1. Introduction
Degenerative and inflammatory bone-joint disorders are significant health concerns that affect millions of individuals worldwide. In developed countries, approximately half of the chronic diseases in individuals over 50 years old are of orthopedic origin [
1]. This has increased demand for surgical interventions such as total joint replacements, highlighting the need for advanced biomedical implants.
At present, 70–80% of orthopedic implants in clinical use are composed of metallic biomaterials [
1,
2,
3]. These materials are widely employed in a broad range of orthopedic and dental applications, including hip and knee prostheses, spinal instrumentation, fixators, anatomical plates, and maxillofacial surgery [
1,
4]. Metallic biomaterials are preferred for their high mechanical strength, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance [
1,
2,
3].
Among these, cobalt–chromium–molybdenum (CoCrMo) alloys are regarded as optimal candidates for total joint replacements due to their exceptional fatigue strength, corrosion resistance, and well-established clinical history. CoCrMo alloys find application in a variety of medical devices, including hip and knee implants, particularly in joint surfaces, dental implant skeletal structures, bridge supports, mechanical heart valves, and pedicle screws and plates in spine implants [
5,
6,
7].
Titanium and its alloys are also extensively used due to their low density, high corrosion resistance, and elastic modulus values that approximate those of cortical bone [
8,
9,
10]. Ti alloys are used in orthopedics in bone plates, screws, hip-knee implant components, dental screw-type root implants, spinal systems such as vertebral cages and interbody fusion implants, and cranial and maxillofacial implants [
5,
11].
Furthermore, precipitation-hardened stainless steels, particularly 17-4 PH, present a compelling alternative due to their high strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. 17-4 PH stainless steel alloys are utilized in a variety of applications, including fixation elements such as plates, screws, and nails; dental instruments; implant-supported components; short-term orthopedic implant applications; and surgical instruments [
14,
17,
18].
Polymers, particularly PEEK, exhibit a degree of flexibility comparable to that of bone, a low elastic modulus, and resistance to corrosion. However, their mechanical strength is inferior to that of metals. Consequently, they are employed more frequently in low-load-bearing areas or in conjunction with metal implants [
19,
20]. Given the inherent advantages and limitations of each material, the selection of an implant should be made in accordance with the clinical needs and the intended application of the implant.
In order to further enhance the performance of metallic materials, ceramic reinforcements are increasingly being incorporated into metal matrix composites (MMCs). Boron carbide (B
4C) is particularly noteworthy as a reinforcing phase due to its high hardness, low density, excellent wear resistance, and notable corrosion resistance [
21,
22,
23].
The powder metallurgy (PM) method is a versatile and cost-effective manufacturing technique that facilitates the homogeneous distribution of ceramic particles within metallic matrices. PM facilitates precise porosity control and allows for the fabrication of complex geometries with high surface quality [
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29].
Despite significant advancements in the field, orthopedic implant failure remains a persistent challenge, often attributed to mechanical and chemical factors such as wear, corrosion, and stress shielding [
30,
31,
32,
33]. It is important to note that when the elastic modulus of an implant material exceeds that of bone, stress shielding can occur. This phenomenon can lead to bone resorption and eventual implant loosening [
31]. Additionally, the degradation of passive oxide films formed on the implant surface due to mechanical wear can accelerate corrosion [
32,
33].
Recent research has begun to explore the effects of B
4C reinforcement on the properties of CoCrMo and Ti alloys. For instance, Grądzka-Dahlke et al. demonstrated improvements in mechanical and tribological behavior with B
4C-reinforced CoCrMo [
34]. Toptan et al. reported that B
4C incorporation enhances the corrosion resistance of Ti composites, although excessive B
4C content may induce localized corrosion due to increased porosity [
35]. In a similar vein, Mohanavel and Vijayakumar [
36] demonstrated enhancements in hardness and compressive strength. Concurrently, Yoganandam et al. observed augmented mechanical performance in Ti composites reinforced with 5% B
4C [
21].
While these individual studies offer valuable insights, there remains a lack of comparative, systematized evaluations of B4C-reinforced CoCrMo, Ti, and 17-4 PH alloys using identical fabrication and testing protocols. The objective of this study is to address this research gap by evaluating the microstructural, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of these alloys reinforced with varying B4C contents. The ultimate objective is to ascertain compositions that demonstrate optimal performance for load-bearing orthopedic and dental implant applications.
This work makes a significant contribution to the field by providing a comprehensive analysis using a unified experimental design, enabling direct comparison of three widely used biomedical alloys. Furthermore, the incorporation of Weibull statistical analysis serves to enhance the reliability and predictive value of the reported findings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
The fabrication of B4C-reinforced CoCrMo, Ti, and 17-4 PH alloys was accomplished through the implementation of conventional powder metallurgy (PM) techniques. The raw materials included cobalt powder with 99.5% purity, produced by Alfa Aesar, chromium, molybdenum, and titanium powders with purity levels ranging from 99.5% to 99.9% and a particle size of 44 μm, produced by Nanokar Nanotechnology. The 17-4 PH stainless steel powder, characterized by a grain size of 22 μm and a purity of 99.9%, is produced by (Carpenter Technology, Philadelphia, PA, USA). The boron carbide (B4C) powder employed as the reinforcing phase exhibited a purity of 99%, a density of 2.52 g/cm3, and a particle size ranging from 100 to 150 μm, produced by (Nanokar Nanotechnology, Istanbul, Türkiye).
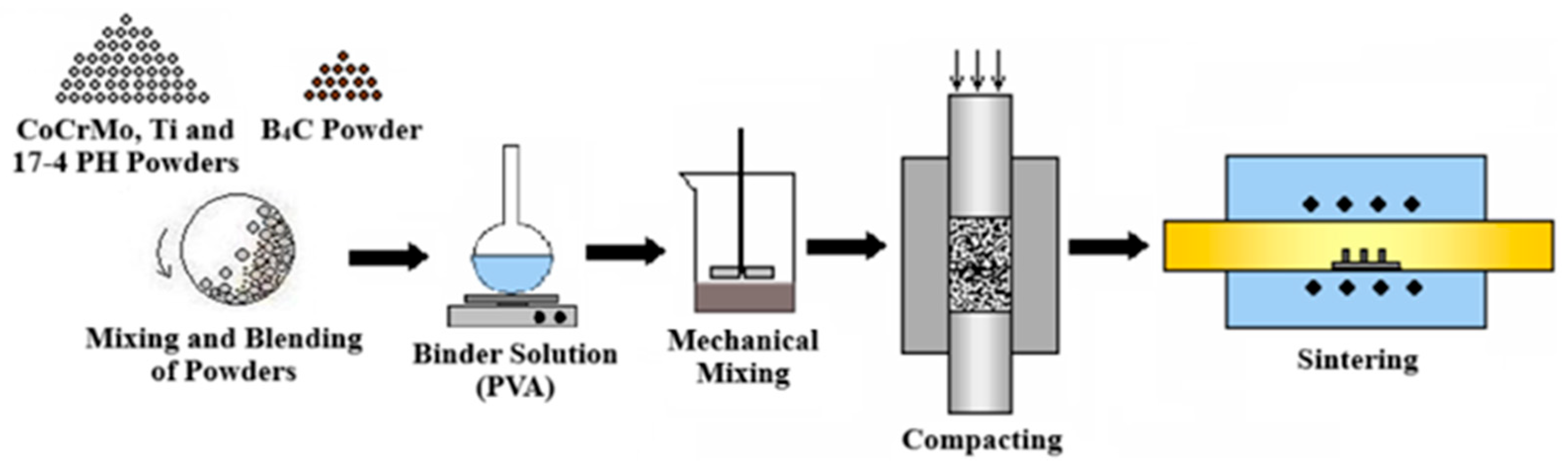
As illustrated in
Figure 1, the PM process is comprised of three distinct steps: mechanical alloying, uniaxial cold pressing, and vacuum sintering. The addition of a 0.6% PVA aqueous binder solution (1–3 wt%) was added to ensure adequate particle cohesion. The B
4C and metal powder mixtures were mechanically alloyed in a ball mill (MSE Technology, BM-S38003, Istanbul, Türkiye) for 20 h at 380 rpm using zirconia balls (3 mm diameter) with a ball-to-powder ratio of 10:1.
The mixture of powders was subjected to a cold-pressing process employing a uniaxial hydraulic press (MSE Technology, LP-M2S10, Istanbul, Türkiye) at pressures ranging from 400 to 450 MPa. This resulted in the formation of cylindrical green compacts with a diameter of 10 mm. Sintering was carried out in a horizontal tube vacuum furnace (MTI, GLS-1500X, New York, NY, USA) at 1200 °C for 60 min with a heating rate of 4 °C/min. This step led to a densification of the specimens, achieved by facilitating interparticle bonding and eliminating residual porosity.
2.2. Microstructural Characterization
The microstructures of the sintered composites were examined using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (JEOL NeoScope JCM-5000, Tokyo, Japan). Samples were analyzed to observe the distribution of B4C particles, the porosity, and the integrity of the phases. In order to ascertain the phase structure and crystal properties of B4C-reinforced Ti alloys, X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) (Rigaku, Smartlab, Tokyo, Japan) was conducted in the 20–90° 2θ range.
2.3. Hardness and Wear Test
Vickers microhardness measurements were performed using a hardness tester (Zwick/Roell, ZHU 187.5, Kennesaw, GA, USA). The wear resistance of the materials was assessed using a pin-on-disk tribometer (Devotrans, DVT DA 6, Istanbul, Türkiye) with SiC disks, applying a constant load and a wear track length of 20 m.
2.4. Elastic Modulus Measurement
The elastic modulus was determined non-destructively using ultrasonic pulse-echo testing with a 4 MHz probe (GE, USM Go+, Boston, MA, USA). Longitudinal (V
L) and transverse (V
T) wave velocities were recorded and substituted into the elastic modulus equation:
where the variable ρ denotes the sample density [
37].
