Transmission of Heavy Metals in River Water and Self-Purification Capacity of Ile River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Analytical Methods
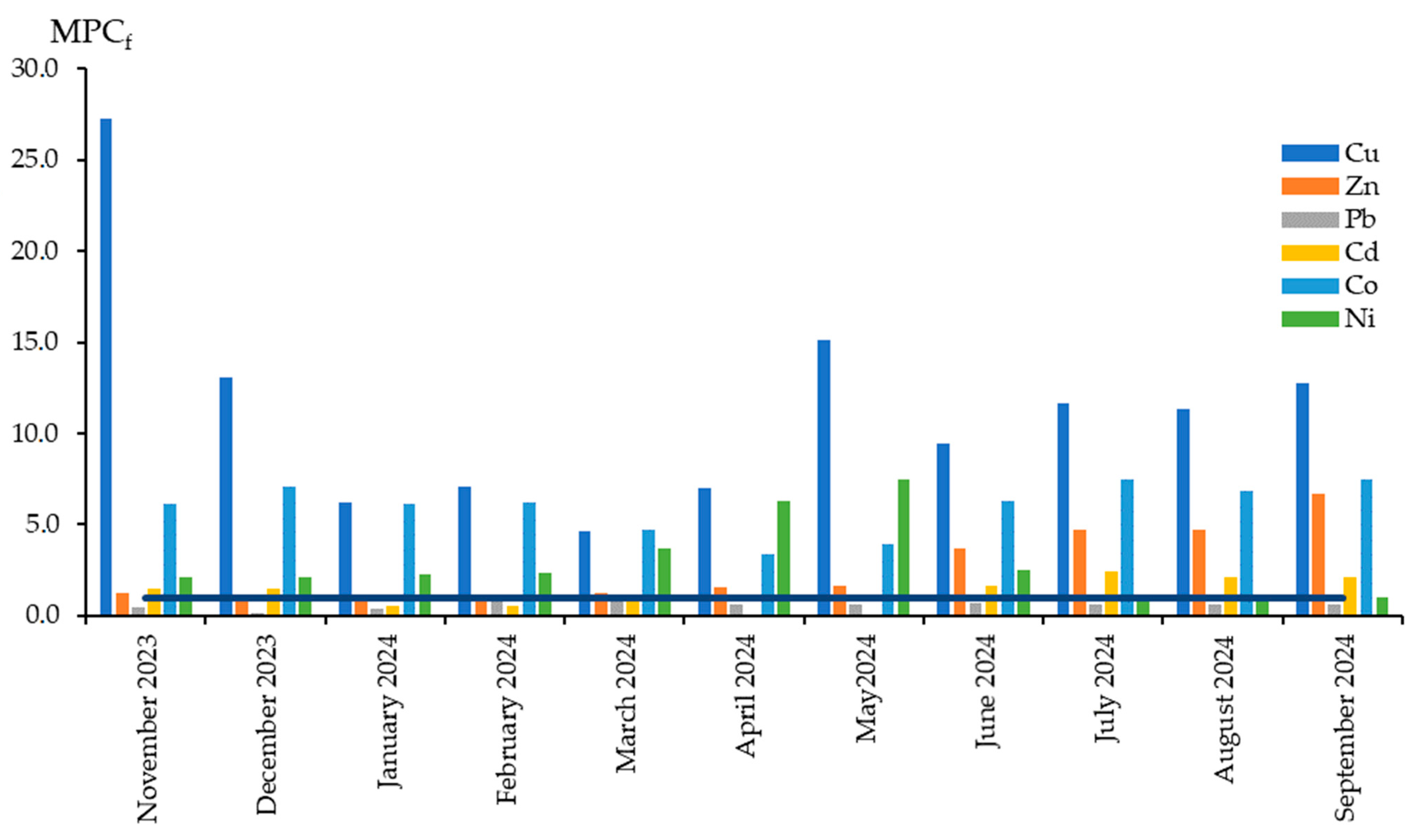
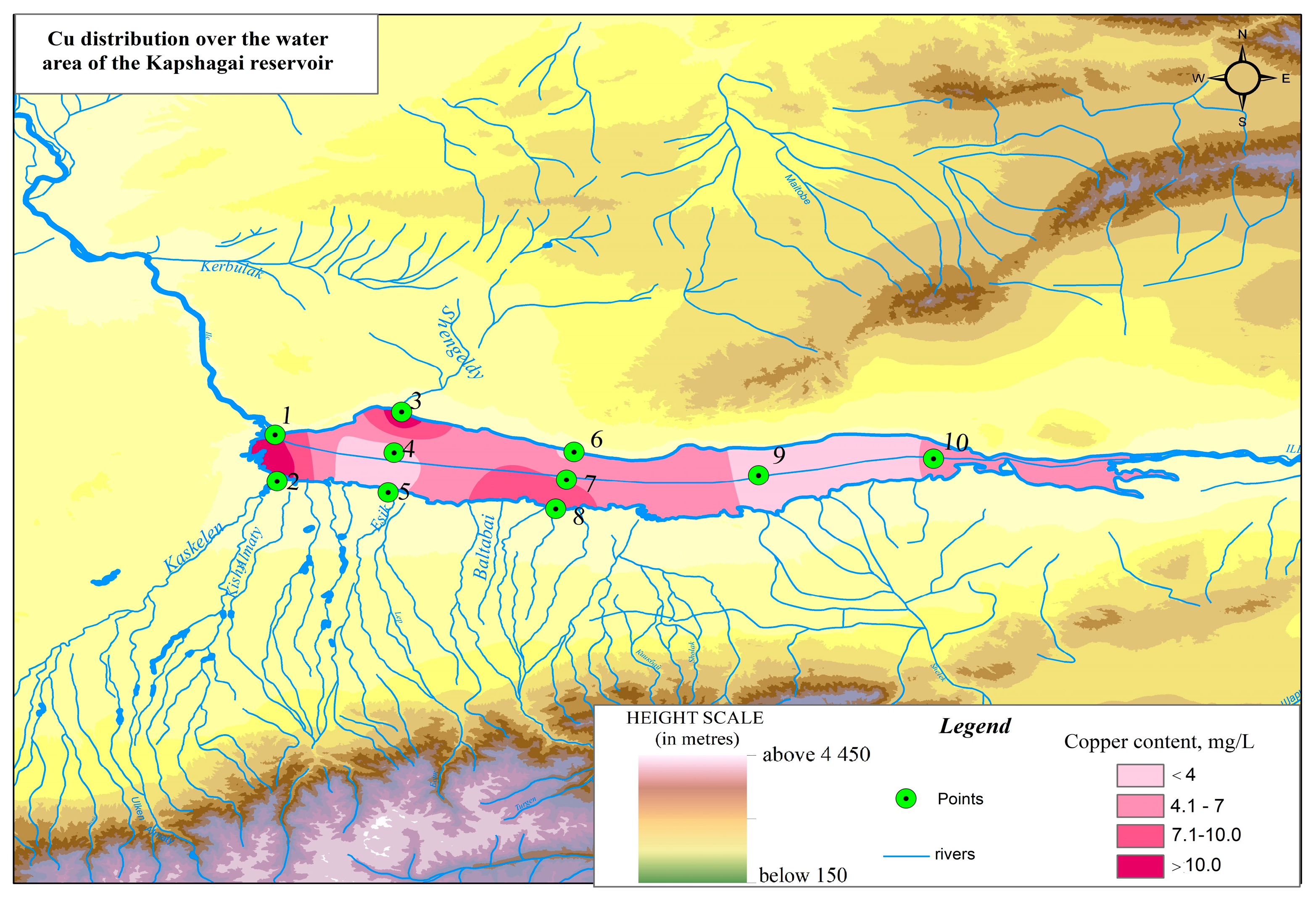
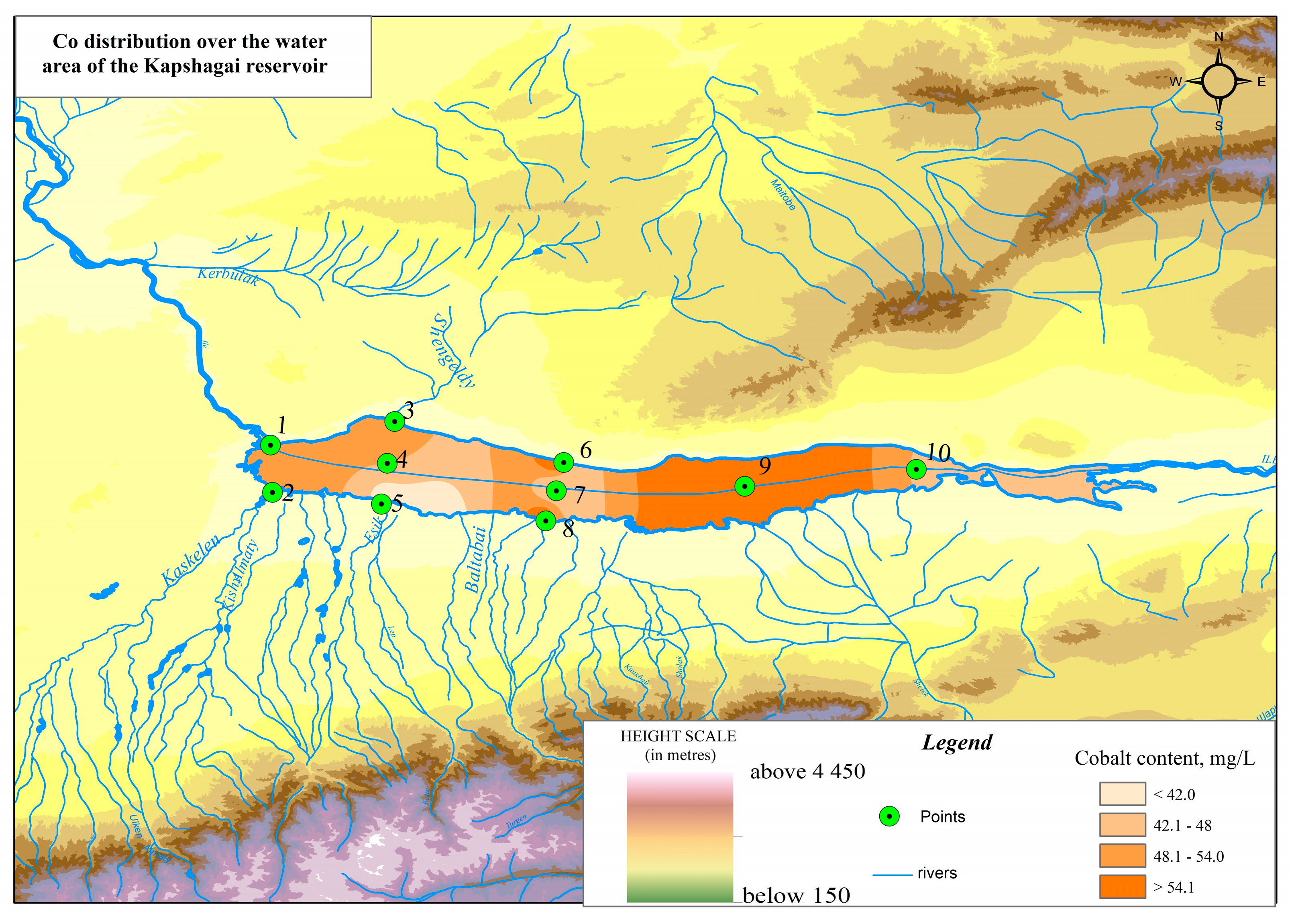
3. Research and Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giri, S. Water quality prospective in Twenty First Century: Status of water quality in major river basins, contemporary strategies and impediments: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; Wei, L.; Ma, W.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, X. Geochemistry and Sources Apportionment of Major Ions and Dissolved Heavy Metals in a Small Watershed on the Tibetan Plateau. Water 2022, 14, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talipova, E.; Shrestha, S.; Alimkulov, S.; Nyssanbayeva, A.; Tursunova, A.; Isakan, G. Influence of climate change and anthropogenic factors on the Ile River basin streamflow, Kazakhstan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; He, B.; Chen, Y.; Zou, S.; Wang, Y.; Nover, D.; Chen, W.; Yang, G. Identification of long-term trends and seasonality in high-frequency water quality data from the Yangtze River basin. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0188889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. 1 in 3 People Globally Do Not Have Access to Safe Drinking Water. Available online: http://www.who.int/.2019 (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Huang, X.; Sillanpaa, M.; Gjessing, E.T.; Vogt, R.D. Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: Major ions and trace elements in the headwaters of four major Asian rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6242–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimkulov, S.; Makhmudova, L.; Talipova, E.K.; Baspakova, G.; Tigkas, D.; Gulsaira, I. Response of the water level of the Balkash Lake to the distribution of meteorological and hydrological droughts under the conditions of climate change. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 3395–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayat, A.; Lyazzat, M.; Elmira, T.; Gaukhar, B.; Gulsara, M. Assessment of the impacts of climate change on drought intensity and frequency using SPI and SPEI in the Southern Pre-Balkash region, Kazakhstan. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2025, 7, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AWI 2020 Mississippi River Watershed Report Card; America’s Watershed Initiative: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2011; Available online: https://americaswatershed.org/reportcard/ (accessed on 8 December 2020).
- Raymond, P.; Oh, N.H.; Turner, R.; Broussard, W. Anthropogenically enhanced fluxes of water and carbon from the Mississippi River. Nature 2008, 451, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, T.; Kumar, V.; Sarkar, D.J.; Devi, M.S.; Behera, B.K.; Das, B.K. Pollution assessment and mapping of potentially toxic elements (PTE) distribution in urban wastewater fed natural wetland, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2022, 29, 67801–67820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, M.; Kumar, S. Water pollution in India: An economic appraisal. India Infrastruct. Rep. 2011, 19, 285–298. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Kang, S.C.; Sillanpaa, M. Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: Major ions and trace elements in rivers of the “Water Tower of Asia”. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Tang, Y.; Liu, M.; Van Zwieten, L.; Yang, X.M.; Yu, C.G.; Wang, H.L.; Song, Z.L. Carbon-nitrogen isotope coupling of soil organic matter in a karst region under land use change, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 107027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G.L.; Zhang, Q.J.A. Effects of agricultural abandonment on soil aggregation, soil organic carbon storage and stabilization: Results from observation in a small karst catchment, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 288, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madibekov, A.; Ismukhanova, L.; Opp, C.; Saidaliyeva, Z.; Zhadi, A.; Sultanbekova, B.; Kurmanova, M. Spatial Distribution of Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, Co, Ni in the Soils of Ili River Delta and State Natural Reserve “Ili-Balkhash”. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Huang, X. Spatiotemporal variability of heavy metals and identification of potential source tracers in the surface water of the Lhasa River basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7442–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.H.; Gao, B.; He, L.; Hu, X.H.; Dong, L.; Sanjay, D.; Dong, A.; Sun, Z.X.; Wan, W. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Controlling Factors of the Lhasa River under the Influence of Anthropogenic Activities. Water 2019, 11, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W. B, As, and F contamination of river water due to wastewater discharge from the Yangbajing geothermal power plant, Tibet, China. Environ. Geol. 2007, 56, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Scott, C.; Yan, X. Traffic-related trace elements in soils along six highway segments on the Tibetan Plateau: Influence factors and spatial variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, L.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, H.W.; Zou, J.Y.; Gao, F.; Tao, J.X.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xu, P. Distribution characteristics, enrichment patterns and health risk assessment of dissolved trace elements in river water in the source region of the Yangtze River. J. Water Clim. Change 2021, 12, 2288–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sillanpaa, M.; Gjessing, E.T.; Peraniemi, S.; Vogt, R.D. Environmental impact of mining activities on the surface water quality in Tibet: Gyama valley. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4177–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, I.; Figoli, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Brozzo, G.; De Rosa, R.; Gabriele, B.; Apollaro, C. Geochemical modeling of chromium release in natural waters and treatment by RO/NF membrane processes. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuoco, I.; Marini, L.; De Rosa, R.; Figoli, A.; Gabriele, B.; Apollaro, C. Use of reaction path modeling to investigate the evolution of water chemistry in shallow to deep crystalline aquifers with a special focus on fluoride. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.; Asmoay, A.; Alshehri, F.; Abdelrady, A.; Othman, A. Hydro-geochemical applications and multivariate analysis to assess the water-rock interaction in arid environments. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, S.; Tursunova, A. To the question of self-purifying ability of river waters of Kazakhstan. Hydrometeorol. Ecol. 2010, 2, 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafaev, J.; Kozykeeva, A.; Ryskulbekova, L. Geoecological assessment of pollutant transpiration in the catchment of the transboundary Ile River basin. Hydrometeorol. Ecol. 2019, 1, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Samakova, A. (Ed.) Problems of Hydroecological Stability in the Basin of Lake Balkhash; Kaganat Publishing House: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2003; 584p. [Google Scholar]
- Kudekov, T. (Ed.) Modern Ecological State of the Balkhash Lake Basin; Kaganat Publishing House: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2002; 388p. [Google Scholar]
- ST RK GOST R 51592-2003; Water. General Requirements for Sampling. Kazakhstan Institute of Standardization and Metrology: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2003. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=30015812 (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- GOST 17.1.5.01-80; Nature protection. Hydrosphere. Kazakhstan Institute of Standardization and Metrology: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2003. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=37927607&pos=3;-88#pos=3;-88 (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Fellenberg, G. Chemie der Umweltbelastung; Vieweg, Teubner: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ST RK ISO 8288-2005 (ISO 8288:1986); Water Quality. Determination of Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, Zinc, Cadmium and Lead. Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Methods. Kazakhstan Institute of Standardization and Metrology: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2005. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=30362762 (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Federal Agency for Fishery. Order No. 20 of January 18, 2010: On the Approval of Water Quality Standards for Water Bodies of Fishery Importance, Including Maximum Allowable Concentrations (MACs) of Harmful Substances. Registered by the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation on February 9, 2010, No. 16326. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/902199367 (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Burlibayev, M. (Ed.) Methodological Recommendations for Comprehensive Assessment of Surface Water Quality by Hydrochemical Indicators; Printing House “IP Volkova E.V.”: Astana, Kazakhstan, 2012; 80p. [Google Scholar]
- Collection of sanitary and hygienic standards and methods of control of harmful substances in environmental objects. Moscow, 1991.
