Abstract
In the paper analytical and numerical investigations on stable prestressed configurations of prismatic tensegrities with a non-minimal number of members are studied. Up to date, non-minimal prisms were rarely analyzed. Analytical equations are written based on the elastic energy approach and are further solved numerically. The prestressing procedure has a physical meaning due to changing the lengths of selected groups of members and is explained by a simple mathematical model. Also, an example of the physical model is presented. The results show that additional cables commonly used in non-minimal prismatic tensegrities can be replaced by bars, as well as that the total number of bars in non-minimal prismatic tensegrities can be doubled, in regard to minimal prismatic systems.
1. Introduction
Tensegrities are a subclass of spatial trusses known from their intrinsic features such as their ability to be prestressed and infinitesimal mechanisms. Currently the research on these systems is expanding, especially in fields such as space exploration [1,2,3,4], robotics [5,6,7,8,9], deployable structures [10,11,12,13,14,15,16] and civil engineering [10,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Please note that these fields interfere. Tensegrities are considered lightweight and material-efficient [26]. Some basic information and current trends on tensegrities can be found in [27,28,29].
The minimal and regular triplex, presented in Figure 1b, is the first invented and patented tensegrity structure [30,31,32]. Minimal refers to possessing the least number of members required to obtain a stable configuration [33], while regular refers to the fact that members of the same type are of an equal length. For example, structures presented in Figure 1b–d are minimal, while the structure presented in Figure 1e is non-minimal. All of the structures presented in the figure are regular. The triplex belongs to a group of structures called prismatic tensegrities and is the one that has the least number of bars, i.e., three [34]. Prismatic tensegrity systems include the triplex (t = 3), the quartex (t = 4), the pentex (t = 5) and so on—see Figure 1b–d, respectively. Prismatic tensegrities (Figure 1b–d) are built from bars (denoted as thick, black lines), cross cables (thin gray lines connecting upper nodes with lower ones) and horizontal cables (thin gray lines connecting upper nodes with themselves, as well as lower nodes with themselves). Horizontal cables create two parallel bases. It is characteristic that there is a defined angle of rotation between the upper and lower bases—here denoted as α. Angle α is calculated from a theoretical situation in which the bars are vertical, and the upper base starts to twist counterclockwise looking at the structure from top view (see Figure 1a, the structure presented in this figure is unstable). Please note that here the form-finding process is not considered, since it is assumed in advance that some members are bars and some cables. The angle is only a function of the number of bars—denoted as t. Exemplary values of α angles at which prismatic tensegrities remain stable are equal to: the triplex—α = 150° (Figure 1b), the quartex—α = 135° (Figure 1c) and the pentex—α = 126° (Figure 1d).
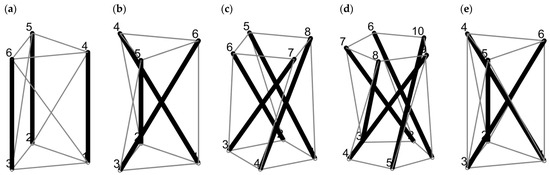
Figure 1.
Prismatic systems: (a) the unstable, theoretical initial configuration, (b) the triplex, (c) the quartex, (d) the pentex and (e) the non-minimal triplex (the first from a group of non-minimal prismatic systems). Drawn numbers indicate nodes.
The first studies on prismatic tensegrities were performed by [35], to be followed by [36] and others [37,38]. In [39] the connectivity, incidence and node matrices for all prismatic tensegrities in an analytical form were given. Ref. [40] studied methods of the morphogenesis of icosahedral and prismatic tensegrities, which was also practically used to analyze a tensegrity footbridge. The stiffness of prismatic tensegrities was studied in [41]. These are general studies on t-bar systems; however, a lot of individual studies were performed on triplex or quartex prisms, as well as on towers created based on these modules, just to mention the latest [42,43,44,45,46,47].
Prismatic tensegrities are categorized as “abstract tensegrities” by the classification presented in [48] and expanded in [49], which is based on the mechanics of trusses. Since the classification is important in the presented study, a short explanation is given here. A total of six features need to be defined in order to classify whether the structure is or is not a tensegrity. These are as follows: T—the structure is a truss; S—there is a self-stress state; C—tensile elements have no rigidity in compression (cables); M–there are infinitesimal mechanisms stiffened by the self-stress state; D—the extremities of compressed components do not touch each other, and bars constitute a discontinuous set; and I—the set of compressed components is included inside the set of tensile components. A total of four categories are considered. An “abstract tensegrity” possesses all of the features, a “pure tensegrity” possesses all of the features excluding D and a “structure with tensegrity features” possesses all of the features T, S and C, as well as at least one of the features M, D or I. A structure which does not meet the above criteria is considered as “not a tensegrity structure”. For example, structures presented in Figure 1b–d are “abstract tensegrities” (T, S, C, M, D and I), while the structure presented in Figure 1e is a “structure with tensegrity features” (T, S, C, D and I), though only additional cross cables were attached. However, this addition did remove the infinitesimal mechanism.
The literature shows that many structures are often not pure tensegrities and lie between trusses and tensegrities. This study also lies in an interesting and increasingly transient area between typical trusses and tensegrity trusses. For example, many deployable trusses are currently designed and analyzed [12,50,51], especially for space exploration as was mentioned before. On the other hand, trusses for a static, high load-bearing capacity and efficiency are created by a combination of bar and cable members, such as in [52]. Practical applications require elasticity in design, regardless of precise definitions. Also, please note that many structures labeled as tensegrities in the cited articles are called so, even though from the mechanical point of view of the presented classification they are not or are somewhere in between. Therefore, modified structures analyzed in this article, such as those presented in Figure 1e, will be called tensegrities. However, when the classification matter will be important, this will be detailed more accurately.
