, Q.X. A Dynamically Phase Tunable Metasurface for a Broad Bandwidth Ultra-Low Radar Cross Section. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 53006–53017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lustrac, A.; Ratni, B.; Piau, G.P.; Duval, Y.; Burokur, S.N. Tri-state Metasurface-Based Electromagnetic Screen with Switchable Reflection, Transmission, and Absorption Functionalities. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, H.X.; Zhang, H.C.; Cui, T.J. Tunable ultrathin mantle cloak via varactor-diode-loaded metasurface. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 13403–13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, M.; Vijay, R.; Anbazhagan, R.R.; Amirtharajan. Reconfigurable Metasurface: Enabling Tunable Reflection in 6G Wireless Communications. Sensors 2023, 23, 9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.Y.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, Q.; Cui, T.J. Independent control of harmonic amplitudes and phases via a time-domain digital coding metasurface. Light-Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Feng, Y.J.; Monticone, F.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhu, B.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, L.; Kim, Y.; Ding, X.M.; Zhang, S.; et al. A Reconfigurable Active Huygens’ Metalens. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, A.; Franke, L.; Klingel, S.; Krieger, J.; Mueller, L.; Stemler, R.; Rahm, M. Continuous beam steering with a varactor-based reconfigurable intelligent surface in the Ka-band at 31 GHz. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 134, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phon, R.; Lee, M.; Lor, C.; Lim, S. Multifunctional Reflective Metasurface to Independently and Simultaneously Control Amplitude and Phase with Frequency Tunability. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2202943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Ratni, B.; Yi, J.; Zhang, K.; Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; de Lustrac, A.; Burokur, S.N. Versatile Airy-beam generation using a 1-bit coding programmable reflective metasurface. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2020, 14, 014081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Cai, W.; Cheng, M.; Hao, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kong, D.; Liu, J.; Dai, H.; et al. Dynamic propagation of an Airy beam in metasurface-enabled gradiently-aligned liquid crystals. Nanophotonics 2023, 12, 4205–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.; Nie, R.; Pan, Z.; Song, Z. Terahertz generation of Airy beam with polarization conversion in a reflective vanadium dioxide metasurface. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 055555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Dai, Y.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. An Optically Controlled Programmable Metasurface Based on Complex Amplitude Modulation for Dynamic Generation of Airy and Vortex Beams. Opt. Commun. 2025, 592, 132254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ref. | Frequency Bandwidth | Type | Electronic Component | Modulation Along Metasurface |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [50] | 9–12 GHz | Reflection | Varactor diodes | Phase |
| [51] | 632.8 nm | Inside | Liquid crystal | Phase |
| [52] | 0.9–1.2 THz | Reflection | Vanadium dioxide | Phase and Amplitude |
| [53] | 1.64 THz | Reflection | Photosensitive silicon | Phase and Amplitude |
| This work | 6–7 GHz | Full space | Varactor diodes | Phase |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, R.; Yu, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Tan, Q. Dynamic Generation of Airy Beam Utilizing the Full-Space Programmable Metasurface. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169177
Feng R, Yu Y, Wu L, Wang J, Li Z, Tan Q. Dynamic Generation of Airy Beam Utilizing the Full-Space Programmable Metasurface. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169177
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Rui, Yaokai Yu, Liangliang Wu, Jiayun Wang, Zhi Li, and Qiulin Tan. 2025. "Dynamic Generation of Airy Beam Utilizing the Full-Space Programmable Metasurface" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169177
APA StyleFeng, R., Yu, Y., Wu, L., Wang, J., Li, Z., & Tan, Q. (2025). Dynamic Generation of Airy Beam Utilizing the Full-Space Programmable Metasurface. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9177. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169177






