BDS-PPP-B2b-Based Smartphone Precise Positioning Model Enhanced by Mixed-Frequency Data and Hybrid Weight Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Smartphone GNSS Observations Generation
2.2. PPP-B2b-Based Orbit and Clock Corrections
2.3. Mixed-Frequency PPP Model
2.4. Hybrid Weight Function
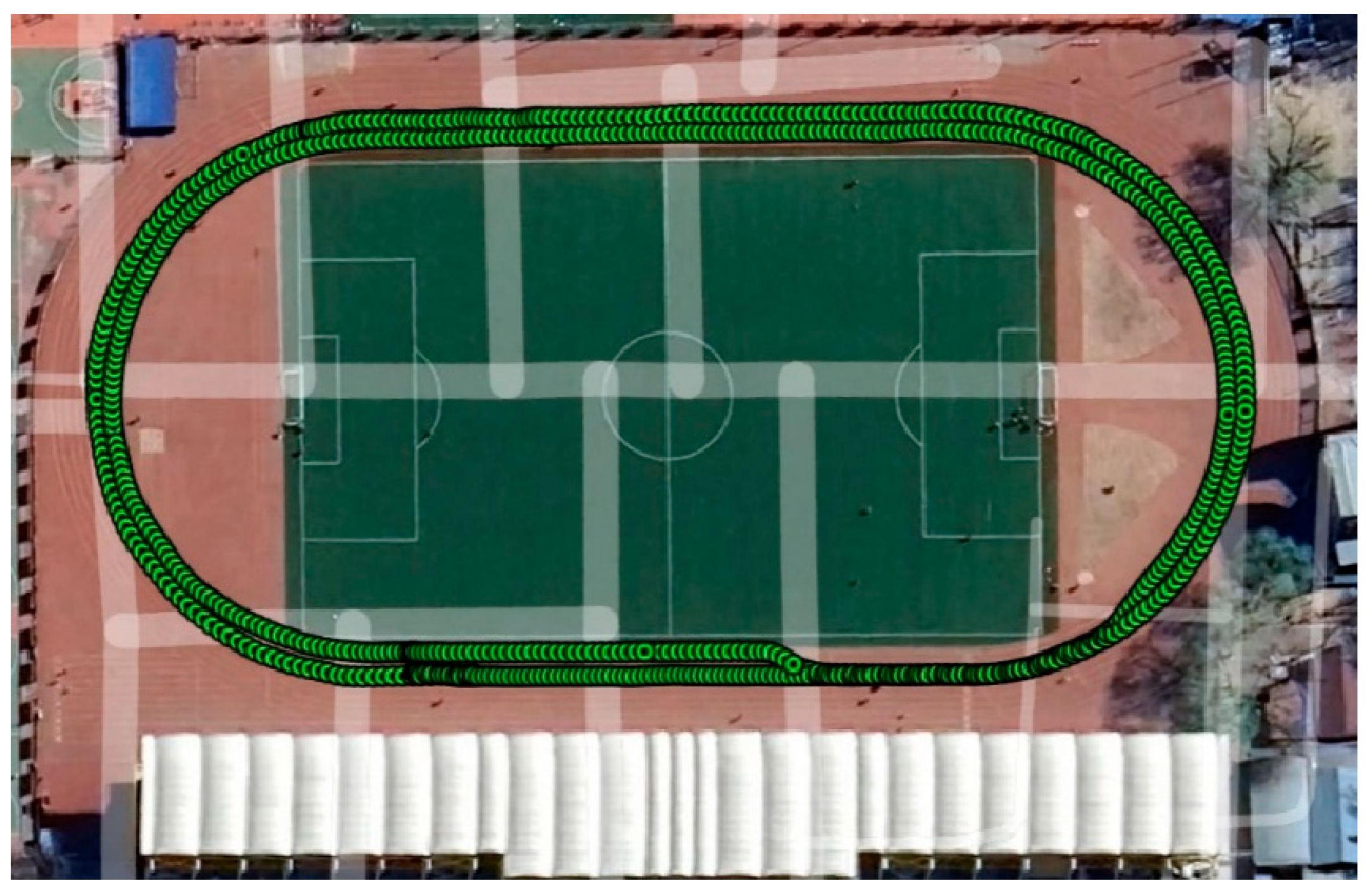
3. Data Collection and Observation Quality Assessment
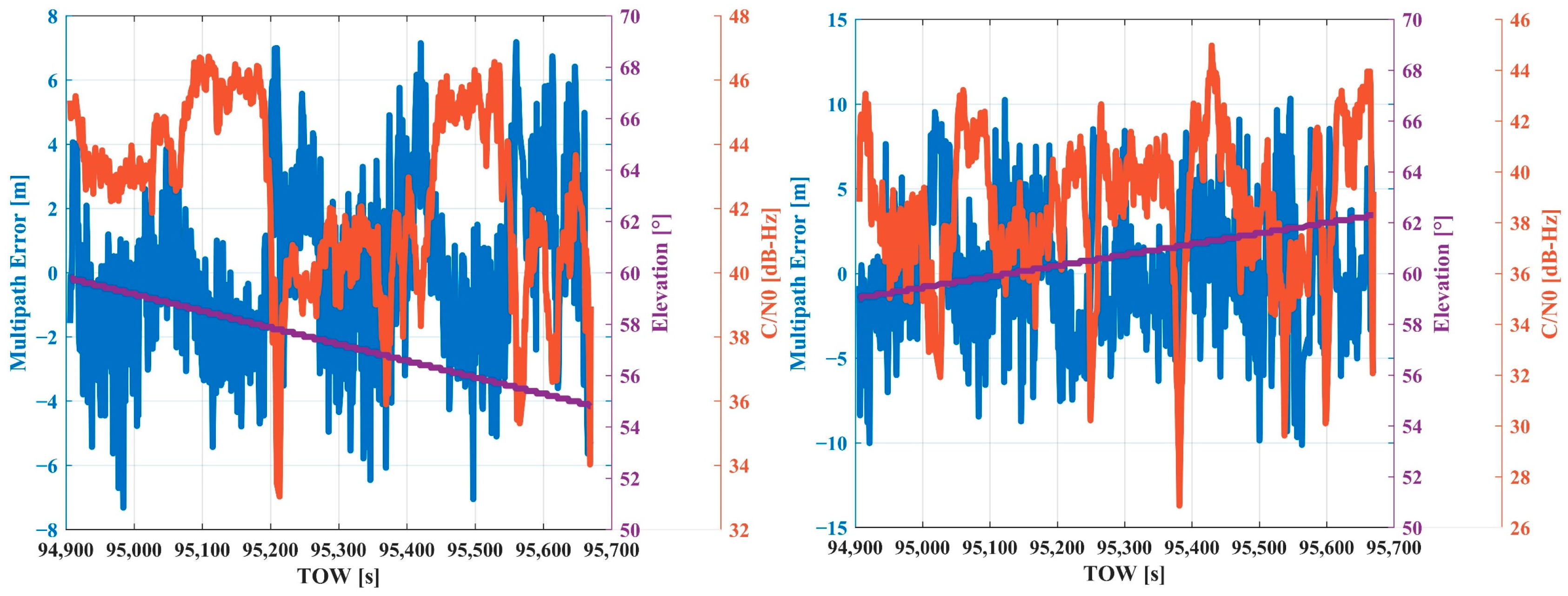
3.1. Carrier-to-Noise Ratio
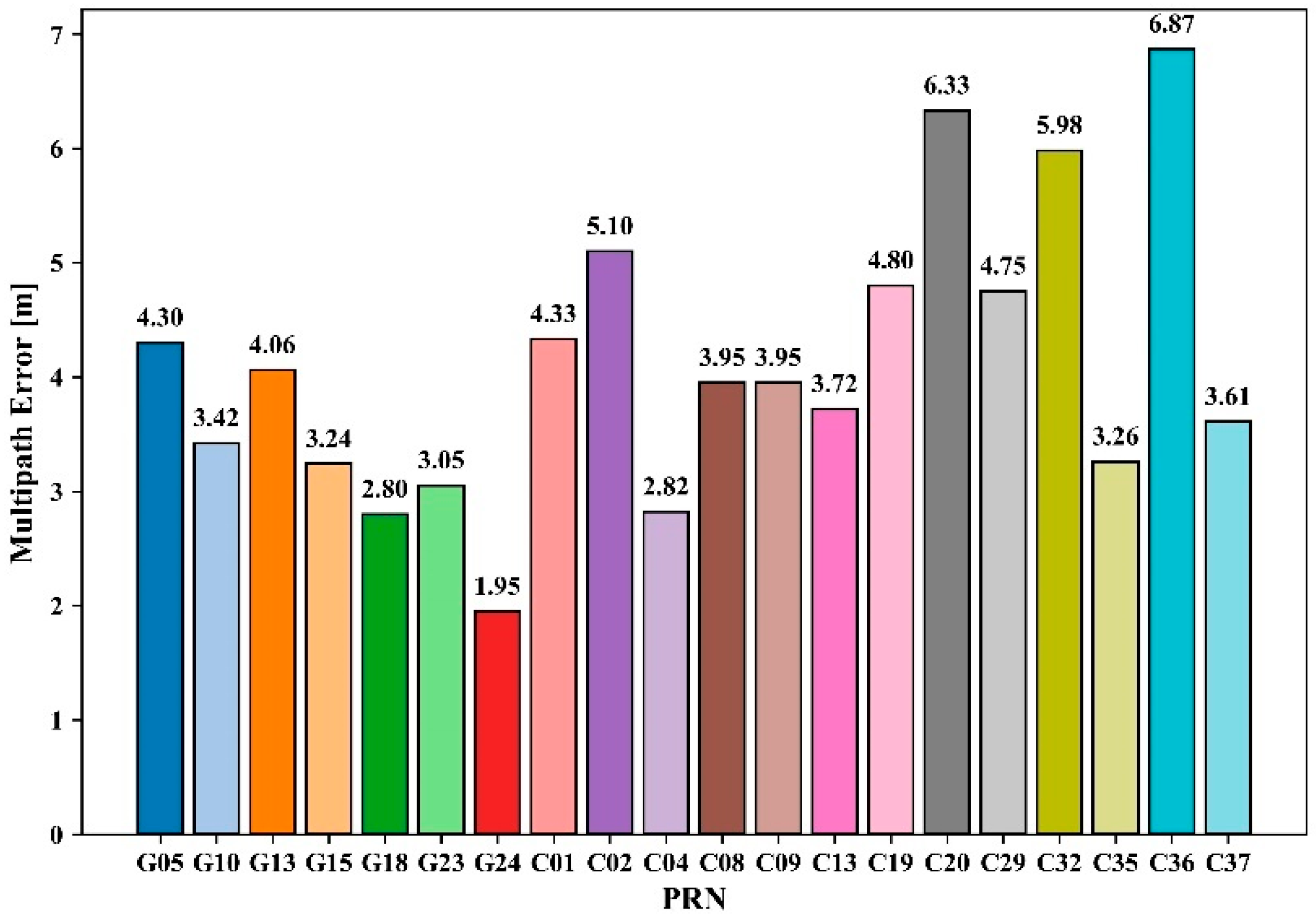
3.2. Multipath Errors
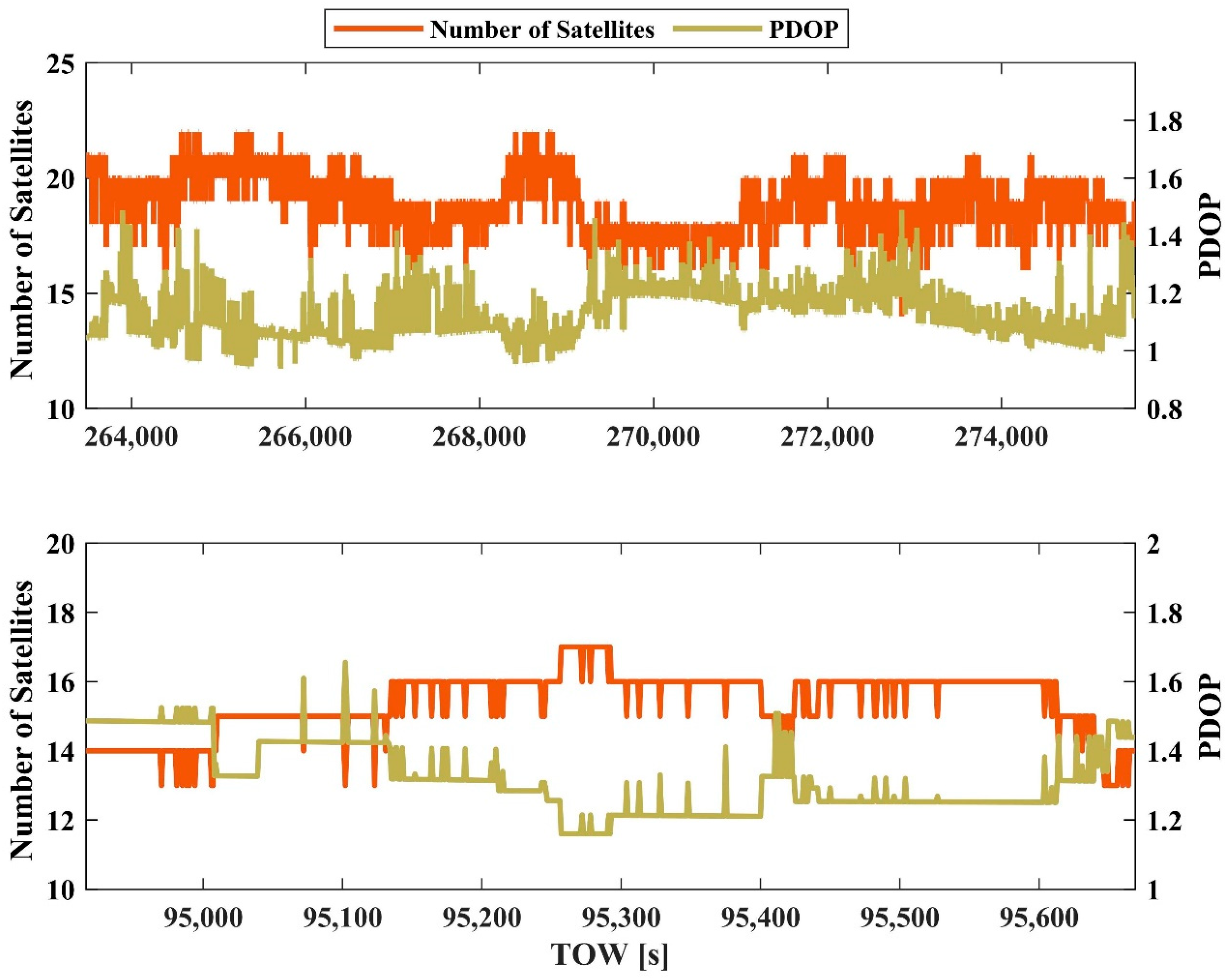
3.3. Satellite Availability and PDOP
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Performance of the Presented Smartphone Static PPP
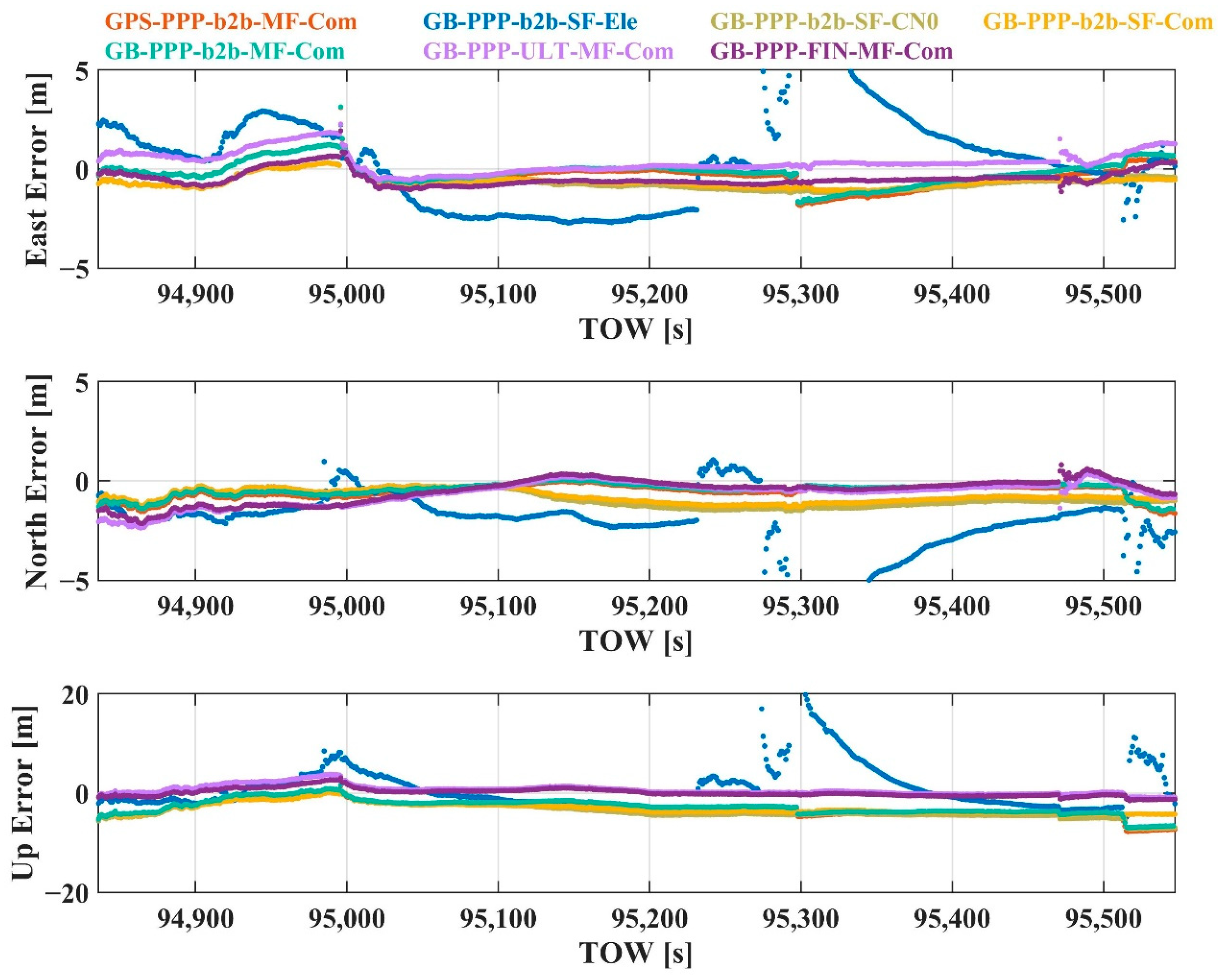
4.2. Performance of the Presented Smartphone Dynamic PPP
4.3. Experimental Result Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, W.; Li, B.; Gao, Y. The Superiority of Multi-GNSS L5/E5a/B2a Frequency Signals in Smartphones: Weight functioning, Ambiguity Resolution, and RTK Positioning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 7315–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Real-time GNSS precise point positioning for low-cost smart devices. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, M. Characterization of GNSS observations from a Nexus 9 Android tablet. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, L.; Heßelbarth, A. GNSS code and carrier phase observations of a Huawei P30 smartphone: Quality assessment and centimeter-accurate positioning. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Zha, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, B. Recent advances and perspectives in GNSS PPP-RTK. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 051002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Geng, J.; Zhang, G.; Ng, H.; Guo, J.; Hsu, L. 3D-mapping-aided PPP-RTK aiming at deep urban canyons. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise point positioning for the efficient and robust analysis of GPS data from large networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid. Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise point positioning using IGS orbit and clock products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinghal, G.; Bisnath, S. Conditioning and PPP processing of smartphone GNSS measurements in realistic environments. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Analysis of 5G Smart Communication Base Station Doppler-Smoothed Pseudorange Single-Point Geodesic Positioning Accuracy. J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2023, 10, 4297044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Geng, J. Characteristics of raw multi-GNSS measurement error from Google Android smart devices. GPS Solut. 2019, 23, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Fortunato, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Odolinski, R. An analysis of multi-GNSS observations tracked by recent Android smartphones and smartphone-only relative positioning results. Measurement 2021, 175, 109162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, F.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shi, C. Instantaneous sub-meter level precise point positioning of low-cost smartphones. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2023, 70, navi.597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, T.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, K. Precise point positioning with mixed single-and dual-frequency GNSS observations from Android smartphones considering code-carrier inconsistency. Adv. Space Res. 2024, 74, 2664–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Geng, J. Android multi-GNSS ambiguity resolution in the case of receiver channel-dependent phase biases. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Geng, J.; Li, G.; Guo, J. Precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution using an external survey-grade antenna enhanced dual-frequency android GNSS data. Measurement 2020, 157, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Gao, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P. Real-time precise point positioning with a Xiaomi MI 8 android smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangenehnejad, F.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, Y. GNSS Observation Generation from Smartphone Android Location API: Performance of Existing Apps, Issues and Improvement. Sensors 2023, 23, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Ying, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P. Pseudorange double difference algorithm based on duty-cycled carrier phase smoothing on low-power smart devices. In China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2018 Proceedings; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume I, pp. 415–430. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xin, S.; Huang, Q.; Shen, S. An Improved Velocity-Aided Method for Smartphone Single-Frequency Code Positioning in Real-World Driving Scenarios. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.; Bisnath, S.; Aggrey, J.; Seepersad, G. Precise point positioning (PPP) using low-cost and ultra-low-cost GNSS receivers. In Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of The Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2017), Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 September 2017; pp. 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, X.; Zhu, F.; Shi, X.; Wang, F. Quality assessment of GNSS observations from an Android N smartphone and positioning performance analysis using time-differenced filtering approach. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; Yang, C. Reliable Positioning Model of Smartphone Sensors and User Motions Tightly Enhanced PDR. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 30925–30938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Gao, W.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, B. Principle and performance of BDSBAS and PPP-B2b of BDS-3. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gao, W.; Liu, T.; Wang, D.; Yao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Nie, X.; Wang, W.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; et al. Design and implementation of a BDS precise point positioning service. Navigation 2020, 67, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Du, J. Initial assessment of BDS PPP-B2b service: Precision of orbit and clock corrections, and PPP performance. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Xie, W.; Yue, F.; Cui, B. Performance Evaluation and Application Field Analysis of Precise Point Positioning Based on Different Real-Time Augmentation Information. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhai, W. Assessment of PPP Using BDS PPP-B2b Products with Short-Time-Span Observations and Backward Smoothing Method. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Global Navigation Satellite Systems Agency. Using GNSS Raw Measurements on Android Devices; Publications Office of the European Union: Prague, Czech Republic, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- China Satellite Navigation Office. BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Signal in Space Interface Control Document Precise Point Positioning Service Signal PPP-B2b (Version 1.0); China Satellite Navigation Office: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q. Evaluation of real-time kinematic positioning performance of the BDS-3 PPP service on B2b signal. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Lv, H.; Shen, Z.; Xia, C.; Gou, H. PPP rapid ambiguity resolution using Android GNSS raw measurements with a low-cost helical antenna. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Geng, J. Single-frequency multi-GNSS PPP-RTK for smartphone rapid centimeter-level positioning. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 21553–21561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Hugentobler, U.; Fride, P. Bernese GPS Software Version 5.0.; University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cai, C.; Xu, Z. A Combined Elevation Angle and C/N0 Weighting Method for GNSS PPP on Xiaomi MI8 Smartphones. Sensors 2022, 22, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Z.; Dai, Z.; Li, J.; Ran, C. Code multipath error extraction based on the wavelet and empirical mode decomposition for Android smart devices. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Fileds | Description |
