1. Introduction
In long-distance navigation tasks, the use of global positioning technology is necessary. Current global positioning technologies mainly include satellite navigation technology and inertial navigation technology. Satellite navigation technology has been extensively implemented into various transportation vehicles, including aircraft, maritime vessels, and automobiles. However, satellite signals are man-made and are susceptible to interference, particularly under extreme conditions, such as in Global Positioning System (GPS)-denied environments. In addition, the positioning error in inertial navigation accumulates over time.
Bionic polarized light-based global positioning technology can effectively overcome the two limitations of satellite navigation and inertial navigation technologies. It employs a completely autonomous global positioning approach without error accumulation. The exploration of this technology can be traced back to 1947, when Frisch et al. reported that bees could perceive polarized light in the atmosphere [
1], prompting scientific inquiry into bionic polarized light navigation. Lambrinos et al. focused on the compound eye structure of insects [
2]. Over several decades, researchers have developed a comprehensive understanding of the way various organisms use polarized light from the sky to obtain information on orientation. In 1997, Rüdiger and Dimitrios developed a sky polarized light compass and performed trajectory control experiments using a four-wheeled robot [
3,
4]. Chu et al. (2005) investigated the polarized light sensitivity model of insect compound eyes [
5] and analyzed its angle measurement mechanism model in detail, subsequently developing a heading measurement sensor [
6]. Chahl and Mizutani (2012) developed and calibrated a polarized light compass and conducted flight tests on a fixed-wing drone; the results demonstrated that the heading accuracy was comparable to that of a traditional magnetic compass [
7]. Further, in 2012, Ropars et al. reported that ancient Vikings might have employed calcite to detect polarized light in the sky for navigational purposes [
8]. Horváth et al. analyzed the errors in the three navigation steps in detail for using polarized light like the Vikings [
9,
10,
11]. The simulation results derived from extensive observational data suggested that it was indeed plausible for the Vikings to navigate from Norway in Northern Europe to Greenland using polarized light information from the sky [
12]. In summary, previous studies have enabled researchers to derive heading information by detecting polarization data from scattered atmospheric light [
13].
However, there are significant distinctions between the long- and short-distance movements along the Earth’s surface. For short distances, such as 3 km, the destination can be seen. In contrast, for long distances, like 1000 km, the destination is out of sight from the starting point. When navigating over bodies of water or through the atmosphere, one might experience yaw because of the influence of water currents and airflows. Due to this phenomenon, it is necessary to perform continuous course adjustments according to one’s global position. Therefore, it is insufficient to attain orientation only, and advancing global positioning technology is imperative.
The technology of polarized light navigation has progressively transitioned in recent years from obtaining the heading to obtaining the global position. Wang and Chu (2015) developed an autonomous real-time global positioning navigation method based on the Earth’s sky polarized light and magnetic field [
14]. Mei et al. (2015) designed a non-real-time autonomous global positioning method [
15], which relies exclusively on the Earth’s sky polarized light and requires at least two independent observations of the sky. However, both studies simulated positioning errors for specific times and locations without addressing the variability of errors across different times and geographical locations globally. Gruev et al. (2018) introduced a non-real-time autonomous global positioning method using underwater polarized light [
16]. Their research involved the development of an innovative biomimetic underwater polarized light detection camera, which was validated for its positioning capabilities across various geographical locations on the Earth. Guo et al. further advanced this field by employing the time differential polarization field to minimize errors in underwater polarization detection [
17]. Yang et al. (2021) developed a non-real-time global positioning method [
18], which determines global positions based on the distribution of the polarization degree of sky polarized light; in contrast, the previous studies were based on the polarization angles of sky polarized light. Viollet et al. (2023) suggested a method that uses the temporal characteristics of the Earth’s sky polarized light and employs a polarization camera to measure this light [
19,
20]. This method calculates the geographic north direction and an observer’s latitude. When combined with additional navigation data, this method can facilitate the global positioning process. Hu et al. (2024) developed an integrated navigation system combining multi-directional polarization sensors [
21], a sun sensor, and an inertial measurement unit (IMU). Moutenet et al. (2024) designed a publicly available detection device computer program [
22], thus promoting international collaboration in advancing polarized navigation technology.
Based on their fundamental principles, global positioning methods can be roughly classified into two distinct categories. The first category uses sky scattering light detection devices and geographic true north information detection devices simultaneously. First, the solar azimuth and elevation angles, defined in the body coordinate system, are derived from the polarization information [
23,
24], including the angle or degree of polarization of the scattered light. This information is then combined with the heading information provided by a geographic true north information detection device to determine the solar elevation and azimuth angles at the carrier’s location. Finally, the geographic location of the carrier is obtained. This approach has real-time capability and necessitates only a single detection of sky-scattered light.
The second category relies only on the sky-scattered light detection device, and the solar azimuth and elevation angles, defined in the body coordinate system, are determined based on the polarization information of the scattered light. However, due to the inability to obtain the true north heading of the carrier from a single observation, this category requires at least two observations to be performed to determine the carrier’s geographic location. Consequently, these methods are classified as non-real-time methods, and if the time interval between the two measurements is very short, the precision of the geographic localization can decrease.
Existing research suggests that the global positioning methods based on polarized light both provide global positioning functionality and maintain the autonomy of methods, meaning that they do not rely on any artificial signals. However, research on the positioning errors of these methods has been relatively scarce [
25], particularly regarding the global distribution patterns of positioning errors at different times and under different error conditions.
Aiming to address the current shortcomings, this paper designs a global error model for the real-time global positioning methods. The proposed model can rapidly and accurately provide the global distribution patterns of positioning errors at different times and under different error conditions. It can also serve as a theoretical framework for navigation task planning, thus enabling the avoidance of non-linear regions where minor measurement inaccuracies might result in substantial positioning discrepancies. Furthermore, the design and development of polarized light sensors and cameras can be determined by the proposed error model. For instance, the positioning accuracy of the GPS is typically within the meter range. Further, the autonomous positioning error model can determine the precision required for measurements of polarized angles, thus enabling the autonomous positioning method to achieve meter-level accuracy. In summary, by analyzing the global error distribution, one can effectively design and optimize the parameters of the autonomous global positioning system, enhancing its reliability and stability.
This paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 introduces the fundamental principles of real-time global positioning methods.
Section 3 develops the error model by employing partial derivatives and outlines the conditions under which the proposed error model is valid.
Section 4 verifies the accuracy of the proposed error model through numerical simulation. Finally,
Section 5 summarizes the spatial and temporal distribution properties of the proposed error model.
2. Autonomous Global Positioning Method
An autonomous global positioning system based on the Earth’s sky polarized light and a true north measurement instrument generally includes several polarized light sensors, a true north measurement device, and a computer. The global position calculation flowchart of an autonomous global positioning system is presented in
Figure 1.
The specific steps of the global position calculation flowchart are as follows. First, a polarization light sensor measures the scattered light in the atmosphere to obtain a polarization vector
e. The orthogonal vector algorithm [
24] obtains a solar vector
Sb in the body coordinate system. Then, the three altitude angles provided by a true north measurement instrument are used to determine a solar vector
Sn in the East–North–Up (ENU) coordinate system. Next, the solar altitude angle and the solar azimuth angle are calculated. Further, the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) is obtained from the clock integrated into a computer; this allows for the retrieval of the corresponding solar declination and solar time difference based on the UTC and the astronomical calendar. Finally, this information is substituted into the system of equations of a global positioning method to obtain the global position of the carrier.
2.1. Global Positioning Method Equation System
The system of equations of the global positioning method is defined as follows:
where
As is the solar azimuth angle;
hs is the solar altitude angle;
δ is the solar declination;
ψ is the geographic latitude;
η is the geographic longitude;
Eω is the difference between the true and mean solar hours;
UTC is the UTC value; and ω is the solar hour angle, which is calculated by
.
The heading angle (
Y), pitch angle (
P), and roll angle (
R) are determined using a true north measurement device. A three-dimensional rotation matrix created by the three angles is defined by Equation (3). This matrix can be used to convert a vector from the body coordinate system to the ENU coordinate system. The body coordinate system
ObXbYbZb is defined as follows. The coordinate origin is set at the center of gravity of a vehicle; the
x-axis points to the right side of the vehicle; the
y-axis points to the front of the vehicle; and the
z-axis is perpendicular to the vehicle pointing upwards, forming a right-handed coordinate system. The ENU coordinate system
OnXnYnZn is defined as follows. The origin of this coordinate system is set at the observation point, the
x-axis points to true east, the
y-axis points to true north, and the
z-axis is perpendicular to the horizontal plane, pointing upwards, also forming a right-handed coordinate system.
