Evaluation of Polypyrrole as a Functional Sorbent for Water Treatment Technologies
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
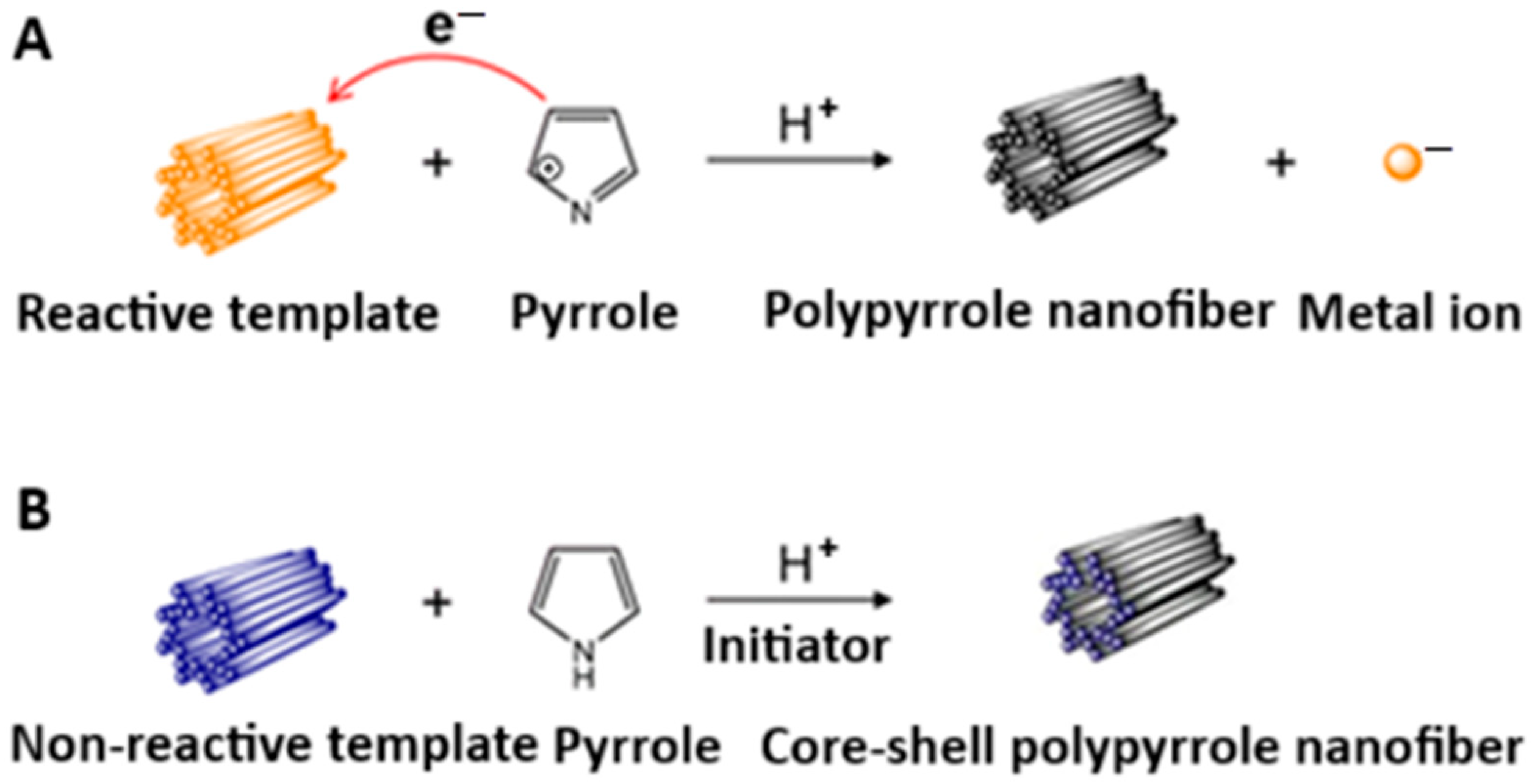
2. Sorbent Synthesis
3. Application Areas
3.1. Water Purification
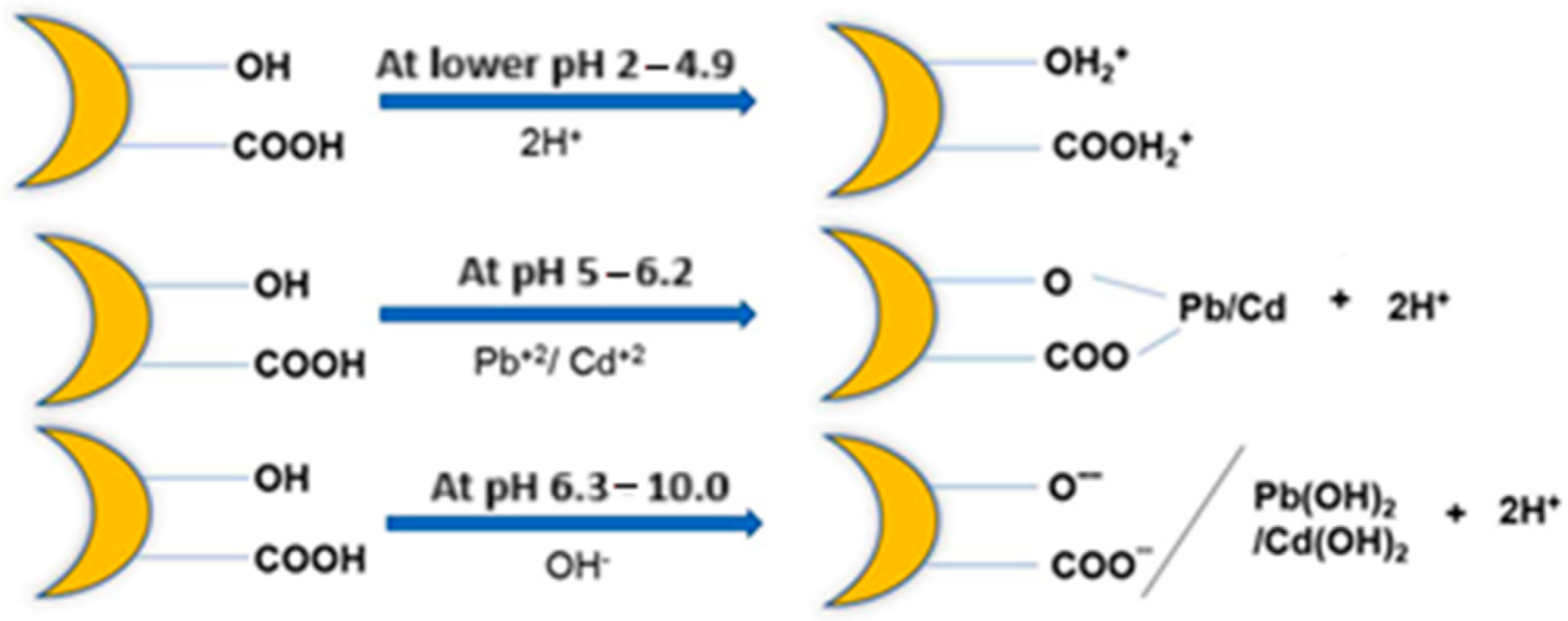
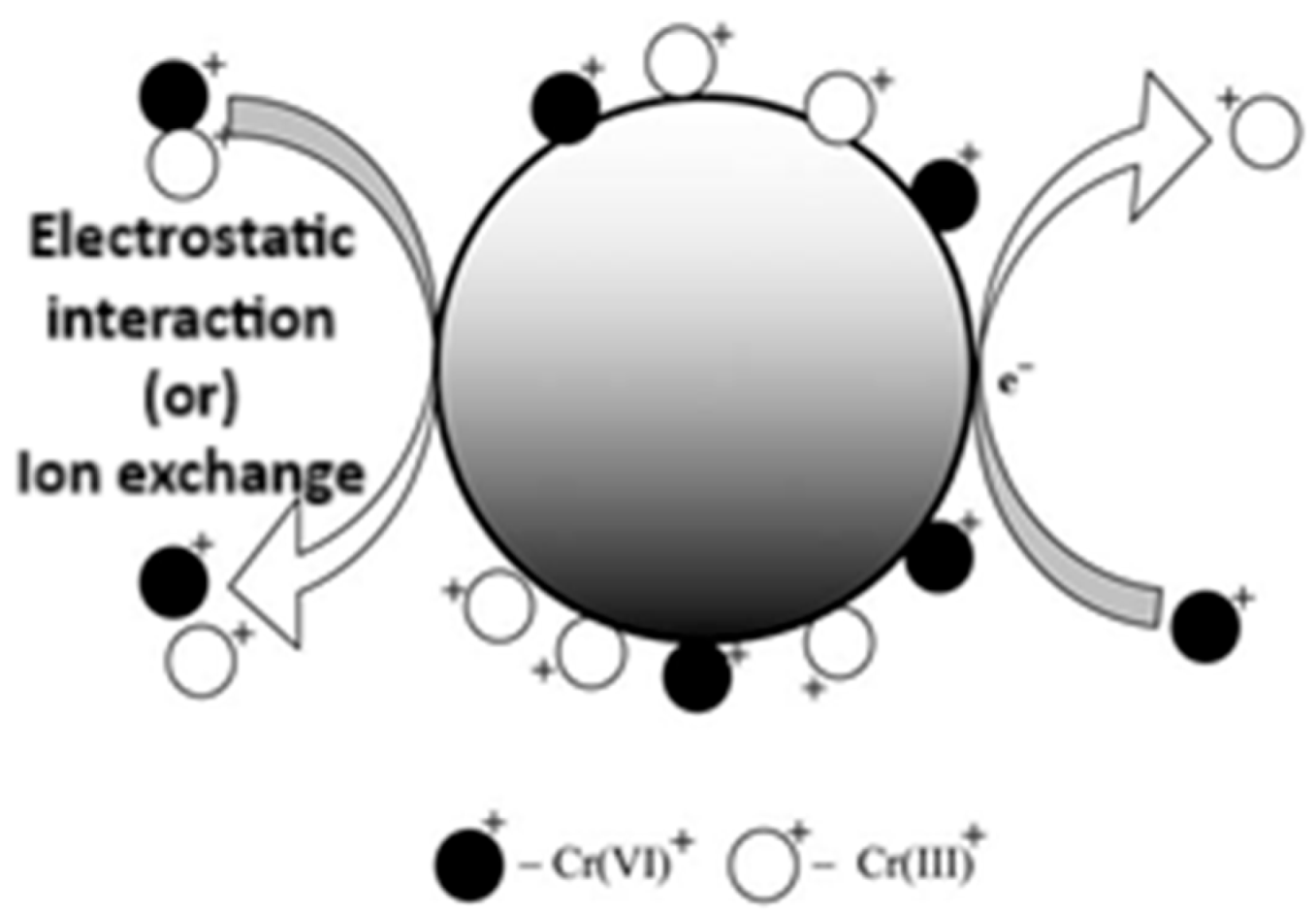
3.2. Sorption of Metal Ions
| Sorbed Metal | Description | Dopant | Morphology | S BET [m2/g] | Adsorption Capacity [mg/g] | Optimal pH | Adsorption Isotherm | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr(VI) | 3D aerogels with PPy on cellulose acetate nanofibers | SO42− | porous structure with cross-linked nanofibers | 244.65 31.92 | 2.0 | Langmuir | [35] | |
| Cr(VI) | sonochemically synthesized | Cl− | a fused globular | 12.21 | 21.87 | [92] | ||
| As(V) | black PPy powder | Cl− | cauliflower-like porous | 10.27 | 1.91 | 6.5 | Freundlich | [93] |
| 137Cs | black PPy powder | DBS− | globular particles | 11.28 | 26.2 | 5.0 | Langmuir | [94] |
| Cr(VI) | colloidal nanocomposites of PPy/hollow mesoporous silica | Cl− | PPy wrapped on the hollow mesoporous silica | 325 | 322 | 2.0 | Langmuir | [96] |
| Hg2+, Ag+, and Pb2+ | PPy/silica nanocomposite | Cl− | cratered surface | 85 (no silica) 306 (46 wt% of silica) | 0.97 (Hg2+), 0.75 (Ag+), and 0.53 (Pb2+) mmol/g | [97] | ||
| Cr(VI) | graphene/SiO2@PPy nanocomposites | SO42− | porous film made with nanospheres | 17.6 (PPy) 37.6 (graphene-silica-PPy nanocomposite) | 429.2 | 2.0 | Langmuir | [101] |
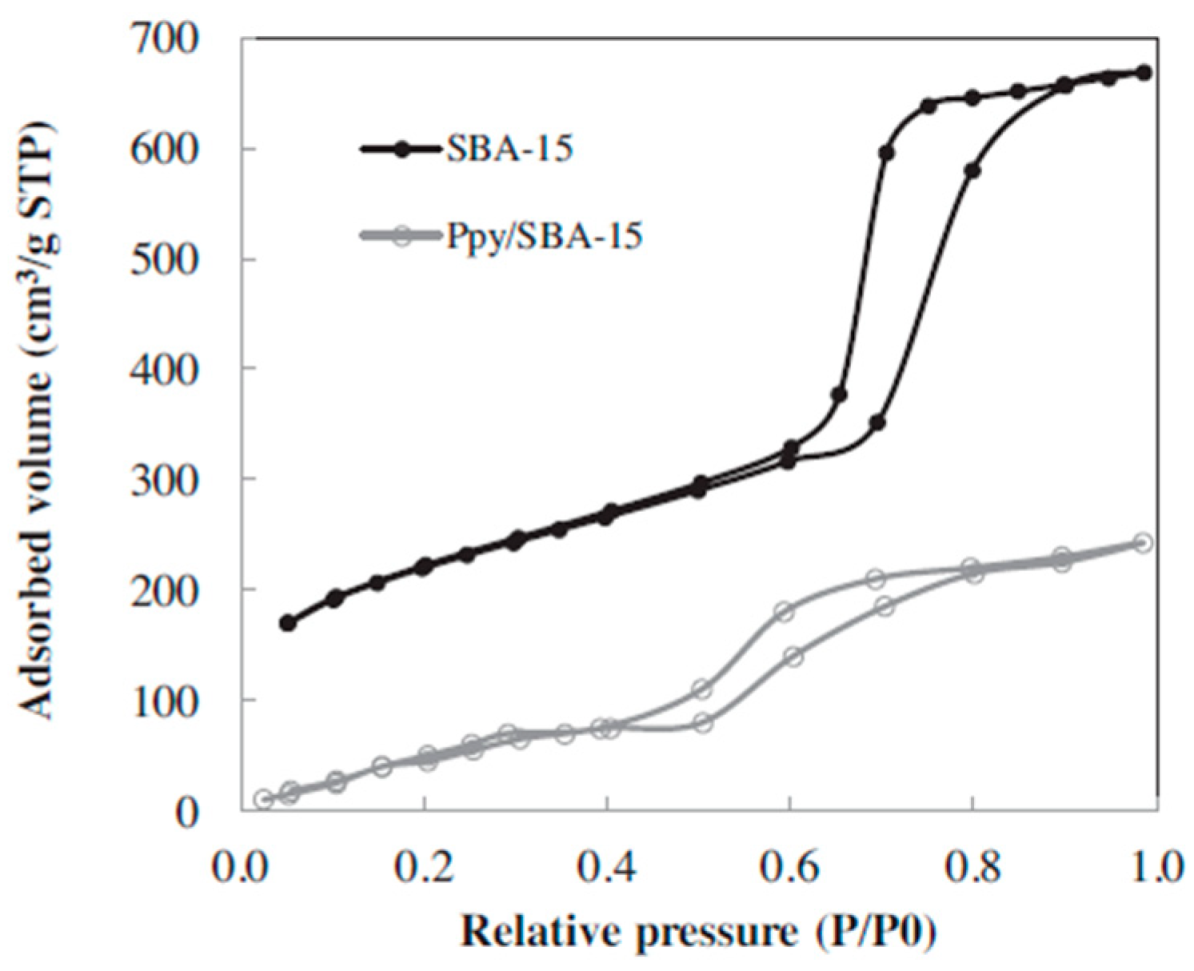
| Hg(II) | PPy/SBA-15 | Cl− | PPy inside and outside of the SBA-15 pores | 97.6 | 200.0 | 8 | Langmuir | [102] |
| Cd | PPy synthesized in the presence of surfactants (PVP, PVA) | Cl− | globular structure, with the size of particles dependent on the type/concentration of surfactant | 5 | Langmuir | [105] | ||
| Cr(VI) | PPy/carbon black | SO42− | core–shell structure | 64.47 | 174.8 | 3 | [106] | |
| Cr(VI) | PPy/oxidized MWCNTs nanocomposite | Cl− | PPy deposit on the surface of the OMWCNT | 6.1 (PPy) 201.4 (OMWCNT) 34.1 (PPy/OMWCNTs NCs) | 249.18 | 2 | Langmuir | [107] |
| Cr(VI) | PPy with electrospun V2O5 nanofibers as templates | Cl− | rough surface of PPy nanotubes with the outer diameter 60–280 nm | 482.6 9.281 mmol/g | Langmuir | [108] | ||
| Pb(II), Cd(II) | cobalt oxide graphene PPy nanocomposite | Cl− | oxide uniformly surrounded by PPy supported by GO | 133 | 780.3 for Pb(II) 794.2 for Cd(II) | 5.5 for Pb(II) 6.1 for Cd(II) | Langmuir and Temkin | [75] |
| Cr(VI) | PPy/bacterial cellulose (PPy/BC) | core–shell of PPy wrapped on cellulose | 95.9 | 555.6 | 2 | [109] | ||
| Cr(VI) | PPy -bacterial extracellular polysaccharide (PPy-EPS) nanocomposite | Cl− | irregular in shape, mostly aggregated | 26.21 (PPy/EPS) 22.59 (PPy) | [113] | |||
| Cr(VI) | glycine doped PPy (PPy-gly) | SO42− zwitter ion of glycin | spherical particles (agglomerated) PPy: 153–538 nm PPy-gly: 150–250 nm | 217.39–232.55 | 2.0 | Langmuir | [114] | |
| Cr(VI) | nanocomposite of Fe3O4 with chitosan (CS) and PPy | Cl− SO42− | granular and irregular particles | 105 | 2–4.5 | Langmuir | [115] | |
| Ni | polyethyleneimine/PPy | SO42− | Globular with an average particle size of 18–34 nm | 17 | 1.756 (20 °C) 1.905 (60 °C) | 4.5 | Freundlich | [116] |
| Pb2+ Cd2+ | rose leaf modified by PPy coating | Cl− | partially sponge-like structures with the pores | 11.76 (for Cd2+) 1.33 (for Pb2+) | 5.0 (for Cd2+) 8.0 (for Pb2+) | Freundlich | [117] | |
| Mn(II) 17β-estradiol (E2), nitrate | PPy/corn cob immobilized with Zoogloea sp. | 6.5 | [118] |
3.3. Sorption of Drugs
| Sorbed Drug | Description | pH/efficiency [%] | S BET [m2/g] | Adsorption Capacity [mg/g] | Equilibrium Times | Cycles of Regeneration [no] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ketoprofen (KETO) | cross-linked β-cyclodextrin (CD) | 4.2 | 7.31 | API 162.20 | 60 min | [127] | |
| salicylic acid, acetylsalicylic acid, atenolol | clinoptilolite modified with sorbed metallic cations or natural clays (kaolin and bentonite, pure or ion-exchanged by octadecyl dimethylbenzyl ammonium chloride) | 0.65–3.5 × 10−5 mol/g for SA 1.1–2.1 × 10−5 mol/g for ASA | [128] | ||||
| sodium salicylate | PPy powder | largely unaffected by pH | [129] | ||||
| salicylic acid, diclofenac | cotton fabrics/PPy or PANI | 90% at pH 5.3 for DCF, 70% at pH 4 for SA) | 65 mg/g for DCF 21 mg/g for SA | 20–30 min | [130] | ||
| sodium salicylate | sunflower seed shell (SFS)/PANI composite | 6/90% for 1 g/L | 28.81 mg/g | 60 min | [131] | ||
| potassium diclofenac | pristine multiwalled carbon nanotube (pristine MWCNT)/PPy | 93.48% for pristine MWCNT 94.98% for PPy/MWCNT | 277.5 (MWCNT) 541.2 (PPy/MWCNT) | 59.67 mg/g (pristine MWCNT) 229.93 mg/g (PPy/MWCNT) | [136] | ||
| potassium diclofenac (PD) moxidectin (MOX) | PPy | pH 6/95.26% for PD, 99.75% for MOX | 27.22 | 221.23 for PD 87.46 for MOX | 20 min | 7 | [137] |
| diclofenac (DCF) salicylic acid | cotton fabrics coated with PPy or PANI | pH 5.3 for DCF, pH 4 for SA/ 90% for DCF, 70% for SA | PPy-coated fabrics: 65 for DCF, 21 for SA | 20–30 min | 3 | [139] | |
| sulfonamides | a magnetic nanoparticle/PPy/silica | 7.0 | 2–20 min | 16 | [141] | ||
| naproxen | magnetic nanocomposite chitosan -polypyrrole (CS-PPy) | 5.0/92% | 15 min | [142] | |||
| carbamazepine (CBZ) | PPy/chitosan—Fe3O4 | 94.5% for PPy/CS/Fe3O4, 65% for bare Fe3O4 | 121.95 | 25 min | 5 | [143] | |
| indomethacin (IDM), diclofenac (DCF) | graphene oxide/covalent organic frameworks/PPy (GO/COF-300/PPy) | 72% for DM, 68% for DCF | 115 (for IDM) 138 (for DCF) | 60 min | 8 | [147] | |
| Rifampin, reactive orange 5 (RO5) | zeolite supported with TiO2/PPy nanoparticles | pH = 5 for Rifampin, pH = 2 for RO5/94% for Rifampin, 88% for RO5 | 20 min (ultrasonic-supported conditions) | [148] | |||
| salicylic acid | TiO2/PANI | 71% for T-Pani-6 (100:1), 75% for T-Pani-7 (200:1), 34% for TiO2 | 5 h (of white light illumination) | [149] | |||
| ciprofloxacin (CIP) methylene blue (MB), Cr(VI) | silver molybdate (Ag2MoO4)/PPy | 99.8% for CIP, 99.9% for MB, 99% for Cr(VI) photocatalytic degradation | 8–10 min | [150] | |||
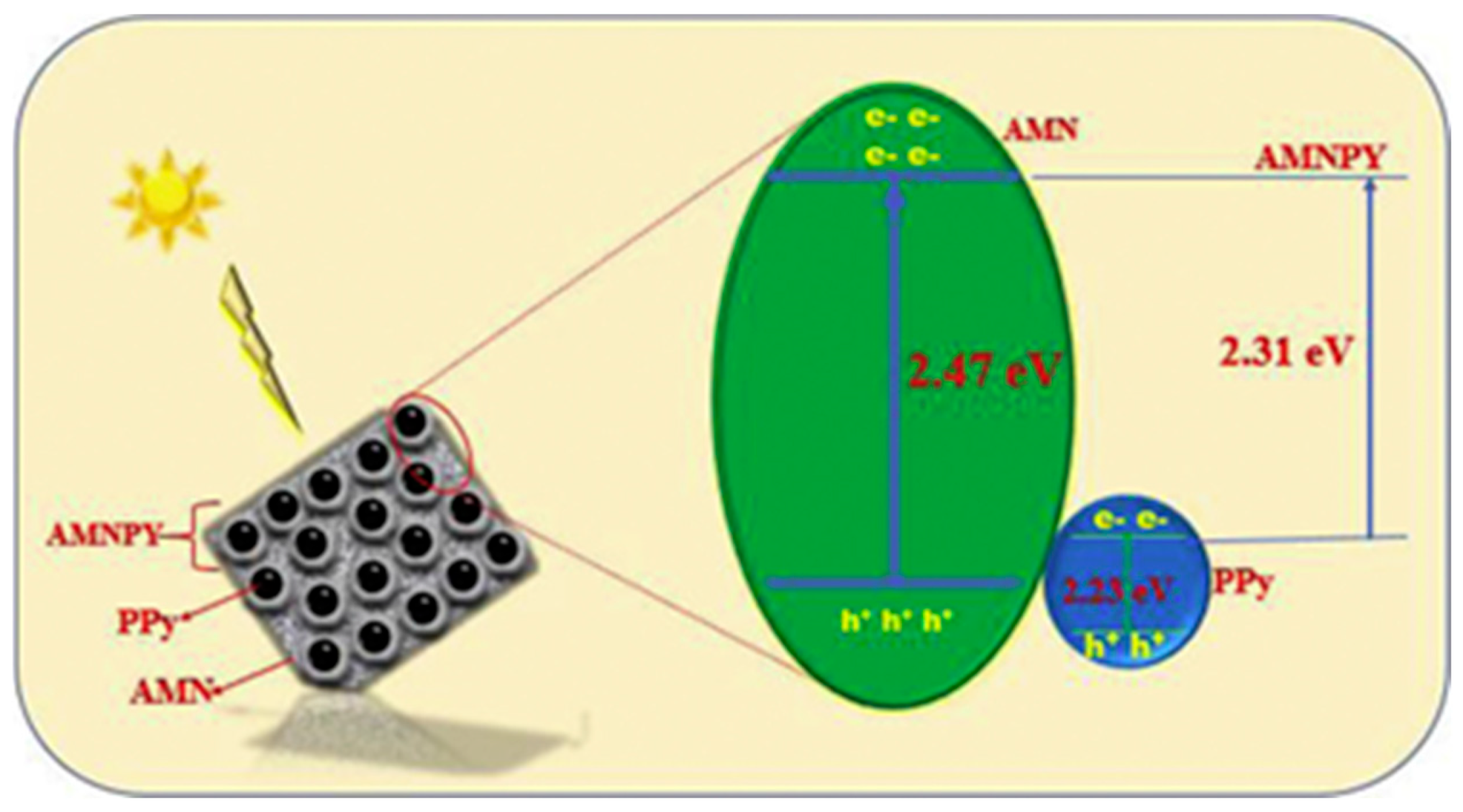
| chloramphenicol (CAP), methyl orange (MO) | silver manganite/PPy (AMNPY) | 99.6% for MO, 98.9% for CAP photocatalytic degradation | 30 min | [151] |
3.4. Sorption of Dyes
3.5. Bacteria Removal
3.6. Membrane Separation
4. Perspective
