Performance Comparison of Lambertian and Non-Lambertian Drone Visible Light Communications for 6G Aerial Vehicular Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Drone Visible Light Communications with Differentiated LED Beams
2.1. Drone Visible Light Communications with Lambertian LED Beam
2.2. Drone Visible Light Communications with Non-Lambertian LED Beam
3. Numerical Results
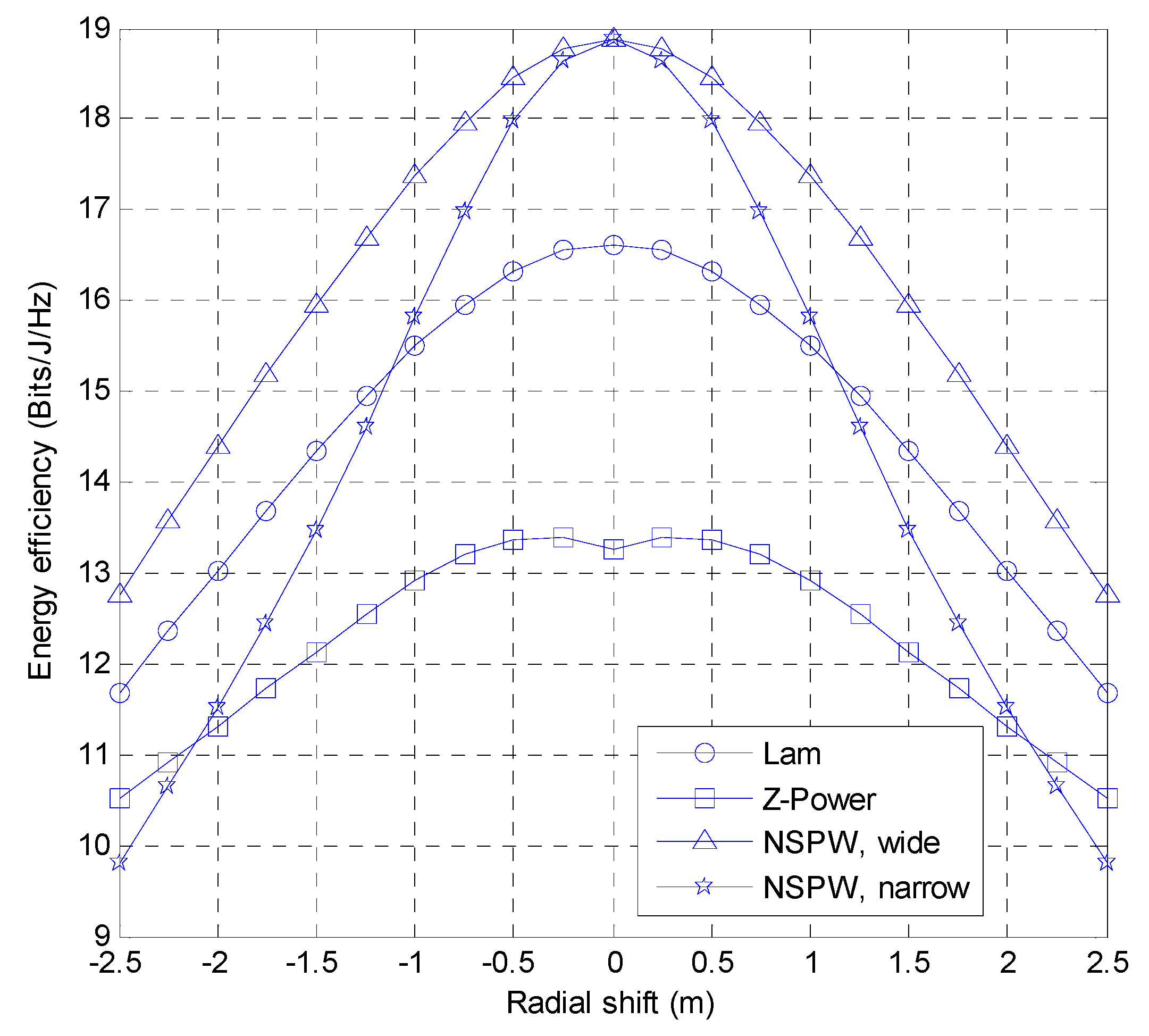
3.1. Effect of Radial Shift
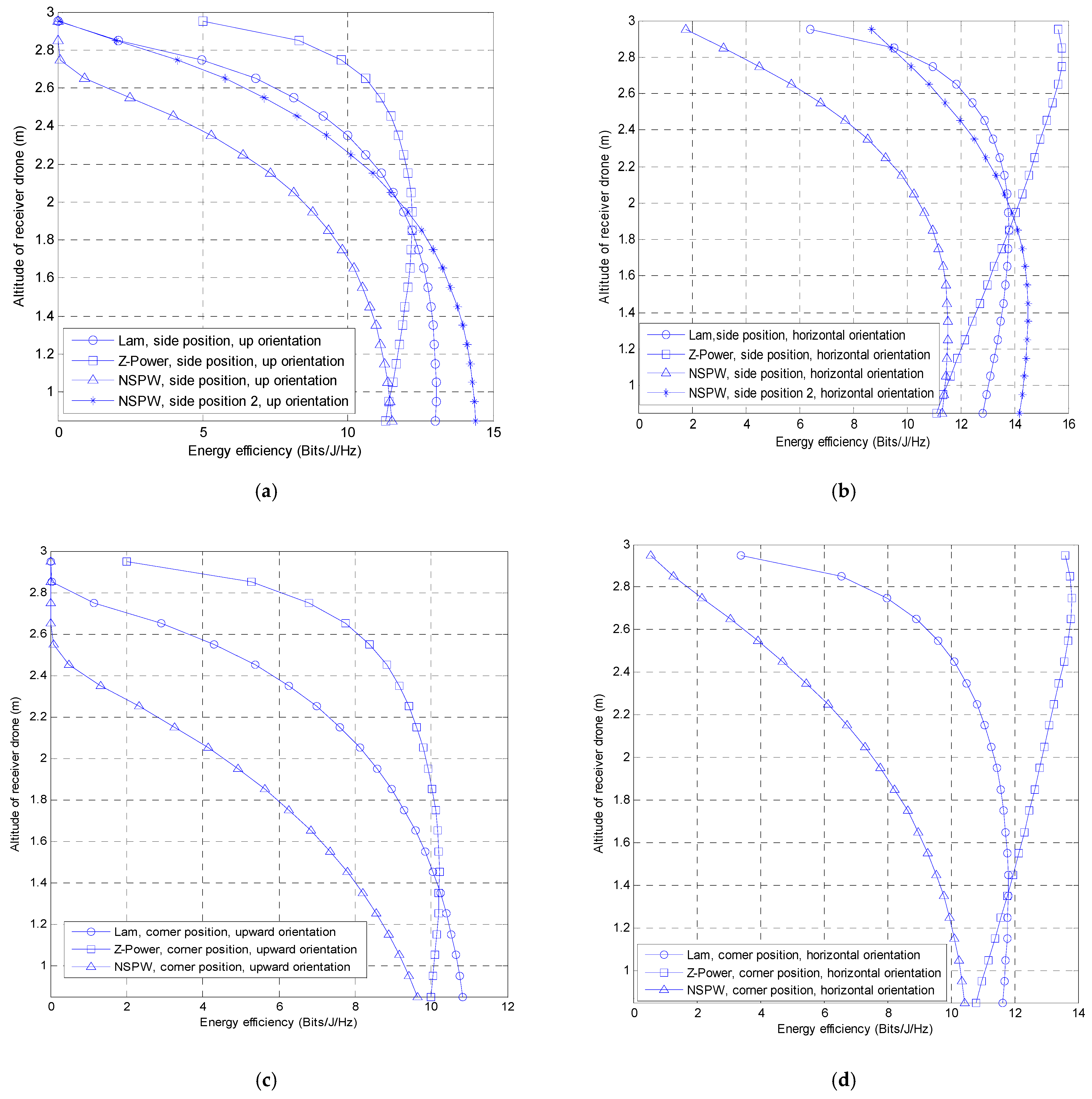
3.2. Effect of Drone Altitude
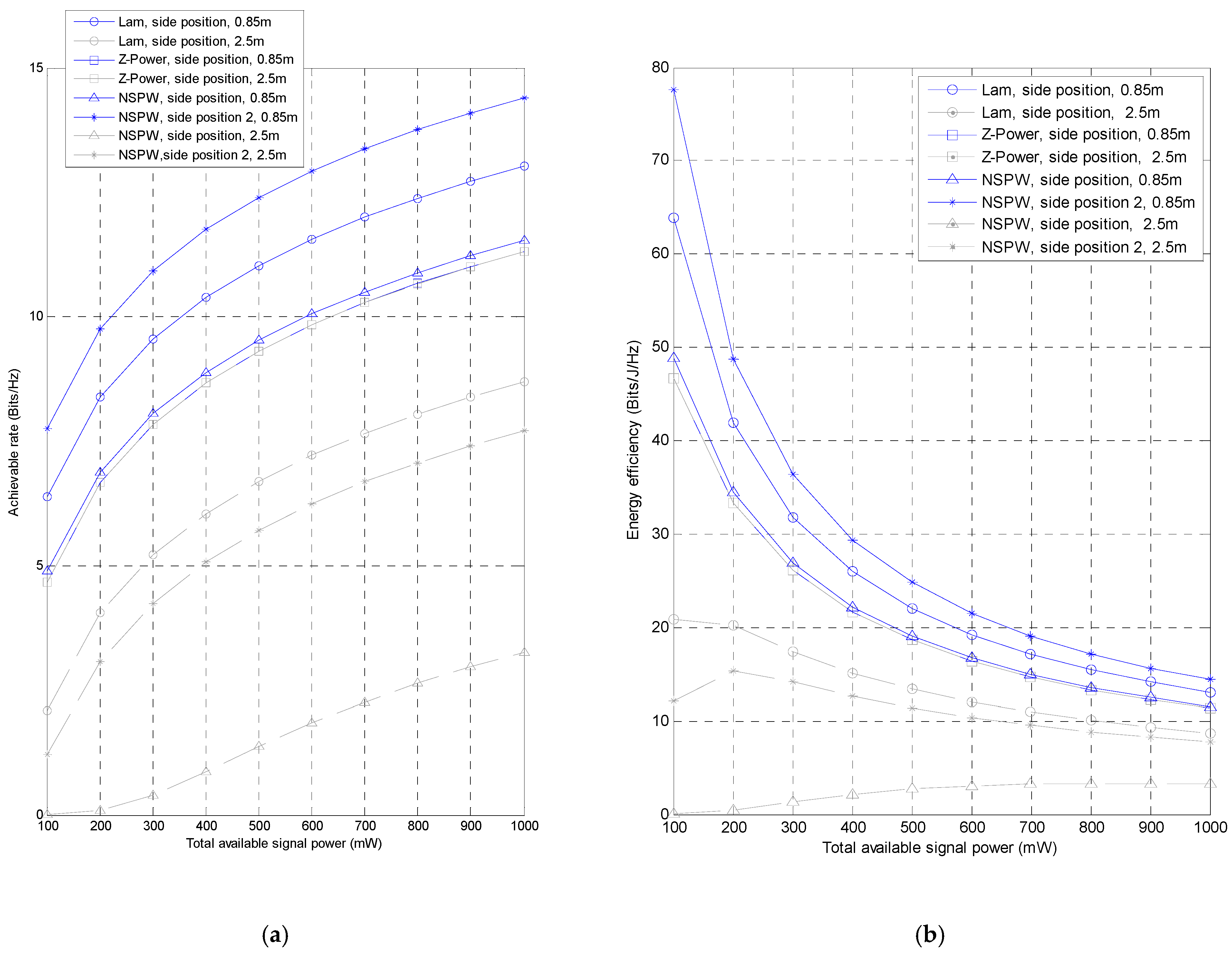
3.3. Effect of Available Emitted Power
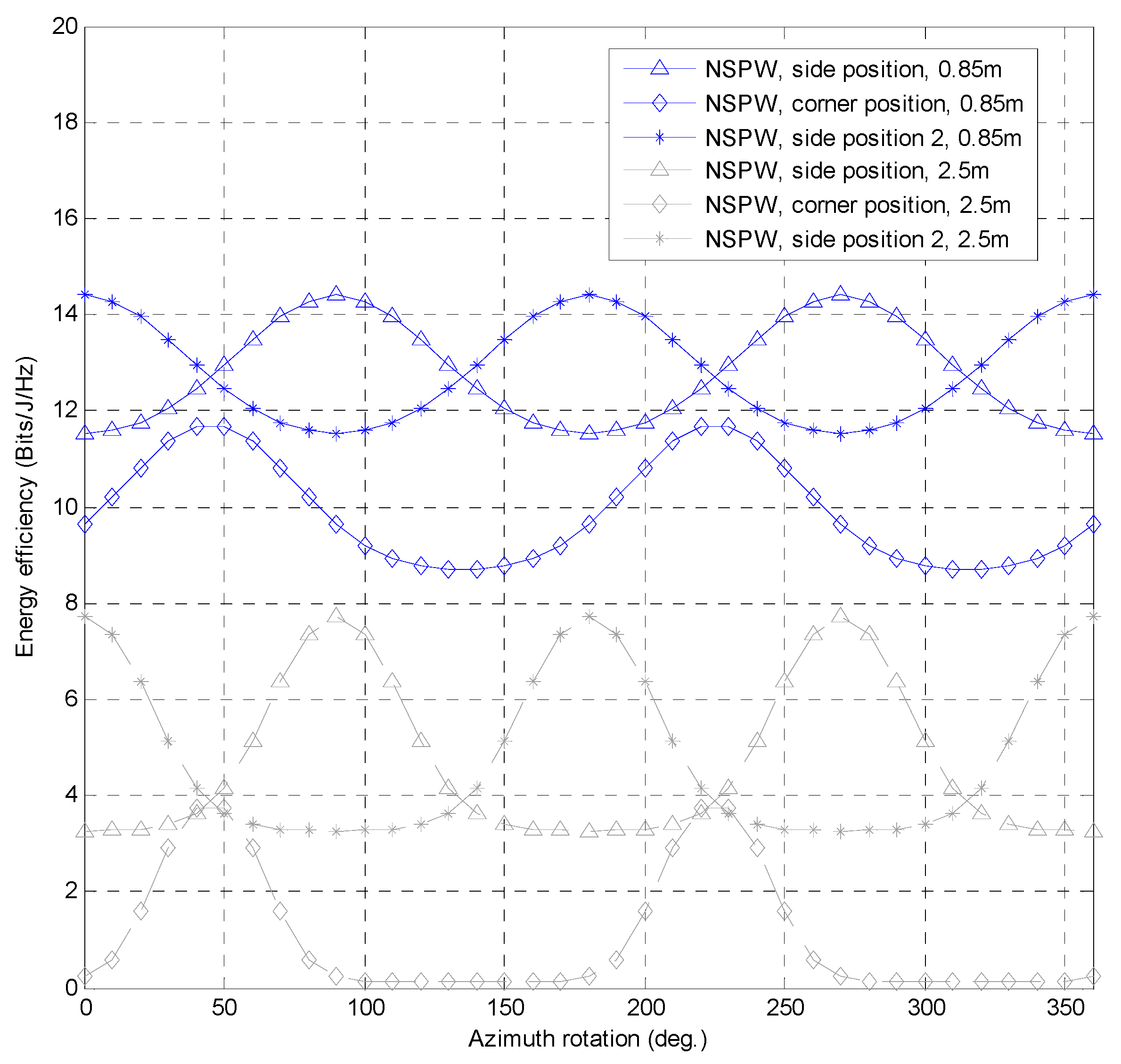
3.4. Effect of Drone Azimuth Rotation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, M.; Guo, K.; Li, X.; Nauman, A.; An, K.; Wang, J. Optimization Design in RIS-Assisted Integrated Satellite-UAV-Served 6G IoT: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2024, 7, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ge, N.; Wang, C.X. Structured Satellite-UAV-Terrestrial Networks for 6G Internet of Things. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.; Lin, X.; Hayes, S. What Will the Future of UAV Cellular Communications Be? A Flight from 5G to 6G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2021, 59, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraci, G.; Garcia-Rodriguez, A.; Azari, M.M.; Lozano, A.; Mezzavilla, M.; Chatzinotas, S.; Chen, Y.; Rangan, S.; Di Renzo, M. What Will the Future of UAV Cellular Communications Be? A Flight From 5G to 6G. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 1304–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEnroe, P.; Wang, S.; Liyanage, M. A Survey on the Convergence of Edge Computing and AI for UAVs: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 15435–15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, S.A.; Moh, S. Survey on computation offloading in UAV-enabled mobile edge computing. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2022, 201, 103341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, T.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided visible light communications: Potentials and challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2022, 17, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Dimming Techniques of Visible Light Communications for Human-Centric Illumination Networks: State-of-the-Art, Challenges, and Trends. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2020, 27, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.S.; Deogun, J.S.; Alexander, D.R. Classification framework for free space optical communication links and systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 1346–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltokhey, M.W.; Khalighi, M.-A.; Ghassemlooy, Z. UAV Location Optimization in MISO ZF Pre-Coded VLC Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraiwish, H.; Eltokhey, M.W.; Alouini, M.S. UAV-Assisted VLC Using LED-Based Grow Lights in Precision Agriculture Systems. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2024, 7, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajahrajasingh, H.; Jayakody, D.N.K. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Assisted Terahertz–Visible Light Communication Systems: An In-Depth Performance Analysis. Sensors 2024, 24, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Wen, W.; Liu, M.; Du, P.; Chen, C. Energy-Efficient Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Aided Visible Light Communication with an Angle Diversity Transmitter for Joint Emergency Illumination and Communication. Sensors 2023, 23, 7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Guo, C.; Chen, M.; Cui, S.; Poor, H.V. Power Efficient Deployment of VLC-enabled UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 31st Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, London, UK, 31 August–3 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, B.