Snow Cover as a Medium for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Deposition and a Measure of Atmospheric Pollution in Carpathian Village–Study Case of Zawoja, Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Experimental Part
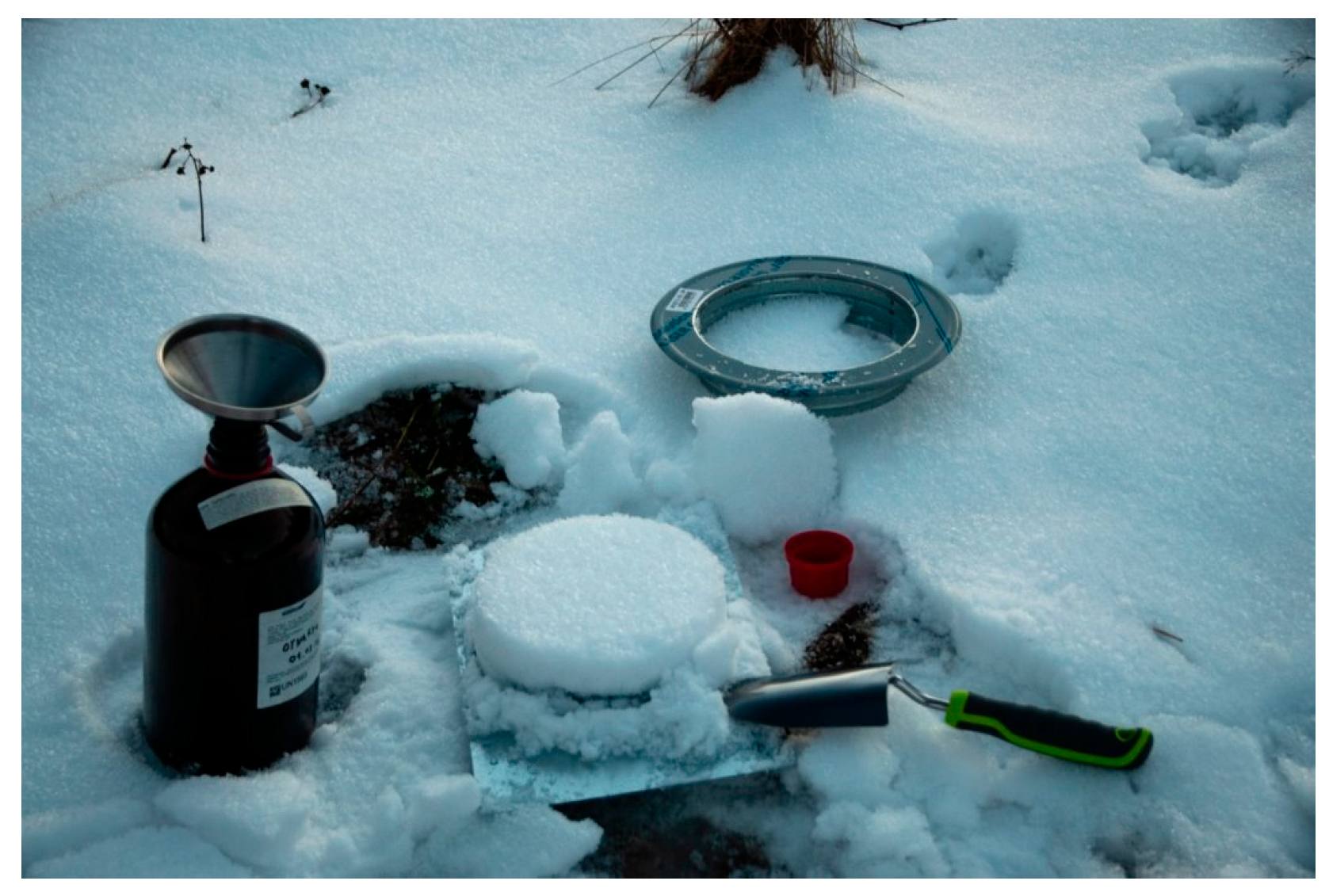
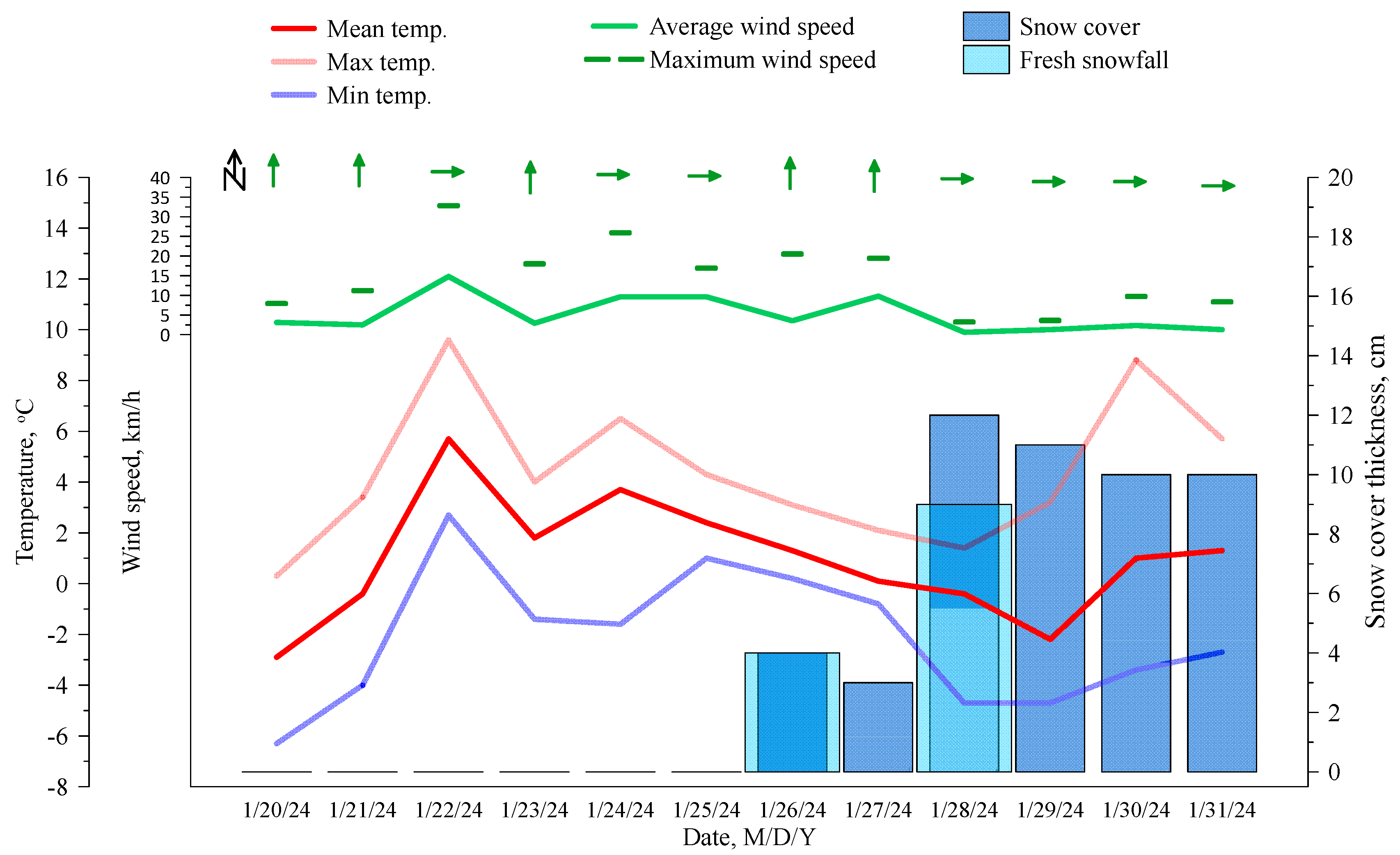
3.1. Sampling
- -
- A set of stainless steel tools: a short pipe fragment (H = 5 cm, ∅ = 21 cm), a 30 × 40 cm sheet metal, a shovel, and a funnel;
- -
- Amber glass bottle (prewashed with GC-MS grade dichloromethane and LC-MS grade water).
