A Computational Investigation of the “Equivalent Substrates” in the Evaporation of Sessile Droplets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
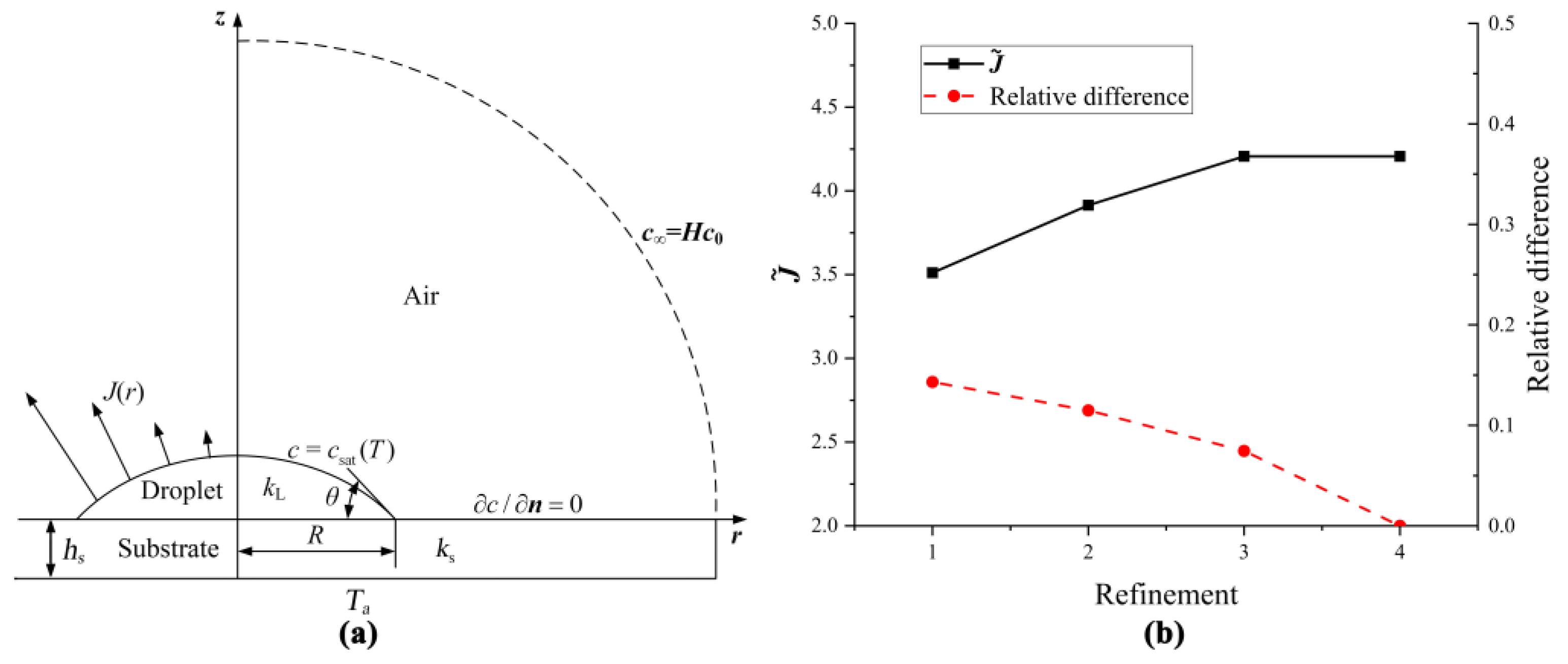
3. Finite Element Method
4. Results and Discussion
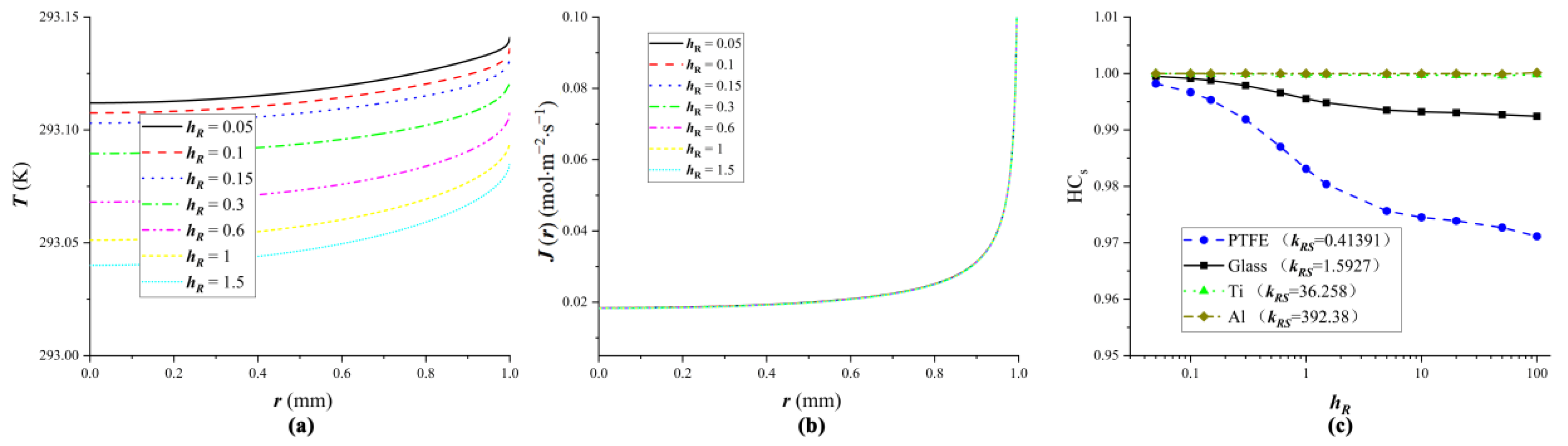
4.1. The Influence of Substrate Heat Transfer on Droplet Evaporation
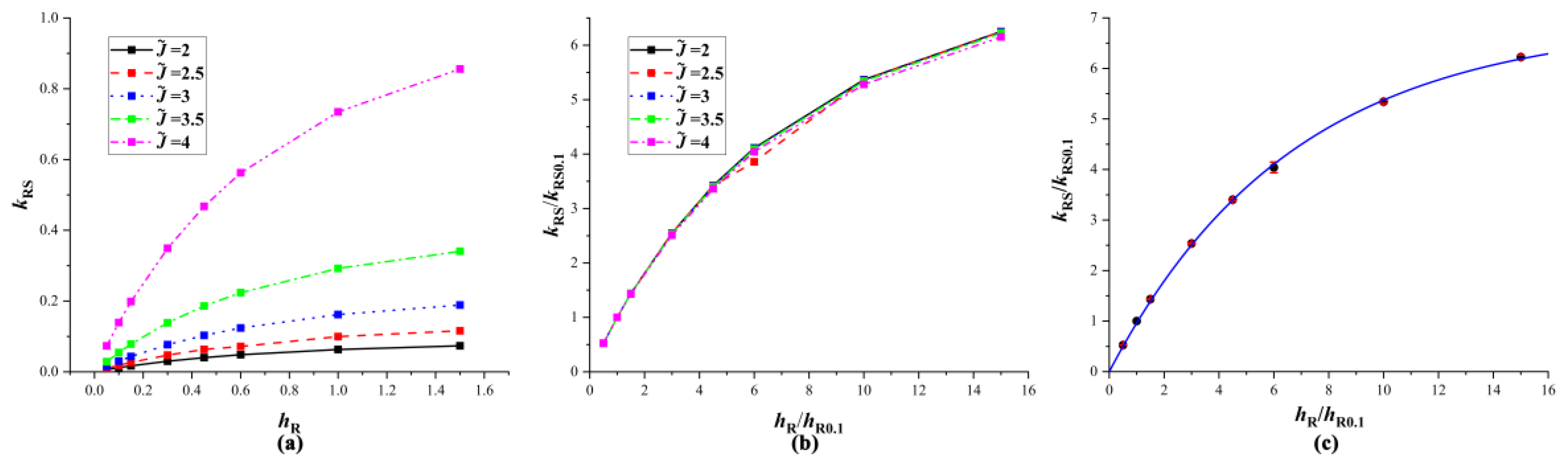
4.2. Equivalent Substrates
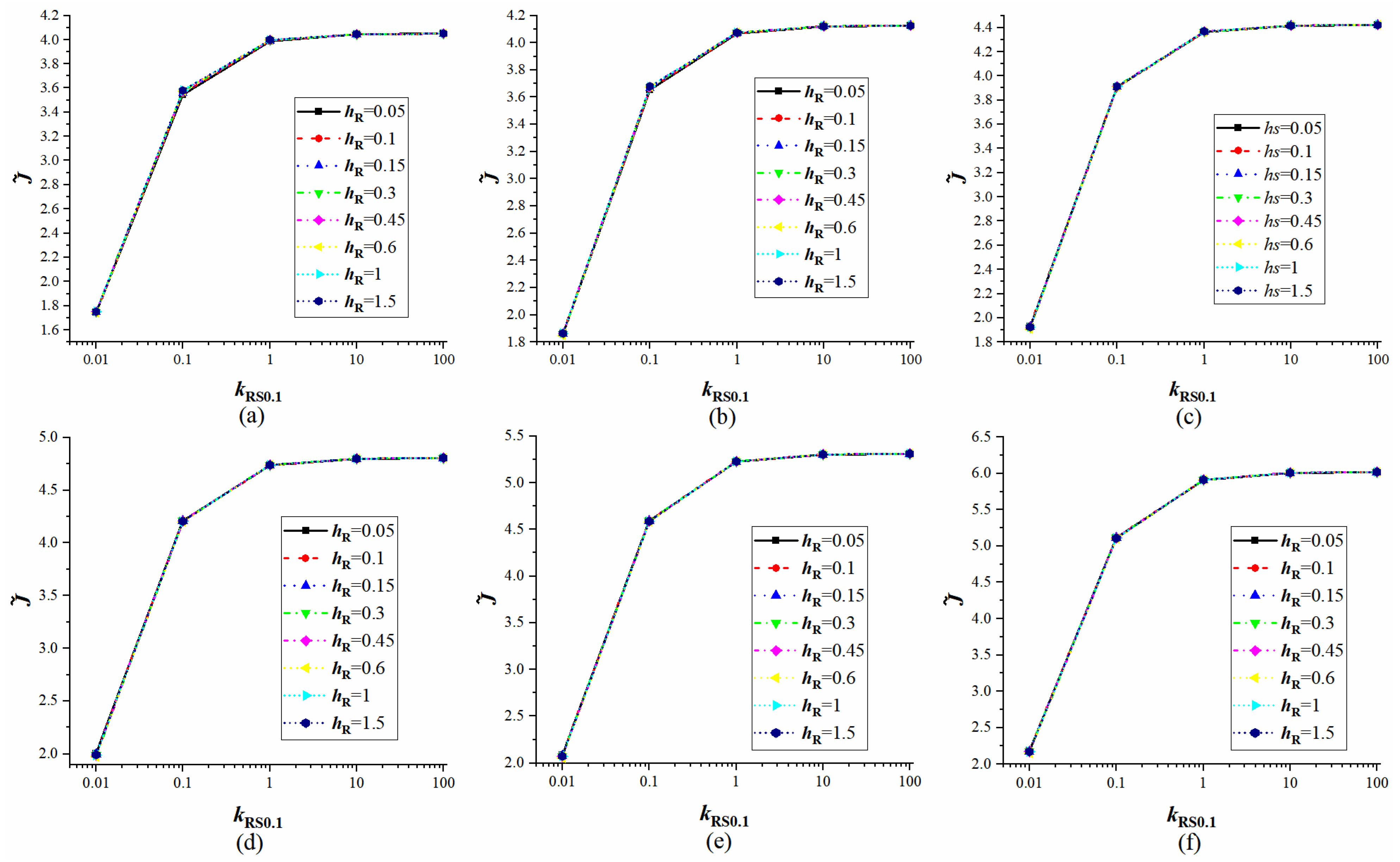
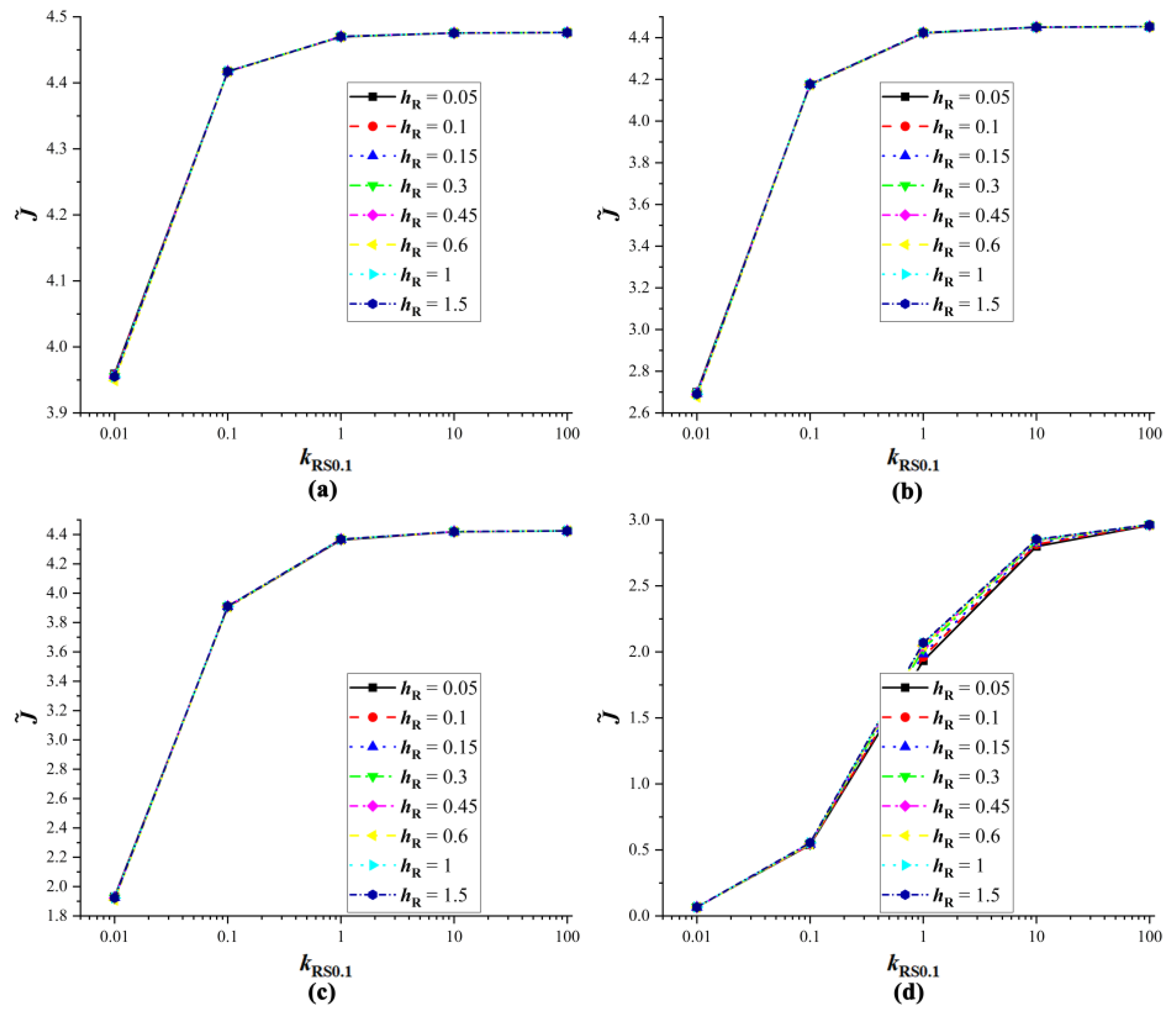
4.3. Verification of Equivalent Substrates
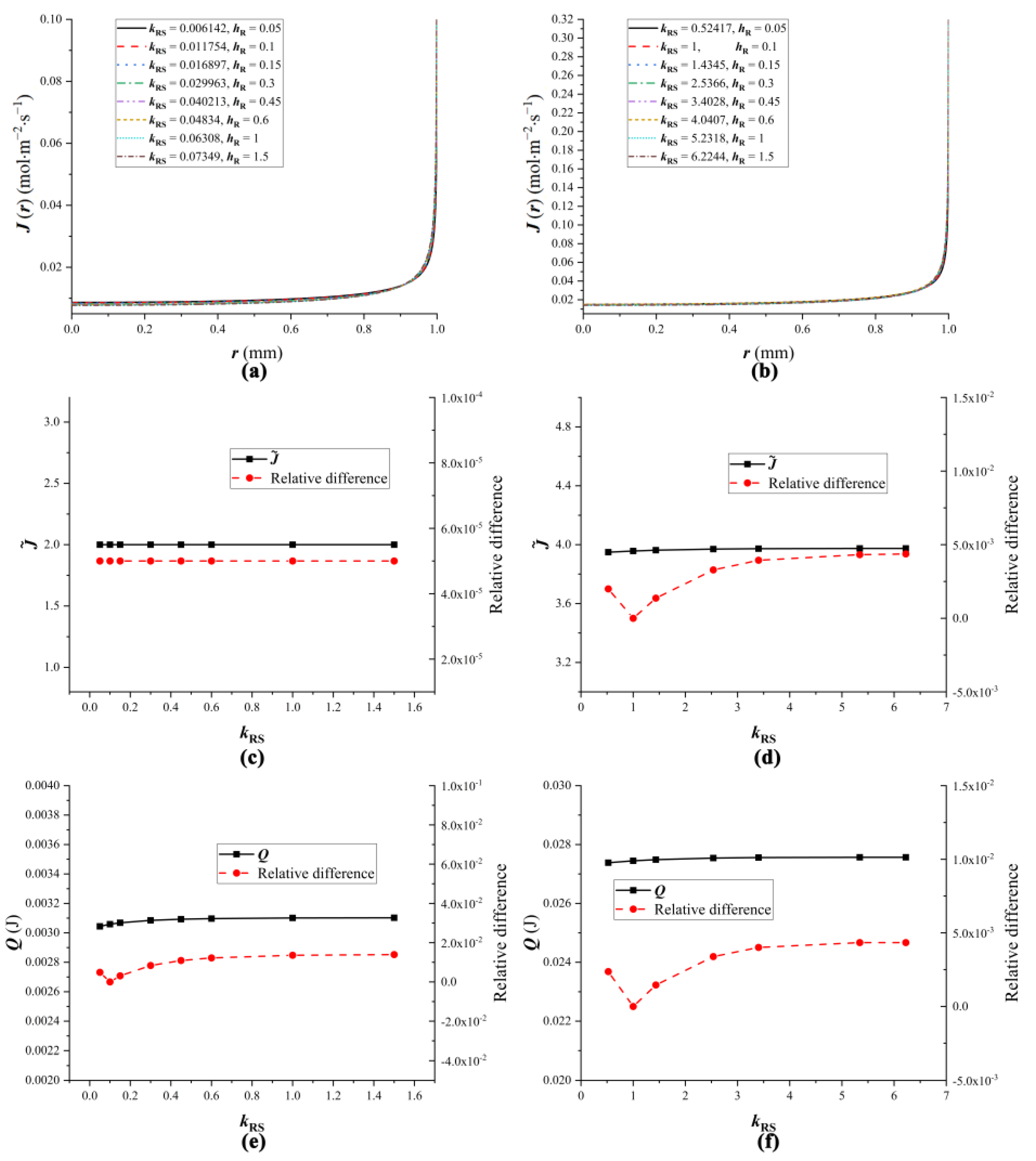
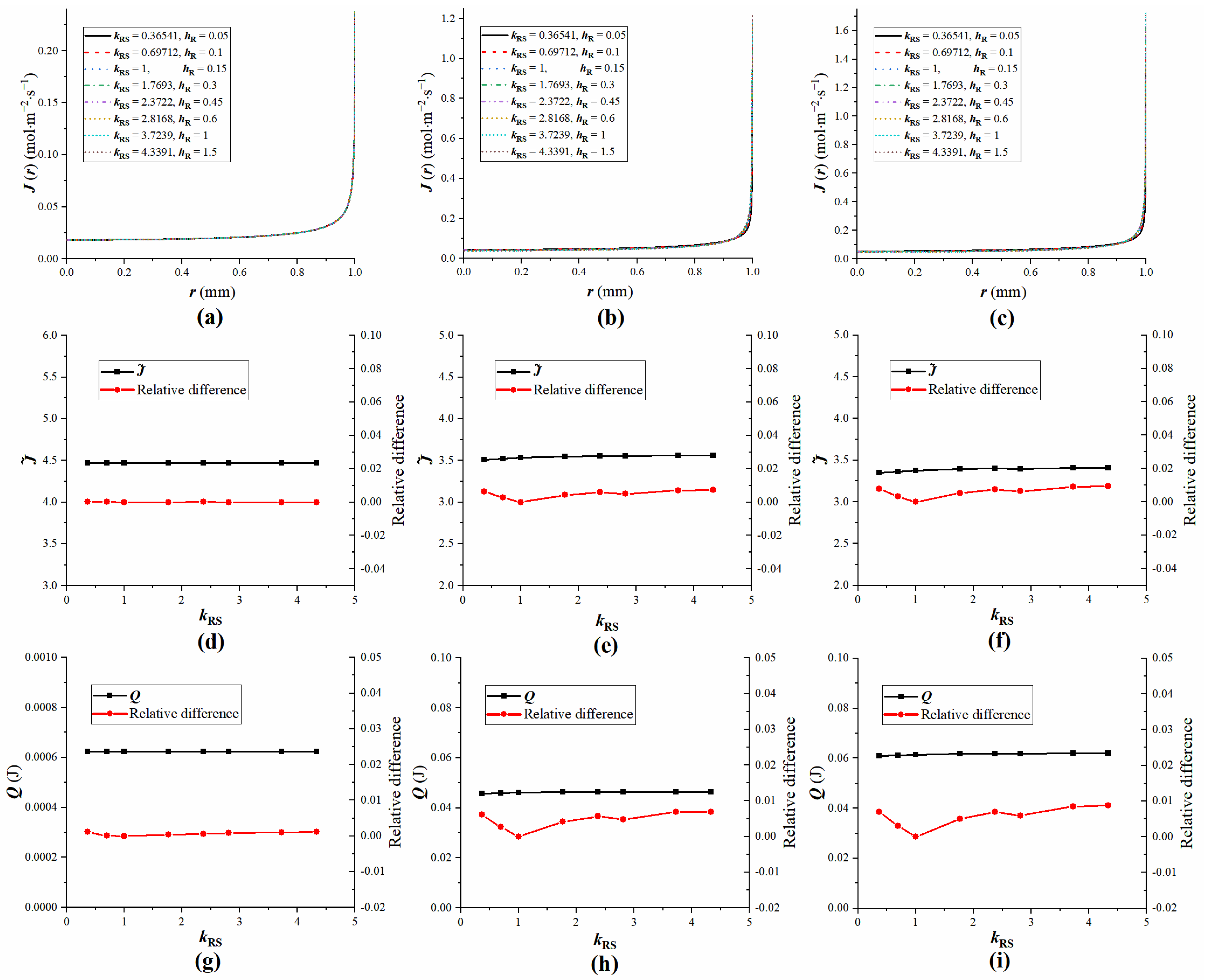
4.4. The Influence of Droplet Properties on Equivalent Substrates
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T | Temperature |
| J(r) | Evaporation flux |
| Dimensionless evaporation rate | |
| Q | Heat transfer |
| Ec | Evaporative cooling number |
| hR | Dimensionless substrate thickness |
| kRS | Relative thermal conductivity |
| kRS0.1 | Relative thermal conductivity of a dimensionless substrate thickness of 0.1 |
References
- Chen, H.; Shi, C.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chang, W. Investigation of the droplet dynamics and thermal performance during dropwise condensation in the wickless heat pipe condenser. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 161, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, L.K.; Dhanalakota, P.; Mahapatra, P.S.; Pattamatta, A. Thermal and flow characteristics in a flat plate pulsating heat pipe with ethanol-water mixtures: From slug-plug to droplet oscillations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 194, 123066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miccichè, C.; Arrabito, G.; Amato, F.; Buscarino, G.; Agnello, S.; Pignataro, B. Inkjet printing Ag nanoparticles for SERS hot spots. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3215–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thokchom, A.K.; Zhou, Q.; Kim, D.; Ha, D.; Kim, T. Characterizing self-assembly and deposition behavior of nanoparticles in inkjet-printed evaporating droplets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 252, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, E.L.; Yang, L.; Berson, A.; Bain, C.D. Control of the Particle Distribution in Inkjet Printing through an Evaporation-Driven Sol–Gel Transition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9572–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.; Zhao, W.; Guo, G.; Dai, J.; Fan, L. Wire-droplet-substrate integrated model for heat transfer and deposition geometry prediction in GMAW-based wire arc additive manufacturing. Weld. World 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Dou, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Sang, H. Study of the interaction of DNA and histones by spin-stretching and droplet evaporation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rathaur, V.S.; Gokhale, N.A.; Panda, S. pH effects on capture efficiency and deposition patterns in sessile droplet immunoassays: An XDLVO analysis. Biomicrofluidics 2024, 18, 054103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Bhardwaj, R. A combined computational and experimental investigation on evaporation of a sessile water droplet on a heated hydrophilic substrate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 122, 1223–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.H.; Biggs, S.; Doi, A.; Nguyen, A.V. A new way of assessing droplet evaporation independently of the substrate hydrophobicity and contact line mode: A case study of sessile droplets with surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, E.; Son, M.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, Y.; Choi, D.; Kim, J.; Yoon, S.H.; Yoon, J.S. A study on arrangement characteristics of microparticles in sedimentation on flat and round substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 264101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Dash, S.; Weibel, J.A.; Garimella, S.V. Assessment of Water Droplet Evaporation Mechanisms on Hydrophobic and Superhydrophobic Substrates. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15831–15841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Su, B.; Shi, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Zi, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Colloidal Photonic Crystals with Narrow Stopbands Assembled from Low-Adhesive Superhydrophobic Substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17053–17058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Y.; Yao, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Controllable Fabrication of Noniridescent Microshaped Photonic Crystal Assemblies by Dynamic Three-Phase Contact Line Behaviors on Superhydrophobic Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 22644–22651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, S.; Tarasevich, Y.Y.; Dutta Choudhury, M.; Dutta, T.; Zang, D. Droplet Drying Patterns on Solid Substrates: From Hydrophilic to Superhydrophobic Contact to Levitating Drops. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2018, 2018, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristenpart, W.D.; Kim, P.G.; Domingues, C.; Wan, J.; Stone, H.A. Influence of Substrate Conductivity on Circulation Reversal in Evaporating Drops. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 234502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, J.; Guo, D. Temperature distribution along the surface of evaporating droplets. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 032404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, F.; Antoni, M.; Sefiane, K. Infrared Thermography Investigation of an Evaporating Sessile Water Droplet on Heated Substrates. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4576–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, F.; Antoni, M.; Sefiane, K. On the Effect of Marangoni Flow on Evaporation Rates of Heated Water Drops. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9207–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefiane, K.; Bennacer, R. An expression for droplet evaporation incorporating thermal effects. J. Fluid Mech. 2011, 667, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ma, L. Analysis of the effects of evaporative cooling on the evaporation of liquid droplets using a combined field approach. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, J. Combined effects of underlying substrate and evaporative cooling on the evaporation of sessile liquid droplets. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 5632–5640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, J. Expressions for the evaporation of sessile liquid droplets incorporating the evaporative cooling effect. J. Colloid. Interface. Sci. 2016, 484, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Ma, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, J. “Phase Diagram” of Surface Temperature Distribution of Sessile Droplets and the Effects of Evaporative Cooling. J. Bionic Eng. 2023, 20, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, A.; Kempers, R.; Amirfazli, A. Modeling of the evaporation process of a pair of sessile droplets on a heated substrate. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 032115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Saada, M.; Chikh, S.; Tadrist, L. Evaporation of a sessile drop with pinned or receding contact line on a substrate with different thermophysical properties. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 58, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.J.; Wilson, S.K.; Duffy, B.R.; David, S.; Sefiane, K. The strong influence of substrate conductivity on droplet evaporation. J. Fluid Mech. 2009, 623, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, J.F.L.; Leermakers, F.A.M.; van Leeuwen, H.P. Electrostatic Interactions between Double Layers: Influence of Surface Roughness, Regulation, and Chemical Heterogeneities. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5052–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Evaporation dynamics of nanodroplets and their anomalous stability on rough substrates. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 012404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ansari, K.J.; Jampa, S.S.K.; Vutukuri, P.; Mukherjee, R. Influence of Substrate Wettability on the Morphology of Thin Polymer Films Spin-Coated on Topographically Patterned Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsi, A.J.; Burganos, V.N. Temperature distribution inside an evaporating two-dimensional droplet lying on curved or flat substrates. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 011201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.L.; Carnevale, L.H.; Klamka, M.; Deuar, P.; Bobinski, T.; Theodorakis, P.E. Oscillations of a water droplet on a horizontally vibrating substrate. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 011201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Tao, Y.; Liu, Q. Experimental study on the evaporation characteristics of sessile droplets under different substrate materials and relative humidity. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 3006, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, L.; Pajor-Swierzy, A.; Magdassi, S.; Kamyshny, A.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Evaporation of Nanosuspensions on Substrates with Different Hydrophobicity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauber, J.M.; Wilson, S.K.; Duffy, B.R.; Sefiane, K. Evaporation of Droplets on Strongly Hydrophobic Substrates. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3653–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Sefiane, K.; Tadrist, L. Experimental investigation of the effect of thermal properties of the substrate in the wetting and evaporation of sessile drops. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 298, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Evaporation of a Sessile Droplet on a Substrate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Analysis of the Effects of Marangoni Stresses on the Microflow in an Evaporating Sessile Droplet. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Analysis of the Microfluid Flow in an Evaporating Sessile Droplet. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3963–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefiane, K.; Wilson, S.K.; David, S.; Dunn, G.J.; Duffy, B.R. On the effect of the atmosphere on the evaporation of sessile droplets of water. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 62101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Di Marzo, M.; Qiao, Y.M.; Tartarini, P. Effect of liquid-solid contact angle on droplet evaporation. Fire Saf. J. 1996, 27, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
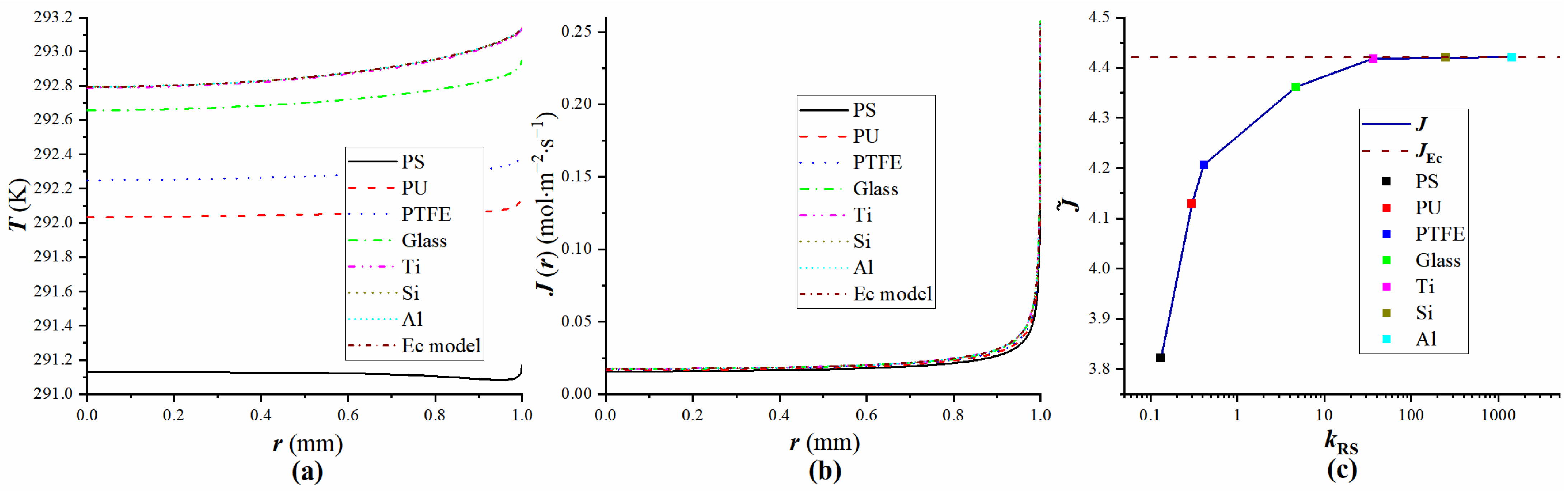
| Droplet | Substrate | kRS | Ec |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | PS | 0.13245 | 0.10986 |
| PU | 0.29801 | 0.10986 | |
| PTFE | 0.41391 | 0.10986 | |
| Glass | 1.5927 | 0.10986 | |
| Ti | 36.258 | 0.10986 | |
| Si | 246.69 | 0.10986 | |
| Al | 392.38 | 0.10986 |
| Refinements | Numbers of Elements |
|---|---|
| 1 | 219,745 |
| 2 | 791,510 |
| 3 | 1,127,187 |
| 4 | 1,788,891 |
| hR | kRS | kRS | kRS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.06142 | 0.52417 | 0.36541 |
| 0.1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.69712 |
