A Survey of Electromagnetic Techniques Applied to Cultural Heritage Conservation
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- There is distrust towards irradiation techniques applied to CH conservation, and in some countries, there is a prohibition on their use;
- The coexistence in some artifacts of different organic materials makes conservation procedures a real technical challenge;
- As for the EM techniques applied to diagnosis, even for those applied to conservation techniques, there are no real standards or best practices.
2. EM Techniques Applied to CH
2.1. Radiation Parameters and Dosimetry for CH Application
- The absorbed dose;
- The absorbed-dose rate.
- Size, density, homogeneity or heterogeneity of the artifact;
- Balance between reliability and harmlessness of treatment.
2.2. Ionizing Radiation vs. Traditional Methods
- Alcohol 70% eliminates fungi but it has no effect on spores;
- Fumigation is effective but carcinogenic;
- Anoxia does not guarantee penetrability;
- Freezing is effective on fungi, but not on spores;
- Dry sanitization performs only a superficial removal [70].
2.3. Ionizing Radiation Risks
- Color changes and surface erosion;
- Compromising of the mechanical integrity of material.
- Transparent materials tint easily;
- Opaque materials do not manifest visible changes;
- Paper may structurally collapse.
3. EM Techniques for CH Restoration
- Irradiating photon energy;
- Atomic number of the absorbing material.
- Direct interaction with the DNA;
- Indirect modification, inducing free radical production through water radiolysis [59].
3.1. EM Techniques for Decontamination of CH
3.1.1. Application of Gamma and X-Ray for Decontamination of CH
- Hair;
- Skin;
- Teeth;
- Textiles.
3.1.2. Microwave (MW) Heating and Radiofrequency (RF) for Decontamination of CH
- Eubacteria (five different species isolated in their research);
- Cyanobacteria (10 different species isolated in their research);
- Green algae (13 different species isolated in their research).
3.2. EM Techniques for Consolidation of CH
4. Deterioration of CH Artifacts: Causes and Process
- The constituent(s) of the material(s) the manufacture is made of;
- The level of deterioration;
- How the constituents interact with the deterioration agent(s) (hence the mechanism of deterioration processes).
4.1. Inorganic Materials
4.2. Organic Materials
- Wood;
- Paper;
- Parchment;
- Leather;
- Textiles.
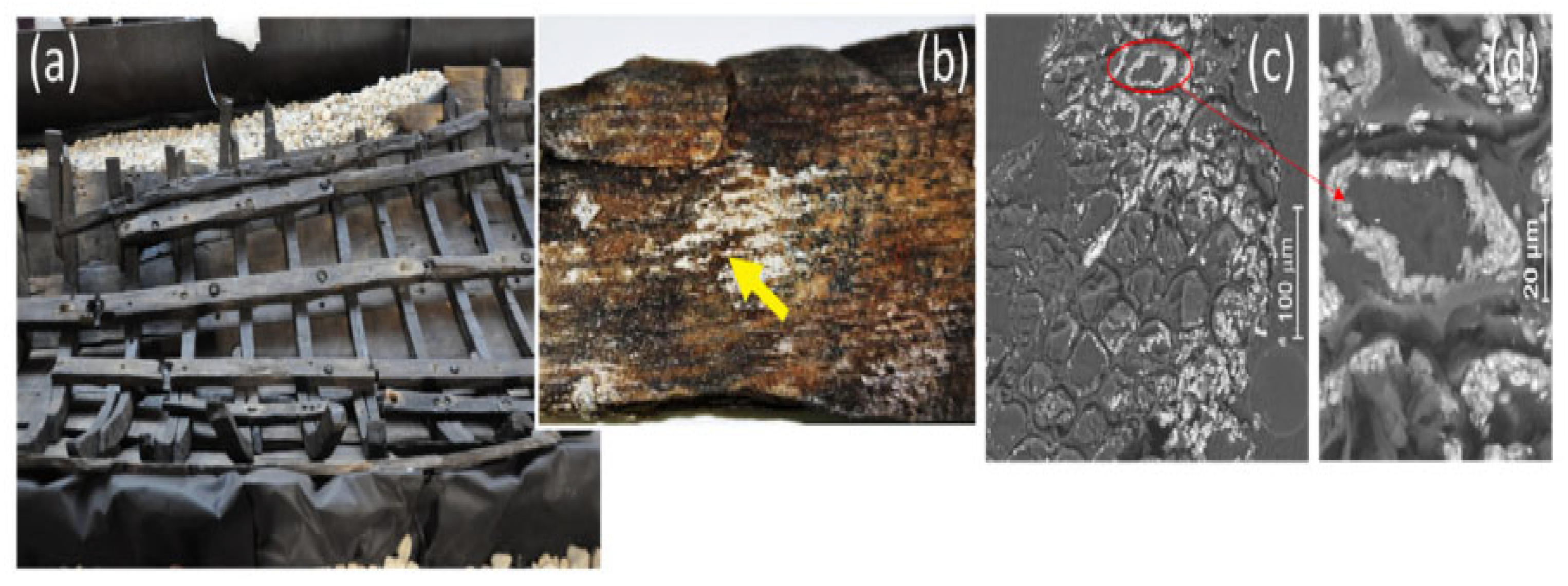
4.2.1. Wood
4.2.2. Paper
- 1799, the Fourdrinier machine;
- 1844, groundwood pulp.
