Abstract
Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) is valued for its fibers and nutrient-rich seeds, which are increasingly consumed for their health benefits. However, flaxseeds can also accumulate potentially toxic elements (PTEs), raising concerns about safety. This study quantified 11 essential elements (e.g., Ca, Fe, Mg, and Zn) and 9 PTEs (e.g., Al, Cd, Pb, and Ni) in commercial flaxseed samples using inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry. Two intake scenarios (15 g/day and 30 g/day) were analyzed to estimate dietary exposure, with health risks assessed through the target hazard quotient (THQ) and hazard index (HI). The results showed that organic flaxseeds had higher levels of certain elements (e.g., Cu, K, and Pb), while Al and Ni were more abundant in conventional samples. Cadmium levels in both remained below the EU regulatory limit. The highest estimated daily intakes were for K, Mg, and Ca, highlighting the seeds’ nutritional value. However, HI values suggested that Al and Pb could pose health risks. These findings emphasize flaxseeds’ dual nature as both beneficial and potentially harmful, particularly given the lack of specific regulatory limits and limited data on elemental composition. Continued monitoring and risk assessment are recommended to safeguard public health.
1. Introduction
Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) is an herbaceous plant that can grow up to a height of one meter and is primarily cultivated for two commercial products: fibers and seeds. The plant’s fibers are highly valued in the textile industry due to their exceptional tensile strength, which is largely attributed to their high cellulose content [1,2]. Flaxseeds, on the other hand, have gained prominence in the food industry because they are rich in bioactive compounds, including alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), proteins, and lignans [3,4,5]. Additionally, flaxseeds are notable sources of essential elements such as calcium (Ca), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), sodium (Na), phosphorus (P), and zinc (Zn) [6]. They can be consumed whole or in flour form and are included in both human and animal diets [3,7,8].
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in 2022, the largest producers of raw or retted flax fibers were countries within the European Union—specifically France, Belgium, and Belarus—followed by China and Russia [9]. In contrast, the leading producers of flaxseeds in 2022 were Russia (1.77 million tons), Kazakhstan (0.85 million tons), and Canada (0.47 million tons). The global market value for flaxseeds is projected to reach USD 0.89 billion in 2024 and could rise to USD 1.54 billion by 2029 [10].
Seeds such as chia and flax are increasingly recognized for their nutritional value, particularly as sources of vitamins and essential elements [6,11]. However, these agricultural products are also susceptible to contamination via multiple environmental pathways. Contaminants, especially heavy metals and other trace elements, may be introduced through the soil, irrigation with contaminated water, or atmospheric deposition [12,13,14]. For example, the application of phosphate fertilizers, waste deposition, metallurgical industry practices, mining operations, and the combustion of fossil fuels are the primary anthropogenic sources of Cd in the soil [15]. Numerous studies have documented the adverse effects of heavy metals on crop quality and food safety [16,17,18,19]. Moreover, many plant species, including food crops, have the capacity to bioaccumulate these elements, leading to potential transfer through the food chain and eventual human exposure [20,21]. In the case of fiber-rich plants, this can pose a problem, given that such bioaccumulation can occur in various plant structures, including the stem, root, and leaves [20].
Although the European Union has established regulatory limits for various contaminants in food products, only cadmium (Cd) currently has a defined maximum limit for flaxseeds [22]. Previous research has demonstrated the presence of multiple metals in seed samples, including chia and flax [11,23,24]. Among these studies, only one quantifies the metal concentration in flaxseeds and is limited to only 10 metals [23]. A recent study analyzing 20 chemical elements in chia seeds highlighted the potential health risks associated with chronic exposure to some of these elements [11]. The ingestion of food contaminated with potentially toxic metals remains a significant public health concern [25].
