Hybrid Mortars Activated with Alternative Steel-Compatible Salts: Impact on Chloride Diffusion and Durability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mortar Formulation and Manufacturing
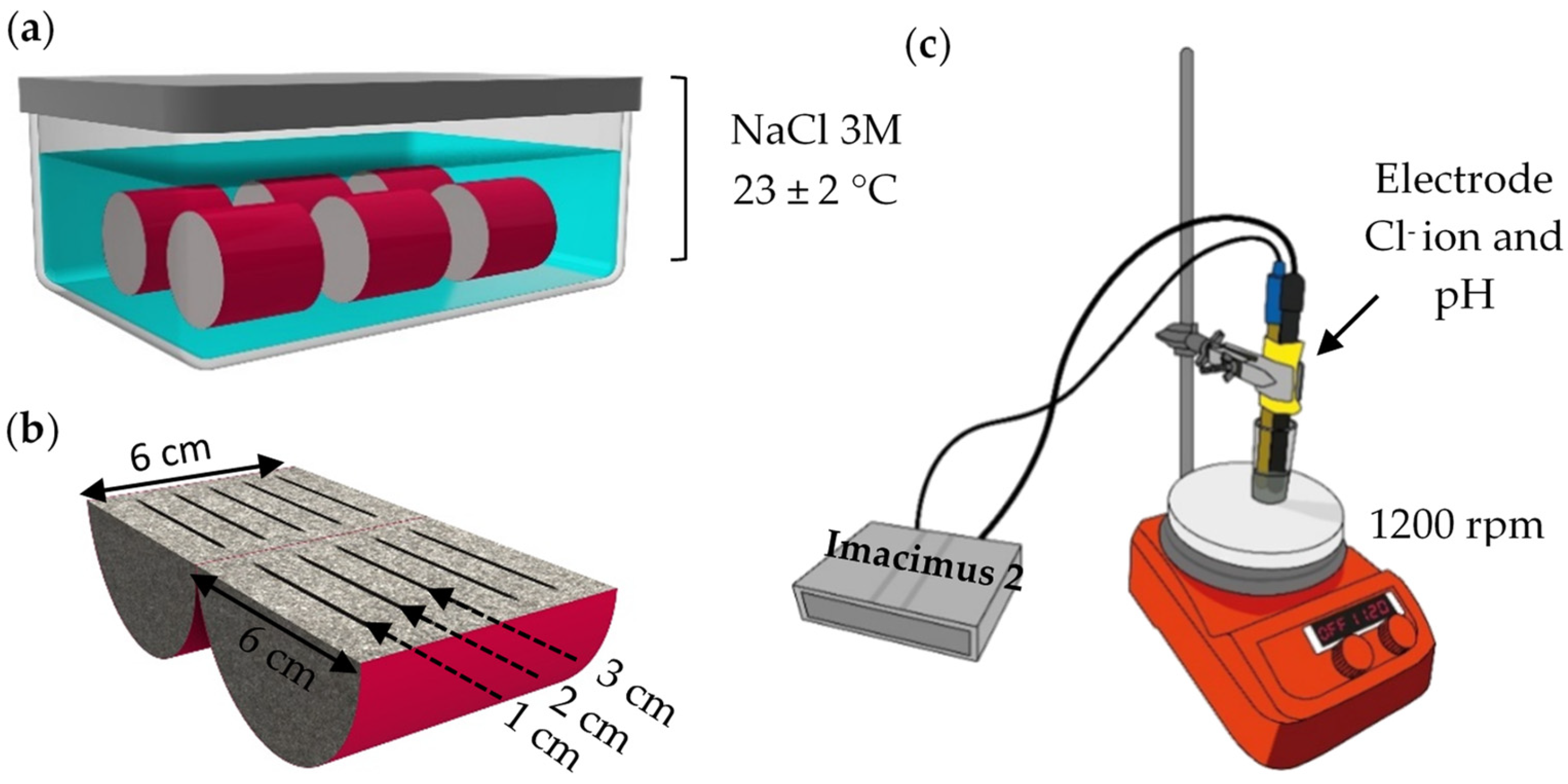
2.2. Mortar Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
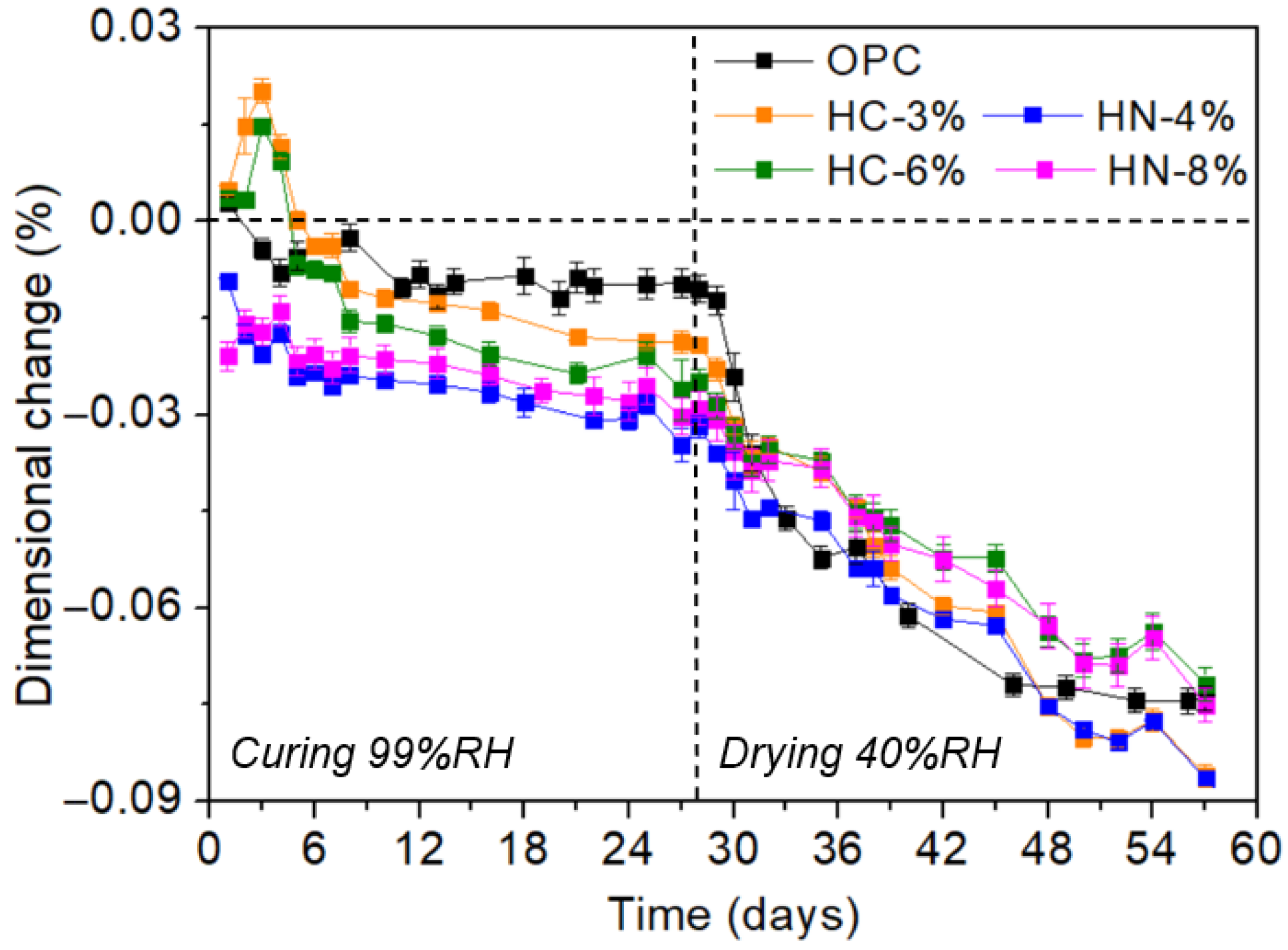
