Novel Bacterial Strains for Nonylphenol Removal in Water and Sewage Sludge: Insights from Gene Expression and Toxicity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Inoculum Preparation
2.3. 4-n-NP Biodegradation in Solution
2.4. Biodegradation Kinetics Modeling
2.5. Acute Toxicity Assessments
2.6. 4-n-NP Mineralization in Solution
2.7. 4-n-NP Mineralization in Sewage Sludge Slurry
2.8. DNA Extraction and Genome Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.9. Analysis of cotA and mhqO Gene Expression in B. safensis CN12 in the Presence of NP
2.9.1. RNA Extraction, DNase Treatment, and cDNA Synthesis
2.9.2. qPCR Primer Design and qPCR Test
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
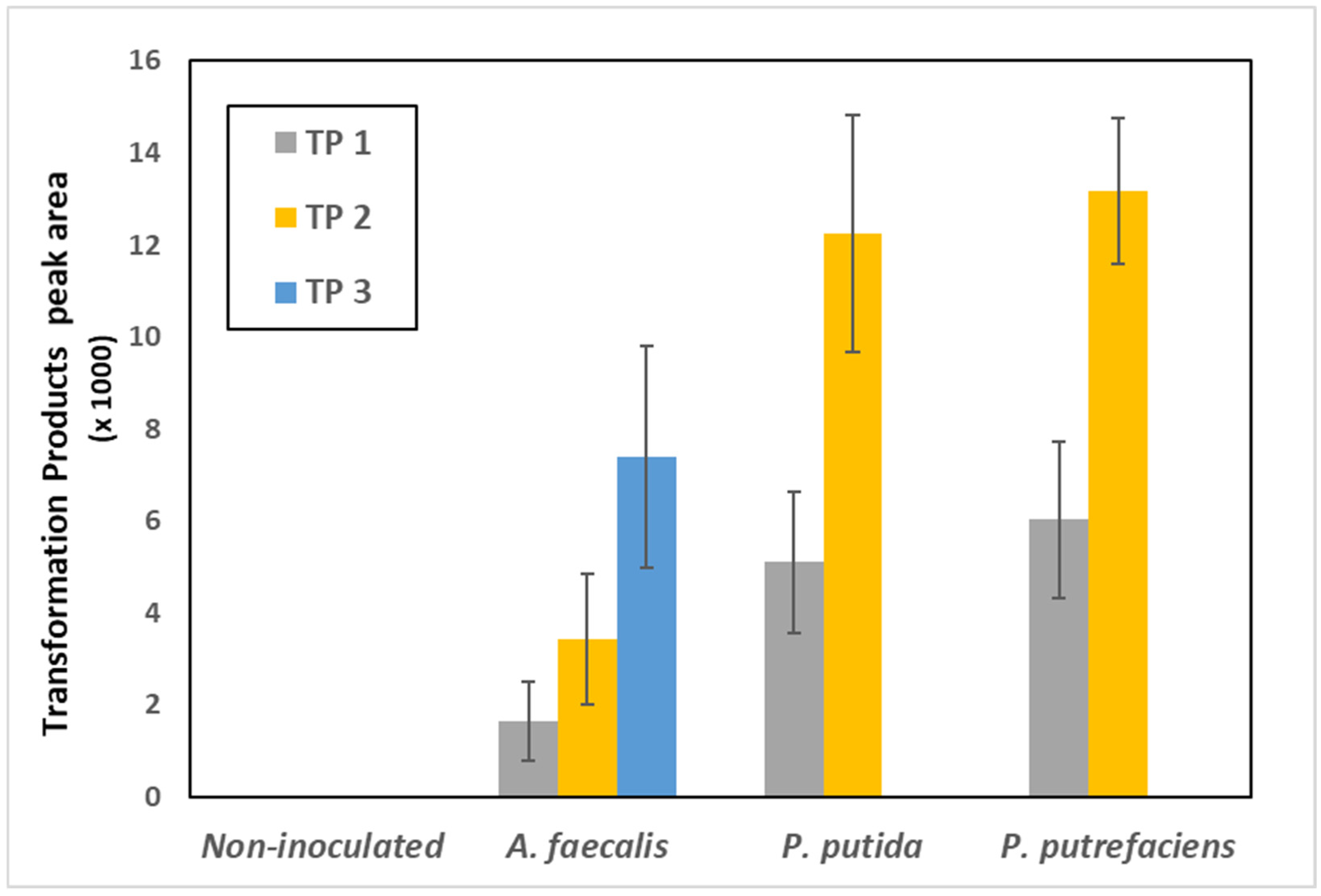
3.1. 4-n-NP Degradation in Solution by Various Bacterial Strains
3.2. Ecotoxicity Studies
3.3. In Silico Analysis of Bacillus safensis CN12 Genome Sequence
3.4. Analysis of cotA and mhqO Gene Expression in B. safensis CN12 in the Presence of 4-n-NP
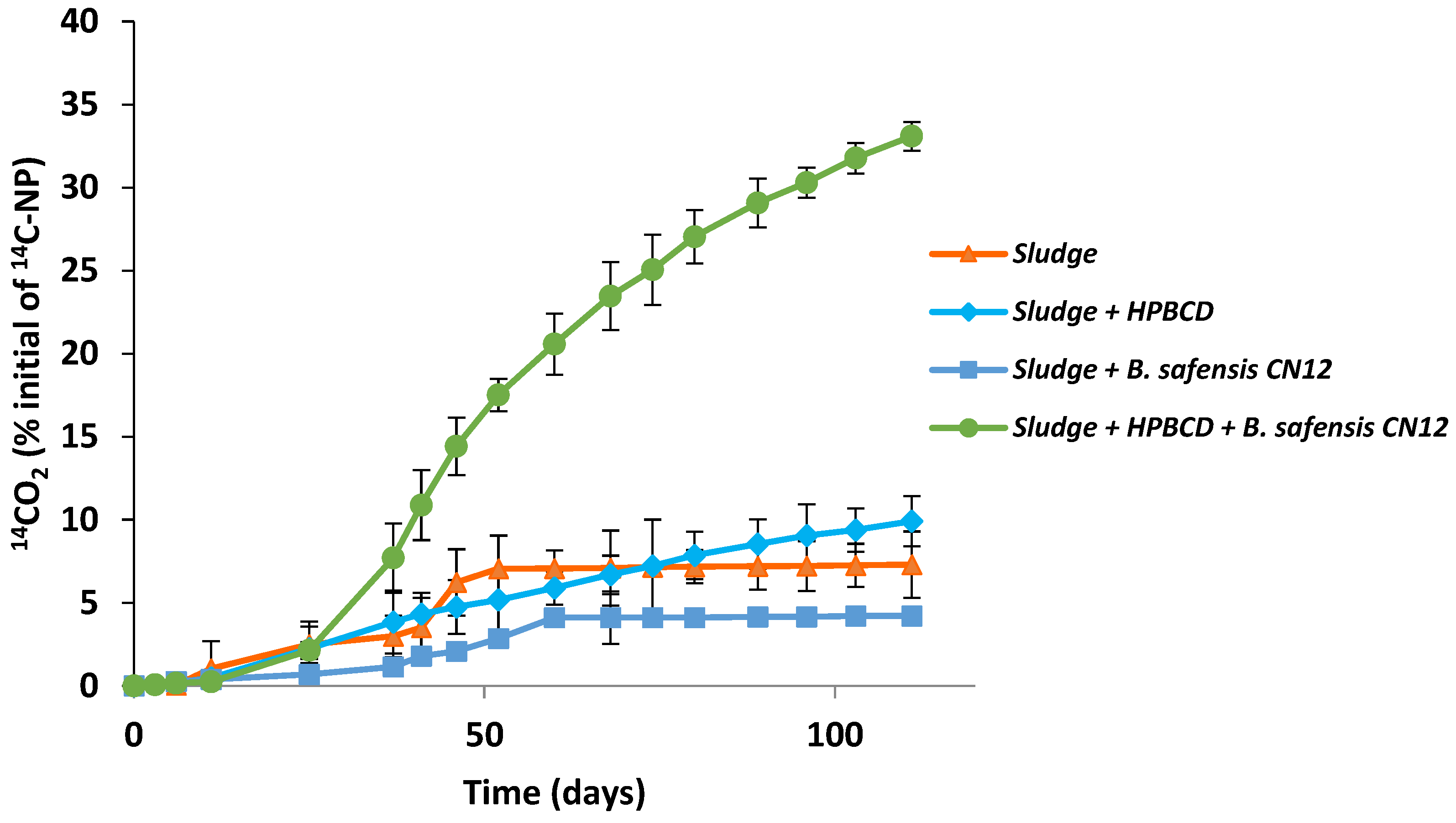
3.5. 4-n-NP Mineralization by Bacillus safensis CN12
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhandari, G.; Bagheri, A.R.; Bhatt, P.; Bilal, M. Occurrence, potential ecological risks, and degradation of endocrine disrupter, nonylphenol, from the aqueous environment. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Feng, C.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liao, W.; Bai, Y. Nonylphenol occurrence, distribution, toxicity and analytical methods in freshwater. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Qi, Z.; Gao, J.; Huang, K.; Li, M.; Springael, D.; Zhang, X. Nonylphenol ethoxylates biodegradation increases estrogenicity of textile wastewater in biological treatment systems. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Ning, X.; Lin, M.; Lai, X. Isomer-specific analysis of nonylphenol and their transformation products in environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 90125, 165982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araujo, F.; Bauerfeldt, G.; Cid, Y. Nonylphenol: Properties, legislation, toxicity and determination. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 1903–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Han, H.; Park, T.; Park, J.; Kim, Y. New findings on the occurrence, removal, and risk assessment of nonylphenol and octylphenol in industrial wastewater treatment plants in Korea. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 4615, 132615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lan, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, W.; Zhu, B.; Sun, D.; Duan, S. Levels of NP and BPA in the Pearl River estuary, China: Fluctuations with country policy changes over the past 40 years. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, L.; Deng, W.; Zhang, C.; Liao, X.; Huang, H.; Han, C.; Hu, Y.; Wu, M. The degradation of a nonylphenol isomer in water and soil of typical sewage irrigation area in China. Water Environ. J. 2024, 38, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Ji, R. Biodegradation of phenolic pollutants and bioaugmentation strategies: A review of current knowledge and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 133906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Cheong, D.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y. Analysis of endocrine disrupting nonylphenols in foods by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Foods 2023, 12, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rang, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, C. The mechanisms of learning and memory impairment caused by nonylphenol: A narrative review based on in vivo and in vitro studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 5530–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Lu, D.; Yu, L.; Ye, Z.; Duan, H.; Narbad, A.; Zhao, J.; Zhai, Q.; Tian, F.; Chen, W. Nonylphenol induces depressive behavior in rats and affects gut microbiota: A dose-dependent effect. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 3441, 123357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringbeck, B.; Bury, D.; Ikeda-Araki, A.; Bamai, Y.; Ketema, R.; Miyashita, C.; Brüning, T.; Kishi, R.; Koch, H. Nonylphenol exposure in 7-year-old Japanese children between 2012 and 2017– Estimation of daily intakes based on novel urinary metabolites. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. European Union Risk Assessment Report: 4-Nonylphenol (Branched) and Nonylphenol: EUR 20387 EN.; European Commission—Joint Research Centre Institute for Health and Consumer Protection European Chemicals Bureau: Ispra, Italy, 2002. Available online: https://www.bfr.bund.de/cm/343/4_nonylphenol_und_nonylphenol.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Directive 2003/53/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 June 2003 Amending for the 26th Time Council Directive 76/769/EEC Relating to Restrictions on the Marketing and Use of Certain Dangerous Substances and Preparations (Nonylphenol, Nonylphenol Ethoxylate and Cement). Official Journal L 178, 17/07/2003 P. 0024–0027. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2003/53/oj/eng (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- The European Parliament and Council of the European Union. DIRECTIVE 2008/105/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 16 December 2008 on Environmental Quality Standards in the Field of Water Policy, Amending and Subsequently Repealing Council Directives 82/176/EEC, 83/513/EEC, 84/156/EEC, 84/491/EEC, 86/280/EEC and Amending Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council: DIRECTIVE 2008/105/EC; The European Parliament and Council of the European Union: Luxemburg, 2008.