Up to date, tensegrities were not widely used in civil engineering. In case of prismatic tensegrities, the only real-scale civil engineering realization is the Rostock Tower in Germany—see Figure 2a. This structure is built from six triplex modules attached to each other by bar endings. In order for the structure to obtain the required stiffness to withstand the crucial wind load, the cross cables needed to be prestressed with a force of 1100 kN [53]. The Rostock Tower can be categorized as a “pure tensegrity” (T, S, C, M and I). The other closest realizations connected to prismatic tensegrities are the White Rhinos—the first was raised in 2001 and the second in 2012 [54,55]. The Rhinos are approximately 10 m tall supports for a membrane roof. The static scheme is closest to the non-minimal triplex modules, i.e., triplex modules with three additional cables (see Figure 1e). Creating such a scheme was beneficial from the point of view of structural stiffness; i.e., it eliminates the infinitesimal mechanisms. However, it categorizes these structures into “structures with tensegrity features” (T, S, C, D and I). Other examples are two sculptures created by Mr. Kenneth Snelson—The Needle Tower I (Figure 2c) and the Needle Tower II—see [29]. Both are self-supporting towers with heights equal to 18 and 30 m, respectively. They are classified as “abstract tensegrities”, since the bars of each layer are not connected to each other (T, S, C, M, D and I). From the point of view of an observer, the precise classification is less important than the architectural beauty. From the structural engineering point of view, the stiffness and economy are crucial. Therefore, the search for more stiff static schemes is driving this research, emphasizing the need to preserve the look-a-like tensegrity forms. Consequently, an analysis on non-minimal prisms is performed here.
It is worth noting that some other tensegrity structures were raised; however, these are not prismatic ones. The most impressive are the Olympic Gymnastic Hall is Seoul (Geiger dome) or the Atlanta Stadium Georgia Dome (Levy dome) [56]. Others are the Blur Building in Switzerland [57] and Kurilpa Bridge in Australia [58]. Some other tensegrity concepts were also considered, such as the Tor Vergata Footbridge [59] or the deployable footbridge [60].
In comparison to minimal prismatic systems, studies on non-minimal prismatic tensegrities are scarce. In general, non-minimal prismatic t-strut tensegrities in their most basic form are understood as prismatic ones with an additional number of t cross cables—see the modification between Figure 1b,e. It is well known that additional cables eliminate the infinitesimal mechanisms and stiffen the structure. Also, that is why “pure or abstract tensegrities” become “structures with tensegrity features”, as was presented in terms of classification. The most complete survey on these basic non-minimal prismatic tensegrities was performed by [61], where prisms of up to seven bars were studied. A procedure called “reconfiguration” was performed—see [62]. In the reconfiguration, the minimal prism is firstly prestressed, then additional cables are attached and afterwards these cables are shortened, creating the non-minimal prism and further prestressing the system. Also, studies on modifications with more additional members were performed. In [63], analyses on different kinds of prismatic tensegrities, with additional cable nets, were performed for space deployable constructions. In [64], a generalized form of prismatic tensegrities, called dihedral-line tensegrity structures, was presented. Also, in [65] three new prismatic tensegrities were created by modifying the three-bar prism by creating specific connections between existing and additional cables. Please note that the existing literature always assumes that additional members are cables (see Figure 1e or Figure 2b for non-minimal triplex). Moreover, it assumes that the angle of rotation between the upper and lower bases α does not change.

Figure 2.
Prismatic-based tensegrity structures: (a) Rostock Tower, (b) White Rhino I [66] and (c) Needle Tower II [29].
The novelty of this study shows that there are other configurations, which possess a doubled number of bars. For example, Figure 3a presents a minimal quartex prism, which possesses four bars in its basic form. Typically, a non-minimal quartex is understood as the modification of the previous one in which additional cables are mounted—see Figure 3b. Please note that these members are called cables, yet in the prestressed configuration they carry zero internal forces. In both cases the angle of the rotation between the upper and lower bases, here denoted as α, is equal to 135 degrees. What was not reported in the literature is that if the number of members is non-minimal, other values of the angle of rotation α are also possible and also create a stable configuration. For example, Figure 3c presents a non-minimal quartex with an angle α equal to 130 degrees, and Figure 3d presents a non-minimal quartex with an angle α equal to 110 degrees—both are stable. These configurations possess eight bars, instead of four. Therefore, it is shown that additional members can serve as bars, as well as that other angles of rotation α are possible to obtain.
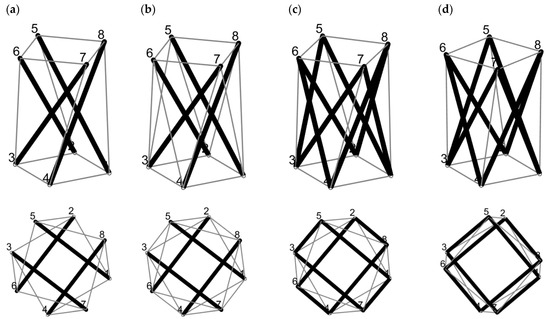
Figure 3.
Quartex: (a) minimal (α = 135°), (b) non-minimal (α = 135°), (c) non-minimal with doubled number of bars (α = 130°) and (d) non-minimal with doubled number of bars (α = 110°).
In this paper, the analysis will be derived based on the minimization of the elastic energy of the system in the prestressed state. This is an analytical approach. Such an approach was already used for analyzing the triplex module in [67,68,69]. However, due to computational limitations, the assumption was that only cross cables store the elastic energy, while other members are infinitely stiff. In general, a more common approach is the force density approach [70], which is a modification of the equation of the equilibrium of forces. In the case of the analytical approach, the triplex was analyzed in [71]. In the case of numerical calculations, the force density method is widely used—see for example [72,73,74]. However, the force density method in its basic numerical form assumes small displacements. The last most common method is the finite element method in its geometrically nonlinear form (updating the tangent stiffness matrix in every iterative load step)—see [75]. Also, more information on the force density method can be found in [76].
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 contains the assumptions and equations derived based on the minimization of elastic energy, as well as the specific approach toprestressing. Section 3 presents verification examples based on a comparison with examples existing in the literature, as well as a physical example of a minimal and non-minimal tensegrity prism. Section 4 presents two numerical examples of the prestressing procedure obtained by changing the lengths of different group members. Section 5 provides a discussion on potential applications. Finally, Section 6 encloses the article with conclusions.
2. Theory
2.1. Basic Assumptions and Limitations
Members of minimal prismatic tensegrities can be divided into three groups; these are as follows (see Figure 4a,b for an example of the quartex prism): 2t horizontal cables with the length denoted as l (black members 1–2, 2–3, 3–4, 1–4 and 5–6, 6–7, 7–8, 5–8), t bars with their length denoted as b (dark blue thick members 1–5, 2–6, 3–7 and 4–8) and t cross cables with their length denoted as s (light blue continuous line members 1–8, 2–5, 3–6 and 4–7).
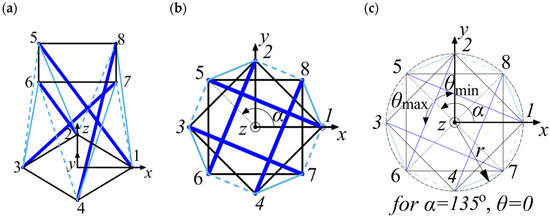
Figure 4.
