Correlation of Optical Constants and Morphologies with Mueller Matrix for Micro-Rough Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Gaussian-Distributed Randomly Micro-Rough Surface Model
2.2. Simulation Method and Jones–Mueller Matrix Conversion
2.3. NSC Descriptions of Mueller Matrix Elements
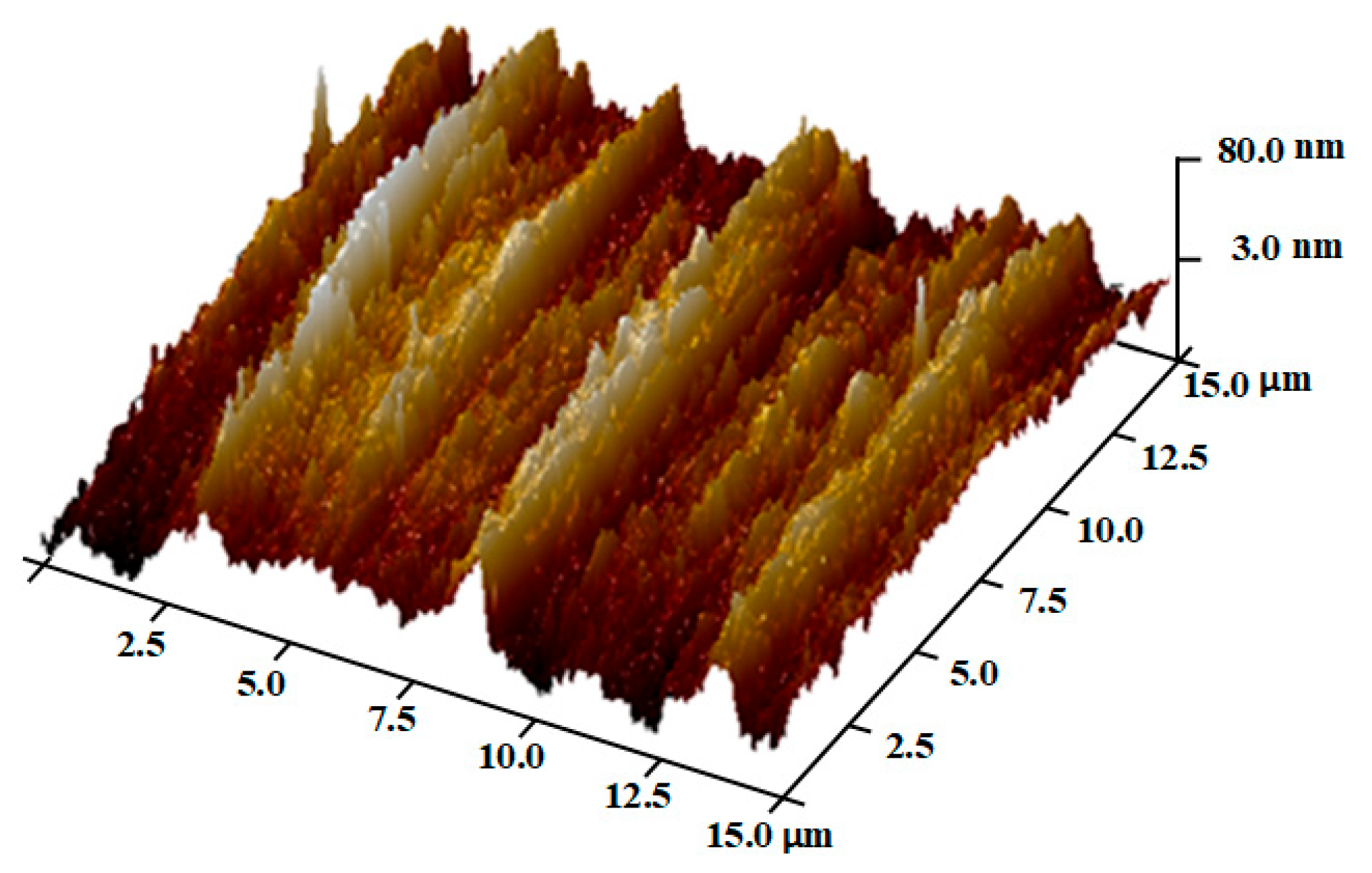
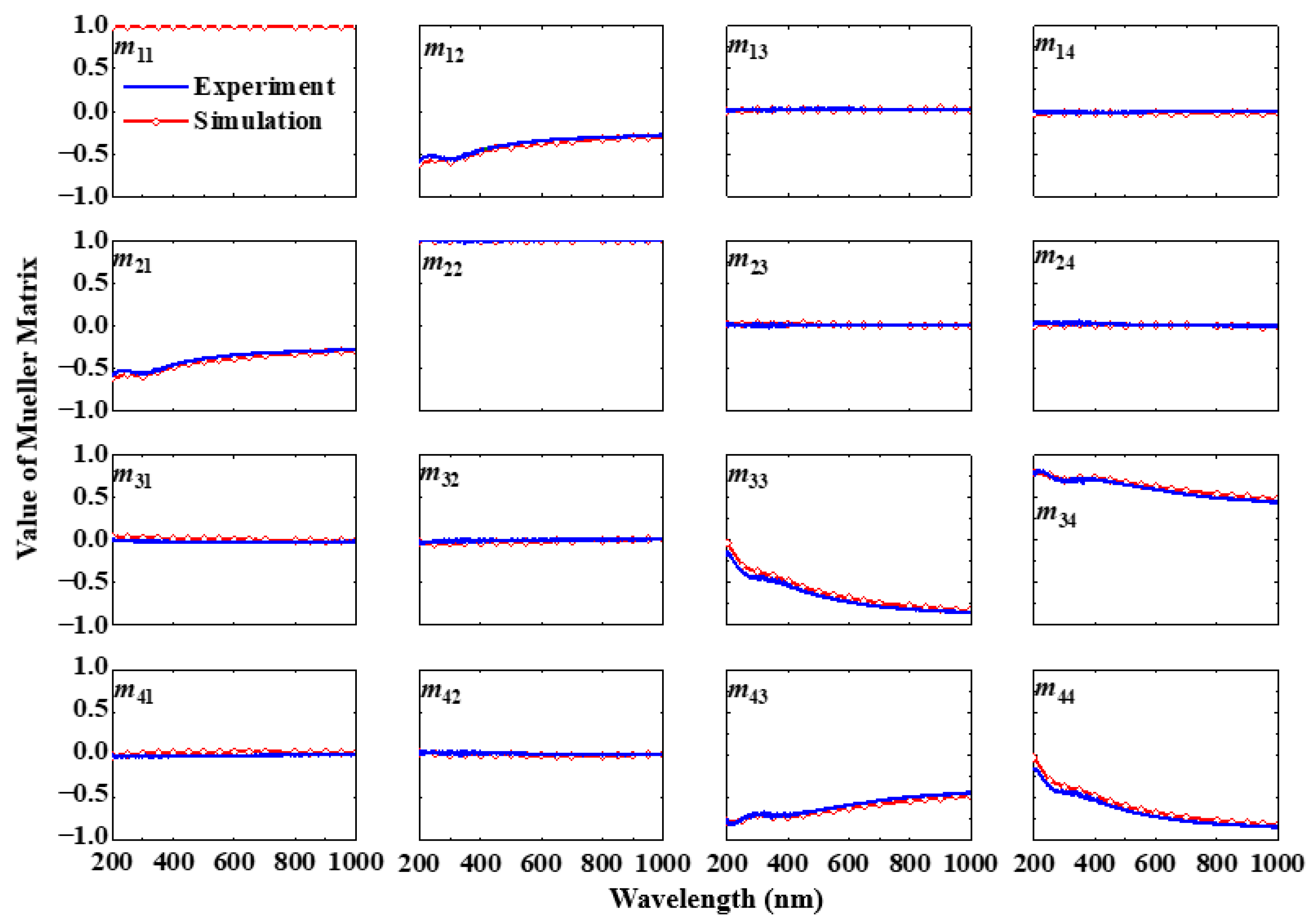
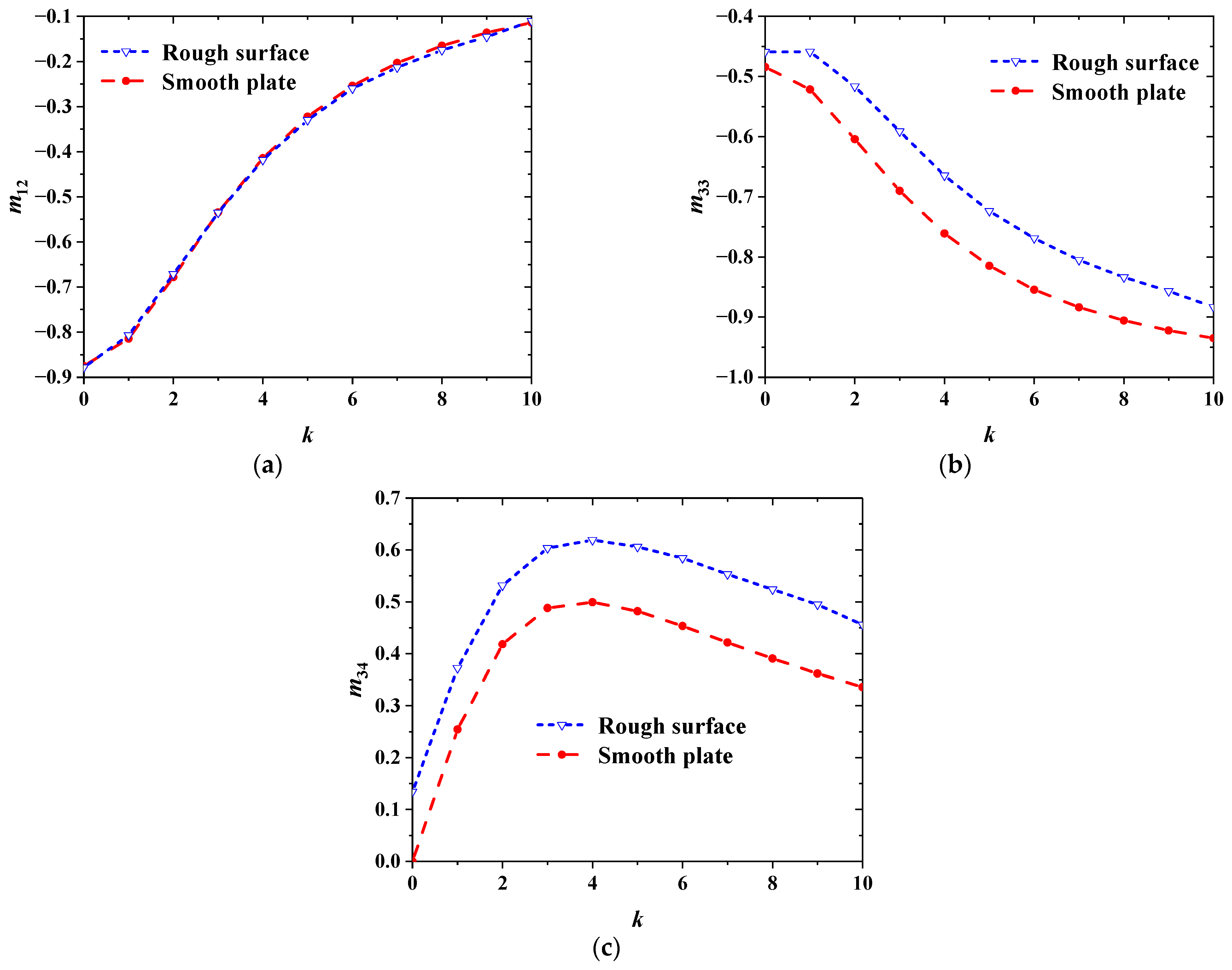
2.4. Experimental Verification of the Simulation Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Relationships Between Optical Constants and Mueller Matrix Elements
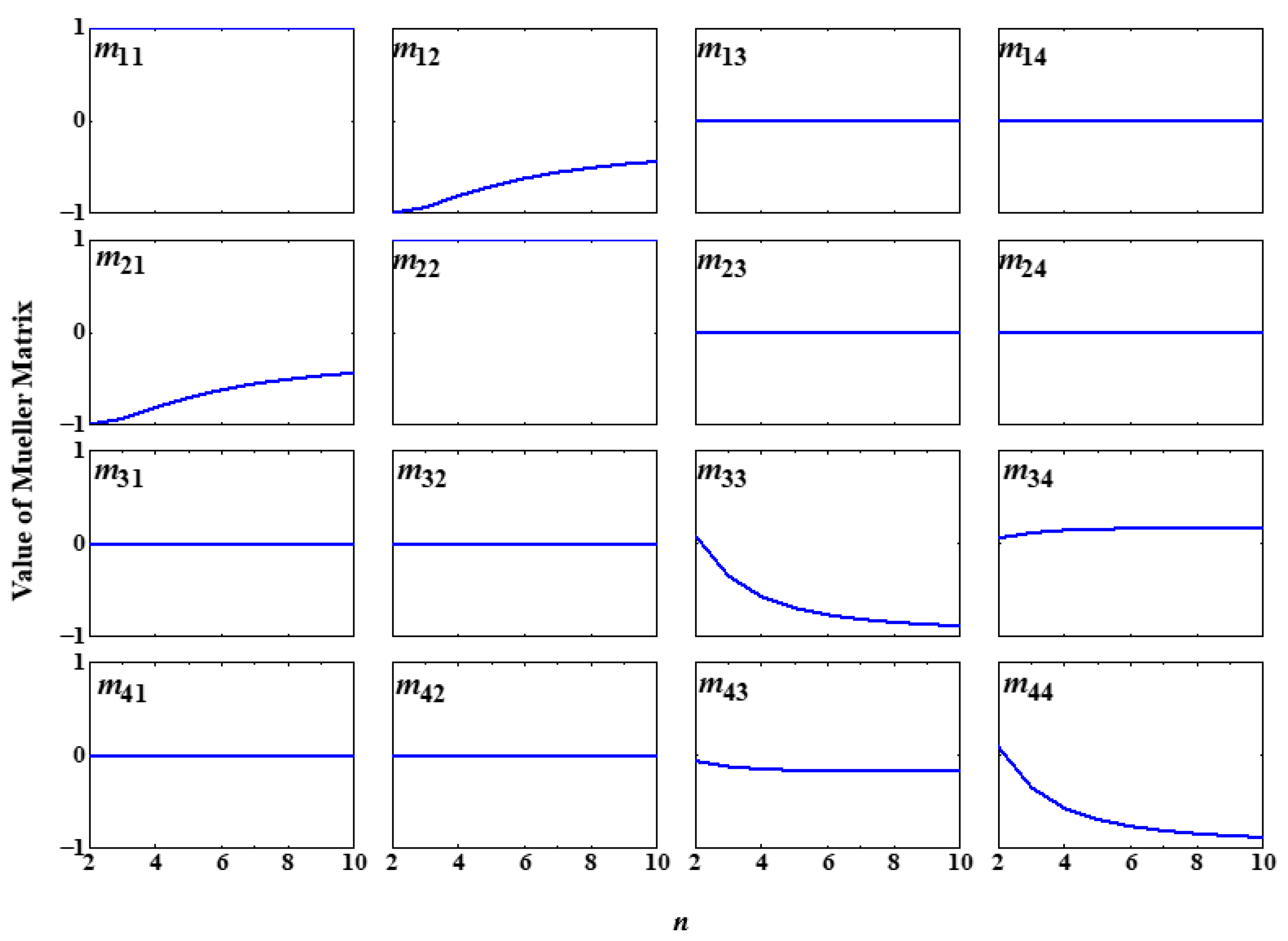
3.1.1. The Relationships Between the Refractive Index and Mueller Matrix Elements
3.1.2. The Relationships Between the Extinction Coefficient and Mueller Matrix Elements
3.2. The Relationships Between Morphological Parameters and Mueller Matrix Elements
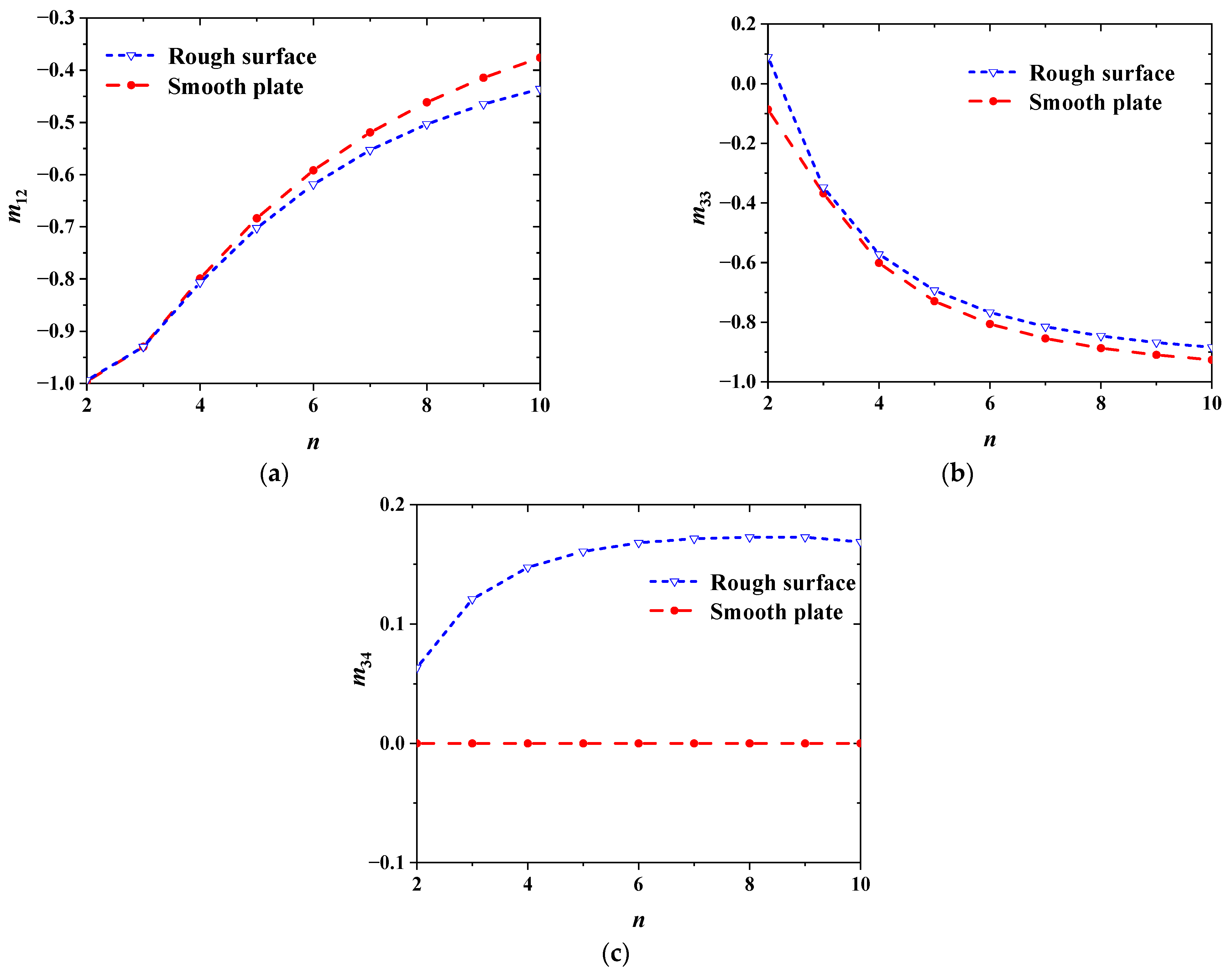
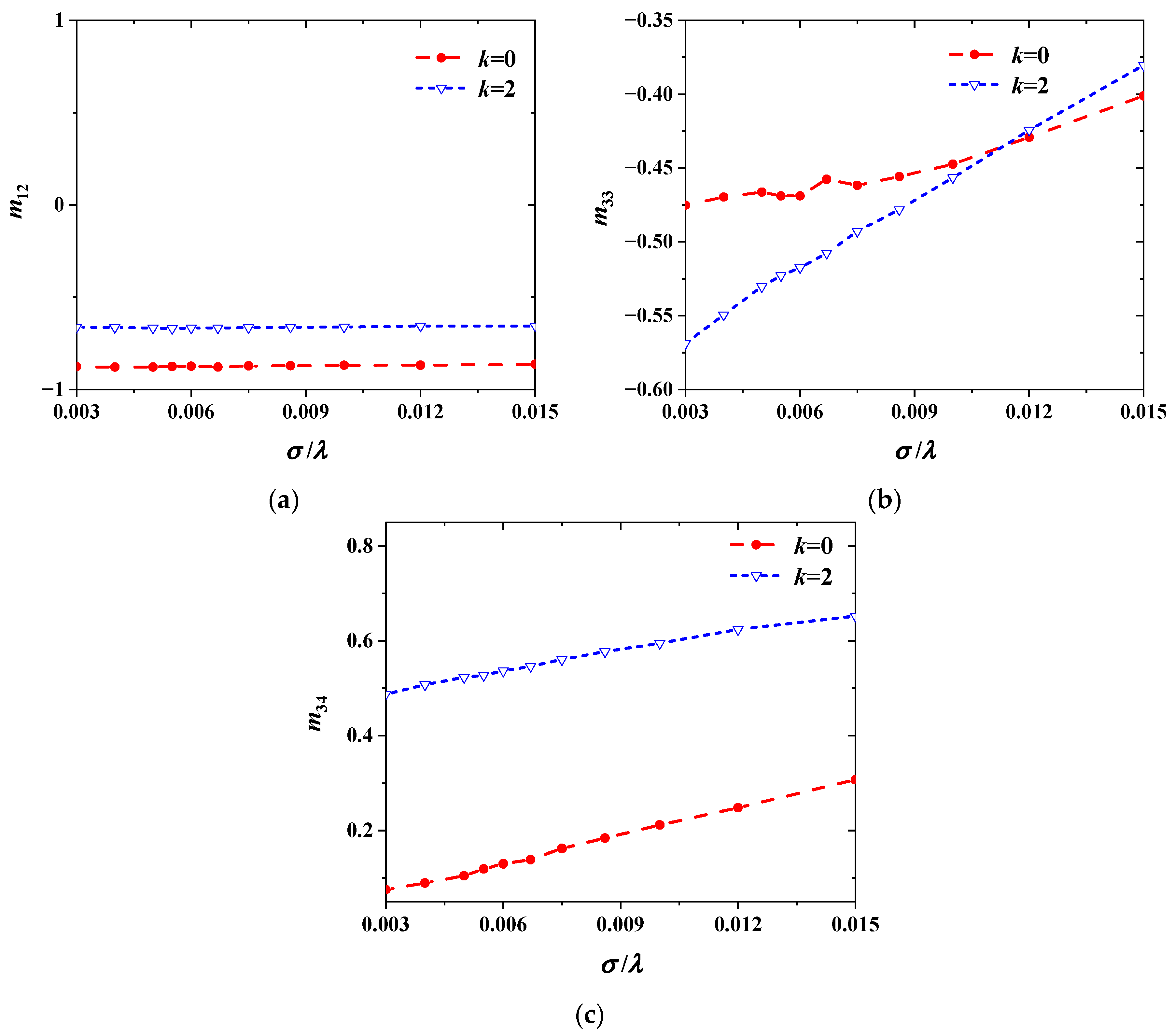
3.2.1. The Relationships Between Relative Roughness and Mueller Matrix Elements
3.2.2. The Relationships Between Correlation Length and Mueller Matrix Elements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, J.; Ran, D.F.; Liu, Y.B.; Liu, L.H. Investigation of ellipsometric parameters of 2D microrough surfaces by FDTD. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 5423–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nee, S.F. Polarization of specular reflection and near-specular scattering by a rough surface. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 3570–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, N.C.; Sant, A.J.; Dainty, J.C. The Mueller matrix for rough surface scattering using the Kirchhoff approximation. Opt. Commun. 1992, 88, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Cao, C.; Feng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yu, C.; Wei, R. Investigation polarimetric scattering of light from the randomly rough surface based on the calculation of the Mueller matrix. Opt. Express. 2023, 31, 24796–24809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.X.; Li, Z. Mueller matrix of laser scattering by a two-dimensional randomly rough surface. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2022, 287, 108225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Cui, C.; Arteaga, O. Quantitative characterization of roughness and polarization on very rough surfaces using spectroscopic ellipsometry. Measurement 2025, 251, 117173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, D.; Hijikata, Y.; Yagi, S.; Yaguchi, H. Differences in SiC thermal oxidation process between crystalline surface orientations observed by in-situ spectroscopic ellipsometry. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 095306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nee, S.F.; Bennett, H.E. Quantitative characterization of rough Si02 surfaces by infrared ellipsometry. Curr. Dev. Opt. Eng. II SPIE 1987, 818, 34–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ohlídal, I.; Franta, D.; Nečas, D. Improved combination of scalar diffraction theory and Rayleigh–Rice theory and its application to spectroscopic ellipsometry of randomly rough surfaces. Thin Solid Films 2014, 571, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serényi, M.; Lohner, T.; Petrik, P.; Zolnai, Z.; Horváth, Z.E.; Khánh, N.Q. Characterization of sputtered and annealed niobium oxide films using spectroscopic ellipsometry, Rutherford backscattering spectrometry and X-ray diffraction. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 8096–8100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.J.; Guo, L.; Jiang, F.Y. Regime Map of the Effective Medium Approximation Modelling of Micro-Rough Surfaces in Ellipsometry. Sensors 2024, 24, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, H.; Koh, J.; Rovira, P.I.; Collins, R.W. Assessment of effective-medium theories in the analysis of nucleation and microscopic surface roughness evolution for semiconductor thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Ghong, T.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Aspnes, D.E.; Klein, M.V.; Ko, D.S.; Kim, Y.W.; Elarde, V.C.; Coleman, J.J. Investigation of effective-medium approximation, alloy, average-composition, and graded-composition models for interface analysis by spectroscopic ellipsometry. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Qiu, J.; Liu, L.H. Applicability of the effective medium approximation in the ellipsometry of randomly micro-rough solid surfaces. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 16560–16571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Qiu, J.; Liu, L.; Cao, B.Y. Extracting optical constants of solid materials with micro-rough surfaces from ellipsometry without using effective medium approximation. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 17667–17680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Hua, M.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, F. Forward modeling of scattering centers from coated target on rough ground for remote sensing target recognition applications. IEEE Trans. Geos. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Quan, W.; Cui, T.; Song, Q.; Lin, C. Remote sensing of absorption and scattering coefficient using neural network model, development, validation, and application. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xue, L.; Yan, K. Numerical calculation of light scattering from metal and dielectric randomly rough Gaussian surfaces using microfacet slope probability density function based method. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 196, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Guo, L.X.; Wu, Z.S. The fast EPILE combined with FBM for electromagnetic scattering from dielectric targets above and below the dielectric rough surface. IEEE Trans. Geos. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3892–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaee, H.; Sahebi, M.R. Incoherent target scattering decomposition of polarimetric SAR data based on vector model roll-invariant parameters. IEEE Trans. Geos. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4392–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comite, D.; Ahmad, F.; Amin, M.G.; Dogaru, T. Detection of low-signature targets in rough surface terrain for forward-looking ground penetrating radar imaging. In Proceedings of the 49th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 8–11 November 2015; pp. 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Du, W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, C.W. Mueller matrix imaging ellipsometry for nanostructure metrology. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 17316–17329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.H.; Zeng, N.; He, H.H.; Yun, T.L.; Du, E.; Liao, R.; He, Y.H.; Ma, H. A study on forward scattering Mueller matrix decomposition in anisotropic medium. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 18361–18370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.W.; An, I.; Fujiwara, H.; Lee, J.; Lu, Y.; Koh, J.; Rovira, P.I. Advances in multichannel spectroscopic ellipsometry. Thin Solid Films 1998, 313, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.; Lai, J.; Wang, C.; Bian, B.; Li, Z. Describing the depolarization characteristic of rough surface by M11/M00 of Mueller matrix. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Optical Instruments and Technology, Advanced Sensor Technologies and Applications, Shanghai, China, 19–21 October 2009; Volume 7508, pp. 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, D.; Powell, J.; Kaplan, A.F.H. A ray-tracing analysis of the absorption of light by smooth and rough metal surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 113504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, M. Diffuse reflection by rough surfaces: An introduction. C. R. Phys. 2005, 6, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.M. Electromagnetic Simulation Using the FDTD Method; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Taflove, A.; Hagness, S. Computational Electrodynamics. In The Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Stover, J.C. Optical Scattering, Measurement and Analysis, 2nd ed.; SPIE Press: Washington, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, H. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry, Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Azzam, R.M.A.; Bashara, N.M.; Ballard, S.S. Ellipsometry and Polarized Light; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Jellison, G.E. Data analysis for spectroscopic ellipsometry. In Handbook of Ellipsometry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 237–296. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; An, I.; Ferreira, G.M.; Podraza, N.J.; Zapien, J.A.; Collins, R.W. Multichannel Mueller matrix ellipsometer based on the dual rotating compensator principle. Thin Solid Films 2004, 455, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, M.; Jiang, F. Correlation of Optical Constants and Morphologies with Mueller Matrix for Micro-Rough Surfaces. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116149
Huang M, Jiang F. Correlation of Optical Constants and Morphologies with Mueller Matrix for Micro-Rough Surfaces. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):6149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116149
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Meijiao, and Fengyi Jiang. 2025. "Correlation of Optical Constants and Morphologies with Mueller Matrix for Micro-Rough Surfaces" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 6149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116149
APA StyleHuang, M., & Jiang, F. (2025). Correlation of Optical Constants and Morphologies with Mueller Matrix for Micro-Rough Surfaces. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 6149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116149




