Abstract
Photovoltaics with energy storage are the current trend in solar energy. Hybrid inverters are the backbone of low-power installations of this type. If a single installation is compromised, there are no significant security concerns. However, multiple devices can be targeted simultaneously. Taking into account their increasing share in the energy mix, distributed cyber-attacks against these devices can threaten grid stability. The Bulgarian electric power system has been analyzed in order to determine its development which is in line with EU-wide trends. It can be concluded that hybrid inverters are expected to grow rapidly in number and in installed power. The vulnerability of hybrid inverters to cyber-attacks has been analyzed, and the possible consequences for the energy system have been identified. The technology allows it to be used as a hybrid means of influence, and this aspect is poorly addressed in existing cybersecurity regulations. A risk assessment has been made, based on which measures to improve security have been proposed.
1. Introduction
Energy is a cornerstone of a nation’s economy and security. The rising necessity to address environmental concerns has pushed academia and industry towards the research, development, and utilization of cleaner energy sources and methods in the context of the smart technology transition [1]. This transition is characterized by the adoption of renewable energy sources (RESs) as the essence of distributed generation (DG), the most predominant of which are photovoltaics (PVs) [2]. PVs’ advances and falling prices have given rise to their appeal not only in industry but also in residential systems throughout the last decade. Despite the numerous advantages of PVs, there are concerns about their reliability, sustainability, safety, and security, to which cybersecurity is intrinsic. The US Department of Energy has used the term “cyber event” in a broad way, which describes any disruption caused by unauthorized access that is not by definition a cyber-attack and can easily be attributed to a human mistake [3]. Due to the inherently intermittent output of PVs [4], it is challenging to evaluate whether a cyber-attack or a human mistake has occurred based solely on parameter observation. The only conclusion that can be drawn is that the PV installation is not operating nominally.
Contemporary power plants, industrial systems, smart grids, and even more so PVs can be treated as cyber-physical systems (CPSs) [5,6]. CPSs are controlled remotely by programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and monitored by supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems [7,8,9,10]. These are heavily reliant on their secure communication. This is where cybersecurity is focused [4,11]. The STUXNET attack in 2010 has shown that there is an evident need to take the cybersecurity of CPSs into account.
The saturation of the energy system with renewable energy sources, mainly photovoltaics, has led to a serious need for balancing, due to the time offset between production and consumption. Therefore, it can be argued that the share of hybrid inverters that support energy storage devices will increase. Such a trend is already observed and can be predicted, with a high probability that it will intensify.
Hybrid inverters, in terms of communications and control, are more like Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices and fundamentally differ from classic control systems in the energy sector. This sets new requirements for cybersecurity.
Critical energy facilities—such as nuclear power plants—are logically and physically segregated from IT networks, and thus prevention against many possible cyber-attacks is achieved. Hybrid inverters are relatively low-power devices and therefore cannot be classified as critical. Indeed, even a successful cyber-attack against one device cannot lead to serious consequences for the entire energy system. Current trends, however, are for a very intensive penetration of hybrid inverters, resulting in significant total installed power. There is a large number of low-power devices, which have a common manufacturer of both hardware and software and use the same cloud for management. Due to their shared platform, a cyber-attack can easily be carried out on all devices and as a result disrupt the operation of a cumulatively large generating capacity. If trends continue, very soon the total power will be so large that it will affect the normal operation of the entire energy system. Because of this, other researchers such as Riurean et al. [12] propose that PVs should be included in the critical infrastructure category of respective national security and national energy resilience.
The penetration of hybrid inverters presents opportunities for both classic cyber-attacks and the weaponization of the technology. Additional concerns arise from the fact that the energy professionals who install and operate the new devices have virtually never encountered cyber issues, simply because classic generators are naturally immune. In residential applications hybrid inverters may be operated by their respective owners—ordinary citizens without any technical qualification.
The paper points out cyber threats to which this emerging technology is vulnerable, as well as some weaknesses of the existing cybersecurity regulations, and it presents a vision for possible solutions. Section 2 presents a literature review, which presents a classification of cyber-attacks and past examples of significant cyber-attacks on CPSs. This is taken as a reference point from the classical grid’s consideration and can be used to compare the evaluated threats in residential systems. Section 3 presents an analysis of the processes in the Bulgarian energy system, which allows for determining the trends in its development—such as what type of technologies will enter intensively and which will become obsolete. Although the Bulgarian system is analyzed, sufficient arguments and literature references are given, which allow for considering how the outlined trends are also valid for other energy systems in the European Union. Section 4 describes a hybrid inverter’s features in light of cybersecurity. The primary consequences due to potential cyber-attacks have been summarized. Real examples are pointed out that are not cyber-attacks but may be classified as cyber issues. A cybersecurity risk assessment of the hybrid inverters is performed in Section 5. Measures that significantly reduce the risk level are in Section 6.
2. Literature Review
While the classical power system is more reliable and sustainable than independent PV systems, both are susceptible to and vulnerable to security breaches caused by cyber-attacks leading to significant equipment and financial damages. As Ye et al. [4] have pointed out, the existing literature on smart grid cybersecurity is focused on cyber-attacks that threaten the grid’s reliability, rather than targeting individual subsystems’ performance. Additionally, electricity markets are also vulnerable [13].
In recent years there has been an increased IoT presence in such systems, which is regarded as the weak link [4,14,15] that can be outlined whenever a cyber-attack has occurred. Most cyber-attacks [6,16] that can impact the whole grid, a single power plant, an industrial system, etc., are first and foremost human-directed social engineering [17,18,19] (phishing, spoofing, eavesdropping, identity theft, ransomware, spam, etc.) based on e-mails and websites and then further communications and equipment-targeted attacks such as a watering hole attack [20], man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack [4,8,9,11,17,21,22], denial of service (DoS) [4,9,11,13,18,23,24], distributed denial of service (DDoS) [9,13,17,18,25,26,27], data integrity attack (DIA) [4,9], false data injection attack (FDIA) [9,22,28,29,30,31,32], cyber-physical attack [28], replay attack [4,5,9,17,33], time-delay attack [9], data manipulation [28], stealthy attack [2,34,35], etc. Of course, purely physical attacks purposed to damage or destroy the respective equipment itself are also present [2].
2.1. Real-World Cyber-Attack Examples
Some of the real-world examples, presented in Table 1, throughout the years have shown firsthand that cybersecurity is a critical subject and its neglect or even the lack of it should be reevaluated.

Table 1.
Chronological summary of real-world cyber-attack examples.
2.2. Cybersecurity of Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration Systems
Heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration (HVAC-R) systems are the other large energy consumers, amounting to 35–40% of total consumption in buildings [43,44] and in public utilities, which are considered in this paper. These systems are also subjected to increased IoT penetration in recent years and are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, primarily DoS and FDI [45,46,47], but also to MITM, eavesdropping, spoofing, replay, etc. [48]. There are gaps in detection strategies that do not distinguish between cyber-attacks and physical faults, which further leads to inadequate defense and mitigation strategies being applied, as many of them are based on numerical models and their respective user-defined assumptions, which do not always accurately represent real-world situation, as noted by Li et al. [49], by Moudgil et al. [50], and by Chen et al. [44]. Based on the shortcomings of HVAC-R’s detection and fault diagnosis methods, Fan et al. [51] have proposed a customized transformer-based neural network design that ensures efficiency in table data analysis and data transfer. Additionally, the study of Karbasi and Farhadi [52] has proposed an approach based on a distributed two-level communication model predictive control of building automation systems that significantly reduces computational overhead. Moosavi et al. [53] have proposed a framework-based methodology using a virtual machine where existing real datasets are converted to a BACnet protocol network traffic.
The secure operation of HVAC-R systems should be prioritized [54,55] as the equipment can be damaged severely [42,56] and can even threaten injury to personnel [42].
