1. Introduction
1.1. Artificial Intelligence and Computational Chemistry
The deep integration of computer simulation and artificial intelligence is reshaping the landscape of scientific research. When traditional chemical calculations meet machine learning technologies, their synergy not only accelerates the processes of drug development and material design but also opens up new perspectives for understanding molecular behavior. By establishing intelligent analytical systems, scientists can more accurately capture key patterns in molecular dynamics, reducing the time required to verify experimental hypotheses from years to mere months. This technological integration not only enhances research efficiency but, more importantly, constructs a learning platform capable of autonomously optimizing experimental schemes. In the exploration of novel catalysts or drug molecules, the system continuously refines predictive models based on historical data, paving new paths to overcoming the limitations of traditional research methods [
1,
2].
1.2. The Origins of Artificial Intelligence and Computational Chemistry
Driven by advancements in computer technology and molecular science research, a multidisciplinary field known as computational chemistry emerged in the mid-20th century. This discipline combines mathematical modeling with computer programming to digitally reconstruct the dynamic behavior of molecular systems. Researchers use the fundamental principles of quantum theory within a classical mechanics framework to develop numerical simulation systems capable of analyzing microscopic processes such as chemical bond formation and breaking and the evolution of intermolecular forces. This numerical experimental approach transcends the spatial and temporal limitations of traditional laboratory research, enabling scientists to observe key information about chemical reactions, such as transition state structures and energy transfer pathways, at atomic-level resolution, thus providing a unique theoretical perspective for uncovering the fundamental laws of chemical phenomena [
3,
4].
However, in the early stages of computer technology development, the exploration of computational chemistry was constrained by hardware performance limitations. Researchers had to reduce the scale of simulations and simplify models, resulting in significant deviations in predicting molecular behavior. With breakthroughs in chip manufacturing technology and parallel computing architectures, particularly the proliferation of supercomputing clusters, this field has achieved a qualitative leap [
5,
6]. Modern computing platforms allow scientists to perform all-atom simulations of complex systems containing tens of thousands of atoms, accurately capturing micro-details such as energy transfer pathways and molecular conformation dynamics in chemical reactions, thus providing powerful digital experimental tools for revealing the fundamental laws of matter.
1.3. Entering the Field of Artificial Intelligence
The evolutionary trajectory of artificial intelligence exhibits significant spatiotemporal coupling with the development of computational chemistry. From the emergence of algorithmic prototypes in the mid-20th century to the data-driven awakening of intelligence in this century, machine learning, as a core technological paradigm, has demonstrated the ability to autonomously analyze high-dimensional data characteristics. This intelligent modeling approach offers unique advantages in molecular system research: by constructing multi-layer feature mapping networks, the system can spontaneously identify nonlinear correlation patterns among parameters such as molecular conformation and electron distribution. This breakthrough surpasses the simplified assumptions of traditional physical models regarding complex interactions, providing a novel research paradigm for accurately predicting material properties and reaction pathways [
7,
8,
9].
Traditional computational methods face significant bottlenecks when analyzing complex interactions between molecules, particularly in systems involving rapid dynamic changes or intertwined variables. This is precisely the domain where artificial intelligence technologies reveal their unique value—by building self-learning analytical models, the system can automatically identify hidden regularities from vast experimental data sets. This intelligent analytical approach not only compensates for the inefficiencies of traditional simulation methods in data processing but more importantly establishes dynamic models capable of continuously optimizing prediction accuracy, offering a new research path for understanding complex chemical phenomena.
1.4. Intelligent Chemical Laboratory
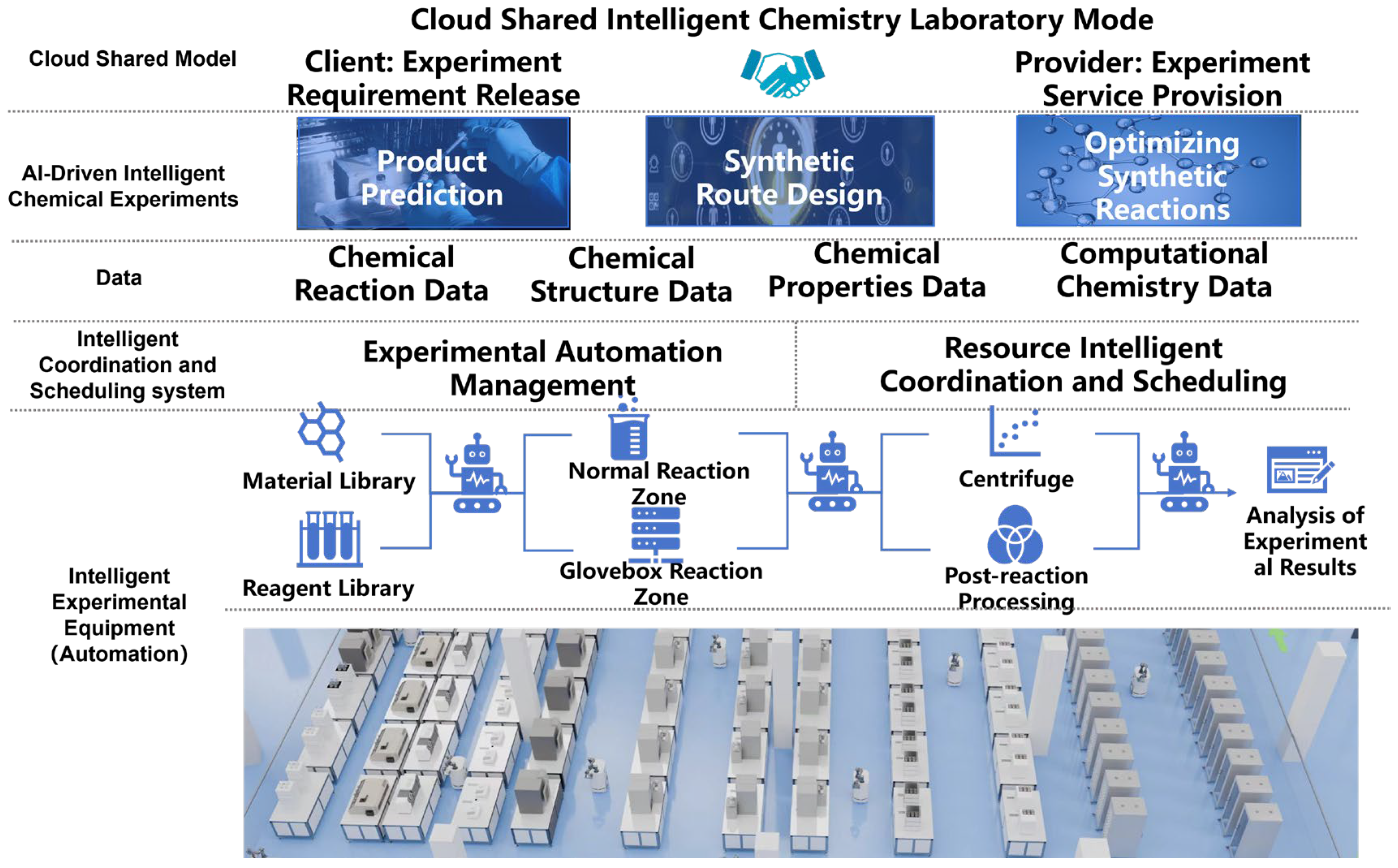
This paper summarizes and organizes the overall framework of the intelligent chemical laboratory from the perspectives of laboratory automation, smart chemical experiments, and cloud-shared laboratory service operation models, as shown in
Figure 1. First, laboratory automation supports the high-throughput execution of chemical experiments and mainly consists of two parts: intelligent experimental equipment hardware and intelligent collaboration and scheduling system software. The intelligent experimental equipment includes modules such as material and reagent management, multi-zone reaction operations (conventional zone/glove box zone), post-processing, and analytical testing. The intelligent collaboration and scheduling software system includes an experiment automation management system and a resource intelligent coordination and scheduling system. Second, during the process of high-throughput chemical experiments, a large amount of experimental data can be accumulated, including types such as chemical reactions, chemical structures, chemical properties, and computational chemistry. Based on the data generated from high-throughput chemical experiments and combined with artificial intelligence algorithms, applications in computational chemistry such as molecular structure prediction, synthesis pathway design, and reaction parameter optimization can be realized. Finally, regarding the cloud-shared chemical laboratory, it clearly demonstrates the core operational model of the cloud-shared intelligent chemical laboratory: using a cloud platform as the link connecting clients who submit experimental requests with service providers who offer experimental services. This overall framework of the intelligent chemical laboratory outlines how such laboratories integrate data, resources, and intelligent management to consolidate cross-regional equipment and data resources, optimize equipment utilization, and promote efficient collaborative chemical research and development.
