Federated Learning for Surface Roughness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Technologies
2.1. Federated Learning
2.2. Mini-GPT with Time-Series Data
- a (measured value dimension): actual sensor readings, such as current, voltage, or vibration intensity;
- b (data type dimension): distinguishes data from different sources or sensor types;
- c (sampling frequency dimension): reflects the number of samples taken per second by the sensors.
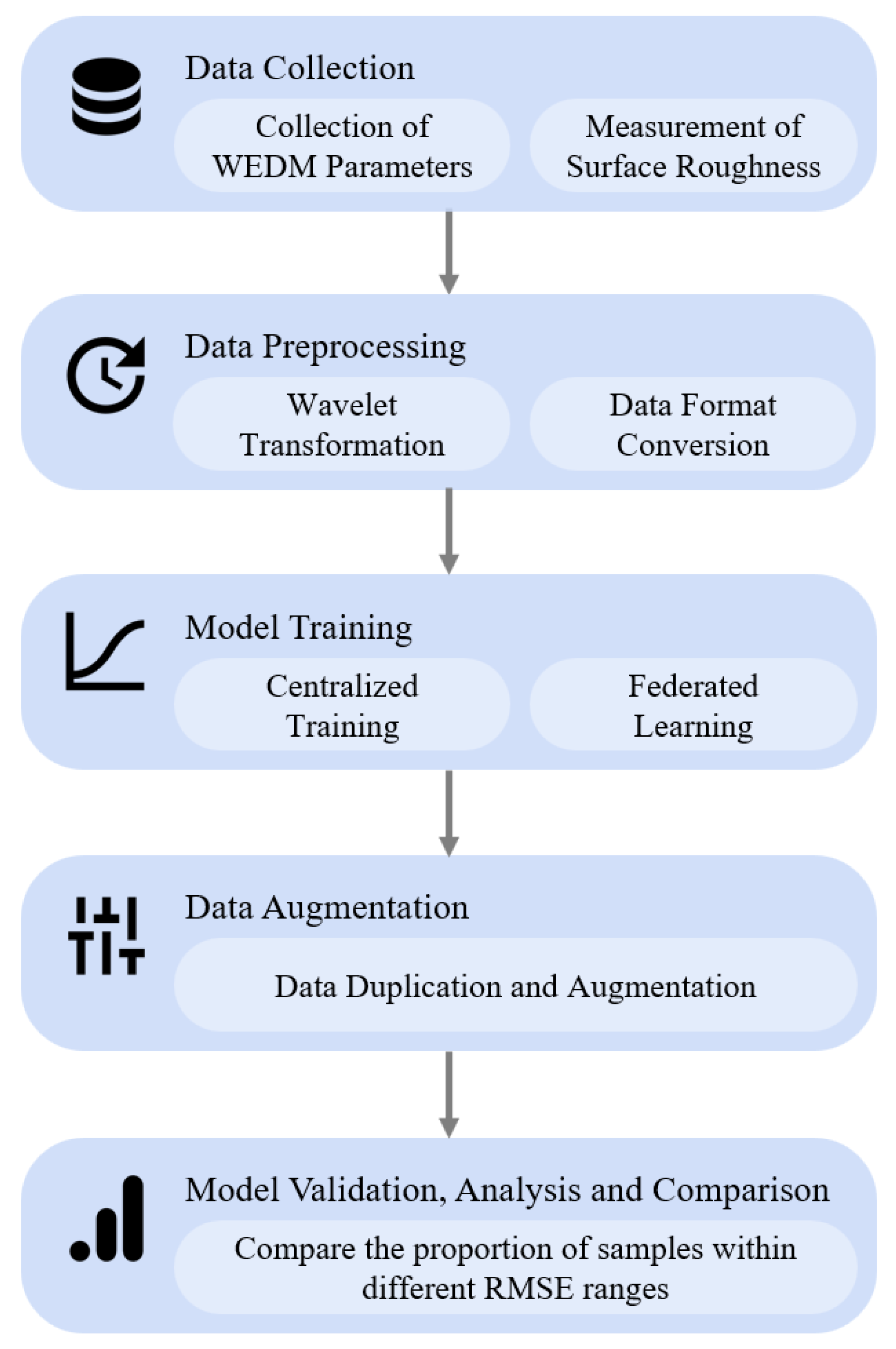
3. Methods
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. WEDM Data Collection
3.3. Measurement of Surface Roughness
3.4. Data Preprocessing
3.5. Federated Learning Framework
4. Results
4.1. Model Results for Surface Roughness Prediction in a Centralized Learning Environment
4.2. Model Results for Surface Roughness Prediction in a Federated Learning Environment
4.3. Federated Learning Prediction Before and After Data Balancing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Yuxi, F.; Mike, T.; Kuo-Yi, L. A review of applications in federated learning. Sci. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 149, 106854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianhui, L.; Xianghu, D.; Ning, J.; Weidong, Z. Federated Learning-Oriented Edge Computing Framework for the IioT. Sensors 2024, 24, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.; Hongwei, L.; Xizhao, L.; Guowen, X.; Haomiao, Y.; Sen, L. Efficient and Privacy-enhanced Federated Learning for Industrial Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 6532–6542. [Google Scholar]
- Tianhao, W.; Johannes, R.; Ce, Z.; Ruoxi, J.; Dawn, S. A Principled Approach to Data Valuation for Federated Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.06192. [Google Scholar]
- Yiqiang, C.; Jindong, W.; Chaohui, Y.; Wen, G.; Xin, Q. A Federated Transfer Learning Framework for Wearable Healthcare. arXiv 2021, arXiv:1907.09173. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, M.; Matthias, R.; Bill, L.; Christos, L. Stable Diffusion-based Data Augmentation for Federated Learning with Non-IID Data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.07925. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, W.; Zhixia, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhihua, C.; Jianghui, C.; Wensheng, Z. A survey on federated learning: Challenges and applications. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2023, 14, 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Kairouz, P.; McMahan, H.B.; Avent, B.; Bellet, A.; Bennis, M.; Bhagoji, A.N.; Bonawitz, K.; Charles, Z.; Cormode, G.; Cummings, R.; et al. Advances and Open Problems in Federated Learning. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 2021, 14, 1–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiting, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wen, W.; Haixia, P.; Ning, Z.; Hongke, Z. Optimizing Federated Learning in Distributed Industrial IoT: A Multi-Agent Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 3688–3703. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Li, C.; Wenyi, Z. Decentralized Federated Learning: Balancing Communication and Computing Costs. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2107.12048. [Google Scholar]
- Conde, A.; Arriandiaga, A.; Sanchez, J.A.; Portillo, E.; Plaza, S.; Cabanes, I. High-accuracy wire electrical discharge machining using artificial neural networks and optimization techniques. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2018, 49, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, U.; Osman, A.; Turan, G.; Cihan, O. Surface roughness prediction of machined aluminum alloy with wire electrical discharge machining by different machine learning algorithms. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12519. [Google Scholar]