2.3. Cybersecurity Regulations Concerning Electric Power Systems
A number of documents regarding the cybersecurity of energy facilities have been published.
- IEC 61850 for intelligent electronic devices in electrical substations [57].
The IEC 61850-7-420 standard defines key points in an electrical substation automation system design. More specifically, it demonstrates which data models need to be set in designs of communication networks for the power utility automation of distributed energy resources. The model allows devices to understand the semantics of the data exchanged between each of them (such as measured parameters with respective units and expected ranges, control commands, alarms, flags, set points, etc.) seamlessly.
- Regulation 2024/2847 on horizontal cybersecurity requirements for products with digital elements known as the Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) [58].
The scope of the CRA is to safeguard businesses and consumers buying software and hardware products with digital components by requiring manufacturers and retailers to ensure cybersecurity throughout the respective product’s lifecycle. Critical products need to undergo a third-party assessment by an EU authorized structure before introducing them on EU markets. Such products are therefore marked with the “CE” marking to indicate compliance.
- Directive 2022/2555 on measures for a high common level of cybersecurity across the EU known as the Network and Information Security Directive (NIS 2) [59].
This directive presents a mandatory cybersecurity framework based on the original NIS directive with an expanded scope of critical infrastructures and essential service operators in the sectors of transport, energy, banking, healthcare, public electronic communications, social platforms, waste and wastewater management, postal and courier services, etc. Medium-sized and large entities operating in these critical sectors have to take cybersecurity measurements, regularly train employees and management in cybersecurity, and notify the relevant authorities of significant incidents.
- The IEC 62443 series of standards on cybersecurity for industrial and automation systems [60].
The IEC 62443 series of standards provides a structured framework to address cybersecurity challenges in industrial and automation systems through a holistic approach between people, processes, and technology, based on shared responsibility. It is also used to help asset owners and stakeholders to determine the necessary security level and to assess risk.
PLCs and SCADA systems have successfully become more secure and continue to be a cornerstone in CPSs due to measures taken by the authorities and industry. However, there are some gaps left unaddressed by these documents as well as the ENISA guidelines [61] and the industry-specific guidance of IEEE standard 1547.3 towards distributed energy resources [62].
There are precedents of devices and technology being compromised and weaponized such as the 2024 attacks in Lebanon [63], the cyber espionage by Huawei [64,65], the SWIFT ban on Russian banks after its invasion on Ukraine, the findings of suspicious components in imported energy technology [66], etc. The regulations cited above do not deal with peaceful technology that has been intentionally weaponized.
Only large utility-scale PVs are subjected to these regulations. Residential PVs are too small to be classified as essential, important, or critical entities. Residential PVs are generally overlooked as individually they are significantly smaller (<30 kWp) than large PV farms (>10 MWp). However, they have increased drastically in recent years and are collectively closing in in terms of power.
The newly developed Network Code on Cybersecurity (NCCS) [67] focuses on grid operators. However, residential PVs are only connected to the grid electrically (internet connection is provided by the inverter’s own network), which in most cases is through the existing point of common coupling. Thus, there is no dedicated professional operator or a cybersecurity branch. As such, when going forward with the NCCS in upcoming years, paying more attention to residential PVs should be addressed, which is also noted by the DNV report [68].
3. The Bulgarian Energy System—Current State, Issues, Trends, and Prospects
3.1. Energy Balance
The Bulgarian energy system is part of the European energy system and its development, despite its purely Bulgarian specifics, is ultimately predetermined by the pan-European energy policy. The data presented here are for the Bulgarian energy system, as the authors know it best, but the forecasts for future development apply to the entire European Union. This statement can be supported by publications by other European [68] and Indian [69] researchers who have come to similar conclusions.
The generation and consumption of electricity in the country over the last 10 years are presented in Figure 1. Electricity consumption remains constant within 5% with no discernible trend. Energy generation has been decreasing over the past 3 years due to the increasingly unfavorable conditions under which coal-fired power plants operate. The statistics on generating capacities are more insightful, particularly on the share of PVs in the total production.
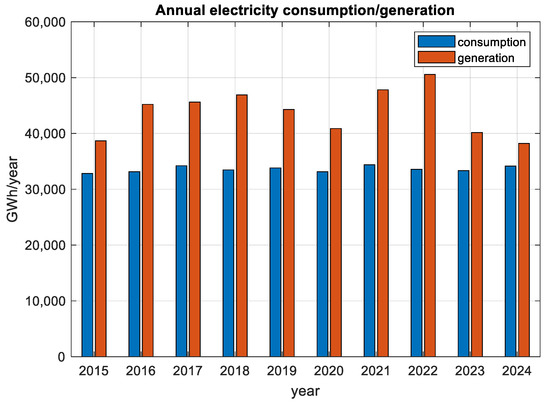
Figure 1.
Bulgarian annual electricity consumption and generation in 2015–2024.
The growth of PV power plants over the last 10 years is shown in Figure 2 with the growth of the total installed capacity in the top plot and the share of PVs of the total installed capacity of all power plants in the country in the bottom one. Only PV power plants connected to the energy system are included in this statistic, so the actual installed PV power is even larger. The significant increase in the number of photovoltaic power plants, constructed over the past 3 years, has created a trend that appears to be set to continue in the near future.
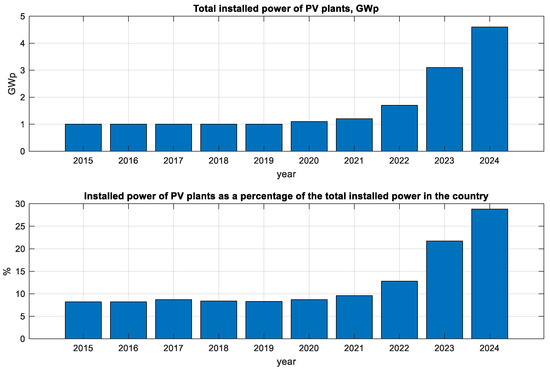
Figure 2.
Growth of PVs in Bulgaria in the period 2015–2024. The top plot shows total installed PV power, while the bottom plot shows the percentage of the total installed power in the electric power system.
The increased construction of PV power plants is associated not only with specific measures to promote renewable energy sources but also with the significant price drop of all PV equipment, thus providing sufficient profit margins.
The change in the price of PV panels is shown in Figure 3. The data are from the authors’ own statistics and represent the average price per Watt-peak. The price increase in 2022 is due to logistics problems, supply chain disruptions, and the corresponding increase in transport costs that were intrinsic to that particular period in time. The average annual electricity price on the Independent Bulgarian Energy Exchange (IBEX) [70] is also shown in the same figure on the right-hand axis. The increasing difference between the electricity purchase price and the cost of PVs is a key factor in the growth of the installed capacity.
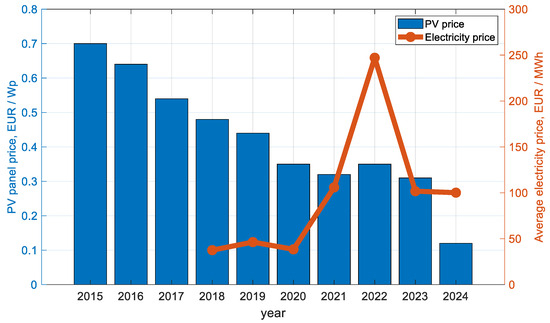
Figure 3.
PV panels and electricity prices’ deviation.
The photovoltaic plants built over the last three years are mainly large-scale, concentrated facilities with a MW capacity. Although PVs account for almost one-third of the total generating capacities, the share of photovoltaic energy in the total annual electricity production is quite modest, as presented in Figure 4.
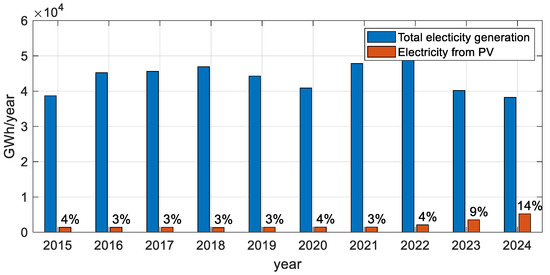
Figure 4.