4.2.3. Leather and Parchment
4.2.4. Textiles
5. Conclusions and Future Prospective
- “There is broad agreement across networks that although attention is paid to the dissemination of sound scientific developments […] improvements can be made in terms of bringing the results to where they have the most impact” [14] (Introduction, p. 2, © IAEA https://www.iaea.org/publications/10937/uses-of-ionizing-radiation-for-tangible-cultural-heritage-conservation (accessed on 2 January 2025));
- “Besides networking, there is a continuous need for establishing good practice procedures and standards in the field of safeguarding cultural artifacts” [14] (Introduction, pp. 1–2, © IAEA https://www.iaea.org/publications/10937/uses-of-ionizing-radiation-for-tangible-cultural-heritage-conservation (accessed on 2 January 2025));
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGLAE | Accélérateur Grand Louvre d’Analyse Élémentaire |
| CH | Cultural Heritage |
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| EMW | Electromagnetic wave |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy |
| FT-Raman | Fourier Transform Raman spectroscopy |
| IAEA | International Atomic Energy Agency |
| MW | Microwave |
| RF | Radiofrequency |
| UNESCO | United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization |
References
- First Aid and Resilience for Cultural Heritage in Times of Crisis (FAR). ICCROM. Available online: https://www.iccrom.org/programmes/first-aid-and-resilience-times-crisis-far (accessed on 9 November 2024).
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre. UNESCO World Heritage Centre—List of World Heritage in Danger. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/danger-list/ (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- World Heritage. UNESCO. Available online: https://www.unesco.org/en/world-heritage (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/conventiontext/ (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Prott, L.V.; O’Keefe, P.J. Unesco Handbook of National Regulations Concerning the Export of Cultural Property; cc.88/ws/27; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Nafziger, J.A.R.; Paterson, R.K. Handbook on the Law of Cultural Heritage and International Trade; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2014; ISBN 978-1-78100-733-4. [Google Scholar]
- Onofri, L. Old Master Paintings, Export Veto and Price Formation: An Empirical Study. Eur. J. Law Econ. 2009, 28, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortella, L.; Albino, C.; Tran, Q.-K.; Froment, K. 50 Years of French Experience in Using Gamma Rays as a Tool for Cultural Heritage Remedial Conservation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 171, 108726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iperion, H.S. Integrating Platforms for the European Research Infrastructure on Heritage Science. Available online: https://www.iperionhs.eu/provider/51/ (accessed on 2 January 2025).