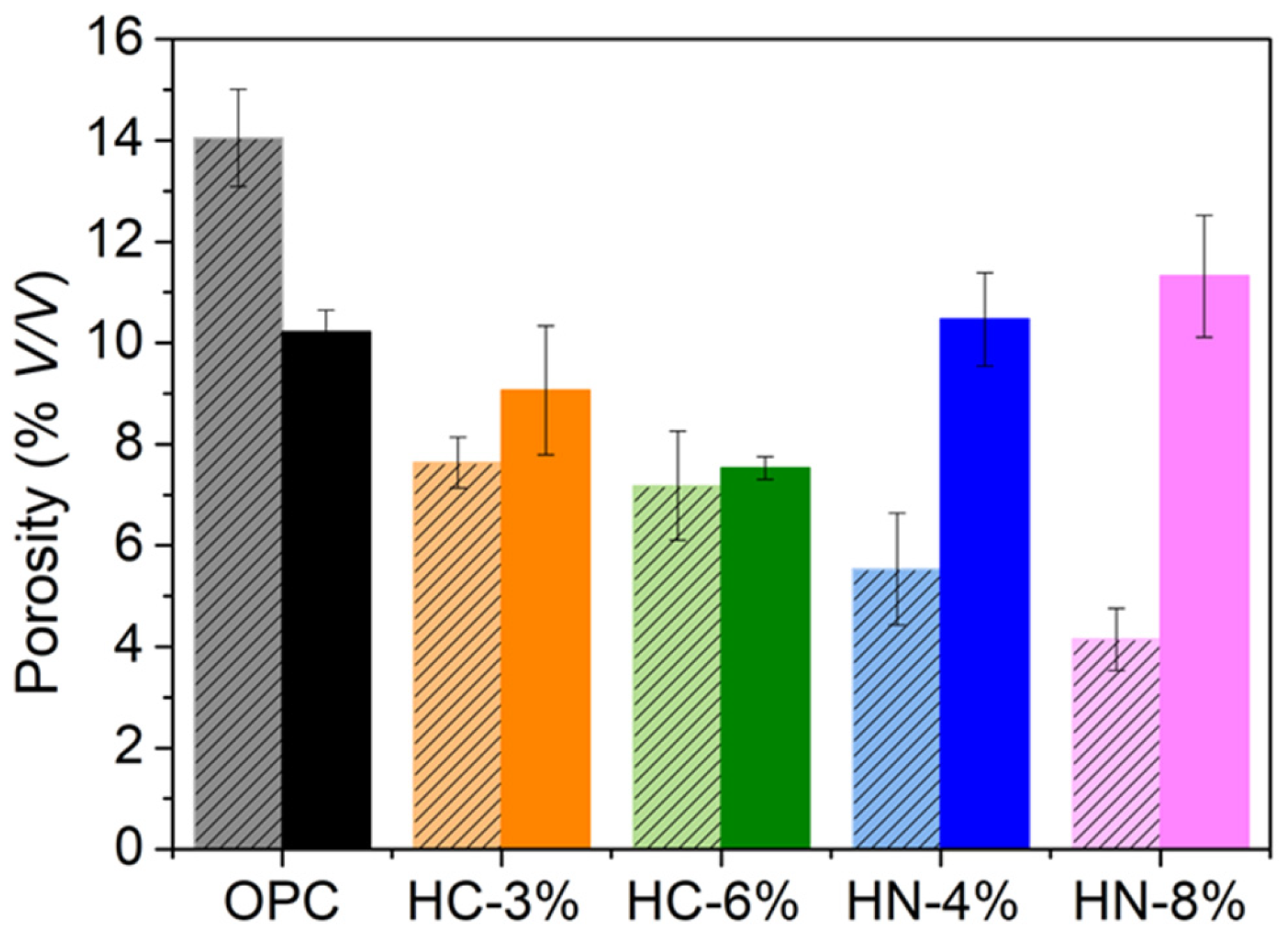
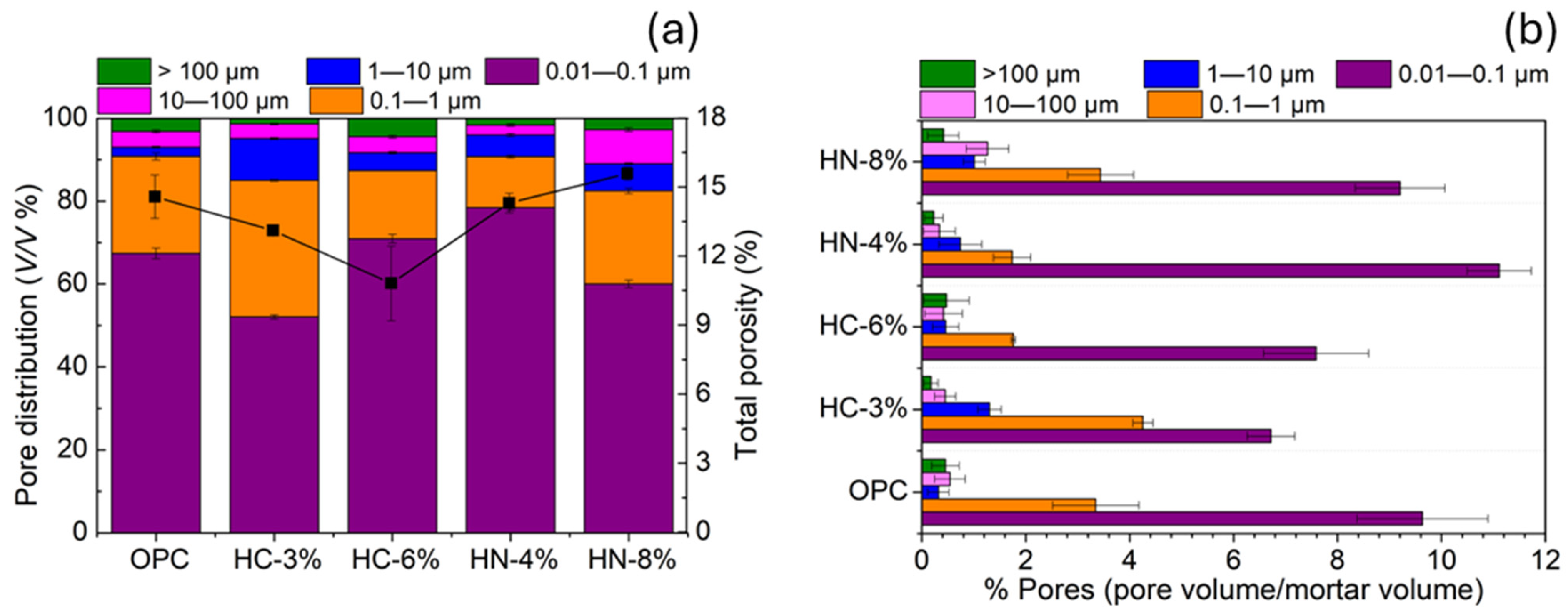
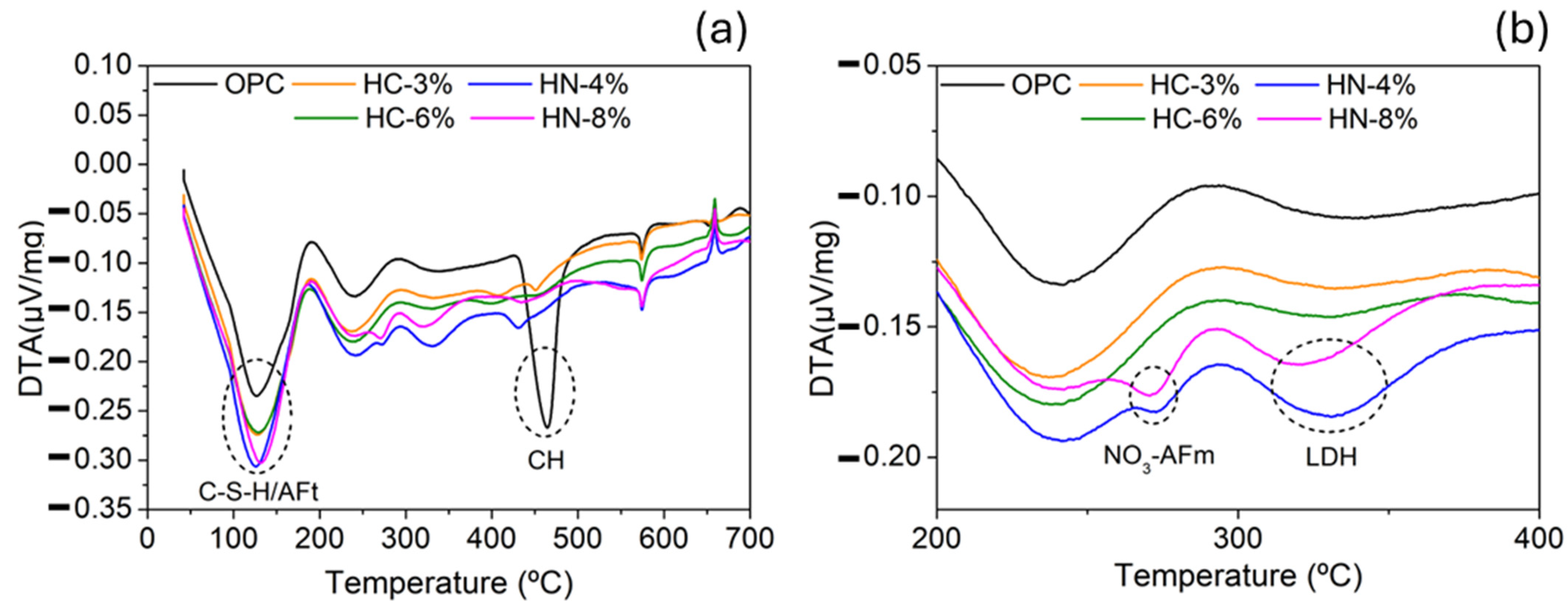
3.1. Dimensional Stability, Porosity and Phases Formed
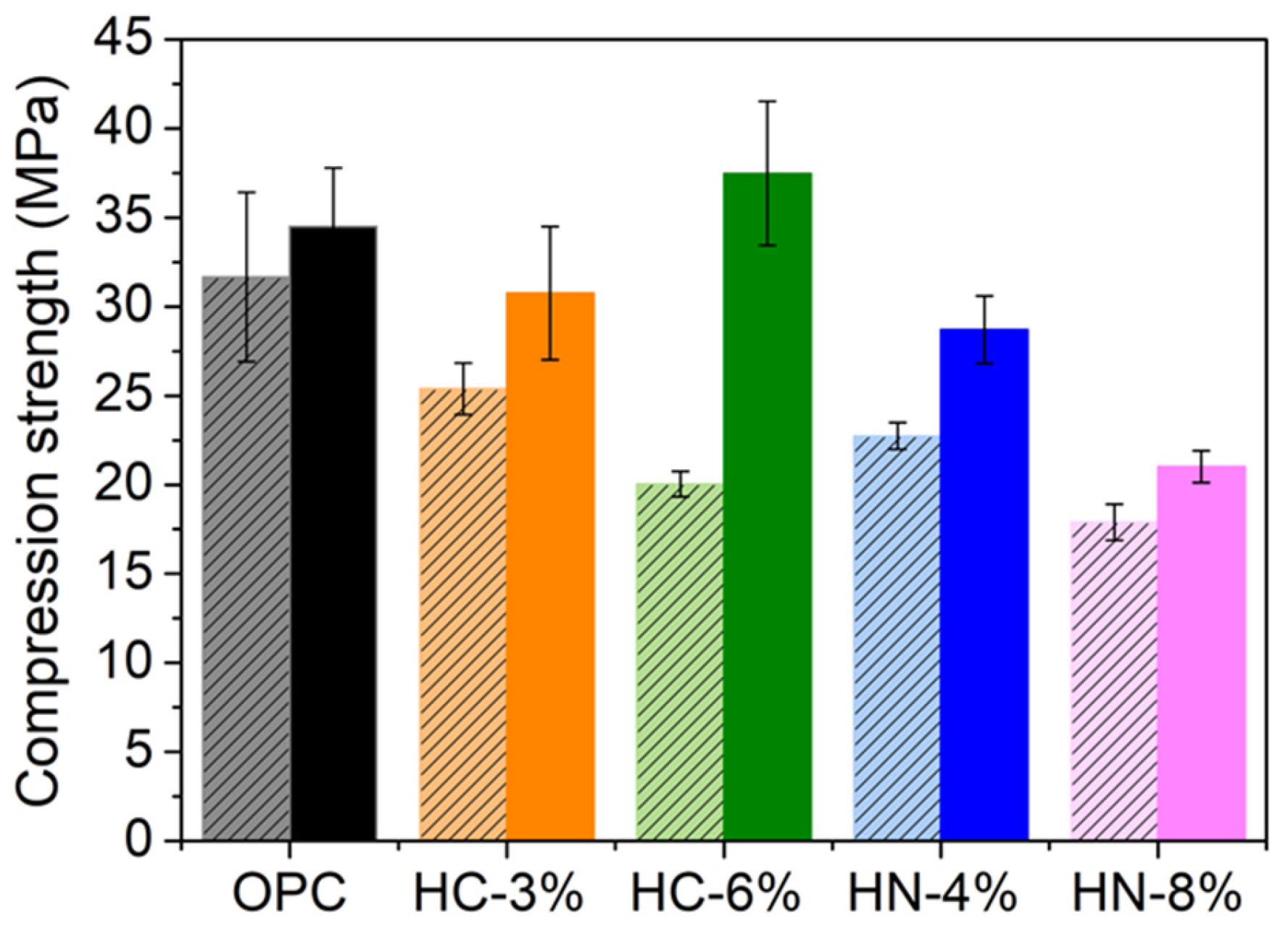
3.2. Mechanical Properties
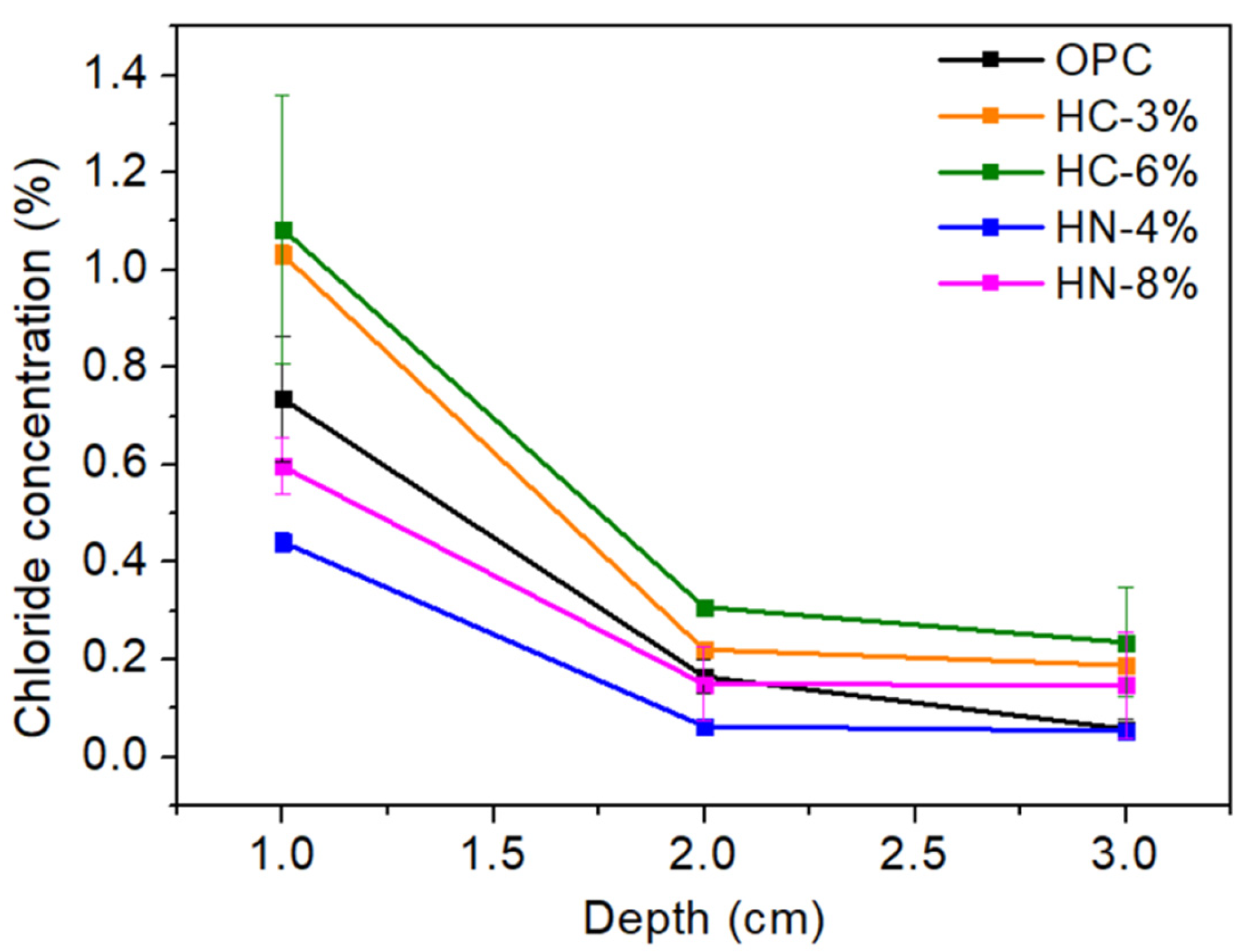
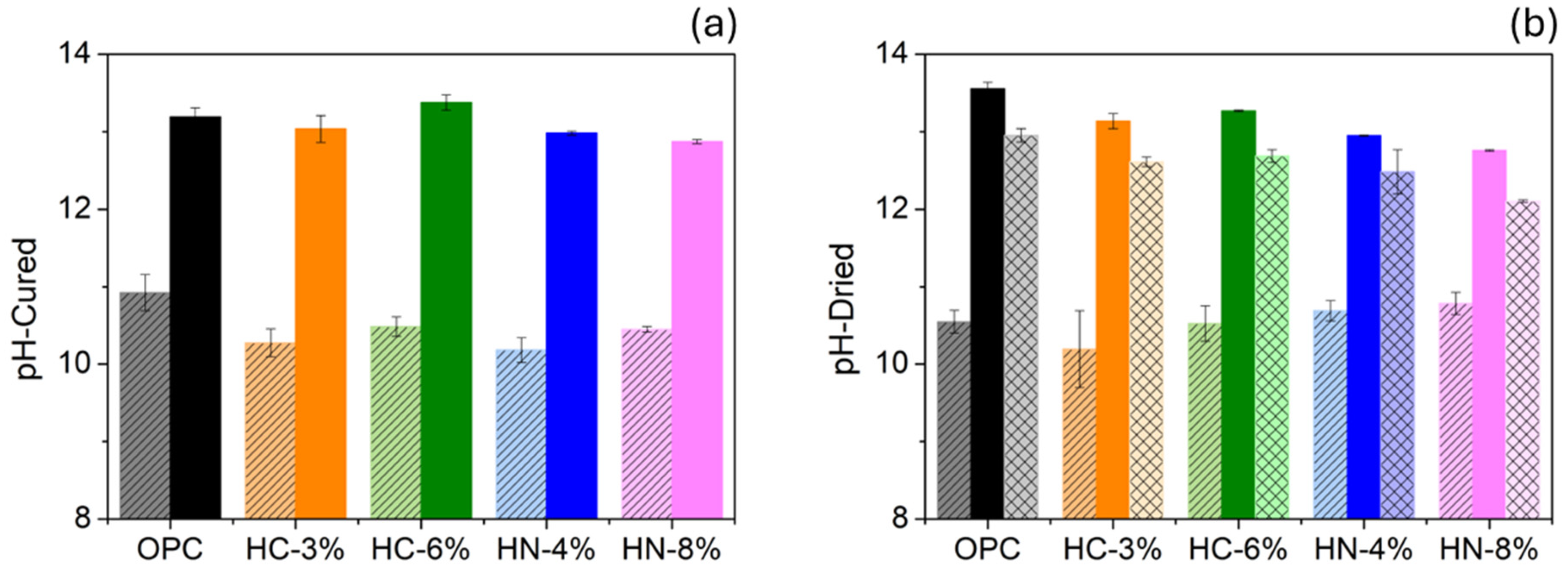
