Clinical, Microbiological, and Biochemical Outcomes of Hyaluronic Acid in Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Question
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Screening and Selection
- P (Population): patients diagnosed with periodontal disease;
- I (Intervention): adjunctive use of HA gel in support of SRP;
- C (Comparison): SRP alone;
- O (Outcome): clinical, microbiological, and biochemical parameters.
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Grading the Body of Evidence
3. Results
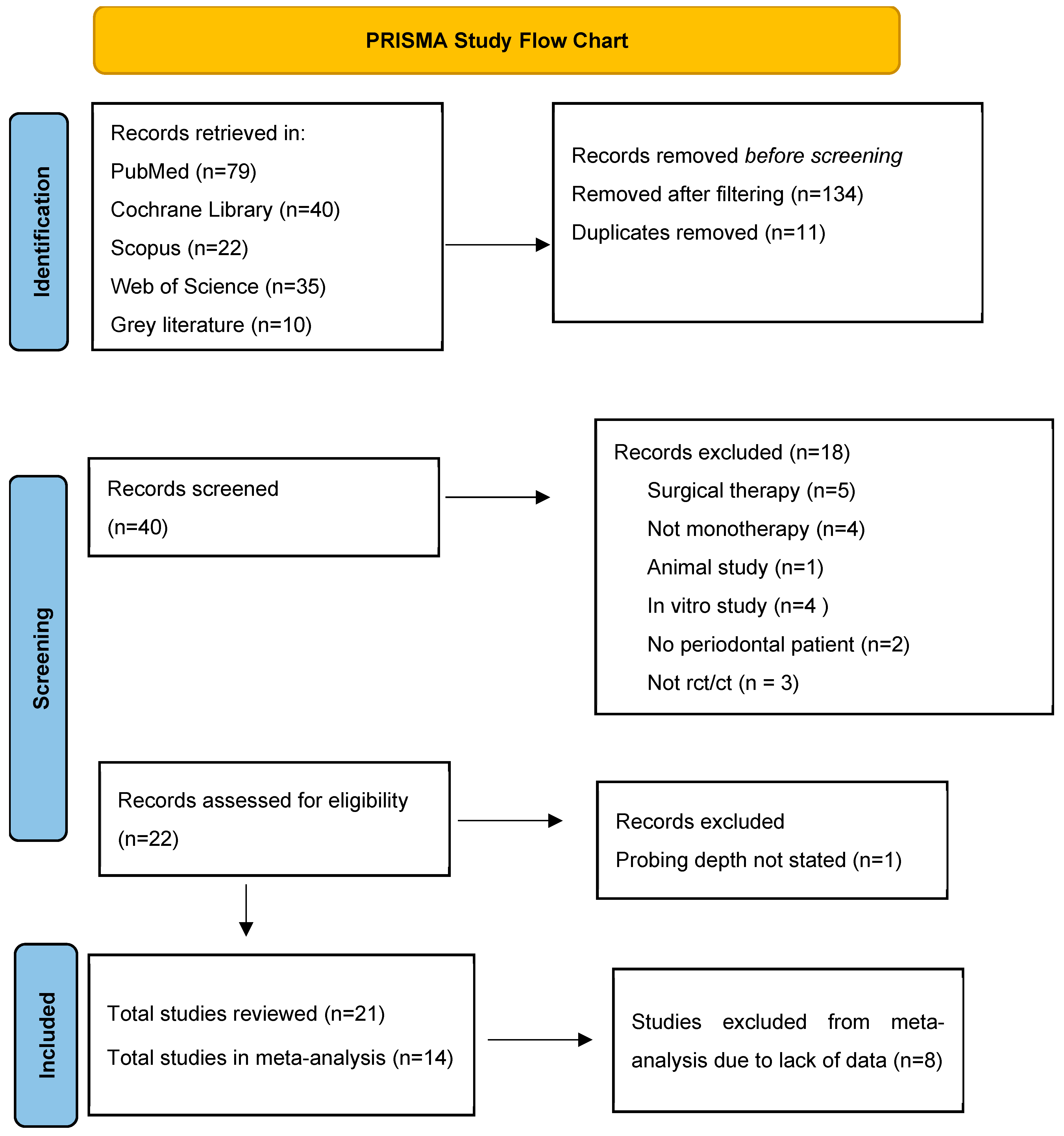
3.1. Study Flow Chart
3.2. Study Characteristics
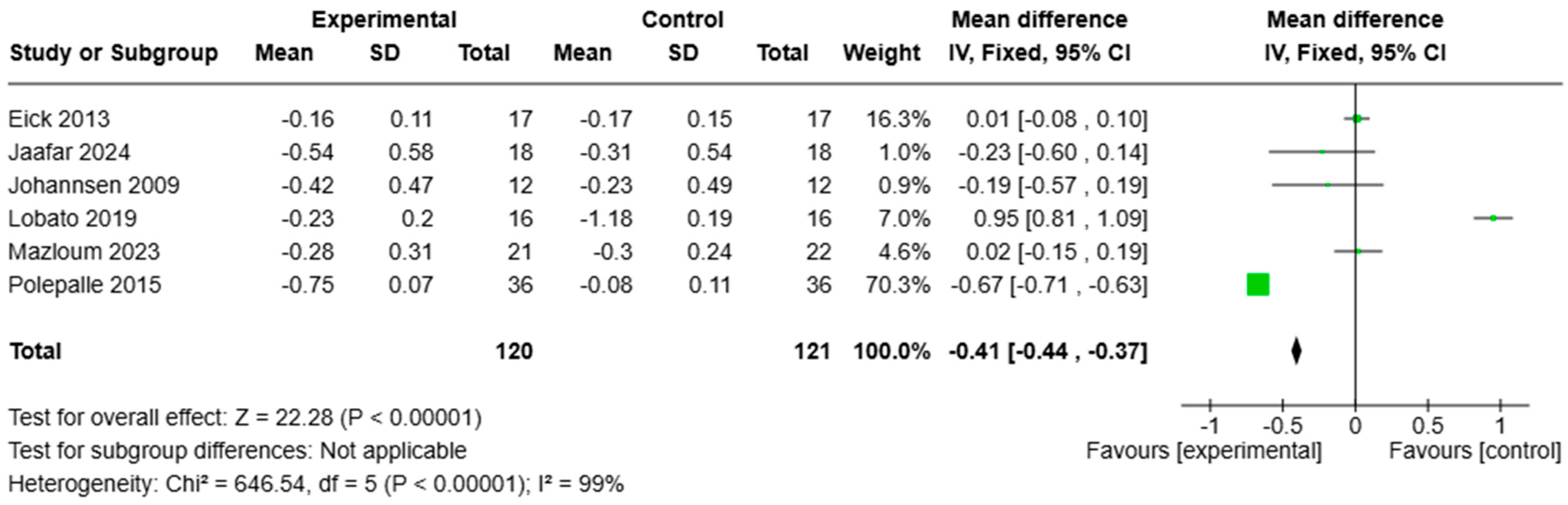
3.3. Microbiological Analysis
Biochemical Analysis
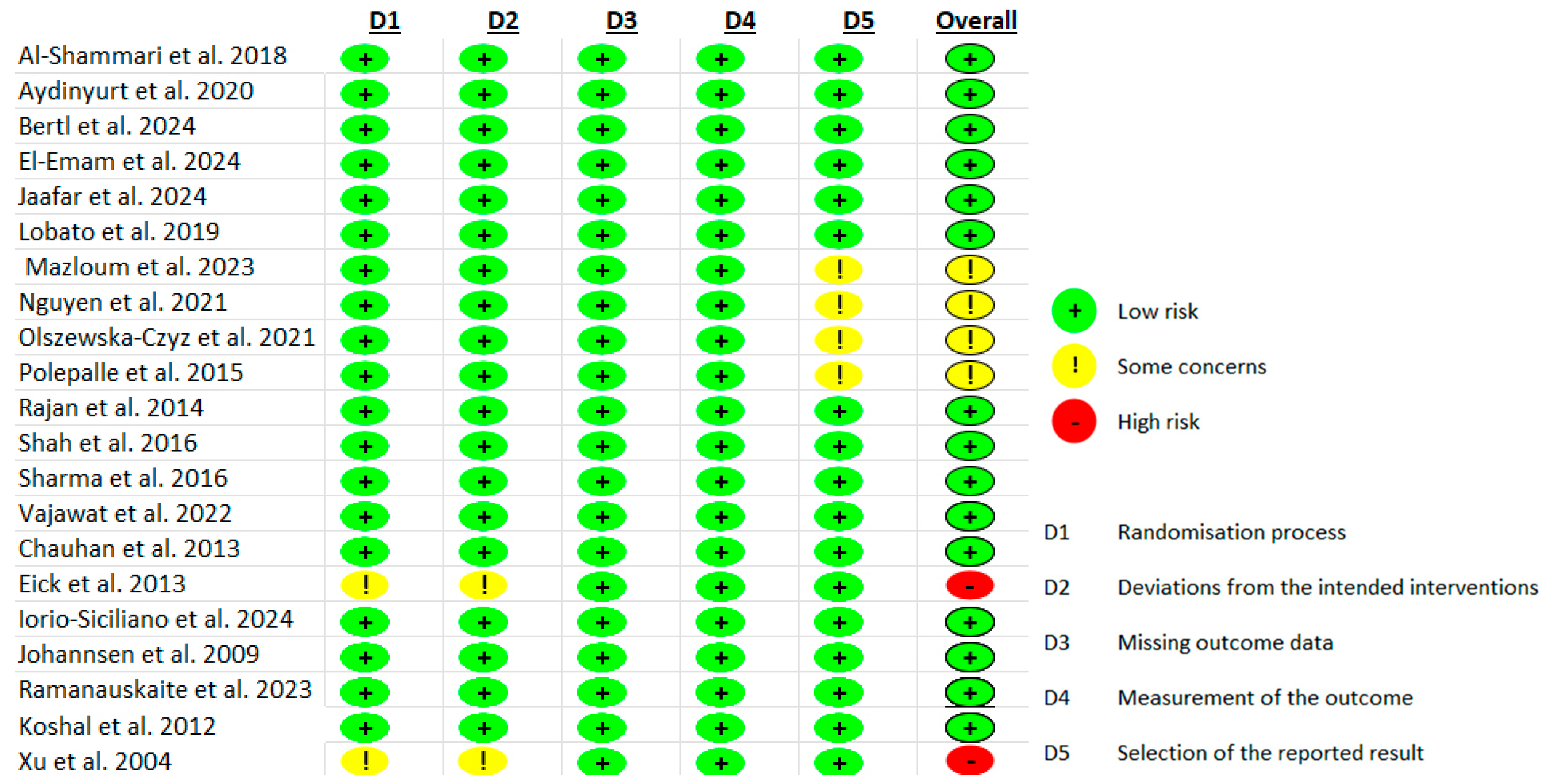
3.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
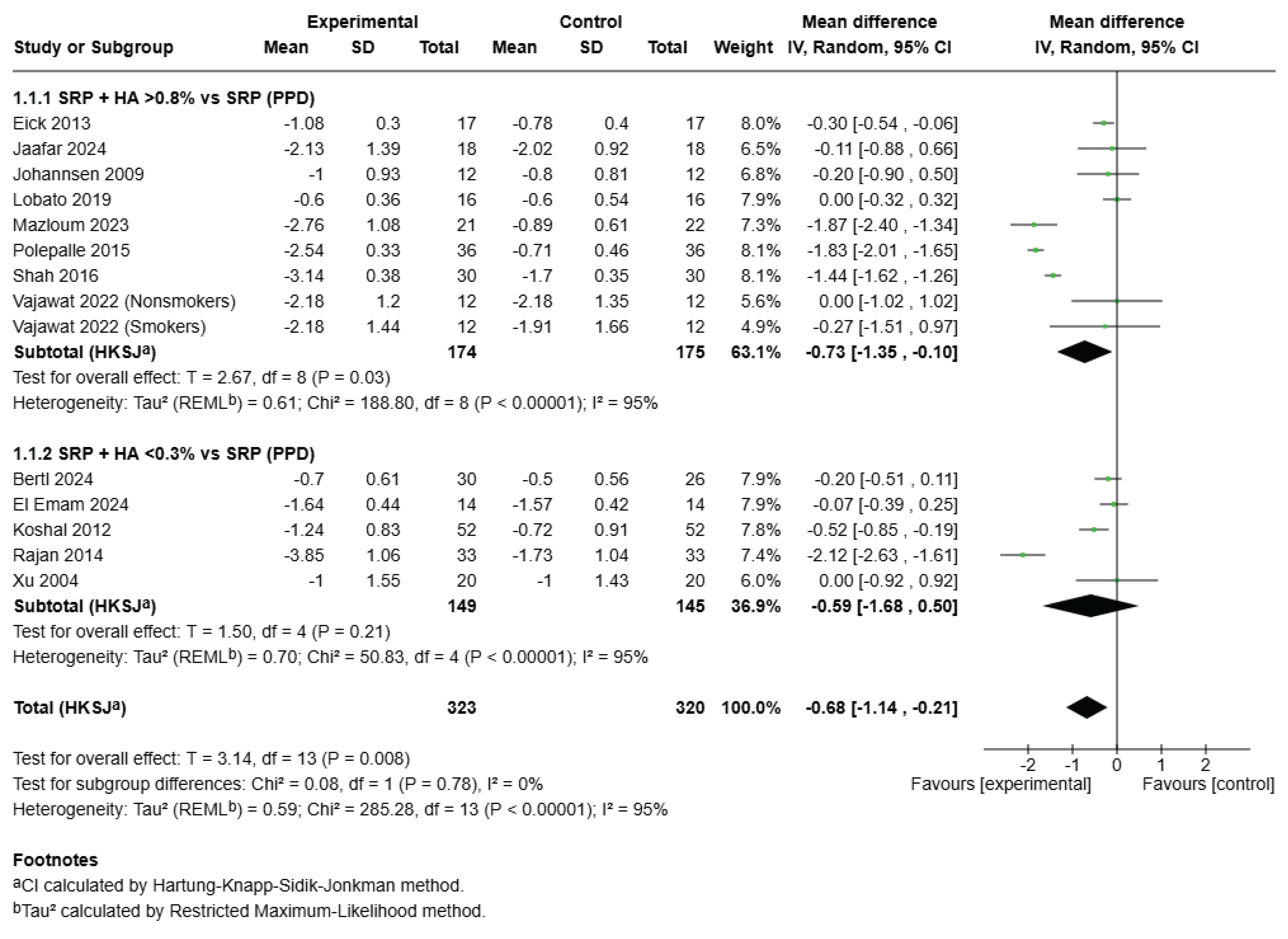
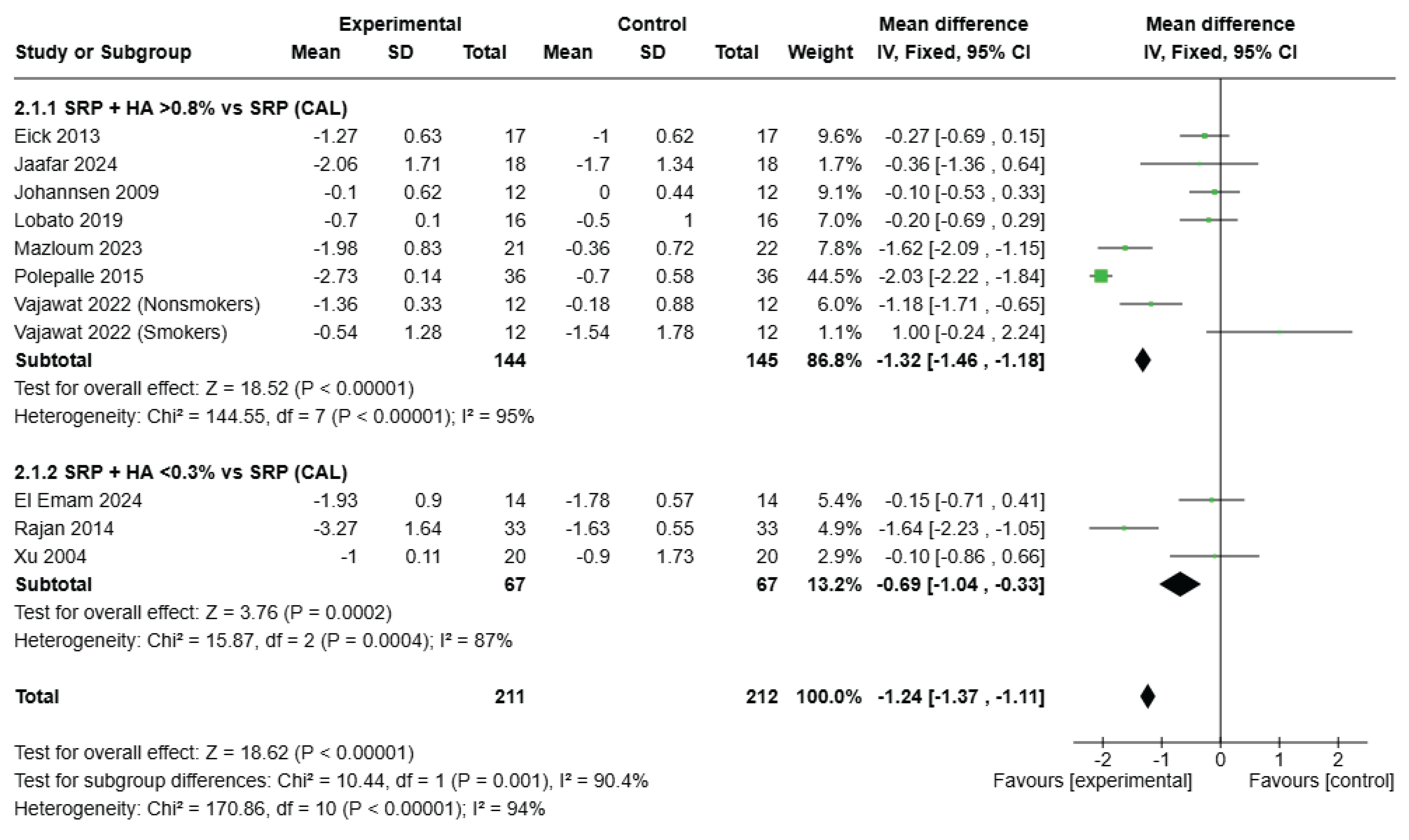
3.5. Meta-Analysis
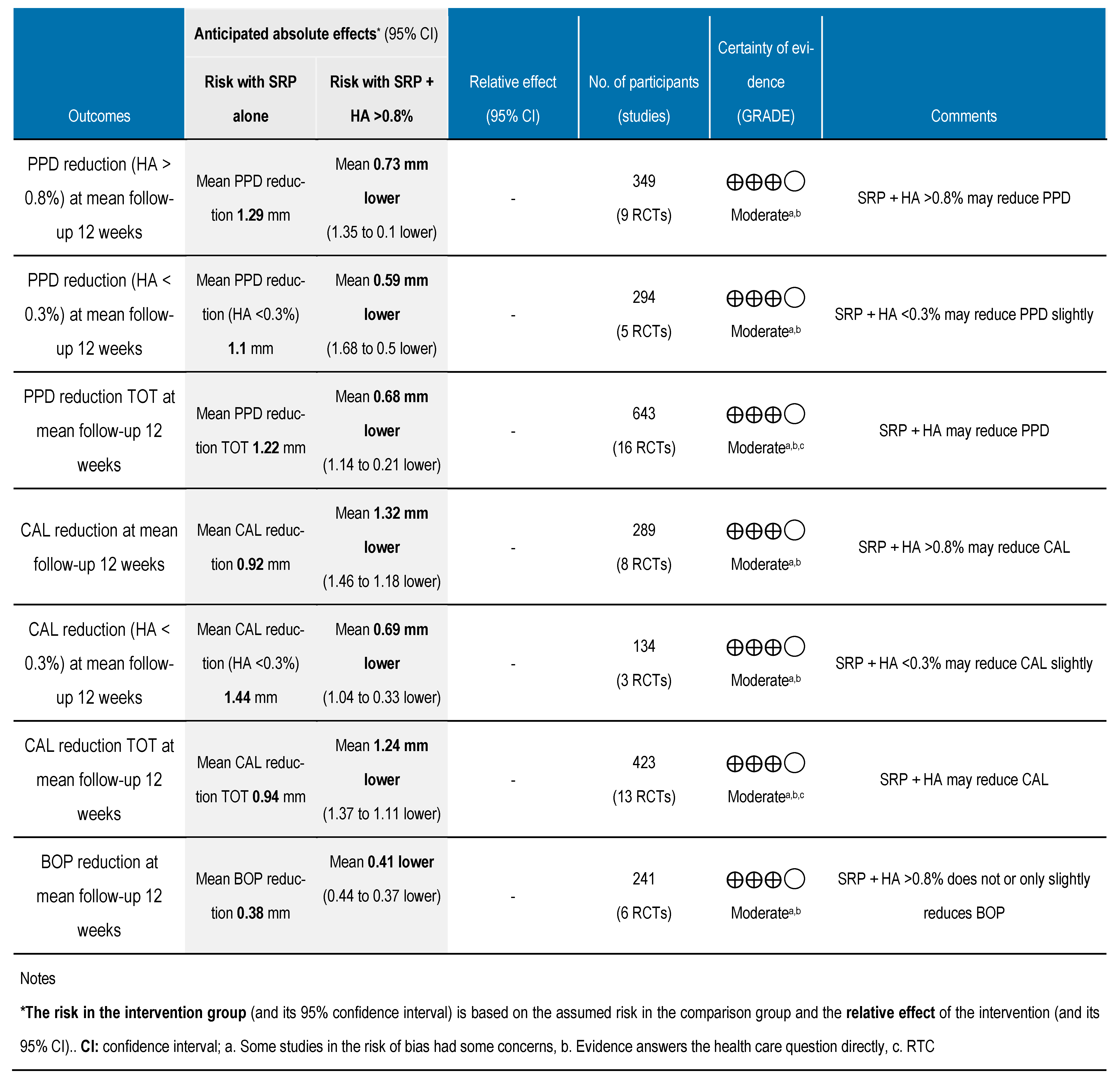
3.6. Grading the Body of Evidence
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Parameters
4.2. Microbiological and Biochemical Analysis
4.3. Formulation of HA and Its Clinical Impact
4.4. Study Limitations
4.5. Implications for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCT | Randomized Clinical Trial |
| NI | No Information |
| PD | Probing Depth |
| PPD | Pocket Probing Depth |
| CAL | Clinical Attachment Level |
| BOP | Bleeding On Probing |
| SRP | Scaling and Root Planing |
| HA | Hyaluronic Acid |
| PI | Plaque Index |
| RAL | Relative Attachment Level |
| GCCI | Gingival Color Change Index |
| EIBI | Eastman Interdental Bleeding Index |
| PBI | Papillary Bleeding Index |
| GI | Gingival Index |
| FMPS | Full Mouth Plaque Score |
| GRH | Gingival Recession level |
| API | Approximal Plaque Index |
| REC | Recession |
| MSBI | Mean Sulcus Bleeding Index |
| FMPS | Full Mouth Plaque Score |
| FMBS | Full Mouth Bleeding Index |
References
- Nocini, R.; Lippi, G.; Mattiuzzi, C. Periodontal disease: The portrait of an epidemic. J. Public Health Emerg. 2020, 4. ePub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könönen, E.; Gursoy, M.; Gursoy, U.K. Periodontitis: A multifaceted disease of tooth-supporting tissues. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, G.M.; Ash, M.M.; Caffesse, R.G. The effectiveness of subgingival scaling and root planing in calculus removal. J. Periodontol. 