A solar vector obtained from the polarization information of polarized sky light is denoted by
Sb and defined in the body coordinate system. The solar vector in the ENU coordinate system is expressed as follows:
Using Equation (4) and the solar altitude angle value, a solar altitude angle
hs and an azimuth angle
An in the ENU coordinate system can be determined. The solar azimuth angle is defined in the plane formed by
Xn and
Yn, with the geographic true north direction (
Yn) as a reference direction and clockwise as positive; therefore, it holds that
The autonomous global positioning method determines the global position of the carrier by solving the system of equations formed by Equations (1) and (2). This study aims to develop a global error model that can provide the global distribution of deviations in the geographic longitude and latitude, which are caused by the measurement angle errors of the two independent variables at different times. In addition, this study aims to translate the angle errors of the geographic longitude and latitude (expressed in degrees) into the corresponding distance errors of the Earth’s surface (expressed in kilometers).
2.2. Number of Solutions to Global Positioning Method Equation System
Before establishing the error model, it is necessary to identify the number of solutions to the autonomous global positioning method because two or more solutions can significantly increase the difficulty of the error model design.
First, based on the symmetry of the trigonometric functions, there are four sets of solutions to the system of equations. Therefore, supplementary criteria are required to eliminate redundant or unreasonable solutions.
The specific steps for solving the system of equations are as follows:
Then, a longitude η can be solved using Equations (2) and (7); there are two equations and only one unknown. Based on Equations (2) and (7), the sine and cosine values of a solar hour angle, (), can be directly calculated, which allows for the determination of a unique value of the solar hour angle; subsequently, a unique longitude η can be obtained. In summary, each latitude ψ corresponds to only one longitude η.
- 4.
The analysis of Steps 1 and 2 indicates that the system of equations has two sets of solutions, so the global positioning method will provide two locations.
- 5.
Exclude solutions that have no practical significance based on the latitude and longitude value ranges. The initial range of tM obtained by Equation (6) is from negative infinity to positive infinity; therefore, the range of ψ/2 is [−90°, 90°]; this further indicates that the range of geographic latitude obtained by the global positioning method is [−180°, 180°]. However, the actual value range of the Earth’s latitude ψ is [−90°, 90°], so solutions that exceed this range have no practical significance and can be excluded. When this situation occurs, the system of equations has only one set of solutions.