Despite the increasing nutritional and commercial relevance of flaxseeds, limited data are available on their content of essential and toxic elements. There is a clear knowledge gap regarding both the nutritional contribution of essential metals and the toxicological risks associated with potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in flaxseeds. Thus, the aims of the present study were to (1) quantify the concentrations of 20 chemical elements in commercially available flaxseed samples; (2) assess nutritional value and toxicological risks based on dietary exposure; and (3) conduct a risk characterization for elements with established reference doses (RfDs).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A total of 52 flaxseed samples, commercially obtained in the European Union and other European countries, were analyzed in this study. Regarding the origin of the seeds, 37 were classified as conventional and 15 as organic. The seeds were obtained from supermarkets, herbalists, and online stores.
2.2. Sample Preparation Procedure
In triplicate, 5 g samples of flaxseeds were weighed into a pre-weighed porcelain capsule (Staatlich, Berlin, Germany) and dried in an oven (Nabertherm, Lilienthal, Germany) at 80 °C for 24 h. After dehydration, the samples were weighed again and transferred to a muffle furnace (Nabertherm, Lilienthal, Germany) at a temperature of 450 °C. The temperature was gradually increased during the first 24 h, followed by an additional 48 h, totaling 72 h in the muffle furnace. After cooling, the ash content was weighed. The ash samples were treated with 65% nitric acid (HNO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) for 24 h and 48 h after the start of the procedure in the muffle furnace. Finally, the ash samples were diluted in 1.5% nitric acid (HNO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) in 25 mL of distilled water.
2.3. Determination of Essential and Toxic Elements
The quantification of the elements, including essential and potentially toxic ones, was performed using inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) with a Thermo Scientific iCAP PRO ICP-OES autosampler (Waltham, MA, USA). Quality control was ensured by utilizing certified reference materials. The instrumental limits of detection and quantification were estimated based on the instrumental response of the equipment. Specifically, these were determined through the analysis of 15 blanks under reproducibility conditions [26]. The operational parameters of the ICP-OES are detailed in Supplementary File Table S1, while the recovery percentages (RPs), detection limits (LODs), quantification limits (LOQs), and wavelengths corresponding to each analyzed element, as part of the quality control, are provided in Supplementary File Table S2.
Although comprehensive studies assessing the concentration of numerous elements in flaxseeds are limited, inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) has proven to be a rapid, sensitive, and reliable method for determining metals such as Cd and Pb specifically in oilseeds, with the potential for quantifying other metals [11,27]. In this regard, as in our study, using ICP-OES to determine the concentration of PTEs allows for understanding the levels of these elements in this group of foods.
2.4. Dietary Exposure Assessment
Exposure assessment consists of calculating the estimated daily intake (EDI) (Equation (1)). The calculation of EDI is a flexible model that allows for variation in its parameters to estimate the daily intake.
where Cmetal is the average concentration of each metal in flaxseeds (mg/kg); DI is the daily intake of flaxseeds (15 or 30 g flaxseeds/day); EF is exposure frequency (365 days/year); ED is the average duration of exposure to flaxseeds (25 years); BW is the average body weight (70 kg); and AT is the average exposure time (EF × ED). To assess the nutritional and toxicological implications of the estimated dietary intake (EDI) of the studied elements via flaxseeds, the nutritional reference intake (NRI), the tolerable daily intake (TDI), the tolerable weekly intake (TWI), and the tolerable upper intake level (UL) served as reference values (Supplementary File Table S3) [28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38].
The calculation of the EDI’s contribution to the nutritional and toxicological reference values was performed and measured as a percentage (Equation (2)).
where EDI means the estimated daily intake; NRI means the nutritional reference intake; TDI means the tolerable daily intake; TWI means the tolerable weekly intake; and UL means the tolerable upper intake level.
2.5. Risk Characterization
Finally, risk characterization was calculated for all elements with a pre-established reference dose (RfD) (Table 1). This was done by calculating the ratio between the EDI and the RfD for each element, yielding the target hazard quotient (THQ). Subsequently, the sum of the THQs for these elements results in the hazard index (HI), where values exceeding 1 indicate a potential health risk under the consumption scenario defined by EDI.