Electricity generated by PVs versus total generation.
The relatively small share in total energy production is due to the low annual hourly utilization of photovoltaics and the large number of winter cloudy days. Large photovoltaic capacities that operate without the ability to store energy create operational problems. There are intervals of the day (on sunny days with reduced consumption) in which there is excess power that needs to be balanced.
The hourly change in the load of the entire energy system of the country on 7 May 2024 is shown in Figure 5. This is the day with the lowest consumption throughout the year (data from the Energy System Operator [71]). The simulated results for the energy generated by 4.6 GW of PV power plants, already operating in Bulgaria, are also shown in the same figure. The simulation used data from the EU Photovoltaic Geographical Information System (PVGIS) [72], which provides statistics on the performance of photovoltaic systems since 2005. The simulated energy generated based on 15-year average data for the generation on 7 May is represented by the solid line, while the dashed line represents the largest generation on that date for those 15 years. Unfortunately, the authors do not have statistical information on PVs’ production for the specific date, but the emerging problem is fundamental.
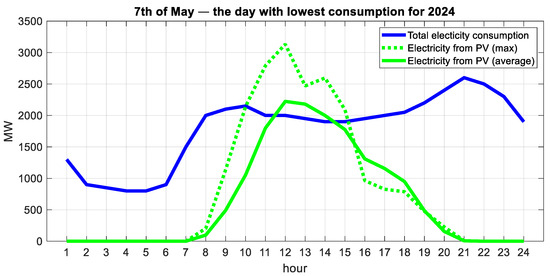
Figure 5.
PV generation and load profile of the day with the lowest consumption—7 May 2024.
A period in the middle of the day when there are no consumers for the potentially generated energy, at least in the country, is apparent. It relies upon the grid’s connectivity to export the excess electricity and also on the compensating (energy storage) capacities in the energy system. For now, such cases can be resolved at the expense of exports, but under unfavorable financial conditions.
This phenomenon also occurs in other energy systems. The term “transition from a camel curve to a duck curve” is often used. It is said that this has been common for the energy system of California [73] and is becoming common for EU countries [74,75].
The free electricity market in the European Union was created as a self-regulating mechanism, and naturally there is a price reaction to imbalances.
3.2. Price Effect
The inherent peak of photovoltaic generation and the saturation of the energy system with PV plants inevitably affect electricity prices. The time variation in the electricity exchange prices (orange) in Figure 6 is shown for summer and winter. Prices are based on the energy exchange and are averaged for the respective month during 2023. For comparison, the generated power from 1 kWp (blue) is also shown, using the averaged data from the PVGIS. The correlation between the daily peak in generation and the daily minimum price is obvious and well-studied [76]. The summer abundance of PV-generated energy is the reason for the very low daily price levels. The decrease in energy prices during periods of abundant sunshine and low consumption is very significant, and negative prices are no longer a surprise to market observers.
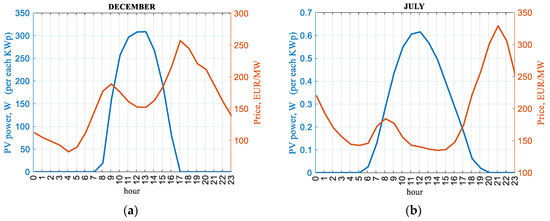
Figure 6.
Correlation between PV production and electricity price: (a) for a day in December, (b) for a day in July.
Furthermore, in just one week in April 2025, there were three days with negative electricity prices, as shown in Figure 7 (data from IBEX). It is striking how low the negative price is. Given that in April stationary PVs without storage generate power in the interval 8:00–19:00 h, it can be seen that for the three days presented in the figure, the PV plants do not generate a real profit, with the worst day, 20 April, resulting in a net loss. Furthermore, the negative energy prices are also subject to transfer costs over the grid, meaning that a nominally positive low price is already negative on the balance sheet, when the energy price is lower than the transmission price. The data, presented here, are only to illustrate how severely negative prices affect investors.
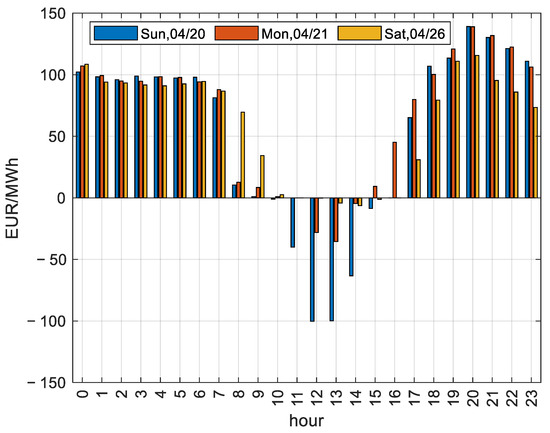
Figure 7.
Negative prices during the third week of April 2025.
The phenomenon of negative prices is observed throughout Europe, with a clear trend of increasing the total number of hours with negative prices [77,78]. For example, according to data from the electricity market information platform “SMARD”, in 2023 in Germany there were a total of 301 h with negative prices, and in 2024—457 h. The reasons are as follows: the rapid solar and wind energy expansion, inflexible conventional generation, and a lack of storage capacity.
Electricity does not become cheaper (at least in nominal terms) as revealed by the analysis of average levels (Figure 3), but profits from PV power plants without energy storage are reduced due to the hourly price distribution.
A typical economic cycle is observed, where oversaturation leads to a decline in the profitability of classical photovoltaic power plants without storage capacity. For this reason, it can be expected that the growth rate in the installation of new grid-connected PVs will slow down, and after the accumulated momentum has dissipated, it will stop.
4. PV Plants with Energy Storage Capability
Increased energy storage capacity seems to be the most probable scenario for solving the energy imbalance problem. Both pumped-hydro power plants and batteries are considered. The big investors already direct their attention to dedicated battery storage that will let them speculate about significant electricity price changes. The fastest growing battery storage capacity is in small (typically less than 100 kWp) PV installations with hybrid inverters. There are no statistics for such installations in Bulgaria, but based on surveys among companies with a combined 80% share of the photovoltaic market, between 10,000 and 50,000 hybrid inverter PV plants with power between 5 and 100 kWp have been installed over the last 2 years. There are economic, psychological, and normative reasons that determine this pace.
The average price of electricity for residential consumers in Bulgaria is 110.5 EUR/MWh, which is approximately equal to the average annual exchange price. There is very strong external political pressure to bring residential consumers into the electricity market, just as commercial consumers had been a decade ago. As illustrated, this should not lead to a serious price hike, but the general populace is very suspicious of such changes and perceives the measure with extreme disapproval and serious concerns. These concerns act as an incentive to install one’s own residential PV power plant.
In certain rural and suburban areas, the electricity for residential consumers is of poor quality. This is mainly due to overbuilding and network congestion. Users in these areas are also forced to install their own power plants to ensure independence from the centralized power supply.
The latest amendments to the Territorial Development Act require that every newly built residential building has renewable energy sources with installed capacity not less than half of the provided electrical power by the grid. The provided electrical power is the maximum power that the building can consume. It is controlled by technical (automatic circuit breakers) and administrative (15 min load check) measures. As already mentioned, the only practical renewable resource available in the country is solar energy.
The structure diagram of a PV system with a hybrid inverter is shown in Figure 8.
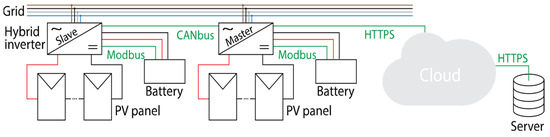
Figure 8.
Structure diagram of a PV system with hybrid inverters.
