The Impact of Seasonality on Air Quality in Terms of Pollution with Substances Hazardous to the Environment
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
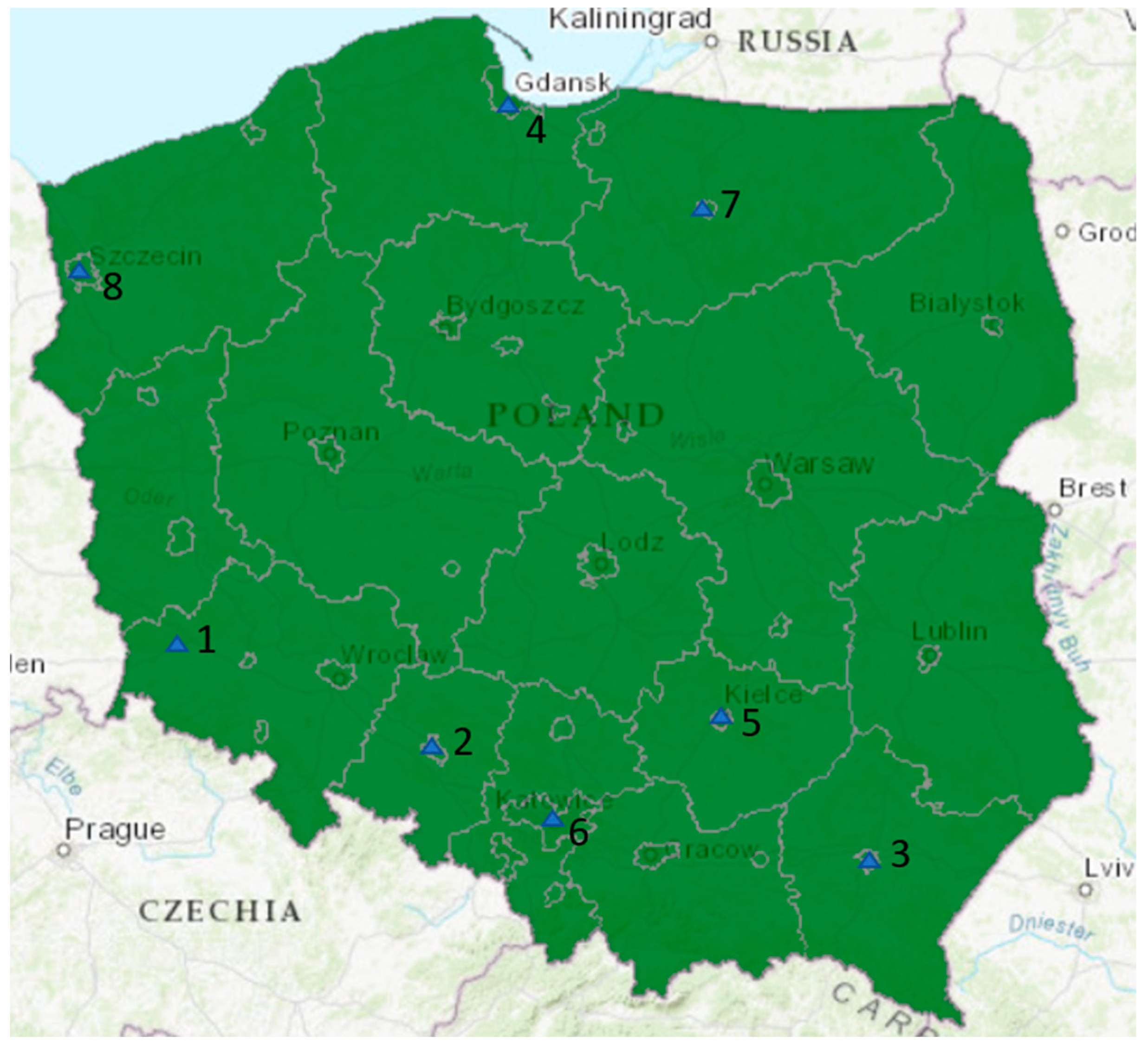
2.1. Monitoring Sites
2.2. Measurement Method
2.3. Health Risk Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
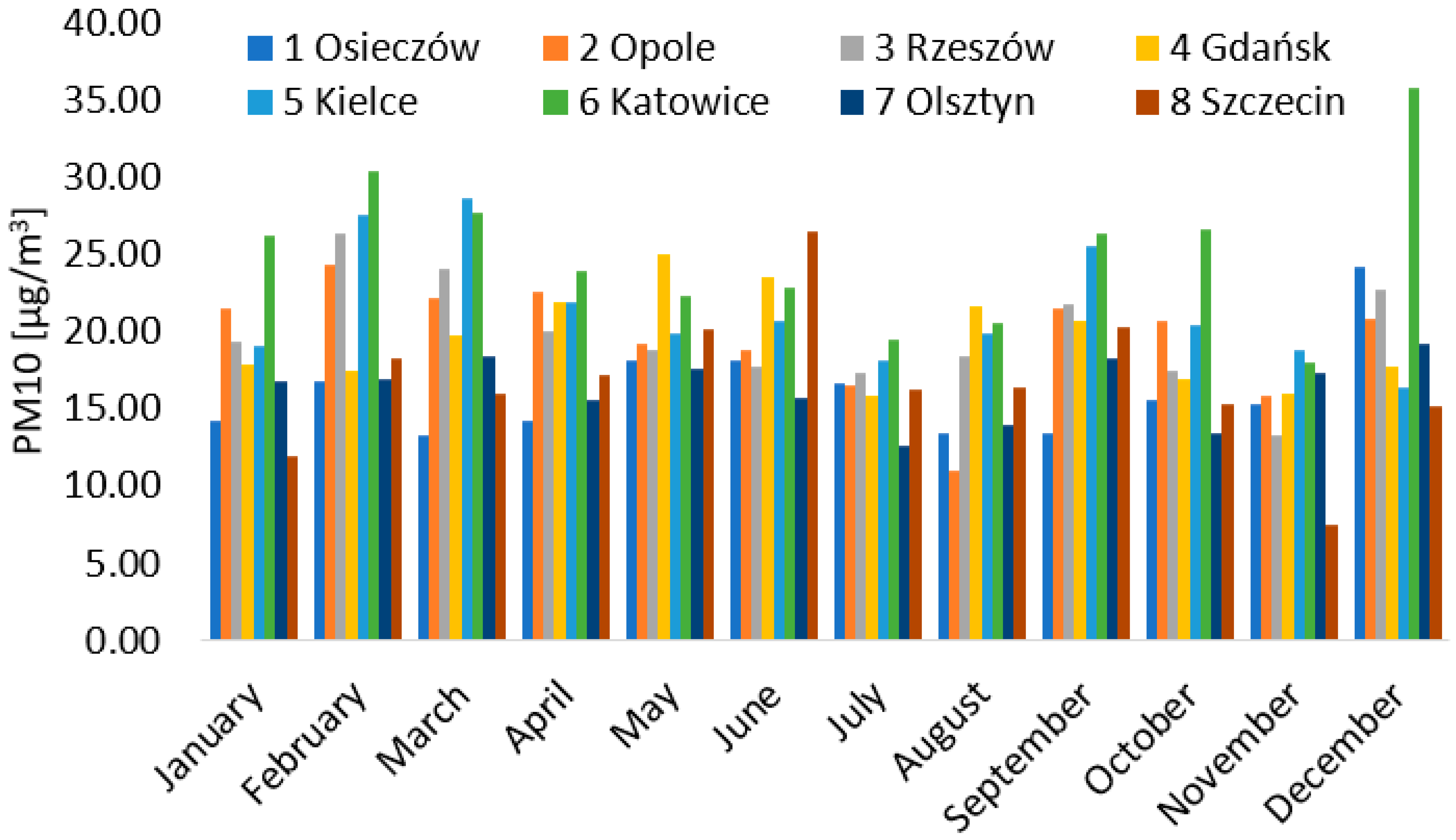
3.1. Concentration of PM10 in the Atmosphere
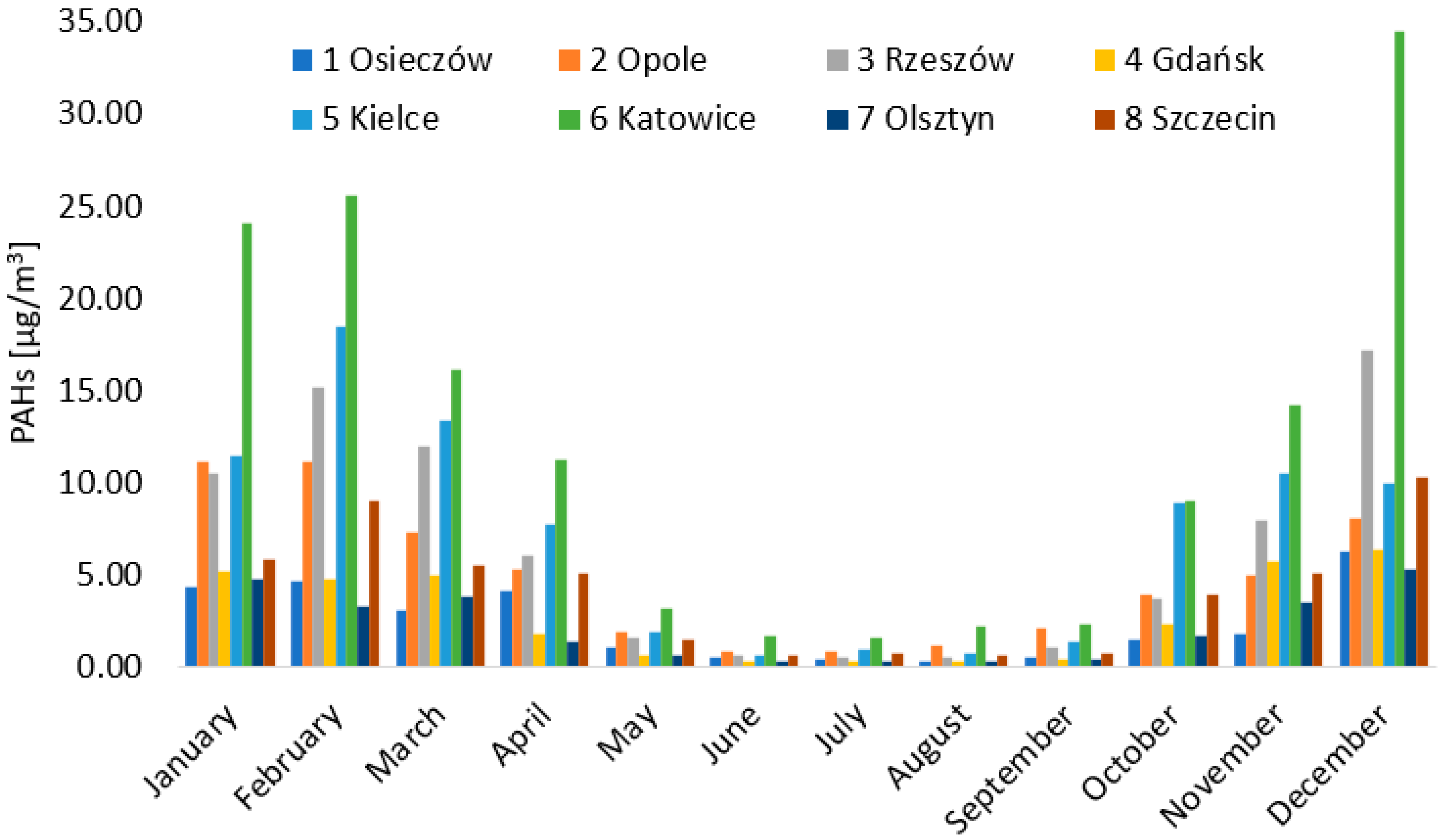
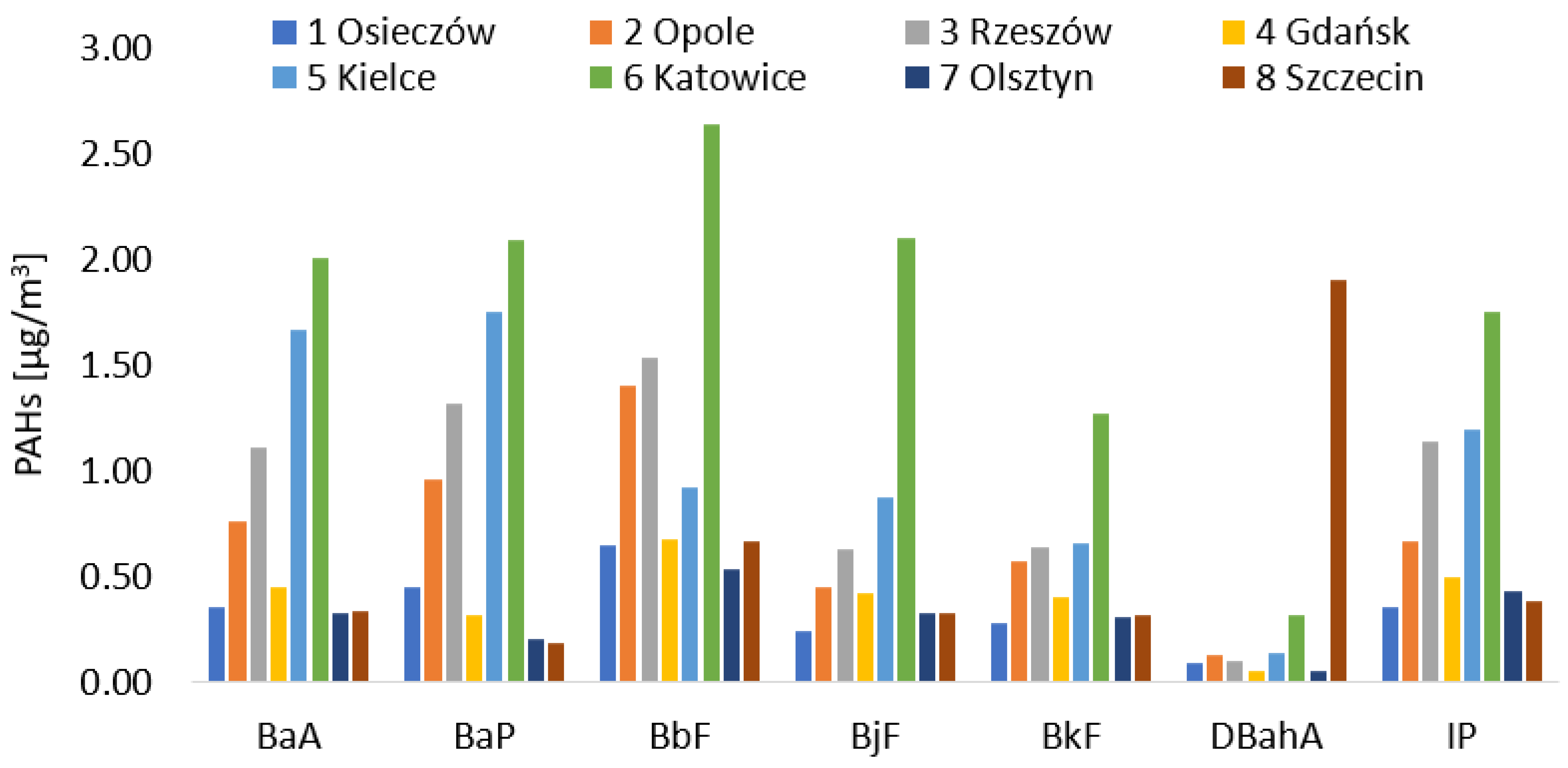
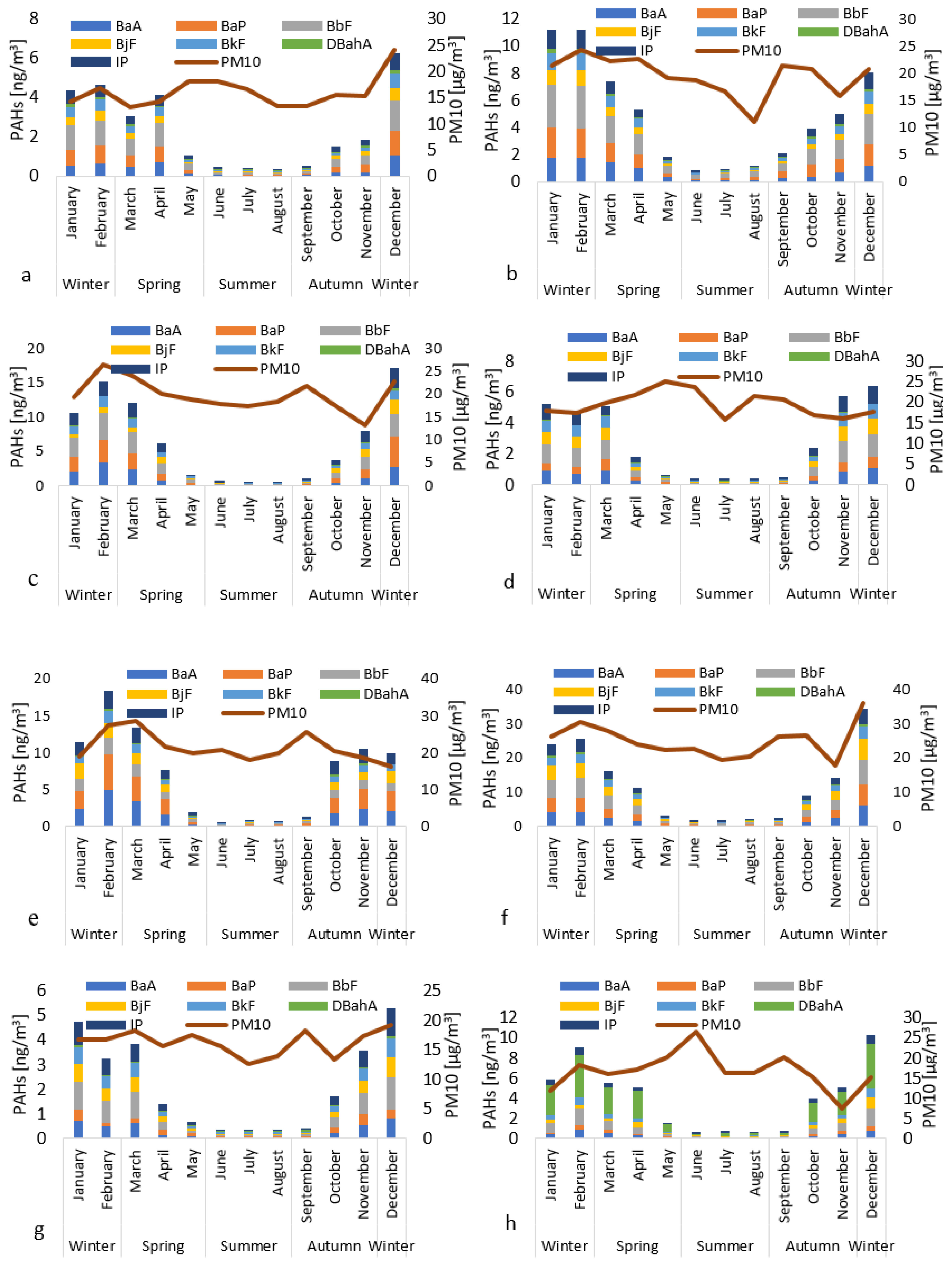
3.2. Concentration of PAHs
3.3. Seasonal Variations
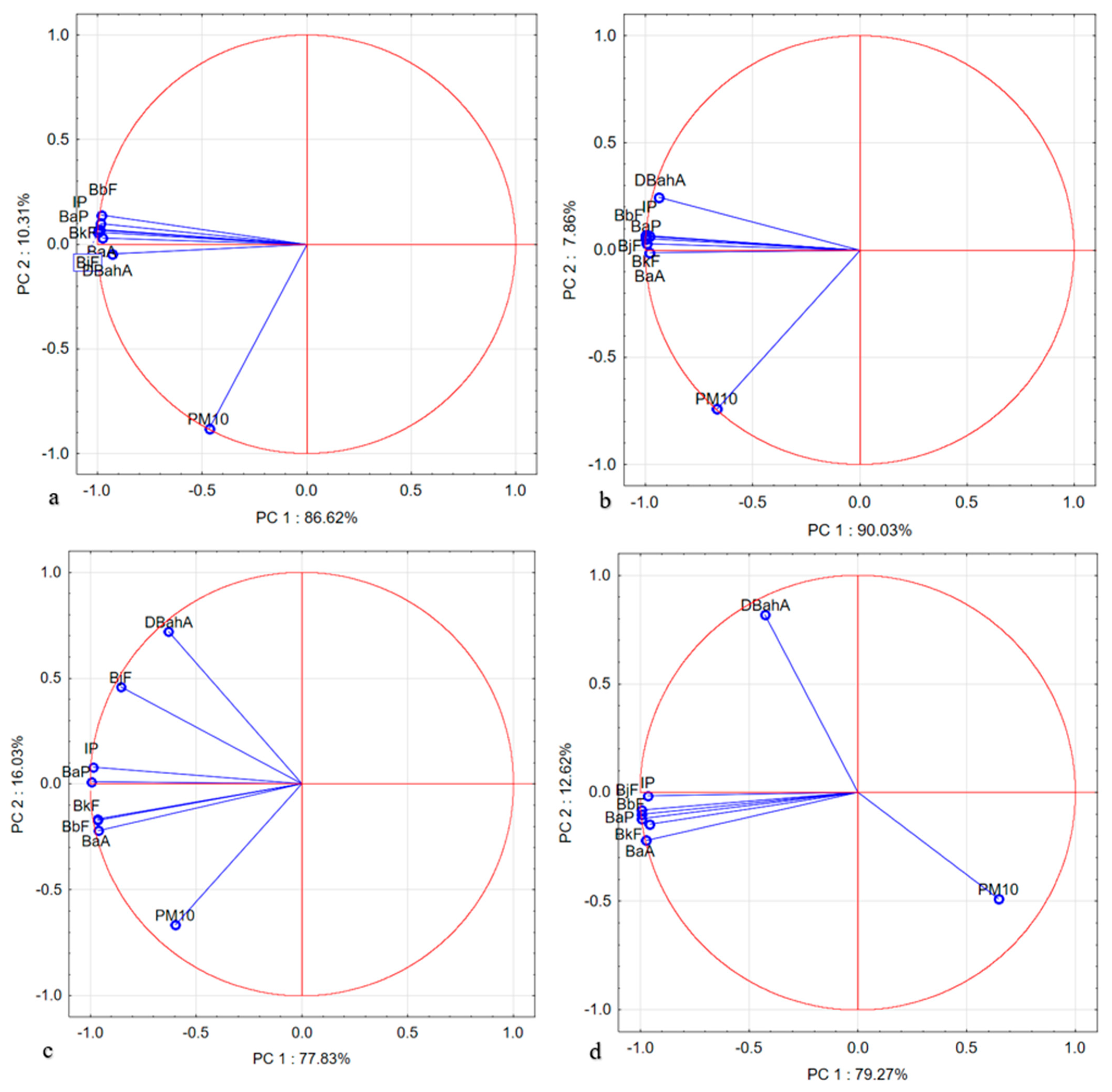
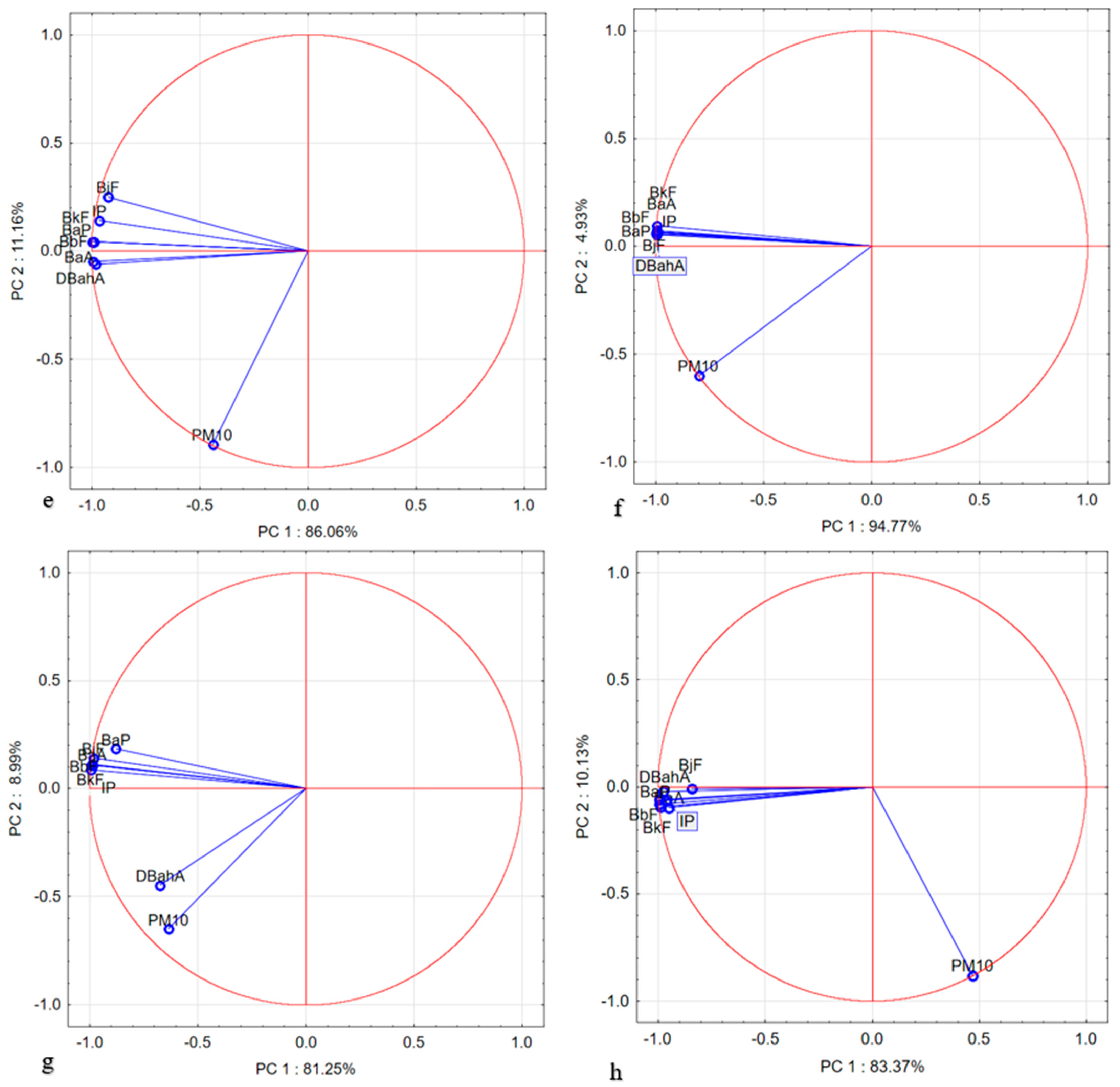
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Different Pollutant Concentrations
