Load Forecasting Using BiLSTM with Quantile Granger Causality: Insights from Geographic–Climatic Coupling Mechanisms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Causality Test Between Environmental Factors and Load Data
2.1. Smoothness Check for Time Series of Load and Meteorological Factors
2.2. Relationship Identification of Load and Influencing Factors Based on QGCT
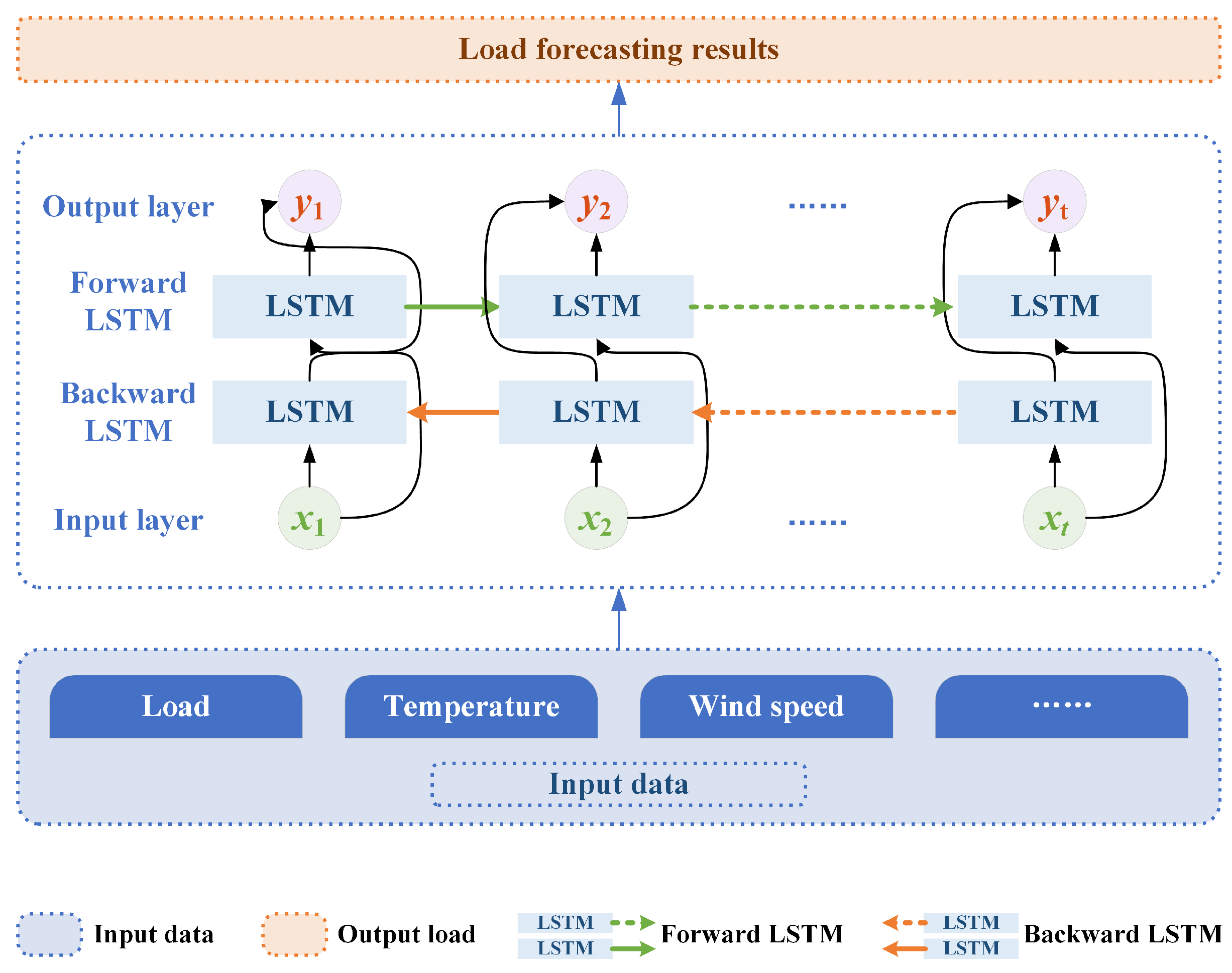
3. Load Forecasting Based on BiLSTM and the Leading Influencing Factors
3.1. BiLSTM-Based Load Forecasting Algorithm
3.2. Procedure of Load Forecasting Method Based on QGCT and BiLSTM
4. Case Study
4.1. Results of the Causality Test Between Environmental Factors and Electricity Loads
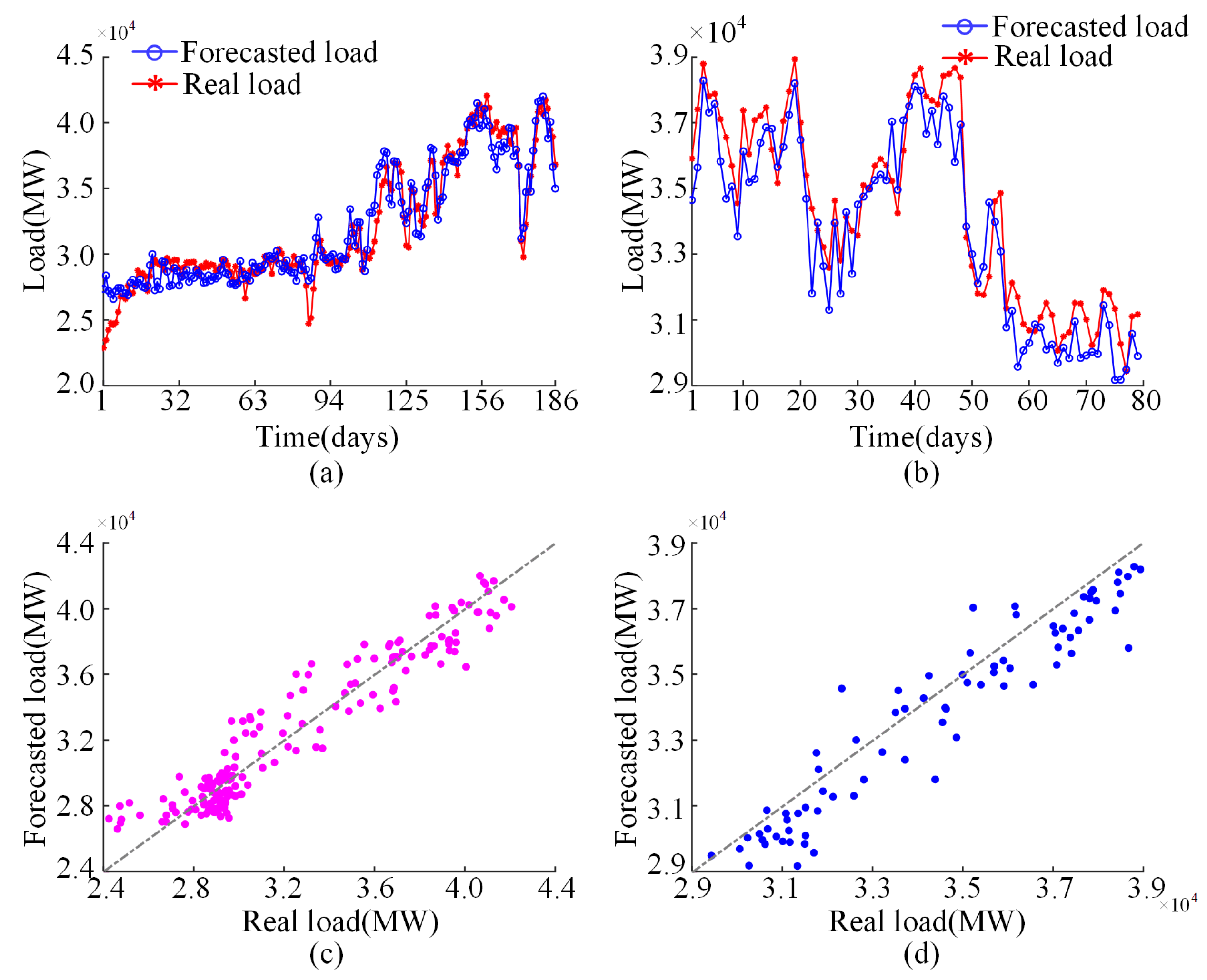
4.2. Effectiveness Analysis of QGCT-BiLSTM for Load Forecasting
4.3. Superiority Analysis of QGCT-BiLSTM for Load Forecasting
4.4. Sensitivity Analysis of Load Influencing Factors at Seasonal Scales
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, W.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Weng, L.G.; Liang, X.Y. Power grid load forecasting using a CNN-LSTM network based on a multi-model attention mechanism. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Liu, L.S.; Guo, K.Q.; Liu, S.R.; He, D.W. Short-term electricity load forecasting based on improved data decomposition and hybrid deep-learning models. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y. Forecasting masked-load with invisible distributed energy resources based on transfer learning and Bayesian tuning. Energy Convers. Econ. 2024, 5, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.J.; Zhu, J.Z.; Li, S.L.; Miao, Y.W.; Chung, C.Y.; Chen, Z.Y. Probabilistic residential load forecasting with sequence-to-sequence adversarial domain adaptation networks. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 1559–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Li, Y.; Qiu, W.Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Lin, Z.Z.; Yang, L. Cooperative-game-based day-ahead scheduling of local integrated energy systems with shared energy storage. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2022, 13, 1994–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Zhang, T.H.; Li, Q.S.; Li, Z.; Liang, H.L.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.Q.; Lin, Z.Z.; Yang, Y. Two-stage multiple cooperative games-based joint planning for shared energy storage provider and local integrated energy systems. Energy 2023, 284, 129114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Z.; Miao, Y.W.; Dong, H.J.; Li, S.L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, D. Short-term residential load forecasting based on k-shape clustering and domain adversarial transfer network. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Waseem, M.; Lin, Z.Z.; Yang, L. Data-driven load forecasting of air conditioners for demand response using Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm-based ANN. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2019, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, P.; Lin, Z.Z. A data-driven bottom-up approach for spatial and temporal electric load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 1966–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Ling, G.; Song, X.X. ELFNet: An effective electricity load forecasting model based on a deep convolutional neural network with a double-attention mechanism. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.B.; Hu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, C.L.; Bai, Q. Enhancing short-term load forecasting accuracy in high-volatility regions using lstm-scn hybrid models. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Hong, T.; Fang, S.C. Robust regression models for load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 5397–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, L.; Lenk, S.; Bretschneider, P. Advancing electric load forecasting: Leveraging federated learning for distributed, non-stationary, and discontinuous time series. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 2065–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Chen, H.N.; Luo, X.W. A Kalman filter-based bottom-up approach for household short-term load forecast. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, G.; Pelda, P.; Smyl, S. A hybrid residual dilated lstm and exponential smoothing model for midterm electric load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 2879–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, B.Y.; Precup, D.; Boulet, B. Multiple kernel learning-based transfer regression for electric load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, H.S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, G.J. Minute-level ultra-short-term power load forecasting based on time series data features. Appl. Energy 2024, 372, 123801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Majumdar, A.; Elvira, V.; Chouzenoux, E. Blind Kalman filtering for short-term load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 4916–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyl, S.; Dudek, G.; Pelka, P. ES-dRNN: A hybrid exponential smoothing and dilated recurrent neural network model for short-term load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 11346–11358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.X.; Wu, D.; Boulet, B. Spatial-temporal residential short-term load forecasting via graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 5373–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, D.; Faria, P.; Vale, Z.; Correia, R. Short time electricity consumption forecast in an industry facility. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Bu, S.R.; Chen, W.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.R. Deep reinforcement learning-assisted federated learning for robust short-term load forecasting in electricity wholesale markets. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 5073–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, N.; Du, E.; Yan, J.; Han, S.; Liu, Y.Q. A comprehensive review for wind, solar, and electrical load forecasting methods. Glob. Energy Interconnect. 2022, 5, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Jain, S.K. A Novel two-stage framework for mid-term electric load forecasting. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.J.; Chen, K.L.; Wang, Q.; He, Z.Y.; Hu, J.; He, J.L. Short-term load forecasting with deep residual networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 3943–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.M.; Zhao, P. A hybrid load forecasting model based on support vector machine with intelligent methods for feature selection and parameter optimization. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Chen, Q.; Yan, J.Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J.Y. A novel asynchronous deep reinforcement learning model with adaptive early forecasting method and reward incentive mechanism for short-term load forecasting. Energy 2021, 236, 121492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, N.; Arora, S.; Taylor, J.W. Probabilistic load forecasting using post-processed weather ensemble predictions. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2023, 74, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, M.; Campbell, A.; Sangamwar, S.; Li, C.L.; Hong, T. Combining weather stations for electric load forecasting. Energies 2019, 12, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.W.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, Y. Short-term load-forecasting method based on wavelet decomposition with second-order gray neural network model combined with ADF test. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 16324–16331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troster, V.; Shahbaz, M.; Uddin, G.S. Renewable energy, oil prices, and economic activity: A Granger-causality in quantiles analysis. Energy Econ. 2018, 70, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.L.; Gu, J.; Meng, L.; Wen, H.L.; Ma, J.H. An explainable framework for load forecasting of a regional integrated energy system based on coupled features and multi-task learning. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2022, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.X.; Ma, H.R.; Chen, L.J.; Wang, B.; Wang, H.X.; Li, X.Z.; Gao, W.Z. Short-term load forecasting of an integrated energy system based on STL-CPLE with multitask learning. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2024, 9, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.F.; Guo, Y.H.; Zheng, J.M.; Hong, W.C. A generalized regression model based on hybrid empirical mode decomposition and support vector regression with back-propagation neural network for mid-short-term load forecasting. J. Forecast. 2020, 39, 737–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Ayub, N.; Farooq, U.; Alvi, M.J.; Albogamy, F.R.; Rukh, G.; Haider, S.I.; Azar, A.T.; Bukhsh, R. Towards electric price and load forecasting using CNN-based ensembler in smart grid. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.D.; Qin, H.; Yan, L.Q.; Lu, J.Y.; Cheng, L.G. Interval prediction method based on long-short term memory networks for system integrated of hydro, wind and solar power. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 6176–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprillia, H.; Yang, H.T.; Huang, C.M. Statistical load forecasting using optimal quantile regression random forest and risk assessment index. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Factors | Threshold of 1% | ADF Value | Probability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum temperature | −1.9424 | −13.294 | 0.0010 ** |
