Structural Connectivity of the Substantia Nigra: A Comprehensive Review of Diffusion Imaging and Tractography Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
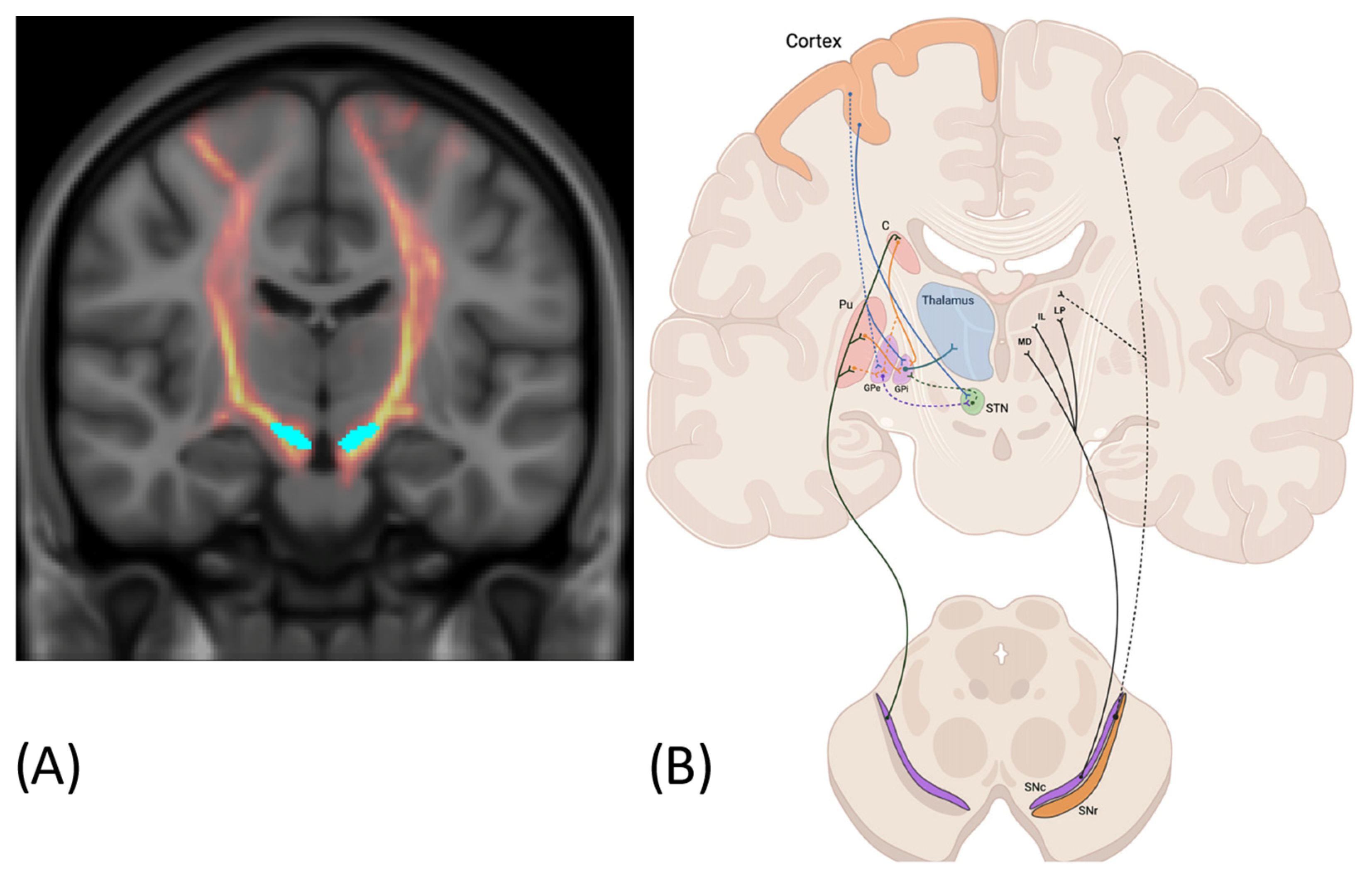
3.1. Connection with the Striatum
3.2. Connection with the Thalamus
3.3. Connection with the Cortex
3.4. Connection with Limbic Structures
3.4.1. Mesolimbic Projection of the SNc/Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA)
3.4.2. Connection to the Hippocampus
3.4.3. Functional Diversity of Limbic Connections
3.4.4. Projection to the Nucleus Accumbens
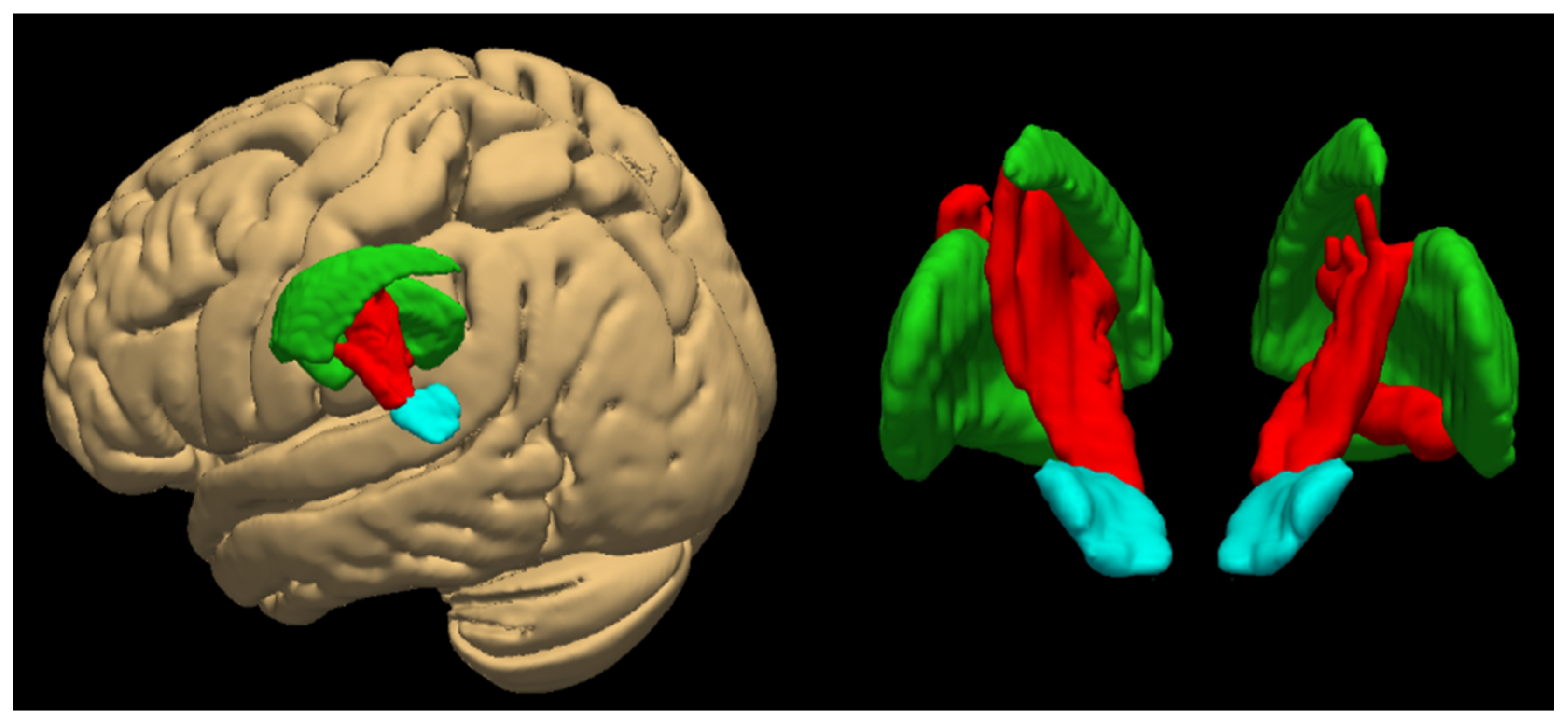
3.5. Regional Subdivisions of the Substantia Nigra
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AL | Ansa lenticularis |
| BD | Basal ganglia |
| C | Caudate |
| DTI | Diffusion tractography imaging |
| FA | Fractional anisotropy |
| GPe | External globus pallidus |
| GPi | Internal globus pallidus |
| IL | Intralaminar nuclei |
| LP | Latero posterior nucleus |
| MD | Medio dorsal nucleus |
| MD | Mean diffusivity |
| MDD | Major depressive disorder |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NAc | Nucleus accumbens |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| Pu | Putamen |
| SN | Substantia nigra |
| SNc | Substantia nigra pars compacta |
| SNr | Substantia nigra pars reticulata |
| STN | Subthalamic nucleus |
| T | Tesla |
| VA | Ventral anterior nucleus |
| VLp | Ventral lateral posterior nucleus |
| VM | Ventromedial nucleus |
| VTA | Area tegmentalis ventralis |
| ZI | Zona incerta |
References
- Alexander, D.C.; Dyrby, T.B.; Nilsson, M.; Zhang, H. Imaging brain microstructure with diffusion MRI: Practicality and applications. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster, E.M.; Newlin, N.R.; Cho, C.; Rudravaram, G.; Saunders, A.M.; Krishnan, A.R.; Remedios, L.W.; Kim, M.E.; Xu, H.; Schilling, K.G.; et al. Sensitivity of quantitative diffusion MRI tractography and microstructure to anisotropic spatial sampling. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.18255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Calamante, F.; Connelly, A. Mapping connectomes with diffusion MRI: Deterministic or probabilistic tractography? Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 83, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mormina, E.; Arrigo, A.; Calamuneri, A.; Granata, F.; Quartarone, A.; Ghilardi, M.F.; Inglese, M.; Di Rocco, A.; Milardi, D.; Anastasi, G.P.; et al. Diffusion tensor imaging parameters’ changes of cerebellar hemispheres in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroradiology 2015, 57, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.T.; Camilleri, J.A.; Hoffstaedter, F.; Eickhoff, S.B. Tract-specific statistics based on diffusion-weighted probabilistic tractography. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y. DTI Tractography. TNS 2024, 44, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.G.; Jang, S.H. Differences in neural connectivity between the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area in the human brain. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrozzi, A.; Gramegna, L.L.; Sighinolfi, G.; Zoli, M.; Mazzatenta, D.; Testa, C.; Lodi, R.; Tonon, C.; Manners, D.N. Methods of diffusion MRI tractography for localization of the anterior optic pathway: A systematic review of validated methods. NeuroImage Clin. 2023, 39, 103494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, T.M.; Hoch, M.J. MRI-Visible Anatomy of the Brainstem. Neuroimaging Clin. N. Am. 2022, 32, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Neuroth, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Liang, R.; Ma, K.