1981, 52, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, A.; Fiorini, V.; Zangani, A.; Faccioni, P.; Signoriello, A.; Albanese, M.; Lombardo, G. Topical agents in biofilm disaggregation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, M.; Moffa, A.; Vella, P.; Sabatino, L.; Capuano, F.; Salvinelli, B.; Lopez, M.A.; Carinci, F.; Salvinelli, F. Hyaluronic acid: Perspectives in dentistry. A systematic review. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waingade, M.; Medikeri, R.S.; Gaikwad, S. Effectiveness of hyaluronic acid in the management of oral lichen planus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. Anesth. Pain Med. 2022, 22, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotti, F.; Nocini, R.; Capocasale, G.; Fior, A.; Peretti, M.; Albanese, M. Malignant transformation evidences of oral lichen planus: When the time is of the essence. Oral Oncol. 2020, 104, 104594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertossi, D.; Malchiodi, L.; Albanese, M.; Nocini, R.; Nocini, P. Nonsurgical rhinoplasty with the novel hyaluronic acid filler VYC-25L: Results using a nasal grid approach. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2021, 41, NP512–NP520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, O.-C.; Boariu, M.; Rusu, D.; Iorio-Siciliano, V.; Sculean, A.; Stratul, S.-I. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of intrabony periodontal defects treated with hyaluronic acid or enamel matrix proteins: A 6-month prospective study. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2024, 22, 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Megally, A.; Zekeridou, A.; Cancela, J.; Giannopoulou, C.; Mombelli, A. Short ultrasonic debridement with adjunctive low-concentrated hypochlorite/amino acid gel during periodontal maintenance: Randomized clinical trial of 12 months. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliezer, M.; Imber, J.-C.; Sculean, A.; Pandis, N.; Teich, S. Hyaluronic acid as adjunctive to non-surgical and surgical periodontal therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 3423–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanauskaite, E.; Machiulskiene Visockiene, V.; Shirakata, Y.; Friedmann, A.; Pereckaite, L.; Balciunaite, A.; Dvyliene, U.M.; Vitkauskiene, A.; Baseviciene, N.; Sculean, A. Microbiological effects of sodium hypochlorite/-amino acids and cross-linked hyaluronic acid adjunctive to non-surgical periodontal treatment. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2024, 22, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.5 (updated August 2024). Cochrane. 2024. Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Pardo, A.; Baccini, F.; De Manzoni, R.; Viviani, M.; Brentaro, S.; Zangani, A.; Faccioni, P.; Luciano, U.; Zuffellato, N.; Signoriello, A.; et al. Air polishing therapy in supportive periodontal treatment: A systematic review. J. Appl. Cosmetol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMaster University and Evidence Prime. GRADEpro GDT: GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool. Available online: https://gradepro.org (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Xu, Y.; Höfling, K.; Fimmers, R.; Frentzen, M.; Jervøe-Storm, P.M. Clinical and microbiological effects of topical subgingival application of hyaluronic acid gel adjunctive to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2004, 75, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, A.; Tellefsen, M.; Wikesjö, U.; Johannsen, G. Local delivery of hyaluronan as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshal, A.; Bolt, R.; Galgut, P.N. A Comparison in Postoperative Healing of Sites Receiving Non-Surgical Debridement Augmented With and Without a Single Application of Hyaluronan 0.8% Gel. Available online: http://www.takara-net.com (accessed on 10 April 2025).
- Chauhan, A.; Bains, V.; Gupta, V.; Singh, G.; Patil, S. Comparative analysis of hyaluronan gel and xanthan-based chlorhexidine gel, as adjunct to scaling and root planing with scaling and root planing alone in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: A preliminary study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2013, 4, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Eick, S.; Renatus, A.; Heinicke, M.; Pfister, W.; Stratul, S.; Jentsch, H. Hyaluronic acid as an adjunct after scaling and root planing: A prospective randomized clinical trial. J. Periodontol. 2013, 84, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, P.; Baramappa, R.; Rao, N.M.; Pavaluri, A.K.; Indeevar, P.; Ur Rahaman, S. Hyaluronic acid as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in chronic periodontitis. A randomized clinical trail. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, ZC11–ZC14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polepalle, T.; Srinivas, M.; Swamy, N.; Aluru, S.; Chakrapani, S.; Chowdary, B.A. Local delivery of hyaluronan 0.8% as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis: A clinical and microbiological study. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2015, 19, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.A.; Vijayakar, H.N.; Rodrigues, S.V.; Mehta, C.J.; Mitra, D.K.; Shah, R.A. To compare the effect of the local delivery of hyaluronan as an adjunct to scaling and root planing versus scaling and root planing alone in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2016, 20, 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Gupta, R.; Dahiya, P.; Kumar, M. Comparative evaluation of coenzyme Q10-based gel and 0.8% hyaluronic acid gel in treatment of chronic periodontitis. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2016, 20, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shammari, N.M.; Shafshak, S.M.; Ali, M.S. Effect of 0.8% hyaluronic acid in conventional treatment of moderate to severe chronic periodontitis. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2018, 19, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobato, J.C.R.F.; Dos Santos Vilhena, M.A.; Izidoro, C.; Alves, R.C.; Proença, L. Single application of 0.8% hyaluronic acid as a coadjuvant of nonsurgical treatment in nonsmoking patients with periodontitis: A split-mouth, randomized, controlled pilot clinical trial. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2019, 23, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin Aydinyurt, H.; Akbal, D.; Altindal, D.; Bozoglan, A.; Seckin Ertugrul, A.; Demir, H. Evaluation of biochemical and clinical effects of hyaluronic acid on non-surgical periodontal treatment: A randomized controlled trial. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2020; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ho, H.T.; Huynh, N.C.; Dien, V.H.A.; Vo, T.L. Hyaluronic acid 0.2% application enhanced periodontitis treatment in non-surgical phase. J. Stomatol. 2021, 74, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska-Czyz, I.; Kralik, K.; Prpic, J. Biomolecules in dental applications: Randomized, controlled clinical trial evaluating the influence of hyaluronic acid adjunctive therapy on clinical parameters of moderate periodontitis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajawat, M.; Rao, D.P.C.; Kumar, G.S.V.; Rajeshwari, K.G.; Hareesha, M.S. Local delivery of hyaluronic acid as an adjunct to scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis in smokers and non-smokers. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2022, 26, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloum, T.A.; Amhaz, G.S.; Abdullah, G.H.; Aboelsaad, N.M. Efficiency of hyaluronic acid versus red injectable platelet-rich fibrin (I-PRF) in treatment of stage III periodontitis: Randomized controlled clinical trial. Int. Arab. J. Dent. 2023, 14, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertl, K.; Vlachou, S.; Pandis, N.; Zampelis, A.; Stavropoulos, A. Repeated local delivery of hyaluronic acid gel as adjunctive treatment of residual pockets in periodontitis patients undergoing supportive periodontal care: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adib Jaafar, M.; Voo Vui Ching, E.; Nisha Ali, S.; Subramaniam, J.; Ahmad Yaziz, Y. Hyaluronic acid in managing deep residual pockets in stage III–IV periodontitis: A randomized controlled trial. J. Dent. Indones. 2024, 31, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Emam, E.; Ezzat, O.; Almalahy, H. Efficacy of locally delivered hyaluronic acid gel as an adjunctive to non-surgical management of stage II or stage III periodontitis: A randomized controlled trial with microbiological analysis. Egypt. Dent. J. 2024, 70, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanauskaite, E.; Machiulskiene, V.; Dvyliene, U.M.; Eliezer, M.; Sculean, A. Clinical evaluation of a novel combination of sodium hypochlorite/amino acid and cross-linked hyaluronic acid adjunctive to non-surgical periodontal treatment: A case series. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2023, 21, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iorio-Siciliano, V.; Blasi, A.; Mauriello, L.; Salvi, G.E.; Ramaglia, L.; Sculean, A. Non-surgical treatment of moderate periodontal intrabony defects with adjunctive cross-linked hyaluronic acid: A single-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Barilli, A.; Signoriello, A.; Gualtieri, M.; Brancato, G.; Colapinto, G.; Lombardo, G.; Albanese, M. Oral health conditions and hygiene procedures in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. Explor. Med. 2024, 4, 852–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocini, R.; Favaloro, E.J.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Lippi, G. Periodontitis, coronary heart disease and myocardial infarction: Treat one, benefit all. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2020, 31, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polizzi, E.; Tetè, G. Manual vs mechanical oral hygiene procedures: Has the role of the dental hygienist in phase 2 post-lockdown really changed? Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2020, 18, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, M.; Herrera, D.; Kebschull, M.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Berglund, T.; Sculean, A.; Tonetti, M.S. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline for treatment of stage I–III periodontitis. J. Evid. Based Dent. Pract. 2021, 21, 101638. [Google Scholar]
- Shirbhate, U.; Bajaj, P. Injectable and self-invigorating hydrogel applications in dentistry and periodontal regeneration: A literature review. Cureus 2022, 14, e29248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gegout, P.-Y.; Stutz, C.; Huck, O. Gels as adjuvant to non-surgical periodontal therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertl, K.; Bruckmann, C.; Isberg, P.; Klinge, B.; Gotfredsen, K.; Stavropoulos, A. Hyaluronan in non-surgical and surgical periodontal therapy: A systematic review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirnazar, P.; Wolinsky, L.; Nachnani, S.; Haake, S.; Pilloni, A.; Bernard, G.W. Bacteriostatic effects of hyaluronic acid. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Database | Search Terms | Boolean Operators | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science | (“Periodontitis”[MeSH] OR non-surgical periodontal therapy OR periodontal disease) AND (“Hyaluronic Acid”[MeSH] OR hyaluronan OR hyaluronate) | AND, OR | Up to January 2025 |
| PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science | (“Hyaluronic Acid”[MeSH] OR hyaluro*) AND (“Periodontal Diseases”[MeSH] OR periodont*) AND non-surgical | AND, OR | Up to January 2025 |
| PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science | (“Hyaluronic Acid” OR hyaluro*) AND (Periodontitis OR periodont*) AND non-surgical | AND, OR | Up to January 2025 |
| First Author and Year | Study Design | Study Design | Country | Sample Size and Sex | Mean Age/Rang (Years) | Test and Control Interventions | Follow-Up | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xu 2004 [18] | RCT | Split-mouth | China | 20 (11 M, 9 F) | 48.6 | 1 SRP 2 SRP + 1 mL 0.2% HA gel | 6 and 12 wks | BOP, CAL, PD |
