FP-Deeplab: A Novel Face Parsing Network for Fine-Grained Boundary Detection and Semantic Understanding
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A Cross-Axis Attention mechanism is introduced, which establishes axial attention along both horizontal and vertical spatial dimensions to enhance long-range pixel-level dependency modeling, improving the semantic consistency and segmentation robustness of facial structures.
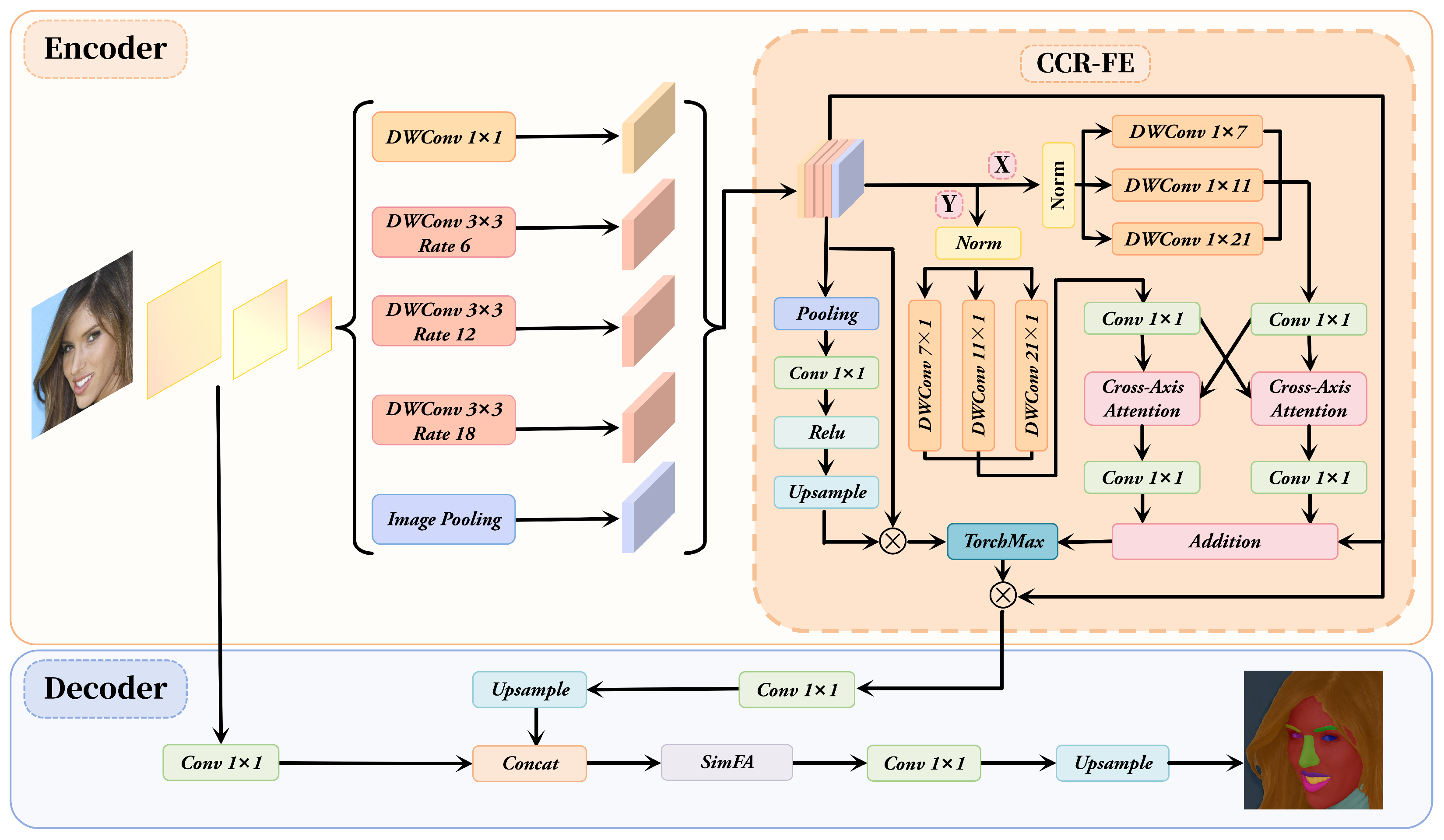
- A Context-Channel Refine Feature Enhancement (CCR-FE) module is proposed to optimize the original ASPP structure by combining multi-scale strip convolutions and a channel attention mechanism, effectively enhancing the perception and representation of local structures and complex facial regions.