- Moise, I.V.; Ene, M.; Negut, C.D.; Cutrubinis, M.; Manea, M.M. Radiation Processing for Cultural Heritage Preservation—Romanian Experience. Nukleonika 2017, 62, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Katušin-Ražem, B.; Ražem, D.; Braun, M. Irradiation Treatment for the Protection and Conservation of Cultural Heritage Artefacts in Croatia. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2009, 78, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.M.; Machado, L.D.B.; Borrely, S.; Sampa, M.H.; Rela, P.; Farah, J.P.; Schumacher, R.I. Effects of Gamma Rays on a Restored Painting from the XVIIth Century. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2002, 63, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraiem, M.; Mejri, A.; Trabelsi, M.H.; Trabelsi, Z. Radiation Processing for Cultural Heritage Preservation—Tunisian Experience; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Vienna, Austria, 2022; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Uses of Ionizing Radiation for Tangible Cultural Heritage Conservation; Radiation Technology Series; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2017; ISBN 978-92-0-103316-1. [Google Scholar]
- Magaudda, G. The Recovery of Biodeteriorated Books and Archive Documents through Gamma Radiation: Some Considerations on the Results Achieved. J. Cult. Herit. 2004, 5, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.E.; Calvo, A.M.; Kairiyama, E. Gamma Radiation for Preservation of Biologically Damaged Paper. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2002, 63, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, M.; Brizzi, M.; Magaudda, G.; Martinelli, G.; Plossi-Zappalà, M.; Rocchetti, F.; Savagnone, F. Gamma Radiation Treatment of Paper in Different Environmental Conditions: Chemical, Physical and Microbiological Analysis. Restaur. Int. J. Preserv. Libr. Arch. Mater. Restaur. 2001, 22, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimat, A.; Schöder, S.; Thoury, M.; Missori, M.; Paris-Lacombe, S.; Dupont, A.-L. Short- and Long-Term Effects of X-Ray Synchrotron Radiation on Cotton Paper. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2795–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marušić, K.; Klarić, M.Š.; Sinčić, L.; Pucić, I.; Mihaljević, B. Combined Effects of Gamma-Irradiation, Dose Rate and Mycobiota Activity on Cultural Heritage—Study on Model Paper. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 170, 108641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellheiser, J.G. Nonchemical Treatment Processes for Disinfestation of Insects and Fungi in Library Collections; IFLA Publications: Washington, DC, USA; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1992; ISBN 978-3-598-21788-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gimat, A.; Schoeder, S.; Thoury, M.; Dupont, A.-L. Impact of the Paper Degradation State and Constituents on Its Behavior During and After X-Ray Exposure. Preprint 2022. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Despot, R.; Sinkovic, T.; Jambreković, V.; Bogner, A.; Humar, M. The Influence of Sterilisation by Gamma Radiation on Natural Durability of Wood. Wood Res. 2008, 53, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kunstadt, P. Radiation Disinfestation of Wood Products. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1998, 52, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despot, R.; Hasan, M.; Brischke, C.; Welzbacher, C.R.; Rapp, A.O. Changes in Physical, Mechanical and Chemical Properties of Wood during Sterilisation by Gamma Radiation. Holzforschung 2007, 61, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despot, R.; Hasan, M.; Rapp, A.O. Changes in Selected Properties of Wood Caused by Gamma Radiation. In Gamma Radiation; Books on Demand: Hamburg, Germany, 2012; pp. 281–304. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, I.; Mesquita, N.; Verde, S.C.; Carolino, M.M.; Portugal, A.; Botelho, M.L. Bioburden Assessment and Gamma Radiation Inactivation Patterns in Parchment Documents. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2013, 88, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, I.; Mesquita, N.; Verde, S.C.; Trigo, M.J.; Ferreira, A.; Carolino, M.M.; Portugal, A.; Botelho, M.L. Gamma Radiation Effects on Physical Properties of Parchment Documents: Assessment of Dmax. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1943–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csepregi, Á.; Szikszai, Z.; Targowski, P.; Sylwestrzak, M.; Müller, K.; Huszánk, R.; Angyal, A.; Döncző, B.; Kertész, Z.; Szarka, M.; et al. Possible Modifications of Parchment during Ion Beam Analysis. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, K.; Gonzalez, L.; Kennedy, C.; Mills, D.; Davis, G.; Wess, T. Is There Evidence for Change to Collagen within Parchment Samples after Exposure to an X-Ray Dose during High Contrast X-Ray Microtomography? A Multi Technique Investigation. Herit. Sci. 2013, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geba, M.; Lisa, G.; Marta, U.; Olaru, A.; Spiridon, I.; Leon, A.; Stanculescu, I. Gamma Irradiation of Protein-Based Textiles for Historical Collections Decontamination. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 118, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujcic, I.; Masic, S.; Medic, M.; Milicevic, B.; Dramicanin, M. The Influence of Gamma Irradiation on the Color Change of Wool, Linen, Silk, and Cotton Fabrics Used in Cultural Heritage Artifacts. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 156, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manea, M.M.; Negut, C.D.; Stanculescu, I.R.; Ponta, C.C. Irradiation Effects on Canvas Oil Painting: Spectroscopic Observations. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
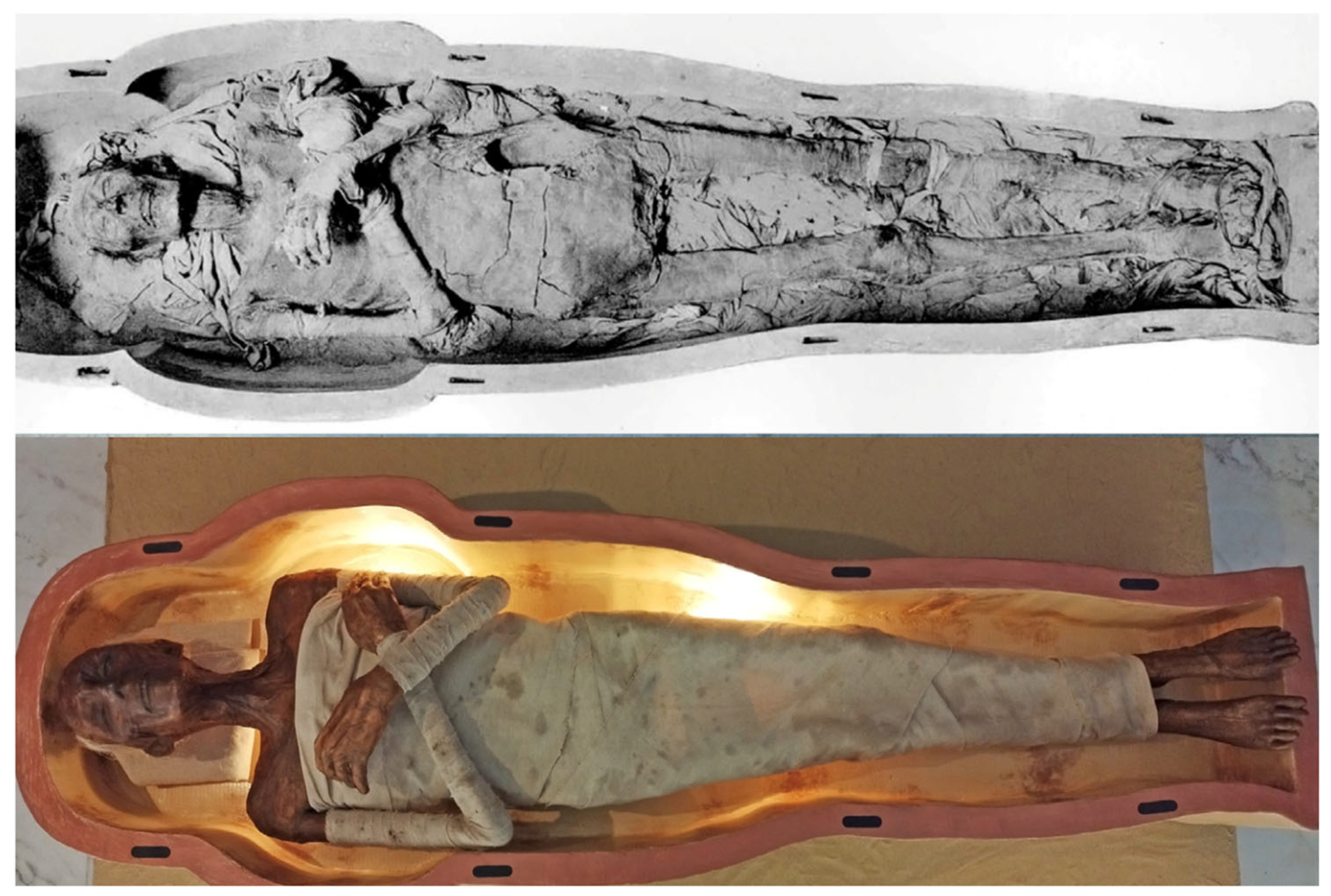
- De Tassigny, C.; Brouqui, M. Adaptation à la Désinfection de la Momie de Ramses II du Procédé de Radiosterilisation Gamma; International Council of Museums: Paris, France, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Balout, L.; Roubet, C.; Azouvi, J.; Desroches-Noblecourt, C. La Momie de Ramsès II: Contribution Scientifique à L’égyptologie; Recherche sur les Civilisations: Paris, France, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Nuclear Techniques for Cultural Heritage Research; Radiation Technology Series; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2011; ISBN 978-92-0-114510-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sinco, P. Use of Gamma Rays in Book Conservation. Nucl. News 2000, 24, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, M.H.; Dietz, G.R. Radiation-Processed Wood-Plastic Materials. In Modern Materials; Gonser, B.W., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1968; Volume 6, pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, S.; Caliendo, E.; Guida, M.; Bisceglia, B. Preliminary Assessment, by Means of Radon Exhalation Rate Measurements, of the Bio-Sustainability of Microwave Treatment to Eliminate Biodeteriogens Infesting Stone Walls of Monumental Historical Buildings. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 251, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzman, O.; Olmi, R.; Riminesi, C.; Tiano, P. Preliminary Study on Controlling Black Fungi Dwelling on Stone Monuments by Using a Microwave Heating System. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2013, 4, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Mascalchi, M.; Osticioli, I.; Riminesi, C.; Cuzman, O.; Salvadori, B.; Siano, S. Preliminary Investigation of Combined Laser and Microwave Treatment for Stone Biodeterioration. Stud. Conserv. 2015, 60, S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, A.; Bisceglia, B.; de Leo, R.; Diaferia, N. An Innovative Microwave System for Wooden Art Object Disinfestation. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. 2012, 31, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivancos-Ramón, V.; Pérez-Marín, E.; Nuño-Fernández, L.; Balbastre, J.; Zona-Ortiz, A. Microwave Treatment for Woodworm Disinfection in Large-Format Works of Art. In Proceedings of the International Heritage, Weathering and Conservation Conference (HWC-2006), Madrid, Spain, 21–24 June 2006; pp. 707–712. [Google Scholar]