In summary, the system of equations typically has two sets of solutions. However, in certain cases, one set of solutions can be excluded due to the actual value range of the Earth’s latitude, resulting in a unique solution. Subsequently, this study uses a combination of numerical and graphical methods to analyze the mathematical characteristics of the system of equations for autonomous global positioning. It also defines the conditions under which the two sets of solutions exist, as well as the conditions under which there is only a unique solution.
This study uses the time moment of 27 May 2024,
UTC = 21 h, as a research sample. It has been found from the astronomical calendar that this time moment corresponds to the solar declination of
δ = 21.4849° and
Eω = 0.0456 h. The contour color maps of the solar azimuth angle and solar altitude angle are shown in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3, respectively.
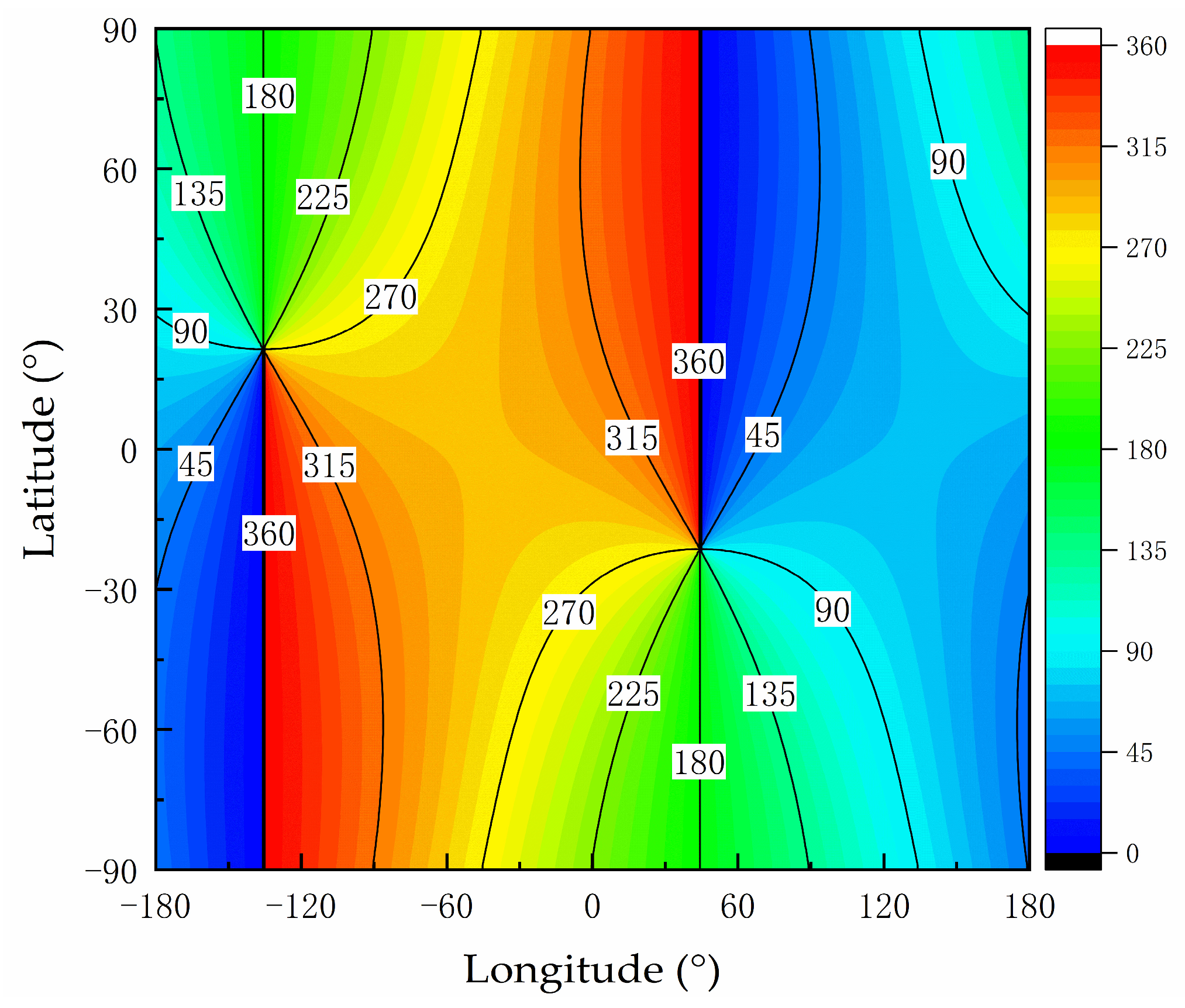
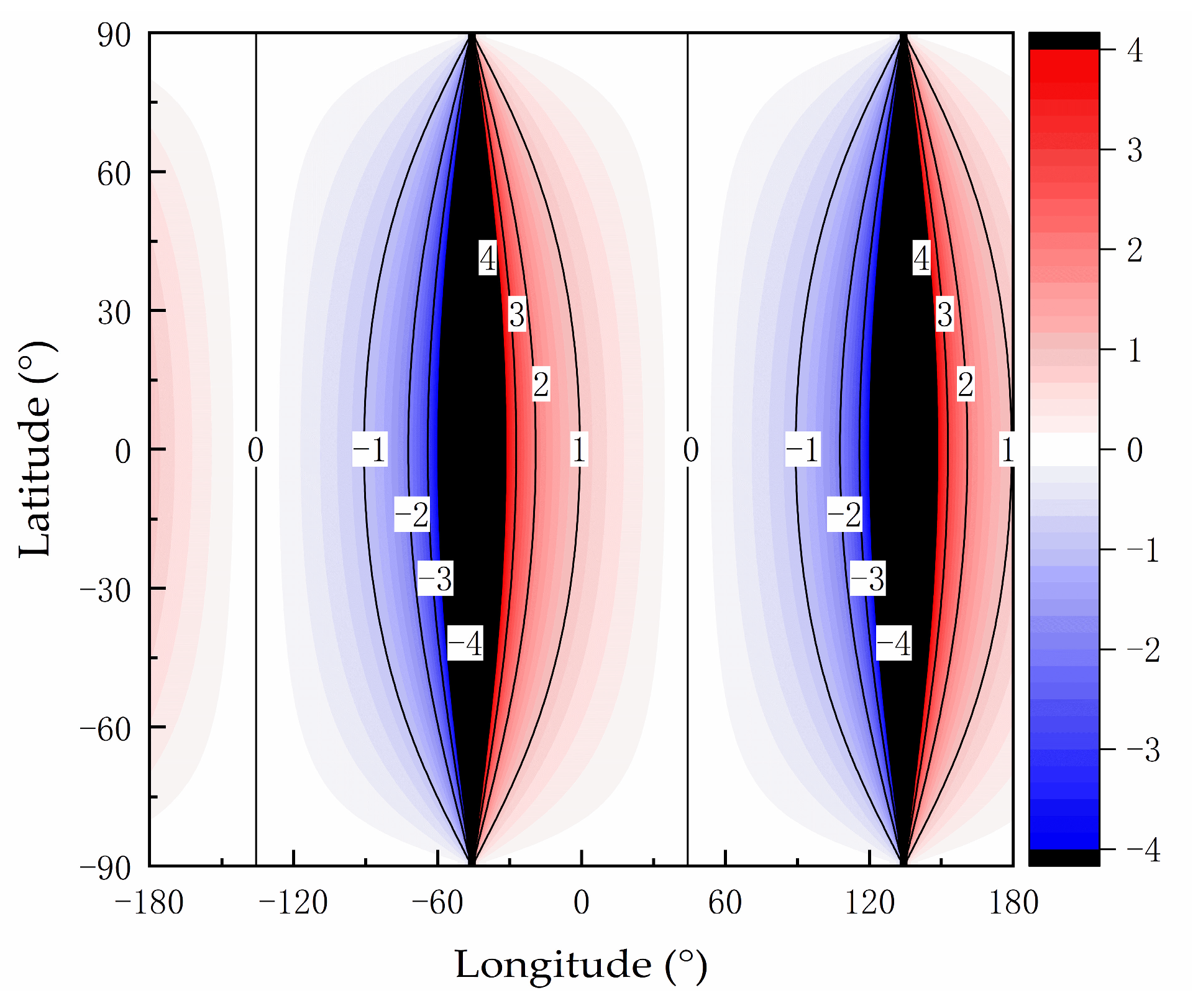
In
Figure 2, the solar azimuth angle is defined as the angle between the line connecting the Earth’s true north point and the observation point and the line connecting the direct point of the sun and the observation point. The direct point of the sun refers to the point on the Earth’s surface where the sun’s rays are perpendicular; at this point,
hs is 90°. The line from the observation point to the true north point is taken as a reference direction (i.e.,
Yn in the ENU coordinate system), where a clockwise direction indicates a positive direction. The value range of
As is [0°, 360°], as indicated by the color bar on the right side of
Figure 2. As shown in
Figure 2, the contour lines representing the solar azimuth angle exhibit a ray-like pattern. It should be noted that
Figure 2 depicts a projection of the three-dimensional spherical Earth onto a two-dimensional plane, which introduces certain distortion. Further, all contour lines intersect at the geographic poles where the latitude is either −90° or 90°, which indicates that at these locations, the azimuth angle can assume any value in the range of [0°, 360°]. Because of this distortion, in
Figure 2, two geographic poles are illustrated as lines rather than points. This situation is very similar to a world map.
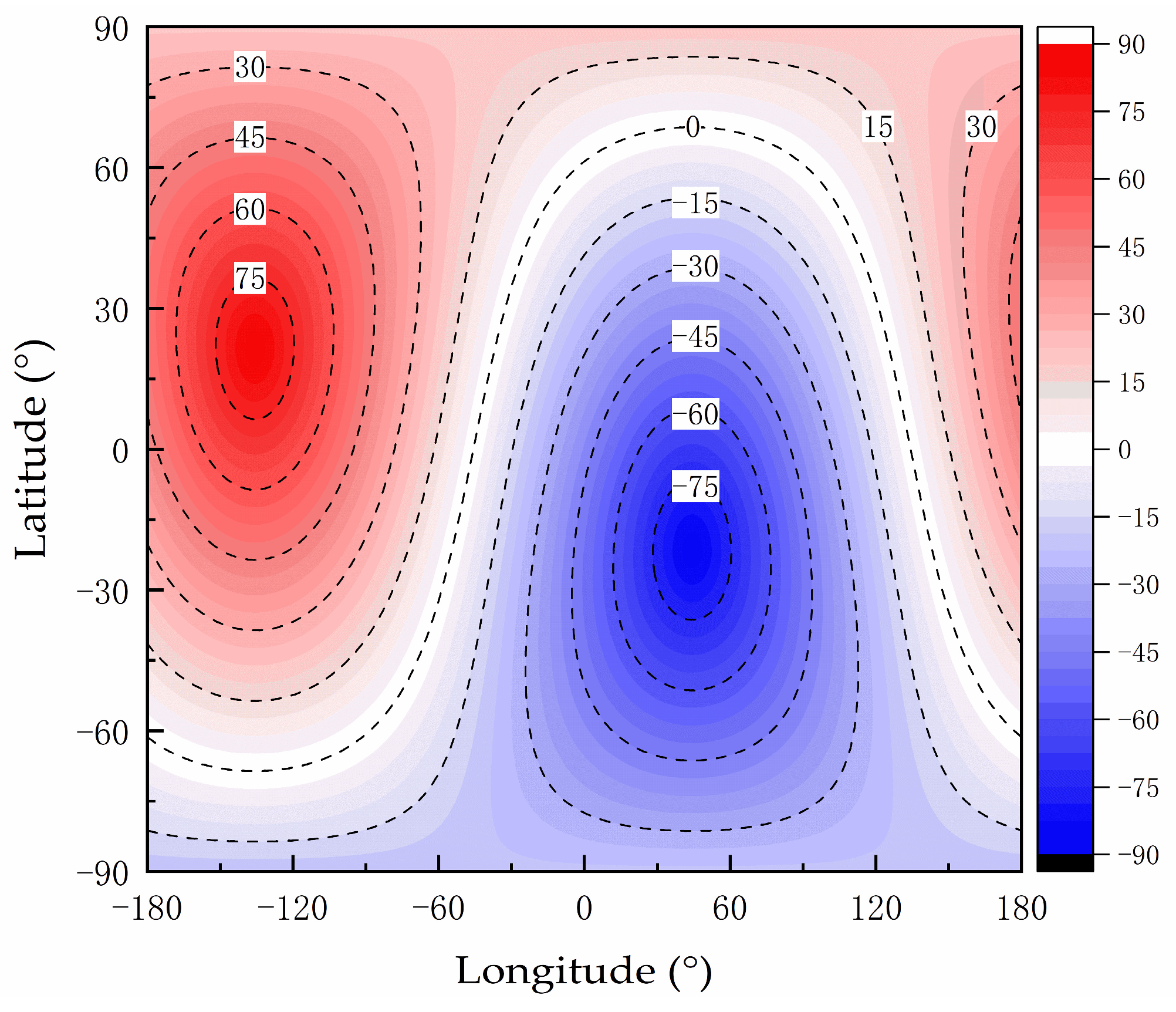
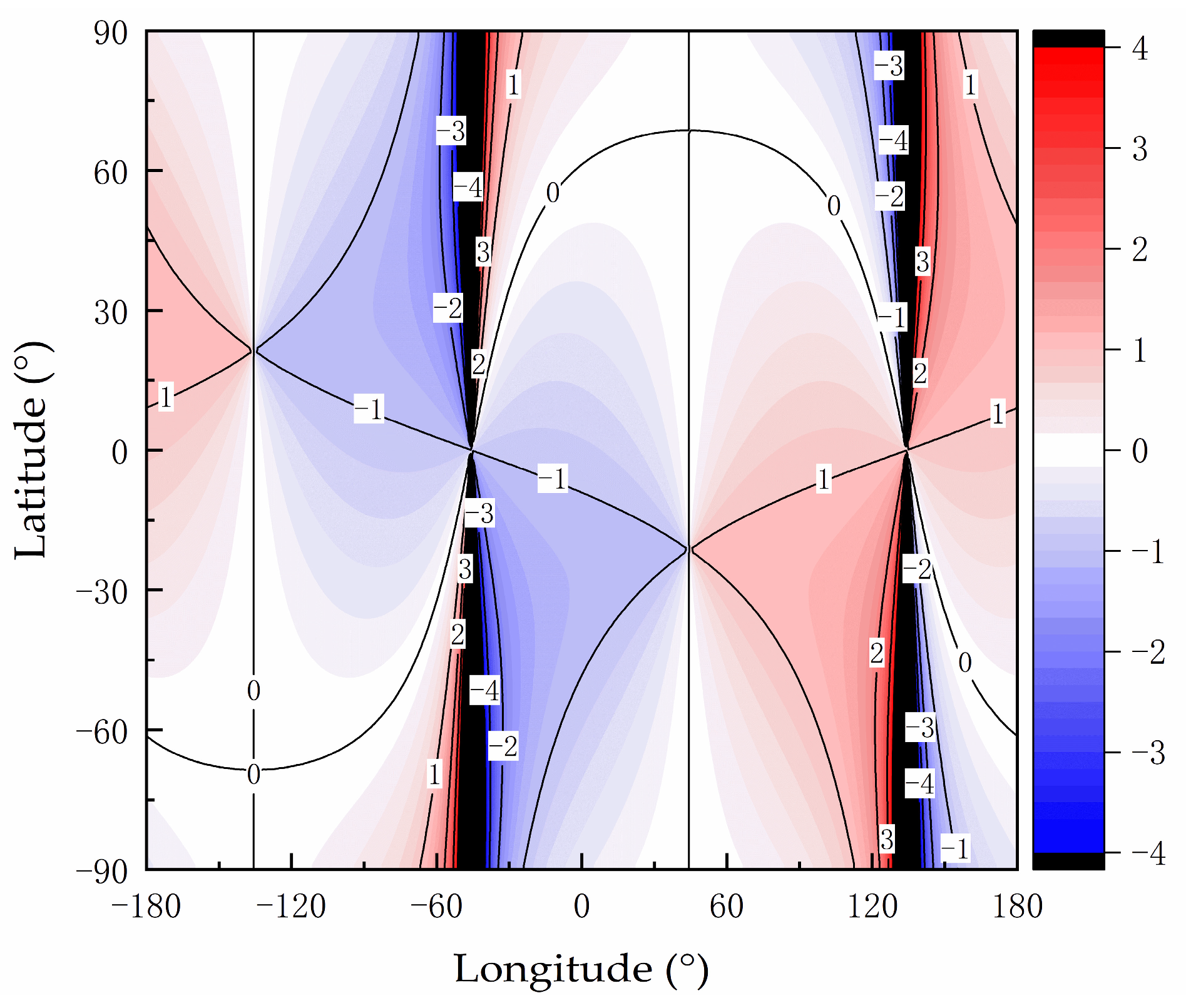
In
Figure 3, the contour lines of the solar altitude angle radiate outward in concentric circles from the direct point of the sun, where the solar altitude angle is 90°, and the anti-direct point of the sun, which corresponds to the solar altitude angle of −90°.
