Design of a Dual-Path Speech Enhancement Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Backgrounds
3. Proposed Multi-Branch SE Model
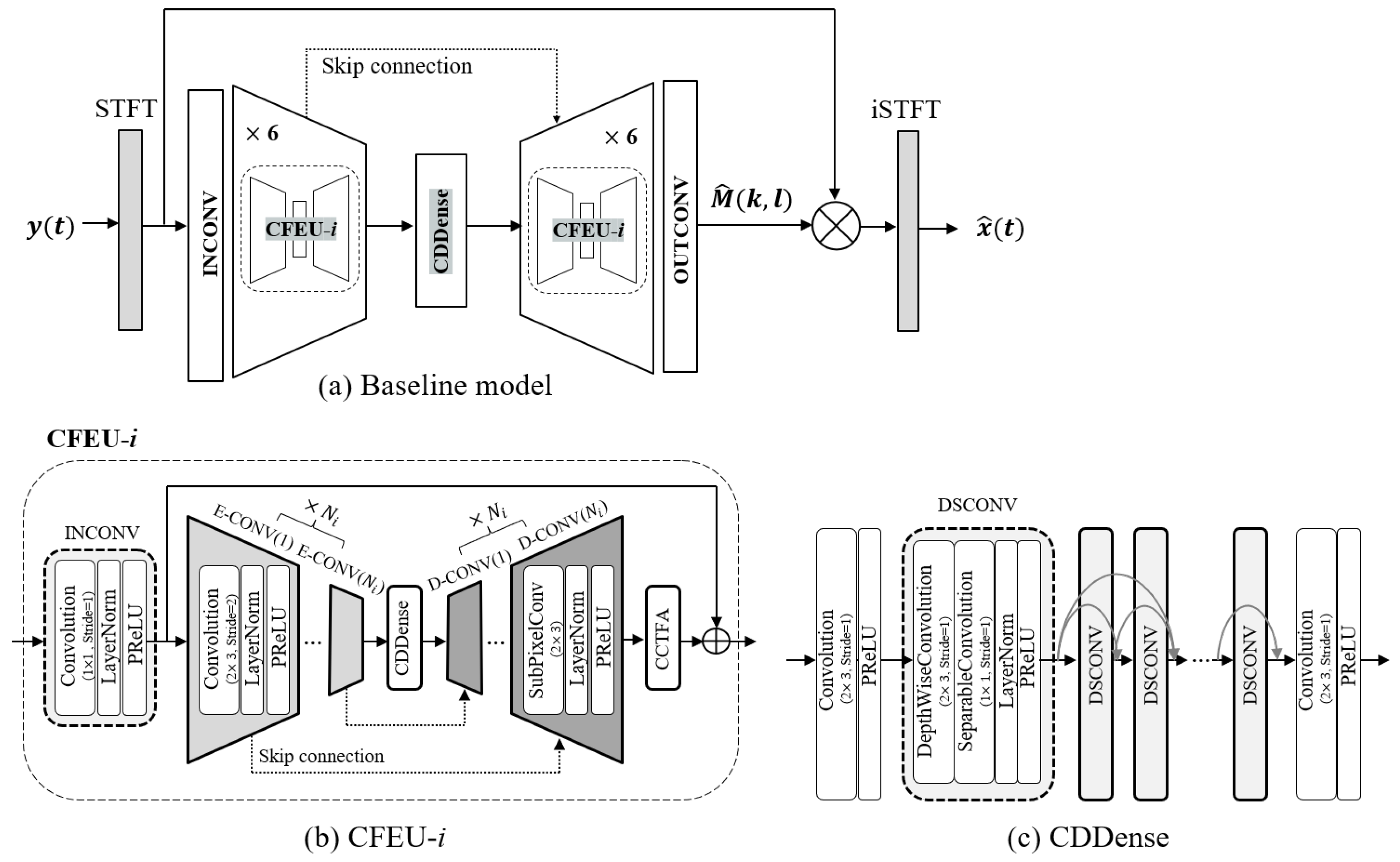
3.1. Baseline Model
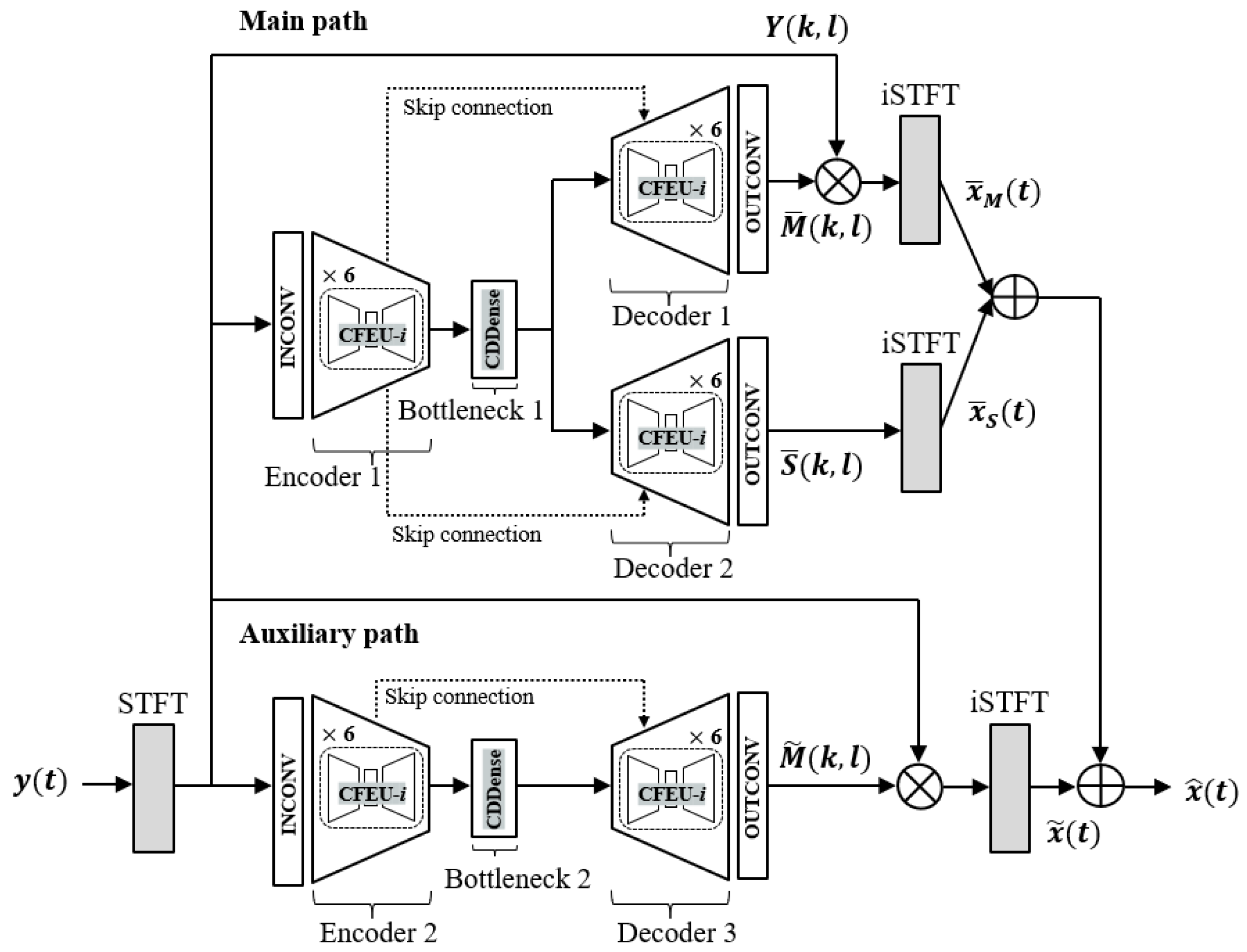
3.2. Overall Architecture
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
5. Results and Discussion
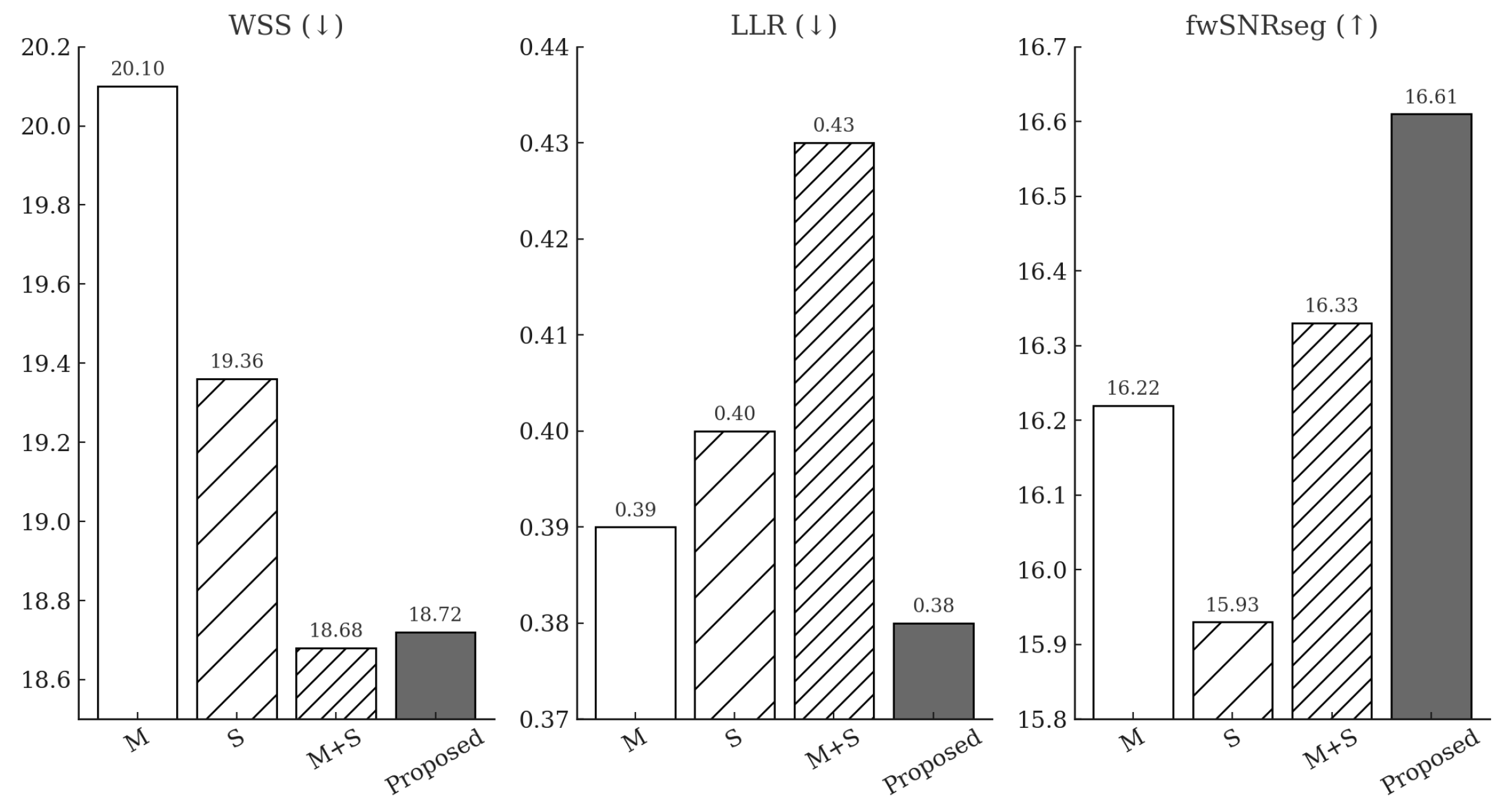
5.1. Ablation Test
5.2. Comparisons with Recently Proposed SE Models
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SE | Speech enhancement |
| DNN | Deep neural network |
| ASR | Automatic speech recognition |
| CFEU | Complex feature extraction unit |
| CCTFA | Complex causal time-frequency attention |
| CDDense | Complex dilated dense network |
| DSCONV | Depthwise-separable convolution |
| FA | Frequency attention |
| TA | Time attention |
| STFT | Short-time Fourier transform |
| VBD | VoiceBank + DEMAND |
| WB-PESQ | Wideband perceptual evaluation of speech quality |
| MOS | Mean opinion score |
| CSIG | Composite metric for signal distortion |
| CBAK | Composite metric for background noise |
| COVL | Composite metric for overall quality |
| STOI | Short-time objective intelligibility |
| SNRseg | Segmental signal-to-noise ratio |
| WER | Word error ratio |
| dB | Decibel |
| M | A single-path masking-based model |
| S | A single-path mapping-based model |
| M + S | A single-path two-branch model (integrates M and M + S) |
| WSS | Weighted spectral slope |
| LLR | Log-likelihood ratio |
| fwSNRseg | Frequency-weighted segmental SNR |
References
- Ochiai, T.; Watanabe, S.; Hori, T.; Hershey, J. Multichannel end-to-end speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; Volume 70, pp. 2632–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sakamoto, S.; Hongo, S.; Akagi, M.; Suzuki, Y. Two-stage binaural speech enhancement with Wiener filter for high-quality speech communication. Speech Commun. 2011, 53, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamin, M.; Sen, A.A. Improving Privacy and Security of User Data in Location Based Services. Int. J. Ambient. Comput. Intell. (IJACI) 2018, 9, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Ashour, A.S.; Shi, F.; Fong, S.J.; Tavares, J.M.R.S. Medical Cyber-Physical Systems: A Survey. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Chaki, J.; Padhy, N.; Dey, N. Fundamentals, Present and Future Perspectives of Speech Enhancement. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2021, 24, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ephraim, Y.; Malah, D. Speech enhancement using a minimum-mean square error short-time spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1984, 32, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousheng, X.; Jianwen, H. Speech enhancement based on combination of wiener filter and subspace filter. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing, Shanghai, China, 7–9 July 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 459–463. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Du, J.; Dai, L.R.; Lee, C.H. A regression approach to speech enhancement based on deep neural networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2014, 23, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weninger, F.; Erdogan, H.; Watanabe, S.; Vincent, E.; Le Roux, J.; Hershey, J.R.; Schuller, B. Speech enhancement with LSTM recurrent neural networks and its application to noise-robust ASR. In Proceedings of the Latent Variable Analysis and Signal Separation: 12th International Conference, LVA/ICA 2015, Liberec, Czech Republic, 25–28 August 2015; Proceedings 12. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, J. Supervised Speech Separation Based on Deep Learning: An Overview. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2018, 26, 1702–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuthakki, R.; Masanta, P.; Yukta, T.N. A Literature Survey on Speech Enhancement Based on Deep Neural Network Technique. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Communications and Cyber Physical Engineering (ICCCE 2021), Hyderabad, India, 9–10 April 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lv, S.; Xing, M.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Xie, L. DCCRN: Deep complex convolution recurrent network for phase-aware speech enhancement. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00264. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Abdulatif, S.; Yang, B. CMGAN: Conformer-based Metric GAN for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2022, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 18–22 September 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, H.G. Two-Stage Refinement of Magnitude and Complex Spectra for Real-Time Speech Enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 2188–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Rao, W.; Yan, X.; Fu, Y.; Lv, S.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, L.; Shang, S. TEA-PSE: Tencent-Ethereal-Audio-Lab Personalized Speech Enhancement System for ICASSP 2022 DNS Challenge. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 9291–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhuang, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, M. FB-MSTCN: A Full-Band Single-Channel Speech Enhancement Method Based on Multi-Scale Temporal Convolutional Network. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 9276–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Glance and gaze: A collaborative learning framework for single-channel speech enhancement. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 187, 108499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, D.; Lv, S.; Jv, Y.; Xie, L. Uformer: A Unet Based Dilated Complex & Real Dual-Path Conformer Network for Simultaneous Speech Enhancement and Dereverberation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 7417–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, S.W.; Park, Y. Causal Speech Enhancement Based on a Two-Branch Nested U-Net Architecture Using Self-Supervised Speech Embeddings. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2025—2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Hyderabad, India, 6–11 April 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, R.; Saabas, A.; Naderi, B.; Ristea, N.C.; Braun, S.; Branets, S. ICASSP 2023 Speech Signal Improvement Challenge. IEEE Open J. Signal Process. 2024, 5, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Dehghan, M.; Zaiane, O.R.; Jagersand, M. U2-Net: Going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 106, 107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, S.W.; Park, Y. Monoaural Speech Enhancement Using a Nested U-Net with Two-Level Skip Connections. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2022, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 18–22 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. A Nested U-Net With Self-Attention and Dense Connectivity for Monaural Speech Enhancement. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 29, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, X.; Ni, Z.; Nicolson, A.; Ambikairajah, E.; Li, H. A Time-Frequency Attention Module for Neural Speech Enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2023, 31, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zheng, C.; Peng, R.; Li, X. On the Importance of Power Compression and Phase Estimation in Monaural Speech Dereverberation. JASA Express Lett. 2021, 1, 014401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini-Botinhao, C.; Wang, X.; Takaki, S.; Yamagishi, J. Investigating RNN-based speech enhancement methods for noise-robust Text-to-Speech. In Proceedings of the 9th ISCA Speech Synthesis Workshop, Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 13–15 September 2016; pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Rix, A.; Beerends, J.; Hollier, M.; Hekstra, A. Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)—A new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Proceedings (Cat. No.01CH37221), Salt Lake City, UT, USA,, 7–11 May 2001; Volume 2, pp. 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Loizou, P.C. Evaluation of Objective Measures for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2006, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 17–21 September 2006; pp. 1447–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Donas, J.M.; Gomez, A.M.; Gonzalez, J.A.; Peinado, A.M. A deep learning loss function based on the perceptual evaluation of the speech quality. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 1680–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Xu, T.; Brockman, G.; Mcleavey, C.; Sutskever, I. Robust Speech Recognition via Large-Scale Weak Supervision. In Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; Krause, A., Brunskill, E., Cho, K., Engelhardt, B., Sabato, S., Scarlett, J., Eds.; PMLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 202, pp. 28492–28518. [Google Scholar]
- Loizou, P.C. Speech Enhancement: Theory and Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 479–487. [Google Scholar]
- Defossez, A.; Synnaeve, G.; Adi, Y. Real time speech enhancement in the waveform domain. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.12847. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Liu, W.; Zheng, C.; Fan, C.; Li, X. Two Heads are Better Than One: A Two-Stage Complex Spectral Mapping Approach for Monaural Speech Enhancement. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2021, 29, 1829–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Tuo, D.; Wu, Z.; Kang, S.; Meng, H. FullSubNet+: Channel Attention FullSubNet with Complex Spectrograms for Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 7857–7861. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Ma, B.; Watcharasupat, K.; Gan, W. FRCRN: Boosting feature representation using frequency recurrence for monaural speech enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 9281–9285. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, A.; Xiang, W.; Zheng, C.; Lv, Z.; Wu, X. CompNet: Complementary network for single-channel speech enhancement. Neural Netw. 2023, 168, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhu, J. A Two-Stage Framework in Cross-Spectrum Domain for Real-Time Speech Enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2024—2024 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–19 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
