An Optimally Oriented Coherence Attribute Method and Its Application to Faults and Fracture Sets Detection in Carbonate Reservoirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
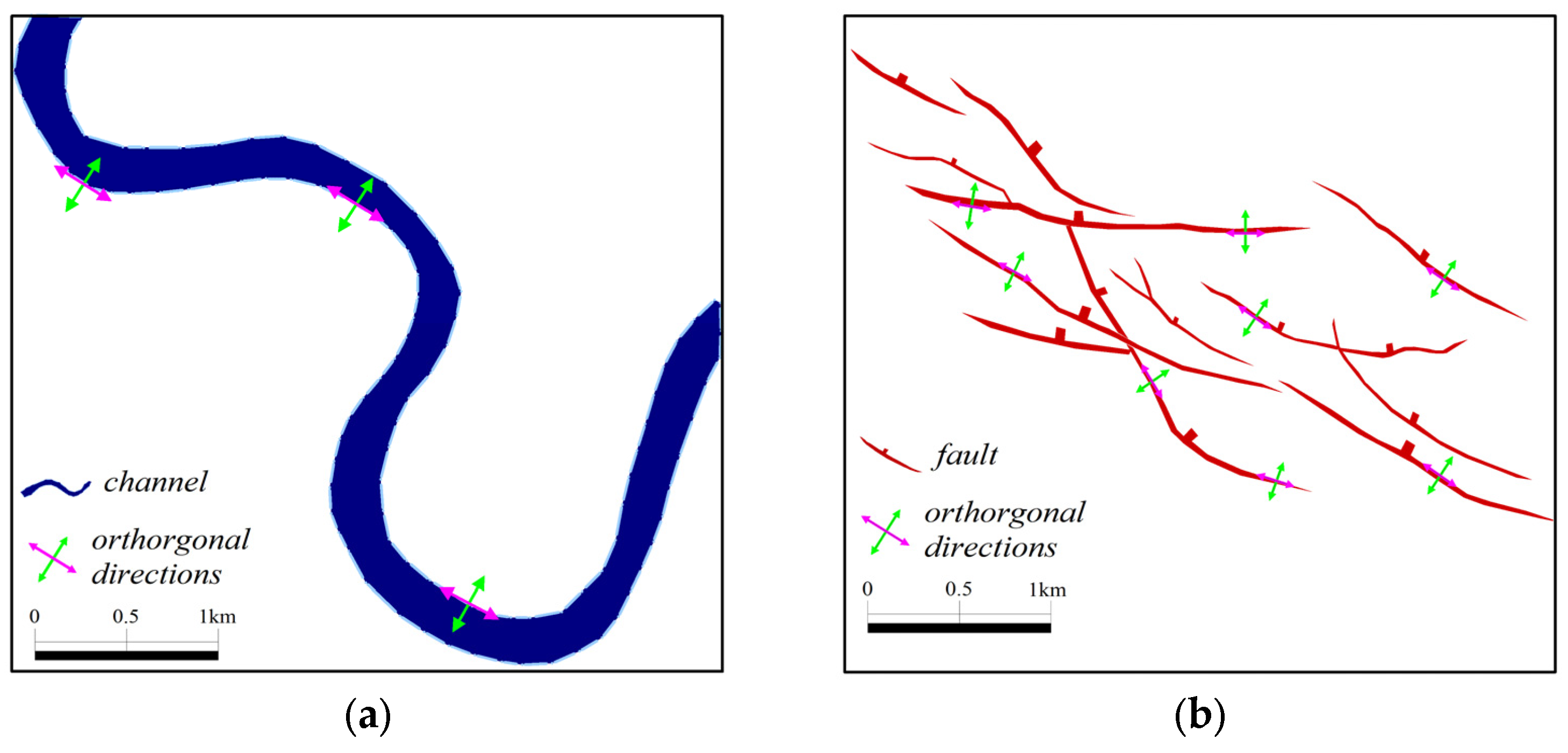
2.1. Directional Framework for Discontinuity Detection
2.2. Dip Estimation Based on Structure Tensor
2.3. Distance-Weighted Structure-Oriented Paired Model Trace Construction
2.4. Optimally Oriented Coherence Calculation with Multi-Frequency Fusion
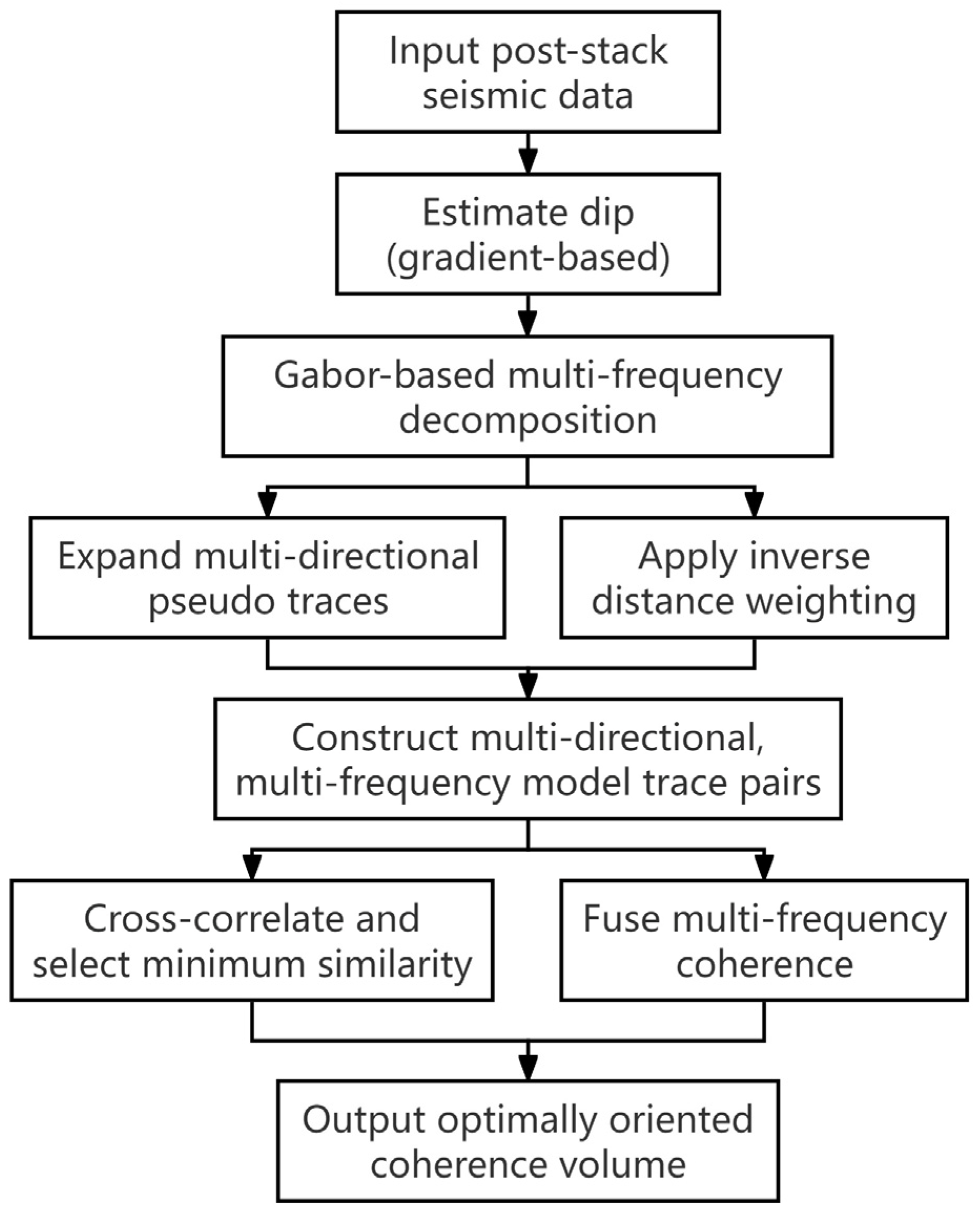
2.5. Methodological Workflow
3. Results
3.1. Physical Modeling Data Example
3.2. Field-Data Example
4. Discussion
- (1)
- Performance Comparison
- (2)
- Frequency Integration
- (3)
- Geological and Engineering Relevance
- (4)
- Limitations and Influencing Factors
- (5)
- Methodological Innovation and Broader Implications
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed approach is fundamentally guided by structural geology. It employs local dip estimation to construct structure-oriented paired model traces and incorporates a distance-weighted scheme to improve spatial response. This configuration enhances sensitivity to reflector geometry variations and lateral discontinuities, enabling more precise delineation of fault boundaries and structural edges.
- (2)
- A Gabor-based multi-frequency fusion strategy is employed to capture both low-frequency continuity and high-frequency structural detail. This fusion enables coherent imaging of large-scale fault zones while simultaneously highlighting subtle secondary fractures, thus achieving enhanced resolution across multiple spatial scales.