| Minimum temperature | −1.9424 | −6.8712 | 0.0010 ** |
| Average temperature | −1.9424 | −3.4273 | 0.0010 ** |
| Maximum humidity | −1.9424 | −13.049 | 0.0010 ** |
| Minimum humidity | −1.9424 | −7.4050 | 0.0010 ** |
| Average humidity | −1.9424 | −5.7568 | 0.0010 ** |
| Maximum wind speed | −1.9424 | −13.657 | 0.0010 ** |
| Minimum wind speed | −1.9424 | −6.1659 | 0.0010 ** |
| Average wind speed | −1.9424 | −6.6557 | 0.0010 ** |
| Rainfall | −1.9424 | −8.2339 | 0.0010 ** |
| Average load | −1.9424 | −3.1475 | 0.0024 ** |
| Quartile | Maximum Temperature | Minimum Temperature | Average Temperature | Maximum Humidity | Minimum Humidity | Average Humidity | Maximum Wind Speed | Minimum Wind Speed | Average Wind Speed | Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0709 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3901 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2270 | 0.0071 |
| 0.10 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7305 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.15 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2979 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0142 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1348 | 0.0071 |
| 0.20 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0142 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.5957 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1064 | 0.0071 |
| 0.25 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0213 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7660 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2695 | 0.0071 |
| 0.30 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7589 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.35 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0709 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2128 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0709 | 0.0071 |
| 0.40 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0993 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2553 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.45 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1064 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0851 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3546 | 0.0071 |
| 0.50 | 0.1773 | 0.0071 | 0.0213 | 0.1631 | 0.0071 | 0.0709 | 0.1135 | 0.0071 | 0.4397 | 0.0071 |
| 0.55 | 0.0355 | 0.0071 | 0.3901 | 0.0355 | 0.0071 | 0.8156 | 0.0426 | 0.0071 | 0.3688 | 0.0071 |
| 0.60 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4113 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3759 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6596 | 0.0071 |
| 0.65 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1773 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.9433 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7376 | 0.0071 |
| 0.70 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0567 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.8369 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1844 | 0.0071 |
| 0.75 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2340 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0851 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0355 | 0.0071 |
| 0.80 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2199 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.85 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3333 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2411 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.90 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0142 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3050 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.95 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0213 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4043 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.5461 | 0.0071 |