- Chidichimo, G.; Dalena, F.; Rizza, A.; Beneduci, A. Insect-Infested Wood Remediation by Microwave Heating and Its Effects on Wood Dehydration: A Case Study of Hylotrupes Bajulus Larva. Stud. Conserv. 2017, 63, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinc, M.; Pavlič, M.; Petrič, M.; Pohleven, F. Influence of Microwave Heating in Wood Preservation on Traditional Surface Coatings. Acta Silvae Ligni 2017, 112, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquino, N.; Cennamo, P.; Caputo, P.; Guida, M.; Giorgio, A.; Morra, V.; Guarino, V.; Trojsi, G.; Moretti, A. Methodologies in the Study of Biofilms on Cultural Heritage. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology, Benevento, Italy, 22–23 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cennamo, P.; Pasquino, N.; Ciniglia, C.; Moretti, A.; Caputo, P. Use of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Radiation to Remove Biofilms from Canvasses. Aerobiologia 2020, 36, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, P.; Pasquino, N.; Guarino, V.; Morra, V.; Giorgio, A.; Caputo, P.; Moretti, A. Use of High-Strength Electromagnetic Radiation to Remove Phototrophic Biofilms from Terracotta Artifacts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29654–29662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuclear Science for Art: Workshop Focuses on Safe Practices. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/newscenter/news/nuclear-science-for-art-workshop-focuses-on-safe-practices (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Cardinali, M. Technical Art History and the First Conference on the Scientific Analysis of Works of Art (Rome, 1930). Hist. Humanit. 2017, 2, 221–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, M.W. From Connoisseurship to Technical Art History: The Evolution of the Interdisciplinary Study of Art; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, B.F. Painting Materials Research in Munich from 1825 TO 1937. Stud. Conserv. 1998, 43, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.A. The History of Spectroscopy as Illustrated on Stamps. Appl. Spectrosc. 1983, 37, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, K. 21 The Spectrum in Historical Context. In Mapping the Spectrum: Techniques of Visual Representation in Research and Teaching; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002; ISBN 978-0-19-850953-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bursey, M.M. A Brief History of Spectroscopy; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.B.; Ham, N.S. Walsh’s Contributions to Molecular Spectroscopy and Its Instrumentation. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 1999, 54, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’vov, B. Fifty Years of Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. J Anal Chem 2005, 60, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy/Alan Walsh. Aust. Paint J. 1964, 10, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, A. The Application of Atomic Absorption Spectra to Chemical Analysis. Spectrochim. Acta 1955, 7, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadet, J.; Delatour, T.; Douki, T.; Gasparutto, D.; Pouget, J.-P.; Ravanat, J.-L.; Sauvaigo, S. Hydroxyl Radicals and DNA Base Damage. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1999, 424, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Units, I.C.R. Measurements Fundamental Quantities and Units for Ionizing Radiation; ICRU Report; International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements: Stockholm, Sweden, 1998; ISBN 978-0-913394-59-5. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/ASTM 51261:2013; Practice for Calibration of Routine Dosimetry Systems for Radiation Processing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO/ASTM 52628; Standard Practice for Dosimetry in Radiation Processing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Farah, K.; Arbi, M.; Hosni, F.; Ben Ouada, H.; Fuochi, P.; Lavalle, M.; Kovács, A. Characterization of a Silicate Glass as a High Dose Dosimeter. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2010, 614, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuochi, P.; Corda, U.; Lavalle, M.; Kovács, A.; Baranyai, M.; Arbi, M.; Farah, K. Dosimetric Properties of Gamma- and Electron-Irradiated Commercial Window Glasses. Nukl. Orig. Ed. 2009, 54, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mclaughlin, W.L.; Desrosiers, M.F. Dosimetry Systems for Radiation Processing. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 1995, 46, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Dosimetry for Food Irradiation; Technical Reports Series; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2002; ISBN 92-0-115502-6. [Google Scholar]