Assumptions based on an example of the quartex module: (a) the axonometric view, (b) the top view and (c) the θ angle introduction.
The non-minimal prismatic tensegrities possess one more group—additional members denoted as a (light blue dashed line members 1–7, 2–8, 3–5 and 4–6).
Another thing is the α angle. For all prismatic tensegrities, this angle is a function of the number of bars t. Therefore, the initial angle α is (see Figure 4b)
Since it will be more convenient to work on a different rotational angle, the angle θ is introduced. This angle denotes a similar rotation as the α angle. However, for α equal to the value presented in Equation (1), the angle θ is equal to zero.
Also, an assumption on symmetry is made, where all members of the same group possess the same initial lengths. Moreover, during prestressing the members of the same group are prestressed simultaneously; i.e., the change in the length is applied to all group members. This implies the simplification of energy equations, making them able to be derived and written in an acceptable form. Due to symmetry, the description of the prism is dependent on only three variables: θ, r and b, where r is the radius of the circle circumscribed on the bases of the prism (Figure 4c). If the prism is not regular, multiple variables would need to be introduced to define the current configuration. For example, eight radii r, eight lengths b and eight θ angles would need to be introduced, in general, to define the nodes of the structure. This, however, would also require us to perform the form-finding procedure, since not whichever of these parameters would create a stable structure. Therefore, the symmetry assumption is crucial, especially for the possibility of writing the energy-based equations in an analytical form.
The angle θ has its limitations (Figure 4c). It possesses a minimal and maxima value. When increasing the rotation of the upper bases (θ > 0°, α > 135°), locking of bars with each other occurs at
while the locking of the bars and additional members occur when the rotation is decreased (θ < 0°, α < 135°):
In other words, the change in angle θ during prestressing is limited by these two bounds.
Also, in this study the material is linearly elastic, and strains are assumed to be small, although the displacements, as in every tensegrity, may be large.
It is also worth mentioning that non-minimal prismatic tensegrities possess three self-stress states, whereas the minimal ones possess only one—see [61]. This means that there are three possible ways of prestressing these structures, as well as infinite linear combinations of these three states, and each of them may or may not include all members of the structure. However, prestressing all members of a single group ensures that all of the three self-stress states are affected. In other words, prestressing whichever of the presented group enables us to prestress the whole structure in a symmetric way.
2.2. The Elastic Energy Approach
Examples of non-minimal prismatic tensegrities are presented in Figure 5a,b. According to Equation (1), angle α is a function of t; therefore, the coordinates of the lower base can be written as
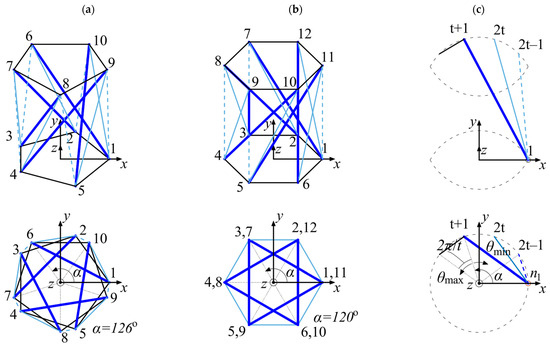
Figure 5.
Non-minimal: (a) pentex, (b) hexaplex and (c) drawing for lengths definition.
while for the upper base as
In order to define the lengths of bars, cross cables and additional members, three vectors are created from four nodes, i.e., n1 (for i = 1), nt+1 (j = t + 1), n2t−1 (j = 2t − 1) and n2t (j = 2t). Here, one node of the lower base is used, i.e., n1, and three nodes of the upper base are used, i.e., nt+1, n2t−1 and n2t. Therefore, the coordinates of these nodes are as follows:
while the lengths of members are , and . After simplifications the lengths of the prisms are as follows:
The elastic energy of the t-bar prism is:
where the last component of the equation originates from the relation between the radius and the base cable length established from the law of cosines as Now, finding the extremum of the energy U and comparing it to zero produces a system of three nonlinear equations (due to the fact, that the system is defined by three variables):
where partial derivatives are given in the Appendix A. Critical points, the local maximum and the local minimum, or saddle point, are verified by analyzing the following Hessian:
The second derivatives of the system, as well as the second derivatives of the energy, are also gathered in the Appendix A. The member forces are:
where are axial forces in cross cables, bars, additional members and horizontal cables, respectively.
A trivial solution to Equation (9) is θ = 0, r = rn and b = bn, which means no energy is in the system and the prism remain unstressed and unstable.
2.3. The Prestressing
In order to induce the prestress into the system (9), selected member groups need to change their lengths. From the computational point of view, an arbitrary value of one of the members’ group lengths can be assumed; i.e., for example s, bearing in mind that s > sn. This induces the energy to the system and enables us to find other prestressed lengths. This approach was used in [71], yet it requires to recalculate the natural length of one member in the iterative process. Here, a different approach to prestressing is proposed. In order to explain it, the quartex prism is analysed as an example—see Figure 6. In general, two configurations of whichever tensegrity are distinguished, i.e., the geometrical configuration (Figure 6a) and the prestressed configuration (Figure 6f). The geometrical configuration (Figure 6a) descents from the necessity of members to connect in nodes and it defines the theoretical values of lengths; i.e., values at which members can “meet” in nodes. Geometrical lengths are g-indexed. Also, a so-called natural lengths are introduced. These are actual physical lengths of members, which will be attached to nodes in order to create the structure (Figure 6c). Natural lengths are n-indexed. Natural lengths can have the same or different lengths as geometrical ones. If the natural lengths of all members are equal to geometrical lengths, then there is no prestress and the system is unstable (Figure 6b). If the natural lengths of bars and horizontal cables are equal to geometrical lengths, while cross cables’ natural lengths are shorter than geometrical ones (Figure 6d), the prestressing occurs (Figure 6f). It can be physically interpreted in a way that after assembling the bars and horizontal cables, one is assembling the cross cables, which are shorter than the theoretical distance between the nodes (Figure 6e). Therefore, the cross cables need to be extended in order to “reach” the two opposite nodes—when tensioned, the forces occur, and the system becomes prestressed. In practice, the cross cable lengths may not be shorter, yet they may be equipped with a roman screw. Therefore, a clear interpretation of the cause of the prestress is given; i.e., shorter cross cables are stressing other members.