3.2. Reagents and Materials
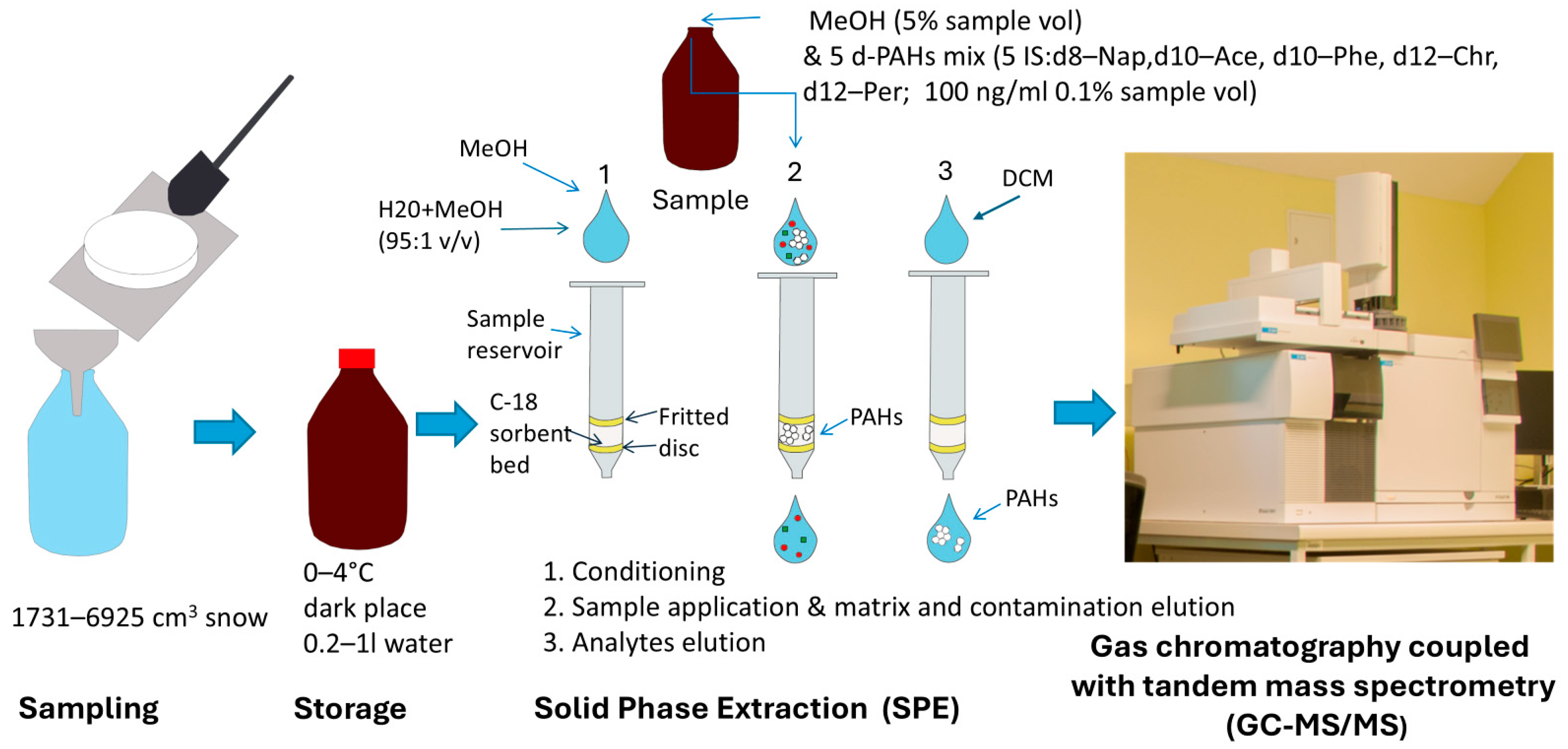
3.3. Sample Preparation
Solid Phase Extraction (SPE)
3.4. GC-MS/MS Analysis
- -
- GC Column: DB-EUPAH capillary column: 20 m × 180 μm × 0.14 μm, 5% phenyl methyl siloxane (Agilent 121–9627);
- -
- Liner: 800 μL Splitless, double taper, Ultra Inert (Agilent 5190–3983);
- -
- Carrier gas: Ultrapurified helium 99,999%, 1 mL/min;
- -
- Injection type: pulsed splitless, 70 psi until 1.9 min, then 22.292 psi;
- -
- Inlet temperature: 325 °C;
- -
- Oven temperature: 70 °C (1,16 min), 70 °C/min to 180 °C (0 min), 7 °C/min to 230 °C (6 min), 40 °C/min to 280 °C (5 min), 25 °C/min to 330 °C (5 min);
- -
- Injection volume: 2.5 µL;
- -
- Mass spectrometer quadrupole temperature: 150 °C;
- -
- Mass spectrometer source temperature: 340 °C.
4. Results and Discussion
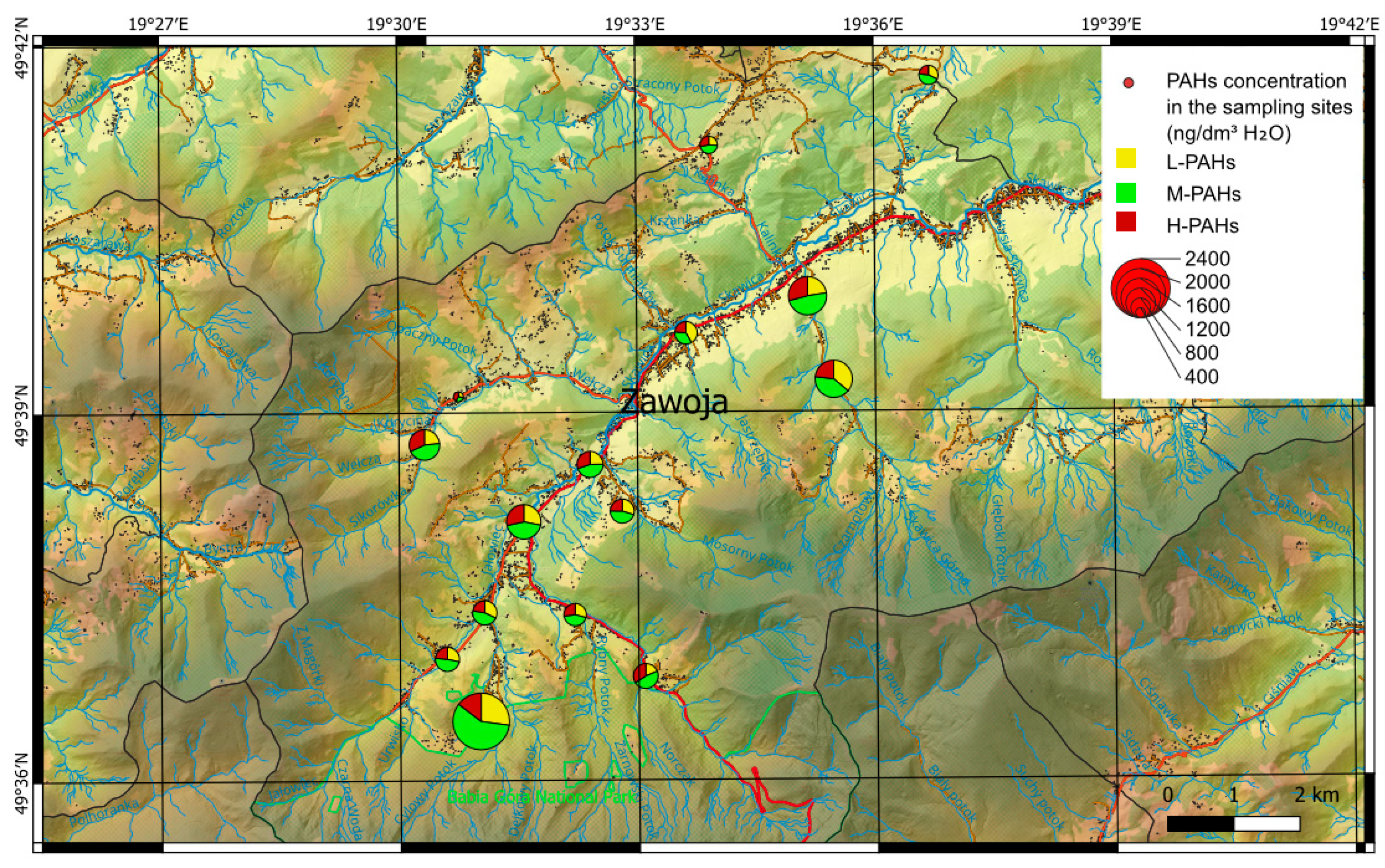
4.1. PAH Concentrations
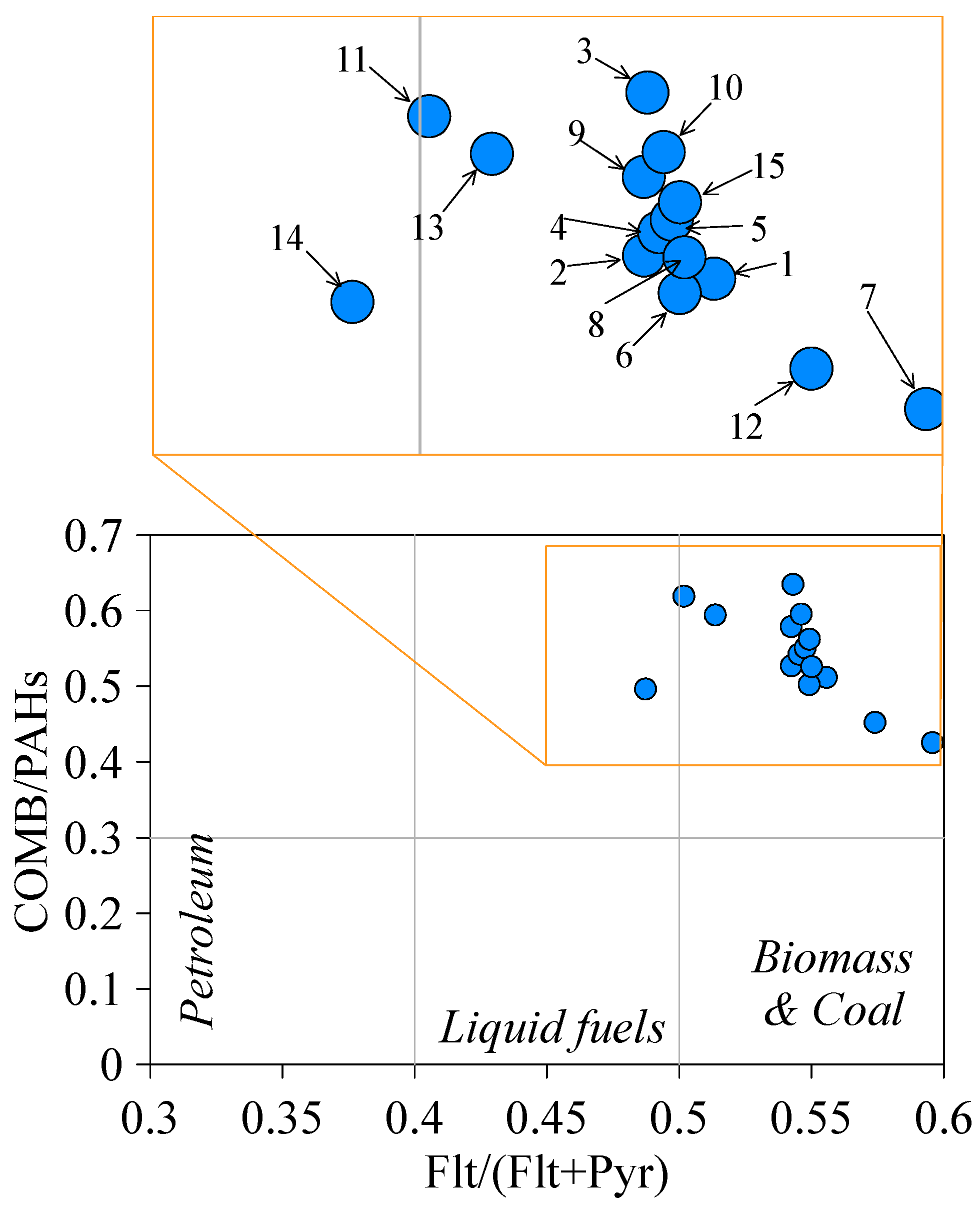
4.2. PAHs Sources
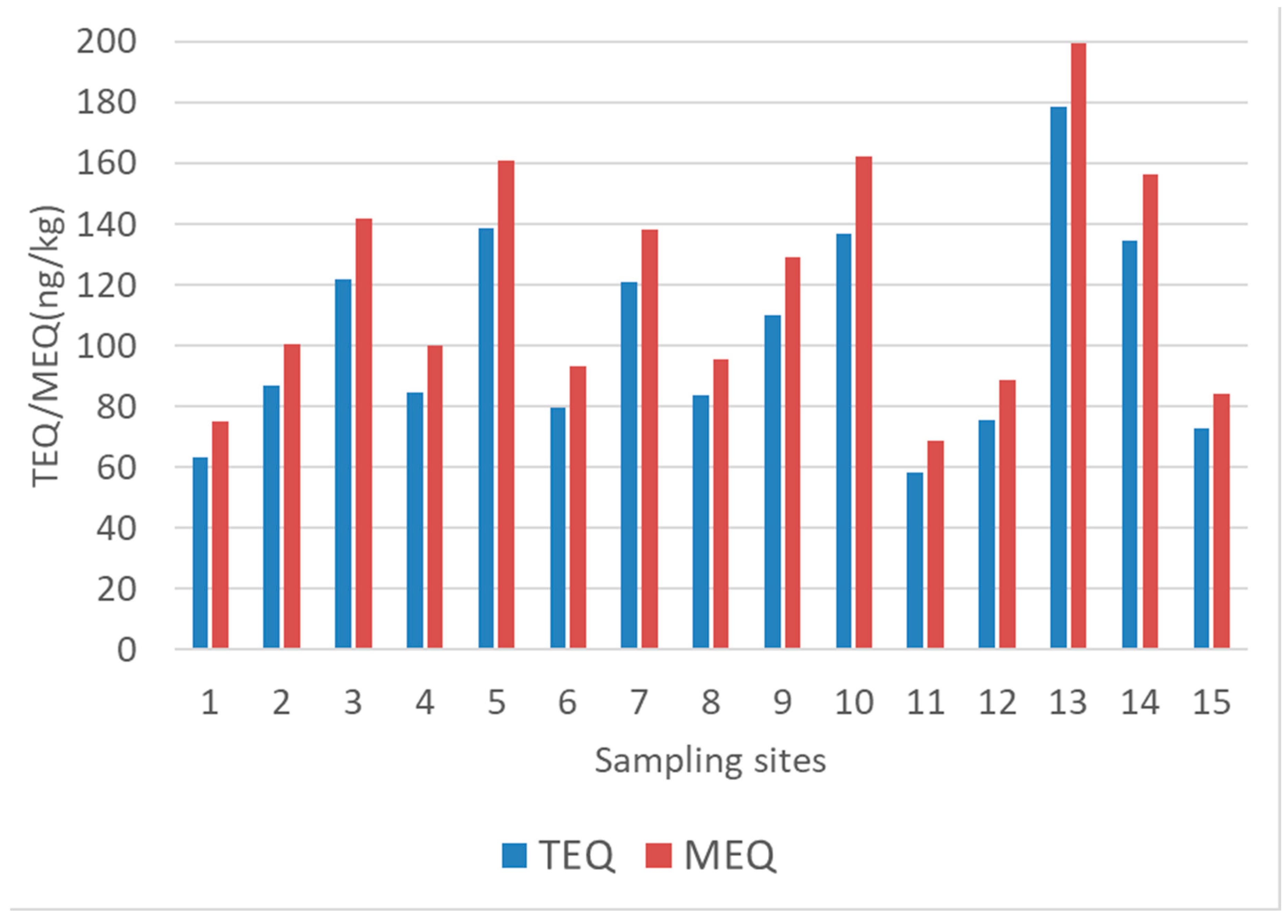
4.3. PAH Toxicity
- -
- Group I: 13 > 5 > 10 > 14 > 3 > 7 > 9;
- -
- Group II: 2 > 4 > 8 > 6 > 12 > 15 > 1 > 11.
- -
- Group I: 13 > 10 > 5 > 14 > 3 > 7 > 9;
- -
- Group II—2 > 4 > 8 > 6 > 12 > 15 > 1 > 11.
- RQNCs = 0 means no risk,
- RQNCs ≥ 1 and RQMPCs < 1 means moderate risk,
- RQMPCs ≥ 1 means high risk.
- RQΣPAHs(NCs) = 0 means no risk;
- 1 ≤ RQΣPAHs(NCs) < 800 and RQ ΣPAHs(MPCs) = 0 means low risk;
- RQΣPAHs(NCs) ≥ 800 and RQΣPAHs(MPCs) = 0 means moderate risk;
- RQΣPAHs(NCs) < 800, RQΣPAHs(MPCs) ≥ 1, means moderate risk;
- RQΣPAHs(NCs) ≥ 800, RQΣPAHs(MPCs) ≥ 1 means high risk.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ace | Acenaphthene |
| Acy | Acenaphthylene |
| Ant | Anthracene |
| B[a]A | Benz[a]anthracene |
| B[a]P | Benzo[a]pyrene |
| B[b]F | Benzo[b]fluoranthene |
| B[ghi]P | Benzo[g.h.i]perylene |
| B[k]F | Benzo[k]fluoranthene |
| BDL | Below Detection Limit |
| Chr | Chrysene |
| CPAHs | Concentration of PAHs |
| CQV | Risk Standard Value of PAHs |
| CQV(MPCs) | The Normative Value of the Maximum Concentrations of PAHs Giving the Maximum Environmental Risk |
| CQV(NCs) | The Normative Value of the Minimum Concentration of PAHs Generating Negligible Risk |
| D[a.h]A | Dibenz[a.h]anthracene |
| dMRM | Dynamic Multiple Reaction Monitoring |
| Fl | Fluorene |
| Flt | Fluoranthene |
| GC-MS/MS | Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| HMW PAHs | High-Molecular-Weight Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons |
| I[cd]P | Indeno[1.2.3-cd]pyrene |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
| MEQ | Mutagenic Equivalent |
| MPCs | Maximum Permissible Concentration |
| NA | Not Available |
| NCs | Negligible/Minimum Concentration |
| ND | Not Detected |
| Nph | Naphthalene |
| PAHs | Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons |
| Per | Perylene |
| PF | Pollution Factor |
| Ph | Phenanthrene |
| POPs | Persistent Organic Pollutants |
| Pyr | Pyrene |
| QQQ | Triple Quadrupole |
| RQ | Risk Quotient |
| SPE | Solid Phase Extraction |
| SVOC | Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds |
| TEF | Toxic Equivalency Factor |
| TEQ | Toxicity Equivalent |
References
- Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. PAH Diagnostic Ratios for the Identification of Pollution Emission Sources. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 162, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybing, E.; Schwarze, P.E.; Nafstad, P.; Victorin, K.; Penning, T.M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air and Cancer. In Air Pollution and Cancer; Straif, U., Cohen, A., Samet, J., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2013; pp. 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Morillo, E.; Romero, A.S.; Maqueda, C.; Madrid, L.; Ajmone-Marsan, F.; Grcman, H.; Davidson, C.M.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Villaverde, J. Soil Pollution by PAHs in Urban Soils: A Comparison of Three European Cities. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostert, M.M.R.; Ayoko, G.A.; Kokot, S. Application of Chemometrics to Analysis of Soil Pollutants. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyna, J.M.; Breivik, K.; Münch, J.; Fudala, J. European Atmospheric Emissions of Selected Persistent Organic Pollutants, 1970–1995. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussar, E.; Richards, S.; Lin, Z.Q.; Dixon, R.P.; Johnson, K.A. Human Health Risk Assessment of 16 Priority Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soils of Chattanooga, Tennessee, USA. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 5535–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichała-Kamrowska, K. Pokrywa Śnieżna Jako Źródło Informacji o Zanieczyszczeniu Środowiska (Na Przykładzie Wyników Badań Próbek Śniegu z Sudetów Zachodnich i Arktyki)/In english: Snow Cover as a Source of Information on Environmental Pollution (Based on the Results of Snow Sample Analyses from the Western Sudetes and the Arctic). Ph.D. Thesis, Gdańsk University of Technology, Gdańsk, Poland, 2012. (In Polish). [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, C.I.; Bergin, M.H.; Kuhns, H.D. The Deposition Of Particles and Gases to Ice Sheets. In Chemical Exchange Between the Atmosphere and Polar Snow; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; Volume I, pp. 275–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. The Distribution Variation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Between Fresh Snow and Seasonal Snowpack in Campus in Changchun City, Northeast China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Song, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hough, R.; Fu, Q.; An, L.; Shen, Z.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, D.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Fresh Snow in the City of Harbin in Northeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wania, F.; Mackay, D.; Hoff, J.T. The Importance of Snow Scavenging of Polychlorinated Biphenyl and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Vapors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, I.; Muir, D.; Charland, J.P. Scavenging Ratios of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds in Rain and Snow in the Athabasca Oil Sands Region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Moran, M.D. Development of a New Semi-Empirical Parameterization for below-Cloud Scavenging of Size-Resolved Aerosol Particles by Both Rain and Snow. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 799–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, H.; Paloluoğlu, C.; Turalioğlu, F.S.; Gaga, E.O. A Multipoint (49 Points) Study of Dry Deposition of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Erzurum, Turkey by Using Surrogated Snow Surface Samplers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12400–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahpoury, P.; Kitanovski, Z.; Lammel, G. Snow Scavenging and Phase Partitioning of Nitrated and Oxygenated Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Polluted and Remote Environments in Central Europe and the European Arctic. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13495–13510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels-Rausch, T.; Jacobi, H.W.; Kahan, T.F.; Thomas, J.L.; Thomson, E.S.; Abbatt, J.P.D.; Ammann, M.; Blackford, J.R.; Bluhm, H.; Boxe, C.S.; et al. Relationship between Snow Microstructure and Physical and Chemical Processes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2012, 12, 30409–30541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahpoury, P.; Lammel, G.; Šmejkalová, A.H.; Klánová, J.; Přibylová, P.; Váňa, M. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, Polychlorinated Biphenyls, and Chlorinated Pesticides in Background Air in Central Europe—Investigating Parameters Affecting Wet Scavenging of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, J.T.; Wania, F.; Mackay, D.; Gillham, R. Sorption of Nonpolar Organic Vapors by Ice and Snow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels-Rausch, T.; Jacobi, H.W.; Kahan, T.F.; Thomas, J.L.; Thomson, E.S.; Abbatt, J.P.D.; Ammann, M.; Blackford, J.R.; Bluhm, H.; Boxe, C.; et al. A Review of Air-Ice Chemical and Physical Interactions (AICI): Liquids, Quasi-Liquids, and Solids in Snow. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1587–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.D.; Wania, F. Is Rain or Snow a More Efficient Scavenger of Organic Chemicals? Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3557–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, T.P.; Eisenreich, S.J. Snow Scavenging of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Minnesota. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, A.; Sinikova, N.; Nikolaeva, S.; Poliakova, O.; Khrushcheva, M.; Pozdnyakov, S. Metals and Organic Pollutants in Snow Surrounding an Iron Factory. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2003, 1, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkowska, Ż.; Demkowska, I.; Cichała-Kamrowska, K.; Namieśnik, J. Pollutants Present in Snow Sample Collected from Various Layers of Snow Covers as a Source of Information about the State of Environment in a Big Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2010, 17, 203–231. [Google Scholar]
