DTI Histogram and Texture Features as Early Predictors of Post-Radiotherapy Cognitive Decline
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Neurocognitive Assessment
2.3. MRI Acquisition
2.4. DTI Data Processing
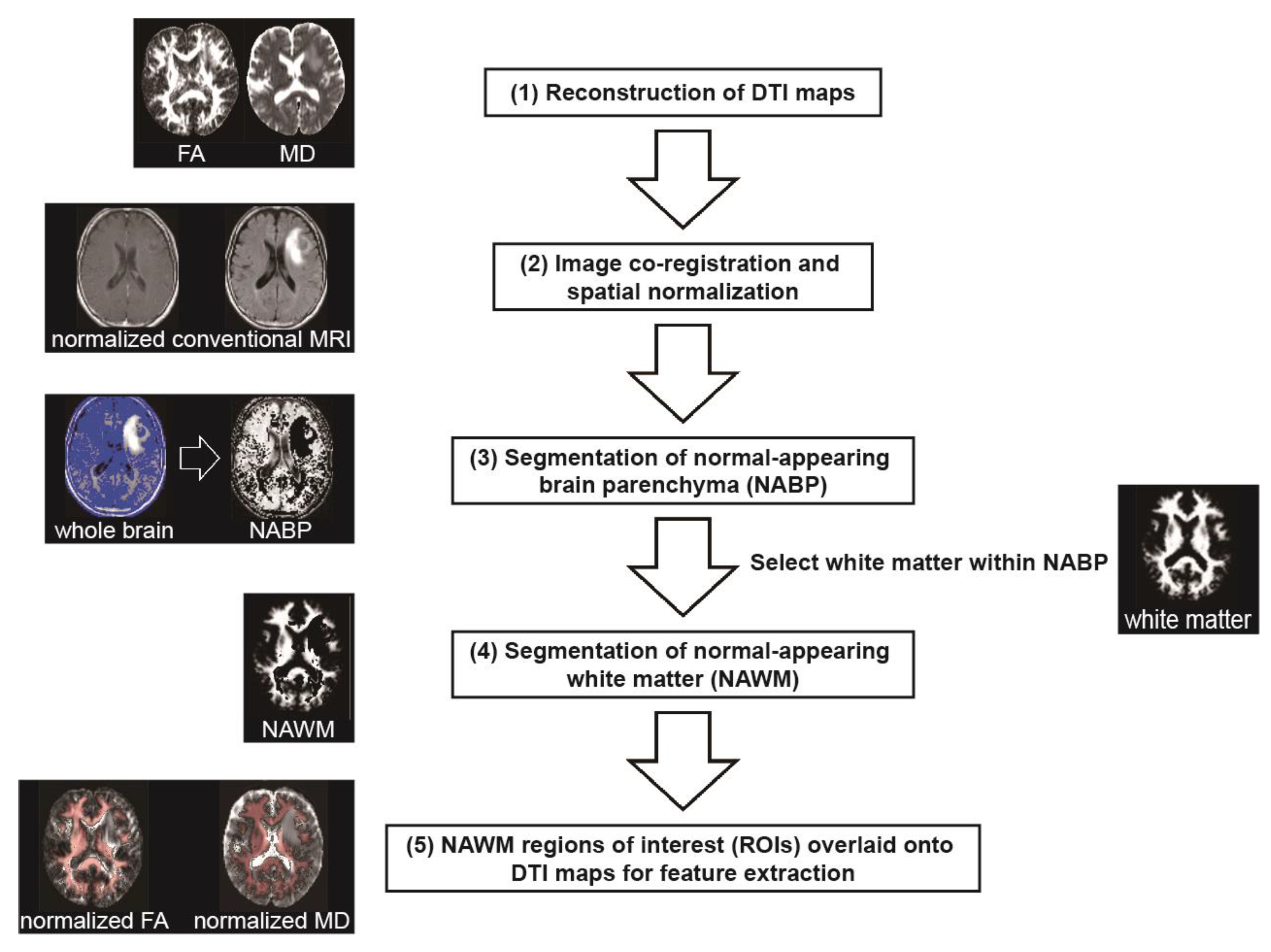
2.5. Image Processing and Region of Interest Definition
2.6. Histogram and Texture Feature Extraction
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. DTI Feature Changes After Radiotherapy
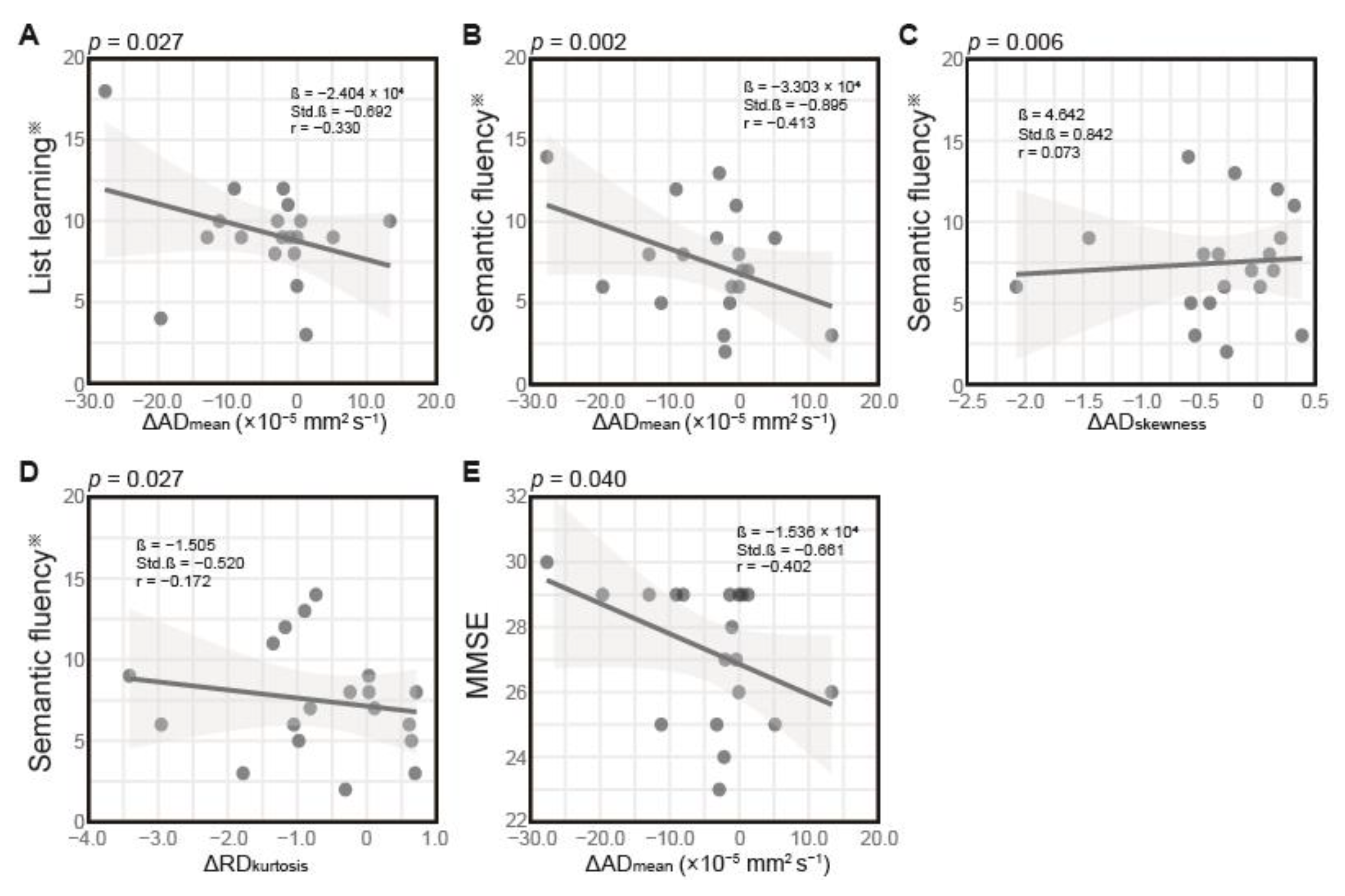
3.3. Correlation Between Changes in DTI Features and Cognitive Performance 4 Months Post-Radiation
3.4. FDR Correction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WBRT | whole-brain radiation therapy |
| STI | stereotactic irradiation |
| WM | white matter |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| DTI | diffusion tensor imaging |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| FA | fractional anisotropy |
| MD | mean diffusivity |
| AD | axial diffusivity |
| RD | radial diffusivity |
| GLCM | gray level co-occurrence matrix |
| NAWM | normal-appearing WM |
| RBANS | Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status |
| TMT | Trail Making Test |
| TR | repetition time |
| TE | echo time |
| NEX | number of excitations |
| FOV | field of view |
| T1WI | T1-weighted imaging |
| Gd-T1WI | gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted imaging |
| FLAIR | fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| TI | inversion time |
| SPM12 | Statistical Parametric Mapping |
| MNI | Montreal Neurological Institute |
| BP | brain parenchyma |
| b0 | echo planar images with no diffusion weighting |
| SD | standard deviation |
| NABP | normal-appearing BP |
| ROI | region of interest |
| Δ | change |
| β | unstandardized coefficient |
| Std.β | standardized coefficient |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| MDkurtosis | kurtosis of MD |
| ADmean | mean of AD |
| ADskewness | skewness of AD |
| RDkurtosis | kurtosis of RD |
References
- Chi, A.; Komaki, R. Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Lung Cancer. Cancers 2010, 2, 2100–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Arbiser, J.; Zelnak, A.; Shu, H.-K.G.; Shim, H.; Robin, A.M.; Kalkanis, S.N.; Whitsett, T.G.; Salhia, B.; Tran, N.L.; et al. Current Approaches to the Treatment of Metastatic Brain Tumours. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene-Schloesser, D.; Moore, E.; Robbins, M.E. Molecular Pathways: Radiation-Induced Cognitive Impairment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2294–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDuff, S.G.R.; Taich, Z.J.; Lawson, J.D.; Sanghvi, P.; Wong, E.T.; Barker, F.G.; Hochberg, F.H.; Loeffler, J.S.; Warnke, P.C.; Murphy, K.T.; et al. Neurocognitive Assessment Following Whole Brain Radiation Therapy and Radiosurgery for Patients with Cerebral Metastases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene-Schloesser, D.; Robbins, M.E.; Peiffer, A.M.; Shaw, E.G.; Wheeler, K.T.; Chan, M.D. Radiation-Induced Brain Injury: A Review. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesny, E.; Jacob, J.; Noël, G.; Bernier, M.