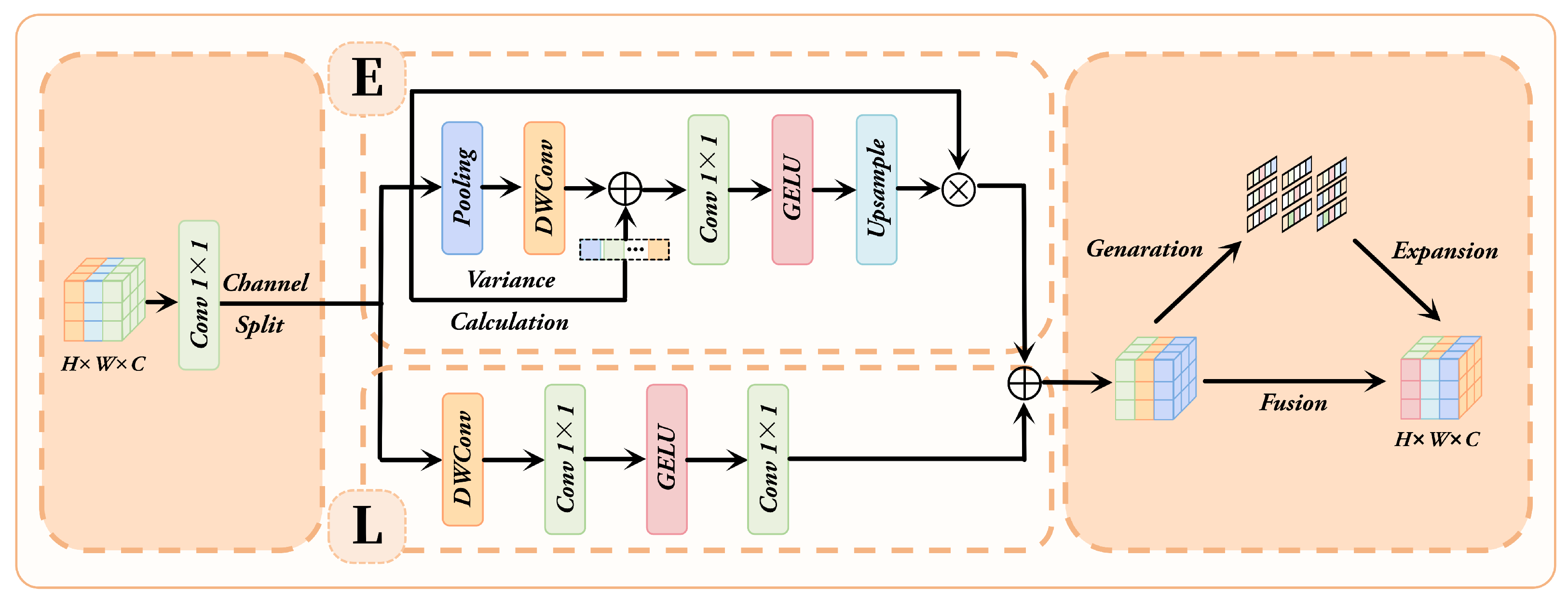
- A SimFA module is developed to refine the feature fusion process in the upsampling stage. By leveraging local feature enhancement and a self-modulated attention mechanism, this module enables adaptive semantic restoration, effectively alleviating boundary blur and structural discontinuities, thus producing more stable and clearer face segmentation results.