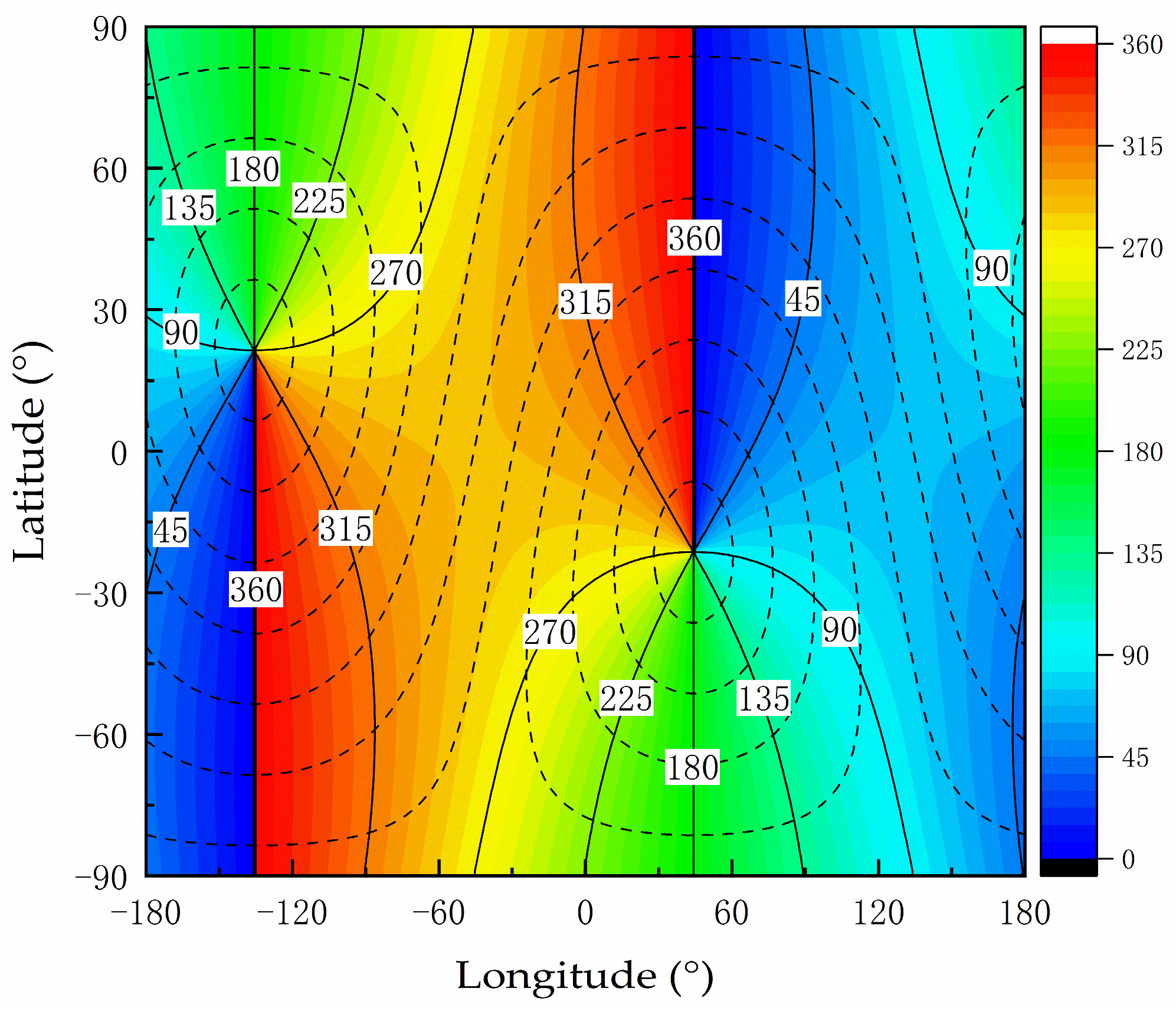
The color map presented in
Figure 4 is constructed by superimposing the contour lines representing solar altitude angles in
Figure 3 onto the contour lines in
Figure 2. In
Figure 4, the contour lines of
hs are denoted by the black dashed lines. In addition, to minimize clutter in the image annotations,
Figure 4 displays only the contour line values corresponding to the azimuth angle, whereas the values for solar altitude angle are omitted. Thus, it can be inferred that the intersection points of the contour lines for solar azimuth angle and solar altitude angle indicate the solutions to the system of equations of the global positioning method. Analysis of
Figure 4 reveals that most intersection points of the contour lines yield a single solution, whereas a minority present two solutions. The results of the analysis are consistent with the conclusions of the specific steps for solving the system of equations.
Figure 4 illustrates the number of solutions of the autonomous global positioning method at a designated time. The subsequent analysis focuses on the number of solutions to the equations of this method under different temporal conditions. As depicted in
Figure 4, the distribution of the contour lines of the two independent variables determines the number of solutions to the equations. The distribution of the contour lines is mainly defined by the direct point of the sun, which is determined by the UTC. According to astronomy, during a 24 h period (i.e., one complete rotation of the Earth), the variations in a solar declination
δ are very small. Therefore, the latitude of the direct point of the sun remains almost constant, whereas the longitude changes with time. For instance, when UTC changes from 21 h to 15 h, the superimposition of the contour lines of the two independent variables is highly similar to the graph obtained by shifting the map presented in
Figure 4 horizontally along the horizontal axis by six hours; their global distribution of the number of solutions is also highly similar.
When looking at a yearly time frame, which represents one full orbit of the Earth around the sun, the changes in the solar declination become relatively apparent, requiring detailed examination. Astronomical data indicate that the solar declination varies throughout the year from −23°27′ to 23°27′. It is zero during the vernal and autumnal equinoxes and reaches its maximum and minimum values at the summer and winter solstices, respectively.