- U.S. EPA. Nonylphenol (NP) and Nonylphenol Ethoxylates (NPEs) Action Plan: [RIN 2070-ZA09]. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2010. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/nonylphenol-np-and-nonylphenol-ethoxylates-npes (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Factors Handbook: 2011 Edition: EPA/600/R-09/052F; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/efp/recordisplay.cfm?deid=236252 (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Hung, C.; Chen, C.; Huang, C.; Shiung Lam, S.; Yang, Y.; Dong, C. Performance and bacterial community dynamics of lignin-based biochar-coupled calcium peroxide pretreatment of waste-activated sludge for the removal of 4-nonylphenol. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Wang, T.; Niu, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T. Biodegradation of nonylphenol during aerobic composting of sewage sludge under two intermittent aeration treatments in a full-scale plant. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Urano, N.; Ushio, H.; Satomi, M.; Kimura, S. Sphingomonas cloacae sp nov., a nonylphenol-degrading bacterium isolated from wastewater of a sewage-treatment plant in Tokyo. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, F.; Giger, W.; Guenther, K.; Kohler, H. Differential degradation of nonylphenol isomers by Sphingomonas xenophaga Bayram. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, F.; Heidlberger, A.; Rentsch, D.; Giger, W.; Guenther, K.; Kohler, H. A novel metabolic pathway for degradation of 4-nonylphenol environmental contaminants by Sphingomonas xenophaga Bayram: Ipso-hydroxylation and intramolecular rearrangement. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15526–15533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvini, P.; Hollender, J.; Ji, R.; Schumacher, S.; Prell, J.; Hommes, G.; Priefer, U.; Vinken, R.; Schäer, A. The degradation of quaternary nonylphenol isomers by Sphingomonas sp. strain TTNP3 involves a type II ipso-substitution mechanism. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 70, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ji, R.; Vinken, R.; Hommes, G.; Bertmer, M.; Schäffer, A. Role of dissolved humic acids in the biodegradation of a single isomer of nonylphenol by Sphingomonas sp. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolvenbach, B.; Corvini, P. The degradation of alkylphenols by Sphingomonas sp. strain TTNP3—A review on seven years of research. New Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.; Guieysse, B.; Delgado, O.; Mattiasson, B. Aerobic biodegradation of nonylphenol by cold-adapted bacteria. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Yu, C.; Chang, B. Biodegradation of nonylphenol in river sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, D.; Michelles, A.; Pierini, M.; Bogialli, S.; Fava, F.; Barberio, C. Selection and characterization of aerobic bacteria capable of degrading commercial mixtures of low ethoxylated nonylphenols. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, W.; Hori, Y.; Nishimura, S.; Takagi, A.; Kikuchi, M.; Sawai, J. Bacterial degradation and reduction in the estrogen activity of 4-nonylphenol. Biocontrol Sci. 2012, 17, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.; Abuduaini, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y. Nonylphenol biodegradation characterizations and bacterial composition analysis of an effective consortium NP-M2. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Xie, S.; Liu, Y. Nonylphenol biodegradation in river sediment and associated shifts in community structures of bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 106, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Chiang, F.; Yuan, S. Biodegradation of nonylphenol in sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, B.; Liu, C.; Yuan, S.; Cheng, C.; Ding, W. Biodegradation of nonylphenol in mangrove sediment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2008, 61, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y. Purification and characterization of a nonylphenol (NP)-degrading enzyme from Bacillus cereus. Frankland. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 19, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Moreno, A.; Aguilar-Romero, I.; Rubio-Bellido, M.; Madrid, F.; Villaverde, J.; Santos, J.; Alonso, E.; Morillo, E. Novel nonylphenol-degrading bacterial strains isolated from sewage sludge: Application in bioremediation of sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 84715, 157647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillo, E.; Madrid, F.; Lara-Moreno, A.; Villaverde, J. Soil bioremediation by cyclodextrins. A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 59115, 119943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Moreno, A.; Merchán, F.; Morillo, E.; Zampolli, J.; Di Gennaro, P.; Villaverde, J. Genome analysis for the identification of genes involved in phenanthrene biodegradation pathway in Stenotrophomonas indicatrix CPHE1. Phenanthrene mineralization in soils assisted by integrated approaches. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 112023, 1158177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pacheco, I.; Salinas-Salazar, C.; Silva-Núñez, A.; Rodas-Zuluaga, L.; Donoso-Quezada, J.; Ayala-Mar, S.; Barceló, D.; Iqbal, H.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Removal and biotransformation of 4-nonylphenol by Arthrospira maxima and Chlorella vulgaris consortium. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FOCUS, 2006. Guidance document on estimating persistence and degradation kinetics from environmental fate studies on pesticides in EU Registration. Report of the FOCUS Work Group on Degradation Kinetics, EC Document Reference Sanco/10058/2005 version 2.0 (434 pp.). Available online: https://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/projects/degradation-kinetics (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- ISO 11348-3; Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio Fischeri (Luminescent Bacteria Test) Part 3: Method Using Freeze-Dried Bacteria. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/40518.html (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes de novo assembler. Curr. Prot. Bioinf. 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST server: Rapid Annotations using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, D.; Santos, C.; Pacheco, L. Bacterial reference genes for gene expression studies by RT-qPCR: Survey and analysis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 108, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWeert, J.; Viñas, M.; Grotenhuis, T.; Rijnaarts, H.; Langenhoff, A. Degradation of 4-n-nonylphenol under nitrate reducing conditions. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemur, R.; Cunha dos Santos, S.; Ouellette, J.; Juteau, P.; Lépine, F.; Déziel, E. Biodegradation of endocrine disruptors in solid-liquid two-phase partitioning systems by enrichment cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4701–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persoone, G.; Marsalek, B.; Blinova, I.; Törökne, A.; Zarina, D.; Manusadzianas, L.; Nalecz-Jawecki, G.; Tofan, L.; Stepanova, N.; Tothova, L.; et al. A practical and user-friendly toxicity classification system with microbiotests for natural waters and wastewaters. Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ji, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, M.; Cao, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Bi, H.; Guan, G.; et al. Nonylphenol and its derivatives: Environmental distribution, treatment strategy, management and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.; Guieysse, B.; Jefferson, B.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J. Nonylphenol in the environment: A critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, A.; Kong, X.; Zhao, B.; Li, H.; Yue, X. Efficient elimination of nonylphenol and 4-tert-octylphenol by weak electrical stimulated anaerobic microbial processes. Chemosphere 2023, 320, 138085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, D.; Vujaklija, D.; Davies, J. Novel pathway of salicylate degradation by Streptomyces sp. strain WA46. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo, F.; Chávez, F.; Jerez, C. Motility and chemotaxis of Pseudomonas sp. B4 towards polychlorobiphenyls and chlorobenzoates. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sei, K.; Inoue, D.; Wada, K.; Mori, K.; Ike, M.; Kohno, T.; Fujita, M. Monitoring behaviour of catabolic genes and change of microbial community structures in seawater microcosms during aromatic compound degradation. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4405–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sei, K.; Toyama, T.; Ike, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, M.; Kamagata, Y. Changes of catabolic genes and microbial community structures during biodegradation of nonylphenol ethoxylates and nonylphenol in natural water microcosms. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, N.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, S. Nonylphenol biodegradation, functional gene abundance and bacterial community in bioaugmented sediment: Effect of external carbon source. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12083–12091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Dai, Y.; Xie, S. Variation of nonylphenol-degrading gene abundance and bacterial community structure in bioaugmented sediment microcosm. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 2342–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeo, M.; Akizuki, J.; Kawasaki, A.; Negoro, S. Degradation potential of the nonylphenol monooxygenase of Sphingomonas sp. NP5 for bisphenols and their structural analogs. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.; Li, L. Complete degradation of bisphenol A and nonylphenol by a composite of biogenic manganese oxides and Escherichia coli cells with surface-displayed multicopper oxidase CotA. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Mao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Hao, K.; He, P.; He, Y. Genome sequencing of Bacillus subtilis strain XF-1 with high efficiency in the suppression of Plasmodiophora brassicae. Genome Announc. 2013, 4, e0006613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.; Lipman, D. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampolli, J.; Di Canito, A.; Cappelletti, M.; Collina, E.; Lasagni, M.; Di Gennaro, P. Biodegradation of naphthenic acids: Identification of Rhodococcus opacus R7 genes as molecular markers for environmental monitoring and their application in slurry microcosms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 2675–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulestia, M.; Flores, A.; Mangas, E.; Pérez-Pulido, A.; Santero, E.; Camacho, E. Isolation and genomic characterization of the ibuprofen-degrading bacterium Sphingomonas strain MPO218. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, K.; Adachi, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Takagi, M. Cloning and sequencing of a novel meta-cleavage dioxygenase gene whose product is involved in degradation of g-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 6712–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, R.; Kamakura, M.; Miyauchi, K.; Fukuda, M.; Ohtsubo, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Nagata, Y. Identification of genes involved in the downstream degradation pathway of g-hexachlorocyclohexane in Sphingomonas paucimobilis UT26. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, F.; Cyris, M.; Jonkers, N.; Giger, W.; Guenther, K.; Kohler, H. Elucidation of the ipso-substitution mechanism for side-chain cleavage of quaternary 4-nonylphenols and 4-t-butoxyphenol in Sphingobium xenophagum Bayram. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3320–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D. Different pathways for 4-n-nonylphenol biodegradation by two Aspergillus strains derived from estuary sediment: Evidence from metabolites determination and key-gene identification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 359, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, N.; Hsieh, H.; Lin, Y.; Huang, S. Analysis of bacterial degradation pathways for long-chain alkylphenols involving phenol hydroxylase, alkylphenol monooxygenase and catechol dioxygenase genes. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4232–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Krumins, V.; Fennell, D.; Kerkhof, L.; Häggblom, M. Anaerobic Degradation of Aromatic Compounds. In Manual of Environmental Microbiology; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 5.1.3-1–5.1.3-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, E.; Sánchez-Trujillo, M.; Villaverde, J.; Madrid, F.; Undabeytia, T. Effect of contact time and the use of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin in the removal of fluorene and fluoranthene from contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, F.; Florido, M.; Rubio-Bellido, M.; Villaverde, J.; Morillo, E. Dissipation of a mix of priority PAHs in soils by using availability enhancers. Effect of aging and pollutant interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 8371, 155744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, H. β-Cyclodextrin enhanced bioavailability of petroleum hydrocarbons in industrially contaminated soil: A phytoremediation field study. Int. J. Phytorem. 2024, 26, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Trujillo, M.; Lacorte, S.; Villaverde, J.; Barata, C.; Morillo, E. Decontamination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and nonylphenol from sewage sludge using hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and evaluation of the toxicity of leachates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, F.; Rubio-Bellido, M.; Morillo, E. Extraction of nonylphenol, pyrene and phenanthrene from sewage sludge and composted biosolids by cyclodextrins and rhamnolipids. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Nie, M.; Diwu, Z.; Wang, L.; Nie, H.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, B. Simultaneous biodegradation of phenolics and petroleum hydrocarbons from semi-coking wastewater: Construction of bacterial consortium and their metabolic division of labor. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittich, R.M.; Haïdour, A.; Aguilar-Romero, I.; de la Torre-Zúñiga, J. Biodegradation of microtoxic phenylpropanoids (phenylpropanoic acid and ibuprofen) by bacteria and the relevance for their removal from wastewater treatment plants. Genes 2023, 14, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