| Quartile | Maximum Temperature | Minimum Temperature | Average Temperature | Maximum Humidity | Minimum Humidity | Average Humidity | Maximum Wind Speed | Minimum Wind Speed | Average Wind Speed | Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0709 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4610 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4681 | 0.0071 |
| 0.10 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6170 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0638 | 0.0071 |
| 0.15 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1844 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0213 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.20 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6950 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2270 | 0.0071 |
| 0.25 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7021 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1844 | 0.0071 |
| 0.30 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0496 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2411 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1560 | 0.0071 |
| 0.35 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1844 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6809 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0284 | 0.0071 |
| 0.40 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0638 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2624 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0213 | 0.0071 |
| 0.45 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0284 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1206 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0426 | 0.0071 |
| 0.50 | 0.2908 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4043 | 0.0071 | 0.0213 | 0.2057 | 0.0071 | 0.4184 | 0.0071 |
| 0.55 | 0.1206 | 0.0071 | 0.7872 | 0.0355 | 0.0071 | 0.7092 | 0.2057 | 0.0071 | 0.8652 | 0.0071 |
| 0.60 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3759 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6738 | 0.0851 | 0.0071 | 0.3688 | 0.0071 |
| 0.65 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4610 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1560 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1631 | 0.0071 |
| 0.70 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4681 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7518 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0922 | 0.0071 |
| 0.75 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4610 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1560 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0426 | 0.0071 |
| 0.80 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1915 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7447 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0142 | 0.0071 |
| 0.85 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3404 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.5035 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.90 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2057 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0213 | 0.0071 |
| 0.95 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1348 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.5887 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7801 | 0.0071 |
| Quartile | Maximum Temperature | Minimum Temperature | Average Temperature | Maximum Humidity | Minimum Humidity | Average Humidity | Maximum Wind Speed | Minimum Wind Speed | Average Wind Speed | Rainfall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0355 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4610 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4326 | 0.0071 |
| 0.10 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6596 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1064 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0567 | 0.0071 |
| 0.15 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1844 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1702 | 0.0071 |
| 0.20 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6879 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1064 | 0.0071 |
| 0.25 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3333 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1489 | 0.0071 |
| 0.30 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0709 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.7092 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0426 | 0.0071 |