-L. A Predictive Visual Analytics System for Studying Neurodegenerative Disease Based on DTI Fiber Tracts. IEEE Trans. Visual. Comput. Graph. 2023, 29, 2020–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.-Q.; Yeoh, C.-S.; Rumpel, H.; Nadkarni, N.; Lye, W.-K.; Tan, E.-K.; Chan, L.-L. Deterministic Tractography of the Nigrostriatal-Nigropallidal Pathway in Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Burock, M.A. Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Parkinson’s Disease and Parkinsonian Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 531993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figley, C.R.; Uddin, M.N.; Wong, K.; Kornelsen, J.; Puig, J.; Figley, T.D. Potential Pitfalls of Using Fractional Anisotropy, Axial Diffusivity, and Radial Diffusivity as Biomarkers of Cerebral White Matter Microstructure. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 799576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamino, M.; Keeling, E.G.; Mishra, V.R.; Stokes, A.M.; Walsh, R.R. Assessing White Matter Pathology in Early-Stage Parkinson Disease Using Diffusion MRI: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C.; Zeng, Q.; He, J.; O’DOnnell, L.J.; Feng, Y. Investigation of local white matter abnormality in Parkinson’s disease by using an automatic fiber tract parcellation. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 394, 112805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, F.G.; Nguyen, C.T.; Cooper, S.R.; LaHue, S.C.; Venugopal, S.; Mukherjee, P. Independent component analysis of DTI reveals multivariate microstructural correlations of white matter in the human brain. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 1431–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchling, J.; Brandt, A.U.; Paul, F.; Scheel, M. Diffusion tensor imaging for multilevel assessment of the visual pathway: Possibilities for personalized outcome prediction in autoimmune disorders of the central nervous system. EPMA J. 2017, 8, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieper, C.C.; Konrad, C.; Sommer, J.; Teismann, I.; Schiffbauer, H. Structural changes of central white matter tracts in Kennedy’s disease—A diffusion tensor imaging and voxel-based morphometry study. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 127, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.-M.; Yeh, C.-H.; Poupon, C.; Calamante, F. Diffusion MRI tractography for neurosurgery: The basics, current state, technical reliability and challenges. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 15TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theisen, F.; Leda, R.; Pozorski, V.; Oh, J.M.; Adluru, N.; Wong, R.; Okonkwo, O.; Dean, D.C.; Bendlin, B.B.; Johnson, S.C.; et al. Evaluation of striatonigral connectivity using probabilistic tractography in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2017, 16, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, T.; Ramamohanarao, K.; Zalesky, A. Mapping connectomes with diffusion MRI: Deterministic or probabilistic tractography? Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 81, 1368–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jbabdi, S.; Johansen-Berg, H. Tractography: Where Do We Go from Here? Brain Connect. 2011, 1, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, T.; Woolrich, M.; Jenkinson, M.