- Jarzyna, K.; Kozłowski, R.; Szwed, M. Chemical Properties of Snow Cover as an Impact Indicator for Local Air Poluttion Sources. Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural Areas 2017, IV, 1591–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Szwed, M.; Kozłowski, R. Snow Cover as an Indicator of Dust Pollution in the Area of Exploitation of Rock Materials in the Świętokrzyskie Mountains. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaga, E.O.; Tuncel, G.; Tuncel, S.G. PAH Composition of Snow Samples in Ankara City. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2004, 13, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhevnikov, A.Y.; Falev, D.I.; Sypalov, S.A.; Kozhevnikova, I.S.; Kosyakov, D.S. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Snow Cover of the Northern City Agglomeration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.P.; Noro, K.; Nabeshima, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Fujii, Y.; Arai, M.; Sakurai, T.; Kawamura, K.; Motoyama, H.; Thi, H.T.; et al. Concentrations of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Antarctic Snow Polluted by Research Activities Using Snow Mobiles and Diesel Electric Generators. Bull. Glaciol. Res. 2019, 37, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerón-Neculpan, M.; Simões, J.C.; Schwanck, F.; Lascani, J. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Antarctic Ice Core: Prior Study by Homogeneous Liquid-Liquid Extraction and High–Performance Liquid Chromatography. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2022, 94, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, G.; Fernandez, P.; Vilanova, R.; Grimalt, J.O. Analysis of Trace Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Organochlorine Compounds in Atmospheric Residues by Solid-Phase Disk Extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 823, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, G.; Fernández, P.; Vilanova, R.M.; Grimalt, J.O. Persistent Organic Pollutants in Snow from European High Mountain Areas. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Tang, N.; Nagato, E.G.; Toriba, A.; Aoki, K. Identification of Long-Range Transported Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Snow at Mt. Tateyama, Japan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahpoury, P.; Hageman, K.J.; Matthaei, C.D.; Alumbaugh, R.E.; Cook, M.E. Increased Concentrations of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Alpine Streams during Annual Snowmelt: Investigating Effects of Sampling Method, Site Characteristics, and Meteorology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11294–11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björklund, K.; Strömvall, A.M.; Malmqvist, P.A. Screening of Organic Contaminants in Urban Snow. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panek, E. Heavy Metals in the Soil and Bed-Rock of the Babia Góra National Park. Environ. Prot. Eng. 1991, 17, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Łyszczarz, S.; Błońska, E.; Lasota, J. The Application of the Geo-Accumulation Index and Geostatistical Methods to the Assessment of Forest Soil Contamination with Heavy Metals in the Babia Góra National Park (Poland). Arch. Environ. Prot. 2020, 46, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, D.; Rzepa, G. Geochemistry of Waters and Bottom Sediments in Landslide Lakes in Babiogórski National Park. Mineralogia 2011, 42, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Musielińska, R.; Kwapuliński, J.; Kowol, J.; Asman, M. The Contamination in the Ground Layer of Air in Zawoja in Terms of the Search for References Areas. Tech. Inform. Inżynieria Bezpieczeństwa 2018, VI, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J. How Decaying Wood Affects the Accumulation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil of Temperate Mountain Forest. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgulat, J.; Borgulat, A. Biomonitoring of Atmospheric PAHs Using Fir and Spruce Needles in Forests in the Vicinity of Mountain Villages. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urząd statystyczny w Krakowie [in English Statistical Office in Krakow]. Gmina Wiejska Zawoja Powiat Suski [in English Rural Commune of Zawoja, Suski County]. 2020. Available online: https://krakow.stat.gov.pl/vademecum/vademecum_malopolskie/portrety_gmin/powiat_suski/zawoja.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Urząd Gminy Zawoja [in English Zawoja Commune Office]. Report on the State of the Zawoja Commune 2023. 2024. Available online: https://ug.zawoja.pl/raport-o-stanie-gminy-zawoja-za-rok-2023/ (accessed on 3 June 2025).