- Jehn-Ruey, J.; Cheng-Tai, Y. Product Quality Prediction for Wire Electrical Discharge Machining with Markov Transition Fields and Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5922. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Dechang, P. Milling Surface Roughness Prediction Based on Physics-Informed Machine Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Jeng, S.Y.; Lin, C.J. Prediction and Analysis of the Surface Roughness in CNC End Milling Using Neural Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlayasiri, K.; Boonmung, S. An investigation on effects of wire-EDM machining parameters on surface roughness of newly developed DC53 die steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 187–188, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodun, O.; Slătineanu, L.; Coteaţă, M.; Merticaru, V.; Nagîţ, G. Surface Roughness at Wire Electrical Discharge Machining. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 760, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.K.; Munira, B.M.A.; Norhashimah, B.M.S. Relationship of Surface Roughness with Current and Voltage During Wire EDM. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 6, 2317–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Rieke, N.; Hancox, J.; Li, W.; Milletari, F.; Roth, H.R.; Albarqouni, S.; Bakas, S.; Galtier, M.N.; Landman, B.A.; Maier-Hein, K.; et al. The future of digital health with federated learning. Digit. Med. 2020, 119, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.; Mehdi, A.; Abdenour, B.; Hussin, L.; Ali, R. Reviewing Federated Learning Aggregation Algorithms; Strategies, Contributions, Limitations and Future Perspectives. Electronics 2023, 12, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharati, S.; Mondal, M.R.H.; Podder, P.; Prasath, V.B.S. Federated learning: Applications, challenges and future directions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.09513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Conde, A.; Arriandiaga, A.; Wang, J.; Plaza, S. Unexpected Event Prediction in Wire Electrical Discharge Machining Using Deep Learning Techniques. Materials 2018, 11, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hard, A.; Rao, K.; Mathews, R.; Ramaswamy, S.; Beaufays, F.; Augenstein, S.; Eichner, H.; Kiddon, C.; Ramage, D. Federated Learning for Mobile Keyboard Prediction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.03604. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, J.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Elhoseiny, M. MiniGPT-4: Enhancing Vision-Language Understanding with Advanced Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.10592. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 25178-2:2021; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Areal—Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.














| Absolute Error | Sample Proportion | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| <0.025 | 29.79 | 87 |
| 0.025–0.05 | 14.72 | 43 |
| 0.05–0.075 | 10.96 | 32 |
| 0.075–0.1 | 16.09 | 47 |
| >0.1 | 28.42 | 83 |
| Absolute Error | Sample Proportion | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| <0.025 | 20.89 | 61 |
| 0.025–0.05 | 13.36 | 39 |
| 0.05–0.075 | 10.62 | 31 |
| 0.075–0.1 | 17.12 | 50 |
| >0.1 | 38.01 | 111 |
| Absolute Error | Sample Proportion | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| <0.025 | 26.03 | 76 |
| 0.025–0.05 | 15.41 | 45 |
| 0.05–0.075 | 11.30 | 33 |
| 0.075–0.1 | 17.12 | 50 |
| >0.1 | 30.14 | 88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, K.-L.; Ting, Y.-H.; Jong, W.-R.; Chen, S.-C.; Zhou, Z.-W. Federated Learning for Surface Roughness. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7046. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137046
Cheng K-L, Ting Y-H, Jong W-R, Chen S-C, Zhou Z-W. Federated Learning for Surface Roughness. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7046. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137046
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Kai-Lun, Yu-Hung Ting, Wen-Ren Jong, Shia-Chung Chen, and Zhe-Wei Zhou. 2025. "Federated Learning for Surface Roughness" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7046. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137046
APA StyleCheng, K.-L., Ting, Y.-H., Jong, W.-R., Chen, S.-C., & Zhou, Z.-W. (2025). Federated Learning for Surface Roughness. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7046. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137046