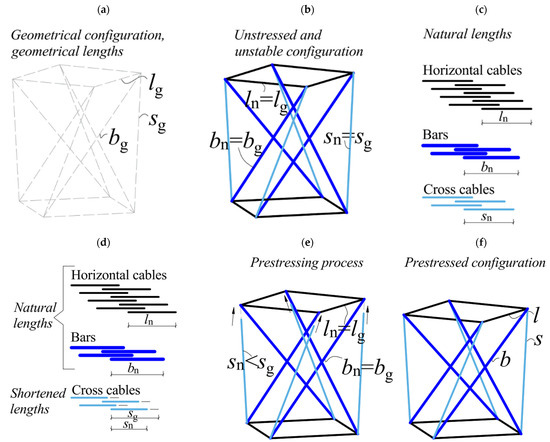
Figure 6.
The idea of prestressing: (a) the geometrical configuration, (b) the unstressed and unstable configuration, (c) natural lengths, (d) cross cables’ modified lengths, (e) the process of prestressing and (f) the prestressed configuration and lengths.
The relations between the geometrical and natural lengths are
where are so called prestress coefficients in cross cables, bars, additional members and horizontal cables, respectively. If one set’s ci > 1.0 the member is lengthened, if ci < 1.0 the member is shortened and if ci = 1.0 the natural length is equal to the geometrical one.
Now, using Equations (7), (9) and (12), as well as substituting the partial derivatives, results in a system of five nonlinear equations:
System (13) is solved numerically for θ, b, r, s and a using the Matlab fsolve function with the chosen Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm, while a positive definition of the Hessian from (10) is verified on specific numbers. The length variables and angle θ without any index denote the prestressed values. Please note that now the prestress is controlled by four coefficients: cb, cs, cl and ca. The system may be prestressed by changes in lengths of one ore more than one group of members. However, changes in coefficients are not made arbitrarily— for example some changes may cause the cables to slack. Since Hessian (10) can only possess positive stiffnesses, at each step a verification on cable slack is also made. This requirement can be easily written as: s < sn, l < ln and a < an for Na > 0 (if the additional member is tensioned; i.e., if in the prestressed state is interpreted to be a cable).
2.4. Simple Model of Behavior During Prestressing
Here, a simple model of the behavior during prestressing is presented in order to explain how prestressing coefficients ci are limited. Prestressing every member can be understood as inserting it between two supports, in which one is rigid and the other one is flexible with a defined stiffness k (see Figure 7). The stiffness k originates from the stiffness of the assembled tensegrity structure and is a function of the material and cross-section parameters, as well as the geometry of other members. It cannot be determined directly, yet for the sake of this example it will be assumed as constant value for understanding.
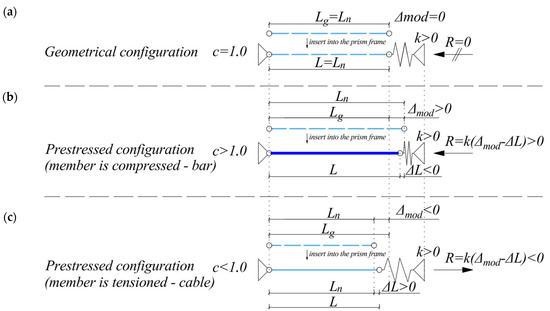
Figure 7.
Simple model of prestressed member, where three possibilities exists—the member is unstressed (a), the member is compressed (b) and the member is tensioned (c) after assemblance.
Prestressing coefficients can be generalized as follows (in regard to Equation (12)):
where L is the length of the considered member, and Δmod is the length modifier. Indexes n and g were explained previously. For positive values of Δmod, the member is lengthened. Please note that this modification has no effect on the prestressing of the member before it is installed between the supports or when is installed for Δmod = 0 (natural lengths are equal to geometrical ones—see Figure 7a). If the inserted member length is different than the distance between supports (Figure 7b,c), the member experiences external force due to the reaction of the flexible support. Assuming small strains, i.e., ε = (L − Ln)/Ln = ΔL/Ln, as well as determining the Δmod from Equation (14), the force R, which is externally interacting with the member, is a function equal to (see Figure 7b,c for spring reaction)
For positive values of Δmod, the ΔL values are always negative—the member, which is initially longer than the distance between supports, is starting to be compressed (Figure 7b). Therefore, it is identified as a bar. If the inserted member is shorter than the distance between supports, it starts to be tensioned—the member is identified as a cable (Figure 7c). In order to define the limitations of prestressing coefficients, the limit state is induced:
where E is the modulus of elasticity, A is the cross-section area and εf is the strain at failure of the material. Substituting (15) into (16) one obtains
For typical steel with E = 210 GPa and εf = 0.2%; a member with a cross-section made from CHS 26.9x2.3, i.e., A = 178 mm2; member length equal to Lg = 2000 mm; as well as assuming that strains in the member are equal to ε = 0.04%; Figure 8 presents the maximal prestressing coefficient in a function of stiffness.
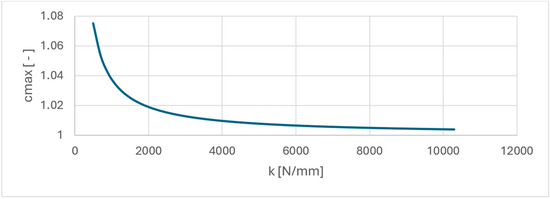
Figure 8.
Maximal values of prestressing coefficients due to material limitations, depending on the stiffness of the tensegrity system.
The solution shown in Figure 8 enables to understand how the prestressing coefficients’ maximal values are dependent on the general stiffness of the tensegrity structure. As can be seen, the greater the stiffness, the lower the values of the maximal prestressing coefficients. This is a simple example. However, in general, in order to verify the load-bearing capacity of members, a full analysis based on Equation (13) needs to be performed.
3. Verification
3.1. Comparison to Different Solution
Here, a comparative analysis on the reconfiguration from [61] and prestressing based on the method presented here is performed. In [61] a quartex prism is reconfigured into a non-minimal one. The reconfiguration involves three steps: (1) prestressing the minimal quartex, (2) attaching additional cables and (3) afterwards shortening them. The initial dimensions of the prestressed module were set as hg = 10 m, rg = 5 m, bg = 13.615 m, lg = 7.071 m, sg = 10.708 m and α = 45°, and the forces were Nl = 2798 N, Nb= −7621.3 N and Ns = 7621.3 N. Afterwards the additional cables were mounted with the length of ag = 10.708 m and Na = 0 N. The prestressing begins by shortening the additional cables, i.e., an < ag. The material properties for cables are N and for struts N. The procedure of the prestressing presented in this paper is different; i.e., the quartex is in its non-minimal form from the beginning and the internal forces at this point are zero. Therefore, it is expected that some differences in the results of this comparative analysis will occur.