| 0.35 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0496 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0993 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1418 | 0.0071 |
| 0.40 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0496 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2695 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2128 | 0.0071 |
| 0.45 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0284 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2553 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1348 | 0.0071 |
| 0.50 | 0.0567 | 0.0071 | 0.0426 | 0.1206 | 0.0071 | 0.6879 | 0.2979 | 0.0071 | 0.3688 | 0.0071 |
| 0.55 | 0.0993 | 0.0071 | 0.9078 | 0.1206 | 0.0071 | 0.2695 | 0.1773 | 0.0071 | 0.7660 | 0.0071 |
| 0.60 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.8085 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1986 | 0.0496 | 0.0071 | 0.6241 | 0.0071 |
| 0.65 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0851 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0638 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4823 | 0.0071 |
| 0.70 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4681 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.8794 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.75 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.4184 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.9504 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2908 | 0.0071 |
| 0.80 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2128 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6950 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.85 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.3121 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1064 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 |
| 0.90 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2624 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.2837 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.0142 | 0.0071 |
| 0.95 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.1631 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.5745 | 0.0071 | 0.0071 | 0.6170 | 0.0071 |
| Evaluation Metrics | Unfiltered | Filtered | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Test Set | Training Set | Test Set | |
| RMSE | 187.91 | 205.15 | 105.81 | 145.27 |
| MAE | 136.05 | 162.49 | 87.60 | 113.65 |
| MBE | 1.89 | −95.56 | 7.49 | −61.61 |
| MAPE | 0.0432 | 0.0469 | 0.0366 | 0.0255 |
| Category | Method | RMSE | MAE | MAPE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression load forecasting | Unfiltered Key Factors | BP [34] | 192.5175 | 160.7176 | 0.0465 |
| CNN [35] | 193.9727 | 157.0710 | 0.0460 | ||
| LSTM [36] | 190.8181 | 155.0108 | 0.0443 | ||
| RF [37] | 188.6064 | 160.7783 | 0.0472 | ||
| QGCT-BiLSTM | 205.1504 | 162.4930 | 0.0469 | ||
| Filtered Key Factors | BP [34] | 170.2113 | 141.0954 | 0.0413 | |
| CNN [35] | 181.3503 | 155.6983 | 00455 | ||
| LSTM [36] | 172.0750 | 137.7569 | 0.0399 | ||
| RF [37] | 185.5207 | 160.2694 | 0.0471 | ||
| QGCT-BiLSTM | 145.2686 | 113.6537 | 0.0255 | ||
| Time-series load forecasting | BP [34] | 321.8326 | 276.0081 | 0.0779 | |
| CNN [35] | 429.9377 | 356.0354 | 0.1027 | ||
| LSTM [36] | 364.3561 | 297.9974 | 0.0834 | ||
| RF [37] | 300.4929 | 261.7523 | 0.0740 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Xu, N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, Z. Load Forecasting Using BiLSTM with Quantile Granger Causality: Insights from Geographic–Climatic Coupling Mechanisms. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5912. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115912
Huang X, Liu L, Xu N, Chen Y, Wang X, Lin Z. Load Forecasting Using BiLSTM with Quantile Granger Causality: Insights from Geographic–Climatic Coupling Mechanisms. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5912. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115912
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xianan, Lin Liu, Nuo Xu, Yantao Chen, Xiaofei Wang, and Zhenzhi Lin. 2025. "Load Forecasting Using BiLSTM with Quantile Granger Causality: Insights from Geographic–Climatic Coupling Mechanisms" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5912. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115912
APA StyleHuang, X., Liu, L., Xu, N., Chen, Y., Wang, X., & Lin, Z. (2025). Load Forecasting Using BiLSTM with Quantile Granger Causality: Insights from Geographic–Climatic Coupling Mechanisms. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5912. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115912