2. Related Work
2.1. Semantic Segmentation Methods
2.2. Face Parsing Techniques
2.3. Feature Fusion and Attention Mechanisms
3. Methods
3.1. Cross-Axis Attention
3.2. CCR-FE Module
3.3. SimFA Module
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Results on HELEN
4.2.1. Comparison with Mainstream Methods
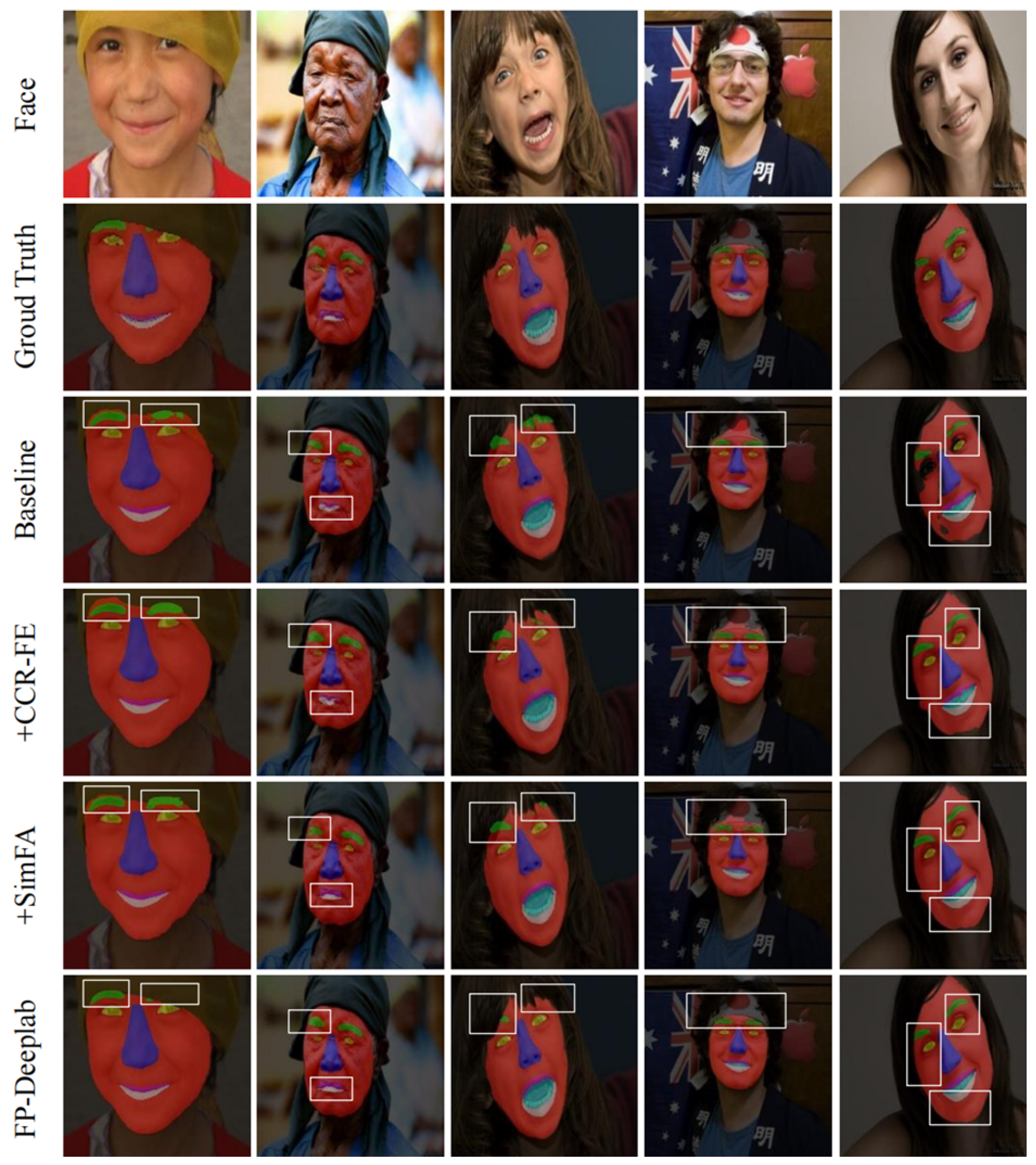
4.2.2. Ablation Study
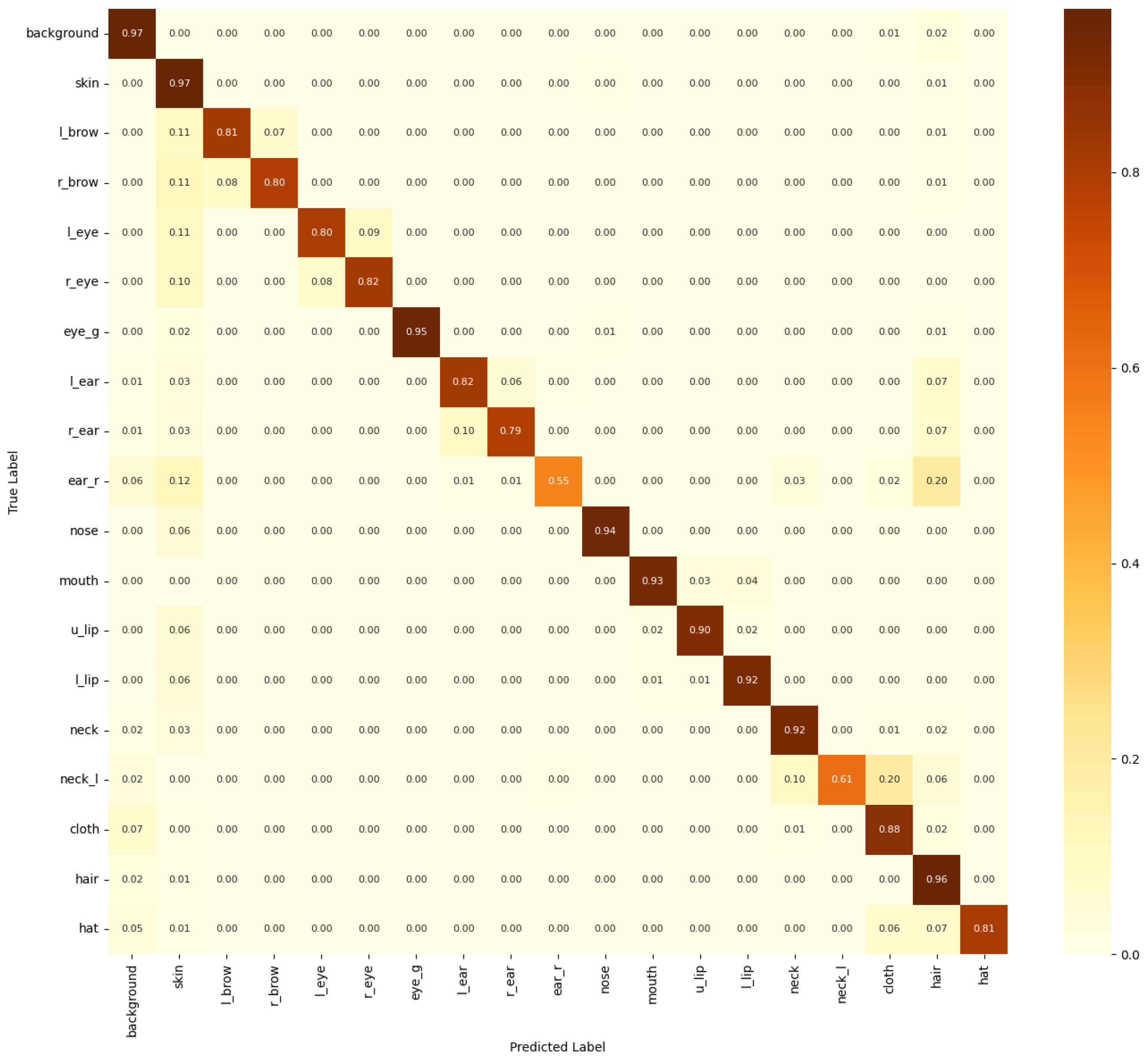
4.3. Results on CelebAMask-HQ
4.3.1. Performance Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
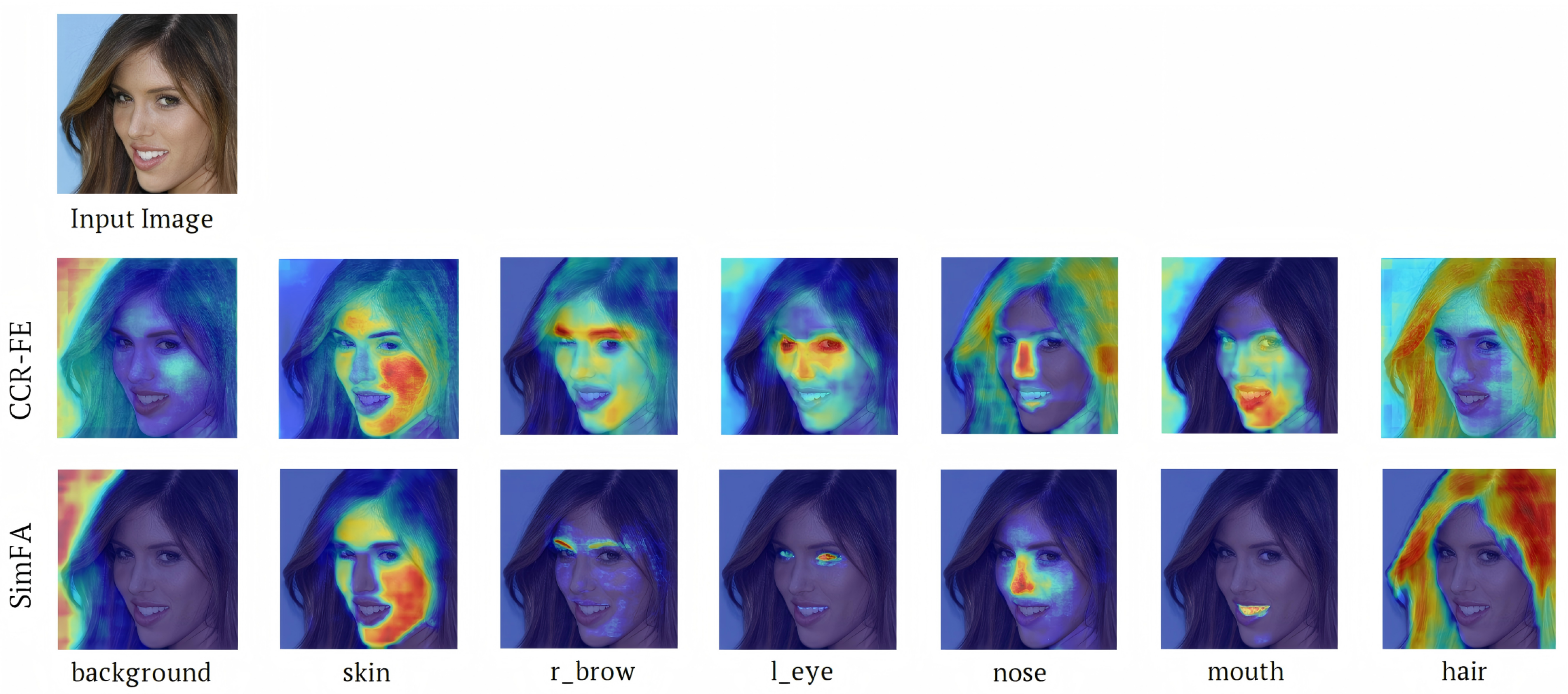
4.3.2. Visualization of Learned Features
4.3.3. Comparison of Different Backbone Networks
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anthes, C.; García-Hernández, R.J.; Wiedemann, M.; Kranzlmüller, D. State of the art of virtual reality technology. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Arena, F.; Collotta, M.; Pau, G.; Termine, F. An overview of augmented reality. Computers 2022, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Hui, Y.; Zhao, P.; Cai, C.-H.; Dai, B.; Dou, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Yu, J. A novel image expression-driven modeling strategy for coke quality prediction in the smart cokemaking process. Energy 2024, 294, 130866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Georgiou, T.; Lew, M.S. A review of semantic segmentation using deep neural networks. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2018, 7, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, V.; Lucas, T. Computer vision and image processing: A paper review. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2018, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, R.; Nishio, M.; Do, R.K.G.; Togashi, K. Convolutional neural networks: An overview and application in radiology. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Ji, S. StructPool: Structured graph pooling via conditional random fields. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Luo, P.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Deep learning Markov random field for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1814–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Object-contextual representations for semantic segmentation. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020, Proceedings of the 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part VI 16; Springer: London, UK, 2020; pp. 173–190. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, B. Interlinked convolutional neural networks for face parsing. In Advances in Neural Networks–ISNN 2015, Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Neural Networks, ISNN 2015, Jeju, South Korea, 15–18 October 2015; Springer: London, UK, 2015; pp. 222–231. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Xue, D.; Feng, X. Ehanet: An effective hierarchical aggregation network for face parsing. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Song, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, M. Parsing R-CNN for instance-level human analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 364–373. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Fu, R.; Huang, L.; Lin, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Hrformer: High-resolution transformer for dense prediction. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.09408. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Weissenborn, D.; Salimans, T. Axial attention in multidimensional transformers. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.12180. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H.; Zeng, Q.; Hou, Q.; Yang, J. Mcanet: Medical image segmentation with multi-scale cross-axis attention. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.08866. [Google Scholar]
- Agarap, A.F. Deep learning using rectified linear units (ReLU). arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.08375. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Sun, L.; Dong, J.; Pan, J. SMFANet: A lightweight self-modulation feature aggregation network for efficient image super-resolution. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2024, Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: London, UK, 2024; pp. 359–375. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrycks, D.; Gimpel, K. Gaussian error linear units (gelus). arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.08415. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Li, N.; Weng, C.; Su, D.; Li, M. Simple attention module based speaker verification with iterative noisy label detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 6722–6726. [Google Scholar]
- Elfwing, S.; Uchibe, E.; Doya, K. Sigmoid-weighted linear units for neural network function approximation in reinforcement learning. Neural Netw. 2018, 107, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.M.; Zhang, L.; Brandt, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J. Exemplar-based face parsing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3484–3491. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-H.; Liu, Z.; Wu, L.; Luo, P. MaskGAN: Towards diverse and interactive facial image manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 5549–5558. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized intersection over union: A metric and a loss for bounding box regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Opitz, J.; Burst, S. Macro f1 and macro f1. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.03347. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Yiu, V.; Hu, X.; Tang, L. End-to-end face parsing via interlinked convolutional neural networks. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2021, 15, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Ling, H. Accurate facial image parsing at real-time speed. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 4659–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, J.; Huang, C.; Yang, M.-H. Multi-objective convolutional learning for face labeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3451–3459. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Liang, J.; Yang, M.-H. Face parsing via recurrent propagation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.01936. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Kim, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qian, D.; Yoo, B.; Xu, J.; Zou, D.; Han, J.-J.; Choi, C. Residual encoder decoder network and adaptive prior for face parsing. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, T.; Bao, J.; Chen, D.; Huang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Chen, D.; Zeng, M.; Wen, F. General facial representation learning in a visual-linguistic manner. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 18697–18709. [Google Scholar]
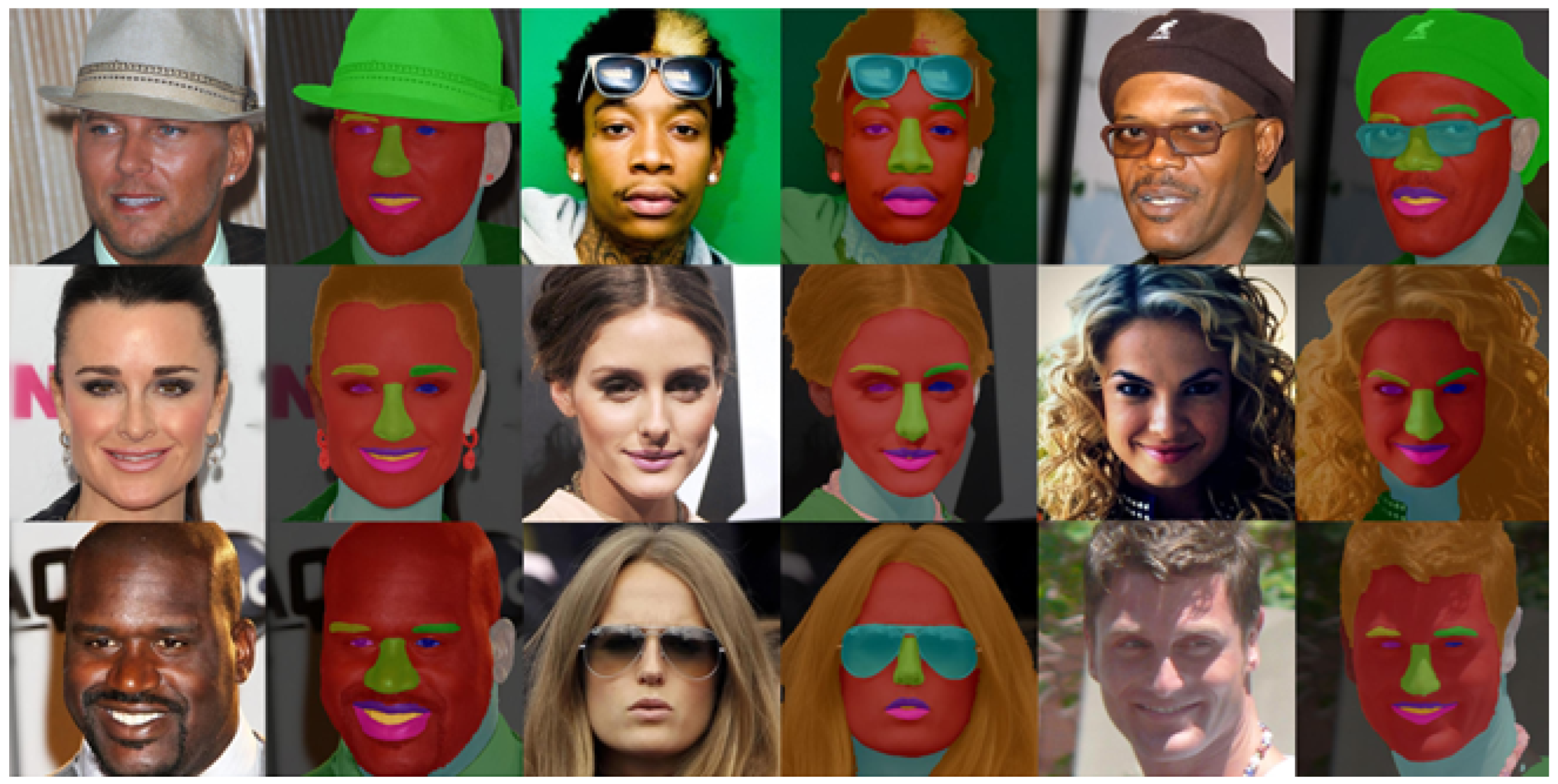



| Methods | Skin | Nose | U-Lip | I-Mouth | L-Lip | Eyes | Brows | Mouth | Overall F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou et al. [17] | - | 92.0 | 82.4 | 77.7 | 80.8 | 77.8 | 86.3 | 88.9 | 84.5 |