| Model | WB-PESQ | CSIG | CBAK | COVL | STOI (%) | SNRseg | WER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noisy | 1.97 | 3.35 | 2.44 | 2.63 | 91 | 1.69 | 5.08 |
| M | 3.22 | 4.41 | 3.69 | 3.85 | 95 | 10.38 | 2.82 |
| S | 3.19 | 4.39 | 3.64 | 3.82 | 95 | 9.79 | 3.09 |
| M + S | 3.29 ↑ | 4.41 | 3.68 ↓ | 3.89 ↑ | 95 | 9.66 ↓ | 2.61 ↑ |
| Proposed | 3.33 ↑ | 4.48 ↑ | 3.75 ↑ | 3.95 ↑ | 96 ↑ | 10.44 ↑ | 2.55 ↑ |
| Model | Params. | WB-PESQ | CSIG | CBAK | COVL | STOI | SNRseg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noisy | - | 1.97 | 3.35 | 2.44 | 2.63 | 91 | 1.69 |
| DEMUCS [32] | 33.5 M | 2.93 | 4.22 | 3.25 | 3.52 | 95 | - |
| CTS-Net [33] | 4.35 M | 2.92 | 4.25 | 3.46 | 3.59 | - | - |
| GaGNet [17] | 5.94 M | 2.94 | 4.26 | 3.45 | 3.59 | - | - |
| FullSubNet+ [34] | 8.67 M | 2.88 | 3.86 | 3.42 | 3.57 | - | - |
| NUNet-TLS [22] | 2.83 M | 3.04 | 4.38 | 3.47 | 3.74 | 95 | 8.27 |
| FRCRN [35] | 6.9 M | 3.21 | 4.23 | 3.64 | 3.73 | - | - |
| CompNet [36] | 4.26 M | 2.90 | 4.16 | 3.37 | 3.53 | - | - |
| FDFNet [37] | 4.43 M | 3.05 | 4.23 | 3.55 | 3.65 | - | - |
| CNUNet-TB [19] | 2.98 M | 3.18 | 4.37 | 3.62 | 3.81 | 95 | 9.41 |
| DPCNU | 18.69 M | 3.33 | 4.48 | 3.75 | 3.95 | 96 | 10.44 |
| DPCNU(S) | 4.78 M | 3.25 | 4.47 | 3.69 | 3.89 | 95 | 10.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, S.; Park, S.W.; Park, Y. Design of a Dual-Path Speech Enhancement Model. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6358. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116358
Hwang S, Park SW, Park Y. Design of a Dual-Path Speech Enhancement Model. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):6358. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116358
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Seorim, Sung Wook Park, and Youngcheol Park. 2025. "Design of a Dual-Path Speech Enhancement Model" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 6358. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116358
APA StyleHwang, S., Park, S. W., & Park, Y. (2025). Design of a Dual-Path Speech Enhancement Model. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 6358. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116358