| 0.15 | 0.016897 | 1.4345 | 1 |
| 0.3 | 0.029963 | 2.5366 | 1.7693 |
| 0.45 | 0.040213 | 3.4028 | 2.3722 |
| 1 | 0.06308 | 5.2318 | 3.7239 |
| 1.5 | 0.07349 | 6.2244 | 4.3391 |
| Parameters | Unit | Water | Methanol | Acetone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | kg·m−3 | 998 | 790 | 788 |
| Thermal conductivity | W·m−1·K−1 | 0.604 | 0.203 | 0.161 |
| Heat capacity | J·kg−1·K−1 | 4180 | 2530 | 2170 |
| Diffusion Coefficient | m2·s−1 | 2.44 × 10−5 | 1.5 × 10−5 | 1.06 × 10−5 |
| Specific heat | m2·s−2 | 2.45 × 106 | 1.2 × 106 | 5.49 × 105 |
| Ec | 1 | 0.10986 | 0.83970 | 1.0265 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Xu, X. A Computational Investigation of the “Equivalent Substrates” in the Evaporation of Sessile Droplets. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116083
Xu L, Xu X. A Computational Investigation of the “Equivalent Substrates” in the Evaporation of Sessile Droplets. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):6083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116083
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Longfei, and Xuefeng Xu. 2025. "A Computational Investigation of the “Equivalent Substrates” in the Evaporation of Sessile Droplets" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 6083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116083
APA StyleXu, L., & Xu, X. (2025). A Computational Investigation of the “Equivalent Substrates” in the Evaporation of Sessile Droplets. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 6083. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116083