This paper will introduce the artificial intelligence-driven intelligent laboratory for organic chemical synthesis from the following chapters. Chapter 2 primarily discusses the full-process reconstruction from hardware to systems achieved through laboratory automation.
Section 2.1 elaborates on the development of intelligent chemical apparatus within laboratory equipment.
Section 2.2 addresses the automation management of experiments and the intelligent coordination and scheduling of laboratory workstation resources and mobile compound robots from the software system perspective. Chapter 3 explores the closed loop of intelligent organic chemistry experiments driven by artificial intelligence.
Section 3.1 introduces various chemical datasets and their characteristics pertinent to organic chemistry.
Section 3.2 summarizes AI-driven predictions of chemical products, molecular retrosynthesis planning, and the optimization of synthetic reactions at different stages of intelligent chemical experiments. In Chapter 4, inspired by the socialized collaboration model of cloud manufacturing in the industrial sector, a cloud-shared chemical laboratory service model is proposed. This model enhances equipment utilization and data accumulation efficiency through the socialized sharing of experimental resources and intelligent matching of supply and demand. Chapter 5 discusses our related work in intelligent chemical laboratories, focusing on intelligent laboratory management, the intelligent scheduling of laboratory resources and multi-task collaboration, and the application of artificial intelligence to organic chemistry experiments. Finally, the paper concludes with a summary and outlook on the development of AI-driven intelligent chemical experiments, aiming to provide a theoretical framework and technical implementation path for constructing the next generation of automated and intelligent chemical laboratories, thereby promoting the transformation and upgrading of chemical research toward a data-driven paradigm.
2. Laboratory Equipment and Intelligent Systems
2.1. Intelligent Experimental Equipment
With the rapid development of AI and robotics technology, laboratories are evolving from workstation automation to flexibility and intelligence. The complexity of chemical experiments leads to a diversity of chemical instruments and devices. The Ullmann reaction is a classic reaction in organic chemical synthesis, involving the nucleophilic substitution between aryl halides (such as iodobenzene or bromobenzene derivatives) and nucleophiles (e.g., amines, phenols, thiophenols) under heating and reflux conditions in the presence of a copper catalyst (such as CuI or copper powder), a base (e.g., K
2CO
3), and a high-boiling solvent (such as xylene or DMF), leading to the formation of carbon–heteroatom bonds. Taking the reaction between bromobenzene and aniline as an example: the main pathway produces diphenylamine as the desired product. However, significant side reactions occur, including the formation of dehalogenation byproducts (e.g., benzene from reduction of aryl halides), homocoupling byproducts (e.g., biphenyl from the self-coupling of aryl halides), and multiple-substituted products (e.g., triphenylamine formed via bis-arylation of the amine). In particular, substrates containing ortho-substituents or highly reactive species (such as 2-iodoanisole) are more prone to generate deiodination byproducts (e.g., anisole) or ether cleavage products (e.g., phenol) [
10]. Ullmann’s reaction steps include sampling, feeding, reaction, post-reaction processing, and product storage, involving experimental equipment such as titration devices, pipetting devices, centrifuges, and filtration devices. Currently, the degree of intelligence in these devices mostly remains at the level of automation, without any significant involvement of AI, and many stages still require human intervention. Ian et al. [
11] noted that as automation is increasingly integrated into the workplace, it has improved the productivity, efficiency, and quality of numerous industrial processes. They pointed out that automation can help enhance experimental reproducibility in three ways: by reducing human-induced variability, increasing data generation rates, and minimizing contamination. As shown in
Table 1, in recent years, many research teams have conducted related practical studies, and the results demonstrate that the application of automation technology can reduce human influence and environmental interference while improving experimental speed. Therefore, in projects where high-throughput and reproducible results are required within a short time frame, automation offers significant advantages over manual procedures.
Additionally, robots that assist researchers in conducting experiments are continuously being developed, and their functionalities are gradually improving. Some robots can complete all experimental steps and analyze results without human intervention for extended periods. For instance, laboratory titration devices [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22] have been automated or enabled for remote operation via the internet, although human involvement is still required in many parts. Choi et al. [
23] proposed the concept of an intelligent pipette tip which uses spontaneously generated electrical signals during pipetting to evaluate the electrolyte concentration of the dispensed solution, providing more reliable and credible results. Jiang et al. developed an intelligent miniature mass spectrometer, which, combined with intelligent algorithms, enables rapid and accurate identification.
In the field of laboratory robotics, for example, Burger’s team [
24] proposed using mobile robots to find improved photocatalysts for hydrogen production in water. The robot autonomously operated for eight days, conducting 688 experiments, and identified a photocatalyst mixture with activity six times higher than the initial formulation. Zhu et al. [
25] demonstrated several AI-based systems or robots with specific chemical skills, including a robot that can organize relevant literature from databases and execute planned experimental steps. This robot can perform basic tasks in chemical research, such as sampling and feeding, and supports online control; it can also independently complete entire experiments across 14 workstations, including chemical synthesis, characterization, and performance testing of products. Additionally, an autonomous synthesis robot (Taesin Ha) combines AI to establish the optimal synthesis formula for certain chemicals and optimizes this formula through feedback, optimization, and iteration during chemical experiments. The robot’s performance has been verified by determining the optimal synthesis formulas for three organic compounds, achieving conversion rates superior to existing reference compounds.
Heidi’s team [
26] proposed a method combining an electronic pipette with a dual-arm robot, allowing the robot to mimic human pipetting operations, such as transferring chemicals during experiments, preparing standard concentration solutions, or diluting samples. Li et al. [
27] designed a system (MAOS) with a unique language and compiler architecture to accelerate certain operational steps. After VR training, MAOS can operate independently without human intervention, reducing time costs and freeing researchers from tedious experimental operations, eliminating the need for the constant exploration of optimal reaction conditions. Granda et al. [
28] introduced a reaction system controlled by machine learning algorithms, which, after expert training, can explore chemical reactions more rapidly. They also introduced a chemical robot for organic synthesis that can perform chemical operations faster than manually, analyze reaction processes and results, and predict the reactivity of reagent combinations after a few experiments. By using real-time data from these robots, chemists manually tracked these predictions and discovered four chemical reactions. Li et al. [
29] showcased a chemical intelligent robot, AIR-Chem, which can be remotely controlled via the cloud, learn parameter programs for given targets, and perform laboratory operations in independent mode, exhibiting high reproducibility, precision, and knowledge regeneration usability. Song’s team [
30] demonstrated an AI chemist equipped with Llama-3.1-70B, capable of executing complex multi-step experiments with minimal human intervention. A summary of these laboratory robots and their functionalities is presented in
Table 2.
2.2. Intelligent Coordination and Scheduling
In intelligent chemical laboratories, intelligent coordination and scheduling refer to the process of controlling and managing smart devices within the laboratory through the establishment of reasonable rules. Current research primarily focuses on two areas: first, intelligent task scheduling and flexible dispatching of laboratory bench/line resources to meet the needs of various types of chemical experimental tasks; second, the scheduling of mobile composite robot groups, which are key components of intelligent laboratories, to achieve collaborative production between laboratory benches and robots.
2.2.1. The Scheduling of Experimental Resource Production
In the field of production scheduling, particularly in smart manufacturing and intelligent chemical laboratory environments, efficient planning and allocation of resources play a crucial role in improving productivity, reducing costs, and adapting to dynamic operational conditions. Various optimization models and methods have been proposed to address the complex constraints and uncertainties inherent in such systems, as illustrated in
Table 3.
Regarding production scheduling, Farhad Angizeh et al. proposed an optimal production scheduling model [
31] aimed at optimizing the production scheduling of smart manufacturing factories with multiple production lines similar to intelligent chemical laboratory environments. Based on the mixed integer linear programming (MILP) problem, this model incorporates several operational constraints, including overall factory energy consumption and related costs, productivity, defect rate, changeover time, and labor costs. The model can easily solve for the optimal operational scheduling scheme of multi-product type production lines in smart factories. The authors applied the model to a smart factory with seven production lines producing six products and conducted repeated experiments under different production demand conditions, verifying that the model can significantly reduce factory production operating costs.