2.5. Electrical Conductivity Measurement
The International Annealed Copper Standard is a method for calculating the electrical conductivity of a material based on the electrical conductivity of annealed copper at room temperature and 100% purity. This conductivity is 5.8 × 107 S/m, which is designated as 100% IACS. Electrical conductivity was measured using an eddy current device (EtherCheck, Ether NDE, St. Albans, UK), and values were reported as a percentage of the International Annealed Copper Standard (%IACS).
2.6. Electrochemical Corrosion Tests
Electrochemical testing was conducted in simulated body fluid (SBF; pH 6.6) at room temperature using a potentiostat (Gamry, Interface 1000, Philadelphia, PA, USA). The three-electrode cell configuration was utilized in this study. The open-circuit potential (OCP) was initially monitored until stabilization was achieved. Subsequently, potentiodynamic polarization scans were conducted from −500 mV to +1500 mV at a scan rate of 1 mV/s. The corrosion rates were derived using Tafel extrapolation, a method of calculating corrosion rates from the anodic and cathodic potentials. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was performed at OCP using a 5 mV AC signal across a frequency range of 105 to 10−1 Hz.
2.7. Statistical Analysis: Weibull Distribution
The Weibull analysis method is a comprehensive approach to understanding the reliability and variability of biomedical alloy performance. The identified shape (β) and scale (η) parameters facilitate robust predictions and critical selection criteria tailored to specific biomedical applications. These rigorous statistical assessments serve to reinforce material choices and reliability considerations, which are vital for patient safety and implant longevity in biomedical engineering.