- (3)
- Comprehensive validation using both physical models and field data demonstrates that the OOCA method outperforms conventional coherence attributes—including amplitude, curvature, and traditional C3 coherence—in terms of structural clarity, resolution, and noise resistance. Notably, in areas with documented lost circulation events, the method exhibits strong alignment with engineering observations, significantly improving the reliability of pre-drilling structural interpretation and risk prediction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dou, L.R.; Wen, Z.X.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, Z.M.; He, Z.J.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, N.N. Analysis of the world oil and gas exploration situation in 2021. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2022, 49, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.H.; Wei, P.F.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, S.S.; Lou, X.Q.; Cui, K.X.; Fu, Y.W. Joint exploration and development: A self-salvation road to sustainable development of unconventional oil and gas resources. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2017, 4, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Nie, Z.; Ding, T.; Zhu, G. Accurate Delimitation of Mine Goaves Using Multi-Attribute Comprehensive Identification and Data Fusion Technologies in 3D Seismic Exploration. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; He, Y.; Tian, H.; Jiang, Z.; Bi, Z.; Miao, H. The Distribution Characteristics and Genesis Analysis of Overpressure in the Qiongzhusi Formation in the Zizhong Area, Sichuan Basin. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.L.; Lu, C.; Hu, G.M. 3D structural modeling for seismic exploration based on knowledge graphs. Geophysics 2022, 87, IM81–IM100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Ma, J.W.; Zhang, H. Curvature-regularized manifold for seismic data interpolation. Geophysics 2023, 88, WA37–WA53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.H.; Hu, L.Y.; Huang, X.D.; Carpenter, B.M.; Marfurt, K.J.; Vasileva, S.; Zhou, Y. Characterizing damage zones of normal faults using seismic variance in the Wangxuzhuang oilfield, China. Interpretation 2020, 8, SP53–SP60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.H.; Zhao, C.D.; Rui, Z.F.; Guan, S.J.; Zheng, W.T.; Fan, H.C. An improved ant-tracking workflow based on divided-frequency data for fracture detection. J. Geophys. Eng. 2022, 19, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.W.; Sun, Z.D.; Li, G.F. A case study of complex carbonate reservoir connectivity analysis, Tarim Basin, China. Interpretation 2021, 9, B77–B87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovsek, C. Multilayer 3D seismic attribute analysis and fault framework modeling of shallow extensional fault systems in the Delaware Basin. Interpretation 2024, 12, T399–T412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahorich, M.S.; Farmer, S.L. 3-D seismic discontinuity for faults and stratigraphic features: The coherence cube. Lead. Edge 1995, 14, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, K.J.; Kirlin, R.L.; Farmer, S.L.; Bahorich, M.S. 3-D seismic attributes using a semblance-based algorithm. Geophysics 1998, 63, 1150–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, K.J.; Sudhaker, V.; Gersztenkorn, A.; Crawford, K.D.; Nissen, S. Coherency calculations in the presence of structural dip. Geophysics 1999, 64, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gersztenkorn, A.; Marfurt, K.J. Eigenstructure-based coherence computations as an aid to 3-D structural and stratigraphic mapping. Geophysics 1999, 64, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehmers, G.C.; Höcker, C.F.W. Fast structural interpretation with structure-oriented filtering. Geophysics 2003, 68, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. Directional structure-tensor based coherence to detect seismic faults and channels. Geophysics 2017, 82, A13–A17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priezzhev, I.; Danko, D.; Veeken, P.; Strecker, U.; Nikiforov, A. New High-Resolution Fault Detection Based on Dynamic Time Warping Discontinuity Edge Attribute. In Proceedings of the 81st EAGE Annual Conference & Exhibition, London, UK, 3–6 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, H.D.; Song, B.Q.; Wang, W.H.; Yu, B.; Xiong, X.D. Fault identification method of attribute fusion based on seismic optimized frequency of seismic data. Chin. J. Geophys. 2023, 66, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, G.; Xu, F.; Yu, Q.; Liang, H. A model for faults to link the Neogene reservoirs to the Paleogene organic-rich sediments in low-relief regions of the South Bohai Sea, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 200, 108360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Niu, R.; Han, Y.; Deng, Q. Construction of a Geological Fault Corpus and Named Entity Recognition. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Bruna, V.; Bezerra, F.H.; Souza, V.H.; Maia, R.P.; Auler, A.S.; Araujo, R.E.; Cazarin, C.L.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Vieira, L.C.; Sousa, M.O. High-permeability zones in folded and faulted silicified carbonate rocks implications for karstified carbonate reservoirs. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 1, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, A.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Cao, W. Seismic Identification and Characterization of Deep Strike-Slip Faults in the Tarim Craton Basin. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Machado, G.; Marfurt, K.J. A workflow to skeletonize faults and stratigraphic features. Geophysics 2017, 82, O57–O70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Niu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Signal detection and enhancement for seismic crosscorrelation using the wavelet-domain Kalman filter. Surv. Geophys. 