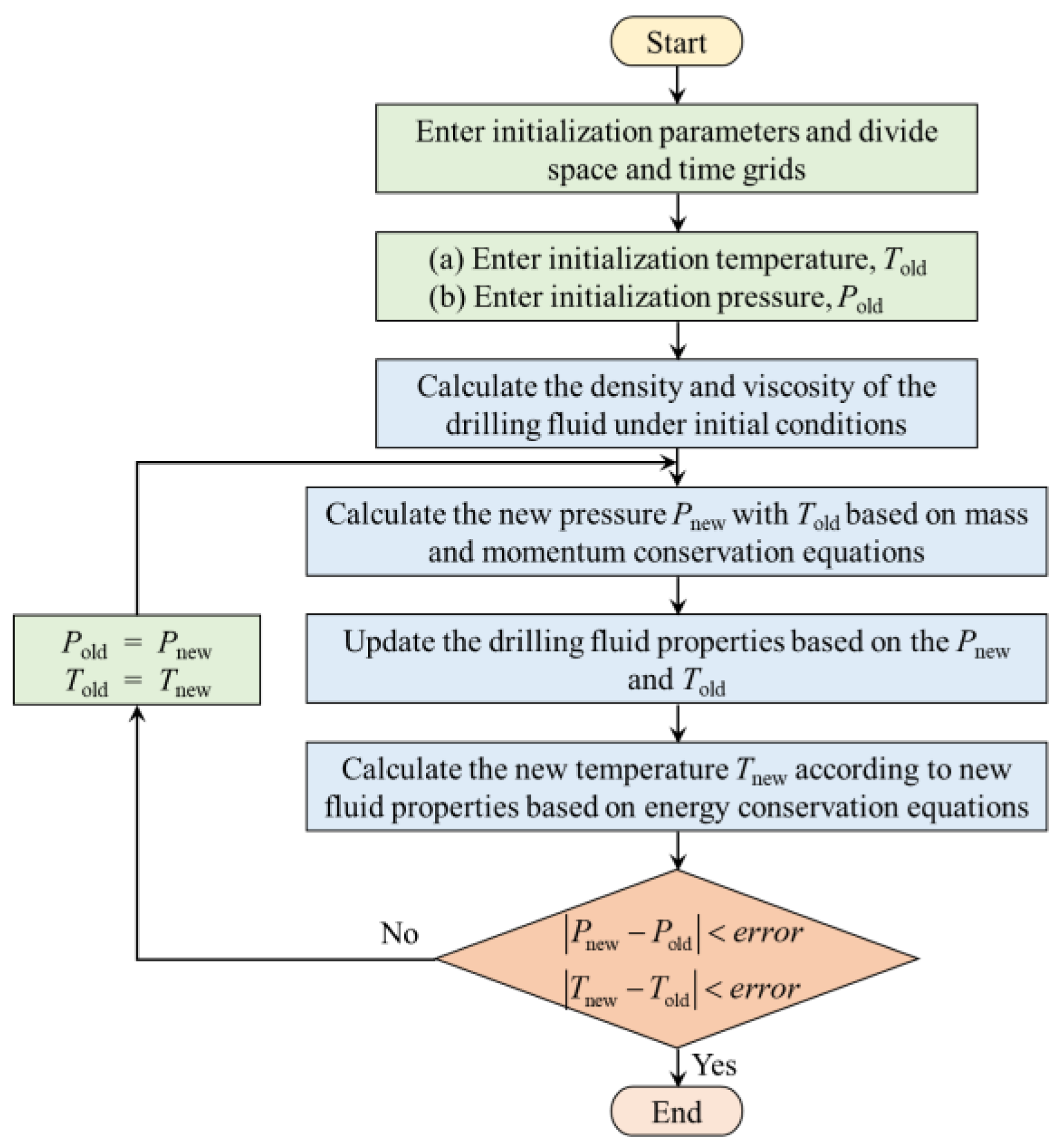
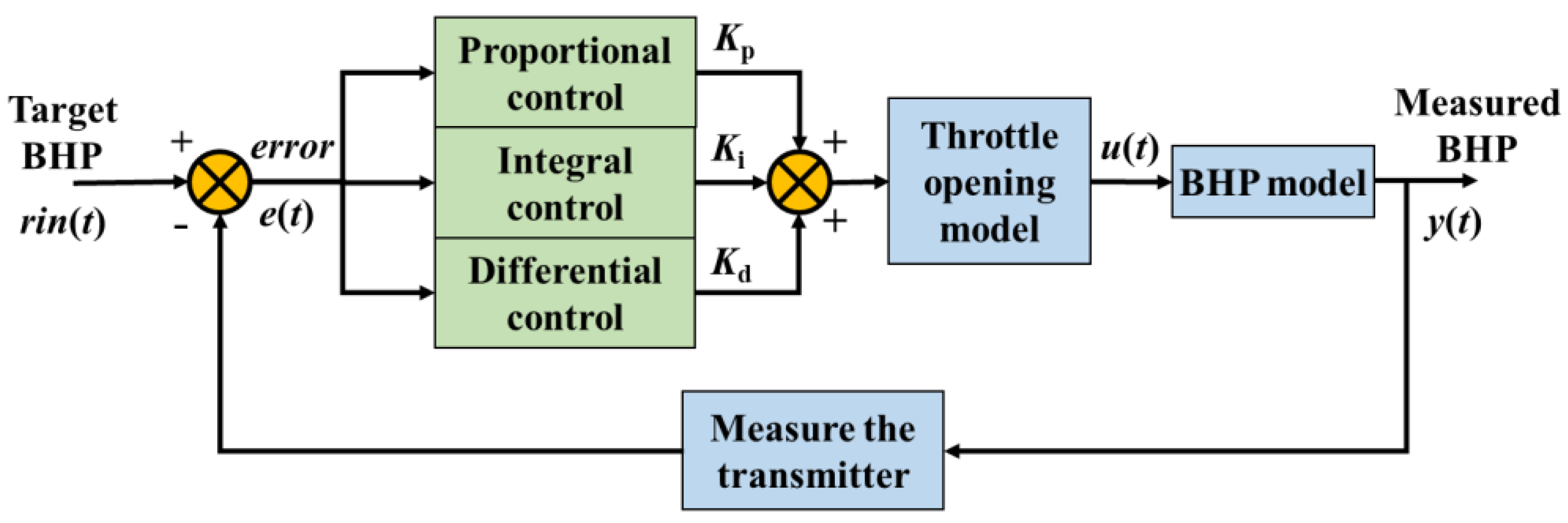
3.2. Proportional–Integral–Derivative (PID) Controller
The classic PID controller is still a key technology in many industrial control fields because of its good stability, high reliability, simple structure, and convenient control. The PID controller mainly includes three control modules: proportional, integral, and differential, as shown in
Figure 3.