|---|---|
| TimesNanos | Android terminal GNSS receiver time |
| BiasNanos | The sub-nanosecond-level deviation between the Android GNSS receiver clock and real GPS time |
| FullBiasNanos | Nanosecond-level deviation between the Android GNSS receiver clock and real GPS time |
| DriftNanosPerSecond | Android GNSS receiver clock drift |
| LeapSecond | Leap second associated with the clock’s time |
| Fileds | Description |
|---|---|
| Svid | Satellite ID |
| ConstellationType | Constellation type |
| State | Current state of the GNSS engine |
| ReceivedSvTimeNanos | Received GNSS satellite time at the measurement time |
| Cn0DbHz | Carrier-to-noise density |
| CarrierFrequencyHz | Carrier frequency at which codes and messages are modulated |
| TimeOffsetNanos | Time offset at which the measurement was taken in nanoseconds |
| CarrierCycles | Number of full carrier cycles between the satellite and the receiver |
| PseudorangeRatemetersperSecond | Pseudo-range rate at the timestamp |
| AccumulatedDeltaRangeMeters | Accumulated distance values since the last channel initialization |
| AccumulatedDeltaRangeState | State parameters of carrier phase observation values |
| Static (dB-Hz) | Dynamic (dB-Hz) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIN | MAX | AVG | MIN | MAX | AVG | |
| GPS | 9.55 | 47.76 | 36.50 | 24.97 | 47.38 | 40.46 |
| BDS | 9.02 | 46.91 | 32.74 | 9.20 | 49.12 | 34.27 |