Due to the heavy bureaucratic procedure, many residential users and small- and medium-sized business owners prefer to build photovoltaic power without injecting energy into the grid, as shown in Figure 9.
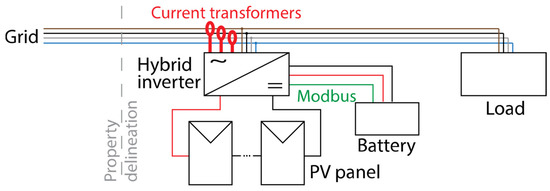
Figure 9.
Hybrid inverter operating in “no-energy return” mode.
Additional current transformers (red) are connected to the inverter, measuring the current at the point of common coupling to the grid. The inverter is operated in a way that prevents energy from being injected into the grid. The energy from the PVs is used to feed the load and to charge the battery, or it is not generated at all. A PV plant operating according to the scheme in Figure 9 has a significantly simplified construction and grid connection procedure, as statutory consent is replaced by tacit consent. Since this setup is for residential users and small businesses, it is very important that the inverter allows phase imbalance when operating in a non-injecting mode. When the load consists of single-phase consumers, it is natural to have working modes in which one of the phases is significantly more loaded or significantly more underloaded than the others, and the inverter must be able to cover the asymmetrical load without injecting energy into the grid.
The typical load profile of a Bulgarian residential consumer is given in Figure 10. Based on the author’s measurements, where common residential loads are taken into account, as the maximum and minimum values for a month were averaged, an area of the most probable change in the household load was identified. Figures for the winter and summer months, December and July, respectively, are shown. For comparison, the data from a simulation for the average production of a 10 kWp photovoltaic plant and the average monthly energy price are shown in the same coordinate system.
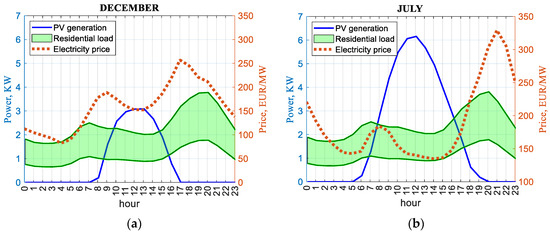
Figure 10.
Residential load profiles: (a) for a day in December, (b) for a day in July.
As can be seen from the load profiles, the load variation is very slight. This can be explained by the fact that the largest residential consumer is the HVAC-R system, which operates in heating mode in winter and cooling mode in summer. A simplified structure of an air conditioning installation is shown in Figure 11.
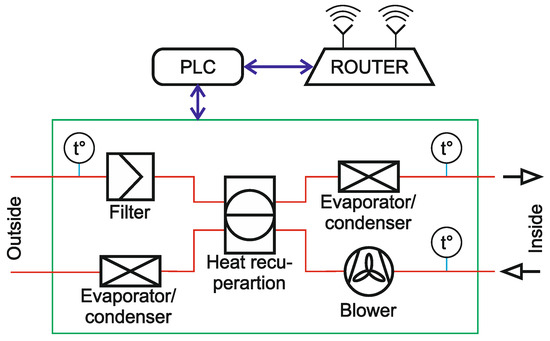
Figure 11.
Simplified structure of an HVAC-R installation.
Attention should be paid to the need for control of PV systems with hybrid inverters. Consumption may not change significantly, but the available PV energy changes considerably throughout the year. The prices of the energy purchased in addition to that generated by the PVs vary not only in magnitude but also in time, with maximum values changing over time. In financial terms, the optimal use of such a system requires frequent changes to the settings. The intervals for prioritized battery charging and the intervals for prioritized battery discharging are set. Such a system cannot be used effectively if it is separated from the global network.
As a counterpoint, the HVAC-R system should be mentioned, which is also complex and seemingly requires frequent adjustments. The vast experience with such systems has revealed that in most cases there is no internet connection, or if there is one, it is only used for monitoring, and the options for changing settings or updating software are disabled. This fully satisfies the customers. A survey of the four largest companies that maintain HVAC-R systems in the country found that none of them could point to a single instance of a cyber-attack or a problem related to remote management.
The situation with the exploitation of hybrid inverters is quite different. Despite their short history so far, they already have a track record of technical problems that are directly related to security.
Hybrid Inverters and Security Concerns
A study was conducted on the most prominent Bulgarian renewable energy equipment suppliers of inverters—hybrid and grid-connected. The companies studied the total market share of the photovoltaic system market of over 80% (according to self-reported figures and turnover by Commercial Register public records). Below is a list of the brands represented in the product catalogs of these companies:
- Huawei;
- Deye;
- GoodWe;
- Solis;
- Solax;
- Growatt;
- Sungrow;
- Afore;
- EASun;
- TBB Power.
As evident from the above, the Bulgarian market is dominated by Chinese manufacturers, while EU brands like SMA, Victron, and Fronius have a niche presence. The market shares of Huawei and Deye are more than 60%. In [68] similar results are published claiming that in 2023 “78% of the PV inverters shipped (to EU), originated from China” and also that there are “seven manufacturers with the ability to remotely manipulate more than 10 GW of generation capacity”. According to our prognosis those numbers will grow. The EU market as a whole is similar. This is further visualized by data from [68] in Figure 12.
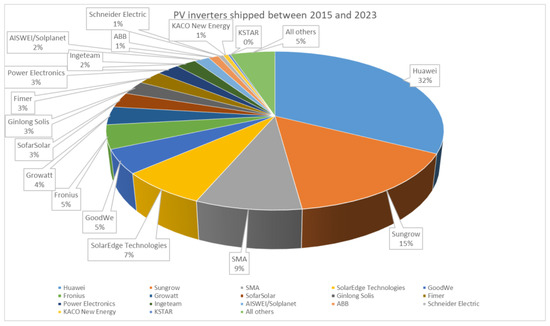
Figure 12.
PV inverters shipped to EU market between 2015 and 2023. Data taken from [68].
The inverters are directly connected to the global network and use entirely in-house-developed proprietary cloud structures, firmware, and hardware. Inverters are an embedded system; i.e. the firmware is solely under the control of the manufacturer. A potential disconnect from the internet and the respective manufacturer servers would lead to deteriorated financial and operational indicators and is therefore not considered acceptable. This applies to both hybrid inverters and battery management systems (BMSs). If the forecast for intensive growth is justified, PV plants with storage capability will soon occupy a significant share of the electricity mix.
Possible consequences of cyber-attacks:
- Attempts to destabilize the entire energy system with subsequent blackout. In the event of a simultaneous loss of large generating capacity, dangerous regimes may occur. It is obvious that after the events in Spain [79] and North Macedonia [80], where the energy system collapsed, system sustainability must be further studied. This is the most serious potential threat.
- Attempts to damage batteries. Batteries can be deactivated, which is associated with very large economic losses, but potentially there are also regimes in which they can be ignited or deflagrated. The mandatory use of BMSs does indeed greatly reduce the risk but does not eliminate it completely. A real event that damaged the batteries is described later.
- Attempts to cause economic losses. Here, the scenarios include an attack against a specific prosumer and also against a large number of inverters. In both cases, it is possible not only to turn off the inverters but to simulate frequent failures, which would completely compromise the reliability of the plant and at the same time make it difficult to detect the attack.
The events described below are observed in PV systems with hybrid inverters studied by the authors. The reasons for these are software/firmware problems inherent in new developments, not malicious actions, and they can be classified as cyber events. However, they are a blueprint for action when planned cyber-attacks are taken into account.