Traditional chemical factory production scheduling generally ignores uncertainties in the production process, and once the production plan is executed, the scheduling is rarely changed. Christian D. Hubbs et al. developed a deep reinforcement learning method for chemical production scheduling [
32], primarily for dynamic scheduling of single-stage multi-product reactors. The scheduling model based on deep reinforcement learning proposed in this paper can naturally capture system uncertainties, greatly improving the optimality of system scheduling. Additionally, by introducing predictions and replacing the MILP model with a short diminishing time window in traditional schedulers with a scaled MILP model, the scheduling effect of this scheduler is significantly better than other scheduling schemes.
Qianxiang Ai et al. proposed a chemical experiment operation scheduling system based on minimizing the time required to complete target products as a constraint [
33], used to schedule various experimental operations in the overall experiment when synthesizing series of chemical substances. This system includes a mixed integer linear programming (MILP) function to consider common laboratory constraints such as delay time, module capacity, and shift schedules, greatly reducing the completion time of linear and tree-like synthetic activities and improving module utilization.
2.2.2. The Scheduling of Robot Swarms
In intelligent chemical laboratories, multiple autonomous mobile robots are often relied upon to transport reaction materials and products, as well as to execute various operations. The scheduling of robot swarms in this context is crucial for the overall efficiency of the system. A well-designed scheduling strategy can significantly enhance experimental efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve system reliability. Robot swarm control is a significant topic in robotics research due to its wide range of applications and consistent research interest.
For the scheduling of mobile robot swarms, Junyi Zhou et al. proposed a multi-robot and multi-task scheduling system [
34] specifically designed for autonomous chemical laboratories to improve the efficiency of executing complex chemical experiments. The system first analyzes task sequences and laboratory resources to obtain the FESP-B (Flexible Experimental Scheduling Problem-B) model, then uses constraint programming algorithms to solve the FESP-B problem by adding constraints based on task sequences, constructing them into a tree structure, and using heuristic searches to find the optimal solution. Due to the similarity between robot swarm scheduling and vehicle routing problems, researchers often employ vehicle routing methods to address robot swarm scheduling issues. BARBARA et al. implemented a method for coordinating robot swarms [
35] that is robust and fast. The core of this method is a distributed task allocation and scheduling algorithm that addresses time and priority constraints between tasks, representing the problem as a variant of the vehicle routing problem, and using a distributed metaheuristic algorithm based on evolutionary computation (CBM-pop) to find solutions. Compared to traditional methods, this approach offers the advantage of quickly and proximally assigning tasks.
Artificial intelligence technologies such as neural networks, with their high-dimensional and nonlinear characteristics, are often applied to various complex industrial scenarios. Zheyuan Wang et al. proposed a robot collaborative scheduling strategy learning scheme based on graph attention networks [
36]. This scheme combines imitation learning and graph neural network algorithms within a non-parametric framework, allowing for rapid and approximately optimal scheduling of robot swarms of various sizes, significantly accelerating computational efficiency while ensuring the approximate nature of the scheduling plan. Zohreh Shakeri et al. introduced a scheduling system for solving the multi-robot flexible job shop scheduling (MRFJS) problem with limited buffers [
37]. The system includes a mixed integer linear programming (MILP) model to minimize completion time and an improved genetic algorithm to find the optimal scheduling scheme. Experiments indicate that this scheme significantly outperforms traditional genetic-based scheduling schemes in terms of relative deviation and other aspects. Robots in swarms typically possess independent computational capabilities, exhibiting characteristics of distributed systems, making distributed algorithms commonly used in multi-robot scheduling systems. Weiheng Dai et al. proposed a reinforcement learning framework to train distributed policy multi-robot scheduling systems suitable for heterogeneous agents [
38], utilizing distributed reinforcement learning algorithms to enable complex cooperative learning among multiple robots and introducing a constraint flash-forward mechanism (CFM) to constrain robot behaviors, achieving optimal scheduling with strong generalization capabilities and planning speed.
In the aforementioned studies (as shown in
Table 4), both production scheduling and multi-robot scheduling are viewed as multi-objective optimization problems, solved by providing different constraints to derive optimal scheduling schemes. Production scheduling generally considers optimal production cost and maximum profit, breaking these two major objectives into multiple sub-objectives and using traditional mathematical methods or deep reinforcement learning for optimization to obtain the best production scheduling plan. Multi-robot system scheduling often focuses on minimizing the total cost of system deployment and operation and achieving optimal real-time performance, with distributed algorithms and artificial intelligence algorithms commonly used to solve their optimal scheduling plans. Given the broad application of these two types of scheduling in modern intelligent industrial production, enhancing the generalization capability of system deployment remains a research hotspot in this field.
3. AI-Driven Intelligent Chemical Experiments
3.1. Data Foundation
Large-scale, high-quality, and accessible databases provide the foundation for efficient artificial intelligence training [
39], enabling AI to more accurately predict chemical reaction outcomes, optimize synthesis routes, and enhance experimental efficiency. The diversity and richness of data contribute to improving the generalization capability of AI, allowing it to be applied to a broader range of organic chemistry research [
40].
Table 5 introduces several commonly used databases in the field of organic chemistry, categorizing them into four types to facilitate subsequent searches and utilization in intelligent chemical experiment research.
3.1.1. A Chemical Reaction Database
The chemical reaction database can provide reliable reaction references for intelligent synthesis route design, supporting the system in simulating reaction processes under different conditions and assisting researchers in quickly screening suitable reaction paths. Reaxys and SciFinder data are commercial databases with high data quality and wide coverage, but they do not support batch export of large-scale datasets, which poses a huge obstacle to downstream applications. As a result, Lowe DM [
41] extracted and structured a large amount of chemical reaction data from the patent documents of the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) through text mining techniques, creating a dataset which can be used for the training of machine learning models. The Open Reaction Database (ORD) [
42], with its consistent data representation and an infrastructure that supports data sharing, significantly improves the technical level of computer-assisted synthesis planning, reaction prediction, and other predictive chemistry tasks. NextMove software [
43] provides open-source text mining tools for identifying information such as chemicals and reactions, and an increasing number of researchers are using NextMove to make their databases public, offering greater convenience for obtaining organic chemistry reaction data. Raccuglia, P [
44] and others established the Dark Reactions database, which aims to collect and analyze “unsuccessful” chemical reactions to better understand which conditions might lead to reaction failures, helping researchers make more informed decisions when designing new reactions and improving the success rate of experiments. The DigiMOF database systematically extracts experimental data such as synthesis methods, solvents, organic linkers, metal precursors, and topological structures using the ChemDataExtractor (CDE) web scraping package and the MOF subset of CSD, generating an open-source database dedicated to the synthesis characteristics of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
3.1.2. The Chemical Structure Database
The Chemical Structure Database is not merely a platform for storing chemical information. It also provides fundamental data for molecular design and structure–activity relationship studies. The Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) [
45] is the most well-known solid material structure database. It contains published information on the crystal structure of organic and organometallic compounds worldwide. The Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) is the most renowned solid material structure database, encompassing crystallographic information of published organic and metal-organic compounds worldwide. The Powder Diffraction File (PDF), compiled, edited, published, and distributed by the International Centre for Diffraction Data (ICDD), serves as a standard powder diffraction database primarily used for phase identification and the quantitative analysis of crystalline materials. In recent years, it has also partially included atomic coordinate entries from CSD, ICSD, NIST, and others. The Reticular Chemistry Structure Resource (CSRC) contains approximately 1600 distinct crystal topologies, including both known chemical compound structures and theoretical structures obtained through systematic enumeration.
3.1.3. The Chemical Properties Database
The Chemical Properties Database plays a crucial role in the process of organic synthesis. It can be used to guide the selection of reaction conditions, determine methods for product separation and purification, and assist in analyzing the structure and reaction mechanisms of compounds, thereby providing comprehensive property information support for intelligent organic chemistry synthesis. The ChemSpider database, provided by the Royal Society of Chemistry, integrates publicly available web databases to offer information on molecular structures and properties. PubChem, managed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), is an open chemical database focusing on chemical and physical properties, biological activities, and substance toxicity. The Chemistry WebBook, published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), collects spectral and thermodynamic data initially published in handbooks and tables, along with other basic physical and chemical data such as ionization energy, solubility, and spectroscopic, chromatographic, and computational data. These datasets are available for bulk download on the website. The ChemBL database focuses on the pharmacological properties of bioactive molecules, helping researchers understand the performance of organic compounds in terms of biological activity. There are also specialized property databases focused on specific areas, such as DrugBank, which specializes in the property information of drug molecules, Tox21 providing compound toxicity data, and Lipophilicity offering lipophilicity data for small organic molecules.
