A Multi-Scale Approach for Finite Element Method Structural Analysis of Injection-Molded Parts of Short Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
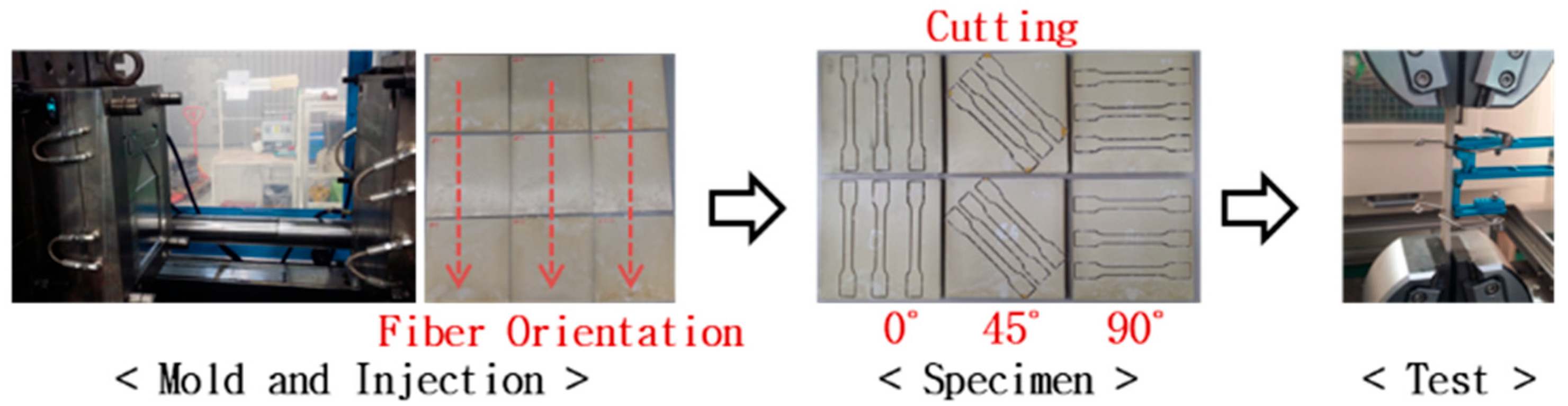
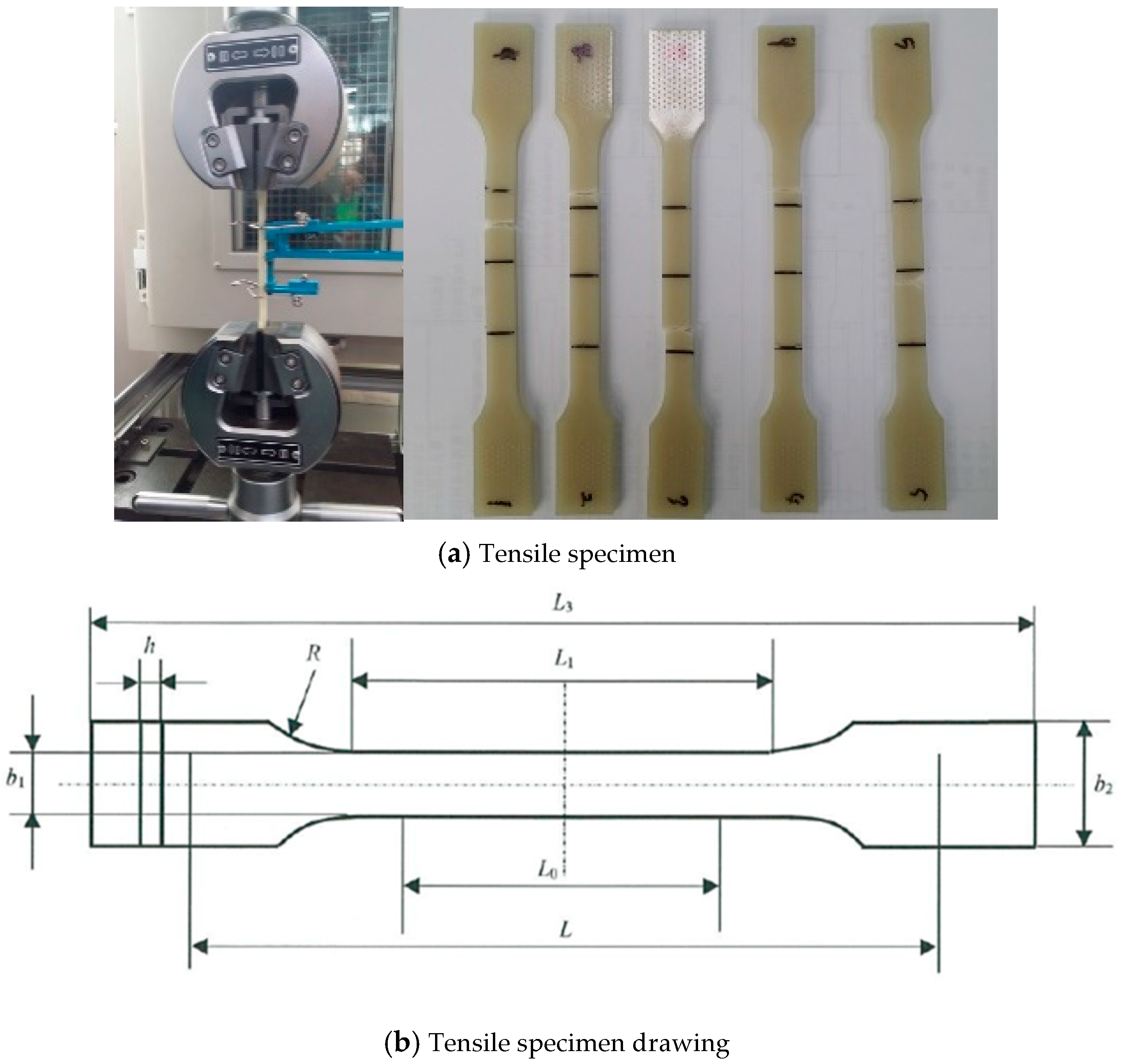
2.2. Specimen of Tensile Test Preparation and Testing Methods
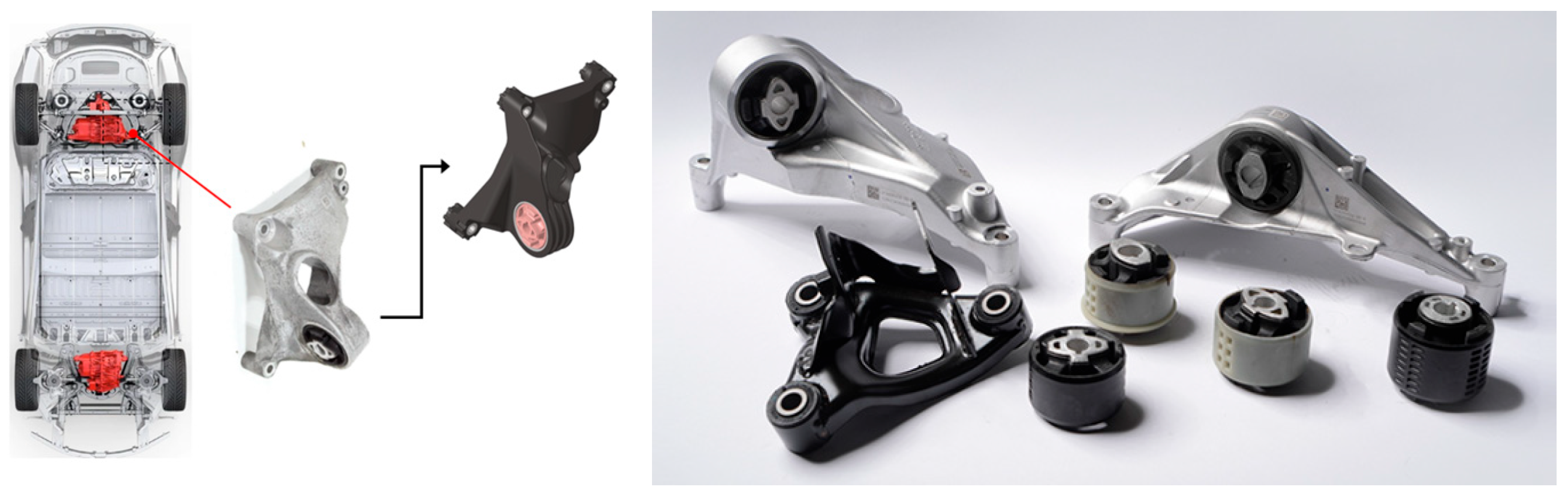
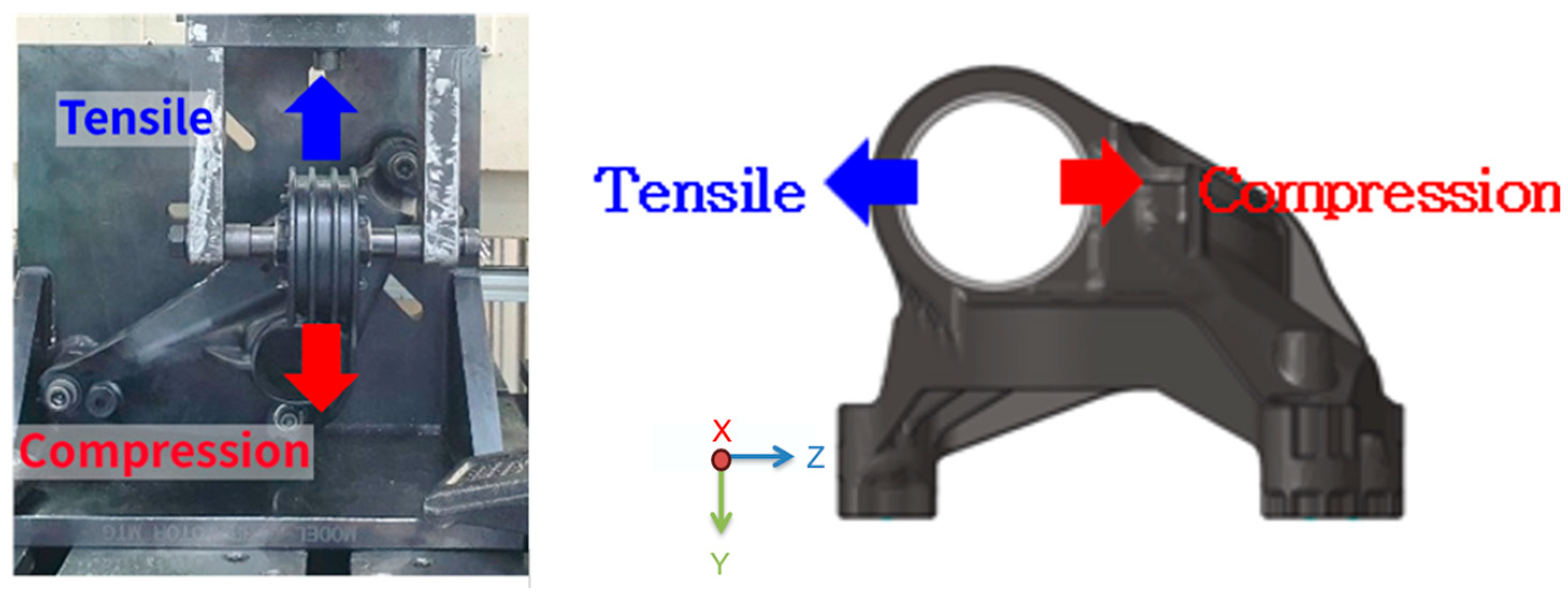
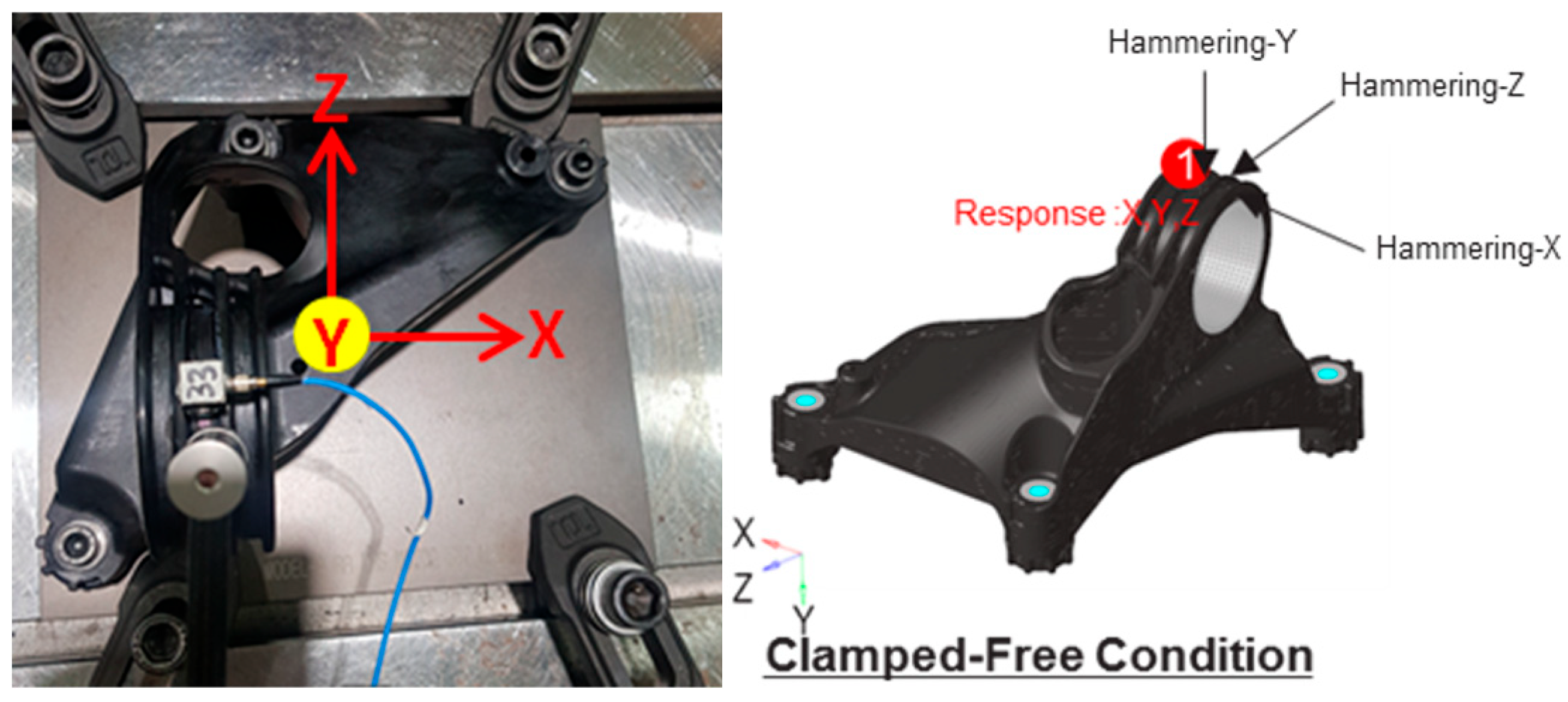
2.3. Product Manufacturing and Testing Methods
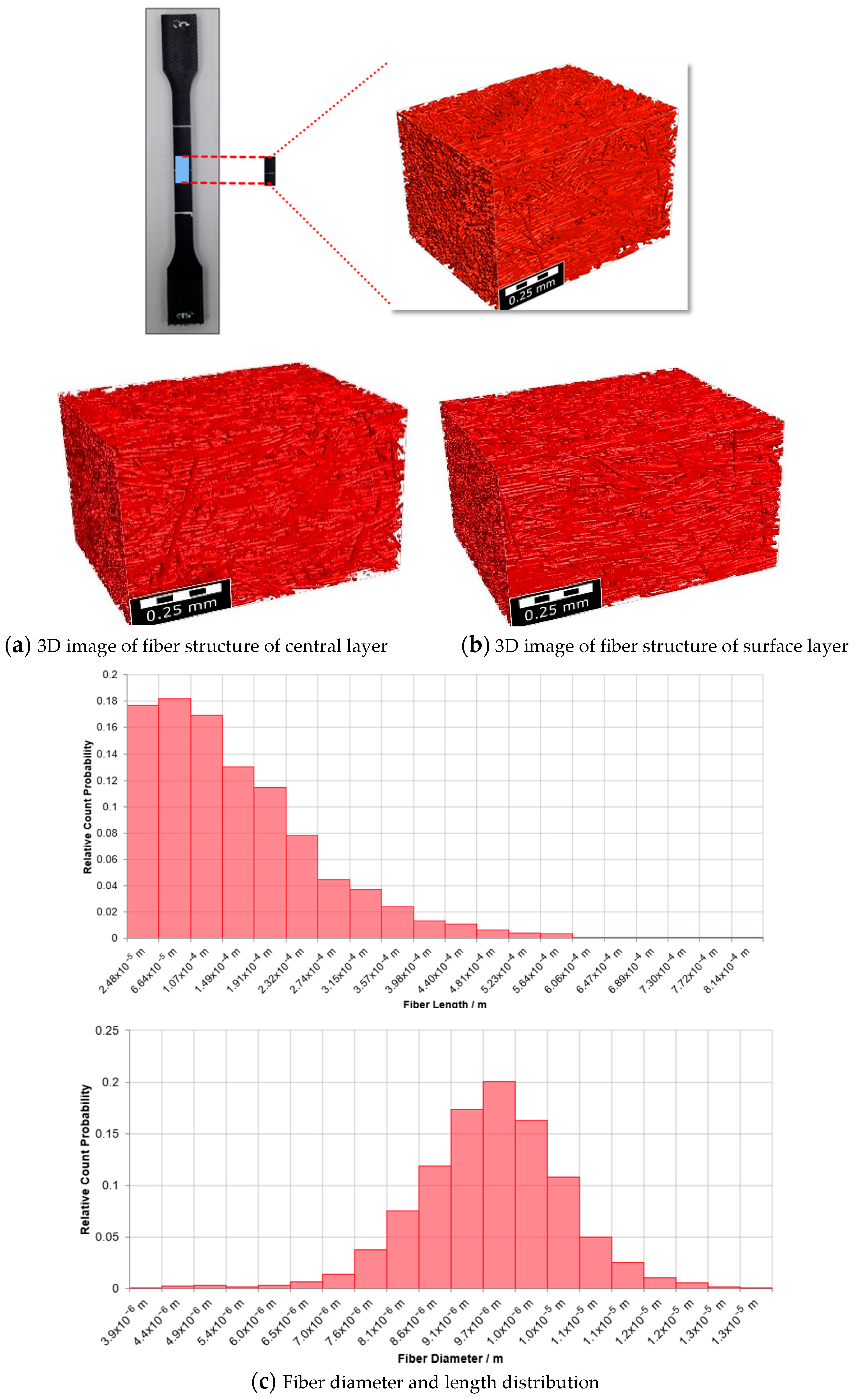
2.4. Fiber Structure Analysis and Generating Mechanical Properties Method
2.4.1. Fiber Orientation Tensor Method and RVE Modeling Method
2.4.2. Mechanical Properties Method
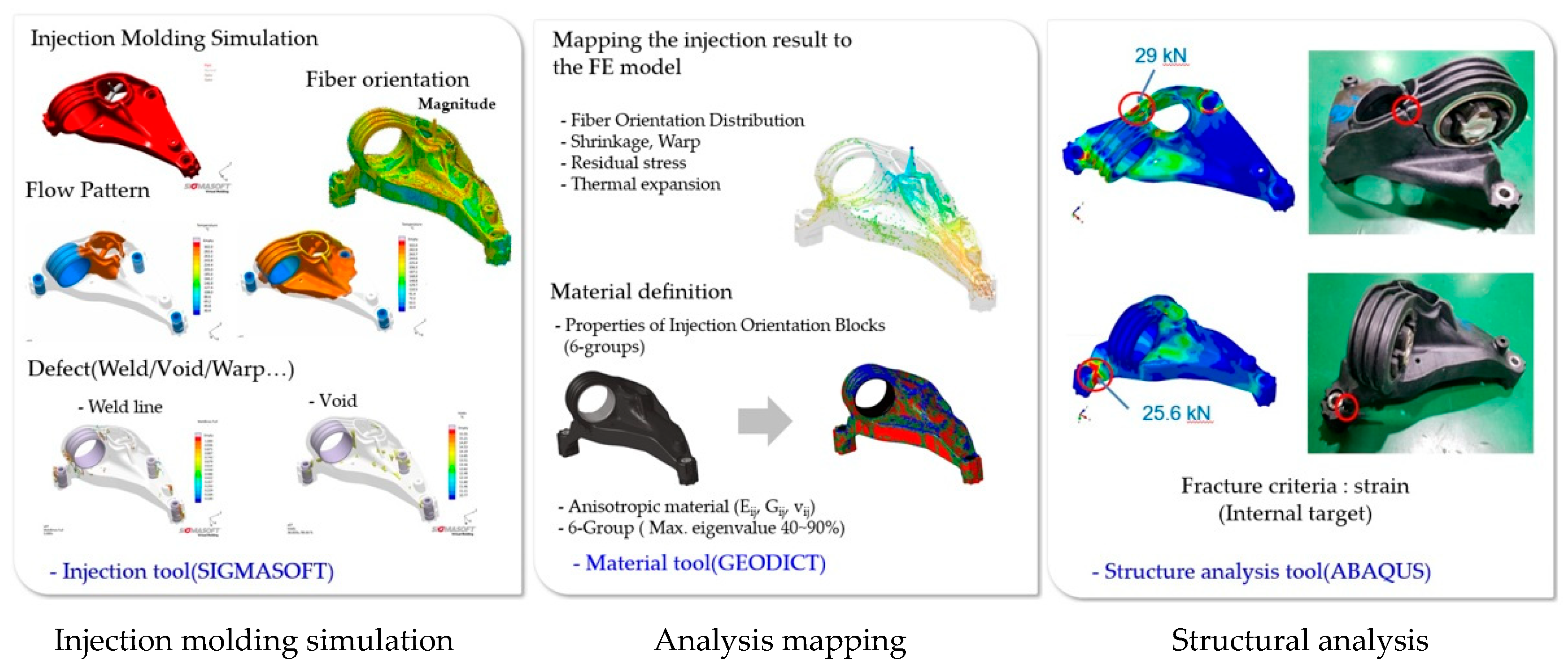
2.4.3. Simulation Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. RVE-Based Prediction of Orthotropic Material Properties for PA66/GF50 (wt%)
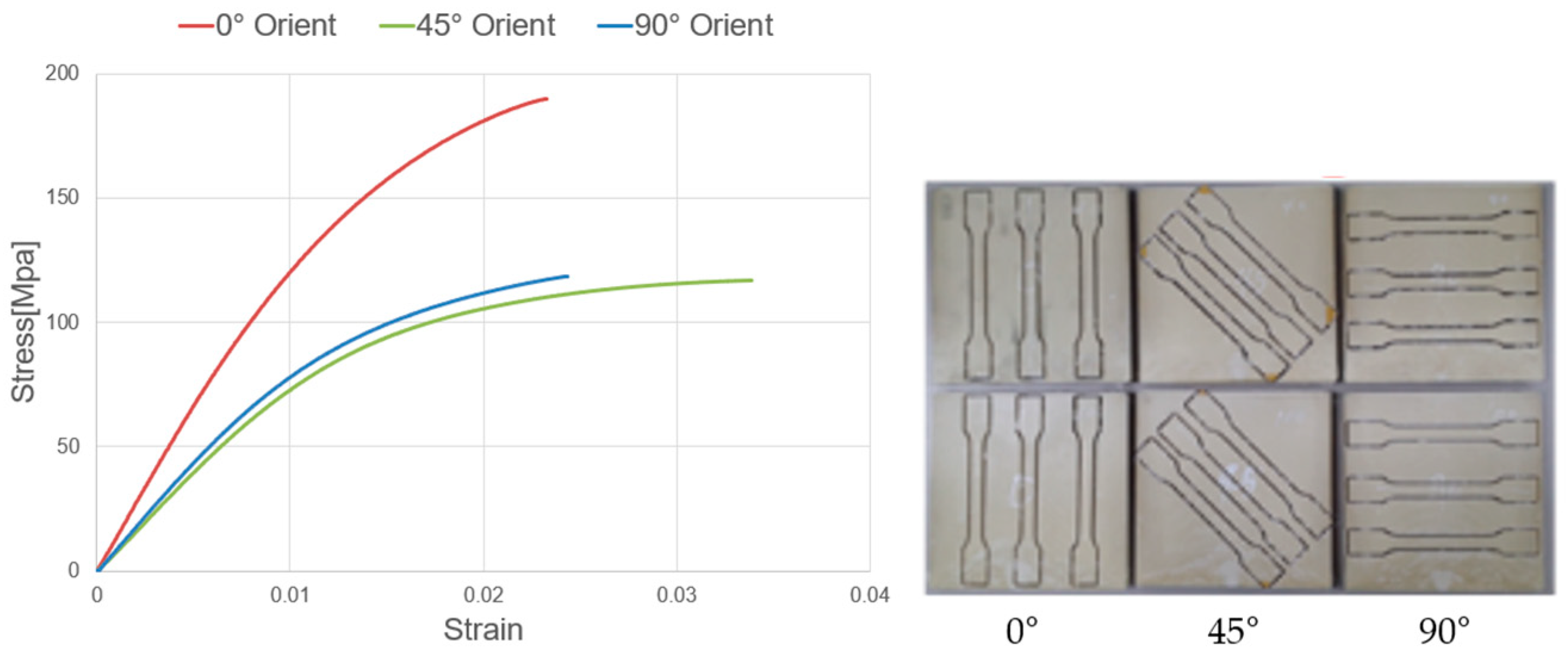
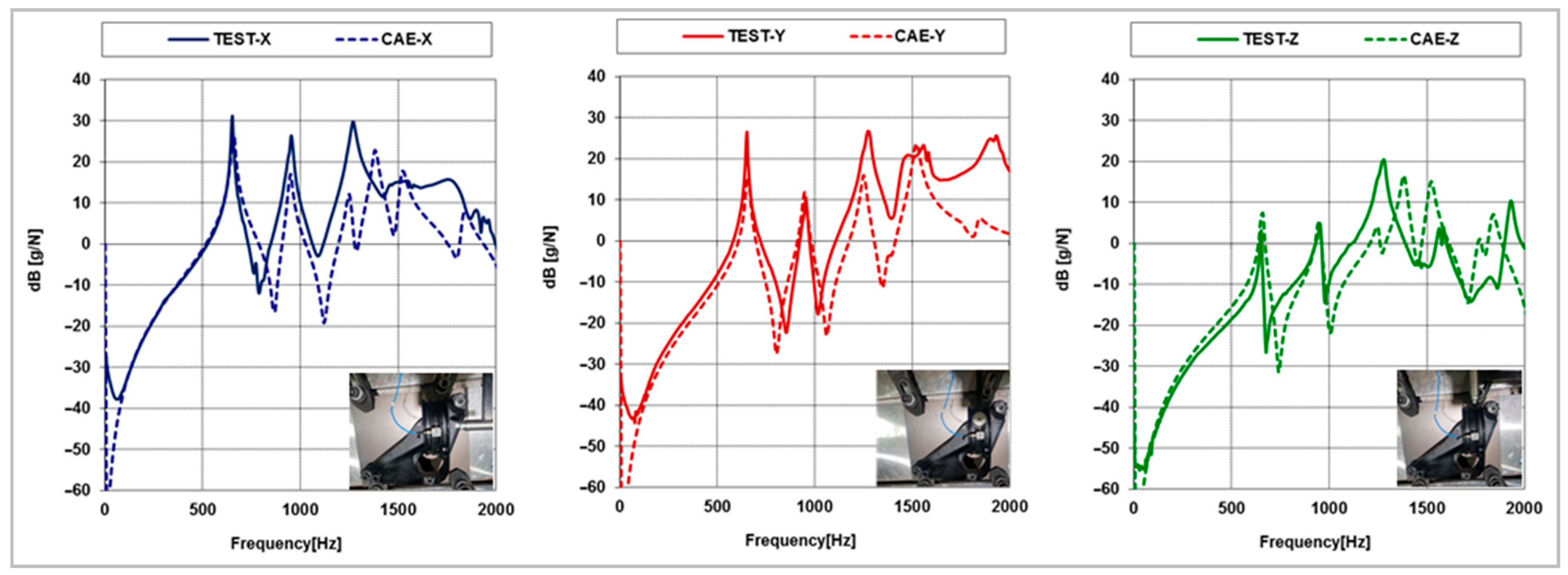
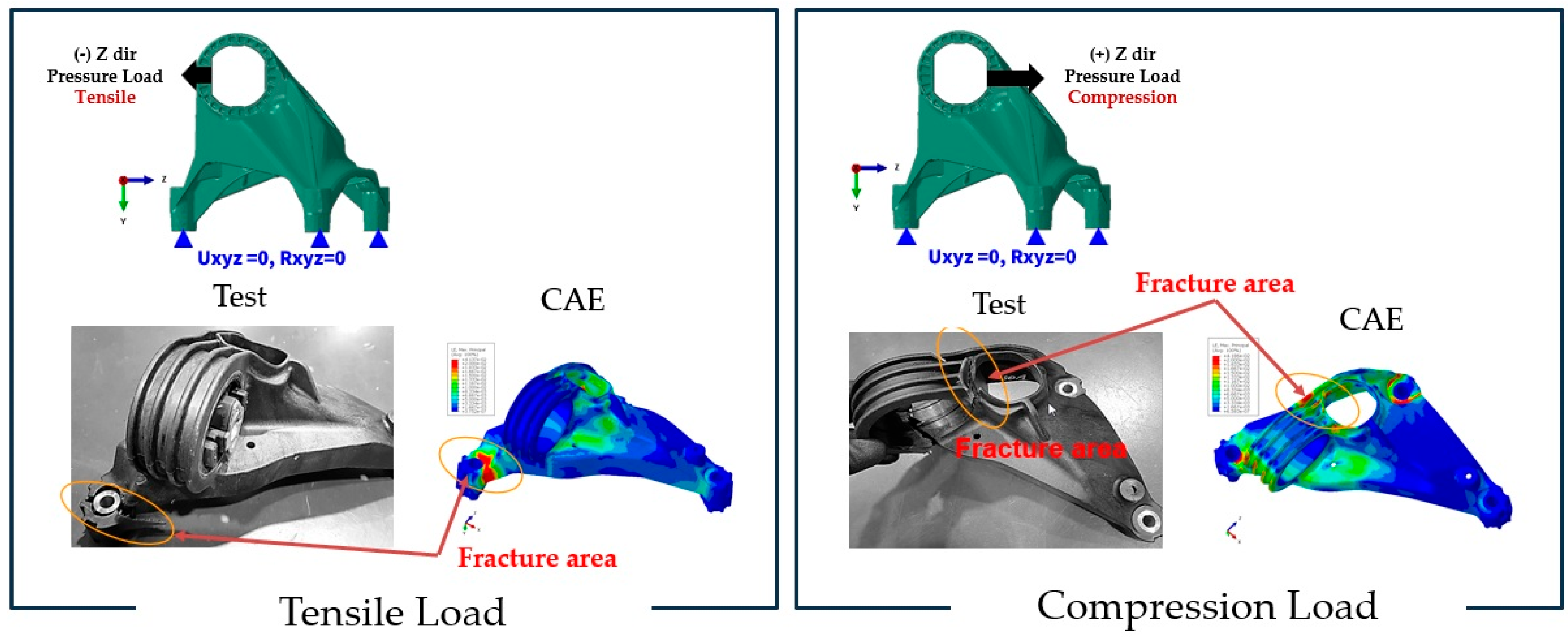
3.2. Experimental Test Results and Simulation Results
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, H.; Wu, C.T.; Lyu, D.; Hu, W.; Rouet, F.H.; Zhang, K.; Ho, P.; Oura, H.; Nishi, M.; Naito, T.; et al. Multiscale Simulation of Short-Fiber-Reinforced Composites: From Computational Homogenization to Mechanistic Machine Learning in LS-DYNA. In Proceedings of the 13th European LS-DYNA Conference 2021, Ulm, Germany, 