-O.; Ricard, D. Specific Radiosensitivity of Brain Structures (Areas or Regions) and Cognitive Impairment after Focal or Whole Brain Radiotherapy: A Review. Cancer Radiother. 2025, 29, 104625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsesfandabadi, P.; Patel, A.; Liang, Y.; Shepard, M.J.; Wegner, R.E. Radiation-Induced Cognitive Decline: Challenges and Solutions. Cancer Manag. Res. 2024, 16, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene-Schloesser, D.; Robbins, M.E. Radiation-Induced Cognitive Impairment--from Bench to Bedside. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14 (Suppl. 4), iv37–iv44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corn, B.W.; Wang, M.; Fox, S.; Michalski, J.; Purdy, J.; Simpson, J.; Kresl, J.; Curran, W.J.; Diaz, A.; Mehta, M.; et al. Health Related Quality of Life and Cognitive Status in Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme Receiving Escalating Doses of Conformal Three Dimensional Radiation on RTOG 98-03. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 95, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.A.; Chhanabhai, T.; McKenzie, M. Feasibility Study of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) in Patients with Brain Metastases. Support. Care Cancer 2008, 16, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitford, T.J.; Kubicki, M.; Pelavin, P.E.; Lucia, D.; Schneiderman, J.S.; Pantelis, C.; McCarley, R.W.; Shenton, M.E. Cingulum Bundle Integrity Associated with Delusions of Control in Schizophrenia: Preliminary Evidence from Diffusion-Tensor Tractography. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 161, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidi, F.; Khanmirzaei, M.H.; Hosseinzadeh, F.; Kolahchi, Z.; Jafarimehrabady, N.; Moghisseh, B.; Aarabi, M.H. Cingulum and Uncinate Fasciculus Microstructural Abnormalities in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Studies. Biology 2023, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.; Przybelski, S.A.; Reid, R.I.; Graff-Radford, J.; Lesnick, T.G.; Zuk, S.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Machulda, M.M.; Mielke, M.M.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. Reduced Fractional Anisotropy of the Genu of the Corpus Callosum as a Cerebrovascular Disease Marker and Predictor of Longitudinal Cognition in MCI. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 96, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, Y.; Pasternak, O. Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)-Based White Matter Mapping in Brain Research: A Review. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 34, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpaoli, C.; Jezzard, P.; Basser, P.J.; Barnett, A.; Di Chiro, G. Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging of the Human Brain. Radiology 1996, 201, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.H.; Zhu, T.; Nazem-Zadeh, M.; Tao, Y.; Buchtel, H.A.; Tsien, C.I.; Lawrence, T.S.; Cao, Y. Diffusion Tensor Imaging Predicts Cognitive Function Change Following Partial Brain Radiotherapy for Low-Grade and Benign Tumors. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 120, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lang, J.