Filtration Challenges in Non-Alcoholic and Low-Alcohol Beer Production with a Focus on Different Yeast Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wort and Beer Production
2.1.1. Wort Production
2.1.2. Fermentation
2.1.3. Filtration, Kegging, and Pasteurization
2.2. Analysis
2.2.1. Physical–Chemical Analysis
2.2.2. Volatile Analysis
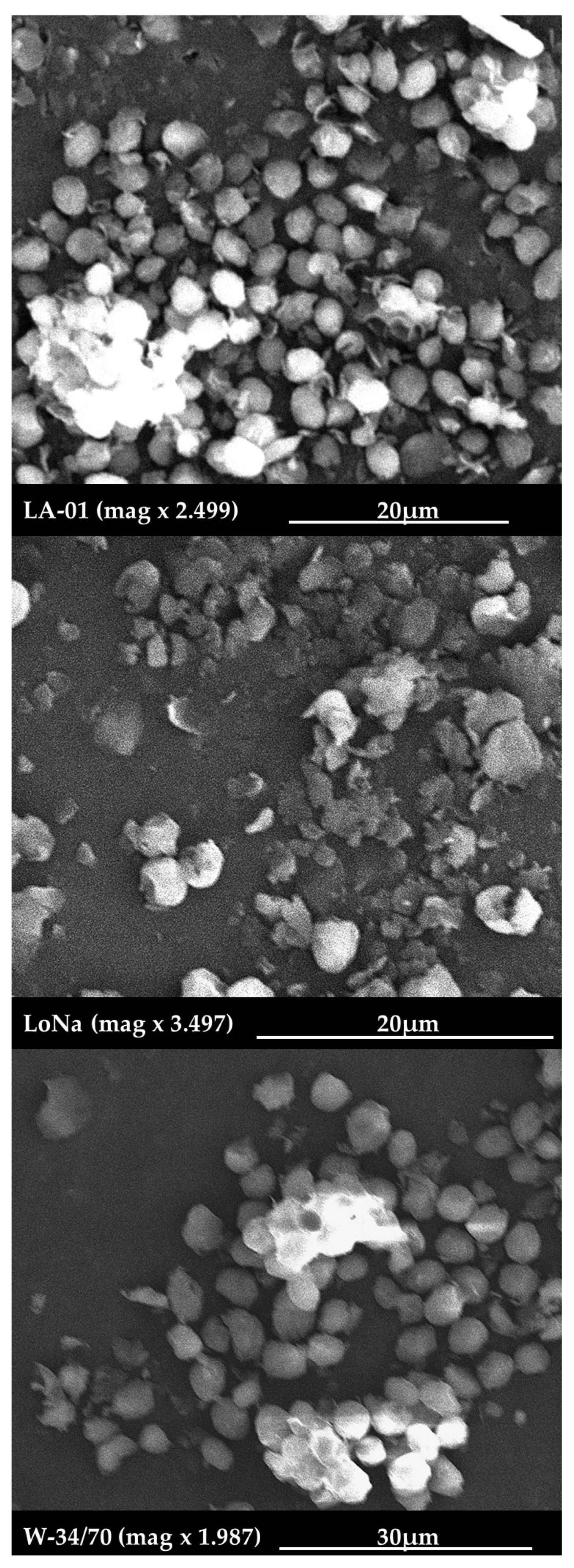
2.2.3. Microscopic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Yeast Analysis
3.2. Basic Beer Analysis
3.3. Filtration Impact on NABs Brewed and Analyzed
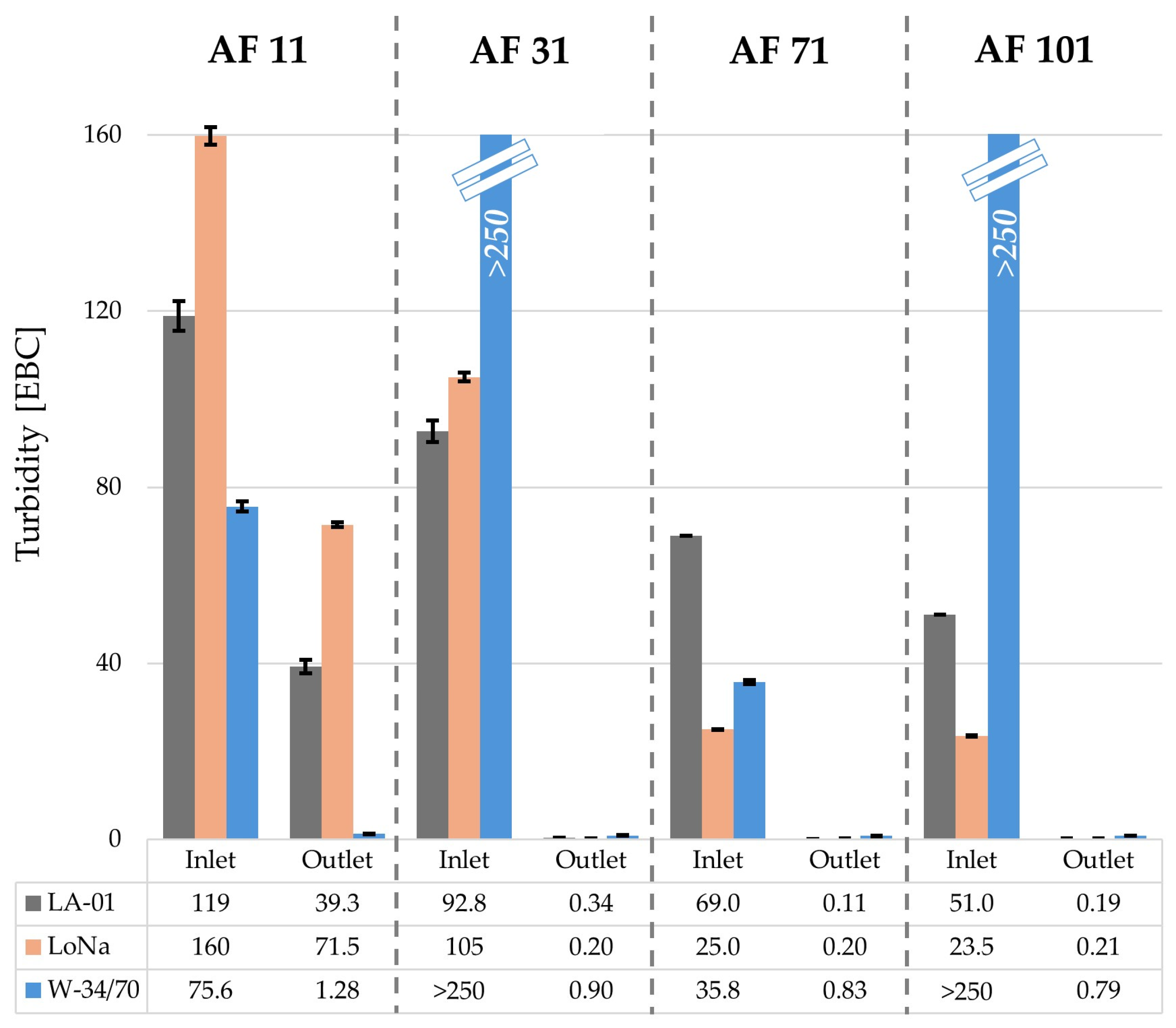
3.3.1. NAB Filtration Performance and Impact on Fresh Products
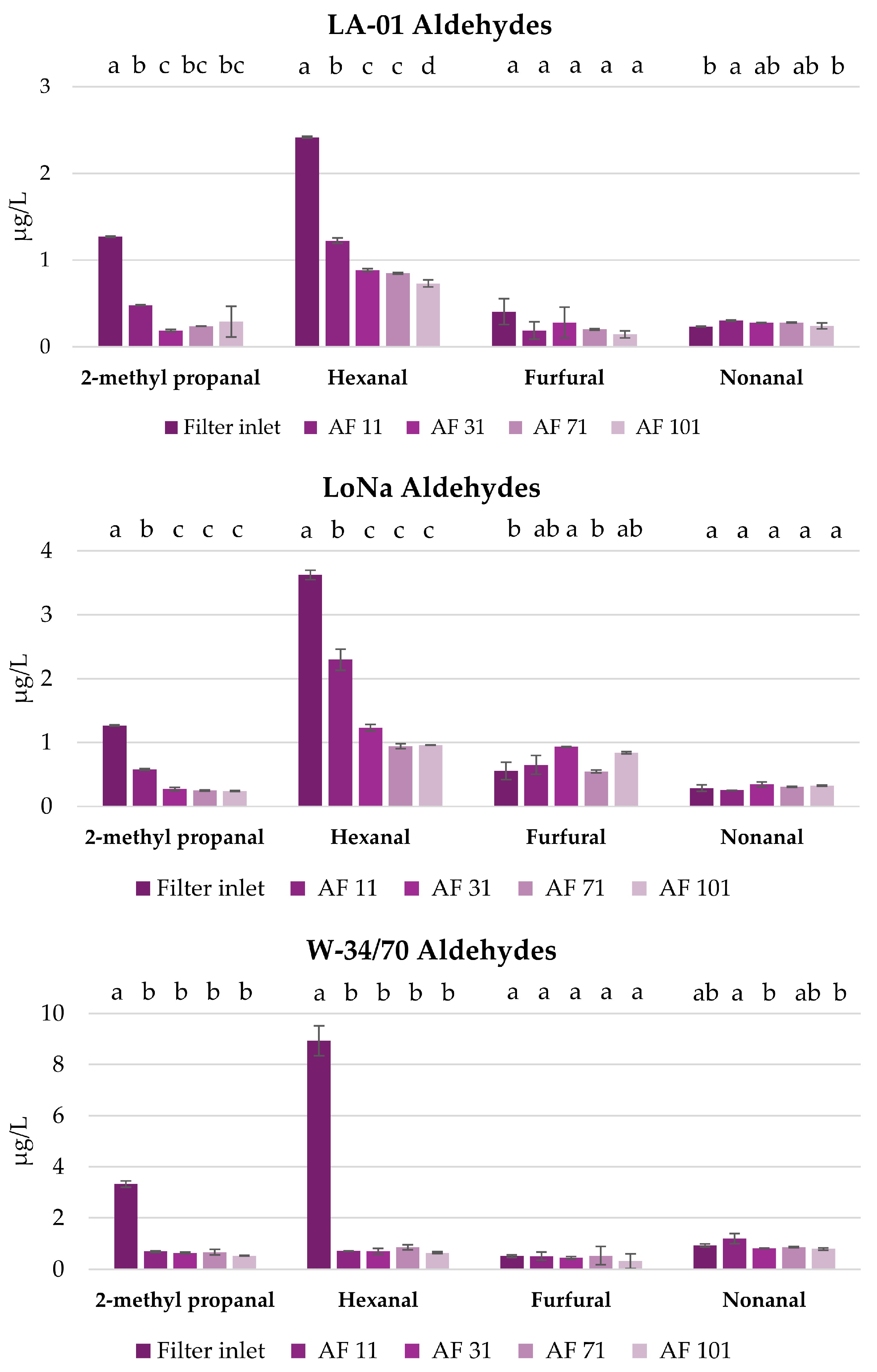
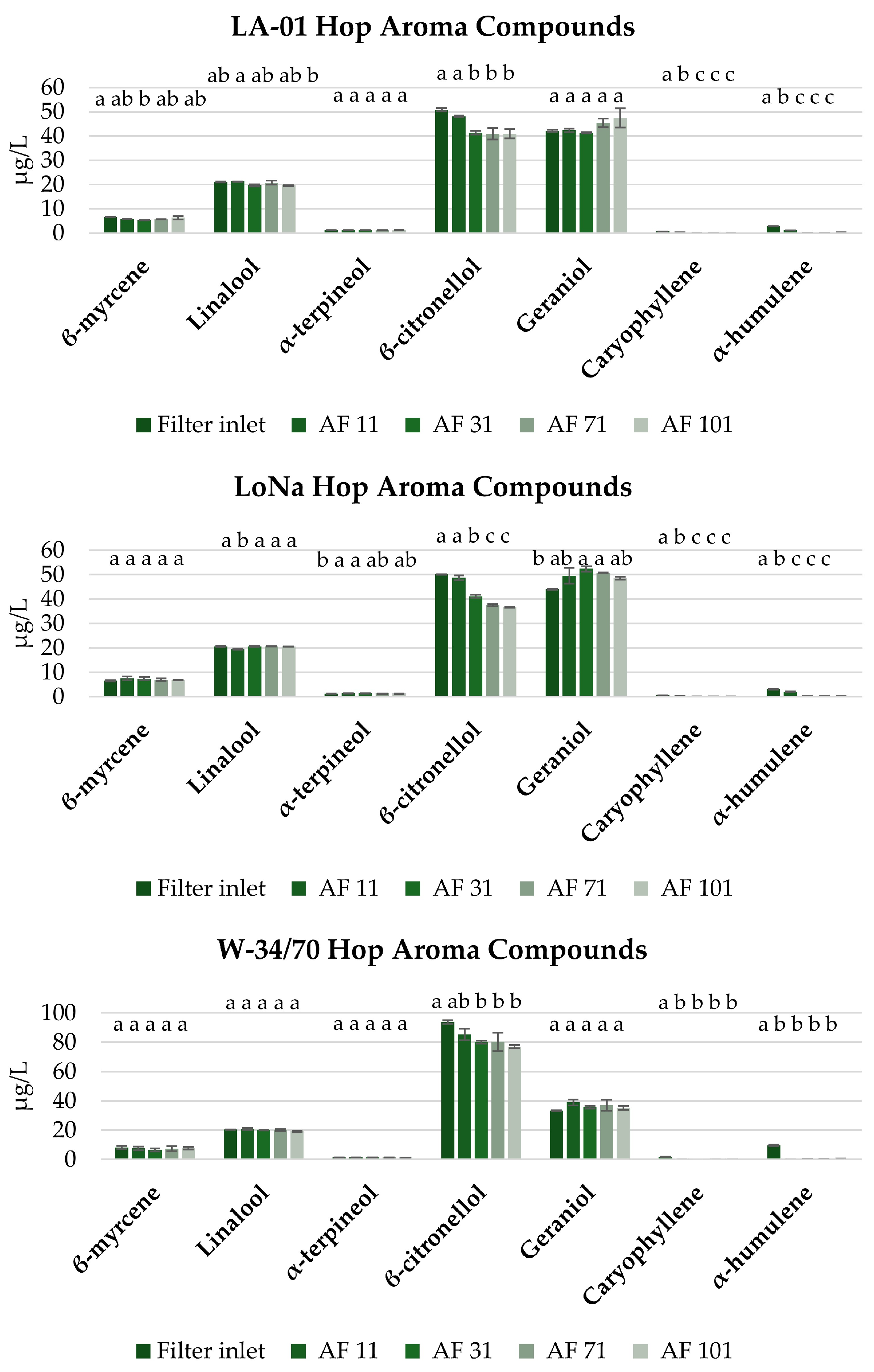
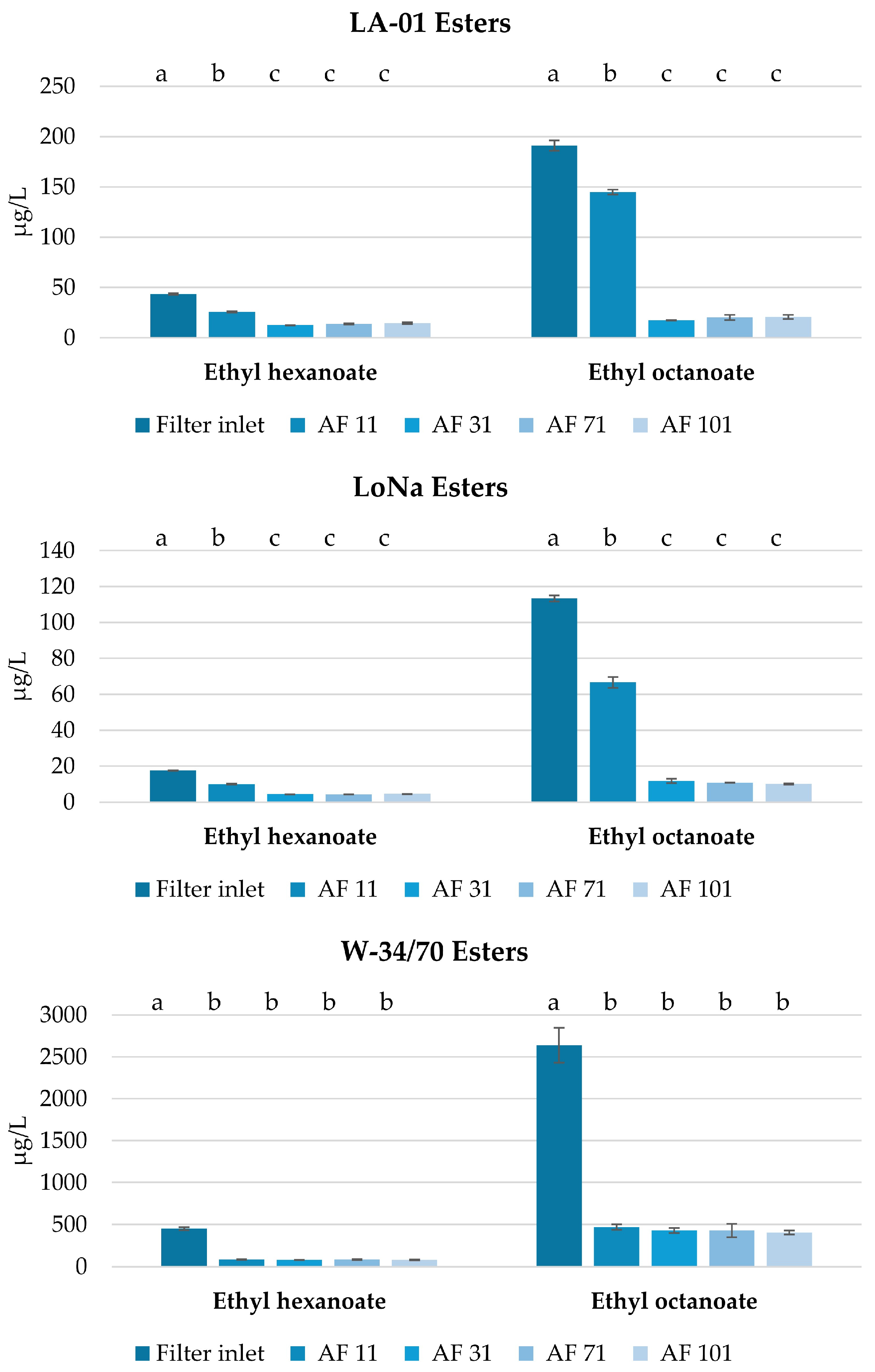
3.3.2. Filtration and Its Impact on Selected Volatile Compounds in Fresh NABs
3.4. Storage-Related Haze Changes
3.5. Applied Strategies for Industrial Implementation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moss, R.; Barker, S.; McSweeney, M.B. An analysis of the sensory properties, emotional responses and social settings associated with non-alcoholic beer. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 98, 104456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Paz, I.; Brunauer, R.; Alavez, S. Beer and its non-alcoholic compounds in health and disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3492–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokole, D.; Jané Llopis, E.; Anderson, P. Non-alcoholic beer in the European Union and UK: Availability and apparent consumption. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2022, 41, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellut, K.; Arendt, E.K. Chance and Challenge: Non- Saccharomyces Yeasts in Nonalcoholic and Low Alcohol Beer Brewing—A Review. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2019, 77, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettberg, N.; Lafontaine, S.; Schubert, C.; Dennenlöhr, J.; Knoke, L.; Diniz Fischer, P.; Fuchs, J.; Thörner, S. Effect of Production Technique on Pilsner-Style Non-Alcoholic Beer (NAB) Chemistry and Flavor. Beverages 2022, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwens, J.; van Opstaele, F.; Eggermont, L.; Weiland, F.; Jaskula-Goiris, B.; de Rouck, G.; de Brabanter, J.; Aerts, G.; de Cooman, L. Comprehensive analytical and sensory profiling of non-alcoholic beers and their pale lager beer counterparts. J. Inst. Brew. 2021, 127, 385–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabaci Karaoglan, S.; Jung, R.; Gauthier, M.; Kinčl, T.; Dostálek, P. Maltose-Negative Yeast in Non-Alcoholic and Low-Alcoholic Beer Production. Fermentation 2022, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackowski, M.; Trusek, A. Non-alcoholic beer production—An overview. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2018, 20, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, C.; Aitkens, M.; Maust, A.; Sen, R.; Kono, M.; Lafontaine, S. The Role of Adjunct Milled Rice, Barley Malt, and different Koji Variations in Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic Beer Production. BrewingScience 2024, 77, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brányik, T.; Silva, D.P.; Baszczyňski, M.; Lehnert, R.; Almeida e Silva, J.B. A review of methods of low alcohol and alcohol-free beer production. J. Food Eng. 2012, 108, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eßlinger, H.M. Handbook of Brewing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 9783527316748. [Google Scholar]