① The proportional part can quickly adjust the control parameters according to the actual deviation of the control target.
② The integral part can evaluate the error of each step of regulation and adjust the control parameters to eliminate the system error.
③ The differential part can control in advance according to the error change ratio and suppress the overshoot effectively.
The PID controller of BHP regulates the opening of the wellhead throttle valve according to the control error (
e) between the target of the BHP (
rin) and the measured value of the BHP (
y) and regulates BHP automatically, where the control error can be expressed as follows:
First, the automatic regulation control equation for the opening of the wellhead throttle valve is established according to the PID control principle, which is expressed as follows:
where
is the control variable for throttle opening;
is the control error, which is the difference between the target BHP and the actual measured BHP;
is the proportionality parameter;
is the integral parameter; and
is the differential parameter.
The real-time opening of the throttle is shown below:
The pressure drop caused by the gas–liquid–solid three-phase in the annulus through the wellhead throttle is calculated by the following equation:
where
is the total mass flow rate through the wellhead throttle in
;
is the fixed constant of the wellhead throttle valve;
is the wellhead throttle opening;
is the pressure at the wellhead throttle in
;
is the pressure at the downstream end of the wellhead throttle in
;
is the mass flow fraction of the liquid–solid mixture in
;
is the mass flow fraction of the gas phase;
is the density of the liquid–solid mixture at the wellhead in
;
is the density of the gas phase at the wellhead in
; and
is the gas expansion factor.
Therefore, the correspondence between throttle opening and throttle pressure can be obtained by solving Equation (14), and the correspondence between the throttle opening and BHP can be established so that the BHP can be controlled by adjusting throttle opening, and then the gas invasion accident can be handled.
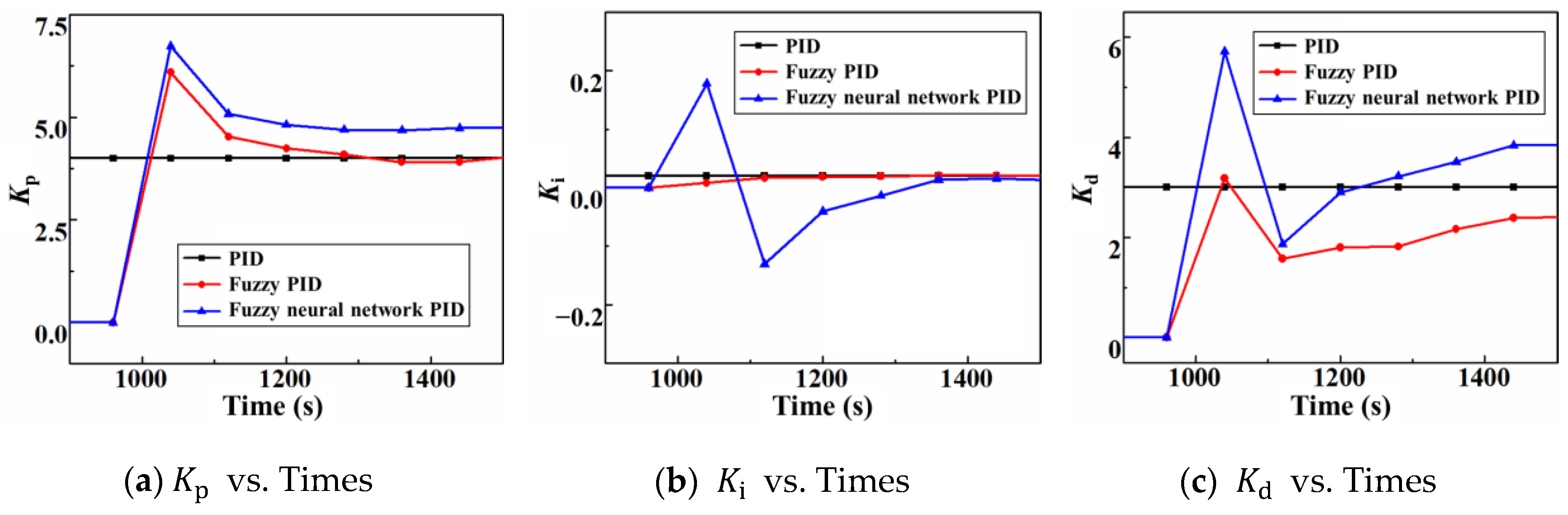
After specifying the target parameters and the control object, this paper searches for the tuning parameters of the PID controller by the grid search method, including
,
, and
, and the search range and step size are shown in
Table 4.
Different combinations of regulation parameters were evaluated according to the regulation efficiency and overshoot, and it was found that when , , and , the PID controller of BHP had the highest regulation efficiency and almost zero overshoot, so this combination was selected as the result of the adjustment of the bottom hole pressure PID controller parameters.