3.1.4. Computational Chemistry Database
Computational chemistry databases are derived from theoretical calculations such as density functional theory (DFT) calculations and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Computational data typically exhibit high consistency and repeatability, offering the advantages of high accuracy and reliability. Due to the principles of first-principles calculations, computational chemistry database data have now become a primary source of chemical data. The GDB-17 [
46] database contains information on the structure of organic molecules for 17 atoms which have been screened by strain topology and stability criteria and indexed by Simplified Molecular Input Linear Notation (SMILES) [
47]. In machine learning applications in organic chemistry, it is often used to construct molecular property predictions. The QM9 dataset is a quantum chemistry benchmark dataset constructed from equilibrium organic compounds containing up to nine “heavy” atoms (C, N, O, F) selected from GDB-17. It provides various property data such as vibrational frequencies, dipole moments, and polarizability, calculated at the DFT B3LYP/6-31G(2df, p) level for energy minima. Its high-precision data aids in modeling the relationship between the electronic structures and properties of organic molecules. The ANI-1 dataset contains 20 million non-equilibrium molecules derived from 57,000 molecular configurations, covering elements such as C, H, N, and O, generated through MD simulations, suitable for studying molecular conformation changes and dynamic behavior in non-equilibrium states. Open Catalyst 2020 (OC20) includes adsorption energy data for catalyst surface-adsorbate combinations. While primarily used in catalytic research, it can also help understand the adsorption behavior and reaction mechanisms of organic molecules on different surfaces. The Organic Materials Database (OMDB) utilizes density functional theory (DFT) to calculate the electronic band structures of crystal structures in open crystallographic databases, focusing mainly on the electronic structures, density of states, and other properties of currently known purely organic and organometallic compounds.
3.2. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Organic Chemistry Research
The deep integration of artificial intelligence and chemical research is giving rise to an innovative experimental model, centered on leveraging intelligent data analysis techniques to tackle scientific challenges. Through the deep mining of massive experimental data, AI systems, driven by algorithmic analytical processes, can accurately capture hidden patterns within the data, extract theoretically valuable insights, and reveal complex logical connections. This intelligent research approach breaks through the efficiency bottlenecks of traditional experimental methods, opening up new pathways for material science exploration.
In the field of organic synthesis research, E.J. Corey’s paradigm shift in 1969 was a milestone—he creatively introduced computer imaging technology to construct a logical deduction system for molecular retrosynthesis. This innovative method transformed abstract reaction mechanisms into spatial topological analyses. Compared to traditional computer-aided methods, the forefront of current chemical research has evolved into a new stage dominated by artificial intelligence, utilizing explainable AI (XAI) models to achieve transparent analysis of reaction mechanisms and employing generative adversarial networks (GANs) to autonomously deduce virtual reaction pathways. This paradigm shift from “computer-aided” to “AI-driven” signifies that synthetic chemistry has officially entered the era of intelligent planning.
3.2.1. Product Prediction
In the fields of drug discovery and advanced materials engineering, multidimensional prediction of compound properties has become a critical technology. The multimodal modeling framework that integrates quantum chemical calculations with high-throughput experimental data has reduced prediction errors in molecular polarizability. Researchers have deployed a separation parameter prediction system based on deep tensor networks on the TLC/HPLC automated platform. This intelligent closed loop of computation and experimentation is reconstructing the research and development paradigm of molecular engineering.
Chengqiang Lu et al. [
48] proposed a general and transferable multi-level graph convolutional neural network (MGCN) for molecular property prediction. This method directly integrates the quantum interactions of molecules, representing each molecule as a graph to preserve its internal structure, and uses a carefully designed hierarchical graph neural network to extract features from conformation and spatial information, thereby achieving effective prediction of molecular properties. Experimental results show that MGCN performs well on both equilibrium and non-equilibrium molecular datasets, which proves the validity, versatility, and transferability of the model.
Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) [
49] plays a crucial role in predicting molecular properties, especially in the field of drug discovery, where unexpected inaccuracies in model predictions during the experimental design process can waste valuable time and resources. Although neural network models are becoming increasingly common in quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) modeling, their poor interpretability makes it particularly difficult to assess their robustness, out-of-domain applicability, and potential failure modes. This paper systematically evaluates several UQ methods for regression tasks and tests them on five datasets using various complementary performance metrics. The study shows that no single method significantly outperforms others across all datasets, nor does any method produce particularly reliable error rankings. While existing tools may be effective for certain tasks, researchers still encounter tasks where all existing methods perform poorly. Therefore, the further development of reliable UQ methods for regression tasks is necessary. Additionally, the paper provides a detailed description of several UQ strategies, including ensemble methods, distance methods, mean-variance estimation, and joint methods, and compares these methods using evaluation metrics such as Spearman rank correlation coefficient, miscalibration area, and negative log-likelihood. Finally, based on results from four benchmark datasets and one synthetic dataset, practical recommendations are provided for which techniques are relatively superior in different scenarios.
Fletcher TL et al. developed a Kriging learning framework that can accurately interpret the response of atomic electron density to changes in the positions of nearby atoms. By modifying their geometric structures through local minimum position vibrations on the Ramachandran plot, the generalization ability of this Kriging model was verified in aromatic amino acid (histidine, phenylalanine, etc.) test systems, where its predicted electrostatic potential energy showed high consistency with actual measurements in novel molecular configurations [
50]. The ability to accurately and effectively predict compound molecular performance is crucial to the design of organic substances. Hansen K’s team developed a series of effective methods to estimate molecular energy, successfully achieving a theoretical leap from classical empirical methods to a machine learning-driven paradigm in the molecular energy calculation system by constructing a technological evolution path from basic atomic contribution models to multi-body quantum synergy analysis frameworks [
51]. This approach helps predict electronic properties such as polarizability and molecular frontier orbital energy.
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is an important tool for dynamically tracking chemical transformation processes and analyzing the interfaces of multi-component systems, enabling precise visual evaluations of the separation efficiency of complex mixtures. Xu H et al. combined TLC technology with automated artificial intelligence, aiming to use specialized desktop robots to collect large amounts of TLC data, laying the foundation for complex steps designed in a subsequent ELC analysis [
52].
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a technique used for separating and identifying components in sample mixtures based on differences in adsorption capacity. Zhang D’s research team introduced machine learning methods into chromatography, using CMRT data to construct HPLC columns driven by the synergistic effect of dual substrates and seven substituents. The team innovatively integrated symbolic regression with chromatographic thermodynamics knowledge graphs, breaking through the dimensional limitations of traditional single-column predictions and establishing a new computational screening paradigm for enantiomer separation, significantly enhancing the cross-platform generalization ability of separation predictions in complex systems [
53].
Schwaller et al. [
54] proposed an innovative approach to solve forward reaction prediction problems by treating reaction prediction as a translation problem, predicting the generated products from known starting materials. They employed a data-driven sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) model based on attention mechanisms; the model is template-free and can accurately predict reaction outcomes without relying on manually encoded reaction templates or explicit atomic features. The model uses the Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System (SMILES) to represent molecules and trains deep neural networks to learn how to transform “reactants > reagents” into the SMILES representation of products.
3.2.2. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Retrosynthetic Analysis Model
In the design of complex molecular synthesis routes, the reverse disassembly strategy has undergone a revolutionary evolution as the core logical framework. With the iterative upgrading of deep learning algorithms and the deep integration of knowledge graph technology, it marks the strategic transformation of organic synthesis from an experience-driven model to a data intelligence paradigm [
55]. In the process of intelligent synthesis chemistry, B.A. Grzybowski’s team developed a reverse synthesis analysis software called Chematica, achieving disruptive technological breakthroughs. This software constructs a multimodal chemical knowledge graph based on data from tens of millions of molecules. Through the collaborative architecture of hypergraph topological association networks and Monte Carlo optimization algorithms, it realizes intelligent decision-making for the reverse synthesis paths of complex organic molecules in sub-second time [
56].