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borges, M.H.R.; Nagay, B.E.; Costa, R.C.; Souza, J.G.S.; Mathew, M.T.; Barão, V.A.R. Recent advances of polypyrrole conducting polymer film for biomedical application: Toward a viable platform for cell-microbial interactions. Adv. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2023, 314, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Tang, W. PEGylated polypyrrole–gold nanocomplex as enhanced photothermal agents against tumor cells. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 5587–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Bao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lu, J.; Su, T.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, J. Bioelectronic Applications of Intrinsically Conductive Polymers. Adv. Elect. Mat. 2023, 9, 2300082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansar, T.M.; Ali, A.; Mustafa, G.M.; Afzal, F.; Ishaq, S.; Kanwal, F.; Naseem, S.; Atiq, S. Polypyrrole-based nanocomposites architecture as multifunctional material for futuristic energy storage applications. J. Alloys Comp. 2021, 855, 157341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.; Aldalbahi, A.; Almoiqli, M.; Alzahly, S. Chemical and Electrochemical Synthesis of Polypyrrole Using Carrageenan as a Dopant: Polypyrrole/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. Polymers 2018, 10, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajesh Kumar, P.; Suryawanshi, P.L.; Gumfekar, S.P.; Sonawane, S.H. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of conducting polymer-based electrocatalysts for fuel cell applications. Chem. Eng. Proc. Proc. Intensif. 2017, 121, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, L.Y.; Jia, P.; Okulov, I.V. Electrochemical Behavior of Nanoporous Gold/Polypyrrole Supercapacitor under Deformation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidlich, C.; Mangold, K.-M.; Jüttner, K. EQCM study of the ion exchange behaviour of polypyrrole with different counterions in different electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizera, A.; Dubis, A.T.; Łapiński, A. Density functional theory studies of polypyrrole and polypyrrole derivatives; substituent effect on the optical and electronic properties. Polymer 2022, 255, 125127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Réhault, J.; Liang, B.; Hambsch, M.; Zhang, Y.; Seçkin, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shivhare, R.; Zhang, P.; Polozij, M.; et al. A Quasi-2D Polypyrrole Film with Band-Like Transport Behavior and High Charge-Carrier Mobility. Adv. Mater. 2023, 30, 2303288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, P.M.; Cortazar, M.; Ochoteco, E.; Calahorra, E.; Pomposo, J.A. Comparison of surface and bulk doping levels in chemical polypyrroles of low, medium and high conductivity. Surf. Interf. Anal. 2007, 39, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carragher, U.; Breslin, C.B. Polypyrrole doped with dodecylbenzene sulfonate as a protective coating for copper. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 291, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syugaev, A.V.; Lyalina, N.V.; Maratkanova, A.N.; Smirnov, D.A. Molecular architecture of highly protective coatings of electrodeposited dodecyl sulfate-doped polypyrrole. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 131, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hien, N.T.L.; Garcia, B.; Pailleret, A.; Desloui, C. Role of doping ions in the corrosion protection of iron by polypyrrole films. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qi, K.; Chen, Z.; Guo, X. Influence of Doping Anions on the Ion Exchange Behavior of Polypyrrole. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golba, S.; Kubisztal, J. The Influence of Roughness on the Properties of Electroactive Polypyrrole. Molecules 2024, 29, 5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samwang, T.; Morishita Watanabe, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Srinives, S.; Umakoshi, H. Study of Chemical Polymerization of Polypyrrole with SDS Soft Template: Physical, Chemical, and Electrical Properties. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 48946–48957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, F. Synthesis and application of polypyrrole nanofibers: A review. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 3606–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, Y.; Singh, K.; Mudila, H.; Lokhande, P.E.; Singh, L.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, A.; Mujawar Mubarak, N.; Hadi Dehghani, M. Insights into properties, synthesis and emerging applications of polypyrrole-based composites, and future prospective: A review. Helion 2024, 10, e33643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Lv, Y.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z. Recent advances in application of polypyrrole nanomaterial in water pollution control. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocchetta, P.; Frattini, D.; Tagliente, M.; Selleri, F. Electrochemical Deposition of Polypyrrole Nanostructures for Energy Applications: A Review. Curr. Nanosci. 2020, 16, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohi Frej, Z.; Ze Zhang, M. A Nanofibrous Polypyrrole Membrane with an Ultrahigh Areal Specific Capacitance and Improved Energy and Power Densities. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 6887–6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Wang, P.; Qin, J. Application of Polypyrrole-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Detection of Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiJianwei Li, H.; Chu, W.; Lin, J.; Xin, J.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Ma, Z. Flexible Hierarchical Polyimide/Polypyrrole/Carbon Nanofiber Composite Films for High-Performance Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 7783–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, R.A.; Arya, S.S.; Alshehhi, K.H.; Teo, J.C.M.; Pitsalidis, C. Conducting polymer scaffolds: A new frontier in bioelectronics and bioengineering. Trends Biotechol. 2024, 42, 760–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namhongsa, M.; Daranarong, D.; Sriyai, M.; Molloy, R.; Ross, S.; Ross, G.M.; Tuantranont, A.; Tocharus, J.; Sivasinprasasn, S.; Topham, P.D.; et al. Surface-Modified Polypyrrole-Coated PLCL and PLGA Nerve Guide Conduits Fabricated by 3D Printing and Electrospinning. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 4532–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, J.; Kumar, A. Scalable and Low Cost Synthesis of Highly Conducting Polypyrrole Nanofibers Using Oil–Water Interfacial Polymerization under Constant Stirring. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6926–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Manohar, S.K. Bulk Synthesis of Polypyrrole Nanofibers by a Seeding Approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12714–12715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Dong, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, K.; Yu, D. Polypyrrole Nanomaterials: Structure, Preparation and Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling Pang, A.; Arsad, A.; Ahmadipour, M. Synthesis and factor affecting on the conductivity of polypyrrole: A short review. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 32, 1428–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Dubey, A.; Chakraborty, S. A review on polypyrrole-coated bio-composites for the removal of heavy metal traces from waste water. J. Ind. Tex. 2019, 51, 152–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, J. Recent Advances in the Removal of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Media with Conducting Polymers, Polyaniline and Polypyrrole, and Their Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 4243–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Shimokawa, D. Polarons, Bipolarons, and Electrical Properties of Crystalline Conducting Polymers. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2023, 96, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, Z.; Nasar, A. Polypyrrole-decorated bentonite magnetic nanocomposite: A green approach for adsorption of anionic methyl orange and cationic crystal violet dyes from contaminated water. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, B.; Pan, K. Ultralight and Superelastic Nanofiber Aerogels with In-Situ Loaded Polypyrrole for High-Efficient Cr(VI) Adsorption. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, M.K.; Disanayaka, H.N.; Fernando, M.S.; Nalin de Silva, K.M.; de Silva, R.M. Development of graphene oxide-based polypyrrole nanocomposite for effective removal of anionic and cationic dyes from water. Res. Chem. 2023, 6, 101079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Low cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Kumari, S.; Muthuraj, M.; Selvaraju, N. Recent Trends in Advanced Oxidation and Catalytic Processes for Removal of Heavy Metals, Dyes, and Xenobiotics. In Recent Trends in Advanced Oxidation and Catalytic Processes, 1st ed.; Bhunia, B., Muthuraj, M., Eds.; Bentham Science Publishers: Potomac, MD, USA, 2022; pp. 45–80. ISBN 9789815049725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzetti, S.; Ghisi, R. The environmental release and fate of antibiotics. Marine Poll. Bull. 2014, 79, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akmal Misman, N.; Sharif, F.; Khan Chowdhury, A.J.; Hafizah, N. Water pollution and the assessment of water quality parameters: A review. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 294, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Yang, F.; Shi, B.; Zhang, H. A comprehensive study on membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors operated under different aeration intensities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 59, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif Irshad, M.; Sattar, S.; Nawaz, R.; Al-Hussain, S.A.; Rizwan, M.; Bukhari, A.; Waseem, M.; Irfan, A.; Inam, A.; Zaki, M.E.A. Enhancing chromium removal and recovery from industrial wastewater using sustainable and efficient nanomaterial: A review. Ecotox. Environ. Safety 2023, 263, 115231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, R.; Raza, A.; Yasmeen, F.; Dar, A.; Al-thagafi, Z.T.; Meraf, Z. Recent Literature Review of Significance of Polypyrrole and Its Biocomposites in Adsorption of Dyes from Aqueous Solution. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 7047832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, S.P.; Patra, S. Innovations and challenges in adsorption-based wastewater remediation: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: A review. Biores. Technol. 2006, 97, 1061–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Lo, I.-T. Theoretical and Experimental Adsorption of Silica Gel and Activated Carbon onto Chlorinated Organic Compounds in Water: A Case Study on the Remediation Assessment of a Contaminated Groundwater Site. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, H.; Foroutan, R.; Jafari, D.; Rezaei, M.A. Effect of interfering ions on phosphate removal from aqueous media using magnesium oxide@ferric molybdate nanocomposite. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, F.; Atar, N.; Olgun, A. Biosorption of acidic dyes from aqueous solution by Paenibacillus macerans: Kinetic, thermodynamic and equilibrium studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 150, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Baghayeri, M.; Hamidi, E. Poly(pyrrole-co-aniline)@graphene oxide/Fe3O4 sorbent for the extraction and preconcentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 16744–16751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.; Raheem, A.; Nasir, M.; Franco, D.S.P. Fractal-like kinetic modelling for sorption of diclofenac onto graphene oxide/polypyrrole composite: Mechanism analysis and response surface methodology for optimization. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 139, 110328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauke, V.P.; Maity, A.; Chetty, A. High-performance towards removal of toxic hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using graphene oxide-alpha cyclodextrin polypyrrole nanocomposites. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 211, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-sayed, M.E.A. Nanoadsorbents for water and wastewater remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahinroosta, M.; Moattari, R.M. Alumina-based nanoadsorbents for wastewater treatment, Adsorption through Advanced Nanoscale Materials. In Applications in Environmental Remediation, Micro and Nano Technologies, 1st ed.; Verma, C., Aslam., J., Ehtisham Khan, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Aalborg, Denmark, 2023; pp. 205–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyaba, L.; Munonde, T.S.; Mpupa, A.; Nomngongo, P.N. Magnetic Fe3O4@Mg/Al-layered double hydroxide adsorbent for preconcentration of trace metals in water matrices. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Qiu, X.; Gao, J.; Ji, M. Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole on polypyrrole decorated volcanics over a wide pH range: Mechanisms and site energy distribution consideration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 283, 120165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Shah, A.U.H.A.; Bilal, S. Comparative Study of the Adsorption of Acid Blue 40 on Polyaniline, Magnetic Oxide and Their Composites: Synthesis, Characterization and Application. Materials 2019, 12, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dago-Serry, Y.; Maroulas, K.N.; Tolkou, A.K.; AbdelAll, N.; Alodhayb, A.N.; Khouqeer, G.A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Composite super-adsorbents of chitosan/activated carbon for the removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug from wastewaters. J. Molec. Struct. 2024, 1298, 137044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazal, M.K. An Overview of Carbon-Based Materials for the Removal of Pharmaceutical Active Compounds. In Carbon-Based Material for Environmental Protection and Remediation, 1st ed.; Bartoli, M., Frediani, M., Rosi, L., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grela, A.; Kuc, J.; Bajda, T. A Review on the Application of Zeolites and Mesoporous Silica Materials in the Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Antibiotics from Water. Materials 2021, 14, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajeh, M.; Laurent, S.; Dastafkan, K. Nanoadsorbents: Classification, Preparation, and Applications (with Emphasis on Aqueous Media). Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 7728–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canpolat, G.; Dolak, İ.; Keçili, R.; Hussain, C.G.; Amiri, A.H.; Hussain, C.M. Conductive Polymer-Based Nanocomposites as Powerful Sorbents: Design, Preparation and Extraction Applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 53, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.; Yamini, Y.; Tahmasebi, E.; Latifeh, F. Extraction and preconcentration of formaldehyde in water by polypyrrole-coated magnetic nanoparticles and determination by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3421–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Salemi, A. On-line trace enrichment of phenolic compounds from water using a pyrrole-based polymer as the solid-phase extraction sorbent coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 513, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuiabc, S.; Mao, J.; Rouabhiaa, M.; Elkoun, S.; Zhang, Z. A biocompatible polypyrrole membrane for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 16996–17006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielichowski, K.; Njuguna, J.; Majka, T.M. Chapter 10—Thermal degradation of conducting polymers. In Thermal Degradation of Polymeric Materials, 2nd ed.; Pielichowski, K., Njuguna, J., Majka, T.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Chapter 4: Chemistries and Biodegradability of Conducting Polymers. In Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polymer Composites, 1st ed.; Gupta, R.K., Ed.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; p. 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gu, Q.; Liu, H.H.S.; Luan, J.; Yan, Z.; Liu, W.; Ke, X. How PPY/CMC aerogels possess selective adsorption capacity for norfloxacin: Coupling molecular scale interpretation with experiments. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y.; He, F. Efficient removal of organic pollutants from aqueous media using newly synthesized polypyrrole/CNTs-CoFe2O4 magnetic nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Pavlinek, V.; Li, C.; Lengalova, A.; He, Y.; Saha, P. Synthesis and characterization of new mesoporous material with conducting polypyrrole confined in mesoporous silica. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 98, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Recent Advances in Composites of Graphene and Layered Double Hydroxides for Water Remediation: A Review. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobbina, S.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, W.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Wu, X.; et al. Toxicity assessment due to sub-chronic exposure to individual and mixtures of four toxic heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waijarean, N.; MacKenzie, K.J.; Asavapisit, S.; Piyaphanuwat, R.; Jameson, G.N. Synthesis and Properties of Geopolymers Based on Water Treatment Residue and Their Immobilization of Some Heavy Metals. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 7345–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 195–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuma, S.; Mishra, P.; Bhat, B.R. Polypyrrole functionalized cobalt oxide graphene (COPYGO) nanocomposite for the efficient removal of dyes and heavy metal pollutants from aqueous effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ayati, A.; Ghanbari, S.; Orooji, Y.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Rouhi, J.; Fu, L.; Sillanpää, M. Recent advances in removal techniques of Cr(VI) toxic ion from aqueous solution: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lu, F. Polyethyleneimine bacterialcellulose bioadsorbent for effective removal of copper and lead ions from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Ramin, S. Fast and Enhanced Removal of Mercury from Aqueous Solutions by Magnetic Starch-g-Poly (Acryl Amide)/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Super Absorbents. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2016, 58, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadiri, A.; Benkhaled, A.; Choukchou-Braham, E. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies of Copper Adsorption onto Poly(n-Vinylpyrrolidone) Modified Clay. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 55, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Kim, H.I. Removal of Lead and Nickel Ions from Wastewater by Genipin Crosslinked Chitosan/Poly (Ethylene Glycol) Films. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2012, 49, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H. Recent Advances in Carbon Nitride-Based Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution. J. Inorg. Mater. 2020, 35, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Alharbi, N.S.; Rabah, S.O.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Synthesis and fabrication of g-C3N4-based materials and their application in elimination of pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, L.; Jena, S.K.; Rath, S.; Misra, P.K. Heavy metal removal from water by adsorption using a low-cost geopolymer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24284–24298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Chitosan-based materials: Preparation, modification and application. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nameni, M.; Alavi Moghadam, M.R.; Arami, M. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by wheat bran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 5, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, D.; Marisa, C.; Almeida, R.; Gomes, C.R.; Balula, S.S.; Granadeiro, C.M. Tailoring of Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials for Enhanced Water Treatment: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Malki, M.; Yaser, A.Z.; Hamzah, M.A.A.M.; Latif, N.A.; Hasmoni, S.H.; Akmar Zakaria, Z. Date Palm Biochar and Date Palm Activated Carbon as Green Adsorbent—Synthesis and Application. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2023, 9, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Jang, J. Heavy metal ion adsorption onto polypyrrole-impregnated porous carbon. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2008, 325, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Huq, A.O.; Yahya, R. The removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater/aqueous solution using polypyrrole-based adsorbents: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14778–14791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Deng, R.; Wang, R.; Xue, E.; Luo, H.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, X. Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution using biochar modified with Mg/Al-layered double hydroxide intercalated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaei, K.; Bagheri, H.; Asgharinezhad, A.A.