Table 1.
Reference doses of the essential elements and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) [39].
Equations (3) and (4) represent the calculations for THQ and HI, respectively.
where THQ means the target hazard quotient, EDI means the estimated daily intake, RfD means the reference dose, and HI means the hazard index.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Mean comparison tests (t-test) and distribution comparison tests (Mann–Whitney test) were performed to analyze organic and conventional flaxseed groups. The choice of tests was based on data distribution, as determined by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov normality test [40]. GraphPad Prism 8.2.1 was used for all statistical analyses and graph construction.
3. Results
The mean and range of concentrations of metals in flaxseed samples are presented in Table 2. The elements were grouped according to seed type (organic and conventional) and categorized as essential elements and potentially toxic elements (PTEs). Among the essential elements (C, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, Na, and Zn), only 4 out of 11 (Cu, K, Mg, and Na–36.4%) showed higher concentrations in the organic group compared to the conventional samples. On the other hand, more than half (55.6%) of the PTEs (B, Ba, Pb, Sr, and V) classified as organic exhibited higher levels when compared to their conventional counterparts.

Table 2.
Concentrations of elements (mg/kg) in organic and conventional flaxseed.
When grouped by seed type (Figure 1 for essential elements and Figure 2 for potentially toxic elements), t-tests and Mann–Whitney tests revealed that metal concentrations varied between organic and conventional seeds for certain elements. Al and Ni exhibited higher levels in conventional flaxseeds compared to organic flaxseeds (p = 0.0312 and p = 0.0142, respectively). Moreover, Na showed a decrease in concentration in the conventional samples compared to the organic group (p = 0.0072).
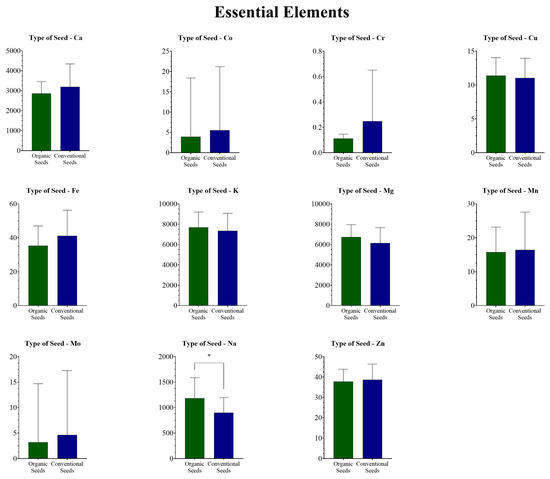
Figure 1.
Essential elements (mg/kg) in organic and conventional flaxseed samples. * Statistically significant difference (p < 0.05).
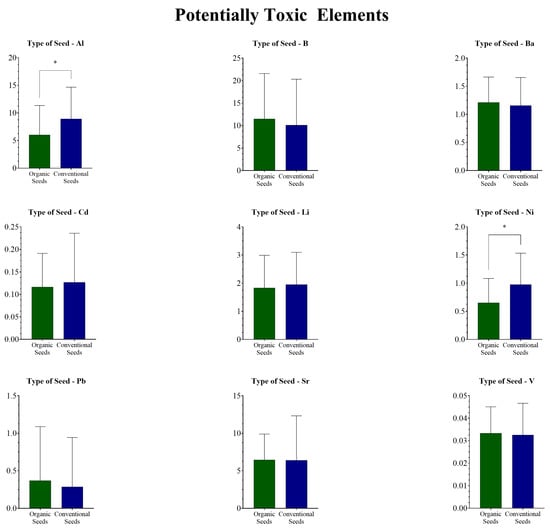
Figure 2.
Potentially toxic elements (PTEs) (mg/kg) in organic and conventional flaxseed samples. * Statistically significant difference (p < 0.05).