| Liu et al. [40] | 91.0 | 90.9 | 62.3 | 80.8 | 69.4 | 76.8 | 71.3 | 84.1 | 84.7 |
| Liu et al. [41] | 92.1 | 93.0 | 74.3 | 79.2 | 81.7 | 86.8 | 77.0 | 89.1 | 88.6 |
| Guo et al. [42] | 93.8 | 94.1 | 75.8 | 83.7 | 83.1 | 80.4 | 87.1 | 92.4 | 90.5 |
| Yin et al. [38] | - | 96.3 | 82.4 | 85.6 | 86.6 | 89.5 | 84.8 | 92.8 | 91.0 |
| Wei et al. [39] | 95.6 | 95.2 | 80.0 | 86.7 | 86.4 | 89.0 | 82.6 | 93.6 | 91.6 |
| FP-Deeplab (Ours) | 94.9 | 96.0 | 81.3 | 87.5 | 88.1 | 89.6 | 84.2 | 94.3 | 92.2 |
| Baseline | CCR-FE | SimFA | Mean IoU | Overall F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✔ | 78.7 | 89.9 | ||
| ✔ | ✔ | 80.2 (+1.5) | 91.1 (+1.2) | |
| ✔ | ✔ | 82.0 (+3.3) | 91.9 (+2.0) | |
| ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 82.5 (+3.8) | 92.2 (+2.3) |
| Methods | Face | Nose | Classes | L-Eye | R-Eye | L-Brow | R-Brow | L-Ear | R-Ear | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I-Mouth | U-Lip | L-Lip | Hair | Hat | Earring | Necklace | Neck | Cloth | ||
| Zhao et al. [14] | 94.8 | 90.3 | 75.8 | 79.9 | 80.1 | 77.3 | 78.0 | 75.6 | 73.1 | 76.2 |
| 89.8 | 87.1 | 88.8 | 90.4 | 58.2 | 65.7 | 19.4 | 82.7 | 64.2 | ||
| Lee et al. [33] | 95.5 | 85.6 | 92.9 | 84.3 | 85.2 | 81.4 | 81.2 | 84.9 | 83.1 | 80.3 |
| 63.4 | 88.9 | 90.1 | 86.6 | 91.3 | 63.2 | 26.1 | 92.8 | 68.3 | ||
| Wei et al. [39] | 96.4 | 91.9 | 89.5 | 87.1 | 85.0 | 80.8 | 82.5 | 84.1 | 83.3 | 82.1 |
| 90.6 | 87.9 | 91.0 | 91.1 | 83.9 | 65.4 | 17.8 | 88.1 | 80.6 | ||
| Luo et al. [18] | 96.0 | 93.7 | 90.6 | 86.2 | 86.5 | 83.2 | 83.1 | 86.5 | 84.1 | 84.0 |
| 93.8 | 88.6 | 90.3 | 93.9 | 85.9 | 67.8 | 30.1 | 88.8 | 83.5 | ||