A 12 kW Deye inverter operating with three 5 kWh lithium-ion iron phosphate (LFP) battery modules (15 kWh battery storage) is connected in parallel. Due to the capability of the inverter to operate with different battery chemistries, including user-defined types, the following issue occurs. The firmware is automatically updated (the automatic update for this model cannot be disabled, being short for disconnecting from the internet). After the update, the inverter switches to factory settings, changing the battery type to “lead-acid or user defined” with a maximum charge voltage of 64 V (2.67 V per cell). Three LFP batteries with a nominal voltage of 48 V and a maximum charge voltage of 58 V are installed. Upon recharging the batteries, which the inverter presumes are of the flooded type, they reach the maximum voltage of 58 V, and the protection of the individual BMS of the battery modules is triggered. In this specific case, it is necessary to replace all three battery modules, as it is not possible to restore the operation of the BMS, and the battery cells themselves work normally.
The widely installed battery modules have a BMS that provides current protection and monitors the voltage and temperature of individual cells but does not perform balancing. The explanation is that the sorted cells with the same parameters are selected and bundled in a series for each battery. For 2 years of operation, the main failure of the battery modules is related to the cell voltage imbalance, which occurs naturally during the operation process. After opening the module and manually balancing the cells, the module’s functionality is restored.
The use of sorted cells and the lack of balancing affect the reliability and expansion capabilities of the systems. High-voltage batteries, in which individual modules are connected in series, cannot be replaced. All cells in all modules are connected in series and must have the same parameters. If an expansion of the system’s storage capabilities is necessary at a later time, i.e., a battery module must be added, it is necessary to replace all the modules, as there is no way to provide a new module with the same parameters that can simply be added to the array. In the event of a module failure, it cannot simply be replaced. Either the total capacity of the array is reduced when the damaged module is removed, or all the modules are replaced, including the healthy ones. This is economically unfeasible.
Battery management and protection are critical functions. Potential software problems can lead not only to battery damage but also to fire hazards and explosion risks. Communication with the BMSs of the currently installed devices is conducted with the proprietary manufacturer over the RS-485 interface and with a complete lack of documentation. Following the events of September 2024, when many electronic devices were blown up in Lebanon, and suspicions that some of the explosions used simple lithium batteries without a special explosive substance [63], a certain paranoia on this issue seems healthy.
The grid injection restriction to which more and more inverters are legally subjected creates many problems. If the system needs to be expanded, the structure from Figure 10 should be used and inverters from the same brand should be connected in a controller/responder (formerly master/slave) configuration. The attempt to connect two independent inverters as shown in Figure 11 results in a collapse. Each inverter measures the energy at the input and regulates its own power so that there is no negative, i.e., injected energy. If two independent inverters are used, they do not synchronize the measurement moments. The first inverter determines its operating mode, but then the second one interferes and changes the power balance, and the first one adjusts its mode, but this leads to a change in the mode of the second one, and so on. The two inverters constantly diverge, and the system becomes completely inoperable. This fine-tuned ensemble can easily be disrupted with a single setting.
5. Risk Assessment of PV Plants with Hybrid Inverters
This section presents possible threat scenarios and assesses risks to each one. There is a lack of statistical data as hybrid inverters are still an emerging technology, but due to their rapid growth, attention must be given.
The risk is assessed by three factors, impact, difficulty, and likelihood, and an effects analysis methodology based a custom matrix is developed. The “impact” counts for how severe the consequences of a given cyber-attack scenario are. The “difficulty” estimates how many resources and how much effort are needed to implement a particular scenario. The “likelihood” determines how likely an attack is to occur. Each factor is divided into three scores (i.e., low, medium, high) according to Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 2.
Impact.

Table 3.
Difficulty.

Table 4.
Likelihood.
The factor takes into account whether the attack is directed at an individual owner (a small number of owners); at an intermediary, such as the installer, who has access to the facilities built and maintained by them; or at a significant number of facilities that can already threaten the entire system.
The highest level of difficulty has a minimal score because it requires huge resources and therefore it comes with minimal risk.
This does not mean an exact, statistically calculated probability, but the factor represents a subjective assessment of the possibility of a given scenario, based on unsystematic historical data. Although it lacks accuracy, the approach allows for some form of geopolitical realities to be taken into account.
For each threat scenario, a score is given for each of the three factors. The scores are then multiplied to obtain an overall score that allows the risk to be classified into four categories, low, medium, high, and critical, according to Table 5.

Table 5.
Risk assessment scale.
Threat Scenarios
Threat scenarios are derived by considering the possible channels for gaining unauthorized access to the control of the inverter or BMSs.
A breach in the access rights authentication system: Unauthorized access can be obtained by bypassing the security measures of different software. The authorization of an individual owner, an installer, or a manufacturer can be breached, with the latter causing the most damage. Such breaches occur regularly, so the likelihood is assessed as moderate. “Difficulty” and “impact” are assessed as moderate, as common measures against such attacks provide a certain level of protection.
Attack through installer access rights: Typically, installers have access, albeit incomplete, to the inverter management system. A breach of their credentials can occur in various ways. In most cases, installers have little training in cybersecurity. Such a scenario is considered moderate to achieve, has a moderate likelihood, and leads to moderate impact.
Attack through manufacturer access rights: An attack that is similar to the above, but through the manufacturer. Large manufacturers are usually well prepared for such scenarios, but this is not always the case with low-cost companies. Manufacturers are usually attacked along the supply chain. Major impact is possible, serious resources are required, and there is a moderate likelihood.
Attack through inverter interface: Inverters are equipped with additional interfaces through which their operation can be controlled. Theoretically, an attack through them is possible. In reality, at least in Bulgaria, this is difficult nowadays. Chinese manufacturers make very frequent and serious changes, do not keep strict communication protocols, etc. For example, control via Modbus RTU is difficult to implement, since the registers are constantly changing (even with updates). The scenario can cause serious damage on a constrained number of devices, but it is difficult to implement and with a low likelihood.
Attacks through unauthorized devices (backdoor): This refers to additional means of communication that are hidden in the inverter. Recently, there have been reports of exactly this type of attack [81], which, however, require further verification. The question arises as to why additional communication channels are needed when the main one is available. In this way, it is difficult to gain simultaneous access to many devices, the likelihood is low, and the difficulty is moderate.
Malicious firmware (manufacturer not involved): This scenario assumes that a hacker group successfully attacks the manufacturer, gaining access to the firmware and the cloud infrastructure. Such an option cannot be ruled out in a highly competitive industry, but it requires very large resources. Such attacks in industry have been documented, but not in the energy sector. A large number of devices could be affected, but the likelihood is low.
Malicious firmware (manufacturer involved): This scenario has two dimensions. On the one hand, data on the location of the inverter, consumption, and generation of electricity can be illegally obtained and processed. On the other hand, the inverter and battery can be used as a weapon, including an attempt to attack the entire energy system. Unfortunately, there is a history of reports of events that can be classified as falling into this scenario [64,65]. However, its likelihood is assessed as low.
Summarized threat scenarios with their respective risk scores and risk levels are presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Risk score and risk levels.
The highest risk score is for the threat involving targeted actions supported by the inverter manufacturer. Special attention should be paid to this scenario, as European regulations practically do not provide measures that can effectively ensure prevention.
A comparison between the performed risk assessment and NIST cybersecurity framework (CSF) as well as ISO/IEC 27005 can be made. According to each of these frameworks, the respective results are presented in Table 7 and Table 8.

Table 7.
Risk scores according to IEC 27005.

Table 8.
Classification of considered threats by NIST CSF and recommended control.
Compared to IEC 27005, it can easily be seen that there is a difference in the assessment of impact, likelihood, and detection quality. The reason for this is that according to IEC 27005 there is a security information and event management system or intrusion detection system. However, in the context of small-scale PVs there are no such systems.
The considered threats fall into the NIST categories of protect, detect, and identify.
It should be taken into account that both of these frameworks are purposed to enhance the cybersecurity of organizations with separate cybersecurity branches. However, the considered threats are most likely targeted towards untrained people. While a requirement to train PV installers in cybersecurity can have merit, it is severely challenging to implement in small businesses. Nonetheless, attention should be given during the development of nation-wide and union-wide policies as the threats with most severe impact can be mitigated with such measures.