- Babiogórski Park Narodowy. Babia Góra National Park. Available online: https://bgpn.gov.pl/english-version (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World Map of the Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification Updated. Meteorol. Zeitschrift 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomadseason. Monthly Climate in Zawoja, Lesser Poland, Poland. Available online: https://nomadseason.com/climate/poland/lesser-poland/zawoja.html (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Franczak, P. Frequency and Thickness of Snow Cover at the Foot of the Babia Góra Massif in the Winter Seasons. For. Res. Pap. 2018, 79, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Global Wind Atlas. Available online: https://globalwindatlas.info/en (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, J. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Gas, PM2.5, and Frost Samples in a Severely Polluted Rural Site of the North China Plain: Distribution, Source, and Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 156919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, T.; Wilkinson, D.; Hummel, S.; Meyer, B.; Culley, A. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Air and Snow from Fairbanks, Alaska. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2010, 1, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izvekova, T.V.; Kobeleva, N.A.; Gushchin, A.A.; Grinevich, V.I.; Rybkin, V.V. Distribution of Policyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in a Snow Cover in the Territory of Ivanovo City, Russia. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levshina, S. Distribution and Characteristic of PAHs in Snow of the Urban and Reserve Areas of Southern Far East Russia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, G.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Ge, L.; Ma, X.; Yao, Z. Distribution and Characteristic of PAHs in Snow of Fildes Peninsula. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, B.M.J.; Halsall, C.J.; Fitzpatrick, L.; Villa, S.; Jones, K.C.; Thomas, G.O. Use and Validation of Novel Snow Samplers for Hydrophobic, Semi-Volatile Organic Compounds (SVOCs). Chemosphere 2004, 56, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskari, E.L.; Rekilä, R.; Roy, S.; Lehto, O.; Ruuskanen, J.; Kärenlampi, L. Airborne Pollutants along a Roadside: Assessment Using Snow Analyses and Moss Bags. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 97, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. Laboratory Melting of Late-Winter Urban Snow Samples: The Magnitude and Dynamics of Releases of Heavy Metals and PAHs. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; Van Grieken, R. Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Source Attribution, Emission Factors and Regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzinski, H.; Jones, I.; Bellocq, J.; Piérard, C.; Garrigues, P. Evaluation of Sediment Contamination by Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Gironde Estuary. Mar. Chem. 1997, 58, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River Basin: A Critical Appraisal of PAH Ratios as Indicators of PAH Source and Composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, S.J.; Cho, S.; Taylor, E.; Yi, Y.; Gibson, J.J. Characterizing the PAHs in Surface Waters and Snow in the Athabasca Region: Implications for Identifying Hydrological Pathways of Atmospheric Deposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Wang, X.M.; Xie, Z.Q.; Xiang, C.H.; Mai, B.X.; Sun, L.G.; Zheng, M.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M.; Pöschl, U. Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Observed over the North Pacific Ocean and the Arctic Area: Spatial Distribution and Source Identification. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoyiannis, A.; Terzi, E.; Cai, Q.Y. On the Use of PAH Molecular Diagnostic Ratios in Sewage Sludge for the Understanding of the PAH Sources. Is This Use Appropriate? Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wan, C.; Yue, D.; Ye, Y.; Wang, X. Source Diagnostics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Road Runoff, Dust, Rain and Canopy Throughfall. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeham, S.G.; Schaffner, C.; Giger, W. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Recent Lake Sediments-I. Compounds Having Anthropogenic Origins. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1980, 44, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Readman, J.W.; Mantoura, R.F.C.; Rhead, M.M. A Record of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Pollution Obtained from Accreting Sediments of the Tamar Estuary, U.K.: Evidence for Non-Equilibrium Behaviour of PAH. Sci. Total Environ. 1987, 66, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Backus, S.M.; Graf Pannatier, E.; Jeffries, D.S.; Macdonald, R.W. Sources and Significance of Alkane and PAH Hydrocarbons in Canadian Arctic Rivers. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 55, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.U.; Kim, J.G.; Jeong, M.J.; Song, B.J. Source Identification of Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Industrial Complex Using Diagnostic Ratios and Multivariate Factor Analysis. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 60, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahl, F.G.; Carpenter, R. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH)-Phase Associations in Washington Coastal Sediment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1983, 47, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Cheng, H.X.; Liu, Y.H.; Xia, X.J.; Xu, X.B. Composition, Distribution, and Characterization of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Soil in Linfen, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.J.; Bradshaw, P.T.; Herring, A.H.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Beyea, J.; Stellman, S.D.; Steck, S.E.; Mordukhovich, I.; Eng, S.M.; Engel, L.S.; et al. Exposure to Multiple Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Breast Cancer Incidence. Environ. Int. 2016, 89–90, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Liang, W.; Wang, J.; Niu, L.; Zhao, X.; Wu, F. Deriving Convincing Human Health Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Benzo[a]Pyrene and Providing Basis for the Water Quality Management: The Impacts of National Bioaccumulation Factors and Probabilistic Modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, I.C.T.; LaGoy, P.K. Toxic Equivalency Factors (TEFs) for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.H.; Yan, B.; Chillrud, S.N.; Perera, F.P.; Whyatt, R.; Camann, D.; Kinney, P.L.; Miller, R.L. Assessment of Benzo(a)Pyrene-Equivalent Carcinogenicity and Mutagenicity of Residential Indoor versus Outdoor Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Exposing Young Children in New York City. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1889–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, R.; Xu, F.; Shen, Z. Environmental Risk Assessments and Spatial Variations of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Sediments in Yangtze River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavar Ashayeri, N.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Kersten, M.; Yazdi, M.; Lahijanzadeh, A.R. Presence of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Sediments and Surface Water from Shadegan Wetland – Iran: A Focus on Source Apportionment, Human and Ecological Risk Assessment and Sediment-Water Exchange. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grmasha, R.A.; Abdulameer, M.H.; Stenger-Kovács, C.; Al-sareji, O.J.; Al-Gazali, Z.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Meiczinger, M.; Hashim, K.S. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Surface Water and Sediment along Euphrates River System: Occurrence, Sources, Ecological and Health Risk Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