Amol Thakkar et al. [
57] proposed a machine learning-based retrosynthesis accessibility score (RAscore) which can quickly assess the feasibility of compound synthesis predicted by computer-aided synthesis planning (CASP) tools like AiZynthFinder. Research indicates that compared to existing synthesis complexity scores (such as SAscore, SCscore, and SYBA), RAscore not only performs better in distinguishing synthesizable from non-synthesizable compounds but also increases computation speed by at least 4500 times. This makes RAscore a powerful tool for pre-screening the synthetic feasibility of millions of compounds in virtual molecular libraries, helping to improve the quality of bioactive virtual screening. Additionally, RAscore can be customized according to specific project or user needs and can reflect advances in synthesis planning technology. By using the Optuna framework to optimize model parameters and employing extended connectivity fingerprints (ECFP6) as descriptors, the study demonstrates RAscore’s superior performance across multiple datasets.
Liu et al. [
58] proposed a novel data-driven model that utilizes neural sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) learning methods to perform retrosynthesis reaction prediction tasks, treating this process as a sequence-to-sequence mapping problem. By training with 50,000 experimental reaction instances from U.S. patent literature, the model not only matches the baseline model of rule-based expert systems but also overcomes some of the latter’s limitations, taking a significant step forward in addressing the challenging problem of computational retrosynthesis analysis.
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, manual rule input systems transition to autonomous learning stages. The intelligent decision framework (MSH) proposed by Segler’s team combines a Monte Carlo tree search with deep reinforcement learning strategy networks, prioritizing learning the most likely retrosynthesis pathways [
59]. P. Schwaller et al. found in experiments that Transformer neural networks can autonomously learn atom-level bonding trajectories in chemical reactions without annotated reaction conditions. The model’s self-attention module can focus on learning the meanings of unannotated chemical reactions. This method achieved a 99.4% accuracy rate on a test set of 49,000, with speed superior to other methods, effectively bridging the direct interaction between data and rule strategies in various chemical reactions [
60].
3.2.3. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Reaction Prediction
In the field of cheminformatics, particularly within quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) studies, multiple linear regression (MLR) has evolved into a standard method for multidimensional feature modeling. Unlike univariate linear models, which capture isolated parameter effects, MLR considers multiple predictive variables simultaneously, providing a computational framework that combines interpretability with predictive accuracy for optimizing complex organic synthesis conditions.
In molecular synthesis, although many reactions are theoretically feasible, achieving high reactivity and selectivity is rare. Typically, most reactions reach the desired efficiency and selectivity only through a clever combination of substrates, catalysts, and conditions. Therefore, accurately assessing the reactivity and selectivity of synthesis predictions is crucial to the successful design of molecular synthesis. However, due to the vast molecular structure space and the diversity of control factors, no simple formula currently exists to quantitatively describe the universal laws of molecular synthesis. Synthetic prediction remains one of the core challenges in AI-driven synthesis. Traditional research often relies on experience-driven strategies: by summarizing the available data, synthetic chemists can derive local structure–activity relationships for specific goals for rational design and improvement of synthetic transformations. However, this empirical approach lacks precision and predictive capability, potentially leading to contradictory rules, which result in inevitable random choices and trial-and-error testing during actual synthetic exploration.
Recently, data-driven methods have brought new perspectives to solving synthesis prediction problems. With the aid of advanced AI algorithms and abundant chemical data, research has shown that machine learning models can accurately predict reaction yields and selectivity, even surpassing the judgments of experienced chemists in some cases. These models can assist chemists in efficiently screening new catalysts for target reactions, providing powerful AI tools for molecular synthesis. These studies reveal the immense potential of machine learning technology in synthetic chemistry, promising to accelerate the process from synthesis method development to the discovery of functional molecules.
The LHASA program developed by E. J. Corey and colleagues facilitates the design of complex molecular synthesis pathways through an interactive graphical interface, embodying the concept of retrosynthetic reasoning from target molecules to simple starting materials, thereby optimizing synthetic routes [
61]. This retrosynthetic analysis emphasizes logical and systematic synthesis planning, effectively preventing combinatorial explosion. These advancements demonstrate how enhanced computational capabilities foster the development of scientific research tools, providing robust support to scientists and driving progress in scientific exploration, fulfilling von Neumann’s prophecy of computers accelerating scientific revolutions.
Toste FD’s research constructs multiscale theoretical models of chiral anion catalytic systems, revealing the dynamic structure–activity relationship between catalysts and substrates, providing a new theoretical paradigm for regulating stereoelectronic effects induced by asymmetry [
62]. R. Biscoe’s team delves deep into cross-coupling reactions, conducting in-depth research. This study, through a cross-dimensional synergistic framework of multiscale computation and multi-conformational molecular dynamics simulation (MDMC), successfully decouples the nonlinear coupling mechanism of stereoselectivity, offering an engineerable system of stereocontrol parameters for the precise regulation of asymmetric catalytic reactions [
63]. On this basis, Sigman et al. [
64] in 2019 pioneered the enantioselective supramolecular regulation theory to provide synthetic design guidance.
Thakkar et al. proposed a machine learning-based method for rapid assessment of compound synthesis feasibility—retrosynthetic accessibility score (RAscore). This method, trained using AiZynthFinder, can classify the synthetic feasibility of molecules at speeds at least 4500 times faster than traditional retrosynthetic analysis. Research indicates that using RAscore not only enhances efficiency when screening large compound libraries but also, by introducing such synthetic accessibility pre-screening tools early in virtual screening workflows, can generate higher-quality bioactive screening databases. Furthermore, RAscore can be customized according to specific project needs and reflects the latest advances in synthesis planning technology.
Bran et al. [
65] developed ChemCrow, a chemical agent integrating 18 expert-designed tools, utilizing GPT-4 as the foundational model to enhance LLM capabilities in chemistry for tasks such as organic synthesis, drug discovery, and material design. ChemCrow can autonomously plan and execute the synthesis of insect repellents and three organic catalysts, as well as guide the discovery of new chromophores. Research shows that ChemCrow performs better in handling complex chemical tasks compared to using GPT-4 alone, especially in terms of accuracy, reasoning ability, and response completeness.
In the evolutionary trajectory of algorithms in computational chemistry, the linear feature space of multiple linear regression (MLR) has gradually been superseded by machine learning paradigms dominated by nonlinear feature engineering. Ensemble decision forests (EDF) and deep tensor networks (DTN), with their nonlinear generalization capabilities in high-dimensional heterogeneous feature spaces, exhibit significant advantages in modeling complex chemical systems through hyperparameter optimization. The multimodal chemical intelligence architecture pioneered by the S.E. Denmark team constructs a quantum chemical parameter space using the principle of molecular fingerprint invariance (MFIP), centered on the constant mapping relationship between the stereoelectronic coupling effect (SECE) of catalysts and molecular topology flexibility (MTF). Based on a hybrid inference engine of feedforward neural networks and support tensor machines (STM), it successfully decouples the nonlinear synergistic mechanism of π-orbital occupancy and phosphorus center cone angle (θ_P) in stereocontrol reaction modeling, achieving a generalized predictive capability for catalysts across reaction types, marking a revolutionary shift in chemical machine learning from specific mechanism modeling to a universal catalyst design paradigm [
66].
4. Cloud-Based Shared Chemistry Experiment Operational Model
Under the impetus of deep integration between cloud computing and intelligent technology, the concept of “cloud sharing” has transcended traditional information science domains, rapidly permeating the realm of scientific research experiments. This has fostered the formation of a resource collaborative innovation system that spans disciplines and regions. As a typical representative of scientific research infrastructure, chemical experiments, with their precision equipment, complex processes, and massive data characteristics, are becoming crucial practice scenarios for the cloud sharing model. By constructing cloud-based experimental service platforms, integrating dispersed experimental resources, optimizing equipment scheduling efficiency, and breaking traditional scientific collaboration barriers, this approach has come to the forefront of global scientific research automation and digital transformation. This model not only enhances resource utilization and shortens research and development cycles but also reconstructs the collaborative ecosystem of scientific experiments, driving the research paradigm toward openness and intelligence.