- Generalized list of MPC and indicatively safe levels of exposure (ISLE) of harmful substances for water of fishery reservoirs; VNIRO (Russian Federal Research Institute of Fisheries and Oceanography): Moscow, Russia, 1999; 304р.
- Nikanorov, A.L. (Ed.) Reference Book on Hydrochemistry; Gidro-Meteoizdat: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1989; 391p. [Google Scholar]
- Unified System of Water Quality Classification in Water Bodies, Approved by the Order of the Chairman of the Committee of Water Management of the Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation of the Republic of Kazakhstan from 20.03.2024 № 70. [Electronic Resource]. Available online: https://adilet.zan.kz/rus/docs/V1600014513 (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Ismukhanova, L. Kapshagai Reservoir: Assessment of Hydrochemical Regime and Toxicological State of Aquatic Ecosystem; Smart University Press: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2024; 150p, ISBN 978-601-08-3905-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ismukhanova, L.; Madibekov, A.; Opp, C.; Zhadi, A.; Sultanbekova, B.; Zhumatayev, S. Status and Migration Activity of Lead, Cobalt and Nickel in Water and in Bottom Sediments of Lake Markakol, Kazakhstan. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimirov, A.; Lekhin, Y.; Matveev, L.; Orlov, V. Environmental Protection; Gidrometeoizdat: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1991; pp. 159–265. [Google Scholar]
- Madibekov, A.; Ismukhanova, L.; Zhadi, A.; Sultanbekova, B.; Zhumatayev, S. Assessment of the Level of Pollution of the Aquatic Ecosystem of Lake Markakol with Mobile Forms of Copper and Zinc. Evergreen 2024, 11, 1568–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Report