- Slabý, M.; Štěrba, K.; Olšovská, J. Fitration of Beer—A Review. Kvasný Průmysl 2018, 64, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rögener, F. Filtration technology for beer and beer yeast treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 941, 12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcocks, K.L.; Smart, K.A. The importance of surface charge and hydrophobicity for the flocculation of chain-forming brewing yeast strains and resistance of these parameters to acid washing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 134, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Sman, R.; Vollebregt, H.M.; Mepschen, A.; Noordman, T.R. Review of hypotheses for fouling during beer clarification using membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupetz, M.; Procopio, S.; Sacher, B.; Becker, T. Critical review of the methods of β-glucan analysis and its significance in the beer filtration process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.; Gierlińska, A.; Knoke, L.; Rettberg, N. Quantitative Analysis of Ferulic Acid Dehydrodimers in Wort and Beer Using UPLC-QTOF: Implications for Water Extractable Arabinoxylan (WEAX) Gel Formation. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2024, 83, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, E.-M.; Zarnkow, M.; Jacob, F. Beer Turbidity Part 1: A Review of Factors and Solutions. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2021, 79, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filtrox AG, St. Gallen. Beer Filtration. Available online: https://www.filtrox.com/applications/clarification-filtration-food-and-beverages/beer/ (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Maust, A.; Sen, R.; Lafontaine, S. Exploring Non-traditional Yeast for Flavor Innovation in Non-Alcoholic Beer. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 5, 2007–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myncke, E.; Vanderputten, D.; Laureys, D.; Huys, J.; Schlich, J.; van Opstaele, F.; Schouteten, J.J.; de Clippeleer, J. Navigating yeast selection for NABLAB production: Comparative study of commercial maltose- and maltotriose-negative strains. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, C.; Rettberg, N. Unveiling the sensorial, chemical, and flavor stability in Pilsner style non-alcoholic beer produced by fermentation with maltose intolerant yeast, thermal dealcoholization, and combined production techniques. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, W.; Hendel, O. Technologie Brauer und Mälzer, 12th ed.; Verlag der VLB Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2023; ISBN 978-3-921690-99-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdanshenas, M.; Soltanieh, M.; Tabatabaei Nejad, S.A.R.; Fillaudeau, L. Cross-flow microfiltration of rough non-alcoholic beer and diluted malt extract with tubular ceramic membranes: Investigation of fouling mechanisms. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarifa, M.C.; Brugnoni, L.I.; Lozano, J.E. Role of hydrophobicity in adhesion of wild yeast isolated from the ultrafiltration membranes of an apple juice processing plant. Biofouling 2013, 29, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafontaine, S.; Senn, K.; Knoke, L.; Schubert, C.; Dennenlöhr, J.; Maxminer, J.; Cantu, A.; Rettberg, N.; Heymann, H. Evaluating the Chemical Components and Flavor Characteristics Responsible for Triggering the Perception of “Beer Flavor” in Non-Alcoholic Beer. Foods 2020, 9, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermentis by Lesaffre. Technical Data Sheet-SafBrewTM LA-01 [Technical Data Sheet], REV: Mar22. 2022. Available online: https://fermentis.com/en/product/safbrew-la%E2%80%9101/ (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Lallemand. Technical Data Sheet-LONA™: Low Alcohol Hybrid ale Yeast, TDS-8.5X11-02232023-ENG. Available online: https://www.lallemandbrewing.com/en/united-states/products/lalbrew-lona/ (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Fermentis by Lesaffre. Technical Data Sheet-SafLagerTM W-34/70 [Technical Data Sheet], REV: Feb21. 