The Weibull statistical analysis was employed to quantitatively assess the reliability and variability of six key properties of the studied biomedical alloys: The parameters of analysis included hardness (HV3), wear (%), elastic modulus (GPa), electrical conductivity (%IACS), corrosion rate (mm/year), and surface oxide resistance (Ω cm
2). The parameters of the Weibull distribution, namely the shape parameter (β) and the scale parameter (η), were determined through maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) by employing the Weibull cumulative distribution function (CDF), which is defined as follows:
where F(x; β, n) is employed to denote the cumulative probability of failure or occurrence falling below the measured value x. The shape parameter (β) is a measure of data dispersion, and it is associated with the consistency of results. The scale parameter (η) is typically set at approximately 63.2% cumulative probability. The confidence intervals for each parameter were calculated via bootstrap resampling with 5000 iterations, thereby ensuring the robustness of the estimation and the statistical rigor of the evaluation of the mechanical integrity and corrosion resistance of the alloys.
3. Results and Discussion
The production of B4C-reinforced CoCrMo, Ti, and 17-4 PH alloys through the powder metallurgy method has been demonstrated to be a successful process. The applied production process yielded a homogeneous particle distribution, with no observable cracks, phase separation, or porosity. The incorporation of high-rate B4C into the Ti matrix, a constituent of the active metals, posed significant challenges in conventional methodologies. However, this study successfully overcame these obstacles by employing the PM process.
3.1. Microstructural Analysis
The XRD patterns of the pure Ti exhibit characteristic α-Ti phase peaks. Peaks corresponding to B
4C were observed in specimens to which B
4C had been added. Increasing B
4C content increased the peak intensity (
Figure 2). The incorporation of 5% B
4C resulted in the maintenance of peak intensity and number, though minor shifts were observed, indicating potential lattice distortion. At 10% and 15% B