on the State of the Environment and the Use of Natural Resources of the Republic of Kazakhstan for 2022; Astana, Kazakhstan, 2023. Available online: https://www.gov.kz/memleket/entities/ecogeo/documents/details/762991?lang=ru (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Program of Development of Small Towns of Almaty Region. Available online: https://adilet.zan.kz/rus/docs/P2300001226 (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Scheme of Integrated Use and Protection of Water Resources in the Ili River Basin with Tributaries: Summary Note; Committee for Water Resources of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Production cooperative “Institute Kazgiprovodkhoz”: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2008; Volume III, 78p.
- Regional Program of Sustainable Development of Agro-Industrial Complex of Almaty Region for 2006–2010, Taldykorgan. 2006. Available online: https://adilet.zan.kz/rus/docs/V02D0001011 (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Smolyar, V.; Smolyar, V.; Mustafaev, S. Hydrogeology of the Balkhash Lake basin. Almaty. Gylym. 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tureniyazova, J. Anthropogenic change of ionic flow of the Ile River In Collection of Scientific Papers: Certain Aspects of Hydroecological Problems of Kazakhstan; Kaganat Publishing: Almaty, Kazakhstan, 2011; pp. 206–210. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, J.; Opp, C.; Ganzenmüller, R.; Ewert, A.; Schneider, B.; Zitzer, N.; Laufenberg, G. Catchment soils as a factor of trace metal accumulation in sediments of the reservoir Klingenberg (Eastern Ore Mountains, Germany). J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 86, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