Table 3 presents the estimated daily intake (EDI) of each element based on daily flaxseed consumption of either 15 g/day or 30 g/day. The highest EDI values were observed for K, Mg, and Ca, respectively. Hazard index (Figure 3) values above 1 were observed for Al and Pb in both exposure scenarios (15 and 30 g/day) for both organic and conventional seed groups. In the 15 g/day exposure scenario, Al yielded an HI of 3.22 and 4.79, while Pb yielded an HI of 789.15 and 612.01 (organic and conventional seeds, respectively). Similarly, in the exposure scenario with flaxseed consumption of 30 g/day, Al yielded an HI of 6.45 and 9.58, whereas Pb presented HI values of 1578.3 and 1224.02 (organic and conventional seeds, respectively).

Table 3.
Estimated daily intakes (EDIs) in both dietary consumption scenarios.
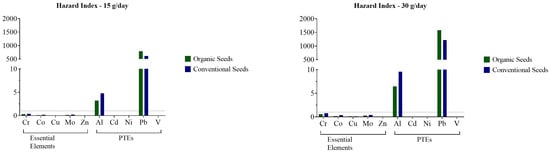
Figure 3.
Hazard indices (HIs) of the analyzed elements in different exposure scenarios: 15 and 30 g flaxseeds/day. The dotted line intersects the Y-axis at 1, where values above this threshold indicate risk.
4. Discussion
This study assessed the concentrations of a range of essential elements and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in flaxseeds, a food increasingly consumed as part of health-conscious diets. In accordance with Regulation (EU) 2023/915—which sets maximum permissible levels for contaminants in food within the European Union—Cd is the only regulated element for linseeds (flaxseeds), with a limit of 0.50 mg/kg. Our findings indicate that Cd concentrations in both organic (0.116 mg/kg) and conventional (0.127 mg/kg) flaxseed samples were well below this regulatory threshold. Traditionally, Cd is recognized for its toxic, carcinogenic, and stimulating effects, in addition to its association with other diseases such as emphysema, asthma, bronchitis, and hypertension, particularly in cases of chronic intoxication [41].
Although Pb is included in the regulation for several food categories, there is currently no specific limit established for flaxseeds or oilseeds more broadly. This regulatory gap is noteworthy given that Pb was detected in our samples and may pose health concerns depending on exposure levels. On the other hand, for certain metals like Al, their concentration in food merely serves as a basis for their potential toxicity, given that the exposure pathway and toxicodynamics of each metal within the organism bear a distinct relevance to the degree of toxicity [42].
Among the elements analyzed, Al exhibited a statistically significant difference between organic and conventional flaxseeds in our study. This finding is of particular concern, as Al has garnered increasing attention due to its potential neurotoxic effects. Several studies have suggested a link between elevated Al exposure and the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease [43]. Although the concentration of Cd is below the legally established limits, it is important to emphasize that the average Cd concentration in European soils is higher than in other regions such as China and the United States [15], and this may influence its concentration in seeds.
When comparing our results with data from the literature, such as a recent study on sesame seeds, the concentrations of Fe, Zn, Cu, and Ni in our flaxseed samples were generally lower, except for manganese (Mn), which was found at comparable or slightly lower levels [44]. Similarly, Gu et al. [23] reported higher concentrations of most analyzed elements in flaxseeds, including Al, Cd, Cu, Fe, Ni, Mn, and Zn, while Pb was found at lower levels than those observed in our study. In their study, the concentration of Al (13.8 ± 3.4 mg/kg), Cd (0.49 ± 0.17 mg/kg), and Pb (0.0048 ± 0.003 mg/kg) was higher than those reported in our study for Al (6.02 and 8.94 mg/kg) and Cd (0.12 and 0.13 mg/kg), but lower for Pb (0.37 and 0.29 mg/kg), for organic and conventional groups, respectively.