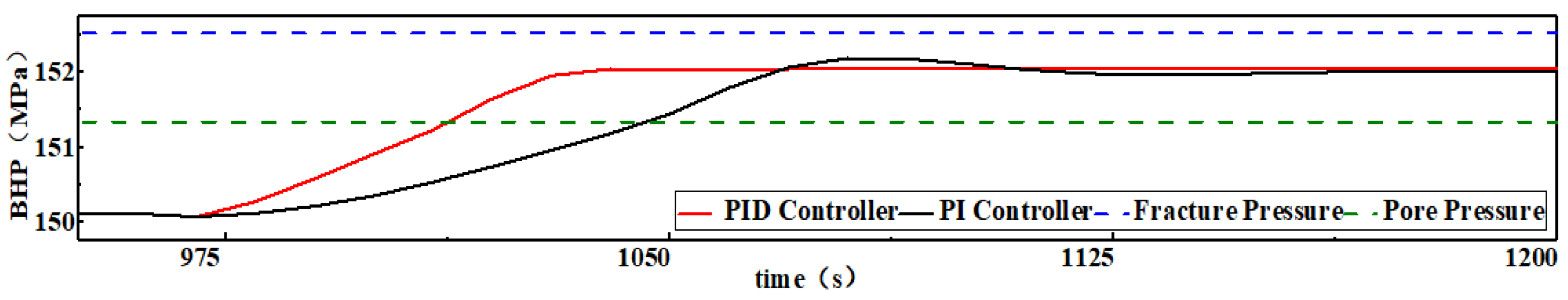
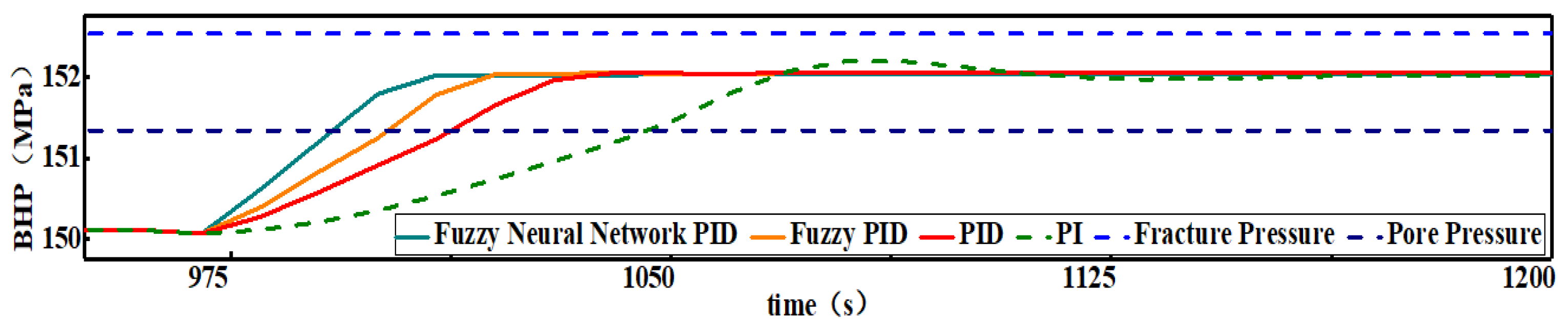
As shown in
Figure 4, the PID controller of BHP established in this section has a significantly higher regulation efficiency compared to the existing PI controller of BHP. Because of the addition of the differential control part, the overshoot of the BHP disappears, which makes the BHP regulation process more stable and more reliable.
The pool level reached the warning value 960 s after the gas invasion occurred. The PID controller and PI controller started to regulate the BHP at the same time. The PI controller regulated the BHP within the safety pressure window after 87 s, while the PID controller only took 53 s to regulate the BHP within the safety pressure window, which was 39% more efficient. On the other hand, the PI controller takes 110 s to regulate the BHP to the target BHP, while the PID controller takes only 73 s, saving 34% of the regulation time. During the entire BHP control process, the root mean square error (RMSE) of the PI controller is 0.31 MPa, and the integral absolute error (IAE) is 3250.39 MPa·s. The RMSE of the PID controller is 0.24 MPa, and the IAE is 1870.05 MPa·s. According to the control principle of the PID controller, the function of the differential partial override control and suppression of overshoot is the main reason for the efficiency improvement and the disappearance of the overshoot.
3.3. Fuzzy PID Controller
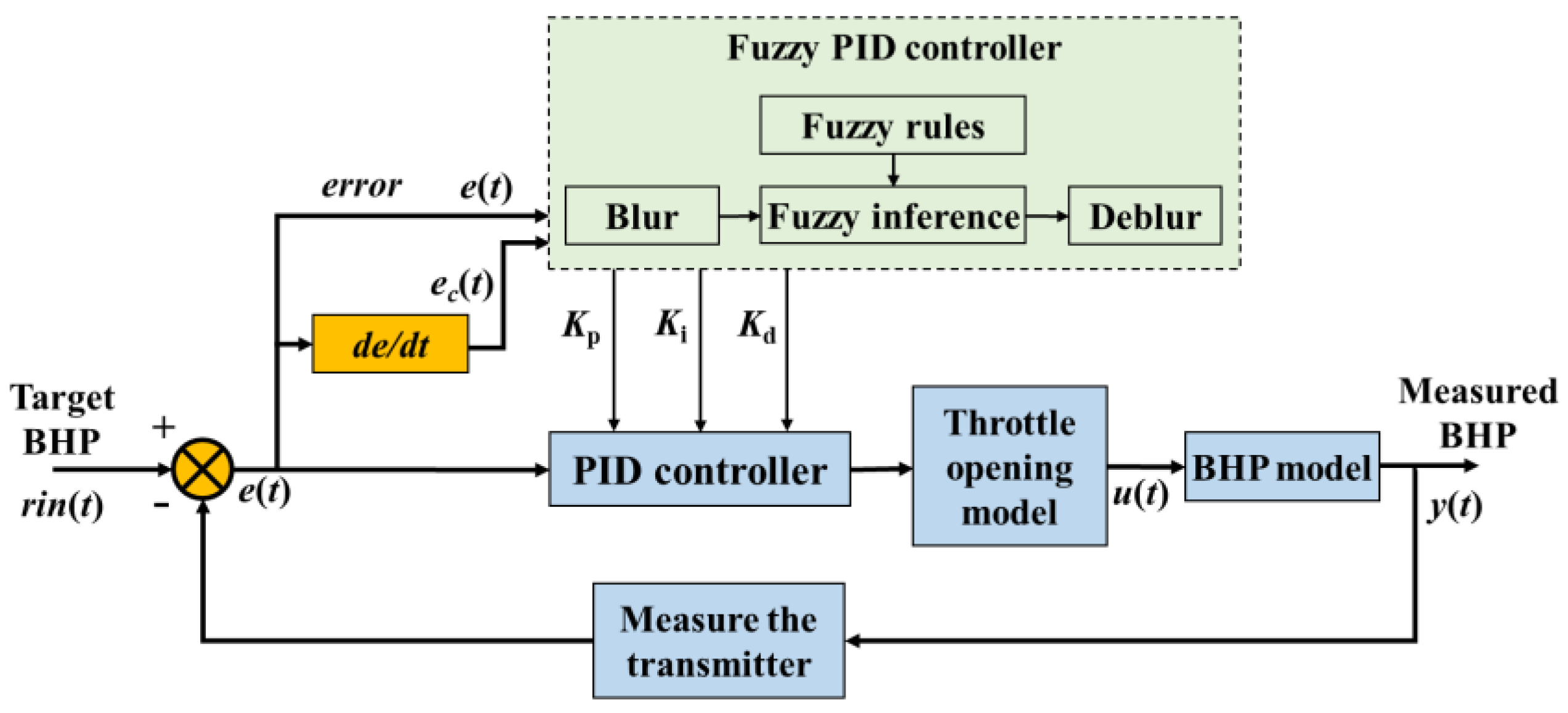
The fuzzy PID controller couples the fuzzy reasoning and the PID controller. It is the adaptive tuning of the control parameters by establishing the membership function of the control parameters, error, and error change ratio and designing the fuzzy control rules. The fuzzy PID controller can adjust the control parameters dynamically, overcome the limitation of fixed parameters in the PID controller, and improve the control efficiency.