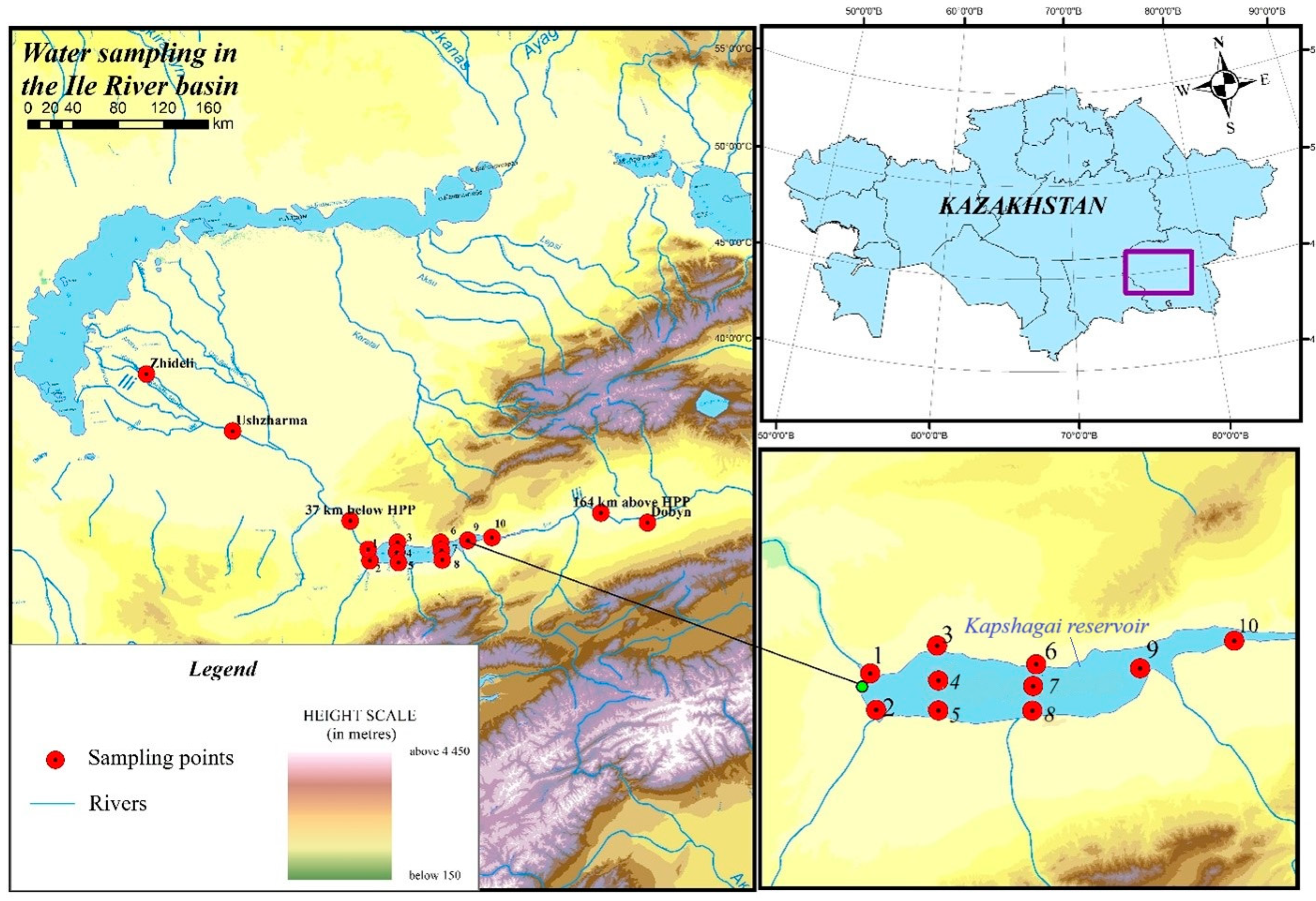

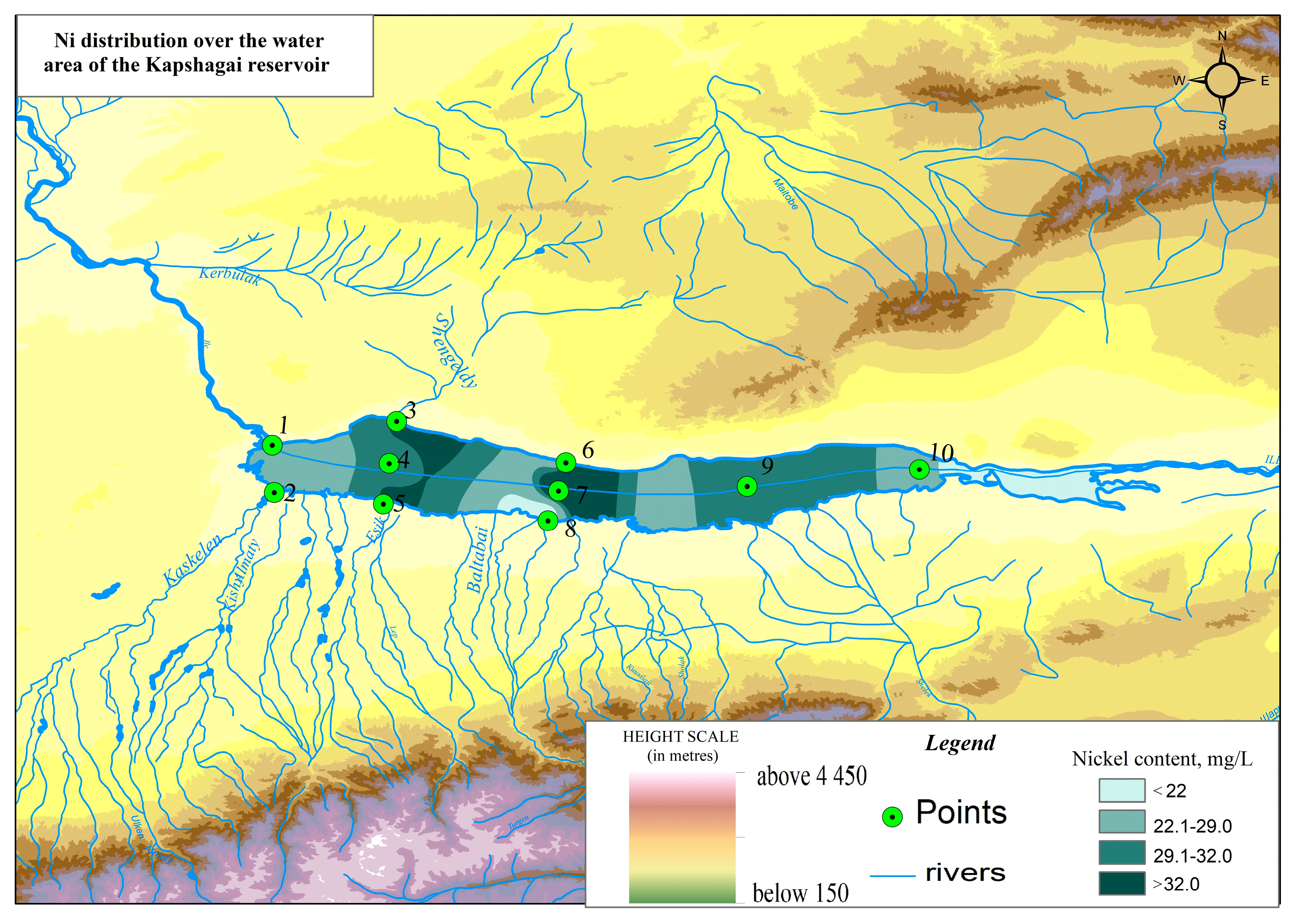
| Sampling Point | Coordinates | Distance from Mouth, km | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | ||
| Ile River | |||
| HP Dobyn | 43°45′31.27″ N | 80°13′53.45″ E | 723 |
| 164 km upstream of Kapchagay HPP | 43°50′15.28″ N | 78°49′43.07″ E | 607 |
| 37 km downstream of Kapchagay HPP | 44°7′53.69″ N | 76°59′5.09″ E | 434 |
| HP Ushzharma | 43°44′14.24″ N | 77°8′46.62″ E | 264 |
| HP Kokzhide | 45°5′22.43″ N | 75°27′3.40″ E | 35 |
| Kapchagay Reservoir | |||
| Point 1 | 43°53′17.64″ N | 77°8′24.94″ E | 311 |
| Point 2 | 43°47′45.34″ N | 77°8′38.58″ E | 320 |
| Point 3 | 43°56′3.82″ N | 77°22′56.08″ E | 328 |
| Point 4 | 43°51′9.43″ N | 77°22′3.29″ E | 331 |
| Point 5 | 43°46′25.57″ N | 77°21′22.46″ E | 334 |
| Point 6 | 43°51′15.97″ N | 77°42′43.07″ E | 350 |
| Point 7 | 43°47′57.07″ N | 77°41′1.26″ E | 353 |
| Point 8 | 43°44′29.07″ N | 77°40′36.31″ E | 358 |
| Point 9 | 43°47′37.82″ N | 77°55′19.78″ E | 367 |
| Point 10 | 43°49′37.26″ N | 78°6′3.65″ E | 377 |
| № | Heavy Metal | Unit | For Fishery Purposes (MPCf) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Copper (Cu) | mg/L | 0.001 |
| 2 | Zinc (Zn) | mg/L | 0.01 |
| 3 | Lead (Pb) | mg/L | 0.01 |
| 4 | Cadmium (Cd) | mg/L | 0.005 |
| 5 | Cobalt (Co) | mg/L | 0.01 |
| 6 | Nickel (Ni) | mg/L | 0.01 |
| Season of Sampling | Sampling Site | Cu | Zn | Pb | Cd | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | |||||||
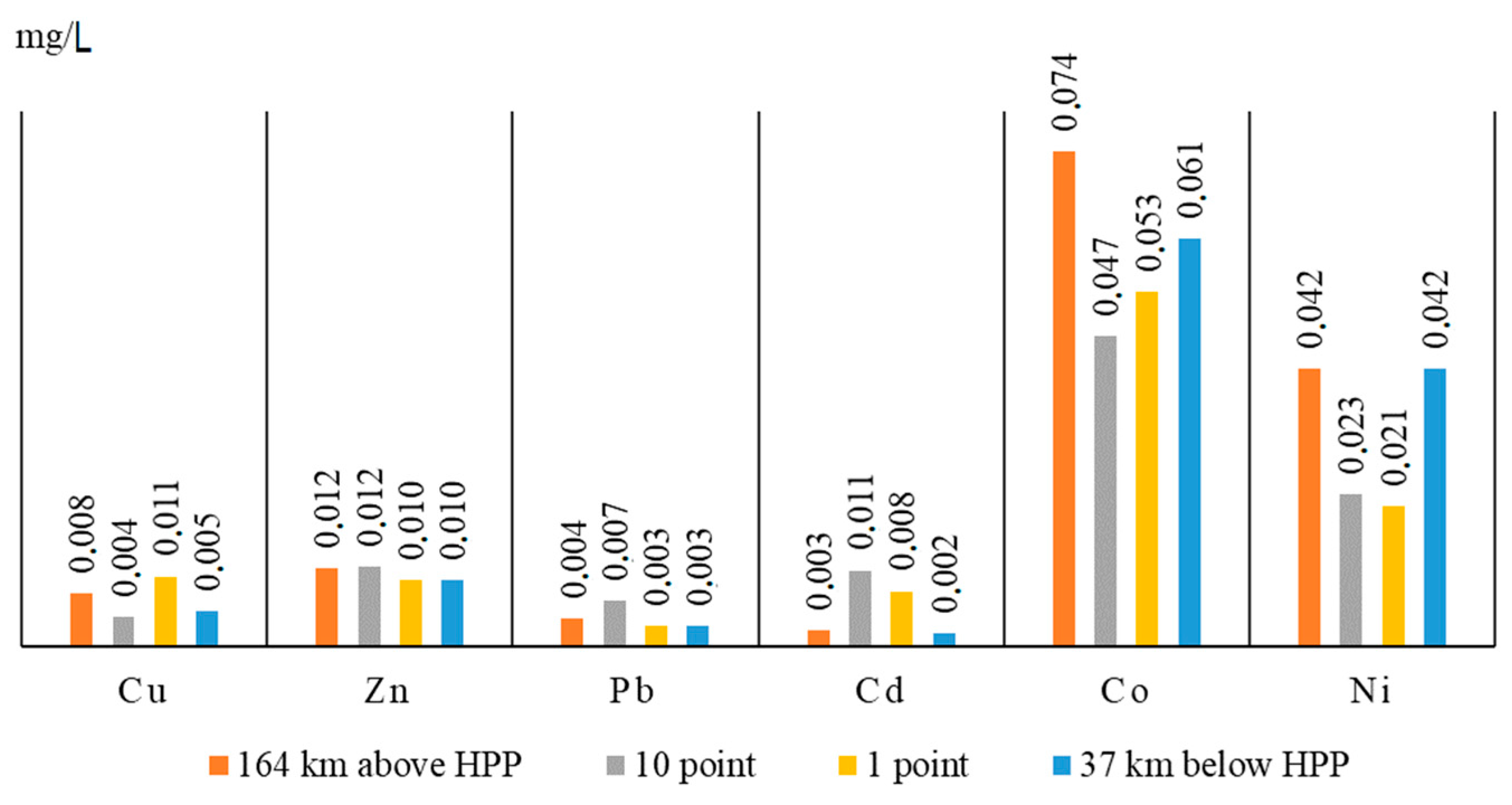
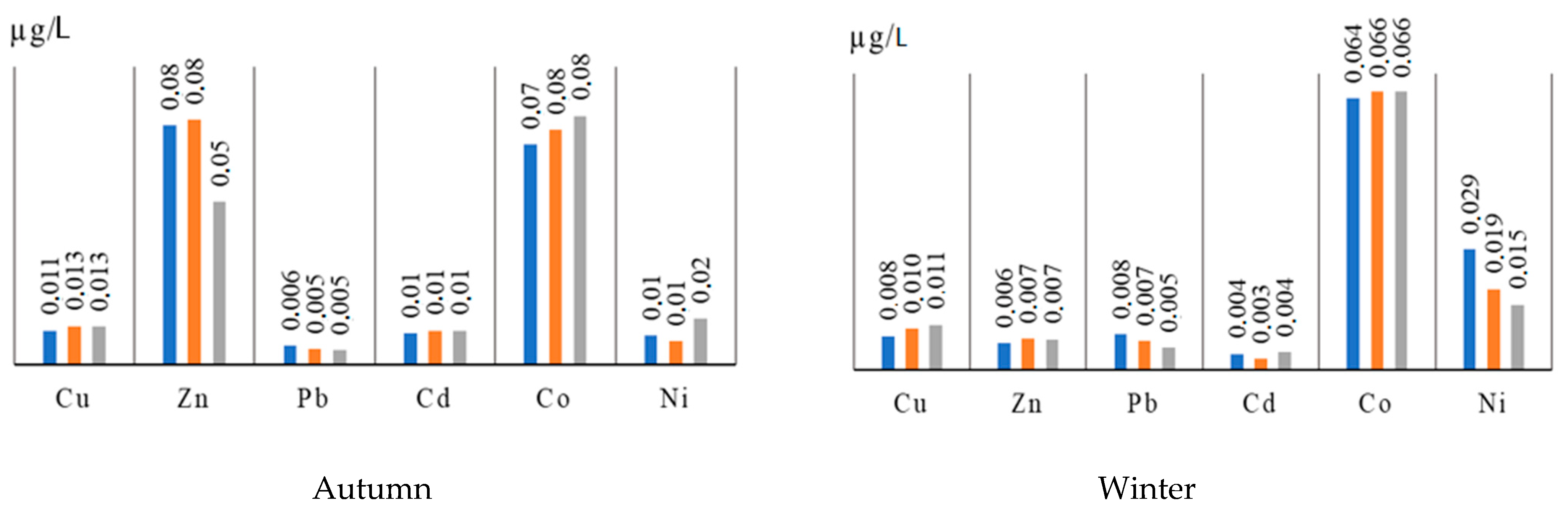
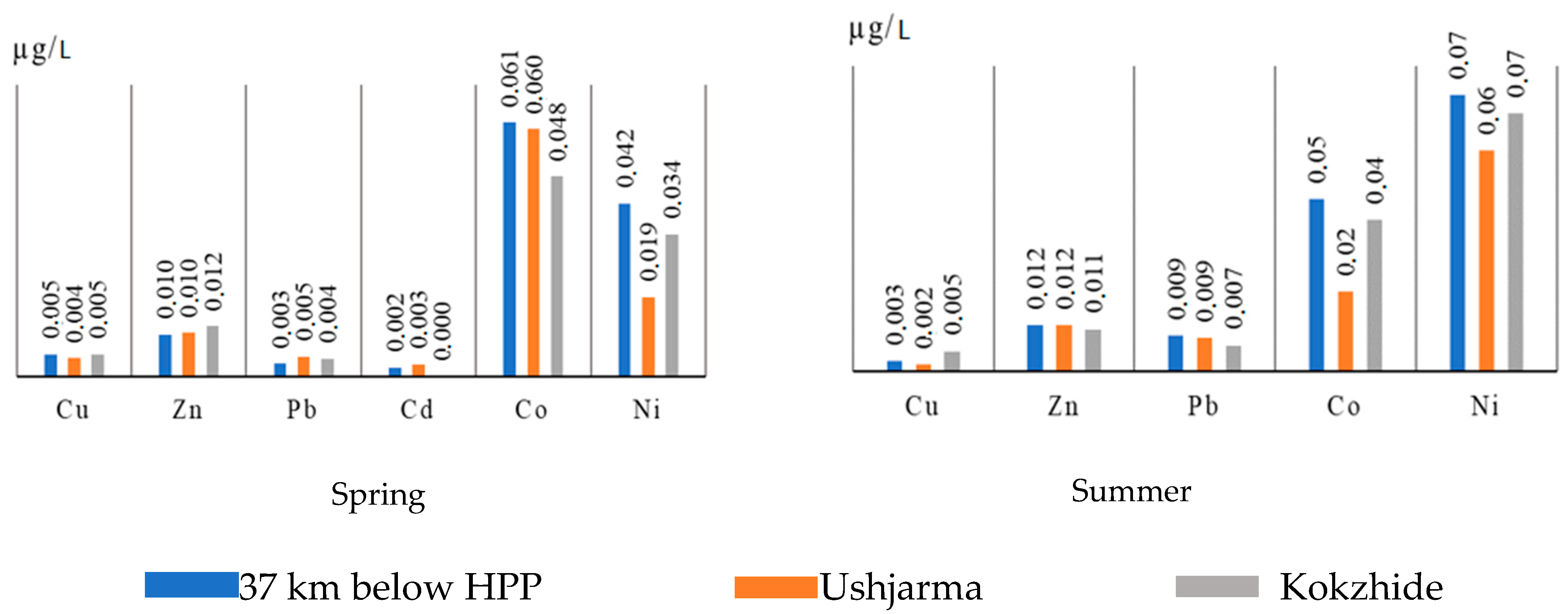
| Winter | Dobyn | 0.0131 | 0.0081 | 0.001 | 0.0072 | 0.0708 | 0.021 |
| 164 km above HPP | 0.0001 | 0.0075 | 0.0099 | 0.0037 | 0.0756 | 0.0191 | |