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Shamsipur, M. SiO2-coated magnetic graphene oxide modified with polypyrrole–polythiophene: A novel and efficient nanocomposite for solid phase extraction of trace amounts of heavy metals. Talanta 2017, 167, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Mondal, P.; Bayen, S.P.; Chowdhury, P. Sonochemical synthesis of polypyrrole salt and study of its Cr(VI) sorption-desorption properties. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2012, 49, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, A.O.; Yahya, R.; Mahmud, H.N. Equilibrium, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics Studies of Polypyrrole Adsorbent for Arsenic Ions. Water Supply 2018, 18, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, M.A.; Khandaker, M.U.; Mahmud, H.E. Adsorption Kinetics, Equilibrium and Radiation Effect Studies of Radioactive Cesium by Polymer-Based Adsorbent. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2018, 24, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ren, H.; Zou, H. Determination, Separation and Application of 137Cs: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Guo, P.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Minama, T. Removal of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution by Polypyrrole/Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.W.; Song, K.; Hyun Kim, S. Synthesis of PPy/silica nanocomposites with cratered surfaces and their application in heavy metal extraction. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.P. (Ed.) The Surface Properties of Silicas, 1st ed.; John Wiley: Chichester, NY, USA, 1998; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Chang, S.K. A new Hg2+-selective chromoionophore based on calix[4]arenediazacrown. Chem. Commun. 2001, 17, 1664–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.D.; Martell, A.E. Ligand design for selective complexation of metal ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Rev. 1989, 89, 1875–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Jiang, X.; Luo, H.; Geng, J. Synthesis of graphene/ SiO2@polypyrrole nanocomposites and their application for Cr(VI) removal in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiabadi, M.; Dashti, A. Removal of Hg (II) from aqueous solution using polypyrrole/SBA-15 nanocomposite: Experimental and modeling. Synt. Met. 2016, 212, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, F.; Yu, C.; Wei, Z. Multicarboxylic hyperbranched polyglycerol modified SBA-15 for the adsorption of cationic dyes and copper ions from aqueous media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 5291–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.F.; Choi, H.J.; Ahn, W.S. Electrorheology of a mesoporous silica having conducting polypyrrole inside expanded pores. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 130, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, T.; Eisazadeh, H. Removal of Cd (II) by Using Polypyrrole and Its Nanocomposites. Synt. Met. 2013, 175, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.J.; Choi, K.; Lee, S.; Jung, K.W.; Hong, S.; Mizuseki, H.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, W.S. Strong chromate-adsorbent based on pyrrolic nitrogen structure: An experimental and theoretical study on the adsorption mechanism. Water Res. 2018, 145, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, M.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Maity, A. Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using polypyrrole wrapped oxidized MWCNTs nanocomposites adsorbent. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2016, 470, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lei, J.; Wang, C. Preparation of bamboo-like PPy nanotubes and their application for removal of Cr(VI) ions in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 378, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhong, M.; Xu, W.; He, C.; Zhang, Z. Polypyrrole/bacterial cellulose nanofiber composites for hexavalent chromium removal. Cellulose 2021, 28, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.; Arpa, A.; Chen, X.; Kumar, R.; Jaworski, J. Engineering bacterial cellulose for diverse biomedical applications. Recent Prog. Mater. 2019, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tavakoli, J.; Tang, Y. Bacterial cellulose production, properties and applications with different culture methods—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 219, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negarestani, M.; Shayesteh, H.; Kheradmand, A.; Pahlevani, F.; Mollahosseini, A.; Javanshir, S. Preparation of polypyrrole-functionalized recycled cotton fiber as a renewable and eco-friendly cellulose-based adsorbent for water decolorization: Comprehensive batch and fixed-bed column study. Surf. Interf. 2024, 48, 104360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswari, V.; Janaki, V.; Shanthi, K.; Kamala-Kannan, S. Adsorption and Subsequent Detoxification of Hexavalent Chromium in Aqueous Solution Using Polypyrrole-Bacterial Extracellular Polysaccharide Nanocomposite. Environ. Prog. Sust. Energy 2016, 35, 1293–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballav, N.; Maity, A. High efficient removal of chromium(VI) using glycine doped polypyrrole adsorbent from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198–199, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, N.; Amari, A.; Katubi, K.; Alzahrani, F.; Rebah, F.; Tahoon, M. Innovative magnetite based polymeric nanocomposite for simultaneous removal of methyl orange and hexavalent chromium from water. Processes 2021, 9, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna Birniwa, A.; Salisu Abubakar, A.; Obidul Huq, A.K.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E. Polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine (PPy-PEI) nanocomposite: An effective adsorbent for nickel ion adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2020, 58, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canoluk, C.; Gursoy, S.S. Chemical Modification of Rose Leaf with Polypyrrole for the Removal of Pb (II) and Cd (II) from Aqueous Solution. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2017, 54, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Ali, A.; Su, J.; Chang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Bioaugmented removal of 17β-estradiol, nitrate and Mn(II) by polypyrrole@corn cob immobilized bioreactor: Performance optimization, mechanism, and microbial community response. Environ. Poll. 2022, 299, 118896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, G.; Qin, L.; Fang, J. Application progress of microbial immobilization technology based on biomass materials. BioResources 2021, 16, 8509–8524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceutical Contaminants in Urine. Water 2023, 15, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira Caixeta, M. Contaminants of Emerging Concern: A Review of Risk Assessment and Treatment Strategies. U. Porto J. Eng. 2023, 9, PEC202122_01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, V.; Pare, B.; Gupta, P.; Jonnalagadda, S.; Shrivastava, R. A Review on Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for Wastewater Remediation. Asian J. Chem. 2020, 32, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, B.; Miądlicki, P.; Przepiórski, J. Development of activated carbon for removal of pesticides from water: Case study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samghouli, N.; Bencheikh, I.; Azoulay, K.; Jansson, S.; El Hajjaji, S. Mechanistic and reactional activation study of carbons destined for emerging pharmaceutical pollutant adsorption. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, F.K.; Silva, T.T.; Boiani, N.F.; Borrely, S.I. Is ionizing radiation effective in removing pharmaceuticals from wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23975–23983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade, J.R.; Oliveira, M.F.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of Pharmaceuticals from Water and Wastewater Using Activated Carbon: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3103–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwierawska, A.; Nowacka, D.; Kozłowska-Tylingo, K. Removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics from wastewater by adsorption on cross-linked β-cyclodextrin. Water Res. Ind. 2022, 28, 100186–100198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakić, V.; Rajić, N.; Daković, A.; Auroux, A. The adsorption of salicylic acid, acetylsalicylic acid and atenolol from aqueous solutions onto natural zeolites and clays: Clinoptilolite, bentonite and kaolin. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 166, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafai, H.; Lotfi, H.; Bazzaoui, M.; Albourine, A. Adsorption du salicylate de sodium et du Cr(VI) par le polypyrrole. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2013, 4, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Farghal, H.H.; Tawakey, S.H.; Amer, W.A.; Ayad, M.M.; Madkour, T.M.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Polypyrrole- and Polyaniline-Coated Cotton Fabrics as Efficient Adsorbents for the Pharmaceutical Water Contaminants Diclofenac and Salicylic Acid. Polymers 2023, 15, 3563–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laktif, T.; Imgharn, A.; Hsini, A.; Elhoudi, M.; Aarab, N.; Laabd, M.; Lakhmiri, R.; Albourine, A. Sunflower seed shells@polyaniline: A novel composite for the removal of pharmaceutical pollutants from wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 104, 2195–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshadi, M.; Mousavinia, F.; Abdolmaleki, M.K.; Amiri, M.J.; Khalafi-Nezhad, A. Removal of Salicylic Acid as an Emerging Contaminant by a Polar Nano-Dendritic Adsorbent from Aqueous Media. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2017, 493, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, Z.; Yang, L.; Yan, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.N. Synthesis and Adsorption Property of Hydrophilic-Hydrophobic Macroporous Crosslinked Poly(Methyl Acryloyl Diethylenetriamine)/Poly(Divinylbenzene) (PMADETA/PDVB) Interpenetrating Polymer Networks (IPNs). RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26616–26624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.J.; Hameed, B.H. Adsorption Behavior of Salicylic Acid on Biochar as Derived from the Thermal Pyrolysis of Barley Straws. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecone, C.; Iudici, M.; Ginepro, M.; Zanetti, M.; Trotta, F.; Bracco, P. Dextrin-Based Adsorbents Synthesized via a Sustainable Approach for the Removal of Salicylic Acid from Water. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro Pires, B.; Aparecida do Nascimento, T.; Viana Avelar Dutra, F.; Bastos Borgeş, K. Removal of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory by adsorption on polypyrrole/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite—Study of kinetics and equilibrium in aqueous medium. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 578, 123583–123595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro Pires, B.; Viana Avelar Dutra, F.; Nascimento, T.A.; Bastos Borges, K. Removal of pharmaceuticals from aqueous samples by adsorption using pristine polypyrrole as adsorbent: Kinetic, isothermal and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 5337–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Choi, Y.; Choe, J.K. Novel phenyl-phosphate-based porous organic polymers for removal of pharmaceutical contaminants in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaipulizan, N.S.; Jamil, S.N.A.M.; Abdullah, L.C.; Choong, T.S.Y.; Kamaruzaman, S.; Subri, N.N.S.; Othman, N. Hypercrosslinked poly (AN-co-EGDMA-co-VBC): Synthesis via suspension polymerization, characterizations, and potential to adsorb diclofenac and metformin from aqueous solution. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2020, 298, 1649–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angosto, J.M.; Roca, M.J.; Fernández-López, J.A. Removal of Diclofenac in Wastewater Using Bio-sorption and Advanced Oxidation Techniques: Comparative Results. Water 2020, 12, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukchuay, T.; Kanatharana, P.; Wannapob, R.; Thavarungkul, P.; Bunkoed, O. Polypyrrole/silica/magnetite nanoparticles as a sorbent for the extraction of sulfonamides from water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3921–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Roostaie, A.; Yahya Baktash, M. A chitosan–polypyrrole magnetic nanocomposite as μ-sorbent for isolation of naproxen. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 816, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezhadali, A.; Easapour Koushali, S.; Divsar, F. Synthesis of polypyrrole-chitosan magnetic nanocomposite for the removal of carbamazepine from wastewater: Adsorption isotherm and kinetic study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105648–105660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.U.; Mahanty, B.; Kim, C.G. Preparation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nano-particles and evaluation of their adsorption capacity toward carbamazepine, and di-atrizoate. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 7789–7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, J.R.; Gonzalez, T.; Palo, P.; Cuerda-Correa, E.M. Removal of common pharmaceuticals present in surface waters by Amberlite XAD-7 acrylic-ester-resin: Influence of pH and presence of other drugs. Desalination 2011, 269, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarcewicz, M.K.; Sobczak, J.; Paździoch, W. Removal of carbamazepine from aqueous solution by adsorption on fly ash-amended soil. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.-B.; Li, Y.-y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.-y.; Cheng, X.-W. Adsorptive removal of indomethacin and diclofenac from water by polypyrrole doped-GO/COF-300 nanocomposites. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedi, M.; Mollahosseini, A.; Negarestani, M. Ultrasonic-assisted batch operation for the adsorption of rifampin and reactive orange 5 onto engineered zeolite–polypyrrole/TiO2 nanocomposite. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 7547–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifi, B.; Noëlle Pons, M.; Zahraa, O.; Alatrache, A. Photosensitization of TiO2 by Polyaniline for Salicylic acid Degradation Under Visible Light. Chem. Afr. 2024, 7, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abinaya, M.; Rajakumaran, R.; Chen, S.-M.; Karthik, R.; Muthuraj, V. Polypyrrole Polymer-Incorporated Ag2MoO4 Nanocomposite for Detection and Degradation of Environmental Pollutants and Pharmaceutical Drugs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38321–38335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abinaya, M.; Muthuraj, V. Bi-functional catalytic performance of silver manganite/polypyrrole nanocomposite for electrocatalytic sensing and photocatalytic degradation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 604, 125321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Huo, P.; Guan, Q. Preparation of polypyrrole-TiO2 and its adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of salicylic acid. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 3291–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedadeep, D.; Shahnaz, T.; Manu Sankar, V.; Sahoo, L.; Narayanasamy, S. Organic polymer doped graphene-based composite for the effective elimination of diclofenac: A detailed study with phytotoxic assessments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Carrillo, M.J.; Melgoza-Alemán, R.M.; Cuevas-Arteaga, C.; Proal-Nájera, J.B. Removal of Persistent Acid Pharmaceuticals by a Biological-Photocatalytic Sequential Process: Clofibric Acid, Diclofenac, and Indomethacin. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkhaya, S.; M’Rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. A review on classifications, recent synthesis and applications of textile dyes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 115, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Osborne, J.W. Biodegradation and Biosorption of Reactive Red 120 Dye by Immobilized Pseudomonas guariconensis: Kinetic and Toxicity Study. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemashenpagam, N.; Selvajeyanthi, S. Textile Dyes and Their Effect on Human Beings. In Nanohybrid Materials for Treatment of Textiles Dyes; Ahmad, A., Jawaid, M., Mohamad Ibrahim, M.N., Yaqoob, A.A., Alshammari, M.B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Kumar, K. Aquatic Toxicity Attributable to Textile Industries. Chapter 1. In Research Trends in Chemical Sciences; Kumar Acharya, A., Ed.; AkiNik Publications: Delhi, India, 2020; Volume 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, H.J. Removal of Acid Orange 7 Dye from Wastewater: Review. In Proceedings of the Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 4 February–9 April 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajjaoui, H.; Soufi, A.; Khnifira, M.; Abdennouri, M.; Zahra Mahjoubi, F.; Barka, N. Mono and binary mixture removal of eriochrome black T and Cr(VI) from water by SiO2/polyaniline composite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 296, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, I.; Pahuja, M.; Wani, H.M.; Dey, A.; Dube, T.; Ghosh, R.; Kankan, N.; Mishra, J.; Jyoti Panda, J.; Maruyama, T.; et al. In-vitro toxicity assessment of a textile dye Eriochrome Black T and its nano-photocatalytic degradation through an innovative approach using Mf-NGr-CNTs-SnO2 heterostructures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 113985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsenbeni, N.L.; Viphrezolie, S.; Pranjal, B.; Latonglila, J. Advancement in Sustainable Wastewater Treatment: A Multifaceted Approach to Textile Dye Removal through Physical, Biological and Chemical Techniques. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202304093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Hamidah Mohd-Setapar, S.; Sing Chuong, C.; Khatoon, A.; Wani, W.A.; Kumard, R.; Rafatullah, M. Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: Novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Leng, L.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zeng, G. Facile synthesis of polypyrrole decorated reduced graphene oxide–Fe3O4 magnetic composites and its application for the Cr(VI) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Surela, A.; Kumari Chhachhia, L.; Kumar Surela, V.; Lal Meena, P. Polypyrrole-Based Composites for Dyes Removal From Contaminated Water. In Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, P.; Agalya, A.; Sivakumar, P. Polypyrrole composite-a potential material for the removal of acid dyes. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 5891–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, H.N.; Jabeen, A.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S.; Naseem, Z. Adsorptive behavior of rice bran-based composites for malachite green dye: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 237, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoor, F.; Nasar, A. Environmental application of agro-waste derived materials for the treatment of dye polluted water: A review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 17, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Dai, Z.; Yu, Q.; Miao, Y.; Xu, R. Facile preparation of a polypyrrole modified Chinese yam peelbased adsorbent: Characterization, performance, and application in removal of Congo red dye. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 9424–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefatle, M.C.; Madikizela, L.M.; Pakade, V.E.; Nomngongo, P.N. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic chitosan-polypyrrole composite for adsorption of tetracyclines from contaminated water. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2024, 78, 178–191. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10520/ejc-chem-v78-n1-a24 (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Chen, Y.; Long, W.; Xu, H. Efficient removal of acid red 18 from aqueous solution by in-situ polymerization of polypyrrole-chitosan composites. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 287, 110888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, S.; Nawaz Bhatti, H.; Iqbal, M.; Hussain, F.; Malik Sarim, F. Chitosan, starch, polyaniline and polypyrrole biocomposite with sugarcane bagasse for the efficient removal of Acid Black dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Kolbadi Nezhad, M.; Tagipour Kolaei, Z.; Tanzifi, M. Characterization of polypyrrole hydroxyethyl cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite: Thermal properties and afm analysis. Int. J. Eng. 2015, 28, 654–661. Available online: https://www.ije.ir/article_72502.html (accessed on 15 June 2025).