The core of a fuzzy PID controller is a fuzzy inference machine, which can develop reasonable control rules based on human expert experience and includes three stages, such as fuzzification of the control object, fuzzy inference process, defuzzification of the control parameters, etc. The error and the error change ratio are the input of the model, and the control parameters of PID can be adjusted adaptively by fuzzy control rules. Its robustness will be significant compared with classical PID controllers. In this paper, by coupling the fuzzy inference and PID controller, an intelligent regulation model of BHP based on the fuzzy PID controller is developed, and its control principle is shown in
Figure 5.
(1) Parameter fuzzification
Firstly, the input parameters are fuzzified. The error
and error change ratio
are two input parameters of the fuzzy PID controller. After parameter fuzzification, fuzzy inference, and defuzzification, the control parameters of PID
,
, and
are obtained. One of the parameters’ fuzzification processes is to calculate the fuzzy quantity of the input parameter based on the actual domain [
] and its corresponding set domain [−b, b] of the fuzzy quantity (
), and the calculation process is as follows:
where
is determined by rounding to the nearest whole number, and
is the quantification factor, which is calculated as follows:
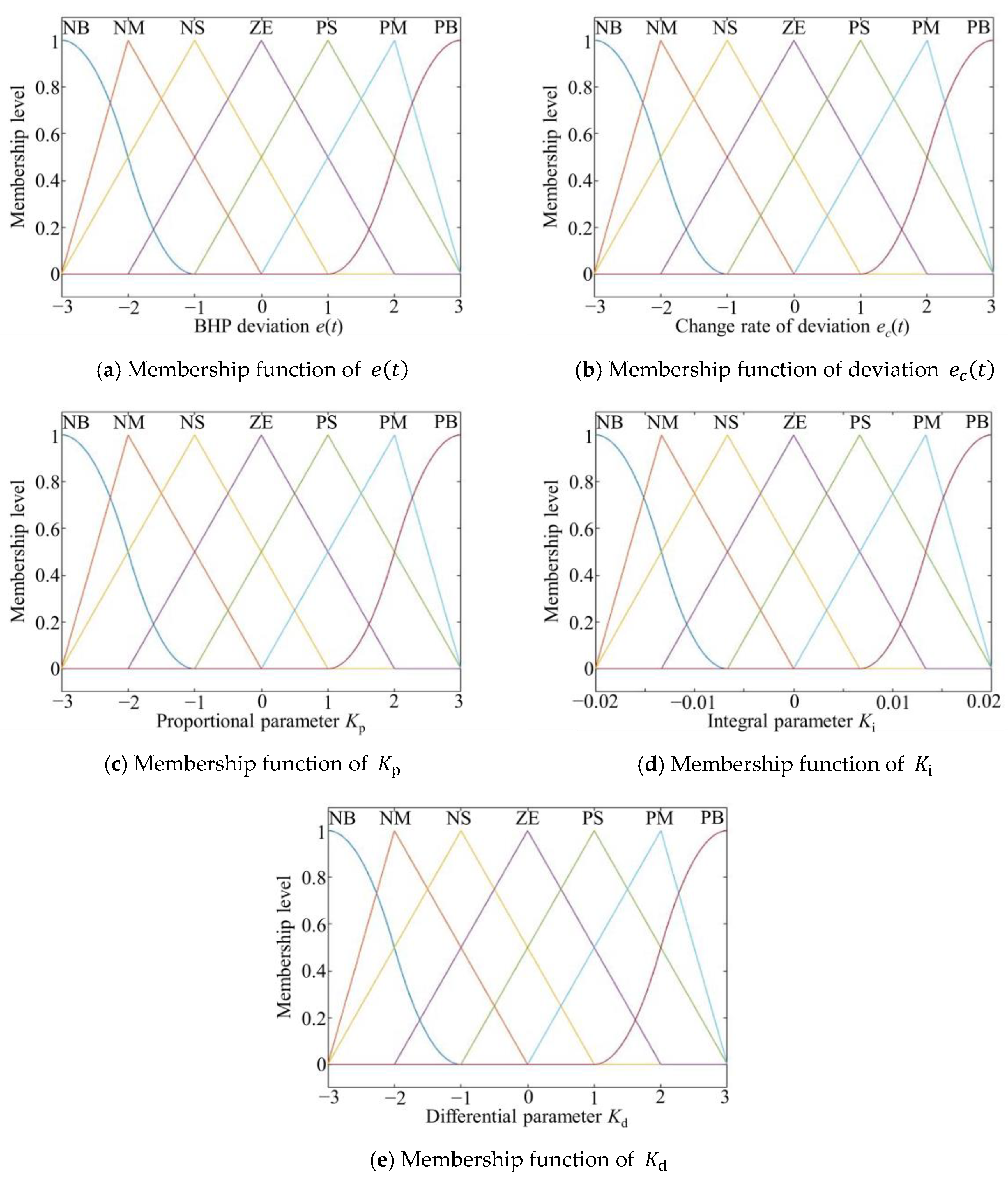
Based on the actual condition, it was determined that the domains of the two input parameters e and were [−3, −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, 3]. The control domains of the three output parameters were [−3, −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, 3], [0.020, 0.013, 0.007, 0, 0.007, 0.013, 0.020], and [−3, −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, 3].