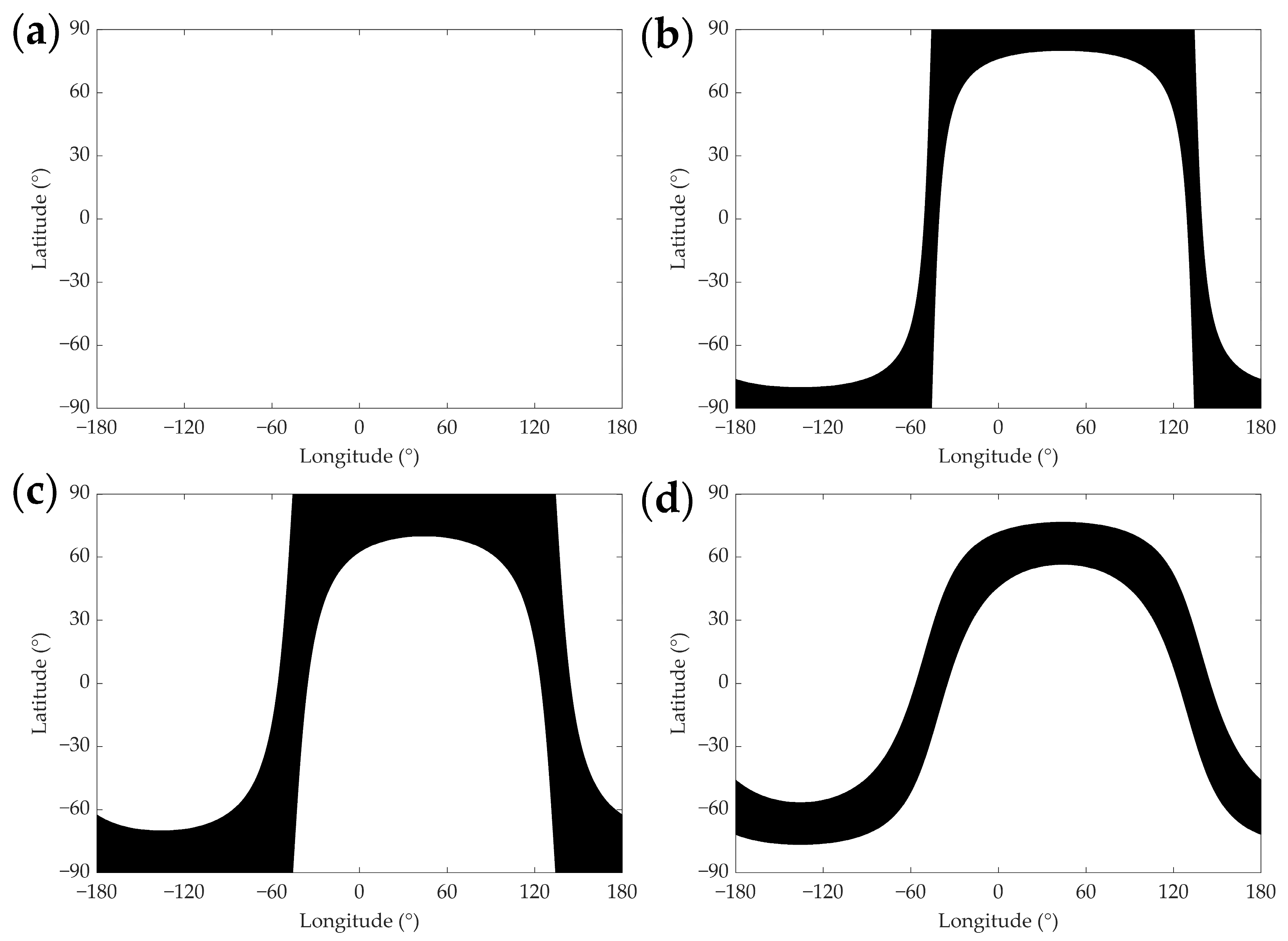
Figure 5a–d show the global distribution of the number of solutions obtained by the autonomous global positioning method at the solar declinations of zero, 5°, 10°, and 23°27′ at the UTC of 21 h and
Eω = 169.8116/60/60 h, respectively.
In
Figure 5, the white regions denote areas with a single solution, whereas the black regions indicate areas with two solutions. As shown in
Figure 5a, when the solar declination is zero, there is only one global solution. In all other scenarios, there are areas with two solutions. It is important to understand that
Figure 5 depicts the projection of the Earth’s three-dimensional spherical shape onto a two-dimensional surface, which can introduce certain distortion; thus, the visible size of the black regions in
Figure 5 might not accurately reflect their actual surface area on the Earth.
3. Materials and Methods
This study presents the design of a global error model for the autonomous global positioning method. The main procedure of the model construction process involves the computation of partial derivatives of the system of equations composed of Equations (1) and (2). This system of equations represents an implicit function system that includes two independent variables: the solar azimuth angle (As) and the altitude angle (hs). The two dependent variables are the longitude (η) and the latitude (ψ). This research aims to analyze the variations in the dependent variables caused by ΔAs and Δhs at different times and geographical locations. In addition, this study aims to evaluate actual geographical deviation (ΔL) associated with the changes in the two dependent variables. Consequently, the designed global error model enables a rapid estimation of the ΔL value based on the changes in the independent variables in practical applications.
First, the expressions for the four partial derivatives of the implicit function equation system are derived, and then the expression for the global positioning distance error (ΔL) is obtained.
Next, the conditions under which the error model is valid are studied, assuming that the implicit function equation system is differentiable during the derivation process of the positioning error expression. When this system is differentiable, the total differentials denote the best linear approximation of the total increments for small changes in As and hs, that is, Δη ≈ dη and Δψ ≈ dψ. The findings of this study indicate that the error model is valid for specific geographical locations. However, for some geographical locations, the proposed model is demonstrated to be invalid.
3.1. Global Positioning Distance Error Expression Derivation
For the implicit function equation system, this study computes the partial derivatives with respect to the two independent variables: the solar azimuth angle (
As) and the solar altitude angle (
hs). During the calculation process of partial derivatives, the solar declination (
δ) is considered constant, resulting in four partial derivatives, which can be expressed as follows:
To ensure an initial understanding of the global distribution of partial derivatives, it is essential to further describe Equation (8) through visual representations. According to Equations (1), (2), and (8), the calculation equation of the partial derivative includes three variables: longitude (η), latitude (ψ), and time (UTC). Because a two-dimensional image can illustrate only the influence of two variables on a partial derivative, in this study, two-dimensional images are created by setting time to a specific value, using longitude as a horizontal axis and latitude as a vertical axis to illustrate the global distribution of partial derivatives.
The specific calculation steps of a partial derivative ∂ψ/∂As are as follows:
Define ƒ (
η,
ψ,
UTC) = ∂
ψ/∂
As, where
η,
ψ, and
UTC are the three calculation variables. Set the time to be consistent with the time in
Figure 2, which is 27 May 2024,
UTC = 21 h. At this time,
δ = 21.4849° and
Eω = 0.0456 h. Consequently, express ƒ (
η,
ψ, 21) = ∂
ψ/∂
As.
Calculate the value of a function ƒ (η, ψ, 21) using the two independent variables, namely η and ψ. The value range of the Earth’s latitude (ψ) is [−90°, 90°], with an interval of 0.01°, resulting in a total of 18,000 data points. The value range of the Earth’s longitude (η) is [−180°, 180°], also with an interval of 0.01°, resulting in 36,000 data points. Therefore, the total number of calculations amounts to 648,000,000. For each calculation, first, the values of solar altitude angle (hs) and azimuth angle (As) are calculated for each geographical location using Equations (1) and (2). Next, the values of the solar declination, geographical latitude, solar altitude angle, and solar azimuth angle of each geographical location are substituted into Equation (8) to calculate the partial derivative ƒ (η, ψ, 21) value.
In summary, the global distribution of a partial derivative (∂
ψ/∂
As) at the UTC of 21:00 on 27 May 2024 is obtained, as illustrated in
Figure 6. The simulation calculations were performed using MATLAB software, R2023a (9.14.0.2206163), 22 February 2023. In
Figure 6, the horizontal axis represents longitude, and the vertical axis indicates the latitude value. The contour lines represent the values of the partial derivative of the latitude angle with respect to the solar azimuth angle. The calculations of the remaining partial derivatives are performed in the same manner as that of ∂
ψ/∂
As, as shown in
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9.
However, in
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9, considering the drastic changes in the partial derivatives’ values at certain locations, areas where the absolute value exceeds four are illustrated in black. This approach is employed to ensure that most regions can accurately show the values of the four partial derivatives.