5–7 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, C.; Zuo, X.; Román, A.J.; Nie, Y.; Su, D.X.; Turng, L.S.; Osswald, T.A.; Cheng, G.; Chen, W. Effective mechanical properties of injection-mfolded short fiber reinforced PEEK composites using periodic homogenization. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 2964–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrahari, R.; Kushwaha, R.; Verma, A.; Banerjee, S. Reinforced Multiscal Polymer Compositer, Properties and Applications. In Polymer Composites; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, J.; Qiu, R.; Liu, A.; Zhu, P. Multiscale modeling based failure criterion of injection modlede SFRP composites considering skin-core-skin layered microstructure and variable parameters. Compos. Struct. 2022, 286, 115277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca, J.; Gonzalez, C.; Molina-Aldareguia, J.M.; Lopes, C.S. Multiscale Modeling of Composites: Toward Virtual Testing… and Beyond. JOM 2013, 65, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Kaxiras, E. An Overview of Multiscale Simulation of Materials. arXiv 2004, arXiv:cond-mat/0401073. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/cond-mat/0401073 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Karim, M.A.; Abdullah, M.Z.; Ahmed, T. An overview: The processing methods of fiber-reinforced polymers(FRPS). Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2021, 12, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, H.; Camanho, P.; Belingardi, G. Elasto-plastic constitutive equations for short fiber reinforced polymers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 165, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oubellaouch, K.; Pelaccia, R.; Bonato, N.; Bettoni, N.; Carmignato, S.; Orazi, L.; Donati, L.; Reggiani, B. Assessement of fiber orientation models predictability by comparison with X-ray µCT data in injection-molded short glass fiber-reinforced polyamide. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 4479–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, J.; Zartmann, L.; Reinel-Bitzer, D.; Andra, H.; Muller, R. Multiscale optimization of the viscoelastic behavior of short fiber reinforced composites. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2023, 19, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuś, W.; Mucha, W.; Jiregna, I.T. Multiscale Analysis of Composite Structures with Artificial Neural Network Support for Micromodel Stress Determination. Materilas 2024, 17, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Bale, H.; Park, S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Hong, S.H. Anisotropic microstructure dependent mechanical behavior of 3D-printed basalt fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Part B 2021, 224, 109184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Ichikawa, M.; Akita, S. A Probabilistic Investigation of Fatigue Life and Comulative Cycle Ratio. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1984, 20, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulinec, H.; Suquet, P. A numerical method for computing the overall response of nonlinear composites with complex microstructure. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1998, 157, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browaeys, J.T.; Chevrot, S. Decomposition of the elastic tensor and geophysical applications. Geophys. J. Int. 2004, 159, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutka, V.; Wiegmann, A. Explicit jump immersed interface method for virtual material design of the effective elastic moduli of composite materials. Numer. Algorithms 2006, 43, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutka, V.; Wiegmann, A.; Andrä, H. EJIIM for Calculation of Effective Elastic Moduli in 3D Linear Elasticity; Berichte des Fraunhofer ITWM: Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2006; Nr. 93; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kabel, M.; Merkert, D.; Schneider, M. Use of composite voxels in FFT-based homogenization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2015, 294, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santharam, P.; Parenteau, T.; Charrier, P.; Taveau, D.; Le Saux, V.; Marco, Y.; Hénaff, G. Complex fibers ori-entation distribution evaluation in short glass fiber-reinforced thermoplastic (PA66 GF50). MATEX Web Conf. 2018, 165, 22026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM, D792-98; Standard Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1998.
- ASTM D683M-96; Standard test method for tensile properties of Plastics(Metric). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1998.
- ASTM D3835-9602; Standard test Method for Determination of Properties of Polymeric Materials by Means of a Capillary Rheometer. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1996.
- Jeffery, G.B. The motion of ellipsoidal particles immersed in a viscous fluid. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A 1922, 102, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advani, S.G.; Trucker, C.L. The Use of Tensors to Describe and Predict Fiber Orientation in Short Fiber Composites. J. Rheol. 1987, 31, 751–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, V.A.; Roth, C. The Effects of Weld Geometry and Glass-fiber-orientation on the Mechanical Performance of Joints-PartⅡ: Kinetics of Glass-fiber-orientation and Mechanical Performance. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2004, 23, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.H.; Kwon, T.H. Fiber orientation in the processing of polymer composites. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2022, 14, 175–188. [Google Scholar]