The discrete theoretical domain of each parameter corresponds to the following fuzzy geometry {PB, PM, PS, ZE, NS, NM, NB}.
Each parameter corresponds to a fuzzy quantity, and its degree of membership to this fuzzy quantity is calculated by the membership function.
where
is the element;
is the set; and
is the membership degree of element
in set
.
In this paper, triangular, bell-shaped, and sigmoid-type membership functions are used to calculate the membership of the input parameters to the fuzzy quantities. The triangular membership function is as follows:
where
is the left foot;
is the peak; and
is the right foot.
The bell-shaped membership function is as follows:
where
is the parameter that controls the width of the function;
is the parameter that indicates the degree of steepness of the slope of the control function; and
is the center position of the function.
The sigmoid-type membership function is as follows:
where
is the parameter for controlling the slope of the curve; and
is the center point of the S-shaped curve.
The error
, error change ratio
, and control parameters
and
of the membership function are shown in
Figure 6.
(2) Fuzzy rules and fuzzy inference
Analyzing the response mechanism of BHP to the wellhead choke valve opening and considering the adjustment effect of
,
and
on the opening degree of the wellhead choke valve and the relationship between them. A fuzzy control rule table for adjusting the
,
and
changes corresponding to the error and the error change ratio is established. The fuzzy control rule table for regulation is shown in
Table 5,
Table 6 and
Table 7. According to the fuzzy rule table of PID control parameters, it can be self-adaptive tuning according to the real-time deviation and deviation change rate of
,
and
, which overcomes the limitation of fixed classical PID control parameters and improves the responsiveness and adaptability of the fuzzy PID controller significantly.
(3) Defuzzification
The input parameters are still fuzzy vectors after the fuzzy rule inference operation; it is necessary to deblur them to obtain the exact values of the three control parameter variations. Commonly used defuzzification methods are the maximum membership method, area center method, weighted average method, median method, etc. In this paper, the area center method is used for defuzzification, and the center of gravity of the area enclosed by the membership function curve is used as the final output value. This method is more sensitive to the input signal; even if the input value changes slightly, the output value can make a corresponding change, and the calculation formula is as follows:
where
is the input signal
x of the theoretical domain of the input signal.
After calculating the parameter changes of the PID controller based on the area center method,
,
and
in the PID controller are determined as follows:
where
, and
are the initial parameters’ fuzzy values.
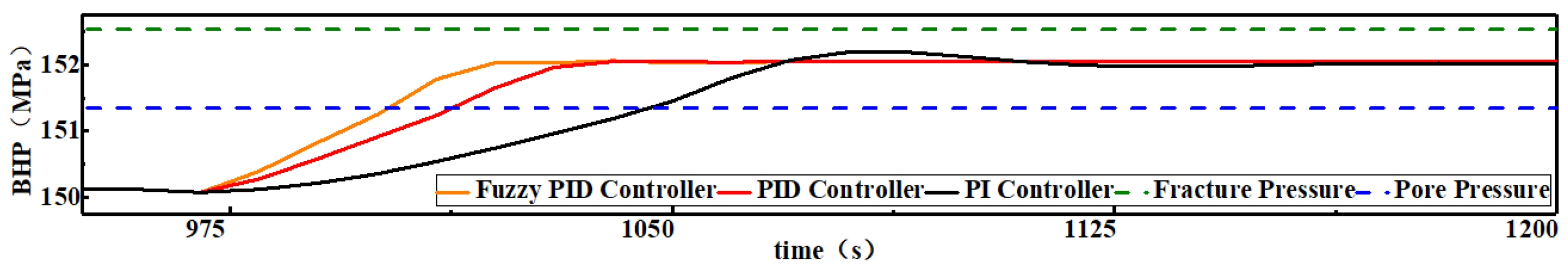
As shown in
Figure 7, compared with the traditional PID controller, the response speed of the fuzzy PID control is faster and reduces from 53 s to 42 s, so the fuzzy adaptive PID control suppresses the gas invasion accident 11 s earlier, and its RMSE is 0.22 MPa and IAE is 1674.84 MPa·s. In addition, the time taken by the fuzzy adaptive PID and the traditional PID to regulate the BHP to the target value is 60 s and 73 s, respectively; it can be considered that the regulation efficiency of the fuzzy adaptive PID is improved by about 18% relative to the PID controller, with no overshoot.