The results are presented in Table 1, where values given in brackets are from [61] for comparison. The graphical results are presented in Figure 9, where thick lines denote compressed members (struts), and thin lines denote tensioned members (cables). Moreover, the member, which is the cause of the prestress, is denoted in red if it is a bar and in blue if it is a cable.

Table 1.
Comparative results on the non-minimal quartex prism.
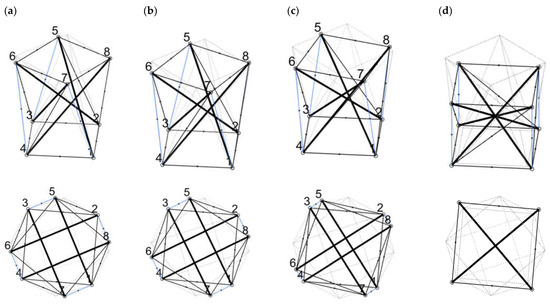
Figure 9.
Prestressing the non-minimal quartex by shortening the additional cables for e/l0 equal to (a) 0.056, (b) 0.093, (c) 0.187 and (d) 0.4632.
The results are comparable; i.e., the differences in the angle of rotation, radius and height are not large, considering the fact that the reconfigured quartex had initial forces at the beginning, as well as that these are rather different procedures of prestressing. Again, the procedure of the reconfiguration may be understood as external loading, whereas here internal forces occur only due to the changes in member group lengths. Unfortunately, there are not many more examples in the literature to be considered.
3.2. Physical Models
Here, two physical models are presented—the minimal quartex module (Figure 10a) and the non-minimal quartex module for θ = −10o (Figure 10b). The geometrical lengths are given in Table 2. Please note that the lengths are called geometrical here, since they are calculated for the unstressed module—for assembling a physical model this approach is accurate enough. Bars are made out of CHS 10x1mm, with the internal M10 thread crafted on each end. Bar endings are filled with M10 screws. Cables are made out of 3 mm diameter braided polypropylene lines, which were attached to M12 pads on both ends. Similar line dimensions were assured by using a simple device presented in Figure 10c, where two bolts with adjustable lengths are blocked with one screw. Polypropylene lines are attached to the bolts by M12 pads and are further attached to them in order to create the cables of the tensegrity structure.
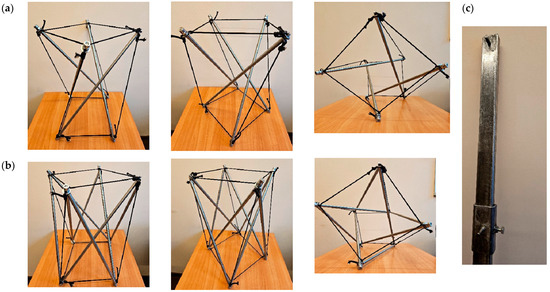
Figure 10.
Two quartex physical models: (a) minimal and (b) non-minimal for θ = −10°, as well as (c) a simple device for creating repetitive lengths of cables.

Table 2.
Geometrical dimensions of quartex physical models (calculated based on (7)).
The minimal quartex physical model is a well-known tensegrity (Figure 10a). The modified one is an example of the stable configuration of the 2t-bar system (Figure 10b). Please note that both models have similar lengths of horizontal cables and bars. In order to obtain similar lengths of bars with the change in the rotation angle θ, the height h needed to rise. Also, small changes in lengths of cross cables were made.
The presented models are simple, yet they show that the stability of these systems is possible.
4. Examples
4.1. Quartex Module
The procedure of prestressing the non-minimal quartex prism presented in Section 3.1 is extended here in order to show that lengthening the additional members, in comparison to shortening them, can also result in a stable configuration with additional members being bars. The initial data is given in Section 3.1 (the stiffness of additional struts remains as for additional cables). The prestressing coefficients in different prestressing scenarios are as follows: (1) ca = 1.05, (2) ca = 1.1, (3) ca = 1.15 and (4) ca = 1.2. The results are presented in Table 3, where other dimensions after prestressing are also given. The graphical behavior of the prism is presented in Figure 11.

Table 3.
Results on the quartex prism.
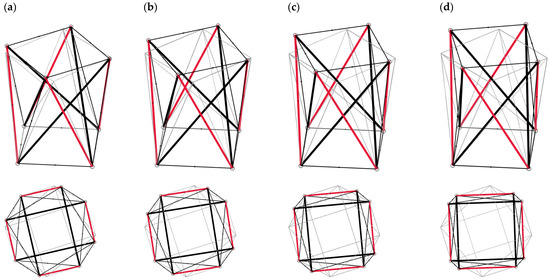
Figure 11.
Prestressing the non-minimal quartex by lengthening additional struts for (a) ca = 1.05, (b) ca = 1.1, (c) ca = 1.15 and (d) ca = 1.2.
Please note that the prism presented in Figure 11 possesses eight bars (thick lines denotes compression). Changes in relative lengths and the values of the rotation angle θ are presented in Figure 12a, while changes in forces are presented in Figure 12b. These values are supplemented by the results presented in Section 3.1. The non-minimal quartexes presented in Figure 11 can be classified as a “structures with tensegrity features” (T, C, S and I).
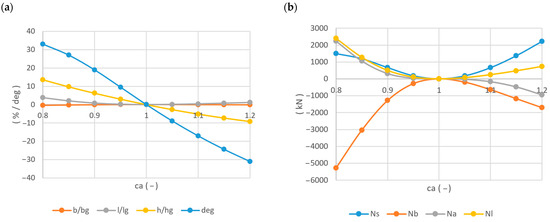
Figure 12.
Charts: (a) the relative lengths and angle of rotation changes and (b) forces—both in a function of the prestressing coefficient of additional members.
4.2. Pentex Module
Based on presented equations, a prism with whichever number of struts can be analyzed. However, in order to retain drawings readable, the pentex (t = 5) was chosen. The geometrical lengths are rg = 500 mm (lg = 587.79 mm) and bg = 2000 mm, and the dependent lengths are sg = 1847.22 mm and ag = 1797.38 mm. The structure’s geometrical height is hg = 1790.56 mm. The assumed product EsAs = EbAb = ElAl = EaAa = 103 N results in stiffnesses equal to ks = 0.5414 N/mm, kb = 0.5 N/mm, ka = 0.5564 N/mm and kl = 1.7013 N/mm. Please note that here stiffnesses are calculated based on geometrical lengths, whereas in numerical calculations they are referred properly to the natural lengths.