4C, the peak number and intensity decreased, indicating possible reduced crystallinity or the onset of amorphization, which can be followed from the corrosion test results. The 20% B
4C sample exhibited a marginal enhancement in peak definition, which may be indicative of microstructural reorganization or phase redistribution [
29,
38,
39].
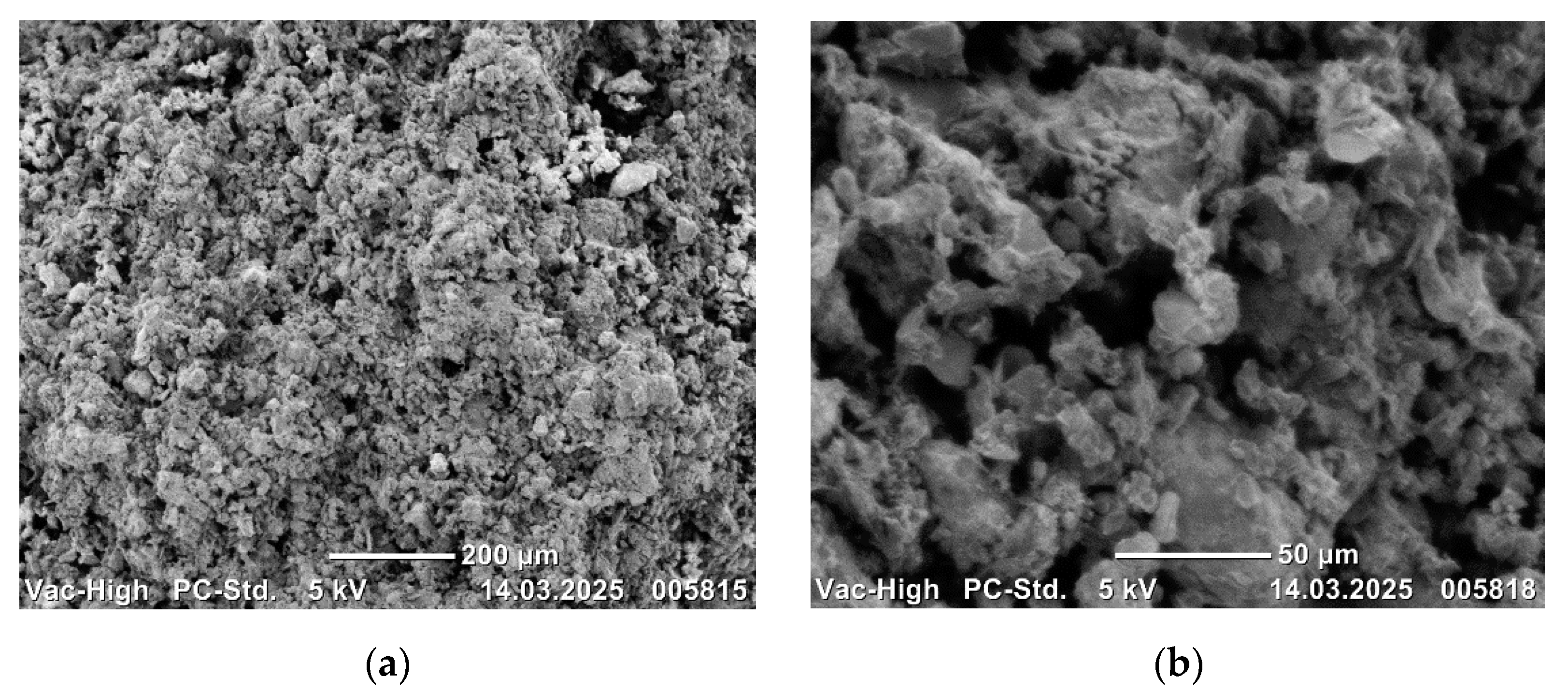
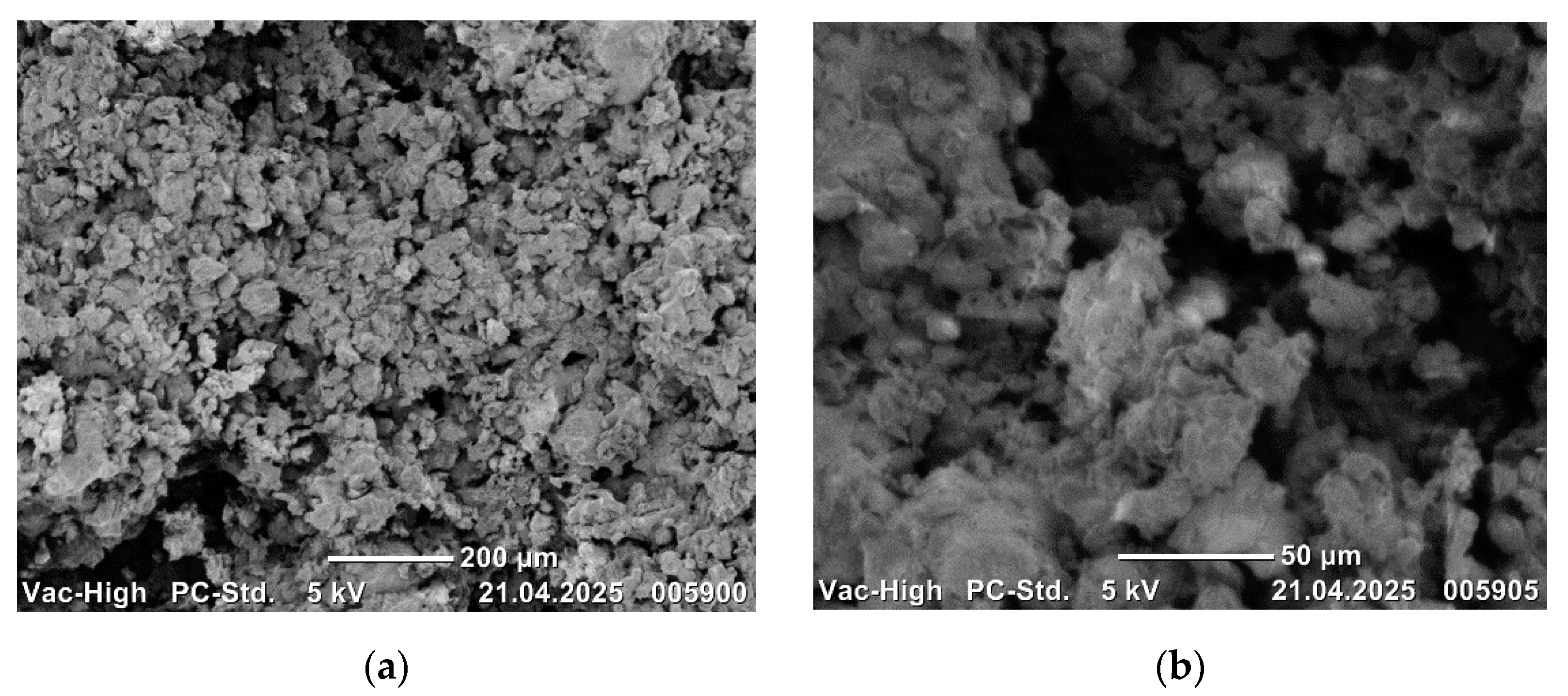
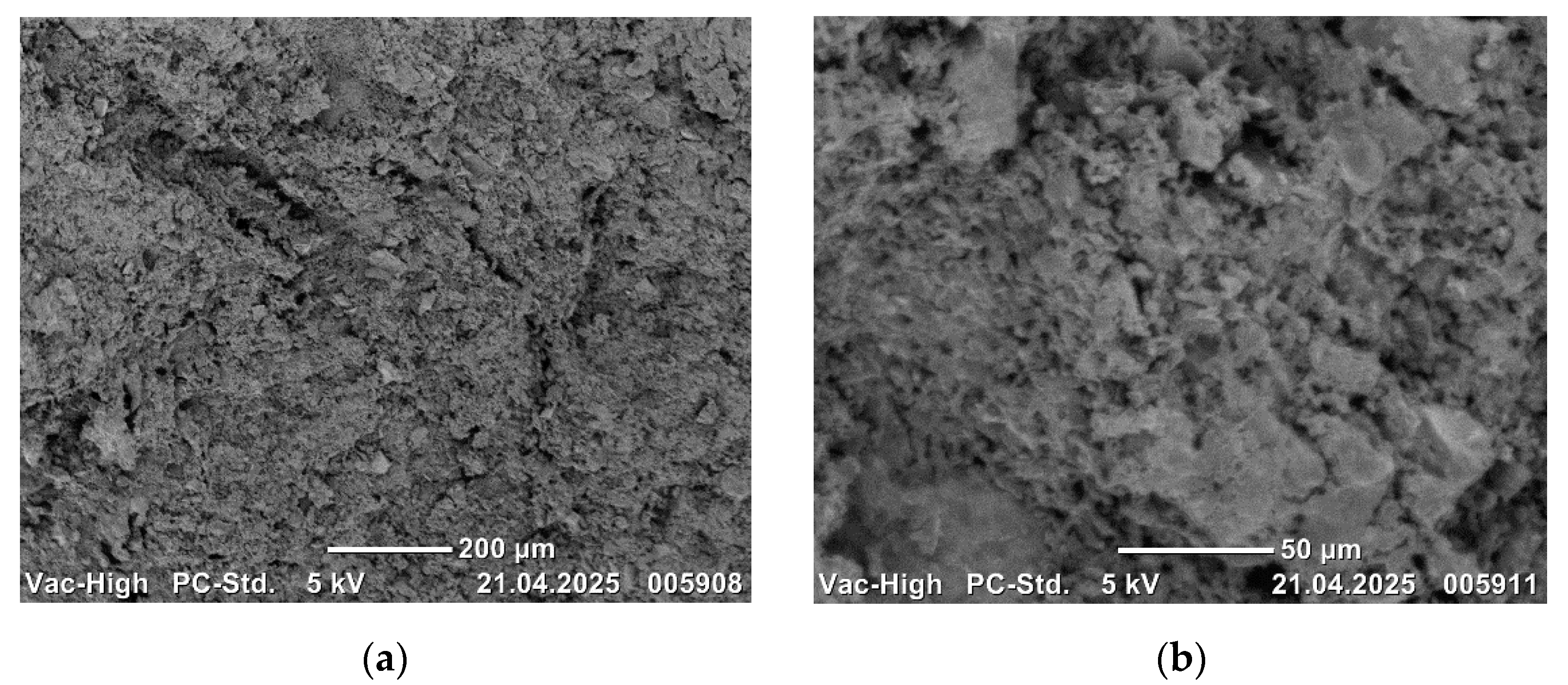
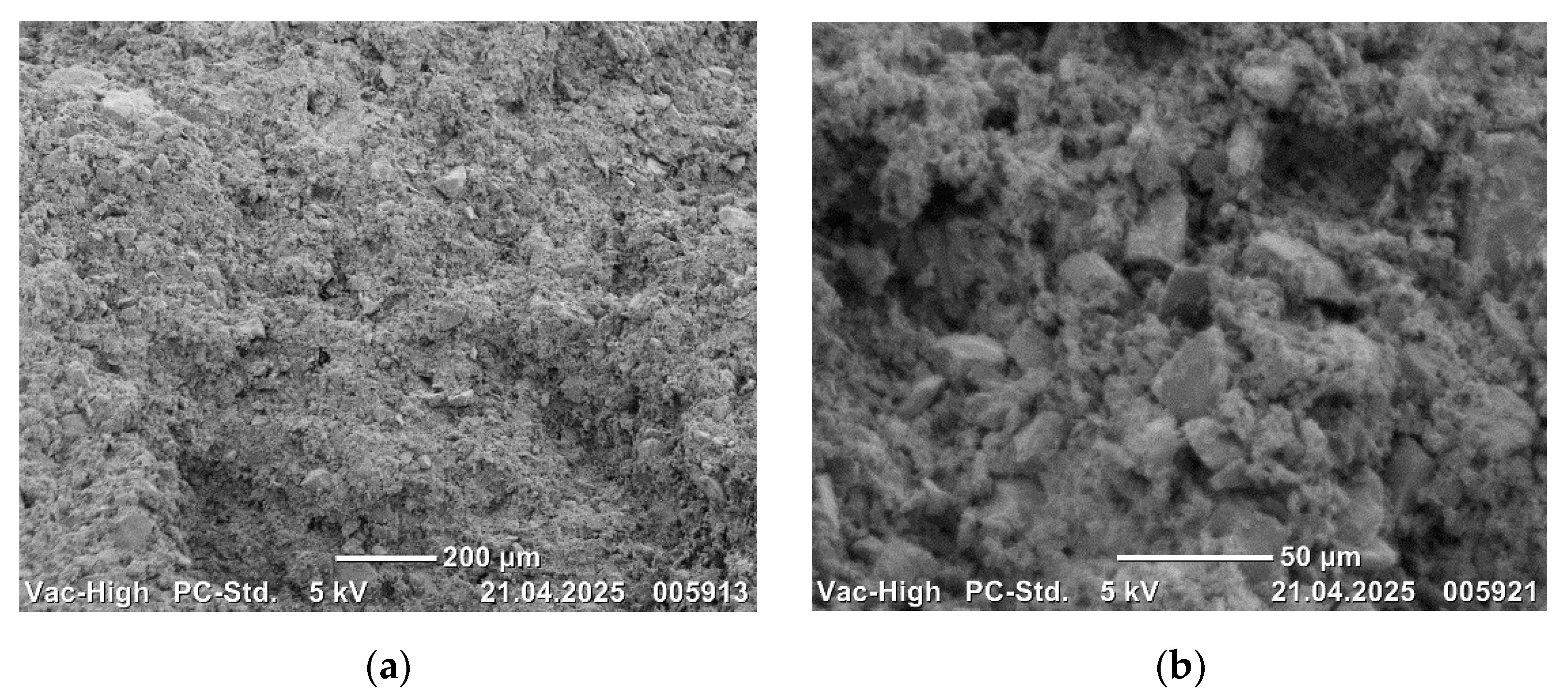
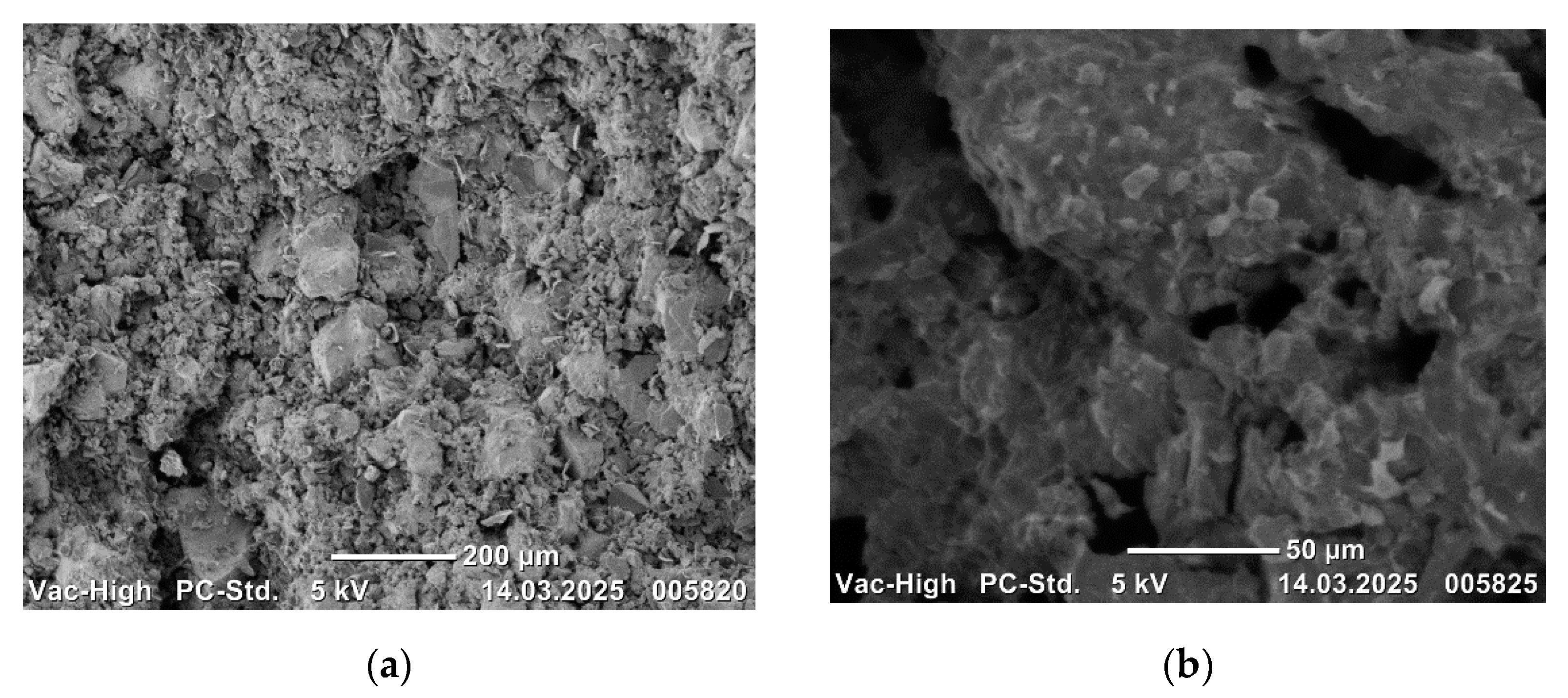
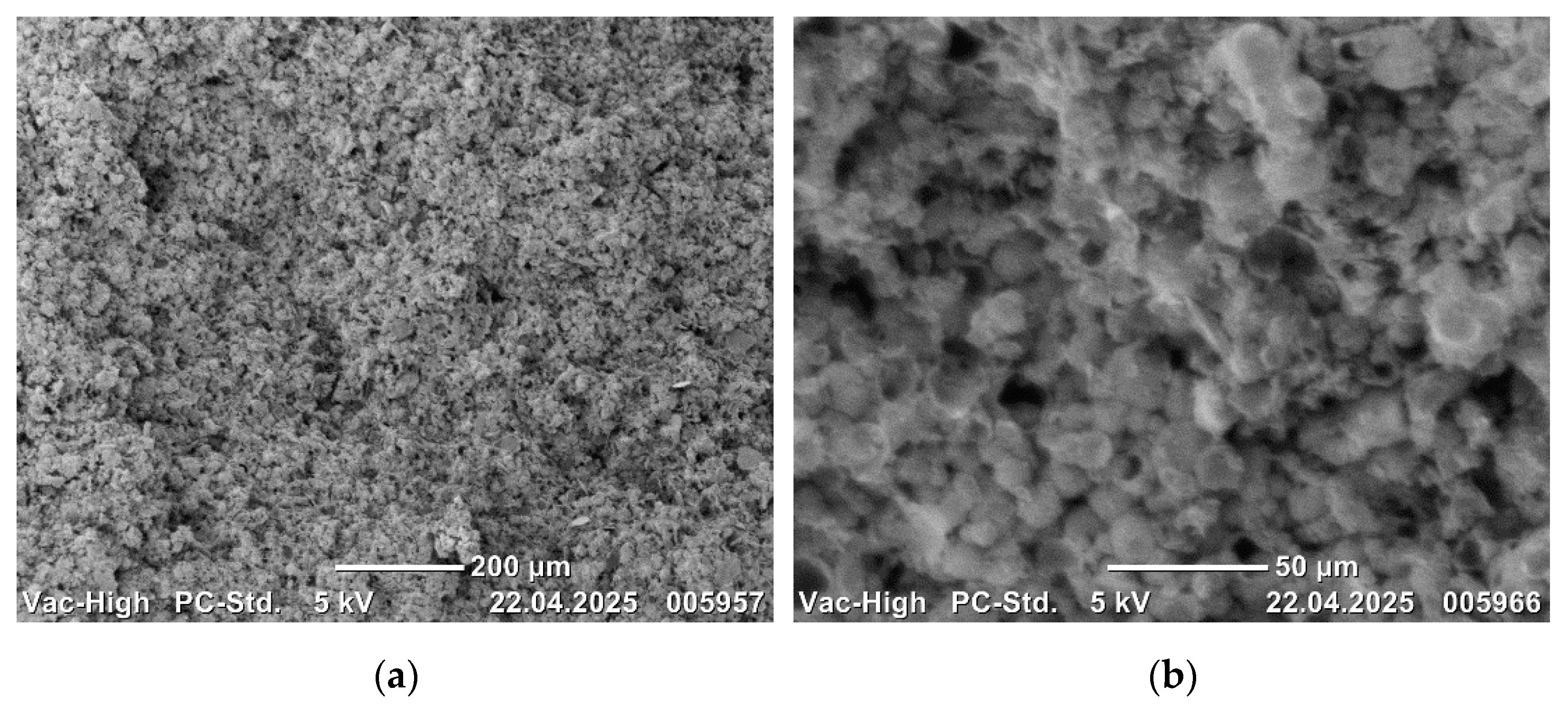
Scanning electron microscope images of the sintered composites are presented in
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11,
Figure 12,
Figure 13 and
Figure 14. Each alloy group (CoCrMo, Ti, and 17-4 PH) was subjected to a process of reinforcement, characterized by an increase in the proportion of B
4C. The compositions exhibited a uniform distribution of B
4C particles, devoid of any discernible porosity, cracks, or phase agglomeration. This observation signifies the efficacy of the mixing and sintering processes.
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5 and
Figure 6: SEM images of CoCrMo with 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% B
4C.
Scanning electron microscope images of CoCrMo alloys are presented in order of increasing B
4C weight ratio. SEM images of CoCrMo-5B
4C are presented in
Figure 3, CoCrMo-10B
4C in
Figure 4, CoCrMo-15B
4C in
Figure 5, and CoCrMo-20B
4C in
Figure 6, both at 200 μm and 50 μm sizes.
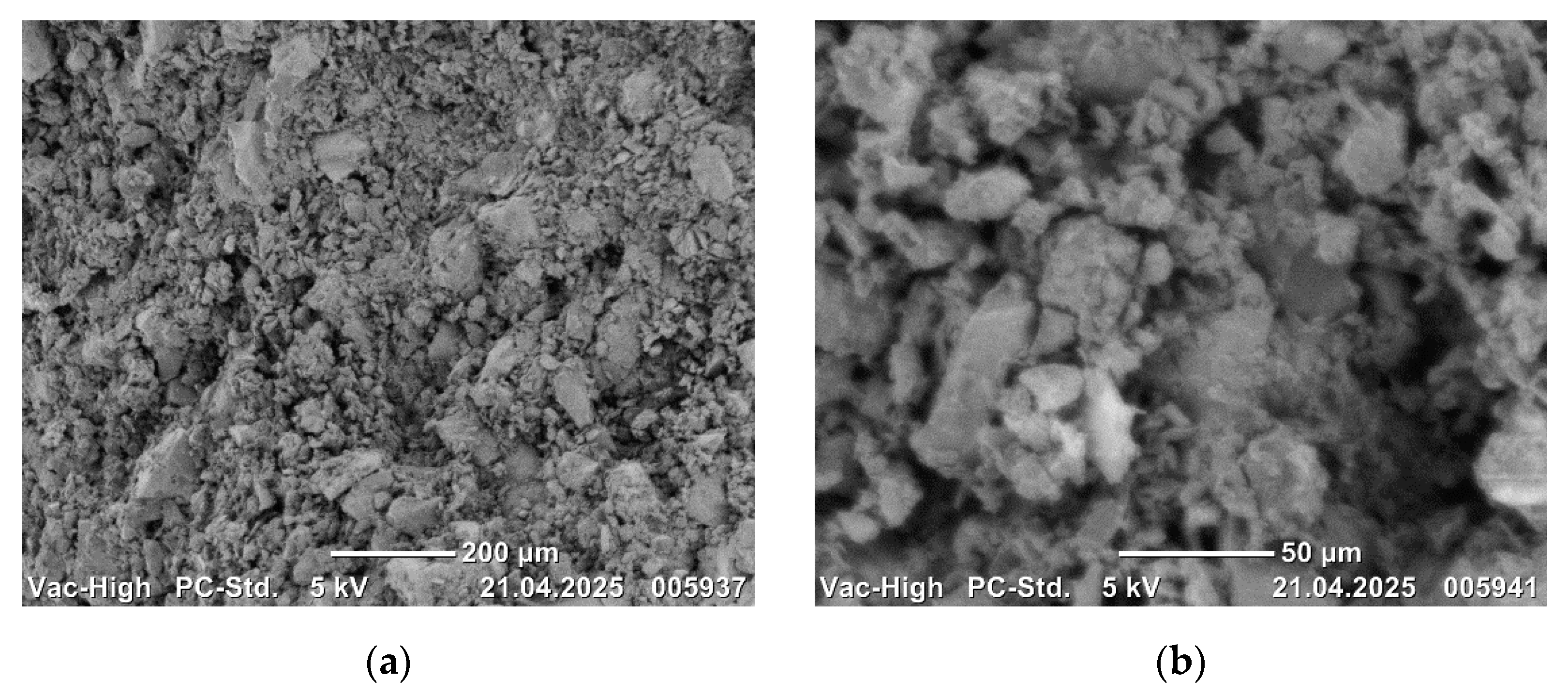
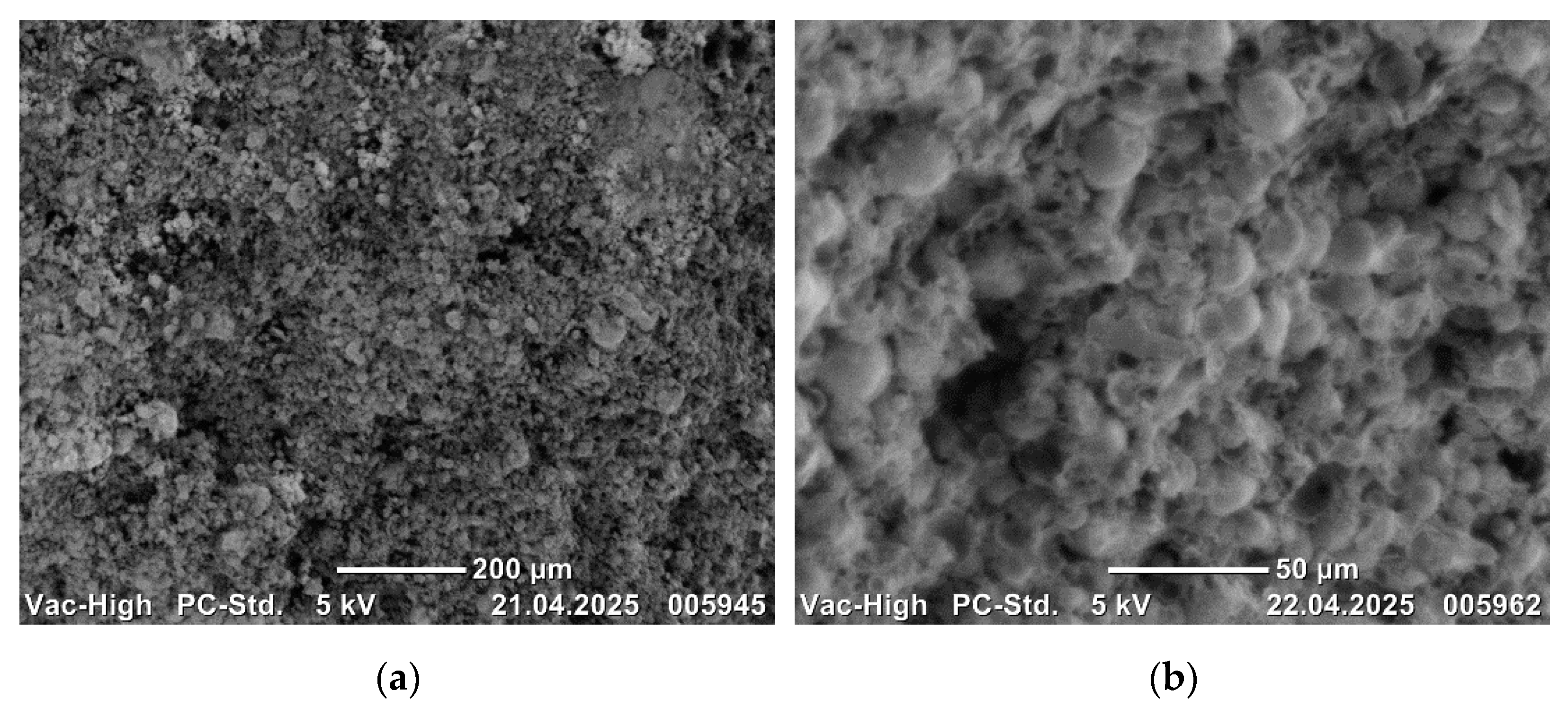
Scanning electron microscope images of 17-4 PH alloys are presented in order of increasing B
4C weight ratio. SEM images of 17-4PH-3B
4C are presented in
Figure 11, 17-4PH-6B
4C in
Figure 12, 17-4PH-9B
4C in
Figure 13, and 17-4PH-12B
4C in
Figure 14.