6. Enhancing the Cybersecurity of Hybrid Inverters
The measure included in the CRA can reduce the risk level of some of the threats listed above. According to the requirements of the CRA, specific guidelines should be created regarding the assessment and verification of the safety of critical infrastructure. A software assessment is also considered. Attention is paid to improving qualifications and training in terms of cybersecurity. All these measures will positively affect the risk level if they are also applied to hybrid inverters, which due to their small unit power are currently not considered critical. However, the risk of the threats specified in rows 6 and 7 of Table 6 remains unchanged.
The following is a list of measures that can reduce risk levels:
1. The development of guidelines, which currently do not exist, that would also allow the application of the measures provided for in the CRA for small-capacity PV plants.
2. The active and accelerated introduction of energy communities. A number of measures provided by the CRA, such as increasing the qualification or periodic inspection and assessment of security, remain purely voluntary when they have to be carried out among small plant owners and even small installers. The energy community is already an organization that can take responsibility for maintaining the above-mentioned practices. In addition, the energy community assumes unified management of all generating capacity, which means an additional layer of control.
3. Introducing an intermediate layer in the control circuit that segregates the inverter and limits direct access to it.
The currently widely used inverter control structure is shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9. The inverter is directly connected to the internet and is managed via the manufacturer’s cloud, which is a source of security concerns.
The control can use a structure like that of the HVAC-R systems shown in Figure 11. There is connection to the internet, the remote control capabilities remain, but the inverter is isolated from the manufacturer’s cloud. The inverter is controlled via a PLC. This is actually the standard way in which most control systems are built. This effectively eliminates the possibility of a simultaneous attack on a large group of inverters (all from the same manufacturer). This is a built-in feature of this control structure and is confirmed by the fact that HVAC-R systems are much less vulnerable.
In order for such a structure to be possible, it is necessary to have access to at least the basic functionality of the inverter. The operational control of the inverter consists in directing the energy flows from the photovoltaics, the grid, and the battery. At the moment, the algorithm is so simple that it can be controlled even through a small number of digital and analog channels. In practice, this type of control is often implemented using MODBUS RTU. In this case, accurate data on the registers are needed, which provide the basic operational controllability. (The problems with the register tables have already been mentioned.) The approach requires some standardization of the set of commands that each inverter must be able to execute. Such unintentional standardization is present even at the moment; it is not imposed administratively but is the result of the identical functions that inverters from different manufacturers perform.
Advantages of this approach:
- Easy to implement and familiar to engineers in practice;
- Provides both operational control and isolation from the manufacturer’s cloud;
- Easy modification of the control and direct entry into the emerging need for centralized dispatching control even of low-power generators.
Disadvantages of this approach:
- Increased costs;
- Complicated system.
4. Update logs and rollback
Similarly to the common practice in IT systems, keeping track of update logs and the capability to rollback to a previous version allows for easier troubleshooting and easier recovery. In the case of malware without the manufacturer’s involvement (row 6 of Table 6), it may serve as a further verification that a third party has breached the manufacturer. Additionally, it is a tried-and-tested method to restore operation with minimal downtime whenever a bug in a newer version is found. Going further with developing and updating the regulations and directives, the authors deem it necessary that manufacturers should be required to implement such options and settings in their inverters. This gives additional rigidness in a secure supply chain.
7. Small-Scale Survey Among Installers and PV Owners
7.1. Survey Goal
An appropriate survey among 11 installers and 50 residential PV owners in Bulgaria via an e-mail questionnaire has been conducted in order to assess the following:
- Level of cyberthreat awareness;
- The frequency of encountered problems that are related to updates or remote control;
- Willingness to adopt the proposed measures;
- Attitude towards future regulations.
7.2. Survey’s Results
The survey’s results are summarized in Table 9.

Table 9.
Small-scale survey among Bulgarian installers and PV owners.
7.3. Discussion
The results show limited awareness among installers and end users and high support for the proposed structural changes, such as the introduction of an intermediate control layer and the ability to “rollback” software.
Although the basis of this study is rooted in the Bulgarian context, the observed threats, risk dynamics, and mitigation strategies reflect a broader European reality. Given the harmonized energy policy under the EU Green Deal and the increasing penetration of hybrid PVs in Member States, the insights provided here can inform and open a discussion on cybersecurity frameworks and policy development at the union level.
8. Conclusions
PV systems with hybrid inverters are a rapidly and widely developing technology. They present new challenges before cybersecurity. The current experience in cybersecurity and the typical measures that are applied are not sufficient to ensure a high level of safety. The paper identifies threats that are covered by the regulatory framework and measures to improve security in this regard. Further research and discussions are needed to reach a consensus and EU-wide measures.
Author Contributions
V.G., V.T., P.T. and S.S. were involved in the full process of producing this paper, including conceptualization, investigation, visualization, and preparing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been accomplished with financial support by the European Regional Development Fund within the Operational Programme “Bulgarian national recovery and resilience plan”, procedure for direct provision of grants ”Establishing of a network of research higher education institutions in Bulgaria”, and under Project BG-RRP-2.004-0005 “Improving the research capacity and quality to achieve international recognition and resilience of TU-Sofia (IDEAS)”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
List of Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Description |
| BMS | Battery management system |
| CPS | Cyber-physical system |
| CRA | Cyber Resilience Act |
| DDoS | Distributed denial of service |
| DG | Distributed generation |
| DIA | Data integrity attack |
| DoS | Denial of service |
| FDIA | False data injection attack |
| HVAC-R | Heating, ventilation, air conditioning, and refrigeration |
| IBEX | Independent Bulgarian Energy Exchange |
| LFP | Lithium-ion iron phosphate |
| MITM | Man-in-the-middle |
| NCCS | Network Code on Cybersecurity |
| NIS | Network and Information Security |
| PLC | Programmable logic controller |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| PVGIS | Photovoltaic Geographical Information System |
| RESs | Renewable energy sources |
| SCADA | Supervisory control and data acquisition |
References
- Su, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, C.; Li, B.; Li, J. Cyber-attacks against cyber-physical power systems security: State estimation, attacks reconstruction and defense strategy. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 413, 126639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrou, F.; Taghezouit, B.; Bouyeddou, B.; Sun, Y. Cybersecurity of photovoltaic systems: Challenges, threats, and mitigation strategies: A short survey. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1274451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E&ENEWS; Sobczak, B. ‘Cyber Event’ Disrupted U.S. Grid Networks—DOE. 2019. Available online: https://www.eenews.net/articles/cyber-event-disrupted-u-s-grid-networks-doe/ (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Ye, J.; Giani, A.; Elasser, A.; Mazumder, S.K.; Farnell, C.; Mantooth, H.A. A Review of Cyber–Physical Security for Photovoltaic Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 4879–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, C.M.; Palleti, V.R.; Mishra, V.K. A practical physical watermarking approach to detect replay attacks in a CPS. J. Process Control 2022, 116, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.P.; Li, S.; Gu, C.; Yan, X.; Hu, P.J.-H.; Wang, Z.; Xie, D.; Cao, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.; et al. Cyber Vulnerabilities of Energy Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Ind. Electron. 2024, 5, 1455–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, L. An effective intrusion-resilient mechanism for programmable logic controllers against data tampering attacks. Comput. Ind. 2022, 138, 103613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Maynard, P.; McLaughlin, K.; Sezer, S.; Andrén, F.; Seitl, C.; Kupzog, F.; Strasser, T. Investigating Cyber-Physical Attacks against IEC 61850 Photovoltaic Inverter Installations. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation (ETFA), Luxembourg, 8–11 September 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, M.; Niknam, T.; Wang, Z.; Mehrandezh, M.; Dehghani, M.; Ghadimi, N. A comprehensive review of cyber-attacks and defense mechanisms for improving security in smart grid energy systems: Past, present and future. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 215 Pt A, 108975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkraouda, H.; Chakkantakath, M.A.; Keliris, A.; Maniatakos, M. SNIFU: Secure Network Interception for Firmware Updates in legacy PLCs. In Proceedings of the IEEE 38th VLSI Test Symposium (VTS), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 April 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Dragičević, T.; Blaabjerg, F. Cyber Security in Control of Grid-Tied Power Electronic Converters—Challenges and Vulnerabilities. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 5326–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riurean, S.; Fîță, N.-D.; Păsculescu, D.; Slușariuc, R. Securing Photovoltaic Systems as Critical Infrastructure. A Multi-Layered Assessment of Risk, Safety, and Cybersecurity. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedrick, J.; Perrin, K.A.; Sabaghian, E.; Wilcoxen, P.J. Assessing cyber attacks on local electricity markets using simulation analysis: Impacts and possible mitigations. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xie, R.; Yang, B.; Guo, L.; Ma, P.; Shi, J. Detection and Identification of Cyber and Physical Attacks on Distribution Power Grids with PVs: An Online High-Dimensional Data-Driven Approach. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SMA Solar Technology AG. Public Cyber Security: Guidelines for a Secure System Communication; Technical Information; CyberSecurity-TI-en-20; SMA Solar Technology AG: Niestetal, Germany, 2025; Available online: https://files.sma.de/downloads/CyberSecurity-TI-en-20.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Terneva, Z.; Nenova, M.; Terneva, V.; Vladimirov, I.; Nikolova, D. Cyberattack types—Methods and technics for protection of communication resources. In Proceedings of the 57th International Scientific Conference on Information, Communication and Energy Systems and Technologies (ICEST), Ohrid, North Macedonia, 16–18 June 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Maynard, P.; McLaughlin, K.; Laverty, D.; Sezer, S. Threat Analysis of BlackEnergy Malware for Synchrophasor based Real-time Control and Monitoring in Smart Grid. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium for ICS & SCADA Cyber Security Research (ICS-CSR), Belfast, UK, 23–25 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, I.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, R.; Singh, P.K.; Satapathy, S.C. Identifying cyber insecurities in trustworthy space and energy sector for smart grids. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharabov, M.; Tsochev, G.; Gancheva, V.; Tasheva, A. Filtering and Detection of Real-Time Spam Mail Based on a Bayesian Approach in University Networks. Electronics 2024, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symantec. Dragonfly: Cyberespionage Attacks Against Energy Suppliers, Security Response. 2014. Available online: https://docs.broadcom.com/doc/dragonfly_threat_against_western_energy_suppliers (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Carter, C.; Onunkwo, I.; Cordeiro, P.; Johnson, J. Cyber Security Assessment of Distributed Energy Resources. In Proceedings of the IEEE 44th Photovoltaic Specialist Conference (PVSC), Washington, DC, USA, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymouri, A.; Mehrizi-Sani, A.; Liu, C.-C. Cyber Security Risk Assessment of Solar PV Units with Reactive Power Capability. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018—44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 2872–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyen, N.D.; Quan, N.S.; Linh, V.B.; Tuyen, V.V.; Fujita, G. A Comprehensive Review of Cybersecurity in Inverter-Based Smart Power System Amid the Boom of Renewable Energy. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 35846–35875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Yang, G.-H. Sampled-data distributed state estimation with multiple transmission channels under denial-of-service attacks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2022, 429, 127229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbacki, M.; Chaczko, Z.; Barton, S.; Wajs-Chaczko, P.; Nikodem, J.; Rozenblit, J.W.; Klempous, R.; Ito, A.; Kulbacki, M. A Review of the Weaponization of IoT: Security Threats and Countermeasures. In Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics (SACI), Timisoara, Romania, 23–25 May 2024; pp. 000279–000284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenova, M.; Atanasov, D.; Kassev, K.; Nenov, A. Intrusion Detection System Model Implementation against DDOS attacks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Antennas, Communications and Electronic Systems (COMCAS), Tel-Aviv, Israel, 4–6 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, M.; Nenova, M.; Iliev, G.; Avresky, D. Integration of Splunk Enterprise SIEM for DDoS Attack Detection in IoT. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Symposium on Network Computing and Applications (NCA), Boston, MA, USA, 23–26 November 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatipatri, N.; Arun, S.L. A Comprehensive Review on Cyber-Attacks in Power Systems: Impact Analysis, Detection, and Cyber Security. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 18147–18167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoufi, S.; Derhab, A.; Guerroumi, M. Survey of false data injection in smart power grid: Attacks, countermeasures and challenges. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2020, 54, 102518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musleh, A.S.; Chen, G.; Dong, Z.Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, S. Vulnerabilities, Threats, and Impacts of False Data Injection Attacks in Smart Grids: An Overview. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Grids and Energy Systems (SGES), Perth, Australia, 23–26 November 2020; pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpourfard, M.; Khalili, A.; Genc, I.; Konstantinou, C. Cyber-Resilient Smart Cities: Detection of Malicious Attacks in Smart Grids. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; He, H. Advance learning technique for the electricity market attack detection. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 100, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.R. Replay Attack Detection in Smart Grids Using Switching Multi-Sine Watermarking. Master’s Thesis, Concordia University, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Khazaei, J.; Asrari, A. Second-Order Cone Programming Relaxation of Stealthy Cyberattacks Resulting in Overvoltages in Cyber-Physical Power Systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 4267–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Liu, M.; Zuo, K.; Tan, W.; Deng, R. Stealthy Data Integrity Attacks Against Grid-tied Photovoltaic Systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE 6th International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS), Wuhan, China, 8–11 May 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnouskos, S. Stuxnet worm impact on industrial cyber-physical system security. In Proceedings of the IECON 2011—37th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 7–10 November 2011; pp. 4490–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, D. The real story of stuxnet. IEEE Spectr. 2013, 50, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosov, A.; Rodionov, E.; Harley, D.; Malcho, J. Stuxnet Under the Microscope. 2010. Available online: https://www.esetnod32.ru/company/viruslab/analytics/doc/Stuxnet_Under_the_Microscope.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Dragos Inc. CRASHOVERRIDE Analysis of the Threat to Electric Grid Operations. 2017. Available online: https://www.dragos.com/wp-content/uploads/CrashOverride-01.pdf?utm_referrer (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Slowik, J.; Dragos Inc. CRASHOVERRIDE: Reassessing the 2016 Ukraine Electric Power Event as a Protection-Focused Attack. 2019. Available online: https://www.dragos.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/CRASHOVERRIDE.pdf?hs (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Rector, S. A Case Study of the CRASHOVERRIDE Malware, Its Effects and Possible Countermeasures; Cybersecurity Undergraduate Research Showcase. 5.; Old Dominion University: Norfolk, VA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Madnick, S. Protecting Chiller Systems from Cyberattack Using a Systems Thinking Approach. Network 2022, 2, 606–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnour, M.; Meskin, N.; Khan, K.; Jain, R. HVAC system attack detection dataset. Data Brief 2021, 37, 107166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, Q.Z.; Qiao, Y. Defending against cyber-attacks in building HVAC systems through energy performance evaluation using a physics-informed dynamic Bayesian network (PIDBN). Energy 2025, 322, 135369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnour, M.; Meskin, N.; Khan, K.; Jain, R. Application of data-driven attack detection framework for secure operation in smart buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ren, L.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Adetola, V.; Wen, J.