| 37 km below HPP | 0.0079 | 0.0062 | 0.0083 | 0.0037 | 0.0643 | 0.0285 | |
| Ushzharma | 0.0096 | 0.0073 | 0.0068 | 0.0025 | 0.0659 | 0.0191 | |
| Kokzhide | 0.0105 | 0.0071 | 0.0052 | 0.0041 | 0.0659 | 0.0154 | |
| Spring | Dobyn | 0.0062 | 0.0158 | 0.0078 | 0.0029 | 0.0643 | 0.0285 |
| 164 km above HPP | 0.0079 | 0.0117 | 0.0042 | 0.0025 | 0.074 | 0.0416 | |
| 37 km below HPP | 0.0053 | 0.01 | 0.0031 | 0.0021 | 0.0611 | 0.0416 | |
| Ushzharma | 0.0044 | 0.0104 | 0.0047 | 0.0029 | 0.0595 | 0.0191 | |
| Kokzhide | 0.0053 | 0.0121 | 0.0042 | 0.0002 | 0.0481 | 0.0341 | |
| Summer | Dobyn | 0.0079 | 0.0156 | 0.0094 | 0.0002 | 0.0416 | 0.0611 |
| 164 km above HPP | 0.0018 | 0.0135 | 0.0099 | 0.0001 | 0.0434 | 0.0627 | |
| 37 km below HPP | 0.0027 | 0.0121 | 0.0094 | 0.0000 | 0.0453 | 0.0724 | |
| Ushzharma | 0.0018 | 0.0121 | 0.0089 | 0.0000 | 0.021 | 0.0578 | |
| Kokzhide | 0.0053 | 0.011 | 0.0068 | 0.0001 | 0.0397 | 0.0675 | |
| Autumn | Dobyn | 0.0125 | 0.0554 | 0.0062 | 0.0118 | 0.0756 | 0.0098 |
| 164 km above HPP | 0.0119 | 0.0444 | 0.0052 | 0.0122 | 0.0708 | 0.0228 | |
| 37 km below HPP | 0.0112 | 0.0804 | 0.0062 | 0.0103 | 0.074 | 0.0098 | |
| Ushzharma | 0.0129 | 0.0823 | 0.0052 | 0.0114 | 0.0789 | 0.0079 | |
| Kokzhide | 0.0127 | 0.0548 | 0.0047 | 0.0114 | 0.0837 | 0.0154 | |
| MPCpx | 0.001 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Period | Initial | Final | Cu | Zn | Pb | Cd | Co | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan | ||||||||
| Winter | Dobyn | Kokzhide | 20 | 12 | −420 | 43 | 7 | 27 |
| Spring | 15 | 23 | 46 | 93 | 25 | −20 | ||
| Summer | 33 | 29 | 28 | 38 | 5 | −10 | ||
| Autumn | −2 | 1 | 24 | 3 | −11 | −57 | ||
| Before the Kapshagai reservoir | ||||||||
| Winter | Dobyn | 164 km above HPP | 99 | 7 | −890 | 49 | −7 | 9 |