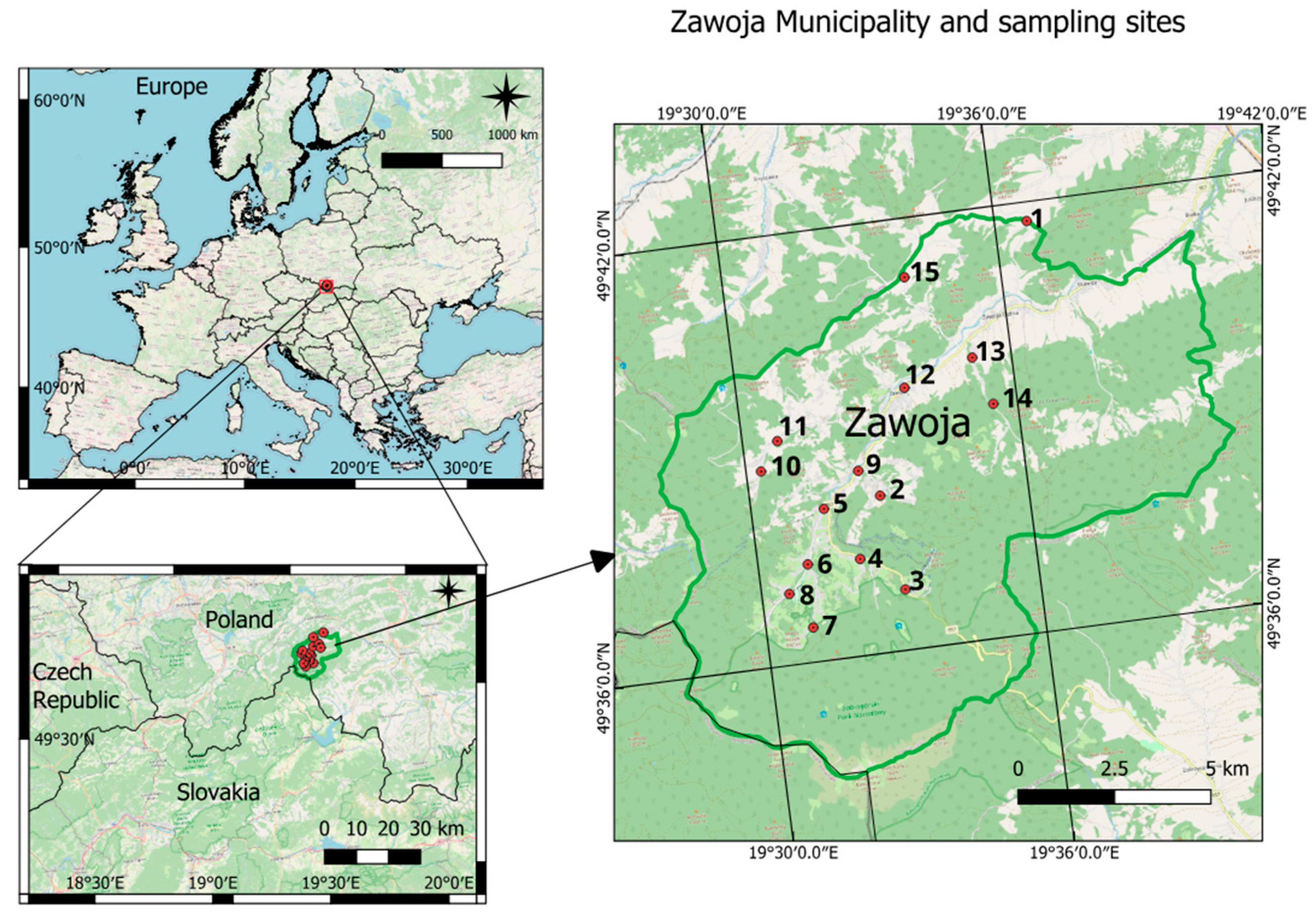



| Sample No | District Name | Coordinates, Altitude (m asl.) | Pollution Factor (PF) 1: I—Distance from the Road, II—Distance from Tourist Attractions, III—Industrial and IV—Commercial Sites, V—Population Density, VI—Distance from the Forest, VII—Altitude | Photo |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zawoja Snoza | 49°41′43″ N 19°36′41″ E, 630 m asl | I-0, II-0, III-1, IV-0, V-0, VI-2, VII-2 PF = 5 Wasteland, meadow, vicinity of forest, >100 m from the nearest household, 150 m from the sawmill |  |
| 2 | Zawoja Mosorne 650 m asl | 49°38′11″ N 19°32′48″ E, 663 m asl | I-0, II-0, III-0, IV-0, V-2, VI-2, VII-1 PF = 5 Meadow, local agriculture, individual dwellings, vicinity of forest, 25 m from the nearest household |  |
| 3 | Zawoja Policzne | 49°36′50″ N 19°33′05″ E, 707 m asl | I-5, II-5, III-0, IV-4, V-1, VI-2, VII-0 PF = 17 By the transit main road, in the vicinity of ski lift and restaurant, 55 m from the nearest household |  |
| 4 | Zawoja Ryzowana | 49°37′20″ N 19°32′12″ E, 665 m asl | I-2, II-0, III-0, IV-1, V-4, VI-2, VII-1 PF = 10 80 m from the main road, <250 m from the hotel, build up area outside the village centre |  |
| 5 | Zawoja Widły | 49°38′06″ N 19°31′33″ E, 606 m asl | I-3, II-0, III-0, IV-3, V-4, VI-4, VII -3 PF = 17 Near the secondary road and the grocery shop, build up area outside the village centre |  |
| 6 | Zawoja Składy | 49°37′22″ N 19°31′03″ E, 636 m asl | I-2, II-0, III-0, IV-3, V-2, VI-4, VII-2 PF = 13 15 m from the secondary road, 15 m from the nearest household and forest inspectorate building |  |
| 7 | Zawoja Markowa | 49°36′28″ N 19°31′00″ E, 718 m asl | I-2, II-0, III-0, IV-4, V-2, VI-0, VII-0 PF = 8 25 m from the entrance to Babia Góra National Park, 25 m from the secondary road and a car park |  |
| 8 | Zawoja Czatoża | 49°36’59″ N 19°30’35″ E, 671 m asl | I-2, II-2, III-0, IV-0, V-3, VI-3, VII-1 PF = 11 100 m from the ski lift, several meters from the secondary road |  |
| 9 | Zawoja Mosorne School | 49°38’34″ N 19°32’24″ E, 578 m asl | I-3, II-0, III-0, IV-5, V-5, VI-4, VII-4 PF = 21 20 m from the main road, by the school car park, build up area village centre |  |
| 10 | Zawoja Wełcza, final bus stop | 49°38’44″ N 19°30’19″ E, 661 m asl | I-2, II-0, III-0, IV-0, V-2, VI-2, VII-1 PF = 7 20 m from the secondary road, 30 m from the nearest household |  |
| 11 | Zawoja Wełcza PTSM | 49°39’07″ N 19°30’45″ E, 628 m asl | I-3, II-3, III-0, IV-3, V-4, VI-4, VII-2 PF = 19 10 m from the secondary road, 30 m from the nearest household, 20 m from the youth tourist shelter and 20 m from the church |  |
| 12 | Zawoja Centrum church | 49°39’38″ N 19°33’37″ E, 536 m asl | I-3, II-5, III-0, IV-5, V-5, VI-5, VII-5 PF = 28 Village centre, by the church car park |  |
| 13 | Zawoja Dolna | 49°39’56″ N 19°35’09″E, 527 m asl | I-2, II-0, III-3, IV-0, V-3, VI-4, VII-5 PF = 17 Vicinity of PCV window factory, outside of the buildup area |  |
| 14 | Zawoja Podpolice | 49°39’15″ N 19°35’28″E, 603 m asl | I-2, II-0, III-0, IV-0, V-0, VI-0, VII-3 PF = 5 Forest |  |
| 15 | Zawoja Przysłup | 49°41’10″ N 19°33’55″E, 659 m asl | I-1, II-0, III-0, IV-0, V-2, VI-3, VII-2 PF = 8 |  |
| Compound | Rt (min) | Transition | Qualifier | LOD (ng/L) | LOQ (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nph-d8 | 2.871 | 136 → 136 | - | <0.06 | <0.06 |
| Nph | 2.883 | 128 → 102 | 128 → 127 | <0.06 | <0.06 |
| Ace | 4.012 | 152 → 150 | 152 → 151 | <0.06 | <0.06 |
| Ace-d10 | 4.086 | 162 → 160 | - | <0.06 | <0.06 |
| Acy | 4.124 | 154 → 152 | 153 → 152 | <0.06 | <0.06 |
| Fl | 4.637 | 166 → 165 | 166 → 163 | <0.06 | <0.06 |
| Ph | 6.331 | 178 → 176 | 178 → 152 | <0.06 | 0.06 |
| Ph-d10 | 6.346 | 188 → 188 | - | <0.06 | <0.06 |
| Ant | 6.387 | 178 → 176 | 178 → 152 | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| Flt | 9.312 | 202 → 200 | 202 → 201 | <0.06 | 0.18 |
| Py | 10.168 | 202 → 200 | 202 → 201 | <0.06 | 0.16 |
| B[a]A | 16.193 | 228 → 226 | 228 → 224 | 0.98 | 1.18 |
| Chr-d12 | 16.438 | 240 → 236 | 118 → 116 | 0.24 | 1.76 |
| Chr | 16.550 | 228 → 226 | 228 → 224 | 0.30 | 0.90 |
| B[b]F | 16.460 | 252 → 250 | 250 → 248 | <0.06 | 0.46 |
| B[k]F | 19.510 | 252 → 250 | 250 → 248 | <0.06 | 0.69 |
| Benzo[a]/[e]pyrene | 20.952 | 252 → 250 | 250 → 248 | 1.50 | 3.65 |
| Per-d12 | 21.350 | 264 → 260 | - | 0.98 | 1.22 |
| I [cd]P | 24.252 | 276 → 274 | 138 → 124 | 0.63 | 4.00 |
| D[ah]A | 24.291 | 278 → 276 | 125 → 124 | 1.28 | 4.42 |
| B[ghi]P | 24.809 | 276 → 274 | 274 → 272 | 0.46 | 3.65 |
| (A) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |||||||||||||||
| Nph | 55.3 | 90.3 | 17.7 | 111.8 | 99.6 | 91.8 | 66.1 | 62.2 | 56.3 | 91.2 | 50.3 | 37.1 | 37.6 | 151.3 | 35.4 | ||||||||||||||
| Acy | 14.3 | 13.9 | 11.6 | 10.4 | 33.2 | 14.8 | 15.9 | 14.3 | 14.7 | 13.2 | 5.7 | 16.0 | 13.9 | 105.6 | 11.2 | ||||||||||||||
| Ace | 6.5 | 4.2 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 4.1 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 3.6 | 2.9 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 23.3 | 16.3 | 2.6 | ||||||||||||||
| Fl | 17.7 | 17.0 | 13.1 | 12.0 | 23.9 | 17.5 | 17.4 | 16.3 | 17.3 | 15.3 | 5.8 | 20.1 | 32.8 | 25.4 | 12.6 | ||||||||||||||
| Ph | 153.2 | 159.1 | 137.0 | 126.2 | 219.6 | 184.6 | 514.8 | 175.1 | 164.1 | 163.8 | 41.9 | 164.8 | 224.2 | 231.7 | 117.8 | ||||||||||||||
| Ant | 6.4 | 7.8 | 7.5 | 5.0 | 13.6 | 8.9 | 10.1 | 9.5 | 8.2 | 6.6 | 2.6 | 145.3 | 21.2 | 17.1 | 5.6 | ||||||||||||||
| Flt | 134.3 | 168.6 | 165.8 | 143.5 | 226.2 | 174.9 | 687.8 | 185.0 | 175.1 | 195.6 | 36.7 | 122.3 | 274.5 | 218.5 | 121.7 | ||||||||||||||
| Pyr | 107.5 | 142.3 | 139.6 | 119.7 | 186.9 | 143.6 | 466.9 | 151.3 | 147.8 | 162.6 | 36.5 | 90.8 | 259.9 | 230.0 | 99.9 | ||||||||||||||
| B[a]A | 36.7 | 53.3 | 64.5 | 48.4 | 74.6 | 51.5 | 66.8 | 54.9 | 56.7 | 72.0 | 24.0 | 36.0 | 99.6 | 72.7 | 39.4 | ||||||||||||||
| Chr | 71.1 | 83.2 | 110.3 | 87.3 | 121.5 | 80.9 | 122.6 | 86.4 | 99.8 | 126.1 | 30.6 | 68.1 | 120.6 | 99.0 | 63.6 | ||||||||||||||