Further, assuming that the implicit function equations are differentiable at all locations globally, the total differential (d
ψ) can be regarded as a total increment (Δ
ψ), and the same rule will apply to the longitude. The total increments of longitude and latitude can be mathematically expressed as follows:
However, total increments of longitude and latitude do not represent the final positioning distance error (Δ
L). If the measured longitude and latitude values at a point (
η,
ψ) on the Earth’s surface are (
η + Δ
η,
ψ + Δ
ψ), the measurement deviations of the two independent variables will be Δ
As and Δ
hs, respectively. In addition, assuming that the Earth’s surface is a standard sphere, the spherical distance between the two points can be calculated as follows:
where
RL is the Earth’s radius, and is set to 6400 km in this study.
Therefore, the global positioning distance error calculated by the proposed error model is obtained by:
In conclusion, the proposed error model is defined by Equations (8), (9), and (11). This model enables the calculation of positioning distance errors of the autonomous global positioning method for any longitude and latitude values on the Earth’s surface.
3.2. Conditions Under Which the Proposed Error Model Is Valid
The accurate assessment of the validity of the proposed error model at a particular geographic location examines whether the four partial derivatives of the two dependent variables, derived from the system of two implicit functions, exist and exhibit continuity at that specific point. The main mathematical symbols employed in
Section 3.2 are presented in
Table 1.
The determination process of a function’s differentiability is complex. By analyzing the properties of the four partial derivatives, this study determines whether this process can be simplified. The four partial derivatives consist of elementary functions, which are derived from the sum, difference, product, and quotient of trigonometric functions. Consequently, the four partial derivatives are classified as elementary functions. Further, according to the mathematical principles, elementary functions are continuous and differentiable at every point within their domain. Thus, determining whether the proposed error model is differentiable at a specific point on the Earth’s surface (η, ψ) can be reduced to the process of verifying whether the four partial derivatives are defined at that point. If all four partial derivatives are defined at a given point, then the error model is considered differentiable at that point. However, if any one of the four partial derivatives is undefined at a particular point, the model is regarded as non-differentiable at that point.
To examine whether an elementary function is defined at a specific point, it is necessary to distinguish the type of elementary function. The function types include fractional forms, radical forms, and logarithmic forms, among others. The four partial derivatives are expressed in fractional form, so they are defined where the denominator is not equal to zero.
In summary, when the denominators of the four partial derivatives are all non-zero, the derivatives are simultaneously defined at a specific point. In addition, as all these functions are elementary functions, they exist and are continuous at that point. Consequently, at that point, the implicit function system is differentiable, and the total differential can be considered the total increment, indicating that the error model is valid at the given point. In contrast, if any one of the four partial derivatives has a denominator that equals zero, the implicit function system is not differentiable at the given point, and the proposed error model is inapplicable at that point.
Next, the denominators of the four partial derivatives are studied. According to Equation (8), the denominators of partial derivatives ∂
ψ/∂
As and ∂
ψ/∂
hs are equal, and the denominators of partial derivatives ∂
η/∂
As and ∂
η/∂
hs are also equal. The two denominators are expressed as follows:
Combining Equations (1), (2), and (12), the relation between
N and
M is expressed as follows:
3.2.1. Denominator N Equals Zero
First, the case when the denominator
N of a partial derivative equals zero is examined. By considering UTC a constant and treating longitude and latitude as two independent variables for further analysis, the following expression can be obtained:
According to the definition of longitude, the value range of
η is from −180° to 180°. The set of all longitude (
η) values is defined as
Uη, and the set of all
η values, where
N = 0, is denoted as
Aη; set
Aη denotes a subset of
Uη. Next, let set
Aη be a universal set; then, the complement of
Aη is
Cη. Similarly, according to the definition of latitude, the value range of
ψ is from −90° to 90°. The set of all latitude (
ψ) values is denoted by
Uψ, and the set of all
ψ where
N = 0 is labeled as
Aψ and represents a subset of
Uψ. Further, let set
Uψ be a universal set; then, the complement of
Aψ is
Cψ. A summary of the set labels is provided in
Table 1.
Based on the latitude (ψ) value, there are two possible cases: (1) ψ equals 90° or −90°, and (2) ψ is in the interval (−90°, 90°).
When
ψ equals 90° or −90°, cos
ψ = 0, as shown in row 2 of
Table 2. According to Equation (13), regardless of the denominator (
M) value, the denominator (
N) is equal to zero. The (
ηN=0,
ψN=0) set of row 2 in
Table 2 corresponds to the geographic locations of the South and North Poles. Every meridian passes through both the South and North Poles; the latitude of the South Pole is −90°, and its longitude can be any value from the [−180°, 180°] range. The latitude of the North Pole is 90°, and its longitude can also be any value from the [−180°, 180°] range.
When
ψ is in the (−90°, 90°) interval, cos
ψ ≠ 0, as shown in row 3 of
Table 2. Further, since
N is zero, according to Equation (13),
M is also zero. Substituting Equations (2) and (12) into Equation (14) yields
Because the value range of solar declination (
δ) is [−23°27′, 23°27′], then cos
δ ≠ 0; therefore, cos
ω = 0. Combining this with Equation (2) yields
where the latitude (
ψN=0) value is in the (−90°, 90°) range.
By combining the two above-presented conclusions, it can be found that (
ηN=0,
ψN=0) satisfies Equation (14), as shown in
Table 2. In other words, sets
Aη and
Aψ are obtained as shown in row 3 of
Table 1. The three-dimensional spatial distribution of sets
Aη and
Aψ forms a circular ring, which consists of two lines of longitude on Earth. At this ring, the denominator of the partial derivative (
N) is zero, and the implicit function system is non-differentiable. Consequently, the proposed error model is invalid at (
ηN=0,
ψN=0).
3.2.2. Denominator N Differs from Zero
Next, the case where the denominator of the partial derivative (
N) differs from zero is analyzed, as shown in row 2 of
Table 1. In this case, it holds that
Based on Equation (13), it follows that cos ψ ≠ 0; thus, ψN≠0 is in the interval (−90°, 90°). Next, according to Equation (13), the denominator M of the partial derivative differs from zero, indicating that the denominators of the four partial derivatives are non-zero. Through a proof by contradiction, it can be proven that all elements ψN≠0 that satisfy Equation (17) belong to set Cη, which is defined as a complement set of set Aη. Similarly, all ψN≠0 that satisfy Equation (17) are in a complement set Cψ of set Aψ.
The specific proof is as follows. All longitudes belong to universal set Uη. Sets Aη and Cη are both subsets of set Uη, and set Cη is a complement set of set Aη. If an element ηN≠0 does not belong to set Cη, then element ηN≠0 belongs to set Aη. Further, it can be concluded that N = 0, which contradicts N ≠ 0. Therefore, all elements ηN≠0 that satisfy Equation (17) are in the complement set Cη. Similarly, the corresponding conclusion can be drawn for latitudes.
3.2.3. Conditions Summary
In summary, the proposed error model is differentiable at points (
ηN≠0,
ψN≠0) where the denominators of the four partial derivatives are simultaneously non-zero, as shown in row 2 of
Table 1. Within the circular ring defined by sets
Aη and
Aψ, as presented in
Section 3.2.1, the error model is not differentiable, meaning it is not valid in this case. According to Equation (16), the circular ring is determined by the UTC and
Eω, and is independent of the solar declination.
4. Global Error Model Verification by Numerical Simulations
The correctness and accuracy of the global positioning error (dL) calculated by the proposed error model were verified by numerical simulations. When the error model was valid, the total increment of the positioning error was approximately equal to the total differential (ΔL ≈ dL).
According to the foundational principles of calculus, when the change in the independent variable was small, the total increment could be effectively approximated by the total differential. This study showed that when the absolute value of the measurement deviation was less than or equal to 5° (|Δ
As| ≤ 5°, |Δ
hs| ≤ 5°), the total increment could be approximated as a total differential. Under these specified conditions, the error model established in
Section 3 was validated.
The presence of multiple variables in Equation (9) could make an effective representation of analysis results using a single two-dimensional graph challenging. Therefore, this study employed a case-by-case discussion to reduce the number of variables, thus facilitating a clearer presentation of the results. The discussion was conducted for two distinct cases: ΔAs = Δhs and ΔAs ≠ Δhs. The simulation calculations were performed using MATLAB (Matrix laboratory) software.
4.1. First Case Analysis: ΔAs Equals Δhs
In this simulation experiment, first, Δ
As = Δ
hs was substituted into Equation (9), which yielded
where d
ψ/Δ
As is the total differential ratio of the latitude to the solar azimuth angle (TDRLAT), and d
η/Δ
As is the total differential ratio of the longitude to the solar azimuth angle (TDRLON). It should be noted that neither TDRLAT nor TDRLON are a partial derivative or a total differential, but were introduced in this study for the convenience of graphical representation of the error analysis results.