2021, 42, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Lyu, B.; AlAli, A.; Machado, G.; Hu, Y.; Marfurt, K. Image processing of seismic attributes for automatic fault extraction. Geophysics 2018, 84, O25–O37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.M.; Bukhari, S.K.; Gull, D.S. The applications of hyperspectral remote sensing techniques in the identification of subsurface faults. An experimental study. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2023, 29, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Huang, L.; Cladouhos, T. Three-dimensional seismic characterization and imaging of the soda lake geothermal field. Geothermics 2021, 90, 101996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, M.; Long, H.; Li, C.; Deng, M. Identification of Strike-Slip Faults and Their Control on the Permian Maokou Gas Reservoir in the Southern Sichuan Basin (SW China): Fault Intersections as Hydrocarbon Enrichment Zones. Energies 2024, 17, 6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Alves, T.M.; Omosanya, K.O.; Li, W. Geometric and kinematic analysis of normal faults bordering continental shelves: A 3D seismic case study from the northwest South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 133, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lu, W. Coherence attribute at different spectral scales. Interpretation 2014, 2, SA99–SA106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Qi, J.; Lyu, B.; Marfurt, K.J. Multispectral coherence. Interpretation 2017, 6, T61–T69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Zheng, X.; Li, Y. A seismic coherency method using spectral amplitudes. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 12, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, F.; Marfurt, K.J. Multiazimuth coherence. Geophysics 2017, 82, O83–O89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Su, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Geosteering phase attributes: A new detector for the discontinuities of seismic images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Yuan, S.Y.; Yan, B.P.; He, Y.X.; Sun, W.J. Directional complex-valued coherence attributes for discontinuous edge detection. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 129, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, A.E. A tutorial on complex seismic trace analysis. Geophysics 2007, 72, W33–W43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, S. An efficient and robust scheme for the implementation of eigenstructure-based coherency algorithms. Geophysics 2020, 85, O97–O108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Xu, Y.; Xie, R.; Chen, S.; Yuan, J. Multi-scale intelligent fusion and dynamic validation for high-resolution seismic data processing in drilling. Petrol. Explor. Dev. 2025, 52, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Li, K.; Dong, M.; Xiao, Y. FaultSSL: Seismic fault detection via semisupervised learning. Geophysics 2024, 89, M79–M91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Huang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, R.; Hu, H.; Cladouhos, T. Automatic fault detection on seismic images using a multiscale attention convolutional neural network. Geophysics 2021, 87, N13–N29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Li, H.; Jing, J.; Yan, H.; Gu, H. 3-D Seismic Fault Detection Using Fault Orthogonal Annotation and Barely Supervised Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5904711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, N.; Liu, R.; Lu, M.; Wei, T.; Gao, J. Adaptive Multifrequency Attribute Analysis and Its Application on Reservoir Characterization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. Sand Bodies Delineation by Fusing Multifrequency Attributes via t-SNE. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 7501205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xiang, M.; Wang, R.; Xu, W.; Song, C. Multi-Frequency Interferometric Coherence Characteristics Analysis of Typical Objects for Coherent Change Detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, K.; Xue, L.; Jiang, T.; Dong, J.; Wang, C.; Ding, H. The Seismic Dynamic Response Characteristics of the Steep Bedding Rock Slope Are Investigated Using the Hilbert–Huang Transform and Marginal Spectrum Theory. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.W.; Margrave, G.F. Seismic depth imaging with the Gabor transform. Geophysics 2008, 73, S91–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, S.X.; Yuan, S.Y.; Wang, T.Y.; Gao, J.H.; Li, S.J. Three-dimensional geosteering coherence attributes for deep-formation discontinuity detection. Geophysics 2018, 83, O105–O113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Method | Fractures Identified (Out of 95) | Detection Accuracy (%) | Minimum Resolvable Width (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C3 Coherence | 71 | 74.7 | 30 |
| Instantaneous Phase | 76 | 80 | 20 |
| OOCA | 88 | 92.6 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Li, S.; Ma, Q.; Qin, L.; Yuan, S. An Optimally Oriented Coherence Attribute Method and Its Application to Faults and Fracture Sets Detection in Carbonate Reservoirs. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137393
Chen S, Li S, Ma Q, Qin L, Yuan S. An Optimally Oriented Coherence Attribute Method and Its Application to Faults and Fracture Sets Detection in Carbonate Reservoirs. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137393
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shuai, Shengjun Li, Qi Ma, Lu Qin, and Sanyi Yuan. 2025. "An Optimally Oriented Coherence Attribute Method and Its Application to Faults and Fracture Sets Detection in Carbonate Reservoirs" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137393
APA StyleChen, S., Li, S., Ma, Q., Qin, L., & Yuan, S. (2025). An Optimally Oriented Coherence Attribute Method and Its Application to Faults and Fracture Sets Detection in Carbonate Reservoirs. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7393. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137393