| Material | Young’s Modulus E (GPa) | Poisson Ratio | Bulk Modulus K (GPa) | Shear Modulus G (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA66 | 0.986 | 0.4 | 1.644 | 0.352 |
| Glass fiber | 72 | 0.22 | 42.857 | 29.508 |
| Cylinder Head Temperature (°C) | Injection Molding Conditions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH | H1 | H2 | H3 | Pressure (%) | Time (s) |
| 315 | 310 | 290 | 280 | 80 | 4 |
| Holding Pressure Conditions | |||||
| Pressure (%) | Time (s) | ||||
| 30 | 10 | ||||
| Specimen Dimension [mm] | b1 | b2 | h | L3 | L | t | A |
| 9.86 | 19.82 | 3.92 | 172.64 | 115 | 3 | 38.65 mm2 |
| Temperature | 26 °C |
| Humidity | 43% |
| Speed | 2.4 mm/min |
| Gauge Length | 50 mm |
| Fiber Orientation Components by Layer (vol.%) | Fiber Orientation | Vf (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-Axis (%) | Y-Axis (%) | Z-Axis (%) | |||
| Micro-CT analysis (Core layer) | 1st Layer | 63.0477 | 17.6956 | 19.2567 | 31.8003 |
| 2nd Layer | 66.1844 | 18.2655 | 15.5502 | 31.9499 | |
| 3rd Layer | 70.9015 | 15.0393 | 14.0592 | 32.2798 | |
| 4th Layer | 76.1767 | 11.3675 | 12.4558 | 32.0796 | |
| Micro-CT analysis (Surface layer) | 1st Layer | 81.4451 | 7.7954 | 10.7565 | 32.7301 |
| 2nd Layer | 79.8369 | 7.9518 | 12.2113 | 32.4027 | |
| 3rd Layer | 80.0405 | 7.8215 | 12.1378 | 32.3877 | |