The metal powders and B
4C additives utilized in CoCrMo, Ti, and 17-4 PH alloys are characterized by their precise dimensional parameters and homogenous distribution, as evidenced by the SEM images, which reveal the presence of complex-shaped structures. The incorporation of complex and irregularly shaped powders has been demonstrated to enhance strength after the pressing process (
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11,
Figure 12,
Figure 13 and
Figure 14).
Figure 11,
Figure 12,
Figure 13 and
Figure 14: SEM images of 17-4 PH with 3%, 6%, 9%, and 12% B
4C.
The presence of increasing B
4C additives in the alloy structures is evident in the SEM images. The metal powders have formed suitable bonds with each other and with the B
4C additive. The homogeneous microstructures of the alloys are clearly evident in the SEM images. The observation of bond formation and homogeneous distribution suggests that the alloys have undergone sufficient sintering. No defects, such as macro or micro pores or cracks/porosity, that may have a negative effect on the mechanical properties of the alloys, were observed in the microstructures (
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10,
Figure 11,
Figure 12,
Figure 13 and
Figure 14).
The mechanical and corrosion test results in this study were obtained through five repeated experiments. As illustrated in
Figure 15,
Figure 16,
Figure 17,
Figure 18,
Figure 19 and
Figure 20, the data distributions are represented visually, accompanied by the maximum and minimum points. The standard deviations of the experiments are as follows: hardness 25 HV3, wear 0.1%, elastic modulus 40 GPa, conductivity 2% (%IACS), corrosion rate 0.3 mm/year, and surface oxide resistance 40 Ω cm
2, respectively.
3.2. Hardness and Wear Performance
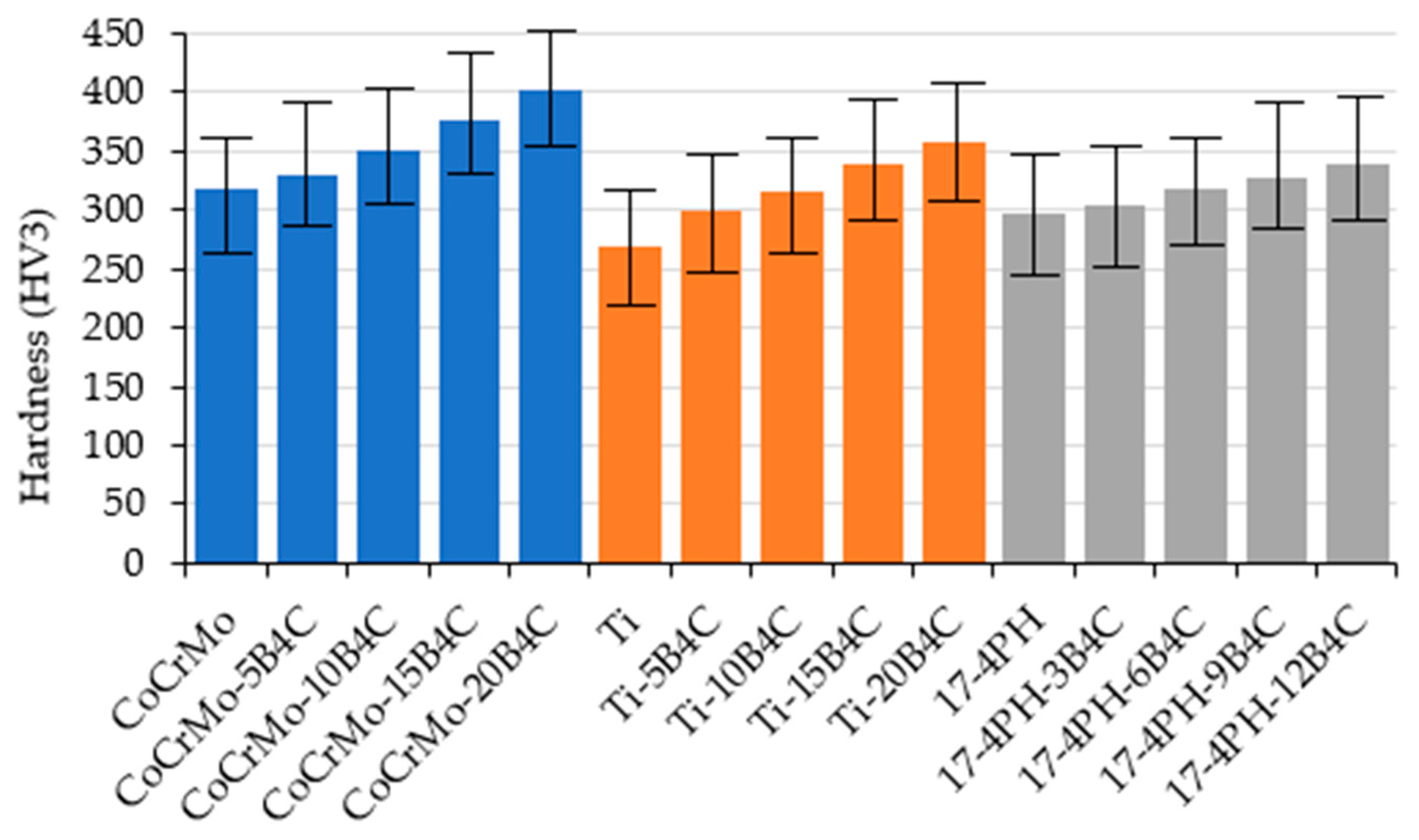
The Vickers microhardness test results (
Figure 15) demonstrate a regular increase in hardness with increasing B
4C content. The highest recorded hardness was observed in the CoCrMo-20B
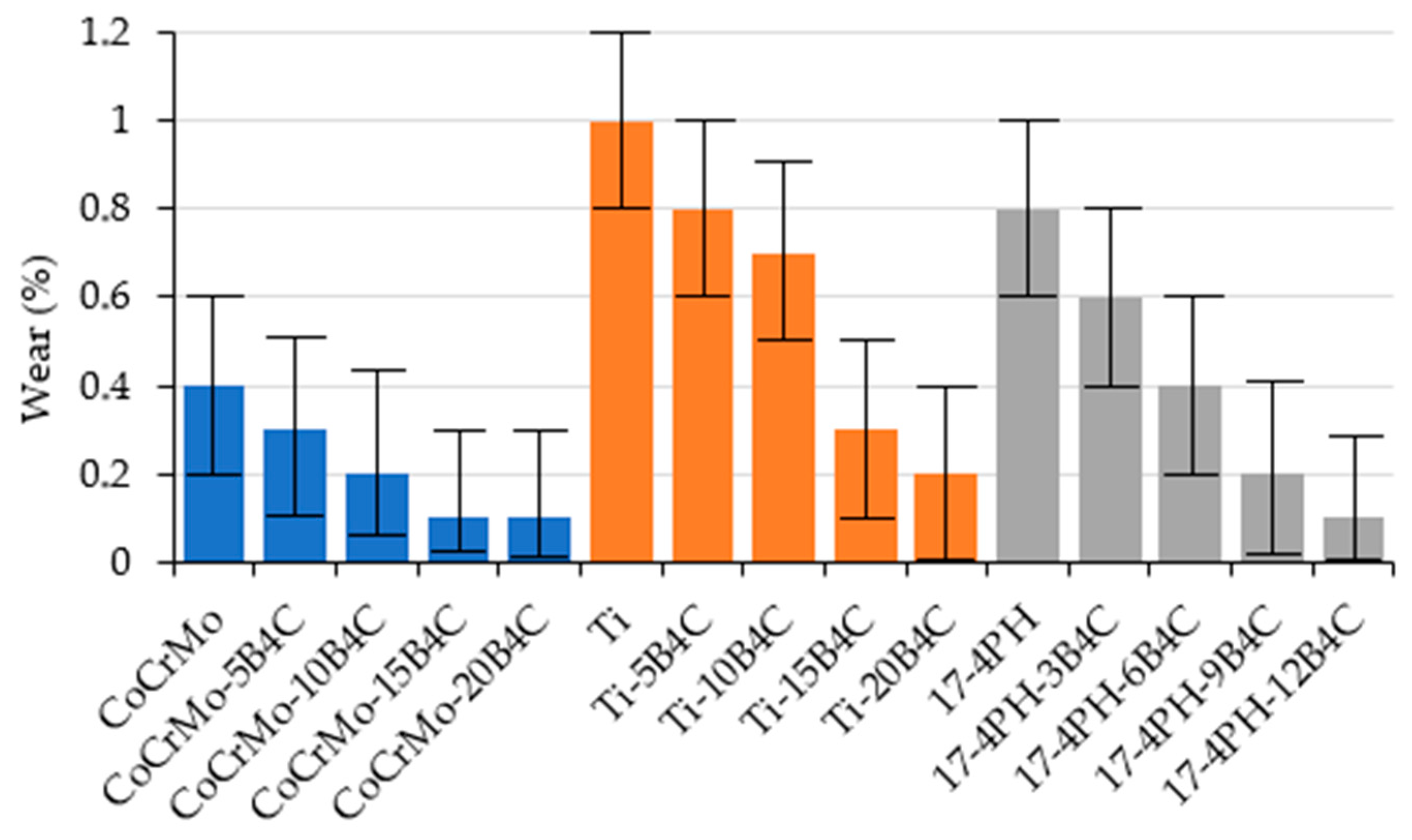
4C specimen. This increase is attributed to the enhanced resistance of the ceramic phase to plastic deformation. In a similar manner, wear tests (
Figure 16) demonstrated that the wear loss decreases as the B
4C content increases, particularly in Ti-B
4C composites. These findings are consistent with the trends reported by Mohanavel and Vijayakumar [
36] and Yoganandam et al. [
21].