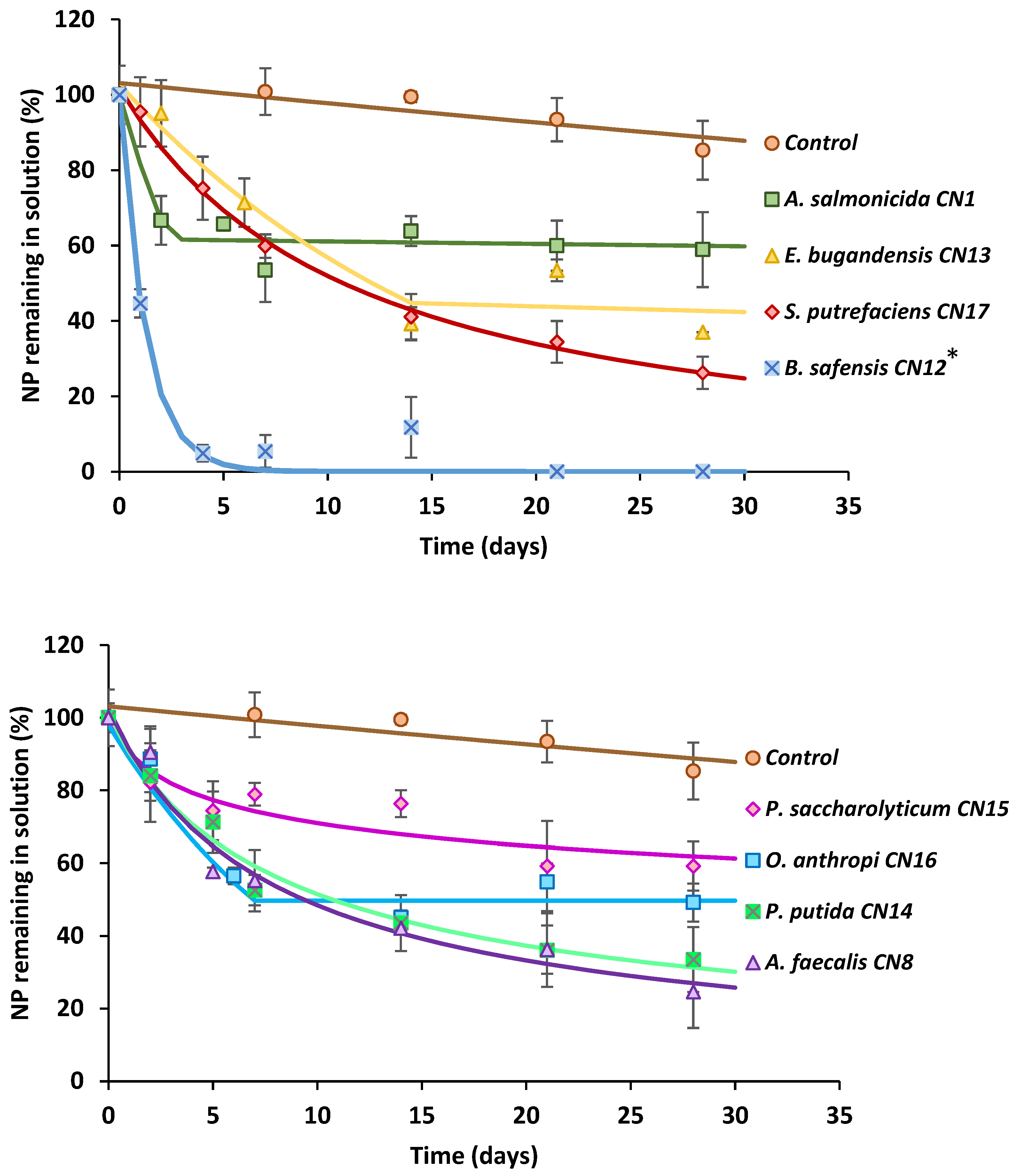

| Kinetic Model | K1 (d−1) | K2 (d−1) | tb (d) | α (d−1) | β (d−1) | DT50 (days) | Extent of Degradation (%) | R2 | χ2 Errscaled | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | SFO | 0.005 | - | - | - | - | 129 | 14.7 | 0.767 | 2.27 |
| B. safensis CN12 * | SFO | 0.790 | - | - | - | - | 0.90 | 100 | 0.986 | 5.39 |
| A. faecalis CN8 | FOMC | - | - | - | 0.785 | 6.265 | 8.9 | 75.4 | 0.969 | 3.91 |
| S. putrefaciens CN17 | FOMC | - | - | 1.182 | 13.02 | 10.4 | 73.8 | 0.997 | 1.36 | |
| P. putida CN14 | FOMC | - | - | - | 0.643 | 5.404 | 10.5 | 66.5 | 0.980 | 2.86 |
| E. bugandensis CN13 | HS | 0.059 | 0.003 | 14.0 | - | - | 11.7 | 63.0 | 0.952 | 0.17 |
| O. anthropi CN16 | HS | 0.093 | 0.000 | 7.7 | - | - | 7.4 | 50.8 | 0.973 | 0.02 |
| A. salmonicida CN1 | HS | 0.202 | 0.001 | 2.4 | - | - | 203 | 41.1 | 0.936 | 0.78 |
| P. saccharolyticum CN15 | FOMC | - | - | - | 0.142 | 1.031 | 136 | 40.8 | 0.879 | 3.89 |
| Bacterial Strain | 4-n-NP Remaining (mg L−1) | TU | Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 10.0 | 5.5 a | Acute toxicity |
| B. safensis CN12 * | 0.00 | 49.4 b | High acute toxicity |
| A. faecalis CN8 | 2.46 | 17.6 ab | High acute toxicity |
| S. putrefaciens CN17 | 2.62 | 19.6 ab | High acute toxicity |
| P. putida CN14 | 3.35 | 28.6 ab | High acute toxicity |
| E. bugandensis CN13 | 3.70 | 31.6 ab | High acute toxicity |
| O. anthropi CN16 | 4.92 | 10.9 ab | High acute toxicity |
| A. salmonicida CN1 | 5.89 | 32.3 ab | High acute toxicity |
| P. saccharolyticum CN15 | 5.92 | 9.20 a | Acute toxicity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lara-Moreno, A.; Aguilar-Romero, I.; Madrid, F.; Villaverde, J.; Carlier, J.D.; Santos, J.L.; Alonso, E.; Morillo, E. Novel Bacterial Strains for Nonylphenol Removal in Water and Sewage Sludge: Insights from Gene Expression and Toxicity. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6408. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126408
Lara-Moreno A, Aguilar-Romero I, Madrid F, Villaverde J, Carlier JD, Santos JL, Alonso E, Morillo E. Novel Bacterial Strains for Nonylphenol Removal in Water and Sewage Sludge: Insights from Gene Expression and Toxicity. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(12):6408. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126408
Chicago/Turabian StyleLara-Moreno, Alba, Inés Aguilar-Romero, Fernando Madrid, Jaime Villaverde, Jorge D. Carlier, Juan Luís Santos, Esteban Alonso, and Esmeralda Morillo. 2025. "Novel Bacterial Strains for Nonylphenol Removal in Water and Sewage Sludge: Insights from Gene Expression and Toxicity" Applied Sciences 15, no. 12: 6408. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126408
APA StyleLara-Moreno, A., Aguilar-Romero, I., Madrid, F., Villaverde, J., Carlier, J. D., Santos, J. L., Alonso, E., & Morillo, E. (2025). Novel Bacterial Strains for Nonylphenol Removal in Water and Sewage Sludge: Insights from Gene Expression and Toxicity. Applied Sciences, 15(12), 6408. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15126408