The module is prestressed based on scenarios presented in Table 4. In scenarios 1–3, cross cables, bars and horizontal cables are the cause of the prestress, respectively. In scenarios 4–5, the additional members are the cause of the prestress. Please note that using the prestressing coefficients, changes in multiple groups of members can be the cause of prestress, yet no such scenario was shown here. The results are given in Table 5 and Figure 13.

Table 4.
Prestressing scenarios.

Table 5.
Results on prestressing the non-minimal pentex.
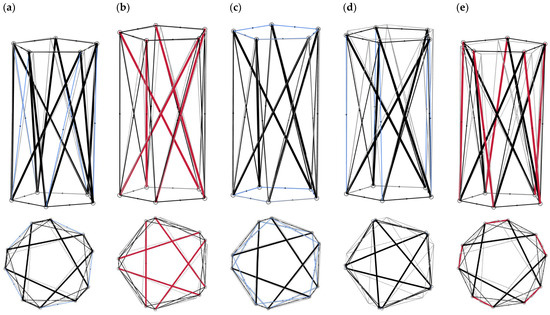
Figure 13.
Prestressed non-minimal pentex configurations–prestressing by (a) shortening the cross cables, (b) lengthening the bars, (c) shortening the horizontal cables, (d) shortening the additional members and (e) lengthening the additional members. Letters a–e match scenarios 1–5 in Table 4, respectively.
Again, one obtains a ten- or five-bar structure. If the sign of the rotational angle θ is positive, one obtains the five-bar prism (scenarios 2, 3 and 4—please note values of forces in additional members in Table 4). If the θ sign is negative, one obtains a ten-bar prism (scenarios 1 and 5). In general, it can be concluded that shortening the additional members and horizontal cables, as well as lengthening the bars, creates a t-bar non-minimal prism, while shortening the cross cables and lengthening the additional members creates a 2t-bar non-minimal prism. Also, it is clear that prestressing by changing the lengths of additional members causes the prism to rotate significantly in comparison to prestressing by changing in the lengths of other groups.
Again, the presented non-minimal pentex is classified as a “structure with tensegrity features”, regardless of whether it is built from ten or five struts.
5. Discussion
In general, these systems, depending on the material properties and selected cross-sections, can produce an interesting set of mechanical responses, which could be used in many fields of tensegrity analyses, such as robotics, civil engineering, meta-materials, etc. However, for the sake of this discussion, mainly potential advantages of their usage in civil engineering are discussed.
The first advantage in terms of the potential usage in civil engineering is the lack of infinitesimal mechanisms. Infinitesimal mechanisms create load paths that have very low mechanical responses and are stabilized by increasing the prestress levels. Increasing the prestress levels requires an increasement of the sizes of the cross-sections. Also, there are no eigenmodes and eigenfrequencies originating from these mechanisms, which are typically the lowest of all modes and frequencies of a particular structure. Another aspect of this change is that increasing the prestress levels also decreases the damping—see for example [77]. Moreover, bars in the 2t-configurations create a continuous frame (see Figure 11 and Figure 13a,d,e). This is expected to increase the stiffness, yet this needs to be verified quantitatively.
Another advantage originates from the increased internal space—see the comparison between a minimal triplex and non-minimal triplex (doubled bars) for θ = −15o in Figure 14. As can be seen, the latter possesses a larger inside radius. This enables to consider such module as usable segments of industrial towers or sightseeing towers, where the internal part would enable to lead the infrastructural or communication paths. Please note that the internal part is actually adjustable by changing the values of the θ angle.
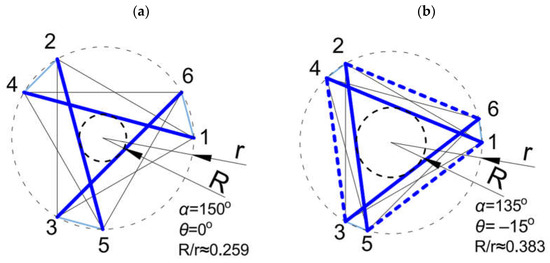
Figure 14.
Top view of (a) minimal and (b) non-minimal triplex module. Compare the difference in internal space.
In practical applications, a typical issue is the creation of joints. Joints of the Rostock Tower were connecting two bars and four cables in each node. Two bars did originate from connecting the lower and upper segments of two different triplex modules (Figure 2a). Here, in the case of the 2t-configurations, a total of four struts and four cables would need to be connected, which complicates the process. However, in the case of steel designs, a starting point can be achieved by using the standard [78], where such connections are considered for rectangular and circular hollow sections.
The potential applications in civil engineering are numerous, including towers with cantilever static schemes; small architecture objects or small modern modules of houses; and potentially every type of structure where modern architectural looks are important. Also, in case of deployable structures or soft robotics, an advantage may come from possibility of mounting the additional member with adjustable lengths. This way, changing the lengths of additional members changes the stiffness of the structure and allows it to rotate at a positive or negative angle θ. However, these matters need to be studied more deeply.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
In this paper, a new group of structures with tensegrity features was proposed based on the elastic energy approach. What is interesting is that depending on the angle of rotation θ one can obtain a 2t-bar and t-cross cable configuration or a t-bar and 2t-cross cable configuration. Also, prestressing using the additional members is very effective in increasing the value of the angle of rotation θ. Even small extensions of the additional member increase the angle rapidly. This is expected due to the fact that the additional members are working more or less in the direction of the infinitesimal mechanism of the minimal prismatic tensegrities.
In addition to the found prismatic systems, a physical and practical interpretation of the prestressing was proposed based on the elastic energy approach. Moreover, a simple model explaining the prestressing coefficients, as well as the behavior of the member during prestressing, was presented. The division of dimensions on the geometrically feasible lengths of the tensegrity prism and natural lengths of the members gives a good insight into the prestressing process.