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Dose-Dependent Early White Matter Alterations in Patients with Brain Metastases after Radiotherapy. Neuroradiology 2023, 65, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.J.; Christodoulou, C.; Bhise, V.; Greenblatt, D.; Patel, Y.; Serafin, D.; Maletic-Savatic, M.; Krupp, L.B.; Wagshul, M.E. Multiple White Matter Tract Abnormalities Underlie Cognitive Impairment in RRMS. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 3713–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunimatsu, A.; Yasaka, K.; Akai, H.; Sugawara, H.; Kunimatsu, N.; Abe, O. Texture Analysis in Brain Tumor MR Imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2022, 21, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.P.; Kim, J.; Jang, H.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.; Na, D.L.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, S.W.; et al. Predicting Amyloid Positivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment Using a Radiomics Approach. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.W.; Han, K.; Ahn, S.S.; Choi, Y.S.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, S.-G.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, S.-K. Whole-Tumor Histogram and Texture Analyses of DTI for Evaluation of IDH1-Mutation and 1p/19q-Codeletion Status in World Health Organization Grade II Gliomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makale, M.T.; McDonald, C.R.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.A.; Kesari, S. Mechanisms of Radiotherapy-Associated Cognitive Disability in Patients with Brain Tumours. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, J.; Major, T.; Auyeung, G.; Policarpio, E.; Menon, J.; Droms, L.; Gutin, P.; Uryu, K.; Tchieu, J.; Soulet, D.; et al. Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Oligodendrocyte Progenitors Remyelinate the Brain and Rescue Behavioral Deficits Following Radiation. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotakos, G.; Alshamy, G.; Chan, B.; Abrams, R.; Greenberg, E.; Saxena, A.; Bradbury, M.; Edgar, M.; Gutin, P.; Tabar, V. Long-Term Impact of Radiation on the Stem Cell and Oligodendrocyte Precursors in the Brain. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Boström, M.; Ek, C.J.; Li, T.; Xie, C.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Blomgren, K.; Zhu, C. Radiation Induces Progenitor Cell Death, Microglia Activation, and Blood-Brain Barrier Damage in the Juvenile Rat Cerebellum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, M.M.; Green, K.N.; Allen, B.D.; Najafi, A.R.; Syage, A.; Minasyan, H.; Le, M.T.; Kawashita, T.; Giedzinski, E.; Parihar, V.K.; et al. Elimination of Microglia Improves Cognitive Function Following Cranial Irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, S.; Aoyama, H.; Tha, K.K.; Hashimoto, N.; Toyomaki, A.; Terae, S.; Shirato, H. The Value of 4-Month Neurocognitive Function as an Endpoint in Brain Metastases Trials. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 120, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorden, C.; Karnath, H.-O.; Bonilha, L. Improving Lesion-Symptom Mapping. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2007, 19, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts HJWL. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztuna, D.; Elhan, A.; Tüccar, E. Investigation of Four Different Normality Tests in Terms of Type 1 Error Rate and Power under Different Distributions. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2006, 36, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, A.; Zahediasl, S. Normality Tests for Statistical Analysis: A Guide for Non-Statisticians. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 10, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, S.; Mesri, H.; Bodiut, V.; Nagtegaal, S.; Elhalawani, H.; de Luca, A.; Philippens, M.; Viergever, M.; Mohamed, A.; Ding, Y.; et al. Dose-Dependent Degeneration of Non-Cancerous Brain Tissue in Post-Radiotherapy Patients: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. medRxiv 2019, 19005157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, T.R.; Vardal, J.; Bjørnerud, A.; Larsson, C.; Arnesen, M.R.; Salo, R.A.; Groote, I.R. Serial Diffusion Tensor Imaging for Early Detection of Radiation-Induced Injuries to Normal-Appearing White Matter in High-Grade Glioma Patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 41, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyan, L.; Si, W.; Qian, W.; Yuhui, S.; Xiaoer, W.; Yuehua, L.; Wenbin, L. Diffusion Kurtosis as an in Vivo Imaging Marker of Early Radiation-Induced Changes in Radiation-Induced Temporal Lobe Necrosis in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2018, 28, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Feng, M.; Rong, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Liao, H.; Shi, L.; He, H.; Tong, Q.; et al. Whole Brain Atlas-Based Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Parameters for the Evaluation of Multiple Cognitive-Related Brain Microstructure Injuries after Radiotherapy in Lung Cancer Patients with Brain Metastasis. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 5321–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, N.; Manan, H.A. Diffusion Tensor Imaging Indices to Predict Cognitive Changes Following Adult Radiotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2021, 30, e13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, B.E.; Mohammad, M.E.; Serour, D.K. What Can DTI Add in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients? Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2019, 50, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xie, L.; Kang, F.; Jiang, J.; Yao, T.; Mao, G.; Fang, R.; Fan, J.; Wu, D. Association between White Matter Alterations and Domain-Specific Cognitive Impairment in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1019088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, M.; Castro, B.; Messas, C.; Martucci, C.; Chaim, K.; Pastorello, B.; Valerio, R.; Jorge, C.; Lyra, K.; Otaduy, M.; et al. Semantic Fluency Impairment in Unilateral Mesial Temporal Sclerosis Related Epilepsy Is Associated with Extensive White Matter Involvement: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. (P2.239). Neurology 2017, 88, P2.239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Lee, G.J. Cognitive Screening for Early Detection of Mild Cognitive Impairment. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2020, 32, 1015–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.C.; Mierzwa, A.J.; Sullivan, G.M.; Sanchez, M.A. Myelin and Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells in White Matter Pathology and Plasticity after Traumatic Brain Injury. Neuropharmacology 2016, 110, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nellessen, A.; Nyamoya, S.; Zendedel, A.; Slowik, A.; Wruck, C.; Beyer, C.; Fragoulis, A.; Clarner, T. Nrf2 Deficiency Increases Oligodendrocyte Loss, Demyelination, Neuroinflammation and Axonal Damage in an MS Animal Model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Miyamoto, N.; Hayakawa, K.; Pham, L.-D.D.; Maki, T.; Ayata, C.; Kim, K.-W.; Lo, E.H.; Arai, K. Oligodendrocyte Precursors Induce Early Blood-Brain Barrier Opening after White Matter Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.; Lo, E.H. Experimental Models for Analysis of Oligodendrocyte Pathophysiology in Stroke. Exp. Transl. Stroke Med. 2009, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Rao, J.-H.; Lan, X.-Y.; Li, X.; Chu, C.-Y.; Liang, Y.; Janowski, M.; Zhang, H.-T.; Walczak, P. White Matter Demyelination Predates Axonal Injury after Ischemic Stroke in Cynomolgus Monkeys. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 340, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkel, J.G.; Lahmer, G.; Mennecke, A.; Hock, S.W.; Richter-Schmidinger, T.; Fietkau, R.; Distel, L.; Putz, F.; Dörfler, A.; Schmidt, M.A. Effects of Hippocampal Sparing Radiotherapy on Brain Microstructure-A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Analysis. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uh, J.; Merchant, T.E.; Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Gajjar, A.; Ogg, R.J.; Hua, C. Differences in Brainstem Fiber Tract Response to Radiation: A Longitudinal Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 86, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerklaan, J.P.; Lycklama á Nijeholt, G.J.; Wiggenraad, R.G.J.; Berghuis, B.; Postma, T.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.B. SMART Syndrome: A Late Reversible Complication after Radiation Therapy for Brain Tumours. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Haridas, S.; Trivedi, R.; Khushu, S.; Manda, K. Early Cognitive Changes Due to Whole Body γ-Irradiation: A Behavioral and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study in Mice. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 248, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.L.; Shera, D.M.; Lustig, R.A.; Phillips, P.C. Phase Measurement of Cognitive Impairment Specific to Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, e319–e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sequence | TR/TE (ms) | Voxel Size (mm3) | Slice Thickness (mm) | Interslice Gap (mm) | Number of Slices | NEX | Acquisition Matrix Size | FOV (mm) | Additional Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTI | 5100/139 | 0.9375 × 0.9375 × 5 | 5 | 1.5 | 23 | 2 | 256 × 256 | 240 × 240 | b-values: 0, 1000 s/mm2; 12 motion-probing gradient directions |
| T1WI | 700/15 | 0.9375 × 0.9375 × 5 | 5 | 1.5 | 19 | 1 | 256 × 192 | 240 × 180 | Pre-contrast |