- Serena Gamma Irradiation CALLIOPE Facility at ENEA Casaccia Research Centre. Available online: https://www.pubblicazioni.enea.it/le-pubblicazioni-enea/edizioni-enea/anno-2019/gamma-irradiation-calliope-facility-at-enea-casaccia-research-centre.html (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Cortella, L.; Khezami, K.; Benmanseur, M. IAEA-CN290-330 Dosimetric Approach for Cultural Heritage Treatments by Gamma Irradiation: Issue and Experience. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Applications of Radiation Science and Technology (ICARST-2022), Vienna, Austria, 22–26 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, M.L.E. Irradiation Protocol for Cultural Heritage Conservation Treatment. Braz. J. Radiat. Sci. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, S. Invasion of the Giant Mold Spore. Available online: https://cool.culturalheritage.org/byauth/nyberg/spore.html (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Methyl Bromide. US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ods-phaseout/methyl-bromide (accessed on 27 April 2025).
- Rutala, W.; Weber, D. HICPAC Guideline for Disinfection and Sterilization in Healthcare Facilities. Facilities 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawks, C.; Selwitz, C.; Maekawa, S. Inert Gases in the Control of Museum Insect Pests. J. Am. Inst. Conserv. 2001, 39, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treatment and Restoration. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/topics/cultural-heritage-restoration (accessed on 26 April 2025).
- Havermans, J.B.G.A.; Dufour, J. Photo Oxidation of Paper Documents. A Literature Review. Restaur. Int. J. Preserv. Libr. Arch. Mater. 1997, 18, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlý, J.; Strlič, M.; Matisová-Rychlá, L.; Kolar, J. Chemiluminescence from Paper I. Kinetic Analysis of Thermal Oxidation of Cellulose. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 78, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, J. Mechanism of Autoxidative Degradation of Cellulose. Restaur. Int. J. Preserv. Libr. Arch. Mater. 1997, 18, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, B.L.; Meinholtz, D.C.; Highley, T.L. Oxygen Free Radical Detection in Wood Colonized by the Brown-Rot Fungus, Postia Placenta. In Biodeterioration Research 2: General Biodeterioration, Degradation, Mycotoxins, Biotoxins, and Wood Decay; O’Rear, C.E., Llewellyn, G.C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 497–509. ISBN 978-1-4684-5670-7. [Google Scholar]
- Corregidor, V.; Cortella, L.; Ferreira, L.; Alves, C.; Bertrand, L.; Stols, M.; Casimiro, M.; Mihaljevic, B.; Calligaro, T.; Thoury, M.; et al. Uses of Ionizing Radiation for Tangible Cultural Heritage Conservation. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Applications of Radiation Science and Technology (ICARST-2022), Vienna, Austria, 22–26 August 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Biancifiori, M.A.; Zappa, G. Evoluzione Delle Tecniche di Spettroscopia Atomica. December 1985. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273888134_Evoluzione_delle_tecniche_di_spettroscopia_atomica (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Ferretti, M. Scientific Investigations of Works of Art/Marco Ferretti.; International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and the Restoration of Cultural Property: Rome, Italy, 1993; ISBN 92-9077-108-9. [Google Scholar]