In the case of classification, please, remember that minimal prismatic tensegrities are considered as “abstract tensegrities” (T, S, C, M, D and I). The non-minimal prismatic tensegrities for θ = 0; i.e., the typical ones reported in the literature, with additional cables, are actually “structures with tensegrity features” (T, S, C, D and I). This is due to the fact that there is no infinitesimal mechanism. Structures analyzed in this paper for θ > 0, i.e., the t-bar systems, are also “structures with tensegrity features” (T, S, C, D and I). Structures for θ < 0, i.e., the 2t-bar systems, are again “structures with tensegrity features” (T, S, C and I). The only difference between the t-bar and 2t-bar systems is that the latter do not create a discontinuous set of compressed elements. However, this does not change the results of the classification from the perspective of the used classification system. Therefore, since the difference between typical non-minimal tensegrities (θ = 0) and tensegrities analyzed here (θ≠0) lies in the fact that they do not possess the feature of a discontinuous set of compressed members, it is proposed to call these systems tensegrities—bearing in mind that all non-minimal systems are actually “structures with tensegrity features”.
Further work can go in many directions. First it would be important to verify the prestressed configurations with more physical models, as well as other numerical methods used in tensegrity analyses—for example the force density method. Second, analyses of the response of these systems under external loading would be valuable, as well as a general comparison to minimal prismatic tensegrities.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Partial derivatives for the non-minimal prismatic tensegrities
First derivatives
Second derivatives
Second derivatives of energy
References
- Jiang, G.; Sun, X.; Xiao, G.; Xu, J. Deep space landing—Soft tensegrity is possible for its designable performances. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2025, 300, 110455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, A.; Liu, H. Design and analysis of a double-helix tensegrity spherical lander. Mech. Res. Commun. 2023, 129, 104091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mi, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, W. Structural design and integral assembly procedure of rigid-flexible tensegrity airship structure. Eng. Struct. 2023, 284, 115803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, M.S.; Chen, M.; Losoya, E.Z.; Rodriguez, L.A.; Gildin, E.; Skelton, R.E. Tensegrity laboratory drilling rig for earth and space drilling, mining, and exploration. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2022, 252, 111785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, K.; Porez, M.; Wenger, P. Modeling and analysis of a four-leg tensegrity mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2025, 211, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Mei, R.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X. Motion behavior of a 30-strut locomotive tensegrity robot. Mech. Res. Commun. 2024, 137, 104270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Fang, H.; Yang, Q. Design and locomotion characteristic analysis of two kinds of tensegrity hopping robots. iScience 2024, 27, 109226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Shen, L.; Guo, S. A jellyfish robot based on two-bar and four-spring tensegrity structures. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 300, 117472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, M.; Skelton, R.E. Markov data-based reference tracking control to tensegrity morphing airfoils. Eng. Struct. 2023, 291, 116430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraternali, F.; de Casto Motta, J.; Germano, G.; Babilio, E.; Amendola, A. Mechanical response of tensegrity-origami solar modules. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2024, 17, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Boni, L.; Fu, Z.; Quarta, A.A.; Han, F.; Deng, Z. Thermal vibration analysis of cables in tensegrity during space deployment. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 616, 119208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, R.; Kou, Z. Design of a deployable aerodynamic decelerator based on a tensegrity structure. Acta Astronaut. 2024, 215, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, T.; Rhode-Barbarigos, L.; Keller, T. Effects of prestress implementation on self-stress state in large-scale tensegrity structure. Eng. Struct. 2023, 288, 116222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Xu, G. A tensegrity-based morphing module for assembling various deployable structures. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 173, 104870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrazmi, I.; Averseng, A.; Quirant, J.; Jamin, F. Deployable double layer tensegrity grid platforms for sea accessibility. Eng. Struct. 2021, 231, 111706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sultan, C. Deployment of foldable tensegrity-membrane systems via transition between tensegrity configurations and tensegrity-membrane configurations. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2019, 160, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charandabi, R.N.; Babilio, E.; Carpentieri, G.; Spagunolo, G.; Amendola, A.; Fraternali, F. A tensegrity structure for a solar stadium roof with sun-tracking capability. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 210, 113033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraternali, F.; Babilio, E.; Charandabi, R.N.; Germano, G.; Luciano, R.; Spaguno, G. Dynamic origami solar eyes with tensegrity architecture for energy harvesting Mashrabiyas. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2024, 19, 100190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vumiliya, A.; Luo, A.; Liu, H. Investigation of static and dynamic responses of tensegrity-based footbridge structures with integrated deck plates subjected to time-independent load. Mech. Res. Commun. 2025, 146, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heping, L.; Jian, S.; Yupeng, Q.; Ani, L. Analysis for a novel folding frame tensegrity tent. Structures 2023, 57, 105085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, P.; Tomasik, J. Influence of the support conditions on dynamic response of tensegrity grids built with Quartex modules. Arch. Civ. Eng. 2023, 69, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Albuquerque, N.B.; Gaspar, C.M.R.; Seixas, M.; Santana, M.V.B.; Cardoso, D.C.T. Design, fabrication and analysis of a bio-based tensegrity structure using non-destructive testing. Eng. Struct. 2022, 265, 114457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logzit, N.; Kebiche, K. Biaxial fatigue analysis model under non-proportional phase loading of tensegrity cable domes. Eng. Struct. 2021, 245, 112791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchione, F.; Chiappini, G.; Rossi, M.; Scoccia, C.; Munfo, P. Experimental assessment of the static mechanical behaviour of the steel-glass adhesive joint on a 1:2 scale tensegrity floor prototype. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 53, 104572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, M.C.; Miranda, R.; Sicignano, E.; Ferreira, A.J.M.; Skelton, R.E.; Fraternali, F. Composite solar facades and wind generators with tensegrity architecture. Compos. Part B 2017, 115, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Viscuso, S.; Zanelli, A.; Chen, J. Experimental Structural Template on Tensegrity and Textile Architecture Integrating Physical and Digital Approaches. Materials 2025, 18, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Jauregui, V.; Carrillo-Rodriguez, A.; Manchado, C.; Lastra-Gonzalez, P. Tensegrity Applications to Architecture, Engineering and Robotics: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, A.; Podio-Guidugli, P. Seventy years of tensegrities (and counting). Arch. Appl. Mech. 2022, 92, 2525–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearney, E.; Snelson, K. Kenneth Snelson—Art and Ideas; Marlborough Gallery: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, R.B. Tensile-Integrity Structures. No. 3,063,521, 13 November 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Emmerich, D.G. Construction de Reseaux Autotendants. Brevet D’invention. No. 1.377.290, 28 September 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Snelson, K. Continuous Tension, Discontinuous Compression Structures. No. 3,169,611, 2 February 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Skelton, R.E.; de Oliveira, M.C. Tensegrity Systems; Springer: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Motro, R. Tensegrity. Structural Systems for the Future; Kogan Page Science: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichs, L.A. Prismic Tensigrids. Struct. Topol. 