Effect of Planting Portulaca oleracea L. on Improvement of Salt-Affected Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of the Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Setup
2.3. Measurement Methods
2.3.1. Plant Biomass
2.3.2. Ash Content in Plant and Salt Accumulation by Plants
2.3.3. Soil Physicochemical and Biological Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Aboveground Biomass of P. oleracea
3.2. Accumulation of Salt by P. oleracea
3.3. Effect of Planting P. oleracea on Soil Physiochemical Properties in Salt-Affected Soils
3.3.1. Salinity Distribution in Soils
3.3.2. Soil Bulk Density
3.3.3. Soil Porosity
3.3.4. Soil pH
3.3.5. Soil Organic Matter
3.4. Effect of Planting P. oleracea on Soil Enzyme Activity
3.4.1. Soil Invertase Activity
3.4.2. Soil Urease Activity
3.4.3. Soil Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
4. Discussion
4.1. Phytoremediation by P. oleracea in Salt-Affected Soils
4.2. Planting P. oleracea Improves Soil Physiochemical and Biological Properties in Salt-Affected Soils
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinha, S.; Ibha, S.; Vaibhav, S.; Singh, C.P.; Pratap, S.R.; Vishal, P. Potential risk assessment of soil salinity to agroecosystem sustainability: Current status and management strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 144164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, F.; Xie, P.; Sun, S.; Qiao, X.; Tang, S.; Chen, C.; Yang, S.; Mei, C.; Yang, D.; et al. A Gγ protein regulates alkaline sensitivity in crops. Science 2023, 379, 6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Society: Realizing China’s urban dream. Nature 2014, 509, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Sun, B.; Chen, H.; Zhou, J.; Song, X.; Liu, X.; Deng, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Approaches and research progresses of marginal land productivity expansion and ecological benefit improvement in China. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2022, 36, 336–348. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W. Drip irrigation in agricultural saline-alkali land controls soil salinity and improves crop yield: Evidence from a global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, T.; He, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Feng, Y. Mechanism of Saline–Alkali land improvement using subsurface pipe and vertical well drainage measures and its response to agricultural soil ecosystem. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Saline-alkali soil applied with vermicompost and humic acid fertilizer improved macroaggregate microstructure to enhance salt leaching and inhibit nitrogen losses. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, L. Combined application of a straw layer and flue gas desulphurization gypsum to reduce soil salinity and alkalinity. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, D.; Kang, Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Okla, M.K.; AbdElgawad, H.; Hamoud, Y.A. Changes in salinity and vegetation growth under different land use types during the reclamation in coastal saline soil. Chemosphere 2024, 366, 143427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Shi, Z.; Diao, F.; Hao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Dang, Z.; Guo, W. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and Na+ accumulation of Suaeda glauca (Bunge) grown in salinized wetland soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 104065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Jiang, P.; Tai, F.; Wang, D.; Feng, J.; Fan, P.; Bao, H.; Li, Y. The V-ATPase subunit A is essential for salt tolerance through participating in vacuolar Na+ compartmentalization in Salicornia europaea. Planta 2017, 246, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Yan, G.; Hua, L.; Liu, H.; Huang, W.; Liang, Z.; Chao, Q.; Hibberd, J.M.; Jiao, Y.; et al. Gene duplications facilitate C4-CAM compatibility in common purslane. Plant physiol. 2023, 193, 2622–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, R.; Gou, J.; Chan, Z. Physiological and metabolic changes of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) in response to drought, heat and combined stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MorenoVillena, J.J.; Zhou, H.; Gilman, I.S.; Tausta, S.L.; Cheung, C.Y.M.; Edwards, E.J. Spatial resolution of an integrated C4+CAM photosynthetic metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, B.R.; Karimi, M.; Soltangheisi, A. Purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) salt tolerance assessment. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 69, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.H.M.; Ali, M.M.E.; Zewail, R.M.Y.; Liava, V.; Petropoulos, S.A. Response of purslane plants grown under salinity stress and biostimulant formulations. Plants 2024, 13, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, C.C.; Kukul, S.Y.; Anaç, D. Performance of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) as a salt-removing crop. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, K.; Mohsin, T.; Tian, C.; Zhao, Z. Reclamation of saline soil by planting annual euhalophyte Suaeda salsa with drip irrigation: A three-year field experiment in arid northwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 159, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Shi, W. Cotton/halophytes intercropping decreases salt accumulation and improves soil physicochemical properties and crop productivity in saline-alkali soils under mulched drip irrigation: A three-year field experiment. Field Crops Res. 2021, 262, 108027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhong, M.; Li, W.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, H.; Lv, X. Cotton straw biochar and Bacillus compound biofertilizer decreased Cd migration in alkaline soil: Insights from relationship between soil key metabolites and key bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Herath, I.; Kumarathilaka, P.; Hseu, Z.Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Vithanage, M. Efficacy of woody biomass and biochar for alleviating heavy metal bioavailability in serpentine soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemeh, A.; Nayer, M.; Moslem, S. Halophytes play important role in phytoremediation of salt-affected soils in the bed of Urmia Lake, Iran. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12223. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, H.; Shloul, T.; Alomari, B.; Alhadidi, L.; Mazahreh, N. Phytoremediation ability of Panicum maximum and Salicornia europaea irrigated with treated wastewater for salt elements in the soil. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2024, 23, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, M.; Yao, L.; Li, P.; Si, E.; Li, B.; Meng, Y.; Ma, X.; Yang, K.; Zhang, H.; et al. Metagenomic analysis reveal the phytoremediation effects of monocropping and intercropping of halophytes Halogeton glomeratus and Suaeda glauca in saline soil of Northwestern China. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagos, P.; Rosa, D.D.; Liakos, L.; Labouyrie, M.; Borrelli, P.; Ballabio, C. Soil bulk density assessment in Europe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, T.; Mlahlwa, A.V.; Elbasit, M.A.M.A.; Newete, S.W. The impact of Tamarix invasion on the soil physicochemical properties. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Steffens, D.; Yan, F.; Schubert, S. Sodium removal from a calcareous saline–sodic soil through leaching and plant uptake during phytoremediation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2003, 14, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, L.; Li, L.; Zhong, S.; Gu, R. Phlomoides rotata adapts to low-nitrogen environments by promoting root growth and increasing root organic acid exudate. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarholm, M.; Skyllberg, U.; Rosling, A. Organic acid induced release of nutrients from metal-stabilized soil organic matter-The unbutton model. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Fu, P.; Liu, G.; Chen, J. Synergistic effects of bio-organic fertilizer and different soil amendments on salt reduction, soil fertility, and yield enhancement in salt-affected coastal soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hamel, C.; Lu, P.; Wang, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.; Gan, G.Y. Using enzyme activities as an indicator of soil fertility in grassland-an academic dilemma. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1175946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajewska, B. Urease-aided calcium carbonate mineralization for engineering applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 13, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Haygarth, P.M. Phosphatase activity in temperate pasture soils: Potential regulation of labile organic phosphorus turnover by phosphodiesterase activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 344, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
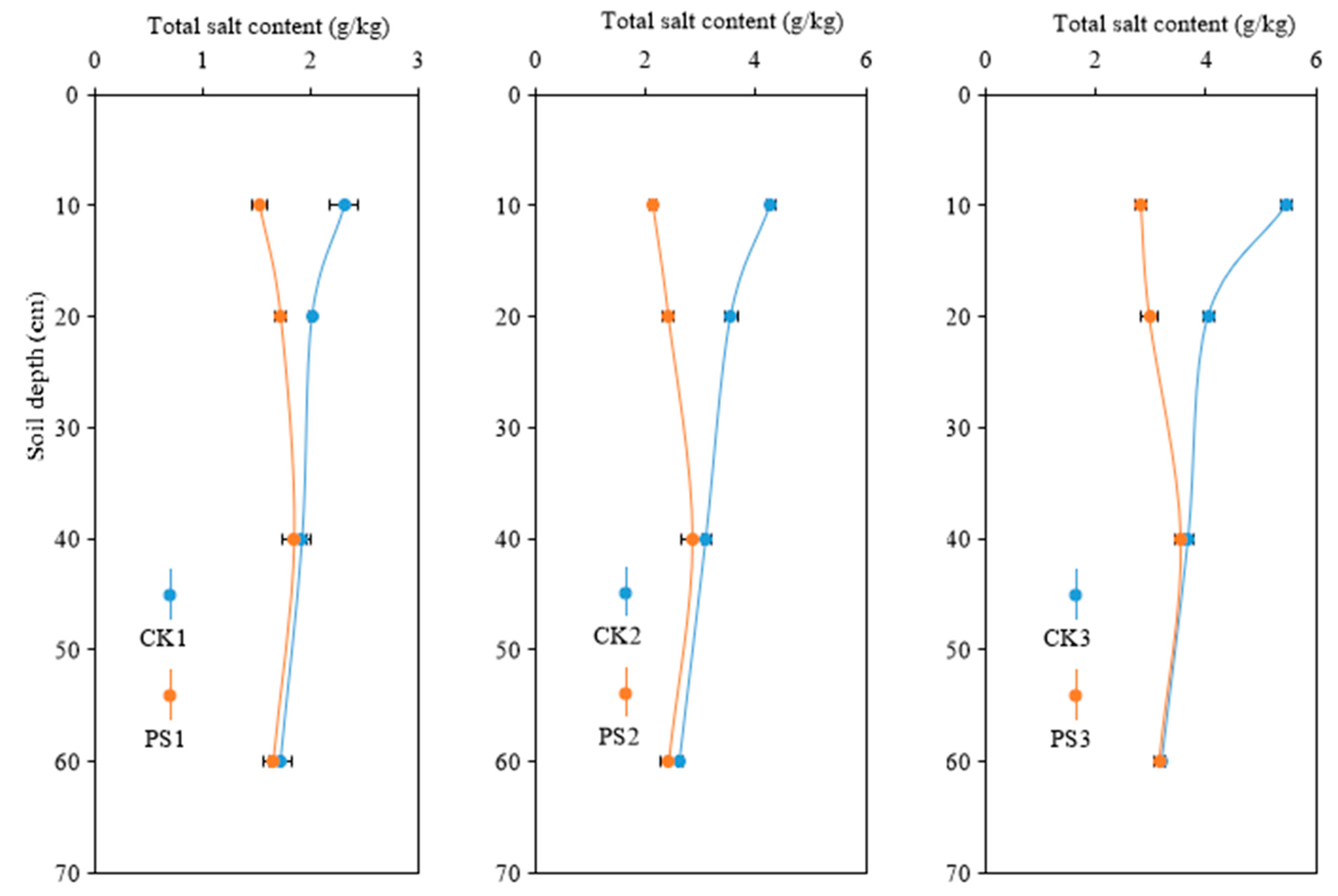


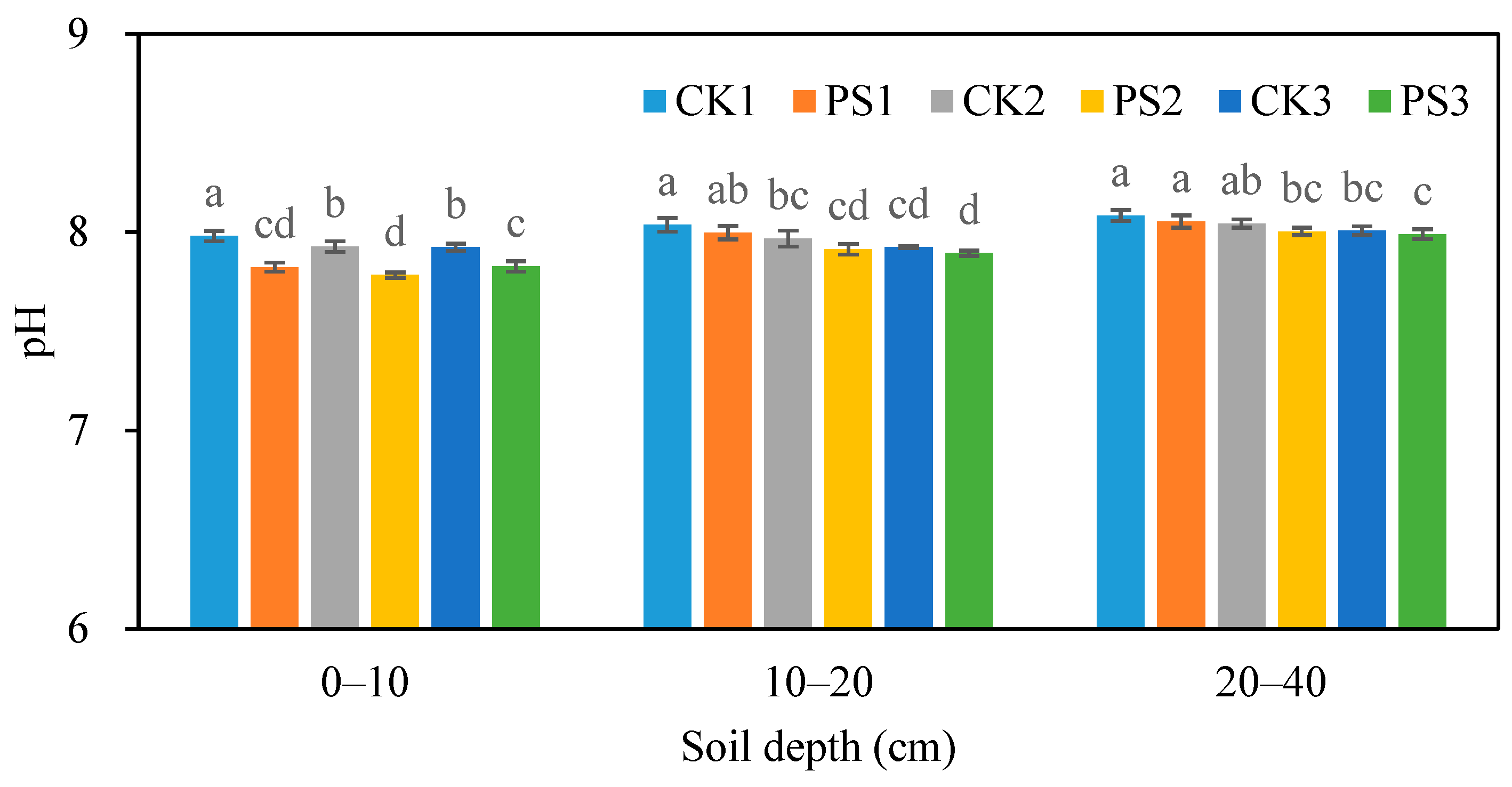



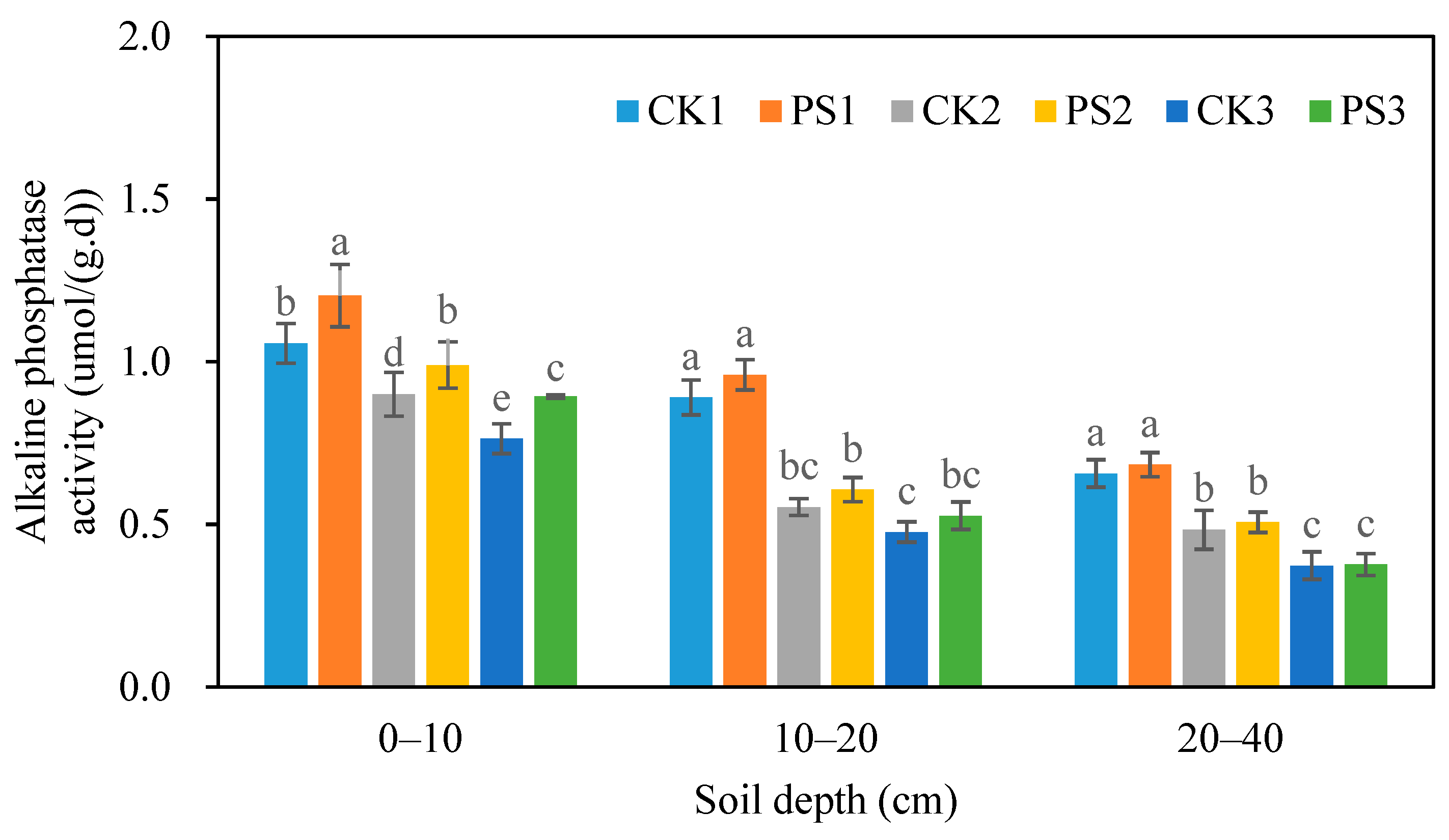
| Blocks | Soil Bulk Density | Soil Salinity | pH | Soil Organic Matter | Available Nitrogen | Available Phosphorus | Available Potassium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/cm3) | (g/kg) | (g/kg) | (mg/kg) | (mg/kg) | (mg/kg) | ||
| S1 | 1.47 ± 0.03 | 2.16 ± 0.08 | 8.01 ± 0.01 | 8.34 ± 0.03 | 28.59 ± 0.80 | 10.42 ± 0.27 | 195.53 ± 4.92 |
| S2 | 1.51 ± 0.02 | 4.08 ± 0.07 | 7.95 ± 0.02 | 6.93 ± 0.04 | 26.45 ± 0.81 | 9.23 ± 0.29 | 187.67 ± 9.51 |