| 4th Layer | 81.2374 | 7.4823 | 11.2802 | 32.7593 | |
| Tensor notationindex(ij) | 11 | 22 | 33 | 23, 32 | 31, 13 | 12, 21 |
| Voigt notationindex | xx | yy | zz | yz | zx | xy |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
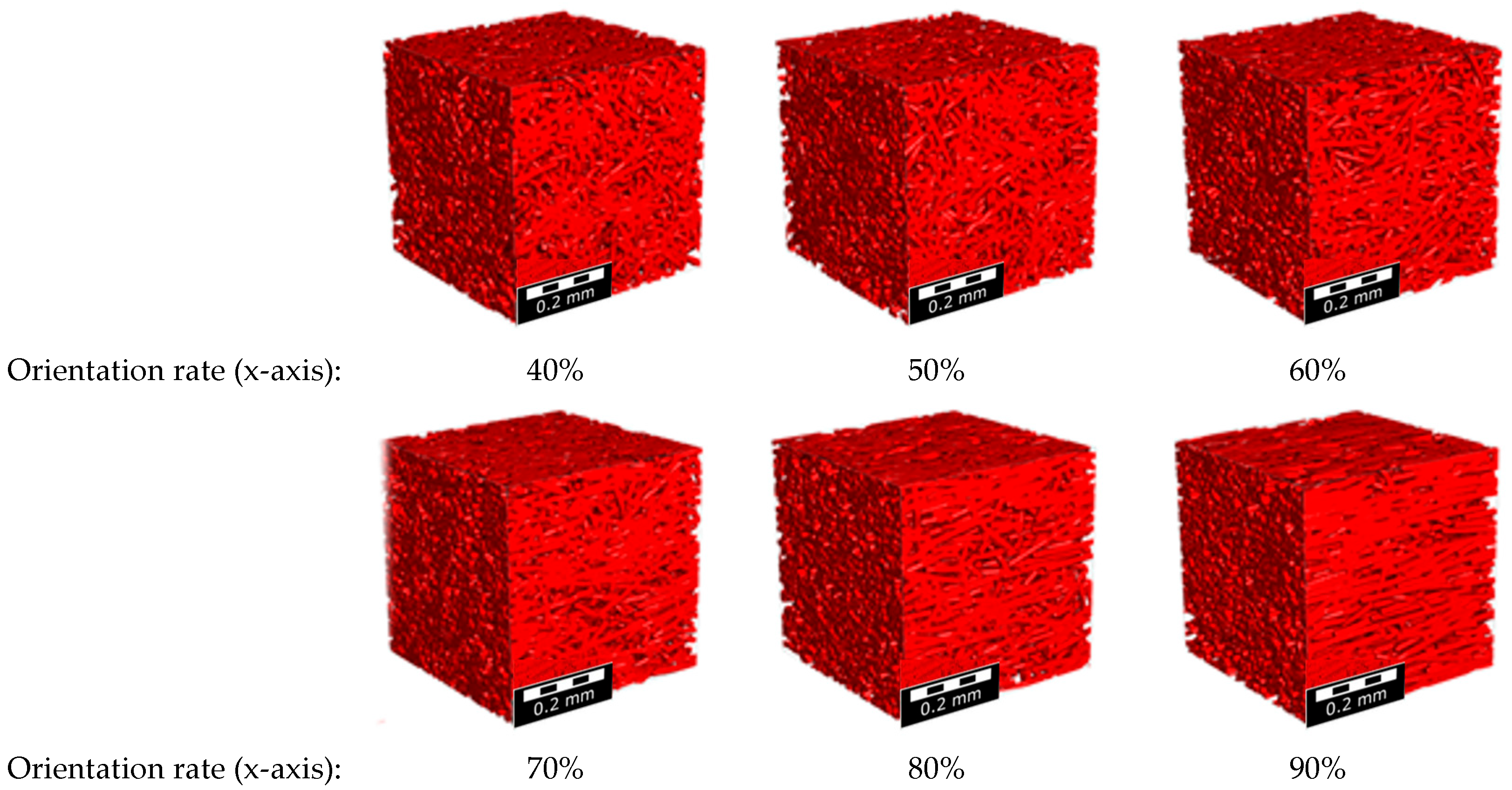
| Fiber Orientation Ratio (Based on the X-Axis) | Fiber Orientation Tensor Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| X-Axis | Y-Axis | Z-Axis | |
| 90% | 0.9 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 80% | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 70% | 0.7 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| 60% | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 50% | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 40% | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| X-Axis (Ratio) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | (GPa) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | 9.881 | 3.497 | 3.507 | 0.387 | 0.386 | 0.499 | 0.137 | 0.137 | 0.499 | 1.358 | 1.371 | 1.132 |
| 80% | 8.564 | 3.736 | 3.677 | 0.384 | 0.398 | 0.499 | 0.167 | 0.171 | 0.499 | 1.526 | 1.537 | 1.229 |
| 70% | 7.461 | 3.929 | 3.982 | 0.391 | 0.384 | 0.469 | 0.206 | 0.205 | 0.476 | 1.615 | 1.629 | 1.327 |
| 60% | 6.424 | 4.053 | 4.113 | 0.388 | 0.384 | 0.437 | 0.245 | 0.246 | 0.443 | 1.676 | 1.719 | 1.427 |
| 50% | 5.632 | 4.290 | 4.225 | 0.373 | 0.383 | 0.412 | 0.284 | 0.287 | 0.406 | 1.722 | 1.727 | 1.535 |
| 40% | 4.967 | 4.462 | 4.484 | 0.366 | 0.368 | 0.375 | 0.329 | 0.332 | 0.379 | 1.699 | 1.719 | 1.620 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, Y.S.; Jeon, B.; Min, J.; Kang, K.; Lee, H. A Multi-Scale Approach for Finite Element Method Structural Analysis of Injection-Molded Parts of Short Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite Materials. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137434
Cho YS, Jeon B, Min J, Kang K, Lee H. A Multi-Scale Approach for Finite Element Method Structural Analysis of Injection-Molded Parts of Short Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite Materials. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137434
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Young Seok, Byungwook Jeon, Juwon Min, Kiweon Kang, and Haksung Lee. 2025. "A Multi-Scale Approach for Finite Element Method Structural Analysis of Injection-Molded Parts of Short Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite Materials" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137434
APA StyleCho, Y. S., Jeon, B., Min, J., Kang, K., & Lee, H. (2025). A Multi-Scale Approach for Finite Element Method Structural Analysis of Injection-Molded Parts of Short Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite Materials. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7434. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137434