Considering the same conditions as those in
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9, the TDRLAT and TDRLON obtained in this experiment are shown in
Figure 10a and
Figure 11a, respectively. These conditions are
UTC = 21 h,
δ = 21.4849°, and
Eω = 0.0456 h.
For Δ
As = Δ
hs = 0.1°, the global distribution map of the total latitude increment Δ
ψ was obtained, as shown in
Figure 10b; the global distribution map of the total longitude increment Δ
η is displayed in
Figure 11b.
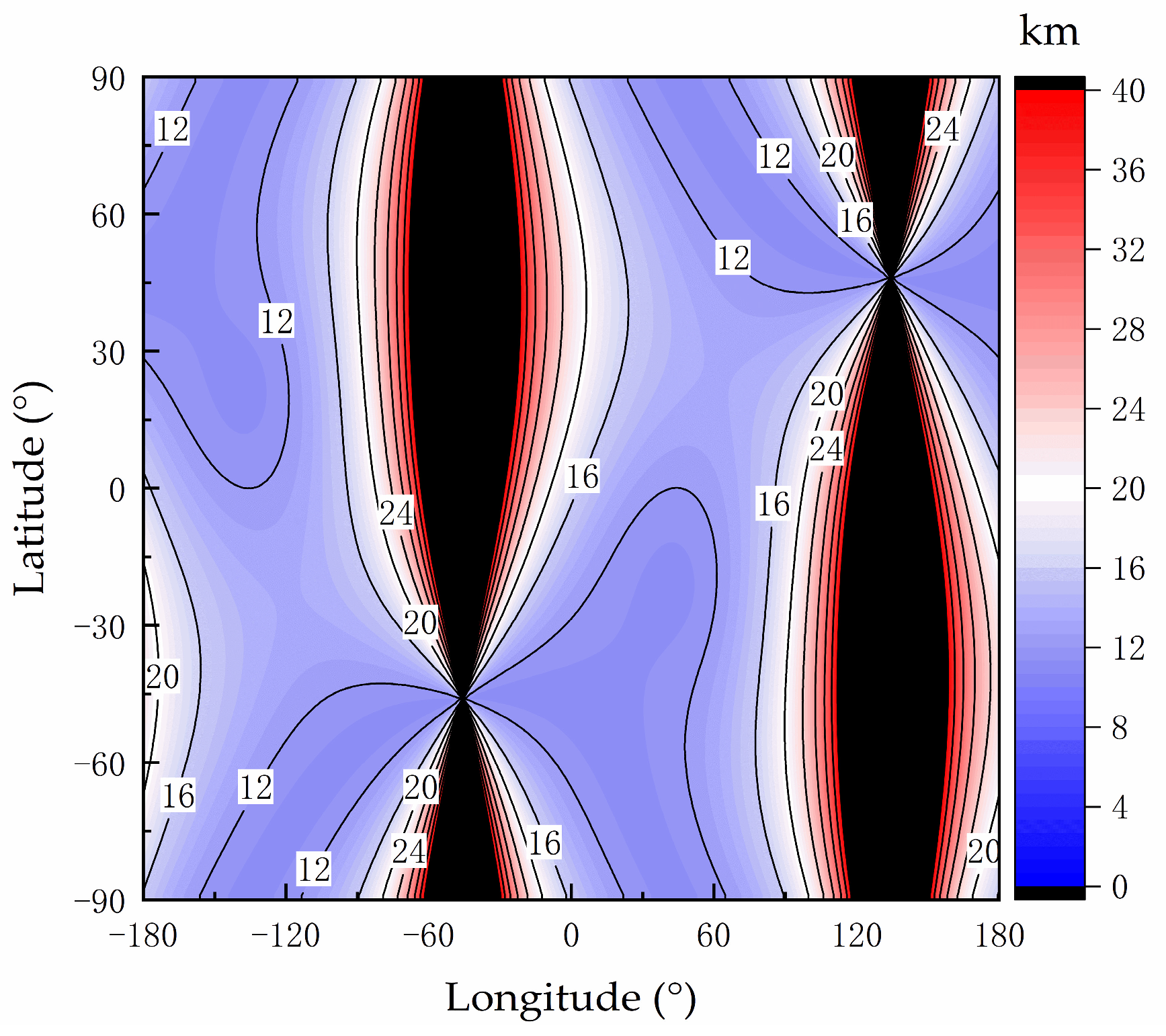
The calculation process was as follows. First, it was assumed that the theoretical solar altitude angle and azimuth angle at a point on Earth (η, ψ) were As and hs, and their measurement deviations were ΔAs and Δhs, respectively; UTC = 21 h, δ = 21.4849°, and Eω = 0.0456 h. Then, the measured solar altitude angle and azimuth angle at point (η, ψ) were obtained as (As + ΔAs) and (hs + Δhs). By substituting the measured solar altitude angle and azimuth angle into Equations (1) and (2), the measured latitude and longitude values were obtained. If the system of equations, composed of Equations (1) and (2), had two sets of solutions, the solution that was closer to the theoretical solution was considered a unique solution, whereas the other solution was excluded. Then, it held that and .
In
Figure 10a and
Figure 11a, in the numerical bar on the right side, the values exhibiting an absolute total differential ratio larger than four (dimensionless) are depicted in black. In
Figure 10b and
Figure 11b, regions where the absolute values of latitude and longitude deviations surpassed 0.4° are also illustrated in black. In
Figure 10a,b and
Figure 11a,b, all other areas are represented in color.
Therefore,
Figure 10 and
Figure 11 depict two distinct regions, namely the colored and black regions, each of which was analyzed independently, as presented in the following sections.
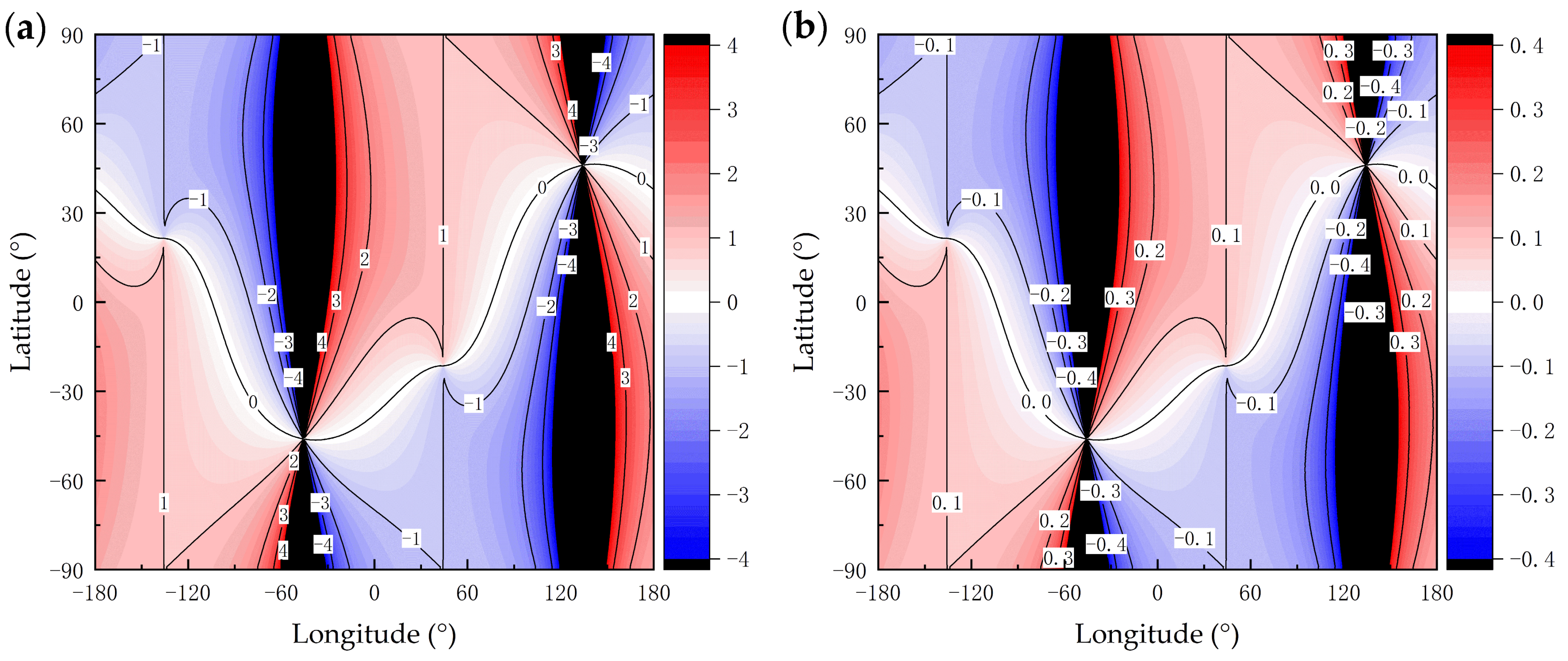
4.1.1. Colored Region
The results presented in
Figure 10a were calculated by Equation (18);
Figure 10b shows latitude deviation Δ
ψ for all global locations when Δ
As = Δ
hs = 0.1°. In
Figure 10a, all points on the contour line labeled as “1” had d
ψ/Δ
As = 1. In
Figure 10b, all points on the contour line labeled as “0.1” had Δ
ψ = 0.1°, which yielded Δ
ψ/Δ
As = 1.