| Positioning Modes | East (m) | North (m) | Up (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-MF-Com | 1.26 | 0.87 | 1.07 |
| GB-SF-Ele | 1.88 | 2.48 | 3.61 |
| GB-SF-CN0 | 0.61 | 0.87 | 0.98 |
| GB-SF-Com | 0.61 | 0.69 | 0.83 |
| GB-MF-Com | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.71 |
| Positioning Modes | East (m) | North (m) | Up (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPS-PPP-b2b-MF-Com | 0.68 | 0.65 | 3.58 |
| GB-PPP-b2b-SF-Ele | 2.76 | 3.06 | 5.21 |
| GB-PPP-b2b-SF-CN0 | 0.78 | 0.98 | 3.87 |
| GB-PPP-b2b-SF-Com | 0.70 | 0.83 | 3.29 |
| GB-PPP-b2b-MF-Com | 0.61 | 0.55 | 3.16 |
| GB-PPP-ULT-MF-Com | 0.65 | 0.88 | 1.14 |
| GB-PPP-FIN-MF-Com | 0.60 | 0.79 | 0.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, C. BDS-PPP-B2b-Based Smartphone Precise Positioning Model Enhanced by Mixed-Frequency Data and Hybrid Weight Function. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137169
Gao Z, Wu Z, Liu S, Yang C. BDS-PPP-B2b-Based Smartphone Precise Positioning Model Enhanced by Mixed-Frequency Data and Hybrid Weight Function. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137169
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zhouzheng, Zhixiong Wu, Shiyu Liu, and Cheng Yang. 2025. "BDS-PPP-B2b-Based Smartphone Precise Positioning Model Enhanced by Mixed-Frequency Data and Hybrid Weight Function" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137169
APA StyleGao, Z., Wu, Z., Liu, S., & Yang, C. (2025). BDS-PPP-B2b-Based Smartphone Precise Positioning Model Enhanced by Mixed-Frequency Data and Hybrid Weight Function. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137169