Our results confirm that flaxseeds can serve as valuable dietary sources of essential elements such as K, Mg, and Na. The nutritional benefits of flaxseed consumption have been well documented, particularly for cardiovascular and metabolic health [45,46]. Daily intake of 15 to 40 g has been associated with improved lipid profiles, reduced blood pressure, and lower fasting glucose and insulin resistance indices [47]. According to our risk assessment, the maximum permissible intake value to avoid a hazard index above 1 for Al would be 3.5 g/day of flaxseeds, but there would still be a risk associated with Pb. It is important to emphasize that risk assessment employs a quantitative approach that depends on a series of variables and that Pb notably elevates the hazard index in many risk assessments conducted within these parameters.
Some metals, such as Cr, Ni, Cd, Pb, Zn, and Cu, can pose risks to plant life and human health [48]. Furthermore, excessive consumption of contaminated foods can trigger adverse health effects, including liver and kidney diseases from Cd [49] and neurotoxic damage from Pb [50]. Conversely, Ni, for example, is highly mobile in plants and does not accumulate in plant tissues, thus posing less harm to consumers [51]. The implications of consuming flaxseeds contaminated by metals are still rarely discussed in literature. In a review study evaluating 67 articles that investigated the benefits of flaxseed consumption, it was observed that none of them mentioned the risk of heavy metal contamination [52]. However, our findings also indicate that these potential health benefits may be accompanied by the risk of exposure to PTEs such as Al and Pb, which are known to exert toxic effects at elevated levels. Although the risk assessment employed in this study is based on predictive and deterministic exposure scenarios, it highlights the need for continued surveillance of chemical contaminants in emerging food products.
Finally, while flaxseeds represent a promising functional food, their safety profile must be closely monitored. Given their growing popularity, regular analytical assessments and the establishment of regulatory limits for a broader range of elements are essential to protect public health and inform evidence-based dietary recommendations.
5. Conclusions
The consumption of novel alternative foods and dietary supplements has increased in recent years, with oilseeds such as flaxseeds gaining popularity. This study evaluated the concentrations of 20 chemical elements in flaxseeds obtained from both organic and conventional sources. Among these, only Cd is currently regulated for this food category within the European Union. Notably, the Cd levels detected in our samples were within the established regulatory limits. The assessment of the hazard index revealed that Al and Pb may pose potential health risks.
These findings highlight a broader concern: the lack of established safety thresholds for potentially toxic elements in flaxseeds and similar emerging food products. Coupled with the limited availability of analytical studies in this area, this regulatory gap may obscure potential risks to human health.
Therefore, we underscore the urgent need for more comprehensive analytical investigations into the elemental composition of such foods. These efforts are essential to support evidence-based policymaking and to enable risk managers to safeguard public health by effectively addressing dietary exposure risks.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app15137004/s1, Table S1: Operational parameters of the ICP-OES; Table S2. Quality control for ICP-OES analysis; Table S3. Nutritional and toxicological reference values of the analyzed elements; Reference List (Supplementary File).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.R., A.H., S.P.-M., R.d.L.B., M.M. and F.M.R.d.S.J.; methodology, C.R., A.H., Á.J.G.-F., S.P.-M. and R.d.L.B.; software, S.A.-V.; validation, D.G.-W., R.d.L.B. and S.A.-V.; formal analysis, R.d.L.B. and K.S.; investigation, C.R., F.M.R.d.S.J., R.d.L.B. and S.P.-M.; resources, A.H., K.S., M.M. and E.P.; data curation, R.d.L.B. and F.M.R.d.S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, R.d.L.B. and C.R.; writing—review and editing, R.d.L.B., C.R., F.M.R.d.S.J. and M.M.; visualization, A.H.; supervision, C.R. and F.M.R.d.S.J.; funding acquisition, M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Project No. 49/ZJZ/2024/DOS, financed from the subsidy granted to the Krakow University of Economics. This research was supported by the Coordenacao de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nivel Superior (CAPES) (Brazil), grant 88881.981046/2024-01.