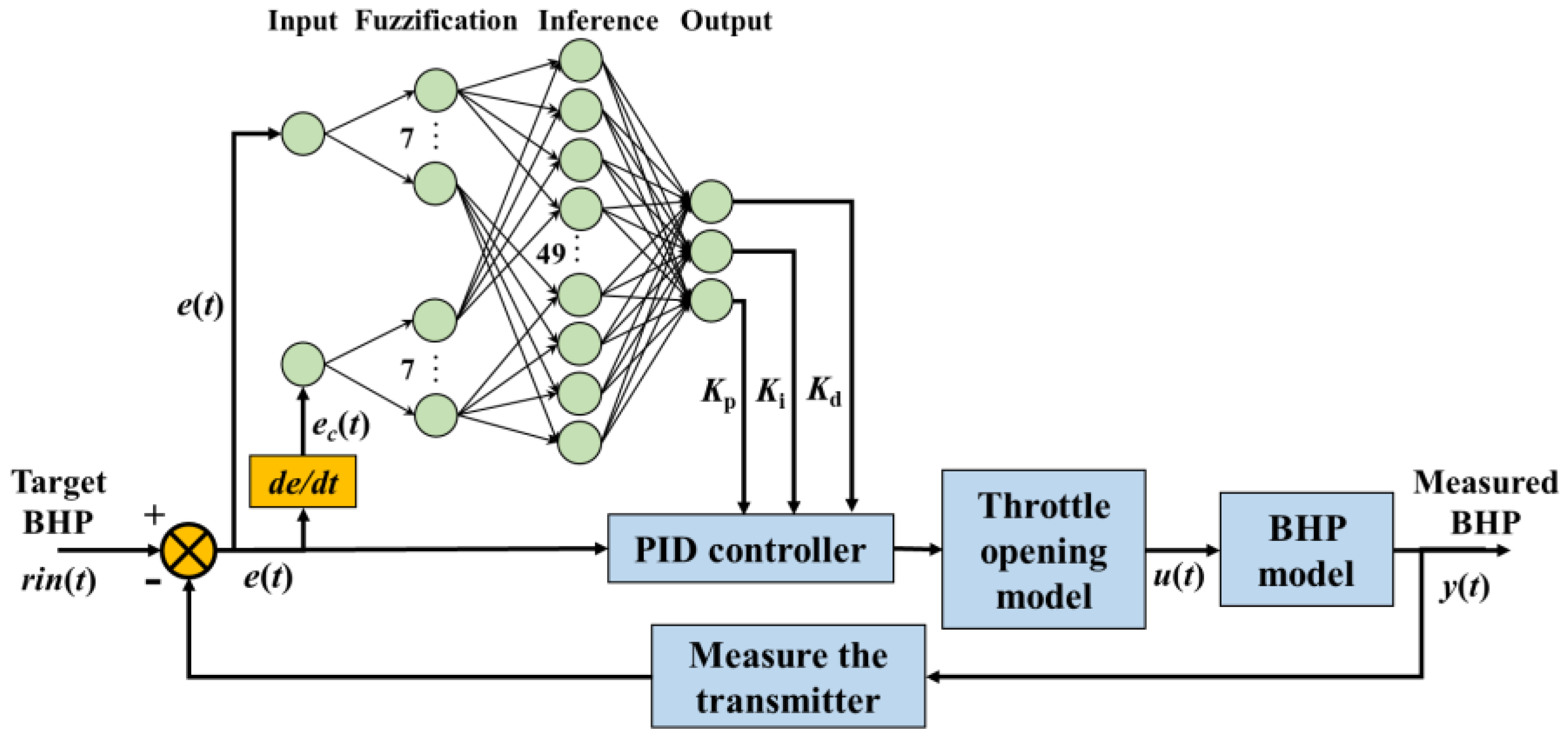
3.4. Fuzzy Neural Network PID Controller
The fuzzy neural network PID controller introduces an artificial neural network into the fuzzy control process and uses a multi-layer neural network to realize fuzzy reasoning and optimize fuzzy control rules online in the control process [
38]. The fuzzy neural network PID controller takes into account the advantages of fuzzy reasoning and ANN, which not only has good logical reasoning ability but also can realize the dynamic optimization of control rules.
As shown in
Figure 8, the fuzzy neural network PID controller is a four-layer neural network that replaces the parameter input, fuzzification, fuzzy inference, and defuzzification processes of the fuzzy PID controller, which not only fully retains the logic inference capability of the fuzzy PID controller but also can overcome the limitation that the neural network PID controller can easily fall into the local optimum, and, at the same time, because the neural network has a strong online learning capability, the fuzzy control rules can be adjusted online to make up for the deficiency in the responsiveness of the controller due to the fixed and unchanging fuzzy control rules. In this paper, based on the fuzzy PID controller established in
Section 3.3, a neural network module is introduced to establish a fuzzy neural network PID controller for wellbore pressure.
The input layer of the fuzzy neural network consists of two neurons for and of the inputs, which are transmitted to the fuzzification layer in the form of a vector with one row and two columns. The fuzzification layer includes 14 neuron nodes, and the two output signals of the input layer are transmitted to 7 neuron nodes, each of which acts as the equivalent of a membership function to divide the theoretical domain of the input values into seven fuzzy intervals of the fuzzy quantity domain, ; the output signal of the input layer is passed to the fuzzy inference layer in the form of a membership matrix with two rows and seven columns after being calculated by the membership function. There are 49 neuron nodes in the fuzzy inference layer, and each node corresponds to a fuzzy rule. The input signal is fuzzed by the fuzzification layer and then logically reasoned using the fuzzy rule function, and the fuzzy matrix obtained by the inference is passed to the output layer. The three neurons in the output layer will obtain the change of control parameters of the PID controller by weighting the fuzzy quantity output from the fuzzy inference layer after the weighting operation , and , which is the defuzzification process.
After determining the fuzzy neural network structure, the solution of the fuzzy neural network PID controller for the BHP is achieved by the following process:
(1) Random initialization of the neural network weight matrix.
(2) Input the present value of the BHP error and the amount of error variation into the neural network.
(3) The input parameters are transmitted through the neural network to output the wellbore pressure regulation parameters , and .
(4) After the controller calculates the control volume of the wellhead throttle, the output value of the BHP is obtained after the calculation of the three-phase flow model in the annulus.
(5) Calculation of the error and the rate of change of the error in the target and output values of the BHP.
(6) Backpropagation of the neural network module to compute the partial derivatives of the objective function for the parameter matrix.
(7) Adjustment of the weight matrix according to the fastest decreasing direction of the objective function and the established learning rate of the neural network.
(8) Cycle steps 2–7 until the wellbore pressure is regulated to the target value.
