Multidimensional Effects of Revegetation on Antimony Mine Waste Slag: From Geochemical Responses to Ecological Risk Regulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
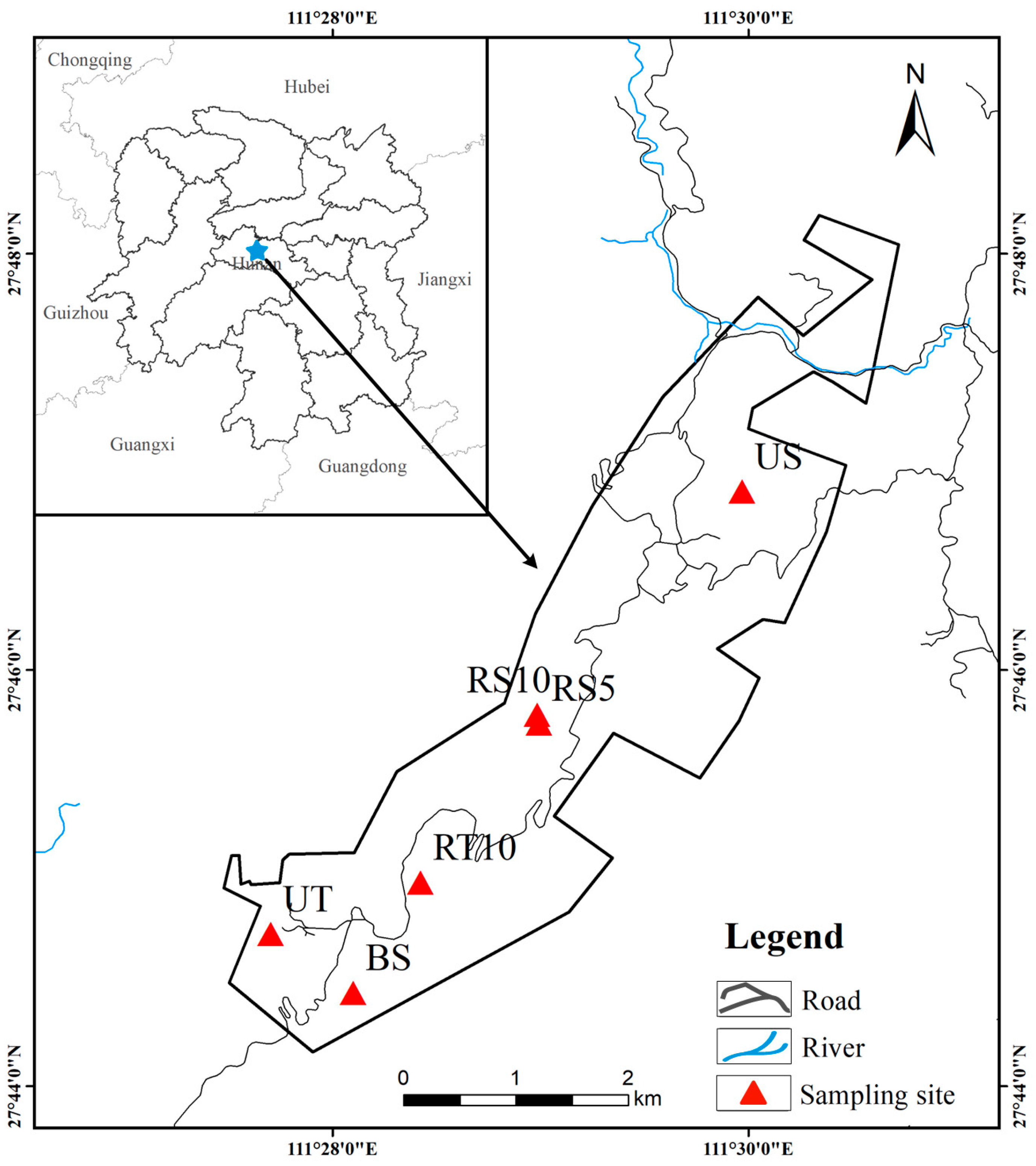
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Physicochemical and Geochemical Characterization
2.3. Analysis of the Total Metal(loid) Content
2.4. Metal(loid)s Chemical Speciation Analysis
2.5. Modified Comprehensive Pollution Risk (MCR) Method
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
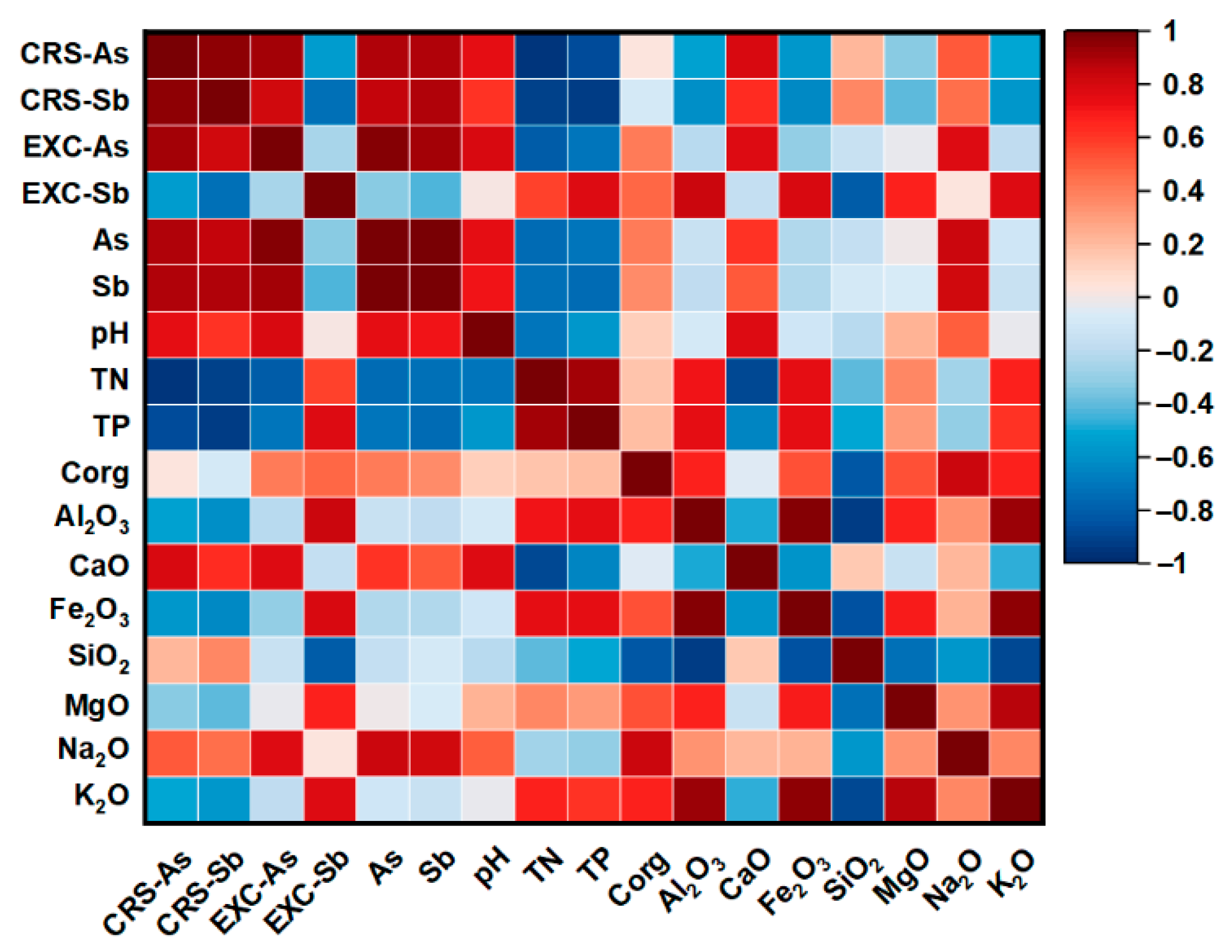
3.1. Effects of Revegetation on the Physicochemical and Geochemical Properties Characteristics of Mining Areas
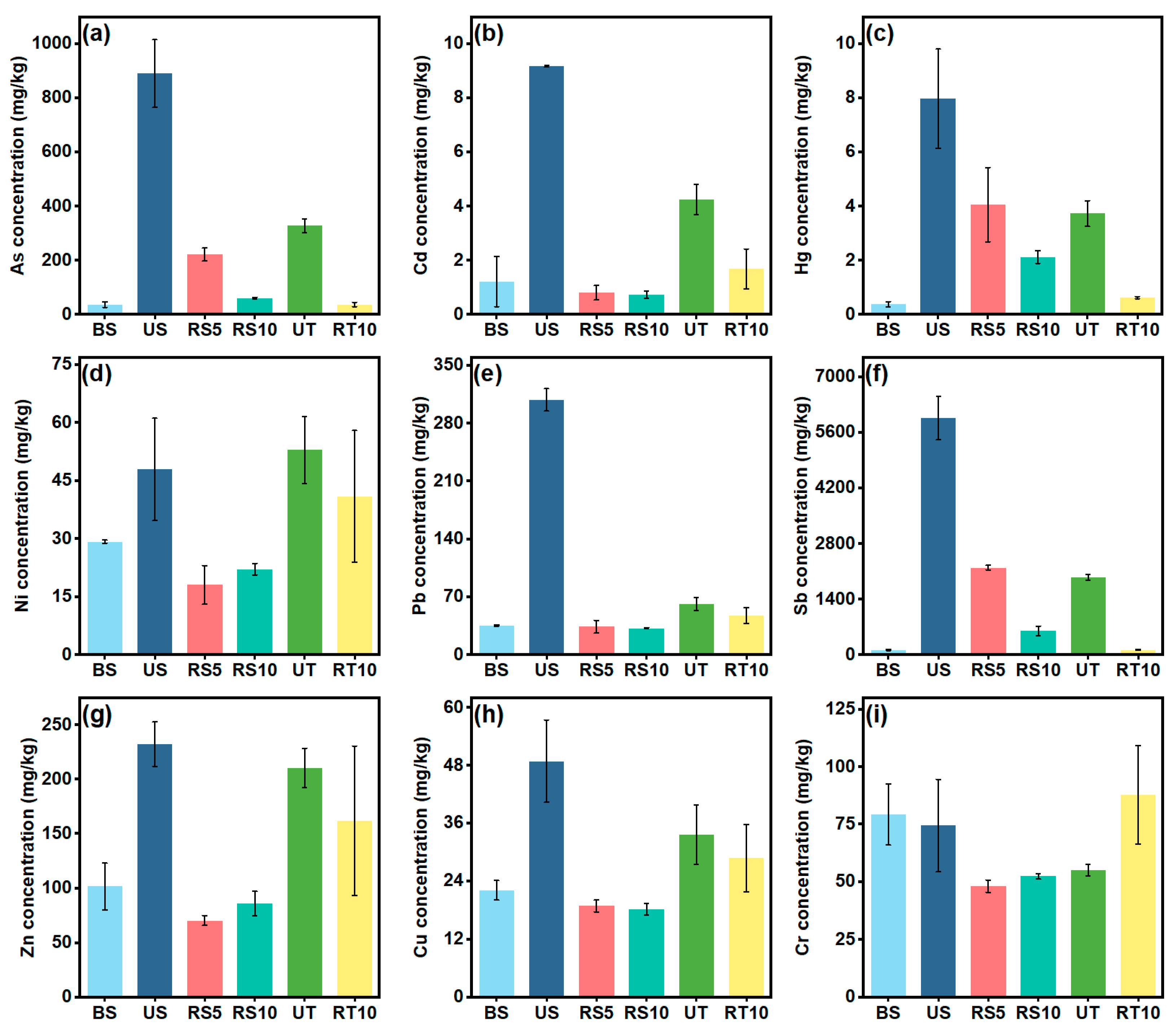
3.2. Effect of Revegetation on Metal(loid) Content in Mining Areas
3.3. Effect of Revegetation on the Chemical Speciation of Metal(loid)s in Mining Areas
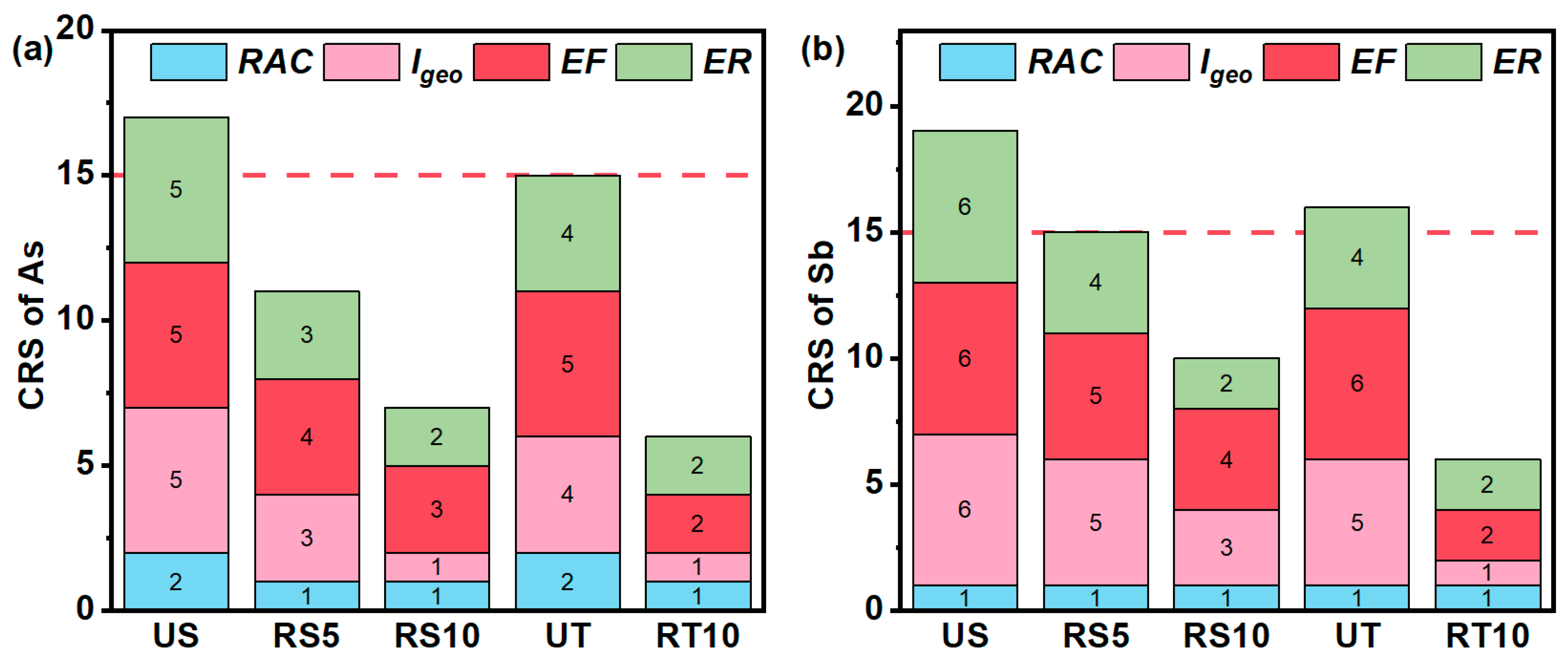
3.4. Impact of Revegetation on Environmental Risks in Mining Areas
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dupont, D.; Arnout, S.; Jones, P.T.; Binnemans, K. Antimony Recovery from End-of-Life Products and Industrial Process Residues: A Critical Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 79–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Qin, H.; Fu, Z. Exposure characteristics of antimony and coexisting arsenic from multi-path exposure in typical antimony mine area. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 289, 112493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ren, B.; Deng, X.; Li, T. Geographic distribution, source analysis, and ecological risk assessment of PTEs in the topsoil of different land uses around the antimony tailings tank: A case study of Longwangchi tailings pond, Hunan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Lan, S. Spatial distribution and transport characteristics of heavy metals around an antimony mine area in central China. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, X.; Dong, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhou, M.; Hou, H. Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in China’s lead–zinc mine tailings: A meta–analysis. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Ran, Y.; Mou, Y.; Cui, Y.; Sun, B.; Yu, L.; Wan, D.; Hu, D.; Zhao, P. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of antimony and arsenic in a typical abandoned antimony smelter. Environ. Geochem. Hlth. 2023, 45, 5467–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Han, Z.; Xiong, J.; He, Y.; Liao, J.; Wu, P. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of tailings in the Qinglong Dachang antimony mine, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 33491–33504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.C.; Leech, C.D.; Butler, L.; Lisle, L.; Ashley, P.M.; Lockwood, P.V. Effects of nutrient and lime additions in mine site rehabilitation strategies on the accumulation of antimony and arsenic by native Australian plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, J.; Min, N.; Duran, R. Comprehensive assessment of environmental and health risks of metal(loid)s pollution from non-ferrous metal mining and smelting activities. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 375, 134049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, N.; Long, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, C.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Pervaiz, A.; Shan, J. Antimony speciation in the environment: Recent advances in understanding the biogeochemical processes and ecological effects. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 14–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Mu, Y.; Ma, S.; Xu, S.; Mu, X. Remediation on antimony-contaminated soil from mine area using zero-valent-iron doped biochar and their effect on the bioavailability of antimony. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 143015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Z.; Chen, W.; Pei, Y. Codisposal of landfill leachate concentrate and antimony mine soils using a one-part geopolymer system for cationic and anionic heavy metals immobilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 464, 132909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xue, H.; Gong, B.; Li, Q.; Guo, W.; Meng, X. Effective immobilization and biosafety assessment of antimony in soil with zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 352, 124082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Pan, W.; Tong, L.; Hu, Y.; Zou, Y.; Huang, X. Remediation of Sb-Contaminated Soil by Low Molecular Weight Organic Acids Washing: Efficiencies and Mechanisms. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Du, Y.; Sun, H.; Yuan, H.; Feng, Y.; Xia, W. Evaluation of the effectiveness of ex-situ stabilization for arsenic and antimony contaminated soil: Short-term and long-term leaching characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahfardi, G.; Sarmadi, M.S.; Rezaee, M.; Khodadadi-Darban, A.; Yazdani, M.; Paz-Garcia, J.M. Comparison of different extracting agents for the recovery of Pb and Zn through electrokinetic remediation of mine tailings. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xing, R.; Wang, H.; Shu, J.; Wu, Z.; Wan, Z. Assessment of chemical, biochemical, and microbiological properties in an artisanal Zn-smelting waste slag site revegetated with four native woody plant species. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 124, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Luo, Y.; Luo, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wan, Z.; Wu, Y. Chemodiversity of dissolved organic matter and its association with the bacterial community at a zinc smelting slag site after 10 years of direct revegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 950, 175322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; Dong, Y.; Qian, L. Soilless revegetation: An efficient means of improving physicochemical properties and reshaping microbial communities of high-salty gold mine tailings. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 207, 111246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Luo, Y.; Wan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, D. Migration and transformation behaviors of potentially toxic elements and the underlying mechanisms in bauxite residue: Insight from various revegetation strategies. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, B.; Chen, X.; Dong, Y.; Lin, H. Insight into soilless revegetation of oligotrophic and heavy metal contaminated gold tailing pond by metagenomic analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, I.T.; Courtney, R.; Mayes, W.M. Antimony and arsenic behaviour in lead/zinc mine tailings during storage under vegetation cover. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 158, 105806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tian, S.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Liang, T. Heavy metal bioaccessibility and health risks in the contaminated soil of an abandoned, small-scale lead and zinc mine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 15044–15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billmann, M.; Hulot, C.; Pauget, B.; Badreddine, R.; Papin, A.; Pelfrêne, A. Oral bioaccessibility of PTEs in soils: A review of data, influencing factors and application in human health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, J.; Liu, J.; Min, N.; Sunahara, G.; Men, D.; Duran, R. Effects of soil metal(loid)s pollution on microbial activities and environmental risks in an abandoned chemical smelting site. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 143, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proto, M.; Newsome, L.; Jensen, E.; Courtney, R. Geochemical analyses of metal(loid) fractions do not predict plant uptake behavior: Are plant bioassays better tools to predict mine rehabilitation success? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, P.; Ye, Z.; Wen, B.; Beckie, R.D.; Zhou, A.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, J. Antimony mobility in soil near historical waste rock at the world’s largest Sb mine, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Zhou, J.; Tang, P.; Jia, X.; Zhou, W.; Huang, J. Antimony (Sb) isotopic signature in water systems from the world’s largest Sb mine, central China: Novel insights to trace Sb source and mobilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Deng, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, L.; Zhu, F.; Xue, S.; Mohammad, A. Standardized framework for assessing soil quality at antimony smelting site by considering microbial-induced resilience and heavy metal contamination. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 148, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.; Jiang, T.; Mei, J.; Tang, H.; Huang, W. Characterization and causes of interannual variation of antimony contamination in groundwater of a typical antimony mining area. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2023, 50, 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; Yan, W.; Liang, X.; Wu, Q.; Fang, J. Influence of Miscanthus floridulus on Heavy Metal Distribution and Phytoremediation in Coal Gangue Dump Soils: Implications for Ecological Risk Mitigation. Plants 2025, 14, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, X.; Weng, W.; Yan, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Peng, T.; Zhong, Q.; Xu, K.; Wang, C.; et al. Synergistic effects of antimony and arsenic contaminations on bacterial, archaeal and fungal communities in the rhizosphere of Miscanthus sinensis: Insights for nitrification and carbon mineralization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 125094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Li, X.; Lin, S.; Jiao, R.; Yang, X.; Shi, A.; Nie, X.; Lin, Q.; Qiu, R. Miscanthus sp. root exudate alters rhizosphere microbial community to drive soil aggregation for heavy metal immobilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Aguiar Santiago, F.L.; Silva, A.O.; Carneiro, M.A.C.; Gastauer, M.; Ramos, S.J.; Caldeira, C.F.; Siqueira, J.O. Revegetation of mined areas influences the physiological profile of bacterial communities and improves the biochemical functions of soil. Pedobiologia 2022, 90, 150793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Bu, C.