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Vaisey-Genser, M.; Morris, D.H. Introduction: History of the Cultivation and Uses of Flaxseed. In Flax; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 13–33. ISBN 978-0-429-20585-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Liu, X.; Yue, Q.; Xian, G. Hydrothermal Durability of Unidirectional Flax/Carbon Fiber Hybrid Composite Plates. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 2043–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorian, T.J.; Pianesso, D.; Bender, A.B.B.; Speroni, C.S.; Mombach, P.I.; Kowalski, É.A.; da Silva, L.P. Fractionation of Linseed and Obtaining Ingredients Rich in Protein and Fibers: Alternatives for Animal Feed. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, M.; Bhatia, N. Linseed and Its Basic Composition. Int. J. Adv. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 8, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambe, H.K.; Wanasundara, J.P.D. Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum, L.) for Protein Based Products. In Sustainable Protein Sources, 2nd ed.; Nadathur, S., Wanasundara, J.P.D., Scanlin, L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 339–356. ISBN 978-0-323-91652-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bernacchia, R.; Preti, R.; Vinci, G. Chemical Composition and Health Benefits of Flaxseed. Austin, J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 2, 1045. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziejczyk, P.; Ozimek, L.; Kozłowska, J. 11—The Application of Flax and Hemp Seeds in Food, Animal Feed and Cosmetics Production. In Handbook of Natural Fibres; Kozłowski, R.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 329–366. ISBN 978-1-84569-698-6. [Google Scholar]
- Olombrada, E.; Mesias, M.; Morales, F.J. Risk/Benefits of the Use of Chia, Quinoa, Sesame and Flax Seeds in Bakery Products. An Update Review. Food Rev. Int. 2024, 40, 1047–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. FAOSTAT—Crops and Livestock Products. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 14 November 2024).
- Mordor Intelligence. Flax Seeds Market Size & Share Analysis—Growth Trends & Forecasts (2024–2029). Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/flaxseeds-market (accessed on 19 November 2024).
- González-Weller, D.; Bethencourt-Barbuzano, E.; Siedzik, K.; Paz-Montelongo, S.; Gutiérrez-Fernández, Á.J.; Hardisson, A.; Alejandro-Vega, S.; Jáudenes-Marrero, J.R.; Rubio, C. Exposure Assessment of Essential and Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) from Chia Seeds. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 1836–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hazmi, H.E.; Mohammadi, A.; Hejna, A.; Majtacz, J.; Esmaeili, A.; Habibzadeh, S.; Saeb, M.R.; Badawi, M.; Lima, E.C.; Mąkinia, J. Wastewater Reuse in Agriculture: Prospects and Challenges. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, S.; Ul-Nisa, M.; Shahzadi; Shahid, H.; Gohar, F.; Gondal, A.S.; Riaz, N.; Younas, A.; de los Santos-Villalobos, S.; Montoya-Martínez, A.C.; et al. Recent Trends and Perspectives in the Application of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanomaterials for Sustainable Agriculture. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 202, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.; Usha, K.; Singh, B. Chapter 10—Air Pollution Mitigation and Global Dimming: A Challenge to Agriculture under Changing Climate. In Climate Change and Crop Stress; Shanker, A.K., Shanker, C., Anand, A., Maheswari, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 271–298. ISBN 978-0-12-816091-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Yang, H.; Pian, R.; Wang, J.; Wu, A.-M. The Uptake, Transfer, and Detoxification of Cadmium in Plants and Its Exogenous Effects. Cells 2024, 13, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Brum, R.; Penteado, J.O.; Ramires, P.F.; Girónes, M.C.R.; Mondelongo, S.P.; del Carmén Rubio Armendáriz, M.; dos Santos, M.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Recommended Guidance and Checklist for Human Health Risk Assessment of Metal (Loid) s in Soil. Expo. Health 2021, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution and Food Safety in China: Effects, Sources and Removing Technology. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramires, P.F.; de Lima Brum, R.; Dos Santos, M.; Mirlean, N.; Paz-Montelongo, S.; Rubio-Armendáriz, C.; da Silva Júnior, F.M.R. Human Health Risk Assessment of Metals in Soil Samples of a Brazilian City with a Historic Contamination Complex. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 9408–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, M.; Bakhshi, K.; Zarei, A.; Hoseinzadeh, E.; Gholizadeh, A. Soil Pollution Indices and Health Risk Assessment of Metal (Loid)s in the Agricultural Soil of Pistachio Orchards. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, L.L.; Tavella, R.A.; da Silva Bonifácio, A.; de Lima Brum, R.; da Silva Freitas, L.; da Rosa Moraes, N.G.; Fiasconaro, M.L.; Ramires, P.F.; Penteado, J.O.; Baisch, P.R.M.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Metals in Spartina Alterniflora Salt Marshes in the Estuary of the World’s Largest Choked Lagoon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 26880–26894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.H.; Ali, S.; Hussain, S.; Kamran, M.; Chattha, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Aqeel, M.; Rizwan, M.; Aljarba, N.H.; Alkahtani, S.; et al. Flax (Linum usitatissimum, L.): A Potential Candidate for Phytoremediation? Biological and Economical Points of View. Plants 2020, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUR-Lex. Regulation—2023/915. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/915/oj (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Gu, S.-Y.; Shin, H.-C.; Kim, D.-J.; Park, S.U.; Kim, Y.-K. The Content and Health Risk Assessment of Micro and Toxic Elements in Cereals (Oat and Quinoa), Legumes (Lentil and Chick Pea), and Seeds (Chia, Hemp, and Flax). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 99, 103881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, C.; González-Weller, D.; Caballero, J.M.; Romano, A.R.; Paz, S.; Hardisson, A.; Gutiérrez, Á.J.; Revert, C. Metals in Food Products with Rising Consumption (Brewer’s Yeast, Wheat Bran, Oat Bran, Sesame Seeds, Flaxseeds, Chia Seed). A Nutritional and Toxicological Evaluation. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivari, I.; Paz, S.; Gutiérrez, Á.J.; González-Weller, D.; Hardisson, A.; Sagratini, G.; Rubio, C. Macroelement, Trace Element, and Toxic Metal Levels in Leaves and Infusions of Yerba Mate (Ilex Paraguariensis). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 21341–21352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, L.A. Nomenclature in Evaluation of Analytical Methods Including Detection and Quantification Capabilities (IUPAC Recommendations 1995). Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 1699–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, G.; Li, X.; Yao, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, Q.; Qiu, C.; Mao, X. Rapid and Sensitive Determination of Se and Heavy Metals in Foods Using Electrothermal Vaporization Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry with a Novel Transportation System. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1201801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso Calleja, C.; Cámara Hurtado, M.M.; Daschner, Á.; Fernández Escámez, P.S.; Franco Abuín, C.M.; Giner Pons, R.M.; González Fandos, E.; González Muñoz, M.J.; López García, E.; Mañes Vinuesa, J.; et al. Informe del Comité Científico de la Agencia Española de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición (AESAN) sobre Ingestas Nutricionales de Referencia para la población española. Rev. Com. Científico AESAN 2019, 43–68. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, J.A.; Cámara, M.; Giner, R.M.; González, E.; López, E.; Mañes, J.; Portillo, M.P.; Rafecas, M.; Estruch, R.; Ros, G.; et al. Ingestas nutricionales de referencia (INR) de minerales y vitaminas para la población española (2019): e202203034. Rev. Esp. Salud Pública 2022, 96, 6. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP). EFSA Scientific Opinion on Safety and Efficacy of Cobalt Compounds (E3) as Feed Additives for All Animal Species: Cobaltous Acetate Tetrahydrate, Basic Cobaltous Carbonate Monohydrate and Cobaltous Sulphate Heptahydrate, Based on a Dossier Submitted by TREAC EEIG. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, E.; Givelet, L.; Amlund, H.; Sloth, J.J.; Hansen, M. Risk Assessment of Rare Earth Elements, Antimony, Barium, Boron, Lithium, Tellurium, Thallium and Vanadium in Teas. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e200410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONTAM; Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.-C.; et al. Update of the Risk Assessment of Nickel in Food and Drinking Water. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Strontium and Strontium Compounds. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/44280 (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Statement of EFSA on the Evaluation of a New Study Related to the Bioavailability of Aluminium in Food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. EFSA Comparison of the Approaches Taken by EFSA and JECFA to Establish a HBGV for Cadmium. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). EFSA Scientific Opinion on Lead in Food. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies. EFSA Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies [NDA] Related to the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of Boron (Sodium Borate and Boric Acid). EFSA J. 2004, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumbo, P.; Yates, A.A.; Schlicker, S.; Poos, M. Dietary Reference Intakes: Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2001, 101, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Regional Screening Levels (RSLs)—User’s Guide. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/regional-screening-levels-rsls-users-guide#toxicity (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Ltaeif, H.B.; Sakhraoui, A.; Castillo, J.M.; Rouz, S.; Vicente, O. Germination and Early Seedling Growth in Four Plantago Species in Response to Zn, Cu and Fe. Eurobiotech J. 2024, 8, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Omeljaniuk, W.J.; Nowak, K.; Garley, M.; Nikliński, J. Cadmium Toxicity and Health Effects—A Brief Summary. Molecules 2023, 28, 6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, R.; Ashtekar, H.; Khot, K.B.; Malngiang, M.; Kumar, M.V.; Mandal, S.; Das, B. Aluminum Toxicity Induced Alzheimer’s Disease and Its Potential Treatment Using Antioxidants—A Review. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 59, e21587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfiglio, R.; Scimeca, M.; Mauriello, A. The Impact of Aluminum Exposure on Human Health. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2997–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehari, B.; Yimer, T.F.; Beletkachew, T.; Alem, E.; Negash, W.; Mulu, M.; Yenealem, D.; Miretie, A. Trace Metals and Their Human Health Risks in Sesame Seeds from the Main Cultivation Areas of Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yari, Z.; Cheraghpour, M.; Hekmatdoost, A. Flaxseed and/or Hesperidin Supplementation in Metabolic Syndrome: An Open-Labeled Randomized Controlled Trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, Z.; Rahimlou, M.; Poustchi, H.; Hekmatdoost, A. Flaxseed Supplementation Improves Anthropometric Measurements, Metabolic, and Inflammatory Biomarkers in Overweight and Obese Adults. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2022, 92, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, W.; Jeziorek, M. The Role of Flaxseed in Improving Human Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angon, P.B.; Islam, M.S.; Kc, S.; Das, A.; Anjum, N.; Poudel, A.; Suchi, S.A. Sources, Effects and Present Perspectives of Heavy Metals Contamination: Soil, Plants and Human Food Chain. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-S.; Lu, A.-X.; Li, W.-H.; Zhang, H.; Hu, C.-P.; Liu, J.-X.; Pan, H.; Wu, M.-Q.; Xu, X.; Yan, C.-H.; et al. Effects of Food-Borne Cholesterol Supplementation on Lead-Induced Neurodevelopmental Impairments of Rats Based on BDNF Signaling Pathway and Cholesterol Metabolism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 259, 115026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovich, A.; Di, R.; Lindert, S.; Heckman, J. Nickel and Soil Fertility: Review of Benefits to Environment and Food Security. Environments 2024, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musazadeh, V.; Abolghasemian, M.; Kavyani, Z.; Moridpour, A.H.; Nazari, A.; Faghfouri, A.H. The Effects of Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) Supplementation on Anthropometric Indices: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2024, 84, 103066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).