Based on the above model construction and solution methods, a fuzzy neural network PID control model for the BHP is constructed. As shown in
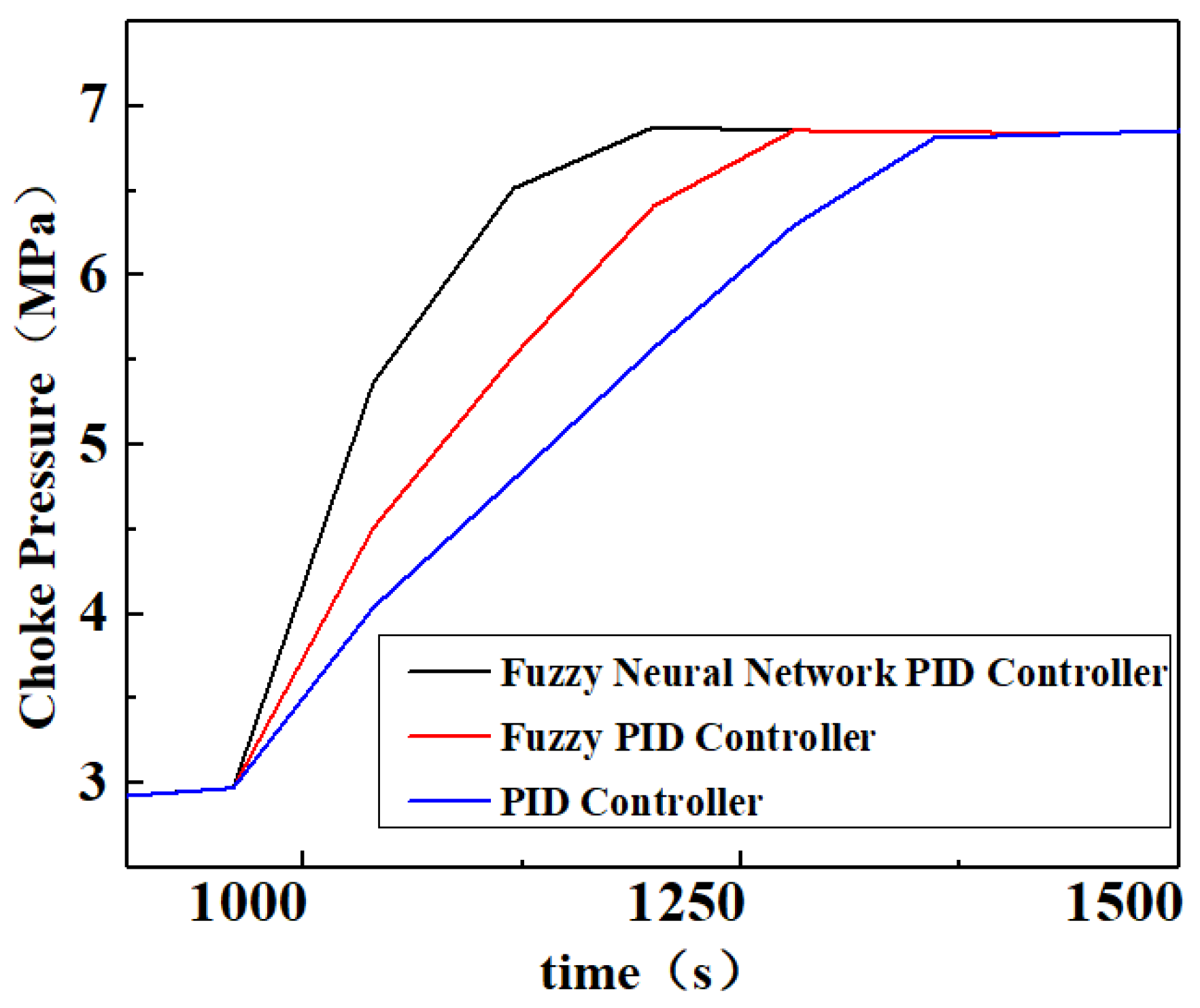
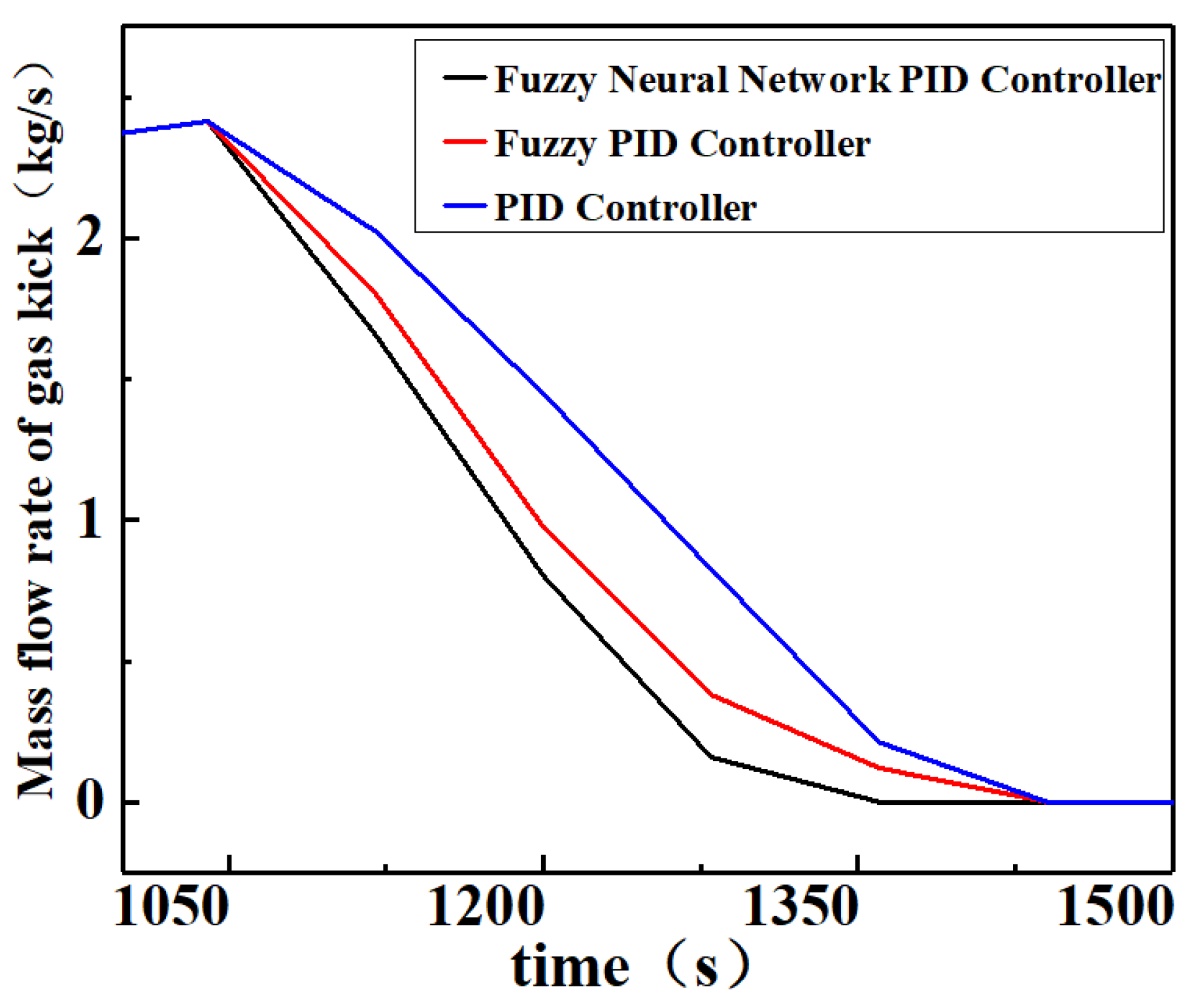
Figure 9, the efficiency of the fuzzy neural network PID controller is further improved for the fuzzy PID controller in terms of BHP regulation. The fuzzy neural network PID controller starts regulating the BHP from 960 s and takes only 32 s to regulate BHP within the safety pressure window, which is 10 s earlier compared to the fuzzy PID controller; the efficiency is improved by 24%, the RMSE is only 0.20 MPa, and the IAE is only 1487.58 MPa·s. On the other hand, the fuzzy neural network PID