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Biocrusts significantly affect the bioavailability and ecological risk of heavy metals in gold mine tailings. Plant Soil 2023, 493, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ781-2016; Solid Waste-Determination of 22 Metal Elements Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2016.
- DZ/T0295-2016; Specification of Land Quality Geochemical Assessment. Ministry of Land and Resources: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Li, H.; Yao, J.; Min, N.; Sunahara, G.; Zhao, Y.; Duran, R. Considering the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of metal(loid)s for risk assessment of soils affected by different non-ferrous metal activities in Southwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Ding, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, Q. Comprehensive evaluation of environmental availability, pollution level and leaching heavy metals behavior in non-ferrous metal tailings. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, X.; Wu, Y. Effects of four woody plant species revegetation on habitat improvement and the spatial distribution of arsenic and antimony in zinc smelting slag. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2021, 23, 1506–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennanen, T.; Strommer, R.; Markkola, A.; Fritze, H. Microbial and Plant Community Structure Across a Primary Succession Gradient. Scand. J. Forest Res. 2001, 16, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, L. Suitability of four woody plant species for the phytostabilization of a zinc smelting slag site after 5 years of assisted revegetation. J. Soil. Sediment. 2019, 19, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, L.; Teng, K.; Ma, J.; Xiang, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, G.; Yang, B.; Fang, J. Potential roles of the rhizospheric bacterial community in assisting Miscanthus floridulus in remediating multi-metal(loid)s contaminated soils. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyenda, T.; Gwenzi, W.; Jacobs, S. Changes in physicochemical properties on a chronosequence of gold mine tailings. Geoderma 2021, 395, 115037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xing, R.; Wan, Z.; Chen, Y. Vertical distribution of nutrients, enzyme activities, microbial properties, and heavy metals in zinc smelting slag site revegetated with two herb species: Implications for direct revegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ji, Y.; Ma, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ji, C.; Zhu, J.; Shao, J.; Li, Y. Positive effects of vegetation restoration on the soil properties of post-mining land. Plant Soil 2024, 497, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Hu, T.; Niu, S.; Bai, Z. Soil organic carbon and nitrogen pools in reclaimed mine soils under forest and cropland ecosystems in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tian, D.; Ning, C.; Yan, W.; Xiang, W.; Peng, C. Roles of Koelreuteria bipinnata as a suitable accumulator tree species in remediating Mn, Zn, Pb, and Cd pollution on Mn mining wastelands in southern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 4549–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.S.; Naidu, R. Rhizosphere-induced heavy metal(loid) transformation in relation to bioavailability and remediation. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2015, 15, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Ren, H.; Li, S.; Gao, M.; Shi, S.; Chang, E.; Wei, Y.; Yao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, J. Comparative proteomic analysis in Miscanthus sinensis exposed to antimony stress. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 201, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 36600-2018; Soil Environmental Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Courtin-Nomade, A.; Rakotoarisoa, O.; Bril, H.; Grybos, M.; Forestier, L.; Foucher, F.; Kunz, M. Weathering of Sb-rich mining and smelting residues: Insight in solid speciation and soil bacteria toxicity. Geochemistry 2012, 72, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Category | RAC | Igeo | EF | ER | CRS | Degree of Pollution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | <1% | ≤0 | - | - | 6 | None |
| 2 | 1–10% | 0–1 | <2 | <40 | 6–8 | Low |
| 3 | 10–30% | 1–2 | 2–5 | 40–80 | 8–12 | Moderate |
| 4 | - | 2–3 | 5–20 | 80–160 | 12–15 | Considerable |
| 5 | 30–50% | 3–4 | 20–40 | 160–320 | 15–20 | High |
| 6 | >50% | 4–5 | >40 | >320 | 20–24 | Very high |
| 7 | - | 5–10 | - | - | 25 | Extremely serious |
| pH | TN (g/kg) | TP (g/kg) | Corg(%) | Al2O3(%) | CaO(%) | Fe2O3(%) | SiO2(%) | MgO(%) | Na2O(%) | K2O(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BS | 5.51 ± 0.03 | 1.21 ± 0.10 | 0.415 ± 0.04 | 1.53 ± 0.38 | 14.86 ± 1.24 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 5.42 ± 0.63 | 66.50 ± 2.69 | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 1.33 ± 0.11 |