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, T.; Candan, K.S.; O’Neill, Z. A critical review of cyber-physical security for building automation systems. Annu. Rev. Control 2023, 55, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Gu, W.; Lu, S.; Yu, R.; Sheng, L. Cyber-attack against heating system in integrated energy systems: Model and propagation mechanism. Appl. Energy 2022, 311, 118650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Gonzalez, C.; Harper, M.; Cash, M.; Luo, L.; Ling, Z.; Sun, Q.Z.; Fu, X. On building automation system security. High-Confid. Comput. 2024, 4, 100236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ren, L.; Pradhan, O.; O’Neill, Z.; Wen, J.; Yang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Chu, M.; Huang, J.; Wu, T.; et al. Emulation and detection of physical faults and cyber-attacks on building energy systems through real-time hardware-in-the-loop experiments. Energy Build. 2024, 320, 114596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudgil, V.; Hewage, K.; Hussain, S.A.; Sadiq, R. Integration of IoT in building energy infrastructure: A critical review on challenges and solutions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 174, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Lei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Mo, L. Novel transformer-based self-supervised learning methods for improved HVAC fault diagnosis performance with limited labeled data. Energy 2023, 278 Pt B, 127972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbasi, A.; Farhadi, A. A cyber-physical system for building automation and control based on a distributed MPC with an efficient method for communication. Eur. J. Control 2021, 61, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, S.A.; Asgari, M.; Kamel, S.R. Developing a comprehensive BACnet attack dataset: A step towards improved cybersecurity in building automation systems. Data Brief 2024, 57, 111192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galler, M. Basic Recommendations For HVAC Cybersecurity. ASHRAE J. 2021, 63, 1–2. Available online: https://tsapps.nist.gov/publication/get_pdf.cfm?pub_id=932229 (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Association of European Refrigeration Component Manufacturers (ASERCOM). ASERCOM Cyber-Security Guideline for Connected HVAC/R Equipment. 2018. Available online: https://asercom.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/English_CyberSecurity-Guideline.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Vijayshankar, S.; Chang, C.-Y.; Utkarsh, K.; Wald, D.; Ding, F.; Balamurugan, S.P.; King, J.; Macwan, R. Assessing the impact of cybersecurity attacks on energy systems. Appl. Energy 2023, 345, 121297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 61850-7-420:2021; Communication Networks and Systems for Power Utility Automation—Part 7-420: Basic Communication Structure—Distributed Energy Resources and Distribution Automation Logical Nodes. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- European Commission. Regulation (EU) 2024/2847 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2024 on Horizontal Cybersecurity Requirements for Products with Digital Elements and Amending Regulations (EU) No 168/2013 and (EU) 2019/1020 and Directive (EU) 2020/1828 (Cyber Resilience Act) (Text with EEA Relevance), OJ L, 2024/2847, 20.11.2024, Document 32024R2847. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2024/2847/oj/eng (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- European Commission. Directive (EU) 2022/2555 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 December 2022 on Measures for a High Common Level of Cybersecurity Across the Union, Amending Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 and Directive (EU) 2018/1972, and Repealing Directive (EU) 2016/1148 (NIS 2 Directive) (Text with EEA Relevance), OJ L 333, 27.12.2022, Document 32022L2555. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2022/2555/oj/eng (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- International Electrotechnical Commission. International Society of Automation, ISA/IEC 62443 Series of Standards. Available online: https://www.isa.org/standards-and-publications/isa-standards/isa-iec-62443-series-of-standards (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- European Union Agency for Cybersecurity, ENISA. Guideline on Security Measures Under the EECC, Fourth edition, July 2021. Available online: https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/guideline-on-security-measures-under-the-eecc (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- IEEE Std 1547.3-2023 (Revision of IEEE Std 1547.3-2007); IEEE Guide for Cybersecurity of Distributed Energy Resources Interconnected with Electric Power Systems. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1–183. [CrossRef]
- Sarker, P.P.; Das, U.; Varshney, N.; Shi, S.; Kulkarni, A.; Farahmandi, F.; Tehranipoor, M. When Everyday Devices Become Weapons: A Closer Look at the Pager and Walkie-talkie Attacks. arXiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.; Ruppersberger, C.A.D. Investigative Report on the U.S. National Security Issues Posed by Chinese Telecommunications Companies Huawei and ZTE; U.S. House of Representatives Permanent Select Committee on Intelligence: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Euronews. Eleven EU Countries Took 5G Security Measures to ban Huawei, ZTE. Available online: https://www.euronews.com/next/2024/08/12/eleven-eu-countries-took-5g-security-measures-to-ban-huawei-zte (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- PV-Magazine. Una Empresa Danesa Descubre «Componentes Sospechosos» en Tecnología Energética Importada (Danish Company Discovers ‘Suspicious Components’ in Imported Energy Technology). Available online: https://www.pv-magazine.es/2025/05/27/una-empresa-danesa-descubre-componentes-sospechosos-en-tecnologia-fotovoltaica-importada/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- European Commission. Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2024/1366 of 11 March 2024 Supplementing Regulation (EU) 2019/943 of the European Parliament and of the Council by Establishing a Network Code on Sector-Specific Rules for Cybersecurity Aspects of Cross-Border Electricity Flows, OJ L, 2024/1366, 24.5.2024, Document 32024R1366. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg_del/2024/1366/oj/eng (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- SolarPower Europe. Solutions for PV Cyber Risks to Grid Stability. 2025. Available online: https://api.solarpowereurope.org/uploads/SPE_2025_Solutions_for_PV_Cyber_Risks_to_Grid_Stability_032dc2ae5a.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Market Data Forecast. Global Solar Hybrid Inverter Market Research Report—Segmentation By Product (Single-Phase Hybrid Solar Inverter and Three-Phase Hybrid Solar Inverter), by End User (Commercial, Residential, and Others), and Region—Industry Forecast 2024 to 2032. Available online: https://www.marketdataforecast.com/market-reports/solar-hybrid-inverter-market (accessed on 31 May 2025).
- Independent Bulgarian Energy Exchange (IBEX). Available online: https://ibex.bg (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Electricity System Operator (ESO). Available online: https://eso.bg (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Photovoltaic Geographical Information System (PVGIS). Available online: https://joint-research-centre.ec.europa.eu/photovoltaic-geographical-information-system-pvgis_en (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Electricity Storage Valuation Framework: Assessing System Value and Ensuring Project Viability; International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2020; ISBN 978-92-9260-161-4. [Google Scholar]
- Schmalensee, R. Competitive Energy Storage and the Duck Curve; MIT CEEPR Working Paper Series, CEEPR WP 2020-012; MIT Center for Energy and Environmental Policy Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://ceepr.mit.edu (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- eRisk Group. The Californian Duck is Coming to Europe, with a Smile; eRisk Group: Baarn, The Netherlands, 2014; Available online: https://eriskgroup.com/ (accessed on 28 May 2025).
- Hartner, M.; Permoser, A. Through the valley: The impact of PV penetration levels on price volatility and resulting revenues for storage plants. Renew. Energy 2018, 115, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlík, M. Ever More, Frequent Negative, Electricity Prices: A New Reality and Challenges for Photovoltaics and Wind Power in a Changing Energy Market—Threat or Opportunity, and Where Are the Limits of Sustainability? Energies 2025, 18, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Understanding Ultralow and Negative Power Prices: Causes, Impacts and Improvements, Eurelectric Position Paper. 2024. Available online: https://www.eurelectric.org/ (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- ENTSO-E. ENTSO-E Expert Panel Initiates the Investigation into the Causes of Iberian Blackout. Available online: https://www.entsoe.eu/news/2025/05/09/entso-e-expert-panel-initiates-the-investigation-into-the-causes-of-iberian-blackout/ (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- ENTSO-E. Incident in the Power System of North Macedonia on May 18th. Available online: https://www.entsoe.eu/news/2025/05/30/incident-in-the-power-system-of-north-macedonia-on-may-18th/ (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- PV-Magazine. El Tema de la Ciberseguridad es un Problema Real, Pero la Información de Reuters hay que Cogerla con Pinzas. (Cybersecurity Is a Real Problem, but Reuters’ Reporting Should Be Taken with a Grain of Salt.). Available online: https://www.pv-magazine.es/2025/05/15/el-tema-de-la-ciberseguridad-es-un-problema-real-pero-la-informacion-de-reuters-hay-que-cogerla-con-pinzas/ (accessed on 29 May 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).