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z. Visible Light Communications for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: Channel Modeling and Experimental Validation. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, J.G.; Baeza, V.M. Enhancing Urban Mobility Through Traffic Management with UAVs and VLC Technologies. Drones 2024, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.J.; AlWaqfi, A.M.; Atoum, J.K.; Yaseen, M.A.; MacKenzie, A.B. A Novel Multi-Objective Sequential Resource Allocation Optimization for UAV-Assisted VLC. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 6896–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, F.H.; Ohtsuki, T. Intelligent Cellular Offloading with VLC-Enabled Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 17718–17733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraiwish, H.; Eltokhey, M.W.; Alouini, M.S. Energy Efficient Deployment of VLC-Enabled UAV Using Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2024, 5, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.R.; Mili, M.R.; Javan, M.R.; Mokari, N.; Jorswieck, E.A. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Trajectory Design and Two-Stage Resource Management in CoMP UAV VLC Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 7464–7476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, X.; Dong, Y. Trajectory Planning for Cross-Interface UAV-Assisted VLC Systems. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems (WUWNet ’23), Shenzhen, China, 24–26 November 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Guo, C.; Feng, C.; Saad, W. Power Efficient Visible Light Communication with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, D.N.; Peer, M.; Lata, K.; Srivastava, A.; Bohara, V.A. 3-D Deployment of VLC Enabled UAV Networks with Energy and User Mobility Awareness. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2022, 6, 1972–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Feng, R. Maritime Target Tracking Algorithm Based on Visible Light Communication. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 9th International Conference on Information, Communication and Networks (ICICN), Xi’an, China, 25–28 November 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, Q.V.; Huynh-The, T.; Alazab, M.; Zhao, J.; Hwang, W.J. Sum-Rate Maximization for UAV-Assisted Visible Light Communications Using NOMA: Swarm Intelligence Meets Machine Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 10375–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, J.; Tang, X.; Dong, Y. Autonomous Obstacle Avoidance and Communication Capacity Optimization for UAV-Assisted VLC Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference/2023 