| US | 8.88 ± 1.71 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.177 ± 0.03 | 1.94 ± 0.51 | 11.86 ± 2.05 | 2.98 ± 1.51 | 4.28 ± 0.25 | 65.93 ± 1.37 | 0.61 ± 0.12 | 0.67 ± 0.08 | 1.30 ± 0.28 |
| RS5 | 6.68 ± 1.33 | 0.76 ± 0.14 | 0.243 ± 0.01 | 0.24 ± 0.06 | 8.47 ± 0.59 | 0.28 ± 0.10 | 3.64 ± 0.23 | 81.23 ± 0.84 | 0.32 ± 0.05 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.92 ± 0.03 |
| RS10 | 5.35 ± 1.27 | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 0.255 ± 0.02 | 1.08 ± 0.09 | 8.61 ± 0.30 | 0.21 ± 0.13 | 3.27 ± 0.16 | 78.70 ± 0.28 | 0.55 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 1.13 ± 0.02 |
| UT | 7.93 ± 0.63 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 4.71 ± 0.26 | 4.56 ± 0.46 | 1.38 ± 0.21 | 82.2 ± 0.34 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.61 ± 0.04 |
| RT10 | 7.71 ± 0.25 | 1.07 ± 0.13 | 0.355 ± 0.02 | 1.04 ± 0.15 | 14.57 ± 2.74 | 1.23 ± 0.60 | 5.96 ± 1.12 | 65.6 ± 7.92 | 0.82 ± 0.13 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 1.58 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Lan, J.; Huang, F.; Wang, D.; Dai, L.; Chen, C.; Xiang, L.; Wu, W. Multidimensional Effects of Revegetation on Antimony Mine Waste Slag: From Geochemical Responses to Ecological Risk Regulation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7587. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137587
Zhu X, Lan J, Huang F, Wang D, Dai L, Chen C, Xiang L, Wu W. Multidimensional Effects of Revegetation on Antimony Mine Waste Slag: From Geochemical Responses to Ecological Risk Regulation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7587. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137587
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiaozhe, Jianmei Lan, Fengcun Huang, Dan Wang, Liangliang Dai, Chuang Chen, Li Xiang, and Wenbin Wu. 2025. "Multidimensional Effects of Revegetation on Antimony Mine Waste Slag: From Geochemical Responses to Ecological Risk Regulation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7587. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137587
APA StyleZhu, X., Lan, J., Huang, F., Wang, D., Dai, L., Chen, C., Xiang, L., & Wu, W. (2025). Multidimensional Effects of Revegetation on Antimony Mine Waste Slag: From Geochemical Responses to Ecological Risk Regulation. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7587. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137587