Numerous multidimensional exploration cases have emerged in the scientific research field, as shown in
Table 6. The Chiappa team [
67] introduced cloud manufacturing as a new production paradigm, allowing clients and suppliers to interact via cloud platforms, i.e., the “Experiment as a Service” (EaaS) model. This model enables the on-demand invocation of equipment like spectrometers across institutions by encapsulating them as standardized API interfaces. Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, is investing heavily in building a “cloud laboratory” [
68,
69], relying on the remote control system of the Emerald Cloud Lab [
70]. This setup has achieved online scheduling of over 200 instruments with high-precision visualization tracking of experimental processes. Researchers can plan experimental steps online (including instrument allocation and parameter tuning) through network platforms, which are then precisely executed by automated robots with immediate feedback of experimental data. Taking the Emerald Cloud Lab’s customers as an example, they can use control panels to view experiment dynamics at any time and watch experiment videos in real time, achieving full visual tracking. The Angelopoulos team [
71] further integrated digital twin and IoT technology to construct a chemical experiment resource pooling model, while noting that cloud laboratories will become a crucial part of future laboratory automation, enabling remote use via the internet and assisting global scientists in conducting experiments. Some cloud laboratories have already achieved commercial deployment, allowing scientists worldwide to overcome geographical limitations and conveniently use advanced experimental facilities for scientific exploration, strongly promoting global collaboration and laboratory automation in scientific experiments.
To address trust issues in resource sharing, a blockchain-based distributed cloud laboratory framework has been developed, using smart contracts and IPFS storage technology to build an experimental protocol execution verification system [
72]. This reduces the risk of data tampering and achieves full traceability of experimental processes. This “technical trust” mechanism provides essential security guarantees for multi-party participation in cloud experimental platforms.
Currently, the cloud sharing chemical experiment model has moved from proof of concept to the early stages of commercialization, with its core value reflected in three aspects: first, elastic resource allocation can enhance equipment utilization; second, intelligent scheduling algorithms compress average experimental cycles; and third, building a knowledge-sharing network promotes cross-disciplinary innovation. Given this, we are committed to creating a distinctive cloud sharing chemical experiment operation model, innovatively proposing the “Cloud-based Chemical Experiment Sharing Service Platform” operation model. This model uses a digital platform as the core link, organically integrating cross-regional customer experimental demands with professional laboratory resource supply, establishing a bidirectional supply-demand collaboration network. Through a full-process online service system, demand parties (encompassing various enterprises/institutions such as A, B, and C) can submit experimental proposals in real time, track experiment progress at any time, and conveniently obtain experimental data reports. For their part, supply parties (professional laboratories) achieve the efficient output of equipment sharing, capacity collaboration, and technical services through intelligent resource scheduling systems.
In this way, this cloud-based collaborative mechanism is expected to break the geographical restrictions and resource barriers existing in traditional experimental services, significantly enhance the utilization rate of experimental equipment, substantially shorten customer research and development cycles, and further promote the intelligent and efficient development of chemical experiments. Simultaneously, it will foster an innovative ecosystem characterized by knowledge sharing and technological complementarity within the industry. However, challenges remain severe: data sovereignty and security risks (such as the cross-border transmission and privacy protection of sensitive data in multi-institution collaboration), technical standardization barriers (compatibility issues of heterogeneous equipment interfaces and experimental protocols), and commercial sustainability (balancing high cloud platform maintenance costs with user payment willingness) still need to be overcome. Additionally, the shortage of professional talent, specifically those who understand both chemistry and cloud computing, may constrain the development and application of this model. Only by overcoming these bottlenecks can cloud sharing chemical experiments truly become the “digital new infrastructure” of global scientific research infrastructure.
5. Implementation of Smart Chemistry Laboratories
In view of the fact that traditional materials synthesis and pharmaceutical research and development still remain at an experiment-driven and experience-based stage, they face typical challenges such as high experimental costs, low success rates, and missing hidden information. We are committed to providing a standardized experimental platform for scientific research and development processes such as chemical synthesis and new material testing, as illustrated in
Figure 2. The visualization interface vividly presents the core architecture of the AI-driven intelligent chemical experiment platform. The central area on the deep-blue background focuses on the modular physical layout of the laboratory, clearly labeling key functional zones including the material database, reagent storage, reaction zone, glove box operation zone, post-processing zone, and product storage zone. Embedded on both sides are dynamic data dashboards: the left side provides real-time tracking of task statistics, equipment status, and personnel dynamics, while the right side enables overall monitoring through equipment utilization charts and alarm notifications. The overall design, with its intuitive modular structure, high-contrast blue-and-white color scheme, and warning indicators, highlights the collaborative operation scenario of automated workstations, multidimensional laboratory monitoring, and intelligent integrated control. It fully interprets the platform’s capabilities in data integration and precise management and control under the “AI + Intelligent Chemical Experiment” framework.
This intelligent laboratory integrates various cutting-edge algorithms. By combining Bayesian optimization, differential evolution, and reinforcement learning with computational chemistry descriptors, it optimizes reaction parameters (temperature, equivalents, solvent) and catalyst combinations, significantly improving reaction efficiency. Using CNN and LSTM, it intelligently interprets NMR and MS spectra, monitors reaction processes in real time via computer vision, and detects anomalies. At the same time, it integrates traditional machine learning and GNN to build compound and catalyst performance prediction models, accelerating R&D. Furthermore, based on RNN and GAN, the platform achieves intelligent molecular generation and leverages chemical reaction templates and Transformer models for retrosynthetic pathway planning. This comprehensively empowers intelligent decision-making in molecular design and synthetic route planning.
As a result, the number of required multi-throughput experiments can be reduced to one-tenth or even less than before, significantly improving experimental efficiency and accelerating the pace of R&D. It promotes the rapid development of chemical synthesis toward intelligent laboratories and offers an intelligent solution—from raw material feeding to reaction outcome analysis—for organic chemical synthesis.
By introducing artificial intelligence on the foundation of flexible automated experimental lines and accumulated experimental data, we aim to build an intelligent chemical experiment system with a “base large model + domain-specific small models”. This supports experimental data analysis, parameter optimization, and molecular/route design, helping to reduce the number of high-throughput experiments to one-tenth or less of the original, significantly enhancing experimental efficiency and accelerating R&D progress. This advancement propels chemical synthesis toward rapidly developing intelligent laboratories, providing an intelligent solution for organic chemical synthesis from material feeding to reaction result analysis.
Currently, we have enabled research institutes, chemical materials, pharmaceutical companies, and university research institutions to conduct experiments with higher efficiency and throughput, quickly generating a large volume of high-quality experimental data to feedback into AI systems. In the future, by gradually integrating the cloud-sharing laboratory model, we aim to establish a large model experimental database, achieving automated R&D applications across the entire chain from “structure design -> synthesis execution -> function realization”. We will continue to build a central experimental platform, promoting the development of intelligent chemical experiment cloud-sharing platform services. Our team will leverage its software and hardware technology advantages to enter vertical industries, accumulate data in niche fields, continuously refine intelligent algorithm technologies, and optimize data governance and data models. This will drive the synchronous iteration of “hardware + software + AI model” intelligent chemical synthesis robot scientist products, achieving intelligent decision-making and autonomous operation across multiple scenarios and tasks. Ultimately, this will lead to breakthroughs in R&D for material science and life science scenarios.
6. Summary
AI-driven organic chemistry synthesis laboratories are revolutionizing traditional chemical research methodologies. By integrating automated equipment with advanced AI technologies, these laboratories significantly enhance the efficiency and precision of chemical synthesis. Melodie Christensen et al. conducted an in-depth exploration of the design and deployment of automated systems in synthetic chemistry, particularly focusing on applications at the benchtop scale, and analyzed the challenges of modular design [
73].
The emergence of automated synthesis platforms enables laboratories to perform complex chemical reactions, reducing human errors and enhancing the reproducibility of experiments. The rapid advancements in AI technology have made AI-driven organic chemistry experiments more sophisticated. For instance, in 2018, deep learning was used to analyze approximately 12.5 million chemical reactions and plan new synthetic pathways in just five seconds. Just two years later, AI achieved breakthroughs in the retrosynthetic analysis of complex natural products, with designed synthetic routes nearly indistinguishable from those crafted by experienced chemists [
74]. Large language models such as ChatGPT have sparked a new wave of applications in the scientific domain, propelling the development of “robot chemists” and making AI applications in scientific research more autonomous and intelligent. Assistant Professor Gabe Gomes and his team developed the Coscientist system, powered by Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT), capable of autonomously designing, planning, and executing complex scientific experiments while analyzing and optimizing the results [
75].