| Johannsen 2009 [19] | RCT | Split-mouth | Sweden | 12 (sex not stated) | 42–63 | 1 SRP 2 SRP + 0.2 mL + 0.8% HA gel | 12 wks | BOP, PI, CAL, PD |
| Koshal 2012 [20] | RCT | Random assignment | Africa | 52 (sex not stated) | / | 1 SRP + placebo 2 SRP + HA | 12 wks | GI, PD |
| Chauhan 2013 [21] | RCT with biochemical analysis | Random assignment | India | 11 (sex not stated) | 30–65 | 1 SRP 2 SRP + HA gel 3 SRP + HA gel + CHX gel | 6 and 12 wks | PD, CAL, PI |
| Eick 2013 [22] | RCT with microbiological analysis | Random assignment | Switzerland | 34 (sex not stated) | 41–72 | 1 SRP 2 SRP + 0.8% HA gel in office + 0.2% HA gel at home | 12, 24, 36 wks | BOP, PI, CAL, PD |
| Rajan 2014 [23] | RCT | Split-mouth | India | 33 (15 M, 18 F) | NI | 1 SRP 2 SRP + 0.2% HA gel | 4 and 12 wks | GI, PI, BOP, PPD, CAL |
| Polepalle 2015 [24] | RCT | Split-mouth | India | 18 (11 M, 7 F) | 30–60 45 | 1 SRP 2 SRP + 0.2 mL 0.8% HA gel | 4 and 12 wks | PI, BOP, PPD, CAL, CFU |
| Shah 2016 [25] | RCT | Split-mouth | India | 9 (sex not stated) | 30–60 45 | 1 SRP 2 SRP + 0.8% HA gel + periodontal dressing | 4 and 12 wks | GI, PI, PPD, RAL |
| Sharma 2016 [26] | RCT | Split-mouth | India | 24 (sex not stated) | 25–55 40 | 1 SRP + d coenzyme Q gel 2 SRP + 0.8% HA gel 3 SRP alone | 1, 2, 6 wks | PI, EIBI, GCCI, PD, CAL |
| Al-Shammari 2018 [27] | RCT with biochemical analysis | Split-mouth | Kingdom of Saudi Arabia | 24 (14 F, 10 M) | 24–57 40.5 | 1 SRP alone 2 SRP + 0.8% HA | 6 and 12 wks | PI, GI, PBI, PPD, CAL, human beta defensin-2 (hBD-2) expression |
| Lobato 2019 [28] | RCT | Split-mouth | India | 16 | 41–68 54.5 | 1 SRP 2 SRP + 0.8% HA | 6 and 12 wks | FMPS, GI, BOP, PD CAL |
| Aydinyurt 2020 [29] | RCT with biochemical analysis | Random assignment | Turkey | 96 (40 M, 56 F) | 22–55 38.5 | 1 SRP + saline irrigation 2 SRP + 0.2% HA gel 3 SRP + 0.2% HA hydrogel mouth rinse 4 SRP + 0.2% HA hydrogel mouth rinse + 0.2% HA gel | 1, 2, 4 wks | PI, GI, BOP, PD, GRH, CAL, biochemicals (ADA, CAT, GSH) |
| Nguyen 2021 [30] | RCT with microbiological analysis | Split-mouth | Vietnam | 34 | ni | 1 SRP + 0.9% NaCl solution rinse 2 SRP + 0.9% NaCl solution rinse + 1 mL 0.2% HA gel | 1, 2, 3, 6 wks | PI, GI, PPD, CAL, BOP |
| Olszewska 2021 [31] | RCT | Random assignment | Poland | 100 (51 F, 49 M) | 25–65 45 | 1 SRP + HA gel (1.6% reticular HA + 0.2% HA natural) 2 SRP alone | 12 wks | API, BOP, PPD, CAL |