3.3. Chlorides and Sulfide Oxidation Profiles and pH
4. Conclusions
- The activation of hybrid mortars is more effective when using carbonates than when using nitrates, if porosity reduction or compression strength are considered. After drying, the hybrid mortars activated with 6% of carbonate are less porous and more compression resistant than OPC.
- Microcracks tend to be generated in the hybrid mortar microstructure when carbonate is used for activation.
- Precipitation of nitrate-AFm hinders chloride diffusion into the mortars.
- Mortar activation with moderate amounts of nitrates (4% wt.) promotes higher resistance to chloride penetration than that of the OPC used as reference, and reasonable high mechanical properties.
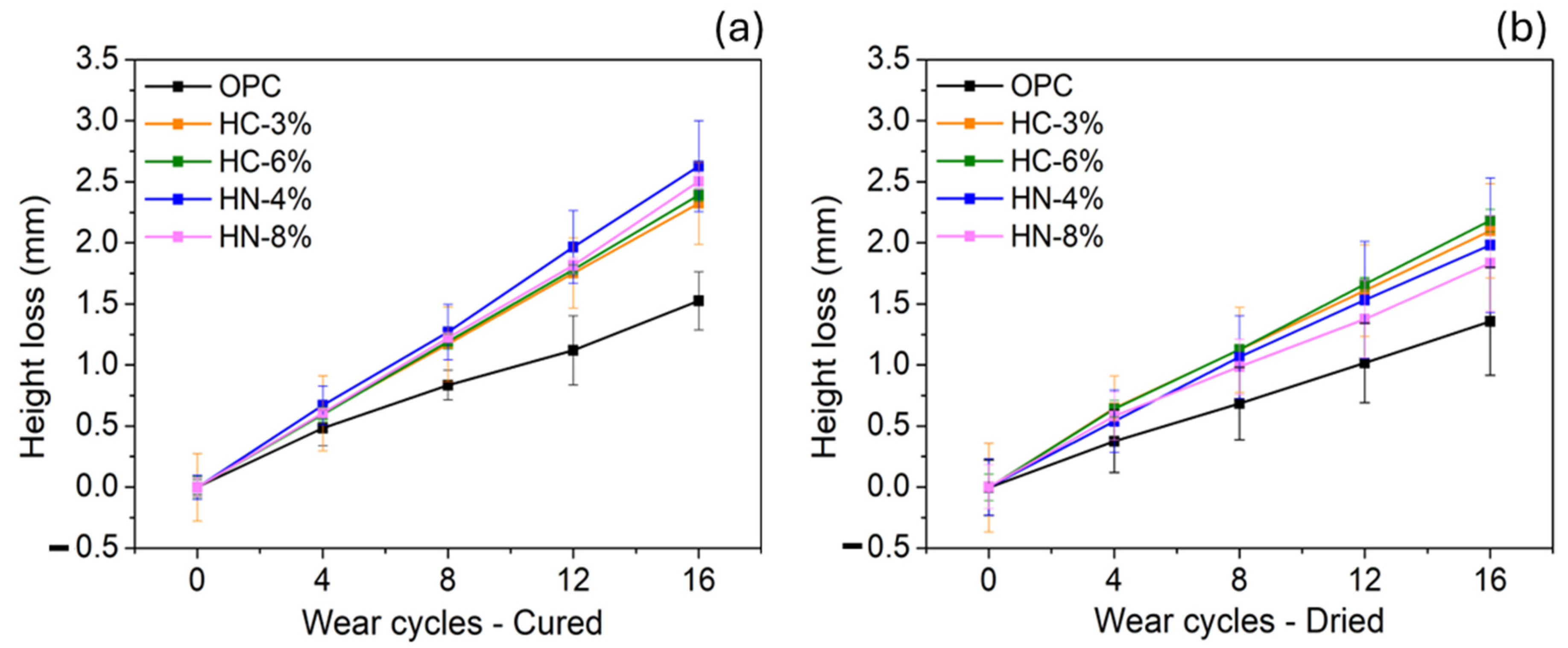
- The wear performances of the hybrid mortars under study are worse than that of OPC. This weakness, if it is not overcome in future formulations, can limit certain eventual applications.