Despite the enormous potential of AI in synthetic chemistry, challenges remain, including insufficient data resources, lack of standardized coding, and the “black box” nature of models. Data scarcity limits the training quality and application accuracy of AI models, while the non-standardized nature of molecular and reaction coding affects the representation capacity of complex structures and reactions. The opaque decision-making process of AI models hinders their ability to provide chemical insights and may lead to trust issues. To overcome these challenges, promoting the widespread adoption of AI technology could enable chemists to utilize AI for synthesis design, fostering data sharing and model openness, adhering to FAIR principles and establishing open data communities, focusing on software and hardware upgrades and optimization, and integrating AI technology with experimental synthesis processes. This requires the collaborative efforts of chemists, computer scientists, and engineers to advance the intelligent progress of synthetic chemistry, facilitating the widespread application of automated synthesis platforms, improving experimental efficiency and precision, and ultimately achieving broader applications and deeper impacts, thereby driving innovation and development in chemical research.
With the rapid evolution of AI, synthetic chemistry is transitioning into an “intelligent” era. AI will integrate with automated synthesis platforms to create intelligent laboratories, enabling automated experiment execution, real-time feedback, and condition optimization. Cloud-based AI systems will support chemists in remotely operating laboratory equipment. AI will also leverage chemical databases and machine learning algorithms for molecular design and synthesis pathway planning. In the future, intelligent decision systems and personalized synthesis technologies will allow chemists to quickly design and synthesize customized compounds. Additionally, chemical education will incorporate AI and data science knowledge, nurturing a new generation of chemists with interdisciplinary backgrounds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L. and W.S.; methodology, T.L. and Y.X.; software, N.C. and Q.W.; formal analysis, T.L., Y.X. and S.W.; investigation, W.S., N.C., F.G., Y.X., S.W., C.S., J.L., Y.L., S.L., C.W. and Z.Z.; resources, W.S., Q.W. and C.W.; writing—original draft preparation, T.L.,W.S., N.C., F.G., Y.X., S.W., C.S., J.L., Y.L., S.L., C.W. and Z.Z.; writing—review and editing, T.L.; visualization, N.C., F.G. and C.S.; supervision, W.S., Y.X. and S.W., All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This is the review paper. No data can be provided.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Dr. Weining Song, Mr. Qi Wang, Mr. Shouluan Wu and Mr. Chao Song was employed by the company QuickTech Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Gupta, R.; Srivastava, D.; Sahu, M.; Tiwari, S.; Ambasta, R.K.; Kumar, P. Artificial intelligence to deep learning: Machine intelligence approach for drug discovery. Mol. Divers. 2021, 25, 1315–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bung, N.; Krishnan, S.R.; Bulusu, G.; Roy, A. De Novo Design of New Chemical Entities for SARS-CoV-2 Using Artificial Intelligence. Futur. Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, I.; Choudhury, A.; Banerjee, T.S. Artificial Intelligence in Biological Data. J. Inf. Technol. Softw. Eng. 2017, 7, 1000207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiao, Y.; Davey, K.; Qiao, S.Z. Data-Driven Machine Learning for Understanding Surface Structures of Heterogeneous Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202216383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, J.; Maskri, S.; Koch, O. Computational ion channel research: From the application of artificial intelligence to molecular dynamics simulations. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 55, 14–45. [Google Scholar]
- Gorgulla, C.; Çınaroğlu, S.S.; Fischer, P.D.; Fackeldey, K.; Wagner, G.; Arthanari, H. VirtualFlow Ants—Ultra-Large Virtual Screenings with Artificial Intelligence Driven Docking Algorithm Based on Ant Colony Optimization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.B.; Hodas, N.O.; Vishnu, A. Deep learning for computational chemistry. J. Comput. Chem. 2017, 38, 1291–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, S.; Toyota, T.; Nomura, S.; Ichiro, M. Molecular Cybernetics: Challenges toward Cellular Chemical Artificial Intelligence. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragno, R.; Esposito, V.; Mario, M.D. Teaching and learning computational Drug Design: Student investigations of 3D quantitative structure-activity relationships through web applications. J. Chem. Educ. 2020, 97, 1922–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Z.; Deng, H.; Zhou, X. Progress in Copper-Catalyzed Ullmann-Type Coupling Reactions in Water. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 33, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, I.; Davies, J.A. Automation in the Life Science Research Laboratory. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 571777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessop-Fabre, M.M.; Sonnenschein, N. Improving reproducibility in synthetic biology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, R.; Mishra, S.; Si, T.; Zhao, H. Engineering biological systems using automated bio-foundries. Metab. Eng. 2017, 42, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crone, M.A.; Priestman, M.; Ciechonska, M.; Jensen, K.; Sharp, D.J.; Anand, A.; Randell, P.; Storch, M. A role for Biofoundries in rapid development and validation of automated SARS-CoV-2 clinical diagnostics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needs, S.H.; Diep, T.T.; Bull, S.P.; Lindley-Decaire, A.; Ray, P.; Edwards, A.D. Exploiting open source 3D printer architecture for laboratory robotics to automate high-throughput time-lapse imaging for analytical microbiology. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crombie, D.E.; Daniszewski, M.; Liang, H.H.; Kulkarni, T.; Li, F.; Lidgerwood, G.E.; Conquest, A.; Hernández, D.; Hung, S.S.; Gill, K.P. Development of a modular auto-mated system for maintenance and differ-entiation of adherent human pluripotent stem cells. Slas Discov. Adv. Life Sci. RD 2017, 22, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Mifflin, T.E.; Estey, C.A.; Felder, R.A. Robotic automation performs a nested RT-PCR analysis for HCV without introducing sample contamination. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 290, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chen, J. Application of Intelligent Automatic Titrator in University Chemistry Practical Teaching. Univ. Chem. 2025, 40, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosenkov, Y.; Kosenkov, D. Computer Vision in Chemistry: Automatic Titration. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 4067–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, R.; Jenne, A.; Lysak, D.H.; Ghosh Biswas, R.; Adamo, A.; Kris, K.S.; Simpson, A. Titrate over the Internet: An Open-Source Remote-Control Titration Unit for All Students. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Lai, V.; Legard, K.; Kozdras, S.; Prieto, P.L.; Grunert, S.; Hein, J.E. Augmented Titration Setup for Future Teaching Laboratories. J. Chem. Educ. 2021, 98, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Feng, Z.; Xu, T.; Xiao, M.; Han, R. Research on Intelligent Experimental Equipment and Key Algorithms Based on Multimodal Fusion Perception. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 142507–142520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Tsao, Y.-H.; Chiu, C.-M.; Yoo, D.; Lin, Z.-H.; Kim, D.S. A smart pipet tip: Triboelectricity and thermoelectricity assisted in situ evaluation of electrolyte concentration. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, B.; Maffettone, P.M.; Gusev, V.V.; Aitchison, C.M.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Alston, B.M.; Li, B.; Clowes, R.; et al. A mobile robotic chemist. Nature 2020, 583, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Song, T.; Tang, X.; Li, X.; He, G.; et al. An all-round AI-Chemist with a scientific mind. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, H.; Baumann, D.; Joshi, S.; Chu, X.; Roddelkopf, T.; Klos, M.; Thurow, K. Analytical Measurements and Efficient Process Generation Using a Dual–Arm Robot Equipped with Electronic Pipettes. Energies 2018, 11, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tu, Y.; Liu, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, X. Toward “On-Demand” Materials Synthesis and Scientific Discovery through Intelligent Robots. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1901957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda, J.M.; Donina, L.; Dragone, V.; Long, D.-L.; Cronin, L. Controlling an organic synthesis robot with machine learning to search for new reactivity. Nature 2018, 559, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Tu, Y.; Ye, S.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhu, X. AIR-Chem: Authentic Intelligent Robotics for Chemistry. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 122, 9142–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Luo, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhang, B.; Zou, G.; et al. A Multiagent-Driven Robotic AI Chemist Enabling Autonomous Chemical Research On Demand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 12534–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angizeh, F.; Montero, H.; Vedpathak, A.; Parvania, M. Optimal production scheduling for smart manu-facturers with application to food production planning. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 84, 106609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbs, C.D.; Li, C.; Sahinidis, N.V.; Grossmann, I.E.; Wassick, J.M. A deep reinforcement learning approach for chemical production scheduling. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 141, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Q.; Meng, F.; Wang, R.; Klein, J.C.; Godfrey, A.G.; Coley, C.W. Schedule optimization for chemical library synthesis. Digit. Discov. 2024, 4, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Luo, M.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, F.; Shang, W.; Jiang, J. A multi-robot–multi-task scheduling system for autonomous chemistry laboratories. Digit. Discov. 2025, 4, 636–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.A.; Petrović, T.; Orsag, M.; Martínez-de Dios, J.R.; Bogdan, S. Distributed Allocation and Scheduling of Tasks With Cross-Schedule Dependencies for Heterogeneous Multi-Robot Teams. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 74327–74342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gombolay, M.Z. Learning Scheduling Policies for Multi-Robot Coordination With Graph Attention Networks. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4509–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, Z.; Benfriha, K.; Varmazyar, M.; Talhi, E.; Quenehen, A. Production scheduling with multi-robot task allocation in a real industry 4.0 setting. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Rai, U.; Chiun, J.; Cao, Y.; Sartoretti, G. Heterogeneous Multi-robot Task Allocation and Scheduling via Rein-forcement Learning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 2654–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, M.; Peskov, M.A.; Ramsden, S.J.; Yaghi, O.M. The Reticular Chemistry Structure Resource (RCSR) Database of, and Symbols for, Crystal Nets. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borysov, S.S.; Geilhufe, R.M.; Balatsky, A.V. Organic materials database: An open-access online database for data mining. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.M. Extraction of Chemical Structures and Reactions from the Literature Dissertation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kearnes, S.M.; Wleklinski, M.; Kast, A.; Doyle, A.G.; Dreher, S.D.; Hawkins, J.M.; Jensen, K.F.; Coley, C.W. The open reaction database. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 18820–18826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhondi, S.A.; Klenner, A.G.; Tyrchan, C.; Manchala, A.K.; Boppana, K.; Lowe, D.; Zimmermann, M.; Jagarlapudi, S.A.R.P.; Sayle, R.; Kors, J.A.; et al. Annotated Chemical Patent Corpus: A Gold Standard for Text Mining. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raccuglia, P.; Elbert, K.C.; Adler, P.D.F.; Falk, C.; Wenny, M.B.; Mollo, A.; Zeller, M.; Friedler, S.A.; Schrier, J.; Norquist, A.J. Machine-learning-assisted materials discovery using failed experiments. Nature 2016, 533, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groom, C.R.; Bruno, I.J.; Lightfoot, M.P.; Ward, S.C. The Cambridge Structural Database. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 2016, 72, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddigkeit, L.; van Deursen, R.; Blum, L.C.; Reymond, J.-L. Enumeration of 166 Billion Organic Small Molecules in the Chemical Universe Database GDB-J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a chemical language and information system. Introduction to methodology and encoding rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; Lin, P.; He, L. Molecular Property Prediction: A Multilevel Quantum Interactions Modeling Perspective. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschfeld, L.; Swanson, K.; Yang, K.; Barzilay, R.; Coley, C.W. Uncertainty Quantification Using Neural Networks for Molecular Property Prediction. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 3770–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.L.; Davie, S.J.; Popelier, P.L.A. Prediction of Intramolecular Polarization of Aromatic Amino Acids Using Kriging Machine Learning. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 3708–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.; Biegler, F.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Pronobis, W.; von Lilienfeld, O.A.; Müller, K.-R.; Tkatchenko, A. Machine Learning Predictions of Molecular Properties: Accurate Many-Body Potentials and Nonlocality in Chemical Space. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lin, J.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Young, M.C.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Mo, F. High-throughput discovery of chemical structure-polarity relationships combining automation and machine-learning techniques. Chem 2022, 8, 3202–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, D.; Mo, F. Retention time prediction for chromatographic enantioseparation by quantile geometry-enhanced graph neural network. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaller, P.; Gaudin, T.; Lányi, D.; Bekas, C.; Laino, T. “Found in Translation”: Predicting outcomes of complex organic chemistry reactions using neural sequence-to-sequence models. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylon, J.L.; Cilfone, N.A.; Gulcher, J.R.; Chittenden, T.W. Enhancing Retrosynthetic Reaction Prediction with Deep Learning Using Multiscale Reaction Classification. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 673–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klucznik, T.; Mikulak-Klucznik, B.; McCormack, M.P.; Lima, H.; Szymkuć, S.; Bhowmick, M.; Molga, K.; Zhou, Y.; Rickershauser, L.; Gajewska, E.P.; et al. Efficient syntheses of diverse, medic-inally relevant targets planned by computer and executed in the laboratory. Chem 2018, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, A.; Chadimová, V.; Bjerrum, E.J.; Engkvist, O.; Reymond, J.-L. Retrosynthetic accessibility score (RAscore)—Rapid machine learned synthesizability classification from AI driven retrosynthetic planning. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3339–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ramsundar, B.; Kawthekar, P.; Shi, J.; Gomes, J.; Nguyen, Q.L.; Ho, S.; Sloane, J.; Wender, P.; Pande, V. Retrosynthetic Reaction Prediction Using Neural Sequence-to-Sequence Models. ACS Central Sci. 2017, 3, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segler, M.H.S.; Preuss, M.; Waller, M.P. Planning chemical syntheses with deep neural networks and symbolic AI. Nature 2018, 555, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaller, P.; Hoover, B.; Reymond, J.-L.; Strobelt, H.; Laino, T. Extraction of organic chemistry grammar from unsupervised learning of chemical reactions. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, E.J.; Long, A.K.; Rubenstein, S.D. Computer-Assisted Analysis in Organic Synthesis. Science 1985, 228, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milo, A.; Neel, A.J.; Toste, F.D.; Sigman, M.S. A data-intensive approach to mechanistic elucidation applied to chiral anion catalysis. Science 2015, 347, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Gensch, T.; Murray, B.; Niemeyer, Z.L.; Sigman, M.S.; Biscoe, M.R. Enantiodivergent Pd-catalyzed C-C bond formation en-abled through ligand parameterization. Science 2018, 362, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.P.; Sigman, M.S. Holistic prediction of enantioselectivity in asymmetric catalysis. Nature 2019, 571, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bran, A.M.; Cox, S.; Schilter, O.; Baldassari, C.; White, A.D.; Schwaller, P. Augmenting large language models with chemistry tools. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2024, 6, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahrt, A.F.; Henle, J.J.; Rose, B.T.; Wang, Y.; Darrow, W.T.; Denmark, S.E. Prediction of higher-selectivity catalysts by computer-driven workflow and machine learning. Science 2019, 363, eaau5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappa, S.; Videla, E.; Viana-Céspedes, V.; Piñeyro, P.; Rossit, D.A. Cloud manufacturing architectures: State-of-art, research challenges and platforms description. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2023, 34, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, M. Coming Soon: The First University-based Cloud Lab. Engineering 2022, 20, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C. Cloud labs: Where robots do the research. Nature 2022, 606, 612–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhr, S. Experimenting with Drugs in the Cloud. TechCrunch, 8 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulos, A.; Cahoon, J.F.; Alterovitz, R. Transforming science labs into automated factories of discovery. Sci. Robot. 2024, 9, eadm6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, M.G.; Raj, N.; Vishrutha, R. Decentralized File Sharing: Leveraging Blockchain and IPFS for Secure Data Storage. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Integration of Emerging Technologies for the Digital World (ICIETDW), Kavaraipettai, India, 13–14 September 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, M.; Yunker, L.P.E.; Shiri, P.; Zepel, T.; Prieto, P.L.; Grunert, S.; Borka, F.; Hein, J.E. Automation isn’t automatic. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 15473–15490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulak-Klucznik, B.; Gołębiowska, P.; Bayly, A.A.; Popik, O.; Klucznik, T.; Szymkuć, S.; Gajewska, E.P.; Dittwald, P.; Staszewska-Krajewska, O.; Beker, W.; et al. Computational planning of the synthesis of complex natural products. Nature 2020, 588, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottweis, J.; Weng, W.-H.; Daryin, A.; Tu, T.; Palepu, A.; Sirkovic, P.; Myaskovsky, A.; Weissenberger, F.; Rong, K.; Tanno, R. Towards an AI co-scientist. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.18864. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.18864 (accessed on 26 June 2025).
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).