| S3 | 1.48 ± 0.03 | 5.43 ± 0.09 | 8.05 ± 0.02 | 6.64 ± 0.06 | 24.72 ± 0.75 | 8.92 ± 0.26 | 176.6 ± 7.41 |
| Treatment | Fresh Weight (t/ha) | Dry Weight (t/ha) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Harvest | Second Harvest | Third Harvest | Total | First Harvest | Second Harvest | Third Harvest | Total | |
| PS1 | 11.54 ± 0.20c | 14.78 ± 0.21c | 30.42 ± 0.41c | 56.74 ± 0.43c | 1.02 ± 0.02c | 1.30 ± 0.02c | 2.68 ± 0.04c | 5.00 ± 0.04c |
| PS2 | 17.44 ± 0.13a | 23.71 ± 0.36a | 47.79 ± 0.38a | 88.94 ± 0.73a | 1.49 ± 0.01a | 2.03 ± 0.03a | 4.09 ± 0.03a | 7.61 ± 0.06a |
| PS3 | 14.48 ± 0.28b | 20.07 ± 0.47b | 42.69 ± 0.31b | 77.24 ± 0.47b | 1.23 ± 0.02b | 1.70 ± 0.04b | 3.62 ± 0.03b | 6.54 ± 0.04b |
| Treatment | Ash Content (%) | Salt Accumulation (t/ha) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Harvest | Second Harvest | Third Harvest | First Harvest | Second Harvest | Third Harvest | Total | |
| PS1 | 26.68 ± 0.53a | 25.81 ± 0.48a | 25.55 ± 0.56a | 0.27 ± 0.01c | 0.34 ± 0.01c | 0.69 ± 0.02c | 1.29 ± 0.02c |
| PS2 | 27.03 ± 0.31a | 26.35 ± 0.34a | 26.57 ± 0.77a | 0.40 ± 0.01a | 0.53 ± 0.01a | 1.09 ± 0.04a | 2.03 ± 0.05a |
| PS3 | 26.90 ± 0.39a | 26.25 ± 0.46a | 26.51 ± 0.50a | 0.33 ± 0.01b | 0.45 ± 0.02b | 0.96 ± 0.02b | 1.74 ± 0.01b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, J.; Xing, J.; He, T.; He, S.; Liu, C.; Zhu, X.; Sun, G.; Wang, K.; Hong, L.; Zhang, Z. Effect of Planting Portulaca oleracea L. on Improvement of Salt-Affected Soils. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137310
Dong J, Xing J, He T, He S, Liu C, Zhu X, Sun G, Wang K, Hong L, Zhang Z. Effect of Planting Portulaca oleracea L. on Improvement of Salt-Affected Soils. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137310
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Jing, Jincheng Xing, Tingting He, Sunan He, Chong Liu, Xiaomei Zhu, Guoli Sun, Kai Wang, Lizhou Hong, and Zhenhua Zhang. 2025. "Effect of Planting Portulaca oleracea L. on Improvement of Salt-Affected Soils" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137310
APA StyleDong, J., Xing, J., He, T., He, S., Liu, C., Zhu, X., Sun, G., Wang, K., Hong, L., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Effect of Planting Portulaca oleracea L. on Improvement of Salt-Affected Soils. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7310. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137310