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Nunes, R.; Clare, S.; Matthews, P.; Brady, J.; Smith, S. Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 50, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, T.E.J.; Berg, H.J.; Jbabdi, S.; Rushworth, M.F.S.; Woolrich, M.W. Probabilistic diffusion tractography with multiple fibre orientations: What can we gain? NeuroImage 2007, 34, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.K.; Cercignani, M. Twenty-five pitfalls in the analysis of diffusion MRI data. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.G.; Nath, V.; Hansen, C.; Parvathaneni, P.; Blaber, J.; Gao, Y.; Neher, P.; Aydogan, D.B.; Shi, Y.; Ocampo-Pineda, M.; et al. Limits to anatomical accuracy of diffusion tractography using modern approaches. NeuroImage 2019, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Ye, F.Q.; Irfanoglu, M.O.; Modi, P.; Saleem, K.S.; Leopold, D.A.; Pierpaoli, C. Anatomical accuracy of brain connections derived from diffusion MRI tractography is inherently limited. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16574–16579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, G.; Caiazzo, G.; Franza, F.; Cirillo, M.; Papa, M.; Esposito, F. Evidence for direct dopaminergic connections between substantia nigra pars compacta and thalamus in young healthy humans. Front. Neural Circuits 2025, 18, 1522421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, K.T.; Steinberg, E.E.; DeLoach, K.E.; Xie, S.; Miyamichi, K.; Schwarz, L.; Gao, X.J.; Kremer, E.J.; Malenka, R.C.; Luo, L. Circuit Architecture of VTA Dopamine Neurons Revealed by Systematic Input–Output Mapping. Cell 2015, 162, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Guenther, D.T.; Maurer, A.P.; Hansen, C.A.; Zalesky, A.; Khoshbouei, H. Dopamine Transporter Is a Master Regulator of Dopaminergic Neural Network Connectivity. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 5453–5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenewegen, H.J. The basal ganglia and motor control. Neural Plast. 2003, 10, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, H.; Serra-Mestres, J. Neuropsychiatry of the basal ganglia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.P.; Burrell, J.C.; Struzyna, L.A.; Chen, H.I.; Serruya, M.D.; Wolf, J.A.; Duda, J.E.; Cullen, D.K. Emerging regenerative medicine and tissue engineering strategies for Parkinson’s disease. npj Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciola, A.; Milardi, D.; Anastasi, G.P.; Basile, G.A.; Ciolli, P.; Irrera, M.; Cutroneo, G.; Bruschetta, D.; Rizzo, G.; Mondello, S.; et al. A Direct Cortico-Nigral Pathway as Revealed by Constrained Spherical Deconvolution Tractography in Humans. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.-P.; Koo, D.-K. Aging of the Nigrostriatal Tract in the Human Brain: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Medicina 2021, 57, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, V.; Döbrössy, M.D.; Thompson, L.H.; Kirik, D.; Fuller, H.R.; Gates, M.A. State of the Art in Sub-Phenotyping Midbrain Dopamine Neurons. Biology 2024, 13, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.; Margolis, E.B. Ventral tegmental area: Cellular heterogeneity, connectivity and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, J.M.; Charbit, A.R.; Snyder, B.J.; Fong, P.T.K.; Dias, E.V.; Himmels, P.; Lock, H.; Margolis, E.B. Relative contributions and mapping of ventral tegmental area dopamine and GABA neurons by projection target in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 2019, 527, 916–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Badurek, S.; Dileone, R.J.; Nashmi, R.; Minichiello, L.; Picciotto, M.R. GABAergic and glutamatergic efferents of the mouse ventral tegmental area. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 3308–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kwon, H.; Song, Y.; Yun, B.; Lee, Y.; Cho, Y.; Joo, A.; Han, P.-L. A Group of Descending Glutamatergic Neurons Activated by Stress in Corticolimbic Regions Project to the Nucleus Accumbens. Exp. Neurobiol. 2018, 27, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Hao, M.; Duan, J.; Han, M.-H. The Formation and Function of the VTA Dopamine System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeso, J.A.; Rodríguez-Oroz, M.C.; Benitez-Temino, B.; Blesa, F.J.; Guridi, J.; Marin, C.; Rodriguez, M. Functional organization of the basal ganglia: Therapeutic implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, S548–S559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.-M.; Lee, C.R. Intrinsic and integrative properties of substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons. Neuroscience 2011, 198, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, K.; Isa, T.; Takakusaki, K. Nigral GABAergic inhibition upon mesencephalic dopaminergic cell groups in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 2399–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhong, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Spatial Distribution of Neurons Expressing Single, Double, and Triple Molecular Characteristics of Glutamatergic, Dopaminergic, or GABAergic Neurons in the Mouse Ventral Tegmental Area. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 73, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, K.; Sullivan, B.; Lopez, E.; Sun, L.; Cai, H. Diverse midbrain dopaminergic neuron subtypes and implications for complex clinical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Neur. Dis. 2021, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorn, P.; Vanderschuren, L.J.M.J.; Groenewegen, H.J.; Robbins, T.W.; Pennartz, C.M.A. Putting a spin on the dorsal–ventral divide of the striatum. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, C.S.; Petersen, M.V.; Parent, M.; McIntyre, C.C. Evolving characterization of the human hyperdirect pathway. Brain Struct. Funct. 2023, 228, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier-Hein, K.H.; Neher, P.F.; Houde, J.-C.; Côté, M.-A.; Garyfallidis, E.; Zhong, J.; Chamberland, M.; Yeh, F.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Ji, Q.; et al. The challenge of mapping the human connectome based on diffusion tractography. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, M. Mapping brain anatomical connectivity using white matter tractography. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 821–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, T.E.J.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Woolrich, M.W.; Smith, S.M.; Wheeler-Kingshott, C.A.M.; A Boulby, P.; Barker, G.J.; Sillery, E.L.; Sheehan, K.; Ciccarelli, O.; et al. Non-invasive mapping of connections between human thalamus and cortex using diffusion imaging. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leergaard, T.B.; Hilgetag, C.C.; Sporns, O. Mapping the Connectome: Multi-Level Analysis of Brain Connectivity. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerfen, C.R.; Staines, W.A.; Fibiger, H.C.; Arbuthnott, G.W. Crossed connections of the substantia nigra in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1982, 207, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacciola, A.; Calamuneri, A.; Milardi, D.; Mormina, E.; Chillemi, G.; Marino, S.; Naro, A.; Rizzo, G.; Anastasi, G.; Quartarone, A. A Connectomic Analysis of the Human Basal Ganglia Network. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartarone, A.; Cacciola, A.; Milardi, D.; Ghilardi, M.F.; Calamuneri, A.; Chillemi, G.; Anastasi, G.; Rothwell, J. New insights into cortico-basal-cerebellar connectome: Clinical and physiological considerations. Brain 2020, 143, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahata, I.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Fukunaga, K. Dopamine D1–D5 Receptors in Brain Nuclei: Implications for Health and Disease. Receptors 2024, 3, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.E.; O’Malley, K. Axon degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 246, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-C.; Ulane, C.M.; Burke, R.E. Clinical progression in Parkinson disease and the neurobiology of axons. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andica, C.; Kamagata, K.; Hatano, T.; Okuzumi, A.; Saito, A.; Nakazawa, M.; Ueda, R.; Motoi, Y.; Kamiya, K.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the nigrostriatal pathway in Parkinson’s disease: Retrograde degeneration observed by tract-profile analysis. Park. Relat. Disord. 2018, 51, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhr, L.; Tsolaki, E.; Pouratian, N. Diffusion tensor imaging correlates of depressive symptoms in Parkinson disease. J. Comp. Neurol. 2022, 530, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, H.S.; Dolatshahi, M.; Mohebi, F.; Aarabi, M.H. Structural white matter alterations as compensatory mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review of diffusion tensor imaging studies. J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 98, 1398–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, I.-W.; Ba, S.B.; Coffey, C.S.; Foster, E.; Mendick, S.; Seibyl, J.; Schuff, N. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Nigrostriatal Fibers in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.-H.; Baek, H.-M. White Matter Connectivity between Structures of the Basal Ganglia using 3T and 7T. Neuroscience 2022, 483, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.-H.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, Y.-B.; Lee, H.; Cho, Z.-H. In vivo 3D Reconstruction of the Human Pallidothalamic and Nigrothalamic Pathways with Super-Resolution 7T MR Track Density Imaging and Fiber Tractography. Front. Neuroanat. 2021, 15, 739576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ribas, E.C.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Chen, G.; Li, M. Tractography of the ansa lenticularis in the human brain. Clin. Anat. 2022, 35, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Larcher, K.M.-H.; Misic, B.; Dagher, A. Anatomical and functional organization of the human substantia nigra and its connections. eLife 2017, 6, e26653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, B.L.; D’Ardenne, K.; Murty, V.P.; Brewer, G.A.; McClure, S.M. Midbrain-Hippocampus Structural Connectivity Selectively Predicts Motivated Memory Encoding. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 9426–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gomar, M.G.; Singh, K.; Cauzzo, S.; Bianciardi, M. In vivo structural connectome of arousal and motor brainstem nuclei by 7 Tesla and 3 Tesla MRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 4397–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNiven, K.H.; Leong, J.K.; Knutson, B. Medial forebrain bundle structure is linked to human impulsivity. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, R.A.; Jbabdi, S.; Miller, K.L.; Matthews, P.M.; Zarei, M. Connectivity-based segmentation of the substantia nigra in human and its implications in Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage 2010, 52, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, G.A.; Bramanti, A.; Bertino, S.; Cutroneo, G.; Bruno, A.; Tisano, A.; Paladina, G.; Milardi, D.; Anastasi, G. Structural Connectivity-Based Parcellation of the Dopaminergic Midbrain in Healthy Subjects and Schizophrenic Patients. Medicina 2020, 56, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.; Lambert, C.; Dolan, R.J.; Duezel, E. Parcellation of the human substantia nigra based on anatomical connectivity to the striatum. Neuroimage 2013, 81, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanarajah, S.E.; Hanssen, R.; Melzer, C.; Tittgemeyer, M. Increased meso-striatal connectivity mediates trait impulsivity in FTO variant carriers. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, A.T.; Hassan, A.A.O.; Brüggemann, N.; Sharma, N.; Breiter, H.C.; Blood, A.J.; Waugh, J.L. In humans, striato-pallido-thalamic projections are largely segregated by their origin in either the striosome-like or matrix-like compartments. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1178473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Heij, J.; Liu, S.; Liebrand, L.; Caan, M.; van der Zwaag, W.; Veltman, D.J.; Lu, L.; Aghajani, M.; van Wingen, G. Structural connectivity of dopaminergic pathways in major depressive disorder: An ultra-high resolution 7-Tesla diffusion MRI study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2024, 89, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Cho, M.J. Relationship of the Nigrostriatal Tract with the Motor Function and the Corticospinal Tract in Chronic Hemiparetic Stroke Patients: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wende, T.; Kasper, J.; Wilhelmy, F.; Dietel, E.; Hamerla, G.; Scherlach, C.; Meixensberger, J.; Fehrenbach, M.K. Assessment of a Reliable Fractional Anisotropy Cutoff in Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract for Neurosurgical Patients. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Knoop, L.E.; Frigerio, I.; Bol, J.G.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Berendse, H.W.; Pouwels, P.J.; van de Berg, W.D.; Jonkman, L.E. Nigral Pathology Contributes to Microstructural Integrity of Striatal and Frontal Tracts in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, M.; Beneduce, B.M.; Regehr, W.G. The Substantia Nigra Conveys Target-Dependent Excitatory and Inhibitory Outputs from the Basal Ganglia to the Thalamus. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 8032–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, K.; Mori, S.; Troncoso, J.C.; Lenz, F.A. Mapping tracts in the human subthalamic area by 11.7T ex vivo diffusion tensor imaging. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 1293–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiu, M.; Xie, R.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Shi, L. The zona incerta system: Involvement in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 382, 114992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-L.; Chen, S.-H.; Li, J.-N.; Zhao, L.-J.; Wu, X.-M.; Hong, J.; Zhu, K.-H.; Sun, H.