2021. Available online: https://fermentis.com/en/product/saflager-w%E2%80%9134-70/ (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Anton Paar EasyDens (Anton Paar GmbH, Graz, Austria) with Brew Meister Software, iOS Version 4.5.0; Anton Paar ConsumerTec GmbH: Graz, Austria, 2024.
- EBC Analytica. 9.4—Original, Real and Apparent Extract and Original Gravity of Beer. 2004. Available online: https://brewup.eu/ebc-analytica/beer/original-real-and-apparent-extract-and-original-gravity-of-beer/9.4 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- EBC Analytica. 9.43.2—Specific Gravity of Beer Using a Density Meter. 2004. Available online: https://dev.brewup.brewersofeurope.eu/ebc-analytica/beer/specific-gravity-of-beer-using-a-density-meter/9.43.2 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- EBC Analytica. 9.2.6—Alcohol in Beer by Near Infrared Spectroscopy. 2008. Available online: https://brewup.eu/ebc-analytica/beer/alcohol-in-beer-by-near-infrared-spectroscopy/9.2.6 (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- ASBC Methods of Analysis, Online. Beer Method 9. pH (Hydrogen Ion Concentration). American Society of Brewing Chemists, Ed.; St. Paul, MN, USA. Available online: https://www.asbcnet.org/Methods/BeerMethods/pages/default.aspx (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- ASBC Methods of Analysis, Online. Beer Method 10. Color. American Society of Brewing Chemists, Ed.; St. Paul, MN, USA. Available online: https://www.asbcnet.org/Methods/BeerMethods/pages/default.aspx (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- ASBC Methods of Analysis, Online. Beer Method 23. Bitterness. American Society of Brewing Chemists, Ed.; St. Paul, MN, USA. Available online: https://www.asbcnet.org/Methods/BeerMethods/pages/default.aspx (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- ASBC Methods of Analysis, Online. Microbiology Yeast 3. Yeast Stains. American Society of Brewing Chemists, Ed.; St. Paul, MN, USA. Available online: https://www.asbcnet.org/Methods/Methods/Yeast-3.pdf (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- ASBC Methods of Analysis, Online. Microbiology Yeast 4. Microscopic Yeast Cell Counting. American Society of Brewing Chemists, Ed.; St. Paul, MN, USA. Available online: https://www.asbcnet.org/Methods/MicrobiologyMethods/Pages/Yeast-4-MasterMethod.aspx (accessed on 13 December 2024).
- Köhler, S.; Schmacht, M.; Malchow, S.; Wolff, L.; Senz, M. Preparation of freeze dried and vacuum dried yeast starter cultures: Evaluation of relevant viability detection analyses-YEAST-SPECIAL. BrewingScience 2020, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbelen, P.J.; Mulders, S.; Saison, D.; Laere, S.; Delvaux, F.; Delvaux, F.R. Characteristics of High Cell Density Fermentations with Different Lager Yeast Strains. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Viet Man, L.V. Using high pitching rate for improvement of yeast fermentation performance in high gravity brewing. Int. Food Res. J. 2009, 16, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, G.G.; Anstruther, A.M. Yeast Flocculation, Sedimentation, and Centrifugation. MBAA TQ 2021, 58, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, G. Yeast Flocculation—Sedimentation and Flotation. Fermentation 2018, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electronic Code of Federal Regulations. Code of Federal Regulations: Title 27: Alcohol, Tobacco Products and Firearms Part 7-Labeling and Advertising of Malt Beverages. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-27/chapter-I/subchapter-A/part-7 (accessed on 27 April 2024).