1984, 9, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Connelly, R.; Terrell, M. Globally rigid Symmetric Tensegrities. Topol. Struct. 1995, 1995, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Guest, S.D.; Ohsaki, M. Symmetric prismatic tensegrity structures: Part I. Configuration and stability. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Li, S.X.; Zhu, S.X.; Zhang, B.Y.; Xu, G.K. Automatically assembled large-scale tensegrities by truncated regular polyhedral and prismatic elementary cells. Compos. Struct. 2018, 184, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, V.A.S.M.; Kurka, P.R.G.; Izuka, J.H. Analytical definitions of connectivity, incidence and node matrices for t-struts tensegrity prisms. Mechanics Res. Commun. 2024, 137, 104271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M. Morphogenesis analysis of icosahedral and prismatic tensegrity modules. Thin-Walled Struct. Part B 2024, 205, 112500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Luo, A.; Liu, H.; Feng, Y. Stiffness properties of regular p-bars tensegrity prisms under the compressive loading. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkiewicz, A. Tensegrity Simplex column analysis with different support conditions. Eng. Struct. 2024, 317, 118655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, P.; Tomasik, J. Dynamic Stability of Tensegrity Structures—Part II: The Periodic External Load. Materials 2023, 16, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, P.; Tomasik, J. Dynamic Stability of Tensegrity Structures—Part I: The Time-Independent External Load. Materials 2023, 16, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feron, J.; Latteur, P. Implementation and propagation of prestress forces in pin-jointed and tensegrity structures. Eng. Struct. 2023, 289, 116152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Zhu, W. A Cartesian spatial discretization method for nonlinear dynamic modeling and vibration analysis of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2023, 270, 112179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkiewicz, A.; Małyszko, L. Experimental and numerical static tests of tensegrity triplex modules. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2024, 72, e151674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, P.; Kłosowska, J.; Gilewski, W. Truth and Myths about 2D Tensegrity Trusses. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosowska, J. Assessment of the Possibility of Applying Tensegrity Structures to Building Construction. Ph.D. Thesis, Kielce University of Technology, Kielce, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sattar, M.; Rahman, N.U.; Ahmad, N. Design, kinematics and dynamic analysis of a novel double—Scissors link deployable mechanism for space antenna truss. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Cai, J.; Li, B. Design of deployable mesh reflector antenna based on cable-dome tensegrity structure. Structures 2024, 68, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, X. Experimental study on a novel cable-strut truss. Eng. Struct. 2022, 265, 114491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaich, M. The Messeturm in Rostock—A Tensegrity Tower. J. Int. Assoc. Shell Spat. Struct. 2004, 45, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Ohya, S.; Vormus, S. Long-Term Monitoring of White Rhino, Building with Tensegrity Skeletons. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium of IABSE/52nd Annual Symposium of IASS/6th International Conference on Space Structures: Taller, Longer, Lighter—Meeting Growing Demand with Limited Resources, London, UK, 20–23 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Ohya, S. Monitoring of full-scale tensegrity skeletons under temperature change. In Proceedings of the International Association for Shell and Spatial Structures (IASS) Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 28 September–2 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Obara, P.; Solovei, M.; Tomasik, J. Qualitative and quantitative analysisof tensegrity domes. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2023, 71, e144574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilewski, W.; Kłosowska, J.; Obara, P. Verification of Tensegrity Properties of Kono Structure and Blur Building. Procedia Eng. 2016, 153, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsote, O.O.; Arum, C.; Prucnal-Ogunsote, B. Aesthetic and economic imperatives in the design of the Kurilpa Pedestrian Bridge as a functional tensegrity structure. In Infrastructure, Economic Development and Built Environment: A Book of Readings; School of Environmental Technology, Federal University of Technology: Akure, Nigeria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Micheletii, A. Modular Tensegrity Structures: The “Tor Vergata” Footbridge. In Mechanics, Models and Methods, LNACM; Fremond, M., Maceri, F., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 61, pp. 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Veuve, N.; Safaei, S.D.; Smith, I.F.C. Active control for mid-span connection of a deployable tensegrity footbridge. Eng. Struct. 2016, 112, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Kawaguchi, K.; Feng, J. Prismatic tensegrity structures with additional cables: Integral symmetric states of self-stress and cable-controlled reconfiguration procedure. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 4294–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, C.; Corless, M.; Skelton, R.E. Symmetrical reconfiguration of tensegrity structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2002, 39, 2215–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Li, T.; Shao, M. Self-equilibrium, stability, and accuracy degradation of imperfect prismatic tensegrities with additional cable nets. Eng. Struct. 2023, 284, 115981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cai, J. Generalized prismatic tensegrity derived by dihedral symmetric lines. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2024, 205, 113068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ohsaki, M. New 3-bar prismatic tensegrity units. Compos. Struct. 2018, 184, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilewski, W.; Kłosowska, J.; Obara, P. Applications of Tensegrity Structures in Civil Engineering. Procedia Eng. 2015, 111, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheim, I.J.; Williams, W.O. Geometric Efffects in an Elastic Tensegrity Structure. J. Elast. 2000, 59, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheim, I.J.; Williams, W.O. Vibration of an elastic tenserity structure. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 2001, 20, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheim, I.J.; Williams, W.O. Vibration and damping in three-bar tensegrity structure. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2001, 14, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schek, H.J. The force density method for form finding and computation of general networks. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1974, 3, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraternali, F.; Carpentieri, G.; Amendola, A. On the mechanical modeling of the extreme softening/stiffening response of axially loaded tensegrity prisms. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2015, 74, 136–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Initial self-stress design of tensegrity grid structures. Comput. Struct. 2010, 88, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.C.; Lee, J. Self-stress design of tensegrity grid structures with exostresses. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 2660–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.P.; Feng, X.Q.; Gao, H. Self-equilibrium and super-stability of truncated regular polyhedral tensegrity structures: A unified analytical solution. Proc. R. Soc. A 2012, 468, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, S.; Kuhl, D. Non-linear static and dynamic analysis of tensegrity structures by spatial and temporal Galerkin methods. J. Int. Assoc. Shell Spat. Struct. 2005, 46, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L. The Finite Element Method; Butterworth-Heinemann: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Małyszko, L.; Rutkiewicz, A. Response of a Tensegrity Simplex in Experimental Tests of a Modal Hammer at Different Self-Stress Levels. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1993-1-8; Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures—Part 1–8: Design of Joints. European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2005.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).