controller regulates BHP to the target value at 1010 s with no overshoot, which is 10 s earlier compared to the fuzzy PID controller and has a 17% efficiency improvement. The further improvement of the fuzzy neural network PID regulation performance is due to its ability to achieve adaptive tuning of the control parameters and online optimization of the control rules through fuzzy control rules and neural network modules simultaneously.
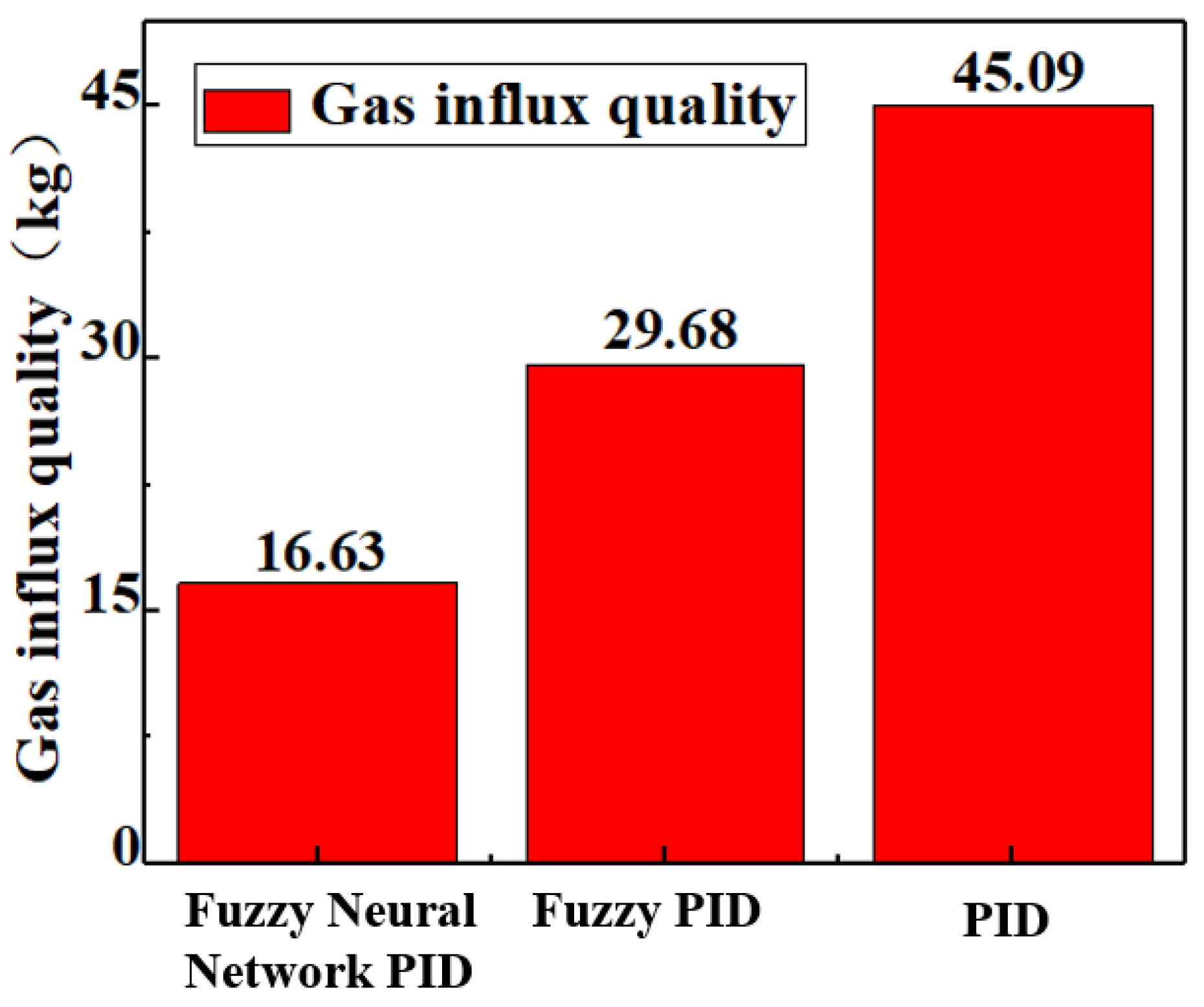
The time and error comparison of the four controllers to control the BHP to the target value is shown in
Table 8. It can be seen that the fuzzy neural network PID takes the least time, has the lowest error, and has good BHP control performance.