The colored areas in
Figure 10a,b indicate that the contour line distribution patterns displayed in these figures were consistent, meaning that d
ψ/Δ
As ≈ Δ
ψ/Δ
As. Consequently, it could be determined that Δ
ψ ≈ d
ψ.
The contour line distribution patterns presented in
Figure 11a,b were also consistent, indicating that Δ
η ≈ d
η.
Further research indicated that when ΔAs = Δhs ≠ 0.1°, for example, ΔAs = Δhs = 0.5° or ΔAs = Δhs = 3°, the global error model remained valid in the colored region.
4.1.2. Black Region
First, the black areas in
Figure 10a and
Figure 11a contained the region where the proposed error model was not valid. As noted in
Section 3.2, the region where the error model was not valid was a circular ring. In
Figure 10 and
Figure 11, the time was 27 May 2024,
UTC = 21 h, and
Eω = 169.8116/60/60 h. According to Equation (16), the
ηN=0,cos ω=0 value was either −45.7° or 134.3°. The black areas in
Figure 10a and
Figure 11a are distributed around the circular ring defined by the longitude value,
ηN=0,cos ω=0. Therefore, the black areas contained the region where the proposed error model was invalid.
Then, in
Figure 10 and
Figure 11, the areas in black, excluding the circular ring, were examined; these black areas outside the circular ring were called the valid black areas. In
Figure 10a and
Figure 11a, the valid black area was characterized by a gradual increase in the absolute value of the ratio of total differentials of latitude and longitude (i.e., the TDRLON and TDRLAT values), ranging from four to positive infinity. By zooming in on this area, it was observed that the contour line distribution patterns in
Figure 10a,b were consistent, as well as those in
Figure 11a,b, meaning that the distribution pattern of total increments was consistent with the distribution pattern of total differential ratios. Consequently, it could be inferred that the error model remained applicable within the valid black area. Nevertheless, it should be noted that due to the excessively high absolute value of the total differential ratio (the TDRLON and TDRLAT values), even minimal measurement errors in the independent variables could cause significant deviations in latitude and longitude.
Further research indicated that when ΔAs = Δhs ≠ 0.1°, for instance, or ΔAs = Δhs = 0.5° or ΔAs = Δhs = 3°, the conclusions regarding the valid black areas and the invalid circular ring still held true.
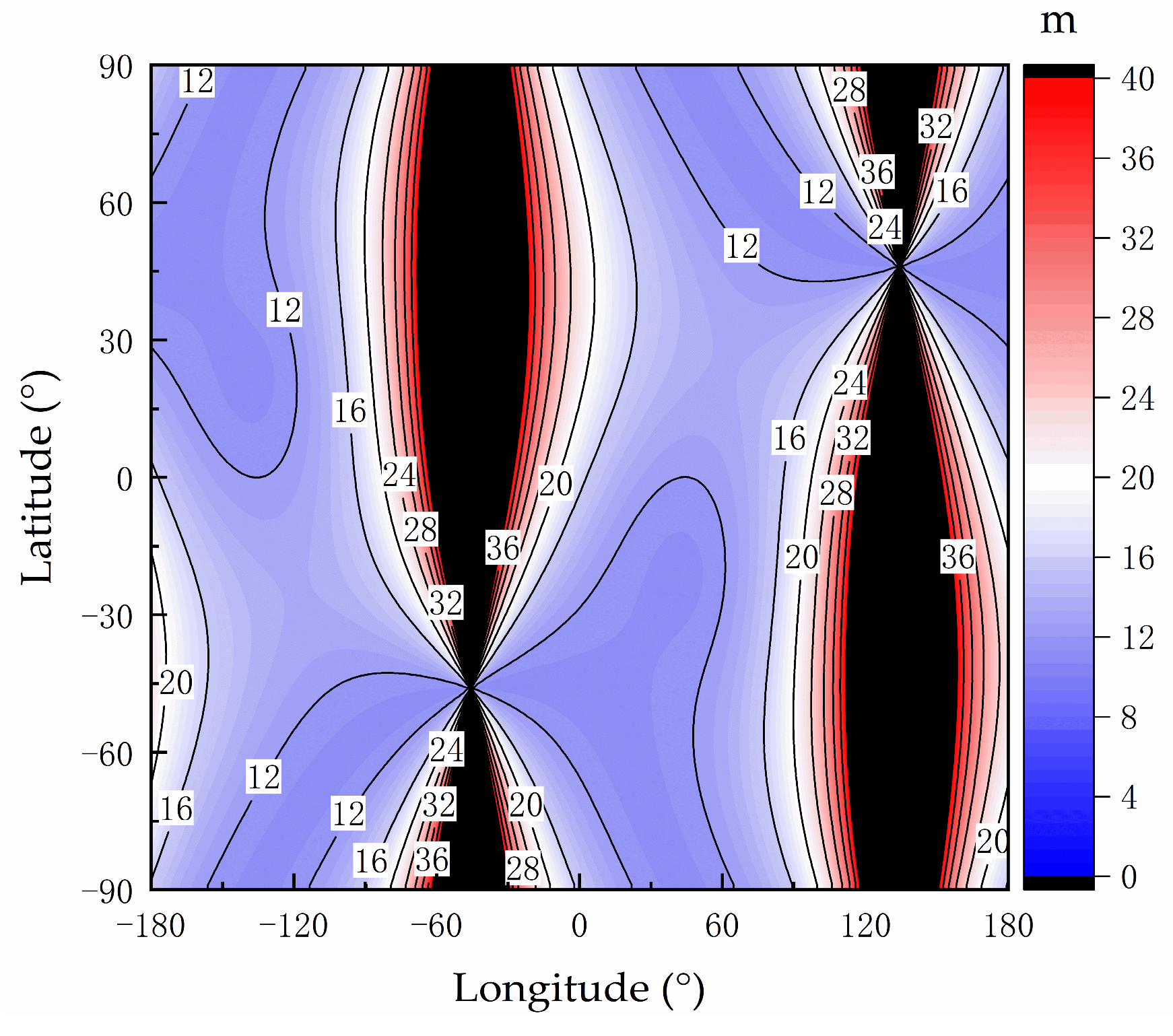
4.2. Second Case Analysis: ΔAs Differs from Δhs
This case analyzed the situation when ΔAs ≠ Δhs. This case could include many possibilities, such as ΔAs = −2 × Δhs, ΔAs = 5 × Δhs, and ΔAs = −Δhs.
This study selected cases of Δ
As = −2 × Δ
hs, Δ
As = 0.2°, and Δ
hs = −0.1° for the analysis, and two global distribution maps were obtained by the calculation process described in
Section 4.1, as shown in
Figure 12 and
Figure 13. Similar to
Figure 10 and
Figure 11,
Figure 12a and
Figure 13a display the total differential ratios, and
Figure 12b and
Figure 13b depict the total increments. After analysis, it was concluded that the results obtained in the colored and black areas in
Section 4.1 still held true. In
Figure 12 and
Figure 13, the global error model remained valid in the colored region; the black areas contained the region where the proposed error model was invalid; and the error model remained applicable within the valid black area.
Finally, when the ratio of ΔAs to Δhs is other value, the same conclusions for both the colored region and the black region could be drawn.
4.3. Summary
The results presented in
Section 4.1 and
Section 4.2 demonstrate that when the absolute value of the measurement deviation was less than 5° (|Δ
As| ≤ 5°, |Δ
hs| ≤ 5°), the proposed error model’s accuracy was validated. This also confirmed the correctness of the conditions under which the proposed error model was valid.
Conversely, when the absolute value of the measurement deviation exceeded 5° (|ΔAs| > 5°, |Δhs| > 5°), the proposed error model’s accuracy decreased.