- Shahnaz, T.; Padmanaban, V.; Narayanasamy, S. Surface modification of nanocellulose using polypyrrole for the adsorptive removal of Congo red dye and chromium in binary mixture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.L.; Dhar, N.; Liu, H.L.; Tam, K.C. Chemistry and Applications of Nanocrystalline Cellulose and its Derivatives: Nanotechnology Perspective. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 89, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Hossein Mahvi, A.; Balarak, D.; Dokht Khatibi, A. Adsorption of Acid orange 7 dyes from aqueous solution using Polypyrrole/nanosilica composite: Experimental and modelling. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Jamaleddin Peighambardoust, S.; Jalali, S.; Ramavandi, B. Application of nano-silica particles generated from offshore white sandstone for cadmium ions elimination from aqueous media. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarak, D.; Jaafari, J.; Hassani, G.; Mahdavi, Y.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. The use of low-cost adsorbent (Canola residues) for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution: Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Coll. Interf. Sci. Commun. 2015, 7, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanna Suvaitha, S.; Venkatachalam, K. Adsorption of Anionic Dyes by Polypyrrole-Grafted Mesoporous SBA-15 Composite: Isotherms, Kinetics, Thermodynamics, Interaction Mechanism and Recycling. Chem. Sel. 2023, 8, e202302878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Debnath, A.; Saha, B. Polypyrrole-encapsulated metal oxide nanocomposite for adsorptive abatement of anionic dye from dye laden wastewater: Cost analysis and scale up design. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Xu, Z.; Pei, Y. The Adsorption Performance of Polyaniline/ZnO Synthesized through a Two-Step Method. Crystals 2022, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Pi, M.; Jiang, C.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J. Synthesis of hierarchical porous zinc oxide (ZnO) microspheres with highly efficient adsorption of Congo red. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2017, 490, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Ansari, A.; Habibi, M.H.; Asghari, A.R. Removal of malachite green from aqueous solution by zinc oxide nanoparticle loaded on activated carbon: Kinetics and isotherm study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishn Goswami, M.; Srivastava, A. Polypyrrole/CoFe2O4 Nanocomposite for the Removal of Basic Blue 3 Dye from Wastewater: Kinetic, Adsorption Isotherm, and Thermodynamic Study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2025, 142, 56713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.; Liu, C.; Li, G.-G.; Liu, Y.-F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.-Y. Adsorption and desorption of dyes by waste-polymer-derived activated carbons. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Chmielewska, E.; Lesny, J.; Koprda, V. Zeolites as (Potential) Decorporating Agents. In NBC Risks Current Capabilities and Future Perspectives for Protection; NATO Science Series; Sohns, T., Voicu, V.A., Szinicz, L., Finke, E.-J., Mircioiu, C., Lundy, P., Brain, K.R., Kempf, H., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 25, pp. 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, M.L. Hydroxyl groups on silica surface. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1975, 19, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, A.; Mariani, G.; Gröhn, F. Ionic dye–surfactant nanoassemblies: Interplay of electrostatics, hydrophobic effect, and π–π stacking. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Zhaoyang, L.; Aimin, L.; Wei, L.; Zhenmao, J.; Jinlong, C.; Quanxing, Z. Adsorption of reactive dyes onto polymeric adsorbents: Effect of pore structure and surface chemistry group of adsorbent on adsorptive properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, N.A.; EL-Daly, H.A.; El Sharkawy, R.G.; Nasr, B.T. Adsorption of Dyes from Aqueous Solutions onto Multi-functional PPy/CS Exfoliated Nanohybrid for Fashionable Layered Polymer Nanocomposites. In Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions, 2nd ed.; Environmental Science and Engineering; Ksibi, M., Ghorbal, A., Chakraborty, S., Chaminé, H.I., Barbieri, M., Guerriero, G., Hentati, O., Negm, A., Lehmann, A., Römbke, J., et al., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtera, S.; Prokeš, J.; Kopecká, J.; Vrňata, M.; Trchová, M.; Varga, M.; Stejskal, J.; Kopecký, D. Dye-stimulated control of conducting polypyrrole morphology. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 51495–51505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Cang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, T.-T.; Song, X.-R.; Farris, S.; Li, Y.-Y.; Fu, Y.-J. Magnetism and NIR dual-response polypyrrole-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles for bacteria removal and inactivation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 126, 112143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.B.; Brugnoni, L.I.; Flamini, D.O.; Quinzani, L.M.; Saidman, S.B. Removal of Escherichia coli from well water using continuous laminar flow in a channel system containing PPy/Cu modified electrodes. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Kang, E.-T.; Xu, L. Surface co-deposition of polypyrrole nanoparticles and tannic acid for photothermal bacterial eradication. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 212, 112381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, P.; Hao, W.; Han, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Liang, P. Additional polypyrrole as conductive medium in artificial electrochemically active biofilm (EAB) to increase the sensitivity of EAB based biosensor in water quality early-warning. Biosensens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113453–113458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, N.; Liang, Q.; Hao, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, P.; Zeng, R.J. Microbial electrochemical sensor for water biotoxicity monitoring. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 127053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Heijne, A.; Pereira, M.A.; Pereira, J.; Sleutels, T. Electron Storage in Electroactive Biofilms. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, X. An electroactive biofilm-based biosensor for water safety: Pollutants detection and early-warning. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 173, 112822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, S.; Chen, X. Ultrahigh flux and strong affinity poly(N–vinylformamide)-grafted polypropylene membranes for continuous removal of organic micropollutants from water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 20796–20809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulahcene, L.; Skiba, M.; Bounoure, F.; Benamor, M.; Milon, N.; Hallouard, F.; Lahiani-Skiba, M. New polymer inclusion membrane containing β-Cyclodextrin polymer: Application for pharmaceutical pollutant removal from wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Coppens, M.-O.; Jiang, Z. Mixed-dimensional membranes: Chemistry and structure property relationships. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 11747–11765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansor, E.; Abdallah, H.; Shaban, A.M. The role of membrane filtration in wastewater treatment. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2024, 34, e22251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarleton, S.; Wakeman, R. Solid/Liquid Separation: Scale-Up of Industrial Equipment, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 140–196. ISBN 10 1856174204. [Google Scholar]
- Razavi, S.M.A.; Mortazavian, M.M.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.M. Recent Advancements of UF-Based Separation for Selective Protein Enrichment: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lin, S.; Jin, H.; Gao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, J. Nanoparticle-templated nanofiltration membranes for ultrahigh performance desalination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwenke, A.M.; Hoeppener, S.; Schubert, U.S. Microwave synthesis of carbon nanofibers—The influence of MW irradiation power, time, and the amount of catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23778–23787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudaib, B.; Abu-Zurayk, R.; Waleed, H.; Alqader Ibrahim, A. Fabrication of a Novel (PVDF/MWCNT/Polypyrrole) Antifouling High Flux Ultrafiltration Membrane for Crude Oil Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Das, R.; Ho, W.H.; Srinivasu, V.; Maity, A. A novel method for removal of Cr(VI) using polypyrrole magnetic nanocomposite in the presence of unsteady magnetic fields. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.; Chibowski, E. Superhydrophilic and superwetting surfaces: Definition and mechanisms of control. Langmuir 2010, 26, 18621–18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Bayarkhuu, B.; Han, Y.; Kim, H.-W.; Jeong, S.; Boo, C.; Byun, J. Multifunctional photo-Fenton-active membrane for solar-driven water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, S. Antifouling Conductive Composite Membrane with Reversible Wettability for Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Hu, C.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Electrically Pore-Size-Tunable Polypyrrole Membrane for Antifouling and Selective Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Shortcomings |
|---|---|
| Adsorption | Multiple parameters govern the process |
| Flocculation | Development of sludge precipitates |
| Electrolytic precipitation | Demands significant processing time |
| Electrochemical oxidation | High operational cost driven by electrical energy usage |
| Ion exchange | Effective for selected dyes |
| Fenton process | Excessive generation of anionic species |
| Membrane filtration | Characterized by limited stability and high cost |
| Phytoremediation | Provides a non-permanent remediation solution |
| Bioremediation | Inhibits microbial growth and activity |
| Photocatalytic degradation | Requires a light source, which contributes to increased operational costs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Golba, S.; Jurek-Suliga, J. Evaluation of Polypyrrole as a Functional Sorbent for Water Treatment Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169153
Golba S, Jurek-Suliga J. Evaluation of Polypyrrole as a Functional Sorbent for Water Treatment Technologies. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169153
Chicago/Turabian StyleGolba, Sylwia, and Justyna Jurek-Suliga. 2025. "Evaluation of Polypyrrole as a Functional Sorbent for Water Treatment Technologies" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169153
APA StyleGolba, S., & Jurek-Suliga, J. (2025). Evaluation of Polypyrrole as a Functional Sorbent for Water Treatment Technologies. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9153. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169153