| Vajawat 2022 [32] | RCT with microbiological analysis | Split-mouth | India | 24 | 35–65 50 | 1: SRP + placebo 2: SRP + 0.8% HA gel | 4, 12 wks | CAL, PD, BI, GI, PI |
| Mazloum 2023 [33] | RCT | Random assignment | Lebanon | 75 | 20–60 40 | 1 SRP + 0.8% HA gel 2 SRP + with red i-PRF 3 SRP alone | 4, 8, 12 wks | CAL, PD, PI, GI, BOP |
| Bertl 2024 [34] | RCT | Random assignment | Sweden | 56 (37 F, 19 M) | 35–75 55 | 1 SRP + 0.3% HA gel 2 SRP + saline solution | 12, 24, 36, 48 wks | PPD, PI, GI, BOP, CAL |
| Jaafar 2024 [35] | RCT | Random assignment | Malaysia | 36 (25 F, 11 M) | 30–60 45 | 1 SRP + 0.8% HA gel 2 SRP alone | 12 wks | PI, PD, CAL, BOP, REC |
| El Emam 2024 [36] | RCT | Random assignment | Egypt | 28 (14 M, 14 F) | 28–40 34 | 1 SRP + local 0.2% HA gel 2 SRP alone | 12 wks | PI, BI, CAL, MSBI, PD |
| Ramanaus kaite 2023 [37] | RCT | Random assignment | Lithuania | 21 | 30–72 | 1 SRP alone 2 SRP+ crosslinked HA gel baseline | 12 and 24 wks | PD, CAL, BOP, PI |
| Iorio-Siciliano 2025 [38] | RCT | Random assignment | Italy | 38 (14 M, 24 F) | Test 49.3 ±11.6 Control 50.8 ± 10.8 | 1 SRP 2 SRP + HA | 4, 12, 24 wks | PD, FMPS, FMBS, CAL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pardo, A.; Magnani, V.; Montagna, P.; Ala, A.; Brancato, G.; Melloni, F.; Lombardo, G.; De Santis, D. Clinical, Microbiological, and Biochemical Outcomes of Hyaluronic Acid in Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5975. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115975
Pardo A, Magnani V, Montagna P, Ala A, Brancato G, Melloni F, Lombardo G, De Santis D. Clinical, Microbiological, and Biochemical Outcomes of Hyaluronic Acid in Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5975. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115975
Chicago/Turabian StylePardo, Alessia, Veronica Magnani, Pietro Montagna, Andrea Ala, Gabriele Brancato, Federica Melloni, Giorgio Lombardo, and Daniele De Santis. 2025. "Clinical, Microbiological, and Biochemical Outcomes of Hyaluronic Acid in Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5975. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115975
APA StylePardo, A., Magnani, V., Montagna, P., Ala, A., Brancato, G., Melloni, F., Lombardo, G., & De Santis, D. (2025). Clinical, Microbiological, and Biochemical Outcomes of Hyaluronic Acid in Non-Surgical Periodontal Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5975. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115975