3.5. Health Risk Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IARC. Outdoor Air Pollution. In Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2016; Volume 109. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Billions of People Still Breathe Unhealthy Air: New WHO Data. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/04-04-2022-billions-of-people-still-breathe-unhealthy-air-new-who-data (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. PAH diagnostic ratios for the identification of pollution emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Książek, S.; Kida, M.; Koszelnik, P. The occurrence and source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in bottom sediments of the Wisłok river. Polish J. Natural Sci. 2016, 31, 373–386. [Google Scholar]
- Arregocés, H.A.; Bonivento, G.J.; Ladino, L.A.; Beristain-Montiel, E.; Restrepo, G.; Miranda, J.; Alvarez-Ospina, A.; Rojano, R. Human health risk assessment of PM10-bound heavy metals and PAHs around the Latin America’s Largest opencast coal mine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 125915–125930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Yin, H.; Wang, X.; Ye, C. Seasonal variation of PM10-bound PAHs in the atmosphere of Xiamen, China. Atmos. Res. 2007, 85, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, S.; Villanueva, F.; Martín, P.; Salgado, S.; Moreno, A.; Sánchez-Verdú, P. Investigation of PAHs, nitrated PAHs and oxygenated PAHs in PM10 urban aerosols. A comprehensive data analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Some Non-Heterocyclic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Some Related Exposures. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2010; Volume 92, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. Monographs on the Identification of Carcinogenic Hazards to Humans; IARC Publications: Lyon, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Vangrieken, R. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewska, M.; Artichowicz, W.; Kida, M.; Kołecka, K.; Fitobór, K.; Ulańczyk, R. Occurrence of specific pollutants in a mixture of sewage and rainwater from an urbanized area. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandacka, D.; Durcanska, D.; Nicolanska, M.; Holubcik, M. Impact of Seasonal Heating on PM10 and PM2. 5 Concentrations in Sučany, Slovakia: A Temporal and Spatial Analysis. Fire 2024, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, Z.J.; Badyda, A.; Tzivian, L.; Dzhambov, A.M.; Paunovic, K.; Savic, S.; Jacquemin, B.; Dragic, N. Air pollution inequalities in Europe: A deeper understating of challenges in Eastern Europe and pathways forward towards closing the gap between East and West. Environ. Epidemiol. 2025, 9, e383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandowe, B.A.M.; Meusel, H.; Huang, R.J.; Ho, K.; Cao, J.; Hoffmann, T.; Wilcke, W. PM2.5-bound oxygenated PAHs, nitro-PAHs and parent-PAHs from the atmosphere of a Chinese megacity: Seasonal variation, sources and cancer risk assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 473, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chief Inspectorate of Environmental Protection (GIOŚ). Air Quality Report in Poland 2022. 2023. Available online: https://powietrze.gios.gov.pl/pjp/archives (accessed on 6 December 2024).
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Guidelines for Carcinogenic Risk Assessment. 2005. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/guidelines-carcinogen-risk-assessment (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Levels of PAHs in soil and vegetation samples from Tarragona County, Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortey-Sam, N.; Ikenaka, Y.; Akoto, O.; Nakayama, S.M.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Baidoo, E.; Mizukawa, H.; Ishizuka, M. Levels, potential sources and human health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in particulate matter (PM10) in Kumasi, Ghana. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 9658–9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). 2013. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?dirEntryId=284802&Lab=NHSRC&fed_org_id=1253&subject=Homeland%20Security%20Research&view=desc&sortBy=pubDateYear&showCriteria=1&count=25&searchall=decontamination%20AND%20conference (accessed on 26 January 2025).
- Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on ambient air quality and cleaner air for Europe. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2008, 152, 1–44.
- Callén Romero, M.S.; Iturmendi, A.; López Sebastián, J.M.; Mastral Lamarca, A.M. Source apportionment of the carcinogenic potential of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) associated to airborne PM10 by a PMF model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Pinero, J.; Moreda-Pineiro, J.; Concha-Grana, E.; Fernandez-Amado, M.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Lopez-Mahía, P. Inhalation bioaccessibility estimation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from atmospheric particulate matter (PM10): Influence of PM10 composition and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S.; Oliveira, M. Environmental contamination with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and contribution from biomonitoring studies to the surveillance of global health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 54339–54362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakovljević, I.; Pehnec, G.; Vađić, V.; Čačković, M.; Tomašić, V.; Jelinić, J.D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM 10, PM 2.5 and PM 1 particle fractions in an urban area. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, S.; Veli, A.; Mustafa, Z.; Hudai, S.; Hristova, E.; Gonsalvesh-Musakova, L. Atmospheric levels, distribution, sources, correlation with meteorological parameters and other pollutants and health risk of PAHs bound in PM2. 5 and PM10 in Burgas, Bulgaria—A case study. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2022, 57, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2004/107/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council relating to arsenic, cadmium, mercury, nickel and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2005, 23, 3–16.
- Khalili, N.R.; Scheff, P.A.; Holsen, T.M. PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and, gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emissions. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, C.H. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2917–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, P.; Cocozziello, B.; Corvino, A.; Fiorino, F.; Frecentese, F.; Magli, E.; Onorati, G.; Saccone, I.; Santagada, V.; Settimo, G.; et al. Level, potential sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in particulate matter (PM10) in Naples. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.A.; Baumbach, G.; Kuch, B.; Scheffknecht, G. Particle-phase concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air of rural residential areas in southern Germany. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2010, 3, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PAHs | BaPeq | LADD [mg/kg/d] | ILCR | ||
| Child | Adult | Child | Adult | ||
| BaA | 0.03–0.20 | 2.14·10−7–13.44·10−7 | 7.6·10−8–4.78·10−7 | 1.31·10−7–8.2·10−7 | 4.6·10−8–2.92·10−7 |
| BaP | 0.04–3.66 | 1.2·10−7–14.04·10−7 | 4.3·10−8–4.99·10−7 | 7.34·10−7–8.56·10−6 | 2.61·10−7–3.04·10−6 |
| BbF | 0.06–2.42 | 3.54·10−7–17.70·10−7 | 12.6·10−8–6.3·10−7 | 0.22·10−7–1.08·10−7 | 0.8·10−8–3.8·10−8 |
| BjF | 0.02–1.83 | 1.59·10−7–14.09·10−7 | 5.7·10−8–5.01·10−7 | 0.1·10−7–0.86·10−7 | 0.3·10−8–3.01·10−8 |
| BkF | 0.03–0.83 | 1.88·10−7–8.53·10−7 | 6.7·10−8–3.04·10−7 | 0.11·10−7–0.52·10−7 | 0.4·10−8–1.9·10−8 |
| DBahA | 0.005–0.10 | 0.34·10−7–12.77·10−7 | 1.2·10−8–4.54·10−7 | 2.09·10−7–7.79·10−6 | 7.4·10−8–2.77·10−6 |
| IP | 0.04–2.08 | 2.36·10−7–11.77·10−7 | 8.4·10−8–4.19·10−7 | 1.44·10−7–7.18·10−7 | 5.1·10−8–2.55·10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kida, M.; Ziembowicz, S. The Impact of Seasonality on Air Quality in Terms of Pollution with Substances Hazardous to the Environment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126551
Kida M, Ziembowicz S. The Impact of Seasonality on Air Quality in Terms of Pollution with Substances Hazardous to the Environment. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126551
Chicago/Turabian StyleKida, Małgorzata, and Sabina Ziembowicz. 2025. "The Impact of Seasonality on Air Quality in Terms of Pollution with Substances Hazardous to the Environment" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126551
APA StyleKida, M., & Ziembowicz, S. (2025). The Impact of Seasonality on Air Quality in Terms of Pollution with Substances Hazardous to the Environment. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6551. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126551