| B[b]F | 48.7 | 55.6 | 80.0 | 59.7 | 86.2 | 50.5 | 73.5 | 51.6 | 73.1 | 98.6 | 34.0 | 54.2 | 83.4 | 69.8 | 43.9 | ||||||||||||||
| B[k]F | 11.8 | 16.0 | 26.4 | 19.7 | 33.3 | 16.7 | 28.7 | 18.5 | 25.8 | 16.4 | 8.9 | 14.8 | 37.8 | 20.1 | 13.1 | ||||||||||||||
| B[a]P | 34.4 | 46.5 | 65.8 | 44.3 | 73.6 | 45.3 | 63.1 | 43.9 | 58.6 | 73.7 | 32.9 | 40.4 | 104.3 | 82.4 | 40.0 | ||||||||||||||
| I[cd]P | 43.9 | 60.8 | 84.6 | 61.7 | 98.7 | 48.9 | 84.1 | 56.2 | 78.9 | 99.2 | 44.5 | 53.7 | 106.8 | 82.6 | 51.0 | ||||||||||||||
| D[ah]A | 13.3 | 20.1 | 28.4 | 19.7 | 33.1 | 16.9 | 29.0 | 19.7 | 25.6 | 31.1 | 13.4 | 16.2 | 38.7 | 25.2 | 16.8 | ||||||||||||||
| B[ghi]P | 29.6 | 42.7 | 60.2 | 43.7 | 72.8 | 43.1 | 59.7 | 39.6 | 57.6 | 68.1 | 32.8 | 39.4 | 82.6 | 72.9 | 35.9 | ||||||||||||||
| ∑PAH | 785 | 981 | 1015 | 915 | 1401 | 992 | 2310 | 987 | 1063 | 1246 | 404 | 923 | 1561 | 1521 | 710 | ||||||||||||||
| ∑L-PAH | 253 | 292 | 190 | 268 | 394 | 320 | 627 | 279 | 264 | 293 | 110 | 387 | 353 | 548 | 185 | ||||||||||||||
| ∑M-PAH | 350 | 447 | 480 | 399 | 609 | 451 | 1344 | 478 | 479 | 556 | 128 | 317 | 755 | 620 | 325 | ||||||||||||||
| ∑H-PAH | 182 | 242 | 345 | 249 | 398 | 221 | 338 | 230 | 320 | 397 | 166 | 219 | 454 | 353 | 201 | ||||||||||||||
| ∑carcPAH | 260 | 335 | 460 | 341 | 521 | 310 | 468 | 331 | 419 | 527 | 188 | 283 | 591 | 452 | 268 | ||||||||||||||
| (B) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ankara, Turkey | Wangdu, China | Patriot Hills, South Pole, Antarctica | Fairbanks, Alaska, USA | Mt. Tateyama, Japan | Ivanovo, Russia | Arkhangelsk, Russia | Khabarovsk, Russia | Bolshekhekhtsirsky State Nature Reserve, Station 12, Russia | Fildes Peninsula, King George Island, Antarctica | Redo Lake, Pyrenees, Spain | Minnesota, USA | Minnesota, USA | Punta Indren Glacier, Italian Alps | Punta Indren Glacier, Italian Alps | Kuopio, Finland | Luleå, Sweden | Umeå, Sweden | ||||||||||||
| SM | I | II | III | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII | VIII | NA | NA | IX | IX | X | X | XI | XII | XII | |||||||||||
| Nph | NA | 0.2 | 231.4 | 450 | NA | 152 | 10 | NA | NA | 94.75 | NA | NA | NA | 2.47 | 4.73 | NA | 60 | 80 | |||||||||||
| Acy | ND | 0.26 | NA | 34 | NA | NA | ND | NA | NA | 1.61 | NA | 5 | 02.2 | 1.6 | 0.97 | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Ace | ND | 0.18 | NA | 13 | NA | NA | 2.3 | NA | NA | 11.69 | NA | 211 | 27 | 2.97 | 2.4 | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Fl | 79.9 | 0.5 | NA | 71 | NA | 107 | 8.3 | 2.39 | 5.33 | 13.49 | 0.039 | 364 | 44 | 2.14 | 1.64 | BDL | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Ph | 678 | 4.67 | 78.4 | 377 | NA | 394 | 73.4 | 19.96 | 46.51 | 14.14 | 0.26 | 3590 | 515 | 9.47 | 4.2 | 6600 | 410 | 1260 | |||||||||||
| Ant | ND | 0.7 | 51.6 | 1.9 | NA | 21 | 2 | 1.81 | 1.83 | 1.5 | 0.004 | 300 | 43 | 0.61 | 4.32 | 1400 | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Flt | 85.4 | 5.23 | 96.0 | 125 | 3.93 | 588 | 55.5 | 4.96 | 05.4 | 1.83 | 0.12 | 1890 | 677 | 2.14 | 1.2 | 3800 | 490 | 1760 | |||||||||||
| Pyr | 71.6 | 3.38 | 67.1 | 53 | 3.35 | 267 | 46.8 | 6.54 | 4.97 | 2.23 | 0.13 | 3115 | 491 | 1.9 | 0.94 | 3000 | 580 | 2310 | |||||||||||
| B[a]A | 85.4 | 1.33 | ND | 3.7 | 2.81 | NA | 09.7 | 0.74 | 0.72 | 0.6 | 0.013 | 976 | 65 | 0.57 | 0.09 | 10,600 | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Chr | 64.7 | 2.39 | 35.1 | 29 | 2.44 | 1 | 10.6 | 2.63 | 1.57 | 0.78 | 0.007 | 1420 | 211 | 0.57 | 0.06 | 600 | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| B[b]F | 29.9 | 1.45 | D | 12 | 2.51 | 176 | 5.7 | 1.59 | 0.97 | 0.63 | 0.007 | 2085 (b + k) | 499 (b + k) | 0.50 | 0.1 | BDL | 270 | 1100 | |||||||||||
| B[k]F | NA | 1.28 | 67.2 | 7.0 | 0.77 | 111 | 3.1 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 0.63 | ND | 905 | 179 | 0.38 | NA | 200 | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| B[a]P | 32.7 | 01.4 | 23.5 | 4.8 | 0.86 | 6 | 3.5 | 1.74 | 1.27 | ND | 0.014 | 905 | 179 | 0.07 | NA | BDL | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| I[cd]P | 24.4 | 2.35 | 47.4 | 3.6 | 0.03 | NA | ND | 0.03 | ND | ND | 0.06 | 871 | 169 | 0.09 | 0.06 | NA | 130 | 370 | |||||||||||
| D[ah]A | ND | 0.64 | 43.3 | n.d. | 0.17 | 5 | ND | ND | 0.08 | ND | ND | 186 | 32 | 0.02 | 0.03 | BDL | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| B[ghi]P | 23.8 | 1.92 | D | 9.4 | 0.89 | 7 | 02.3 | 0.20 | 0.50 | ND | ND | 736 | 145 | 0.17 | 0.007 | BDL | 210 | 800 | |||||||||||
| ∑PAH | 1176 | 27.5 | 741.0 | 1194 | 17.8 | 1835 | 233 | 43.0 | 69.3 | 143.9 | 0.7 | 17,580 | 3320 | 24.3 | 20.4 | 26,200 | 2720 | 9640 | |||||||||||
| ∑L-PAH | 757.9 | 6.5 | 361.4 | 946.9 | 0 | 674 | 96 | 24.7 | 53.7 | 137.2 | 0.3 | 4470 | 631.1 | 18.7 | 18.1 | 8000 | 90 | 140 | |||||||||||
| ∑M-PAH | 307.1 | 12.3 | 198.2 | 222.7 | 12.5 | 856 | 122 | 14.9 | 12.3 | 5.4 | 0.3 | 7401 | 1444 | 4.7 | 2.1 | 18,000 | 1540 | 5460 | |||||||||||
| ∑H-PAH | 110.8 | 08.7 | 181.4 | 24.8 | 05.2 | 305 | 15 | 4.3 | 3.3 | 1.3 | 0.08 | 2698 | 525 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 200 | 1090 | 4040 | |||||||||||
| Ref. | [26] | [48] | [29] | [49] | [32] | [50] | [27] | [51] | [51] | [52] | [30] | [21] | [21] | [53] | [53] | [54] | [55] | [55] | |||||||||||
| (A) | |||||||||
| Site | ∑COMB/ ∑PAH | Ant/ (Ant + Ph) | Flt/ (Flt + Pyr) | IcdP/ (IcdP + Bghi) | BaP/ BghiP | ∑LMW/ ∑HMW | BaA/ (BaA + Chr) | BaPTEQ | BaPMEQ |
| 1 | 0.66 | 0.04 | 0.56 | 0.60 | 1.15 | 0.48 | 0.34 | 63 | 75 |
| 2 | 0.68 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.59 | 1.09 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 87 | 101 |
| 3 | 0.79 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 1.09 | 0.23 | 0.37 | 122 | 142 |
| 4 | 0.69 | 0.04 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 1.01 | 0.41 | 0.36 | 85 | 100 |
| 5 | 0.70 | 0.06 | 0.55 | 0.58 | 1.01 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 139 | 161 |
| 6 | 0.66 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 1.05 | 0.48 | 0.39 | 80 | 93 |
| 7 | 0.72 | 0.02 | 0.60 | 0.58 | 1.06 | 0.37 | 0.35 | 121 | 138 |
| 8 | 0.70 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 1.11 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 84 | 95 |
| 9 | 0.73 | 0.05 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 1.02 | 0.33 | 0.36 | 110 | 129 |
| 10 | 0.74 | 0.04 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 1.08 | 0.31 | 0.36 | 137 | 162 |
| 11 | 0.70 | 0.06 | 0.50 | 0.58 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 58 | 69 |
| 12 | 0.56 | 0.47 | 0.57 | 0.58 | 1.03 | 0.72 | 0.35 | 75 | 89 |
| 13 | 0.75 | 0.09 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 1.26 | 0.29 | 0.45 | 179 | 200 |
| 14 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 0.49 | 0.53 | 1.13 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 135 | 156 |
| 15 | 0.72 | 0.05 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 1.12 | 0.35 | 0.38 | 73 | 84 |
| (B) | |||||||||
| PAH ratio | Value | PAH Source | Reference | ||||||
| ∑COMB/∑PAH | ~1 | Combustion | [56] | ||||||
| Ant/(Ant + Ph) | <0.1 | Petrogenic | [58] | ||||||