- pH values of hybrid mortars are highly alkaline, as those of OPC. However, the long-term effect of their lower alkaline reserve warrants further study.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAM | Alkali-Activated Materials |
| ACR | Alkali-Carbonate Reaction |
| AFm | Aluminate Ferrite Monosulfate |
| AFt | Aluminate Ferrite Trisulfate |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing and Materials |
| C-A-S-H | Calcium Aluminum Silicate Hydrate |
| C-S-H | Calcium Silicate Hydrate |
| CH | Calcium Hydroxide (Portlandite) |
| DTA | Differential Thermal Analysis |
| HC | Hybrid Cement activated with Carbonate |
| HN | Hybrid Cement activated with Nitrate |
| LDH | Layered Double Hydroxide |
| N-A-S-H | Sodium Aluminum Silicate Hydrate |
| OPC | Ordinary Portland Cement |
| PC | Portland Cement |
| RH | Relative Humidity |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TG | Thermogravimetry |
| UNE-EN | European Standard–Spanish Implementation |
| XRF | X-ray Fluorescence |
| s/b | Sand-to-Binder Ratio |
References
- Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Recent progress in environmentally friendly geopolymers: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhelal, E.; Zahedi, G.; Shamsaei, E.; Bahadori, A. Global strategies and potentials to curb CO2 emissions in cement industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrell, E.; Price, L.; Martin, N.; Hendriks, C.; Meida, L.O. Carbon dioxide emissions from the global cement industry. Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 2001, 26, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beersaerts, G.; Hertel, T.; Lucas, S.; Pontikes, Y. Promoting the use of Fe-rich slag in construction: Development of a hybrid binder for 3D printing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 138, 104959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Martin, A.; Pastor, J.Y.; Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. Characterisation of pre-industrial hybrid cement and effect of pre-curing temperature. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 73, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martauz, P.; Janotka, I.; Strigáč, J.; Bačuvčík, M. Fundamental properties of industrial hybrid cement: Utilization in ready-mixed concretes and shrinkage-reducing applications. Mater. Constr. 2016, 66, e084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, A.; Monteiro, P.; Martauz, P.; Bílek, V.; Fernandez-Jimenez, A. Hybrid binders: A journey from the past to a sustainable future (opus caementicium futurum). Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Zheng, D.; Du, J.; Bu, Y.; Zhou, A.; Pang, X.; Liu, H. Controlling the hydration rate of alkali-activated slag by the slow release of NaOH. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 228, 211960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagñay, S.; Bautista, A.; Velasco, F.; Ramón-Álvarez, I.; Torres-Carrasco, M. Influence of the early-age length change of alkali-activated slag mortars on the corrosion of embedded steel. J. Sust. Cem. Bas. Mater. 2023, 13, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyaaldin, M.H.; Mosaberpanah, M.A.; Alzeebaree, R. Shrinkage behavior and mechanical properties of alkali activated mortar incorporating nanomaterials and polypropylene fiber. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 23159–23171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; De Belie, N.; Snoeck, D. Internal curing and its application to alkali-activated materials: A literature review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 145, 105360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Niu, H. Study on the effect and mechanism of cement-based material retarder on red mud-based hybrid alkali activated cement. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 70, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Martínez, A.E.; González-López, J.R.; Guerra-Cossío, M.A.; Hernández-Carrillo, G. Sulphate-based activation of a binary and ternary hybrid cement with portland cement and different pozzolans. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.S.; Shi, C.; Hashem, F.S.; Israde-Alcántara, I.; Pfeiffer, H. Exploring diatomite as a novel natural resource for ecofriendly-sustainable hybrid cements. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 202, 107402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahrache, S.; Winnefeld, F.; Champenois, J.B.; Hesselbarth, F.; Lothenbach, B. Chemical activation of hybrid binders based on siliceous fly ash and Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 66, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etcheverry, J.M.; Villagran-Zaccardi, Y.A.; Van den Heede, P.; Hallet, V.; De Belie, N. Effect of sodium sulfate activation on the early age behaviour and microstructure development of hybrid cementitious systems containing Portland cement, and blast furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 141, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkoglu, M.; Yavuz Bayraktar, O.; Benli, A.; Kaplan, G. Effect of cement clinker type, curing regime and activator dosage on the performance of one-part alkali-activated hybrid slag/clinker composites. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 68, 106164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, C.; Kutuk, S.; Kutuk-Sert, T. Influence of processed tea waste ash on the hydration products and mechanical property of hybrid cement as an eco-friendly solution. Waste Manag. 2025, 191, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristelo, N.; Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Rivera, J.F.; Miranda, T.; Palomo, Á.; Coelho, J.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. One-part hybrid cements from fly ash and electric arc furnace slag activated by sodium sulphate or sodium chloride. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, R.; Sturm, P.; Keßler, S.; Gluth, G.J.G. Corrosion of hybrid alkaline cements in saline solution simulating evaporite rock–Effect of the Portland clinker content. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 172, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-L.; Lin, W.-T.; Chen, S.-C.; Sprince, A. Study on the cementation and engineering properties of ternary eco-binder mortar containing pulverized coal fly ash mixed with circulating fluidized bed co-fired fly ash. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 83, 102787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza-Chávez, A.C.; Gómez-Zamorano, L.Y.; Acevedo-Dávila, J.L. Synthesis and characterization of a hybrid cement based on fly ash, metakaolin and Portland cement clinker. Materials 2020, 13, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagñay, S.; Bautista, A.; Donaire, J.; Torres-Carrasco, M.; Bastidas, D.M.; Velasco, F. Chloride-induced corrosion of steel reinforcement in mortars manufactured with alternative environmentally-friendly binders. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 130, 104557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, K.M. Strength and microstructural characteristics of chemically activated fly ash–cement systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, A.K.; Pradhan, B. Hybrid alkali activated cements (HAACs) system: A state-of-the-art review on fresh, mechanical, and durability behaviour. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Fernandez-Jimenez, A.; Palomo, A. Hydration kinetics in hybrid binders: Early reaction stages. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 39, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.H.; Khan, M.; Zhong, R.Y. Strength, porosity and life cycle analysis of geopolymer and hybrid cement mortars for sustainable construction. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagñay, S.; Bautista, A.; Velasco, F.; Torres-Carrasco, M. Carbonation of alkali-activated and hybrid mortars manufactured from slag: Confocal Raman microscopy study and impact on wear performance. Boletín Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2023, 62, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarian, M.; Tao, Z.; Adam, G.; Samali, B. Mechanical properties of ambient cured one-part hybrid OPC-geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Gu, K.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Strength and drying shrinkage of reactive MgO modified alkali-activated slag paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 51, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qiu, J.; Xing, J.; Sun, X. Chemical activation of binary slag cement with low carbon footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 121455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagñay, S.; Bautista, A.; Velasco, F.; Torres-Carrasco, M. Hybrid cements: Towards their use as alternative and durable materials against wear. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahri, W.; Hu, X.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Z. Review on corrosion of steel reinforcement in alkali-activated concretes in chloride-containing environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Du, J.; Wang, C.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Evaluating the chloride diffusion coefficient of cement mortars based on the tortuosity of pore structurally-designed cement pastes. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 317, 111018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Fan, J.; Peng, Z. Chloride transport in alkali-activated materials influenced by different reaction products: A review. Mag. Concr. Res. 2024, 20, 1198–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shi, C.; De Schutter, G.; Audenaert, K.; Deng, D. Chloride binding of cement-based materials subjected to external chloride environment—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, N.; Gómez, E.D.; Duffó, G.S.; Farina, S.B. Effect of sulphate on the corrosion of reinforcing steel in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 354, 129214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Inoue, M.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Sudoh, Y.; Kwon, S.; Lee, B.; Yoneyama, A. Physicochemical study on the strength development characteristics of cold weather concrete using a nitrite–nitrate based accelerator. Materials 2019, 12, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolzoni, F.; Brenna, A.; Ormellese, M. Recent advances in the use of inhibitors to prevent chloride-induced corrosion in reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2022, 154, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zuo, Y. The inhibitive mechanisms of nitrite and molybdate anions on initiation and propagation of pitting corrosion for mild steel in chloride solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 353, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, R.; Bautista, A.; Shagñay, S.; Velasco, F. Licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) as corrosion inhibitor of carbon steel reinforcing bars in mortar and its synergic effect with nitrite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 129, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagñay, S.; Ramón, L.; Fernández-Álvarez, M.; Bautista, A.; Velasco, F.; Torres-Carrasco, M. Eco-efficient hybrid cements: Pozzolanic, mechanical and abrasion properties. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ye, G. Understanding chloride diffusion coefficient in cementitious materials. Materials 2023, 16, 3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, M.; Chen, R.; Weng, L.; Wang, D. Effects of seawater concentration on the drying shrinkage of seawater concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 457, 139437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Radlińska, A. Shrinkage mitigation strategies in alkali-activated slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 101, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Mingshu, T. Correlation between reaction and expansion of alkali-carbonate reaction. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, A.; Paredes, E.C.; Velasco, F.; Alvarez, S.M. Corrugated stainless steels embedded in mortar for 9 years: Corrosion results of non-carbonated, chloride-contaminated samples. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Amankwah, S.; Black, L.; Xianfeng, L.; Hou, P.; Zajac, M. Early age reaction of slag in composite cement: Impact of sulphates and calcite. Cement 2023, 14, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.-X.; Li, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.-F. Physicochemical modelling in chlorides migration in concrete with account of multi-species coupling, reaction kinetic and pore evolution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 460, 139707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, M.A.; Mena, Á.; Mínguez, J.; González, D.C. Use of computed tomography scan technology to explore the porosity of concrete: Scientific possibilities and technological limitations. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Carcelen-Taboada, V.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Manufacture of hybrid cements with fly ash and bottom ash from a municipal solid waste incinerator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, A.; Choi, H.; Inoue, M.; Kim, J.; Lim, M.; Sudoh, Y. Effect of a nitrite/nitrate-based accelerator on the strength development and hydrate formation in cold-weather cementitious materials. Materials 2021, 14, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. Early hydration kinetics and microstructure development of hybrid alkali activated cements (HAACs) at room temperature. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 123, 104200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Luo, L.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y. Study on the effect of cellulose nanocrystals on the pore structure and drying shrinkage of alkali-activated recycled ultra-high performance concrete: A multifractal theory. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 463, 140113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Haha, M.; Le Saout, G.; Winnefeld, F.; Lothenbach, B. Influence of activator type on hydration kinetics, hydrate assemblage and microstructural development of alkali activated blast-furnace slags. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.A.; Gruyaert, E.; Van Tittelboom, K.; De Belie, N. New findings on the contribution of Mg-Al-NO3 layered double hydroxides to the hydration and chloride binding capacity of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 163, 107037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanezaki, E. Thermal behavior of the hydrotalcite-like layered structure of Mg and Al-layered double hydroxides with interlayer carbonate by means of in situ powder HTXRD and DTA/TG. Solid State Ion. 1998, 106, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.Y.; Yu, Q.L.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Relationship between the particle size and dosage of LDHs and concrete resistance against chloride ingress. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 105, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Guo, J.; Tian, J.; Xu, Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, M.; Fan, J. Preparation of Ca/Al layered double hydroxide and the influence of their structure on early strength of cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shagñay, S.; Velasco, F.; del Campo, A.; Torres-Carrasco, M. Wear behavior in pastes of alkali-activated materials: Influence of precursor and alkali solution. Tribol. Int. 2020, 147, 106293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álvarez, M.; Velasco, F.; de la Fuente, D.; Bautista, A. Powder organic coatings functionalized with calcium ion-exchanged silica corrosion inhibitors. Surf. Coat. Techn. 2024, 477, 130377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluth, G.J.G.; Mundra, S.; Henning, R. Chloride binding by layered double hydroxides (LDH/AFm phases) and alkali-activated slag pastes: An experimental study by RILEM TC 283-CAM. Mater. Struct. 2024, 57, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shui, Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, G. Chloride binding of synthetic Ca-Al-NO3 LDHs in hardened cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Yu, Q. In-situ formation of layered double hydroxides in MgO–NaAlO2-activated GGBS/MSWI BA: Impact of Mg2+ on reaction mechanism and leaching behavior. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 140, 105114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Fan, J.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Effect of MgO, Mg-Al-NO3 LDH and calcined LDH-CO3 on chloride resistance of alkali activated fly ash and slag blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Shi, D. Numerical modeling of chloride convection-diffusion-reaction in reinforced concrete under external sulfate attack and drying-wetting cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 472, 140964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Hooton, R.D. Effects of cyclic chloride exposure on penetration of concrete cover. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 9, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvidat, J.; Diliberto, C.; Meux, E.; Izoret, L.; Lecomte, A. Greening effect of concrete containing granulated blast-furnace slag composite cement: Is there an environmental impact? Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 113, 103711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, J.; Rodrigues, A.; Fournier, B. Concrete damage due to oxidation of pyrrhotite-bearing aggregate: A review. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2021, 6, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, I.; Aguado, A.; Agulló, L. Aggregate expansivity due to sulfide oxidation—II. Physico-chemical modeling of sulfate attack. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Geng, Z.; Zhou, X. Reinforcing steels in low-carbon mortars subjected to chloride attack and natural carbonation: Contradictory trends in passivation ability and corrosion resistance. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 152, 105666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.T.; Maekawa, K.; Tan, K.H. Electrochemical corrosion kinetics of steel bars in pseudo-transparent concrete under different alkaline properties and chloride contamination levels. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, S.; Lowke, D. The effect of external load on the chloride migration resistance and the service life of reinforced concrete structures and repair mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Gao, P.; Hu, J.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Investigation on drying-induced microcracks distribution characteristic and its formation mechanism in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 475, 141216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
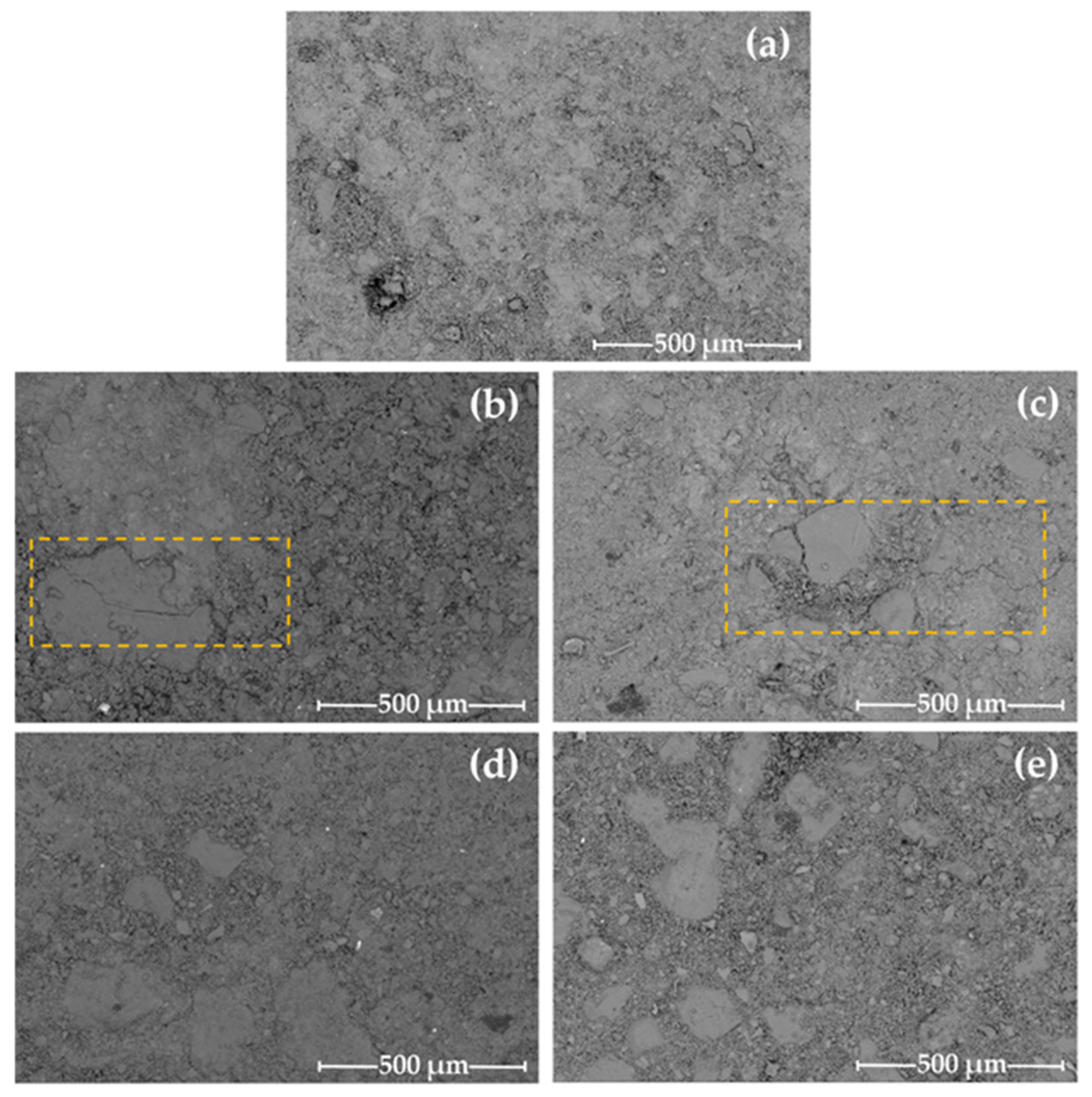
| Composition (% by Weight) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | |
| Type I PC | 1.3 | 4.7 | 17.8 | 4.6 | 1.4 | 67.3 | 0.2 | 2.6 |
| Type II/B-M PC | 2.2 | 6.2 | 19.4 | 4.1 | 1.6 | 61.7 | 0.8 | 4.0 |
| Slag | 10.9 | 10.3 | 31.9 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 44.1 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Particle Size (μm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| d10 | d50 | d90 | |
| Type I PC | 3.2 | 15.9 | 40.7 |
| Type II/B-M PC | 3.5 | 14.1 | 43.0 |
| Slag | 3.7 | 11.2 | 28.5 |
| Label | Precursors | Activator | Na/Ca mol Ratio | Workability (cm) | w/b | s/b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPC | 100% Type II/B-M PC | ----- | ----- | 17.0 ± 0.1 | 0.50 | 3/1 |
| HC-3% | 78.5% slag + 18.5% Type I PC | 3% Na2CO3 | 0.06 | 16.5 ± 0.1 | 0.47 | |
| HC-6% | 77% slag + 17% Type I PC | 6% Na2CO3 | 0.12 | 16.6 ± 0.1 | 0.47 | |
| HN-4% | 78% slag + 18% Type I PC | 4% NaNO3 | 0.06 | 16.8 ± 0.1 | 0.45 | |
| HN-8% | 76% slag + 16% Type I PC | 8% NaNO3 | 0.13 | 18.9 ± 0.1 | 0.45 |
| HC-3% | HC-6% | HN-4% | HN-8% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-sectional view of the mortar samples |  |  |  |  |
| Oxidation depth (mm) | 9.5 ± 0.6 | 9.6 ± 0.5 | 8.6 ± 0.5 | 9.5 ± 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-Hernández, A.; Velasco, F.; Torres-Carrasco, M.; Bautista, A. Hybrid Mortars Activated with Alternative Steel-Compatible Salts: Impact on Chloride Diffusion and Durability. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8055. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148055
Cruz-Hernández A, Velasco F, Torres-Carrasco M, Bautista A. Hybrid Mortars Activated with Alternative Steel-Compatible Salts: Impact on Chloride Diffusion and Durability. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):8055. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148055
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-Hernández, Angily, Francisco Velasco, Manuel Torres-Carrasco, and Asunción Bautista. 2025. "Hybrid Mortars Activated with Alternative Steel-Compatible Salts: Impact on Chloride Diffusion and Durability" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 8055. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148055
APA StyleCruz-Hernández, A., Velasco, F., Torres-Carrasco, M., & Bautista, A. (2025). Hybrid Mortars Activated with Alternative Steel-Compatible Salts: Impact on Chloride Diffusion and Durability. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 8055. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148055