- Olšovská, J.; Kyselová, L.; Kubizniaková, P.; Slabý, M. Non-microbiological turbidity of beer: Part 1—Semireview. Kvasný Průmysl 2021, 67, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadar, O.; Vagner, I.; Miu, I.; Scurtu, D.; Senila, M. Preparation, Characterization, and Performance of Natural Zeolites as Alternative Materials for Beer Filtration. Materials 2023, 16, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, A.; Moresi, M. Towards a Kieselguhr- and PVPP-Free Clarification and Stabilization Process of Rough Beer at Room-Temperature Conditions. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, V.; Soceanu, A.; Dobrinas, S.; Stanciu, G. A study of beer bitterness loss during the various stages of the Romanian beer production process. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justus, A. Tracking IBU Through the Brewing Process: The Quest for Consistency. MBAA TQ 2018, 55, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Shotipruk, A.; Kittianong, P.; Suphantharika, M.; Muangnapoh, C. Application of rotary microfiltration in debittering process of spent brewer’s yeast. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.C. Flavor chemistry of beer: Part II: Flavor and threshold of 239 aroma volatiles. Technol. Quart. Master Brew. Ass. Am. 1975, 12, 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaegen, B.; Neven, H.; Verachtert, H.; Derdelinckx, G. The chemistry of beer aging—A critical review. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, C.; Lafontaine, S.; Dennenlöhr, J.; Thörner, S.; Rettberg, N. The influence of storage conditions on the chemistry and flavor of hoppy ales. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo Trueba, P.; Jaskula-Goiris, B.; Ditrych, M.; Filipowska, W.; de Brabanter, J.; de Rouck, G.; Aerts, G.; de Cooman, L.; de Clippeleer, J. Monitoring the evolution of free and cysteinylated aldehydes from malt to fresh and forced aged beer. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saison, D.; de Schutter, D.P.; Uyttenhove, B.; Delvaux, F.; Delvaux, F.R. Contribution of staling compounds to the aged flavour of lager beer by studying their flavour thresholds. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.; Aumala, V.; Heiniö, R.-L.; Mikkelson, A.; Honkapää, K. Differential evolution of Strecker and non-Strecker aldehydes during aging of pale and dark beers. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 83, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saison, D.; de Schutter, D.P.; Vanbeneden, N.; Daenen, L.; Delvaux, F.; Delvaux, F.R. Decrease of aged beer aroma by the reducing activity of brewing yeast. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettberg, N.; Biendl, M.; Garbe, L.-A. Hop Aroma and Hoppy Beer Flavor: Chemical Backgrounds and Analytical Tools—A Review. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2018, 76, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, C.; Lafontaine, S.; Thörner, S.; Rettberg, N. Impact of Pasteurisation on Terpenes, Terpenoids, Aldehydes and Esters in Hoppy Ales on Ageing. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2024, 82, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, C.; Cook, D.; Wilson, C.; Oliveira, P.; Ford, R. Exploring the multisensory perception of terpene alcohol and sesquiterpene rich hop extracts in lager style beer. Food Res. Int. 2021, 148, 110598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takoi, K.; Itoga, Y.; Koie, K.; Kosugi, T.; Shimase, M.; Katayama, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Watari, J. The Contribution of Geraniol Metabolism to the Citrus Flavour of Beer: Synergy of Geraniol and β-Citronellol Under Coexistence with Excess Linalool. J. Inst. Brew. 2010, 116, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslbeck, K.; Bub, S.; von Kamp, K.; Michel, M.; Zarnkow, M.; Hutzler, M.; Coelhan, M. The influence of brewing yeast strains on monoterpene alcohols and esters contributing to the citrus flavour of beer. J. Inst. Brew. 2018, 124, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, K.; Cioch-Skoneczny, M.; Duda-Chodak, A. Effects of Dry-Hopping on Beer Chemistry and Sensory Properties—A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovic, R.; Grujic, O.; Pejin, J. Conventional and alternative principles for stabilization of protein and polyphenol fractions in beer. Acta Per. Technol. 2003, 34, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, K.J.; Lynn, P.Y. Effects of Alcohol and pH on Protein–Polyphenol Haze Intensity and Particle Size. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2003, 61, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnhardt, F.; Gastl, M.; Becker, T. Forced into aging: Analytical prediction of the flavor-stability of lager beer. A review. Crit Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2642–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method B-420.02.900. Forced Aging. Rev. 2023-08; Mitteleuropäische Brautechnische Analysenkommission (MEBAK®) e.V., Ed.; Freising, BY, Germany, Rev. 2023. Available online: https://www.mebak.org/en/methode/b-420-02-900/forced-aging/3360 (accessed on 13 December 2024).