| >0.1 | Pyrogenic | ||||||||
| Flt/(Flt + Pyr) | <0.4 | Petrogenic | [58] | ||||||
| 0.4–0.5 | Fossil fuel combustion | ||||||||
| >0.5 | Grass, wood, coal combustion | ||||||||
| IcdP/(IcdP + Bghi) | <0.2 | Petrogenic | [58] | ||||||
| 0.2–0.5 | Petroleum combustion | ||||||||
| >0.5 | Grass, wood and coal combustion | ||||||||
| BaP/BghiP | <0.6 | Non traffic emissions | [61] | ||||||
| >0.6 | Traffic emissions | ||||||||
| ∑LMW/∑HMW | <1 | Pyrogenic | [62] | ||||||
| >1 | Petrogenic | ||||||||
| BaA/(BaA + Chr) | <0.2 | Petrogenic | [58] | ||||||
| >0.35 | Combustion | ||||||||
| Site | PAH | Nap | Acy | Ace | Flu | Phe | Ant | Fla | Pyr | B[a]A | Chry | B[b]F | B[k]F | B[a]P | I[1,2,3-I[c,d]P | D[a,h]A | B[ghi]P | ∑PAHs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CQV(NCs) (ng/L) * | 12 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 3 | 0.7 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 3.4 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | ||
| CQV(MPCs) (ng/L) * | 1200 | 70 | 70 | 70 | 300 | 70 | 30 | 70 | 10 | 340 | 10 | 40 | 50 | 40 | 50 | 30 | ||
| 1 | RQ(NCs) | 4.6 | 20.4 | 9.2 | 25.4 | 51.1 | 9.2 | 44.8 | 153.5 | 366.7 | 20.9 | 486.8 | 29.5 | 68.9 | 109.8 | 26.5 | 99.6 | 1526.8 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.51 | 0.09 | 4.48 | 1.54 | 3.67 | 0.21 | 4.87 | 0.29 | 0.69 | 1.10 | 0.27 | 1.00 | 12.99 | |
| 2 | RQ(NCs) | 7.5 | 19.9 | 6.1 | 24.3 | 53.0 | 11.1 | 56.2 | 203.2 | 533.1 | 24.5 | 556.3 | 39.9 | 93.0 | 151.9 | 40.2 | 142.2 | 1962.5 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 5.6 | 2.0 | 5.3 | 0.2 | 5.6 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 19.4 | |
| 3 | RQ(NCs) | 1.5 | 16.6 | 3.8 | 18.7 | 45.7 | 10.8 | 55.3 | 199.4 | 644.9 | 32.4 | 800.0 | 66.1 | 131.5 | 211.4 | 56.8 | 200.7 | 2495.6 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.46 | 0.11 | 5.53 | 1.99 | 6.45 | 0.32 | 8.00 | 0.66 | 1.32 | 2.11 | 0.57 | 2.01 | 19.41 | |
| 4 | RQ(NCs) | 9.3 | 14.8 | 3.1 | 17.2 | 42.1 | 7.1 | 47.8 | 171.0 | 483.6 | 25.7 | 596.7 | 49.2 | 88.5 | 154.2 | 39.3 | 145.6 | 1895.3 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.07 | 4.78 | 1.71 | 4.84 | 0.26 | 5.97 | 0.49 | 0.89 | 1.54 | 0.39 | 1.46 | 20.3 | |
| 5 | RQ(NCs) | 8.3 | 47.4 | 5.8 | 34.2 | 73.2 | 19.4 | 75.4 | 267.0 | 745.9 | 35.7 | 862.4 | 83.3 | 147.2 | 246.7 | 66.2 | 242.8 | 2960.8 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.73 | 0.19 | 7.54 | 2.67 | 7.46 | 0.36 | 8.62 | 0.83 | 1.47 | 2.47 | 0.66 | 2.43 | 32.66 | |
| 6 | RQ(NCs) | 7.6 | 21.1 | 4.0 | 25.0 | 61.5 | 12.6 | 58.3 | 205.2 | 515.1 | 23.8 | 505.4 | 41.7 | 90.6 | 122.3 | 31.9 | 143.8 | 1870.0 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 0.62 | 0.13 | 5.83 | 2.05 | 5.15 | 0.24 | 5.05 | 0.42 | 0.91 | 1.22 | 0.32 | 1.44 | 18.69 | |
| 7 | RQ(NCs) | 5.5 | 22.7 | 4.4 | 24.9 | 171.6 | 14.5 | 229.3 | 667.0 | 668.3 | 36.1 | 735.4 | 71.8 | 126.2 | 210.2 | 58.0 | 199.0 | 3244.9 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.04 | 0.25 | 1.72 | 0.14 | 22.93 | 6.67 | 6.68 | 0.36 | 7.35 | 0.72 | 1.26 | 2.10 | 0.58 | 1.99 | 44.03 | |
| 8 | RQ(NCs) | 5.2 | 20.4 | 2.9 | 23.3 | 58.4 | 13.6 | 61.7 | 216.2 | 548.6 | 25.4 | 516.1 | 46.3 | 87.8 | 140.6 | 39.4 | 132.1 | 1937.9 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.58 | 0.14 | 6.17 | 2.16 | 5.49 | 0.25 | 5.16 | 0.46 | 0.88 | 1.41 | 0.39 | 1.32 | 21.71 | |
| 9 | RQ(NCs) | 4.7 | 21.0 | 5.1 | 24.7 | 54.7 | 11.8 | 58.4 | 211.1 | 567.4 | 29.3 | 730.9 | 64.5 | 117.2 | 197.3 | 51.3 | 192.0 | 2341.5 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.55 | 0.12 | 5.84 | 2.11 | 5.67 | 0.29 | 7.31 | 0.64 | 1.17 | 1.97 | 0.51 | 1.92 | 25.99 | |
| 10 | RQ(NCs) | 7.6 | 18.8 | 4.1 | 21.9 | 54.6 | 9.4 | 65.2 | 232.3 | 720.0 | 37.1 | 986.5 | 66.1 | 147.4 | 248.0 | 62.2 | 227.0 | 2908.1 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.04 | 0.22 | 0.55 | 0.09 | 6.52 | 2.32 | 7.20 | 0.37 | 9.86 | 0.66 | 1.47 | 2.48 | 0.62 | 2.27 | 32.12 | |
| 11 | RQ(NCs) | 4.2 | 8.2 | 4.7 | 8.4 | 14.0 | 3.7 | 12.2 | 52.1 | 240.2 | 9.0 | 339.6 | 22.3 | 65.8 | 111.2 | 26.7 | 109.2 | 1031.6 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 1.22 | 0.52 | 2.40 | 0.09 | 3.40 | 0.22 | 0.66 | 1.11 | 0.27 | 1.09 | 9.22 | |
| 12 | RQ(NCs) | 3.1 | 22.8 | 5.5 | 28.7 | 54.9 | 207.6 | 40.8 | 129.7 | 360.2 | 20.0 | 541.8 | 37.0 | 80.8 | 134.3 | 32.3 | 131.3 | 1831.0 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.29 | 0.55 | 2.08 | 4.08 | 1.30 | 3.60 | 0.20 | 5.42 | 0.37 | 0.81 | 1.34 | 0.32 | 1.31 | 17.83 | |
| 13 | RQ(NCs) | 3.1 | 19.9 | 33.3 | 46.8 | 74.7 | 30.2 | 91.5 | 371.4 | 996.3 | 35.5 | 834.1 | 94.4 | 208.6 | 266.9 | 77.4 | 275.3 | 3459.5 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.03 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.75 | 0.30 | 9.15 | 3.71 | 9.96 | 0.35 | 8.34 | 0.94 | 2.09 | 2.67 | 0.77 | 2.75 | 38.67 | |
| 14 | RQ(NCs) | 12.6 | 150.9 | 23.3 | 36.3 | 77.2 | 24.5 | 72.8 | 328.5 | 726.8 | 29.1 | 697.6 | 50.3 | 164.7 | 206.6 | 50.5 | 242.9 | 2894.9 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.13 | 1.51 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.77 | 0.24 | 7.28 | 3.29 | 7.27 | 0.29 | 6.98 | 0.50 | 1.65 | 2.07 | 0.50 | 2.43 | 32.48 | |
| 15 | RQ(NCs) | 2.9 | 16.0 | 3.7 | 17.9 | 39.3 | 7.9 | 40.6 | 142.7 | 393.5 | 18.7 | 439.3 | 32.8 | 80.1 | 127.6 | 33.5 | 119.6 | 1516.2 |
| RQ(MPCs) | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.08 | 4.06 | 1.43 | 3.94 | 0.19 | 4.39 | 0.33 | 0.80 | 1.28 | 0.34 | 1.20 | 16.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wencel, K.; Żukowski, W.; Berkowicz-Płatek, G.; Łabaj, I. Snow Cover as a Medium for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Deposition and a Measure of Atmospheric Pollution in Carpathian Village–Study Case of Zawoja, Poland. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6497. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126497
Wencel K, Żukowski W, Berkowicz-Płatek G, Łabaj I. Snow Cover as a Medium for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Deposition and a Measure of Atmospheric Pollution in Carpathian Village–Study Case of Zawoja, Poland. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6497. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126497
Chicago/Turabian StyleWencel, Kinga, Witold Żukowski, Gabriela Berkowicz-Płatek, and Igor Łabaj. 2025. "Snow Cover as a Medium for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Deposition and a Measure of Atmospheric Pollution in Carpathian Village–Study Case of Zawoja, Poland" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6497. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126497
APA StyleWencel, K., Żukowski, W., Berkowicz-Płatek, G., & Łabaj, I. (2025). Snow Cover as a Medium for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Deposition and a Measure of Atmospheric Pollution in Carpathian Village–Study Case of Zawoja, Poland. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6497. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126497