The wear performance of the materials was evaluated through pin-on-disk testing. As illustrated in
Figure 16, there was a substantial decrease in wear rates with the incorporation of B
4C in all alloy groups. The Ti-B
4C composites demonstrated the most optimal wear resistance, particularly the Ti-20B
4C.
3.3. Elastic Modulus
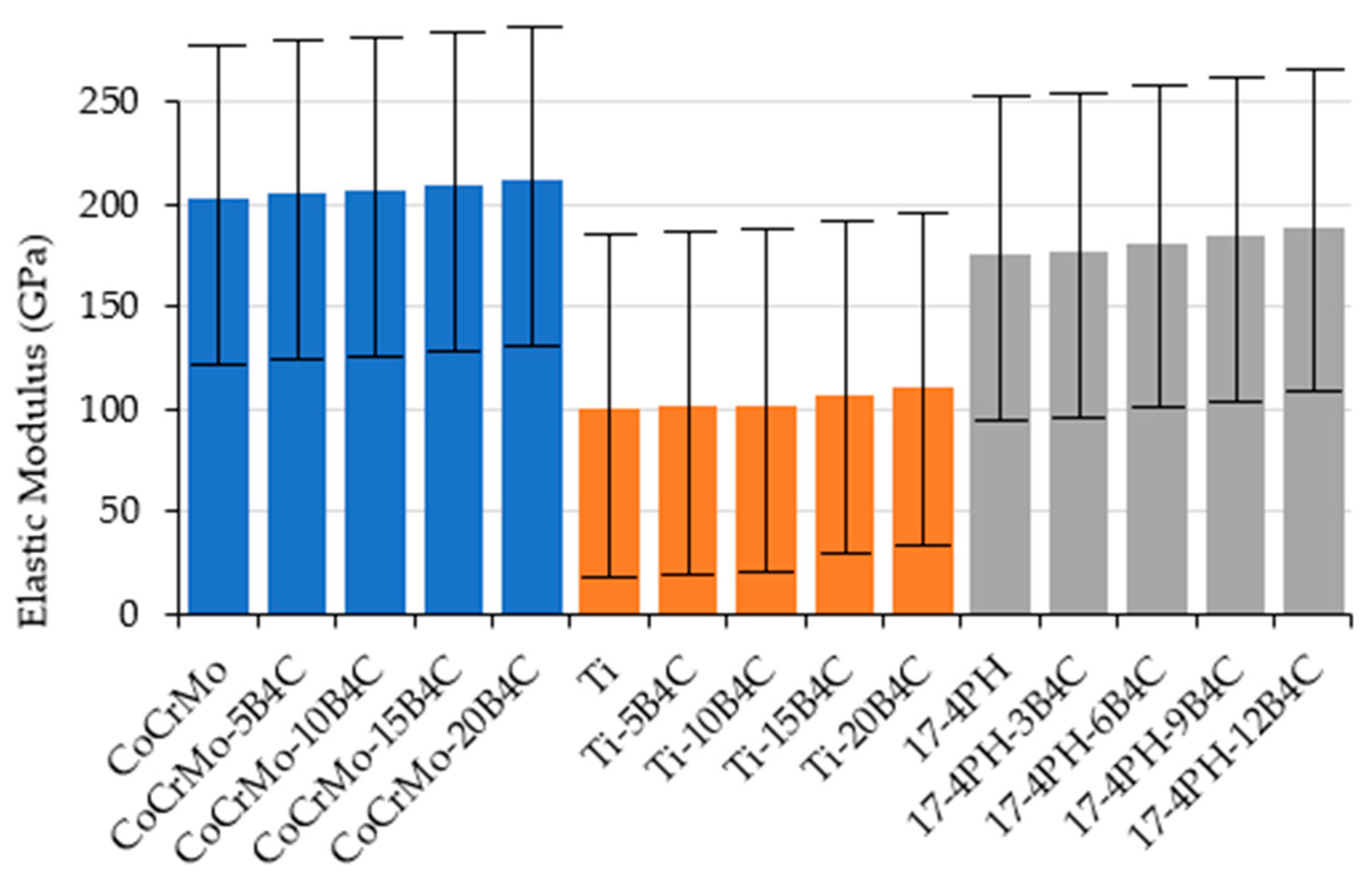
The elastic modulus values, as measured by the ultrasonic pulse-echo method (
Figure 17), demonstrated a positive correlation between the elastic modulus and the B
4C content. While CoCrMo-B
4C samples exhibited the highest values, Ti-B
4C composites have the potential to mitigate the stress-shielding effect by offering elastic modulus values that approximate those of bone. This is of paramount importance in the context of ensuring biomechanical compatibility between the implant and the bone [
30,
31].
3.4. Electrical Conductivity
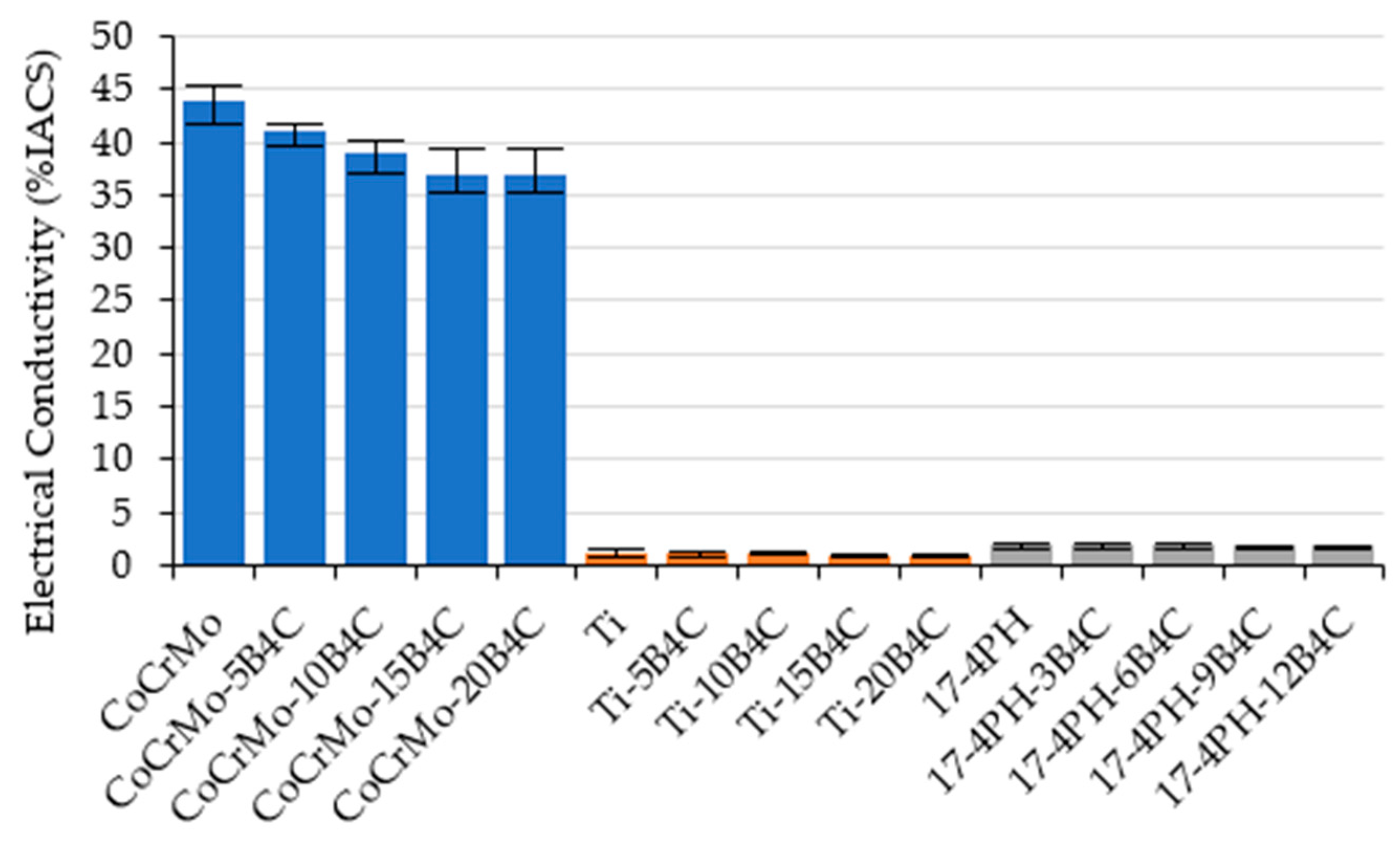
Conductivity measurements (
Figure 18) demonstrated a decline in conductivity across all groups, attributable to the insulating nature of B
4C. The decrease was more pronounced in Ti alloys. This is not a significant disadvantage in biomedical applications because the primary functions of implants are mechanical load bearing and biocompatibility.