| Spring | −27 | 26 | 46 | 14 | −15 | −46 | ||
| Summer | 77 | 13 | −5 | 41 | −4 | −3 | ||
| Autumn | 5 | 20 | 16 | −3 | 6 | −133 | ||
| Taking into account the influence of the Kapshagai reservoir | ||||||||
| Winter | Dobyn | 37 km below HPP | 40 | 23 | −730 | 49 | 9 | −36 |
| Spring | 15 | 37 | 60 | 28 | 5 | −46 | ||
| Summer | 66 | 22 | 0 | 81 | −9 | −18 | ||
| Autumn | 66 | 22 | 0 | 81 | −9 | −18 | ||
| After the Kapshagai reservoir | ||||||||
| Winter | 37 km below HPP | Kokzhide | −33 | −15 | 37 | −11 | −2 | 46 |
| Spring | 0 | −21 | −35 | 90 | 21 | 18 | ||
| Summer | 33 | 0 | 5 | −13 | 54 | 20 | ||
| Autumn | −13 | 32 | 24 | −11 | −13 | −57 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mussakulkyzy, A.; Opp, C.; Amirgaliev, N.; Madibekov, A.; Ismukhanova, L.; Zhadi, A. Transmission of Heavy Metals in River Water and Self-Purification Capacity of Ile River. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126548
Mussakulkyzy A, Opp C, Amirgaliev N, Madibekov A, Ismukhanova L, Zhadi A. Transmission of Heavy Metals in River Water and Self-Purification Capacity of Ile River. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126548
Chicago/Turabian StyleMussakulkyzy, Ainur, Christian Opp, Nariman Amirgaliev, Azamat Madibekov, Laura Ismukhanova, and Askhat Zhadi. 2025. "Transmission of Heavy Metals in River Water and Self-Purification Capacity of Ile River" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126548
APA StyleMussakulkyzy, A., Opp, C., Amirgaliev, N., Madibekov, A., Ismukhanova, L., & Zhadi, A. (2025). Transmission of Heavy Metals in River Water and Self-Purification Capacity of Ile River. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6548. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126548