-X.; Shi, S.-J.; Mao, E.; et al. Projections from the Rostral Zona Incerta to the Thalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Mediate Nociceptive Neurotransmission in Mice. Metabolites 2023, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowska, K. Zona incerta as a therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londei, F.; Arena, G.; Ferrucci, L.; Russo, E.; Ceccarelli, F.; Genovesio, A. Connecting the dots in the zona incerta: A study of neural assemblies and motifs of inter-area coordination in mice. iScience 2024, 27, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pathway | Connection | Significance for Neurology | Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nigrostriatal | SNc → dorsal striatum (putamen, caudate) | A key pathway for motor control; its degeneration leads to the motor symptoms of PD | [11,12,14,57,59,60,61,62,63,70] |
| Nigrothalamic | SNr → VA, VL, VM thalamic nuclei | Influence motor and associative cortical circuits, important for motor and cognitive function, involved in dystonia pathophysiology | [28,64,70] |
| SNc → thalamus | Dopaminergic connections from the SNc directly to the thalamus | Possible dopamine influence on thalamocortical circuits; potential mechanism for non-motor symptoms of PD | [28] |
| Cortico–Nigral | Direct projections from the cortex (prefrontal, sensorimotor areas) → SN | Cognitive and sensory modulation of dopamine neurons; SN responds to cortical inputs | [7,34,74] |
| SN–ventral striatum (mesolimbic pathway) | SNc/VTA → NAc and orbitofrontal cortex | Regulation of reward, emotion, and impulsiveness; key to addictions and behavioral disorders | [28,66,69,72,73] |
| SN–hippocampus | SN/VTA ↔ hippocampus (direct and indirect connections) | Modulation of motivation, novelty, and learning; relevance to stress; major depressive disorder (MDD) | [47,67] |
| SN–amygdala, limbic cortex | SN2 (part of SNc) → amygdala, cingulum, orbitofrontal region | Emotion regulation; involved in mood disorders, anxiety, REM atonia | [68] |
| SN–GPi/ansa lenticularis (GPSN) | Globus pallidus → SN (via specific GPSN branch) | Possible feedback effect of pallidum on SN; integration of BG outputs and feedback | [65] |
| SNc–subcortical circuits (reticular formation) | SNc ↔ brainstem, VTA, PAG, hypothalamus | Involved in regulation of sleep and autonomic functions; important in MDD, stress, and sleep disorders | [68,75] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bublíková, I.; Mareček, S.; Krajča, T.; Malá, C.; Dušek, P.; Krupička, R. Structural Connectivity of the Substantia Nigra: A Comprehensive Review of Diffusion Imaging and Tractography Studies. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147902
Bublíková I, Mareček S, Krajča T, Malá C, Dušek P, Krupička R. Structural Connectivity of the Substantia Nigra: A Comprehensive Review of Diffusion Imaging and Tractography Studies. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147902
Chicago/Turabian StyleBublíková, Iva, Stanislav Mareček, Tomáš Krajča, Christiane Malá, Petr Dušek, and Radim Krupička. 2025. "Structural Connectivity of the Substantia Nigra: A Comprehensive Review of Diffusion Imaging and Tractography Studies" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147902
APA StyleBublíková, I., Mareček, S., Krajča, T., Malá, C., Dušek, P., & Krupička, R. (2025). Structural Connectivity of the Substantia Nigra: A Comprehensive Review of Diffusion Imaging and Tractography Studies. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147902