| FaRLscratch [43] | 96.2 | 93.8 | 92.3 | 89.0 | 89.0 | 85.3 | 85.4 | 86.9 | 87.3 | 84.7 |
| 91.7 | 88.1 | 90.0 | 94.9 | 82.7 | 63.1 | 33.5 | 90.8 | 85.9 | ||
| FP-Deeplab (Ours) | 96.4 | 94.0 | 94.2 | 82.2 | 82.5 | 79.4 | 79.0 | 82.2 | 80.6 | 84.8 |
| 93.2 | 90.2 | 91.6 | 95.7 | 85.8 | 59.6 | 59.7 | 92.0 | 88.3 |
| Backbone | Mean F1 | Mean IoU | Params (M)/ | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV2 | 84.8 | 75.64 | 7.2 | 51.8 |
| Xception | 85.0 | 75.89 | 56.7 | 165.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, B.; Shu, C.; Liao, Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X. FP-Deeplab: A Novel Face Parsing Network for Fine-Grained Boundary Detection and Semantic Understanding. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6016. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116016
Zeng B, Shu C, Liao Z, Yu J, Liu Z, Chen X. FP-Deeplab: A Novel Face Parsing Network for Fine-Grained Boundary Detection and Semantic Understanding. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):6016. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116016
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Borui, Can Shu, Ziqi Liao, Jingru Yu, Zhiyu Liu, and Xiaoyan Chen. 2025. "FP-Deeplab: A Novel Face Parsing Network for Fine-Grained Boundary Detection and Semantic Understanding" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 6016. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116016
APA StyleZeng, B., Shu, C., Liao, Z., Yu, J., Liu, Z., & Chen, X. (2025). FP-Deeplab: A Novel Face Parsing Network for Fine-Grained Boundary Detection and Semantic Understanding. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 6016. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15116016