| Gd-T1WI | 710/17 | 0.9375 × 0.9375 × 5 | 5 | 1.5 | 19 | 1 | 256 × 192 | 240 × 180 | Post-gadolinium |
| FLAIR | 9000/114 | 0.46875 × 0.46875 × 5 | 5 | 1.75 | 19 | 1 | 512 × 384 | 240 × 180 | TI = 2500 ms |
| Neurocognitive Function Test | Mean ± Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|
| RBANS ※ | ||
| List learning | 9 ± 3.1 | |
| List recall | 7 ± 3.3 | |
| List recognition | 9 ± 2.6 | |
| Semantic fluency | 9 ± 2.2 | |
| Z-score TMT | ||
| Part A | −0.33 ± 1.58 | |
| Part B | −0.70 ± 1.19 | |
| MMSE | 27 ± 2.0 | |
| Feature | Baseline Value * | Immediate Post-Radiotherapy Value * | Difference (Δ) * | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDkurtosis | 7.05 ± 1.76 | 6.02 ± 1.28 | −1.04 ± 1.89 | 0.049 |
| ADmean (×10−5 mm2 s−1) | 107.78 ± 7.06 | 103.48 ± 10.47 | −4.30 ± 8.81 | 0.023 |
| ADskewness | −0.32 ± 0.64 | −0.63 ± 0.49 | −0.31 ± 0.59 | 0.032 |
| RDkurtosis | 5.25 ± 1.21 | 4.57 ± 0.78 | −0.68 ± 1.12 | 0.016 |
| Outcome Variable | Predictor | Estimate (β) | Standard Error | t Value | r Value | p Value a | R2 | Adjusted R2 | F(3,15) | p Value b | RSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List learning ※ | ΔADmean | −2.404 × 104 | 9.819 × 104 | −2.448 | −0.330 | 0.027 | 0.308 | 0.169 | 2.223 | 0.128 | 2.864 |
| ΔADskewness | 3.188 | 1.645 | 1.938 | 0.154 | 0.072 | ||||||
| ΔRDkurtosis | −0.289 | 0.694 | −0.416 | 0.147 | 0.683 | ||||||
| Semantic fluency ※ | ΔADmean | −3.303 × 104 | 0.869 × 104 | −3.803 | −0.413 | 0.002 | 0.521 | 0.425 | 5.428 | 0.010 | 2.533 |
| ΔADskewness | 4.642 | 1.455 | 3.191 | 0.073 | 0.006 | ||||||
| ΔRDkurtosis | −1.505 | 0.614 | −2.453 | −0.172 | 0.027 | ||||||
| MMSE | ΔADmean | −1.536 × 104 | 0.683 × 104 | −2.251 | −0.402 | 0.040 | 0.254 | 0.105 | 1.703 | 0.209 | 1.991 |
| ΔADskewness | 1.553 | 1.143 | 1.358 | −0.042 | 0.194 | ||||||
| ΔRDkurtosis | −0.384 | 0.482 | −0.797 | −0.033 | 0.438 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Oppong, P.K.J.; Kitagawa, M.; Aoyama, H.; Onodera, S.; Terae, S.; Tha, K.K. DTI Histogram and Texture Features as Early Predictors of Post-Radiotherapy Cognitive Decline. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6794. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126794
Wang J, Oppong PKJ, Kitagawa M, Aoyama H, Onodera S, Terae S, Tha KK. DTI Histogram and Texture Features as Early Predictors of Post-Radiotherapy Cognitive Decline. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6794. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126794
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jincheng, Philip Kyeremeh Jnr Oppong, Maho Kitagawa, Hidefumi Aoyama, Shunsuke Onodera, Satoshi Terae, and Khin Khin Tha. 2025. "DTI Histogram and Texture Features as Early Predictors of Post-Radiotherapy Cognitive Decline" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6794. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126794
APA StyleWang, J., Oppong, P. K. J., Kitagawa, M., Aoyama, H., Onodera, S., Terae, S., & Tha, K. K. (2025). DTI Histogram and Texture Features as Early Predictors of Post-Radiotherapy Cognitive Decline. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6794. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126794