3.5. Corrosion Behavior
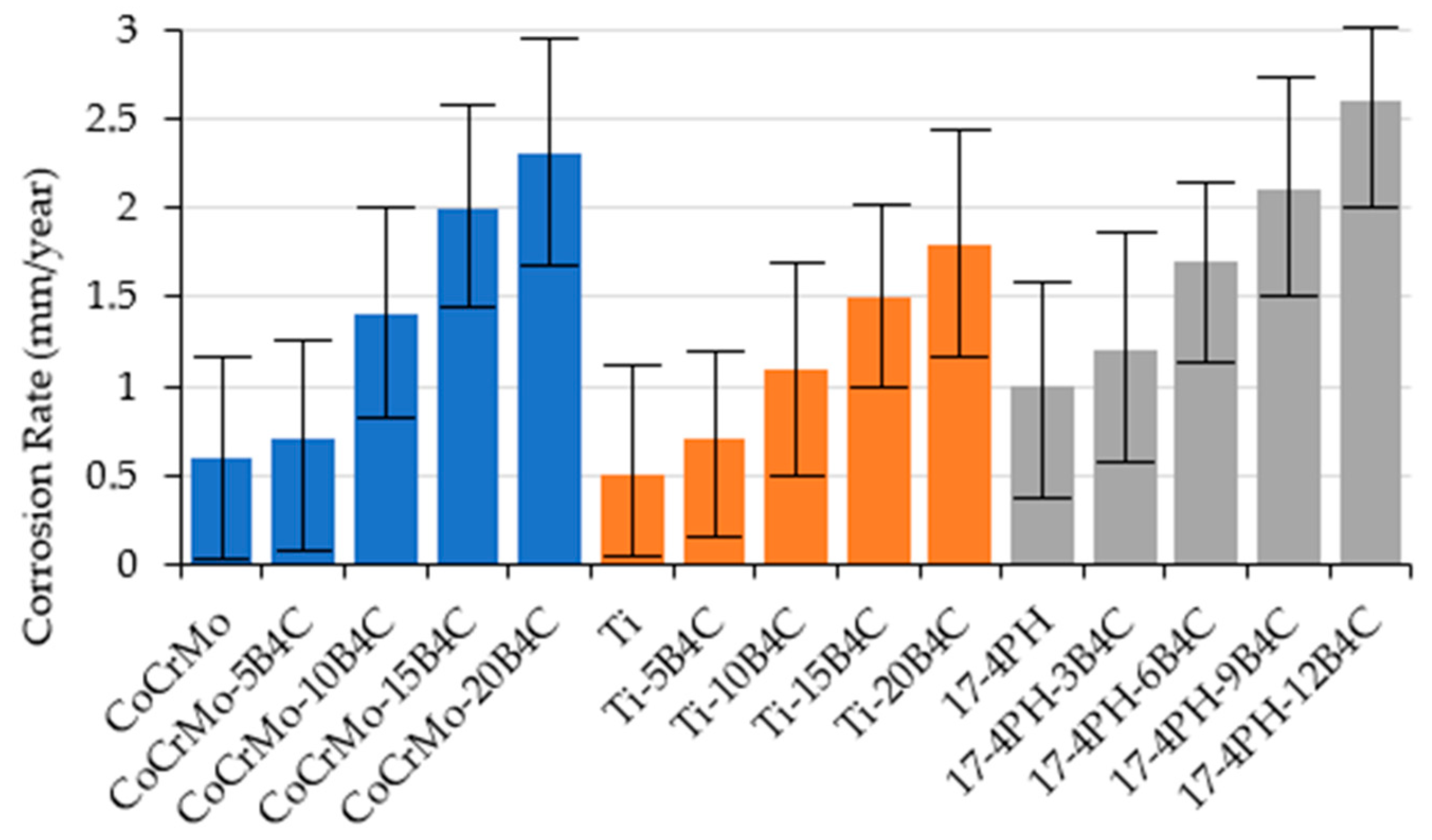
The potentiodynamic polarization measurements (
Figure 19) demonstrate a positive correlation between the corrosion rate and the amount of B
4C reinforcement. This phenomenon can be attributed to the formation of microgalvanic cells and enhanced surface interactions between B
4C and the matrix. The corrosion rate was found to be highest in the 17-4PH-12B
4C specimen. The EIS analyses (
Figure 20) demonstrated a decline in surface oxide film resistance with an increase in the B
4C ratio. This decline was particularly evident in the 17-4 PH group. The findings of Toptan et al. [
35] lend further support to these results.
Throughout the production process, the morphology, particle size, and particle size distribution of the B4C particles used in composite alloys were kept constant, and only the reinforcement ratio was changed. Therefore, the effects of these factors on the corrosion behavior of B4C particles were neglected in the study.
Upon the addition of B4C to the titanium matrix, a reaction occurs between the B4C particles and the titanium, resulting in the formation of boride (TiB) and carbide (TiC) phases. These ceramic-like phases act as reinforcement particles dispersed in the titanium matrix. The presence of boride and carbide phases has been observed to impede the integrity of a passive oxide layer, thereby compromising its stability and functionality. This phenomenon can result in the development of microgalvanic cells, which, in turn, can precipitate local corrosion, such as pitting corrosion. The passive layer is susceptible to damage from various ions, particularly in physiological environments. Despite its limited corrosion resistance, the Ti-5B4C alloy provides successful results in short- and medium-term implant applications due to its high hardness, strength, and wear resistance.
3.6. Statistical Reliability—Weibull Analysis
The Weibull analysis is a statistical method that quantifies the reliability of medical devices, including implants and biomedical alloys. It identifies the causes of failures, predicts lifespan, and contributes to the development of safe, long-lasting implants for patients. The aforementioned process facilitates the enhancement of designs by identifying critical failure points and comparing the reliability of different implant materials. This is achieved by determining failure and failure rates.
In this study, a reliability analysis was conducted to ascertain the optimal B4C reinforcement ratio that should be incorporated into the implant material. This analysis was undertaken to facilitate a comparison of the degradation rate behavior and durability of different materials. The reliability results yielded a prediction of the clinical performance of the implant materials with varying additive ratios under real load conditions in the patient’s body. Thus, it was to reduce the clinical failure and revision risk levels.
Table 1 provides the calculated Weibull shape (β) and scale (η) parameters for each alloy group and output property. The shape parameter is indicative of distribution consistency, while the scale parameter is associated with the characteristic performance level for each property. These values support the graphical results presented in
Figure 21,
Figure 22 and
Figure 23 and allow for a quantitative comparison of the reliability and performance of the studied alloys.
CoCrMo demonstrates the highest mean hardness (η = 364.71) with moderate variability (β = 12.80). The 17-4 PH alloy exhibits the highest degree of consistency (β = 26.09), suggesting reliable hardness properties that are well-suited for predictable biomedical applications (
Figure 21a).
The Ti-based alloys exhibited the highest mean wear (η = 0.74), indicating a significantly higher propensity for degradation under mechanical stress. In contrast, CoCrMo alloys exhibit the lowest mean wear (η = 0.28), suggesting their superior resistance to wear in biomedical applications that demand durability (
Figure 21b).