| Original Extract [% w/w] | Bitterness [BU] | Alcohol [% v/v] | Apparent Degree of Fermentation [%] | pH [-] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LA-01 | 6.56 a ± 0.01 | 11.1 a ± 0.2 | 0.53 c ± 0.00 | 15.51 c ± 0.01 | 4.40 a ± 0.00 |
| LoNa | 6.59 a ± 0.00 | 11.0 a ± 0.0 | 0.56 b ± 0.00 | 16.26 b ± 0.00 | 4.36 a ± 0.01 |
| W-34/70 | 6.56 a ± 0.00 | 11.2 a ± 0.1 | 2.33 a ± 0.01 | 68.91 a ± 0.00 | 3.99 b ± 0.00 |
| Filter Inlet | Filter Outlet AF 11 | Filter Outlet AF 31 | Filter Outlet AF 71 | Filter Outlet AF 101 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color [EBC] | |||||
| LA-01 | 5.5 b ± 0.0 | Haze b,* | 4.7 a ± 0.0 | 4.7 a ± 0.1 | 4.6 a ± 0.0 |
| LoNa | 5.4 c ± 0.0 | Haze b,* | 4.7 a ± 0.0 | 4.4 b ± 0.0 | 4.7 a ± 0.0 |
| W-34/70 | 7.1 a ± 0.0 | 4.4 a ± 0.0 | 4.2 b ± 0.0 | 4.1 c ± 0.0 | 4.2 b ± 0.0 |
| Bitterness [BU] | |||||
| LA-01 | 11.1 a ± 0.2 | 11.3 a ± 0.0 | 11.3 a ± 0.0 | 11.4 a ± 0.1 | 11.4 a ± 0.0 |
| LoNa | 11.0 a ± 0.0 | 11.4 a ± 0.1 | 11.0 ab ± 0.0 | 11.1 b ± 0.1 | 11.0 b ± 0.0 |
| W-34/70 | 11.2 a ± 0.1 | 9.6 b ± 0.1 | 10.3 b ± 0.3 | 9.5 c ± 0.1 | 9.7 c ± 0.0 |
| Filter Sheet | Storage Time @4 °C | LA-01 | LoNa | W-34/70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF 11 | filter outlet | 39.3 e ± 1.5 | 71.5 a ± 0.5 | 1.28 g ± 0.0 |
| 1 week | 37.0 e ± 0.3 | 62.0 c ± 1.0 | 3.62 fg ± 0.0 | |
| 2 weeks | 43.8 d ± 1.3 | 68.4 b ± 0.6 | 4.02 f ± 0.0 | |
| AF 31 | filter outlet | 0.34 f ± 0.0 | 0.20 g ± 0.0 | 0.90 a ± 0.0 |
| 1 week | 0.87 a ± 0.0 | 0.44 e ± 0.0 | 0.71 cd ± 0.0 | |
| 2 weeks | 0.80 b ± 0.0 | 0.68 d ± 0.0 | 0.75 c ± 0.0 | |
| AF 71 | filter outlet | 0.11 i ± 0.0 | 0.20 h ± 0.0 | 0.83 a ± 0.0 |
| 1 week | 0.60 d ± 0.0 | 0.47 g ± 0.0 | 0.70 c ± 0.0 | |
| 2 weeks | 0.56 e ± 0.0 | 0.49 f ± 0.0 | 0.76 b ± 0.0 | |
| AF 101 | filter outlet | 0.19 f ± 0.0 | 0.21 f ± 0.0 | 0.79 ab ± 0.0 |
| 1 week | 0.76 bc ± 0.0 | 0.48 e ± 0.0 | 0.73 c ± 0.0 | |
| 2 weeks | 0.82 a ± 0.0 | 0.60 d ± 0.0 | 0.83 a ± 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schubert, C.; Maxminer, J.; Aitkens, M.; Maust, A.; Guimarães, B.P.; Sen, R.; Lafontaine, S. Filtration Challenges in Non-Alcoholic and Low-Alcohol Beer Production with a Focus on Different Yeast Strains. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126797
Schubert C, Maxminer J, Aitkens M, Maust A, Guimarães BP, Sen R, Lafontaine S. Filtration Challenges in Non-Alcoholic and Low-Alcohol Beer Production with a Focus on Different Yeast Strains. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126797
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchubert, Christian, Jörg Maxminer, Matthew Aitkens, Andrew Maust, Bernardo Pontes Guimarães, Rahul Sen, and Scott Lafontaine. 2025. "Filtration Challenges in Non-Alcoholic and Low-Alcohol Beer Production with a Focus on Different Yeast Strains" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126797
APA StyleSchubert, C., Maxminer, J., Aitkens, M., Maust, A., Guimarães, B. P., Sen, R., & Lafontaine, S. (2025). Filtration Challenges in Non-Alcoholic and Low-Alcohol Beer Production with a Focus on Different Yeast Strains. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6797. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126797