- Garside, P.; Richardson, E. Analytical Techniques in Conservation Science. In Conservation Science: Heritage Materials; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-1-78801-093-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cappitelli, F.; Cattò, C.; Villa, F. The Control of Cultural Heritage Microbial Deterioration. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varella, E.A. Conservation Science for the Cultural Heritage: Applications of Instrumental Analysis; Lecture Notes in Chemistry; 79; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-3-642-30984-7. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, B.D.; Daniels, V.; Eaton, R.; Garside, P.; Inkpen, R.; Jones, M.; Koestler, R.J.; May, E.; Petersen, K.; Roemich, H.; et al. Conservation Science: Heritage Materials, 2nd ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2006; ISBN 1-84755-762-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfigli, F.; Botti, S.; Caponero, M.A.; Cemmi, A.; D’amato, R.; Di Sarcina, I.; Falconi, L.; Francucci, M.; Guarnieri, M.; Loreti, S.; et al. Le Tecnologie Nucleari per La Diagnostica e La Conservazione Dei Beni Culturali. Energ. Ambiente E Innov. 2003, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Radiation Safety of Gamma, Electron and X Ray Irradiation Facilities; Specific Safety Guide; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2010; ISBN 978-92-0-103710-7. [Google Scholar]
- Radiation: Ionizing Radiation. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/radiation-ionizing-radiation (accessed on 4 January 2025).
- Romeo, S.; Zeni, O. Microwave Heating for the Conservation of Cultural Heritage Assets: A Review of Main Approaches and Challenges. IEEE J. Electromagn. RF Microw. Med. Biol. 2023, 7, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortella, L. Gamma Radiation Processing for Cultural Heritage Preservation—Biocide Treatment of Organic Materials and Consolidation of Wooden Degraded Artifacts by Radiation Curing Resin. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Non-Destructive Testing of Cultural Heritage—Radioactive Techniques for Diagnosis and Conservation of Cultural Heritage, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 4 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ponta, C.; Havermans, J.; Cortella, L.; Vasquez, P.; Sabharwal, S.; Tran, K.; Orlandini, V. Uses of Ionizing Radiation for Tangible Cultural Heritage Conservation; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nigro, L.; Montanari, D.; Sabatini, S.; Giuseppe, M.D.; Benedettucci, F.M.; Lucibello, S.; Fattore, L.; Trebbi, L.; Nejat, B.; Rinaldi, T. Caress the Pharaoh. The Tactile Reproduction of Ramses II’s “Mummy” in the Sapienza University Museum of the Near East, Egypt and Mediterranean. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 67, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riminesi, C.; Olmi, R. Localized Microwave Heating for Controlling Biodeteriogens on Cultural Heritage Assets. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2016, 7, 281–294. [Google Scholar]
- Tiano, P. Biodegradation of Cultural Heritage: Decay Mechanisms and Control Methods. ARIADNE 9 Work Hist Mater Their Diagn. 2009, 2, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Price, C.; Amoroso, G.; Fassina, V. Stone Decay and Conservation: Atmospheric Pollution, Cleaning, Consolidation and Protection. Stud. Conserv. 1984, 29, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelli, M.; Pannuzi, S.; Giovannone, C.; Marinelli, A. Metodologie d’indagine e Problematiche Conservative: Gli Affreschi Del Sepolcreto Della via Ostiense a Roma. Con Appendice Di Jana Michalcakova, Lukas Kucera. In Animum pictura pascit (Verg., Aen. I, 464) Abitare con le pitture nel Mediterraneo antico Atti delle Giornate Gregoriane XIII Edizione (Agrigento, 29/11-1/12 2019); Ante Quem: Bologna, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cotte, M.; Gonzalez, V.; Vanmeert, F.; Monico, L.; Dejoie, C.; Burghammer, M.; Huder, L.; de Nolf, W.; Fisher, S.; Fazlic, I.; et al. The “Historical Materials BAG”: A New Facilitated Access to Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction Analyses for Cultural Heritage Materials at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility. Molecules 2022, 27, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querner, P.; Simon, S.; Morelli, M.; Fürenkranz, S. Insect Pest Management Programmes and Results from Their Application in Two Large Museum Collections in Berlin and Vienna. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 84, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzi, L. Calcium Oxalate Films on Works of Art: A Review. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 40, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzi, L.; Andreotti, A.; Bonaduce, I.; Colombini, M.P.; Colombo, C.; Toniolo, L. Analytical Investigation of Calcium Oxalate Films on Marble Monuments. Talanta 2004, 63, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzi, L.; Andreotti, A.; Bressan, M.; Colombini, M.P.; Corti, C.; Cuzman, O.; d’Alessandro, N.; Liberatore, L.; Palombi, L.; Raimondi, V.; et al. An Interdisciplinary Approach to a Knowledge-Based Restoration: The Dark Alteration on Matera Cathedral (Italy). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realini, M.; Colombo, C.; Sansonetti, A.; Rampazzi, L.; Colombini, M.; Bonaduce, I.; Zanardini, E.; Abbruscato, P. Oxalate Films and Red Stains on Carrara Marble. Ann. Chim. 2005, 95, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liers, C.; Arnstadt, T.; Ullrich, R.; Hofrichter, M. Patterns of Lignin Degradation and Oxidative Enzyme Secretion by Different Wood- and Litter-Colonizing Basidiomycetes and Ascomycetes Grown on Beech-Wood. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 78, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botti, S.; Bonfigli, F.; Nigro, V.; Rufoloni, A.; Vannozzi, A. Evaluating the Conservation State of Naturally Aged Paper with Raman and Luminescence Spectral Mapping: Toward a Non-Destructive Diagnostic Protocol. Molecules 2022, 27, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strzelczyk, A.B.; Kuroczkin, J.; Krumbein, W.E. Studies on the Microbial Degradation of Ancient Leather Bookbindings. Part 2. Int. Biodeterior. 1989, 25, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Technique | Application | References |
|---|---|---|
| Gamma/X-ray/ion beam irradiation | Decontamination of: | |
| wood | [10,22,23] | |
| parchment | [26,27] | |
| paper | [11,15,16,17,36] | |
| textile | [30] | |
| Gamma irradiation | Wood consolidation | [14,37] |
| Microwave (MW) heating | Decontamination of: | |
| Stone | [38,39,40] | |
| wood | [41,42,43,44] | |
| Radiofrequency (RF) | Biofilm removal | [45,46,47] |
| EM Irradiation for Restoration |
|---|
| Gamma/X-ray |
| Radiofrequencies |
| Microwave heating |
| Methods | Principles |
|---|---|
| Mechanical 1 | Physical removal of pathogen factors |
| Chemical | Elimination of pathogens by chemicals |
| Biological | Bio-cleaning/bio-mineralization through microorganisms |
| physical | Based on anoxic treatments |
| Methods | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Gamma/X-ray 1 radiation | Can penetrate complex, volumetric shapes |
| Rapidity of treatment | |
| No temperature increase | |
| UV-C irradiation | Disinfection of buried/waterlogged |
| stone artifact |
| Component | Structure | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | Highly organized | hydrophilic |
| Lignin | amorphous | hydrophobic |
| Fiber Source | Cellulose % |
|---|---|
| Cotton | 95 |
| Linen | 80 |
| Wood | 45 |
| Grasses | 30 |
| Aging Factor Typology | ||
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Chemical | Mechanical |
| Oxidative breakdown of collagen | Catalyzation of hydrolytic degradation of collagen | Mechanical degradation |
| Photochemical deterioration of collagen | Pollutants Metallic ions | Temperature and humidity fluctuation 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piersigilli, P.; Citroni, R.; Mangini, F.; Frezza, F. A Survey of Electromagnetic Techniques Applied to Cultural Heritage Conservation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115884
Piersigilli P, Citroni R, Mangini F, Frezza F. A Survey of Electromagnetic Techniques Applied to Cultural Heritage Conservation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115884
Chicago/Turabian StylePiersigilli, Patrizia, Rocco Citroni, Fabio Mangini, and Fabrizio Frezza. 2025. "A Survey of Electromagnetic Techniques Applied to Cultural Heritage Conservation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115884
APA StylePiersigilli, P., Citroni, R., Mangini, F., & Frezza, F. (2025). A Survey of Electromagnetic Techniques Applied to Cultural Heritage Conservation. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5884. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115884