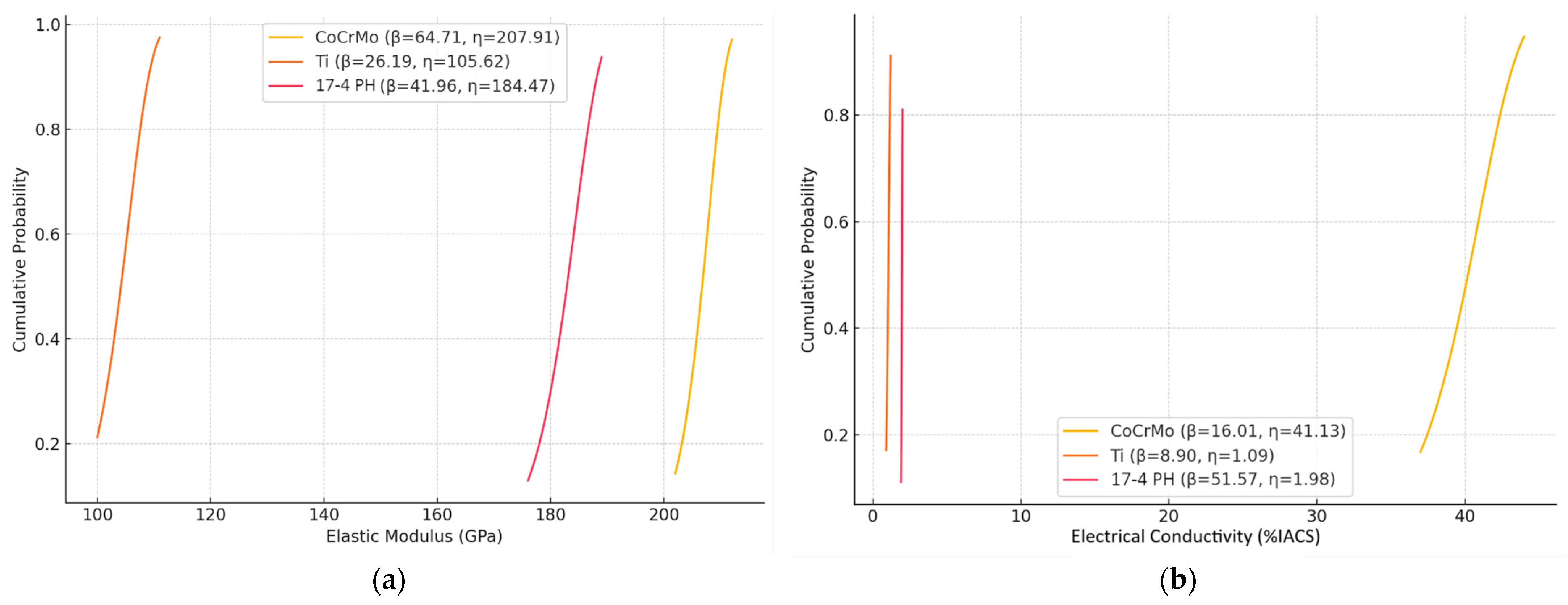
CoCrMo alloys demonstrate the highest degree of stiffness (η = 207.91), a property that is optimal for applications requiring mechanical robustness. The employment of Ti alloys in the domain of orthopedic implants is advantageous due to their considerably lower modulus (η = 105.62), which results in a reduction in stress shielding (
Figure 22a).
The CoCrMo alloy exhibits enhanced electrical conductivity (η = 41.13), rendering it well-suited for applications that demand such properties. The 17-4 PH alloy demonstrated the most consistent conductivity (β = 51.57), though at lower conductivity levels, which renders it predictable but limited in specific electrical biomedical contexts (
Figure 22b).
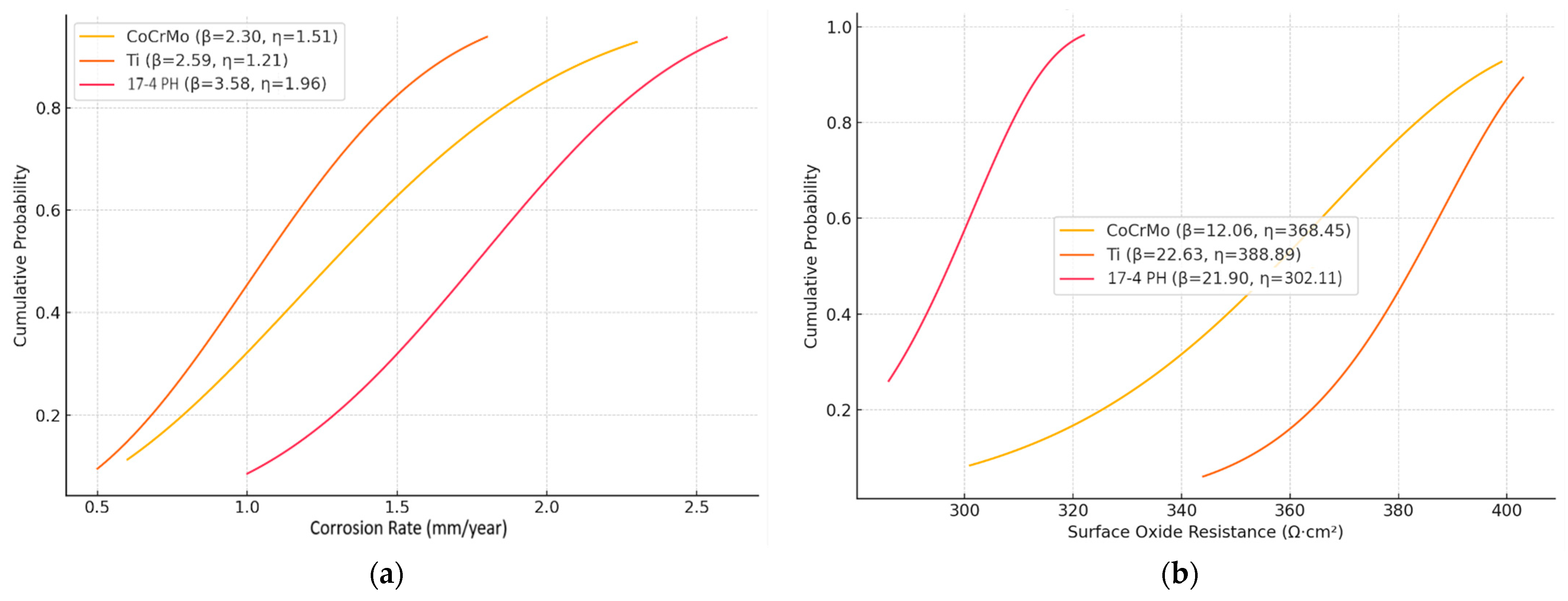
17-4 PH alloys demonstrate higher corrosion rates (η = 1.96) with the greatest consistency (β = 3.58), suggesting predictable yet elevated corrosion rates. Ti-based alloys exhibit intermediate corrosion resistance, rendering them well-suited for environments characterized by moderate levels of corrosion (
Figure 23a).
The highest oxide resistance (η = 388.89) exhibited by Ti alloys is coupled with excellent consistency (β = 22.63), making them especially suited for applications in highly oxidative biological environments. CoCrMo alloys have also demonstrated noteworthy oxide resistance (
Figure 23b).
The Weibull parameters, which have been proven to be consistent and statistically significant, offer crucial insights into the reliability and application-specific suitability of these biomedical alloys.
In these graphs, it was observed that as the β-value increased, the results became more consistent; as the η-value increased, the performance increased. The most consistent structure in terms of hardness was ascertained to be 17-4 PH (β = 26.09), and the highest average value was determined to be CoCrMo (η = 364.71) (see
Figure 21a). In the wear analysis, the lowest average value was observed in the CoCrMo group, and the most variable structure was 17-4 PH (see
Figure 21b). The highest recorded values of hardness in elastic modulus were determined in CoCrMo-B
4C composites (see
Figure 22a). The highest η-value in electrical conductivity values was observed in CoCrMo (η = 41.13), while the lowest variation was found in 17-4 PH (β = 51.57) (see
Figure 22b). The composite with the highest average corrosion rate was identified as 17-4PH-12B
4C (see
Figure 23a). These findings were corroborated by EIS analysis. In surface oxide film resistance, Ti-5B
4C attracted attention with its high η-and β-values (see
Figure 23b). These analyses quantitatively reveal both the stability of the production process and the statistical reliability of the obtained composites.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the powder metallurgy method was employed to synthesize B4C-reinforced CoCrMo, Ti, and 17-4 PH alloys, and these alloys were subsequently investigated in terms of their mechanical, tribological, electrical, and electrochemical performances. The results indicate that the incorporation of B4C ceramic into the base alloys, particularly in Ti and CoCrMo matrices, results in a substantial enhancement of mechanical strength and wear resistance. However, this approach also introduces a trade-off in terms of corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity due to the insulating and electrochemically reactive nature of ceramic interfaces.
The following key findings can be distilled from this study:
Microstructural analysis revealed that the dispersion of B4C was uniform across all matrices, with no evidence of porosity or agglomeration. This finding suggests that the alloying and sintering processes were effective.
XRD analysis revealed a distinct α-Ti phase structure in pure Ti. Peaks corresponding to B4C were observed in samples to which B4C had been added. The incorporation of B4C led to an augmentation in peak intensity.
Hardness and wear resistance increased with rising B4C content. The highest hardness was demonstrated by CoCrMo-20B4C, while the Ti-B4C alloys exhibited the optimal wear resistance, indicating their potential for use in load-bearing orthopedic applications.
Elastic modulus values increased with B4C reinforcement. Ti-B4C alloys exhibited modulus values that closely approximated those of cortical bone, thereby ensuring biomechanical compatibility and minimizing stress shielding.
Electrical conductivity exhibited a decrease in all compositions with an increase in ceramic content, as would be predicted based on the insulating properties of B4C.
Corrosion performance of the alloys exhibited a decline with the addition of B4C, particularly in the 17-4 PH-B4C alloys. This decline was attributed to an increase in interfacial reactivity and the potential for microgalvanic effects.
Electrochemical impedance analysis revealed a significant decrease in surface oxide film resistance at higher B4C levels, emphasizing the necessity for meticulous optimization in corrosive environments.
Weibull reliability analysis corroborated the observed trends, underscoring CoCrMo-5B4C, Ti-5B4C, and 17-4PH-6B4C as the compositions exhibiting the highest statistical reliability, as determined by multiple property distributions.
These findings establish a framework for the evaluation of implant materials, including CoCrMo, Ti, and 17-4 PH, as well as the development of novel implant materials. The findings suggest that a one-dimensional material selection process is insufficient to capture the intricacies inherent in the clinical decision-making process. The multifaceted effects of B4C reinforcement have prompted a shift in the focus of implant material research towards a more holistic, non-uniform, multi-optimized, multi-disciplinary, and application-oriented direction. Consequently, this state of affairs presents an opportunity for innovative, hybrid, and customized solutions.
Among all samples that were tested, Ti-5B4C was identified as the most promising candidate due to its optimal balance between mechanical performance, corrosion resistance, and biomechanical compatibility. This composition demonstrates considerable promise for utilization in orthopedic and dental implants, spinal fixation devices, and other load-bearing biomedical applications.