International Photonics and Optoelectronics Meetings (ACP/POEM), Wuhan, China, 4–7 November 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Panda, K.G.; Kumar, M.L.N.; Sen, D.; Chakraborty, S. 3-D Placement Strategy for VLC Enabled UAV Network with Guaranteed QoS. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 96th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2022-Fall), London, UK, 26–29 September 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.J.; Al-Qreenawi, Y.A.; Atoum, J.K.; MacKenzie, A.B. SteerVLC: A Joint Deployment and Beam-Steering Optimization for VLC-Enabled UAV Networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 88745–88758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.; Peer, M.; Bohara, V.A. Performance Analysis of RF/VLC Enabled UAV Base Station in Heterogeneous Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 32nd Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Helsinki, Finland, 8–11 September 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Su, D.P.; Feng, P.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.B. Optimal Height of UAV in Covert Visible Light Communications. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimen, A.; Kizilirmak, R.C. UAV Assisted Vehicular Communication with VLCusing NOMA. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP), Porto, Portugal, 8–11 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Komine, T.; Nakagawa, M. Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2004, 50, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, I.; Sun, C.-C. Modeling the radiation pattern of LEDs. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1808–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chih-Lin, I.; Xu, Z. Indoor optical wireless channel characteristics with distinct source radiation patterns. IEEE Photonics J. 2016, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; CL, I.; Wang, J.; Song, J. Coverage Performance of Non-Lambertian Underwater Wireless Optical Communications for 6G Internet of Things. Inventions 2024, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-C.; Lee, T.-X.; Ma, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-L.; Huang, S.-M. Precise optical modeling for LED lighting verified by cross correlation in the midfield region. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 2193–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, W.-T.; Sun, C.-C.; Moreno, I. Precise optical model of multi-chip white LEDs. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 7572–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
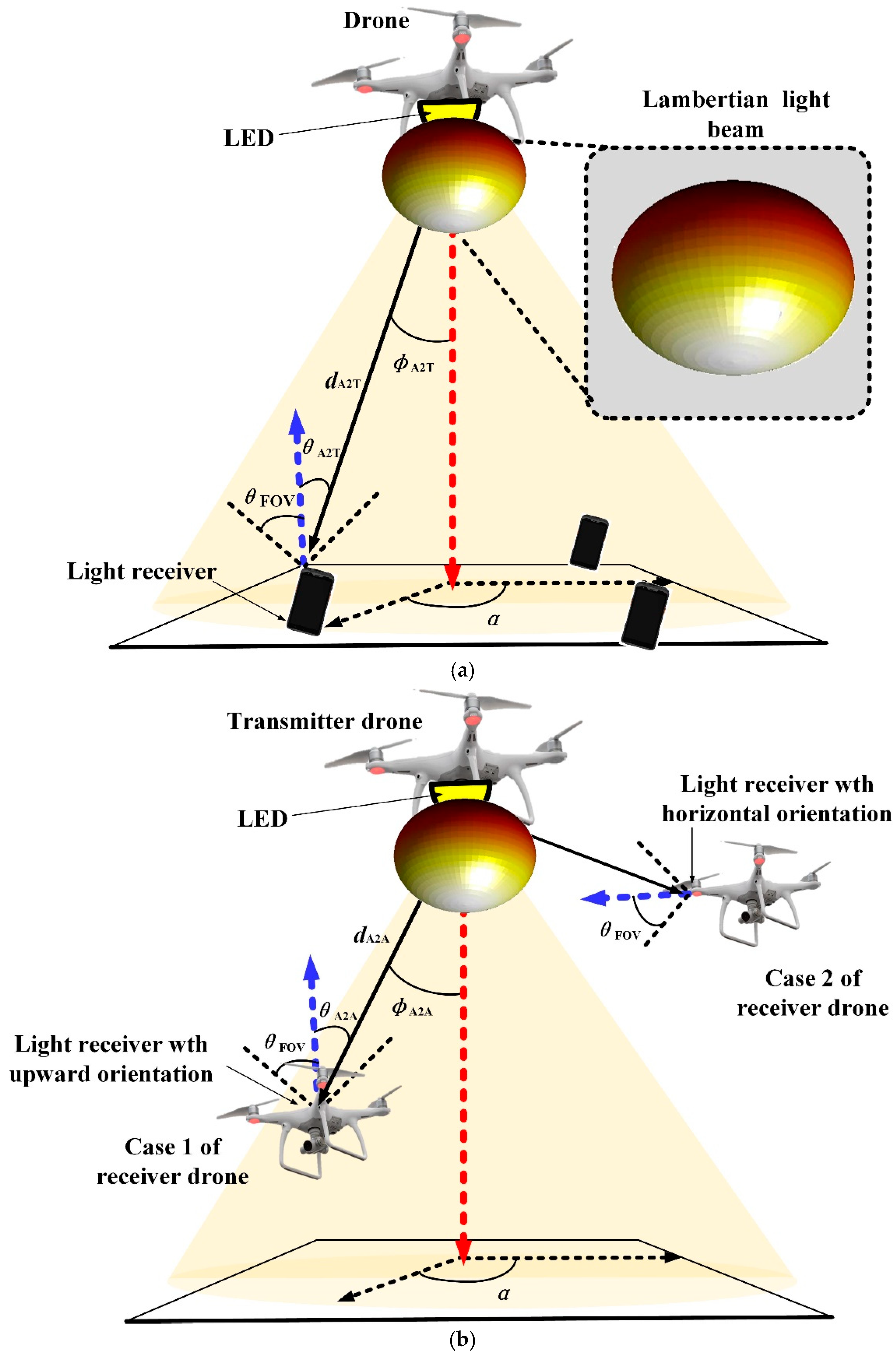
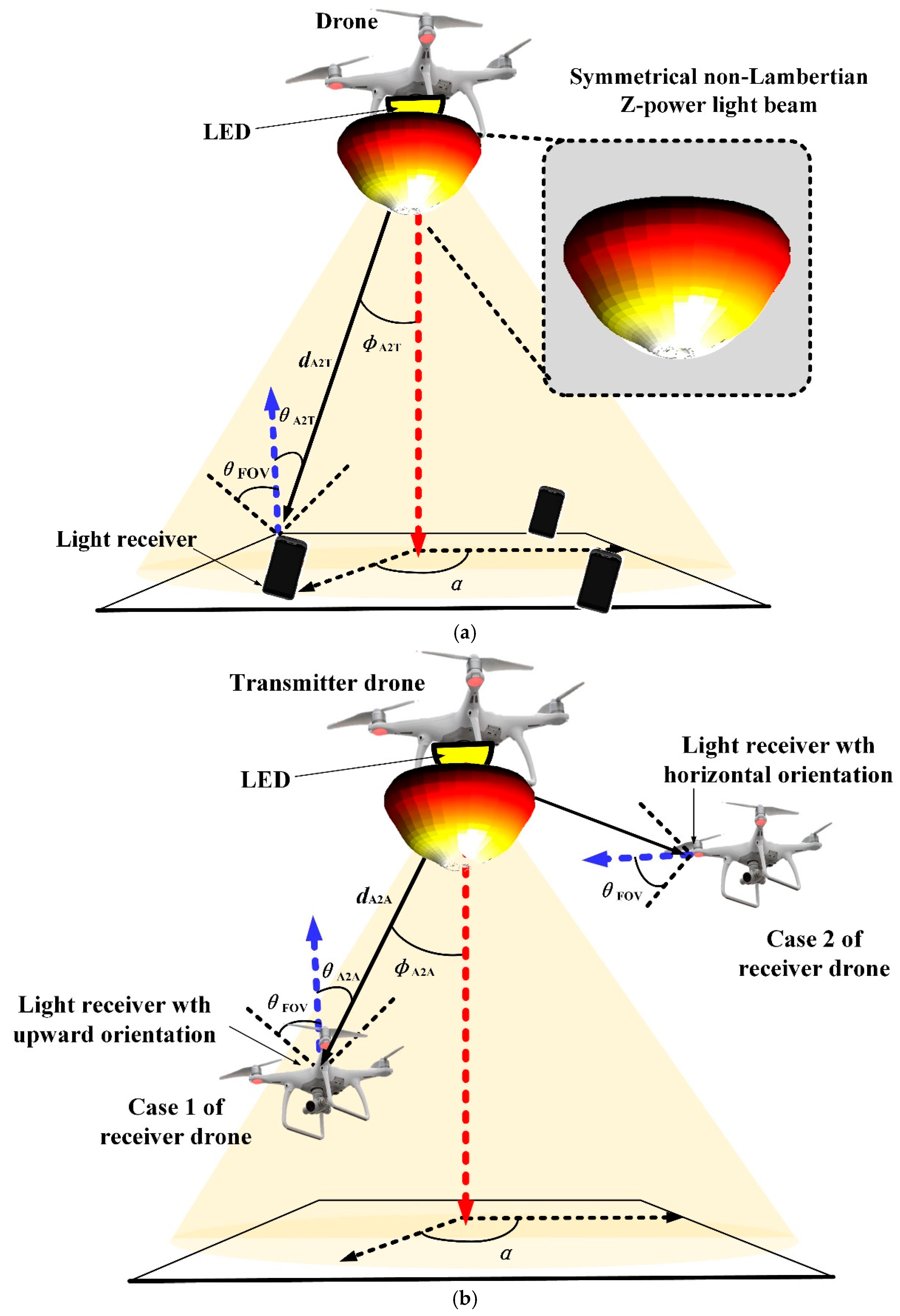
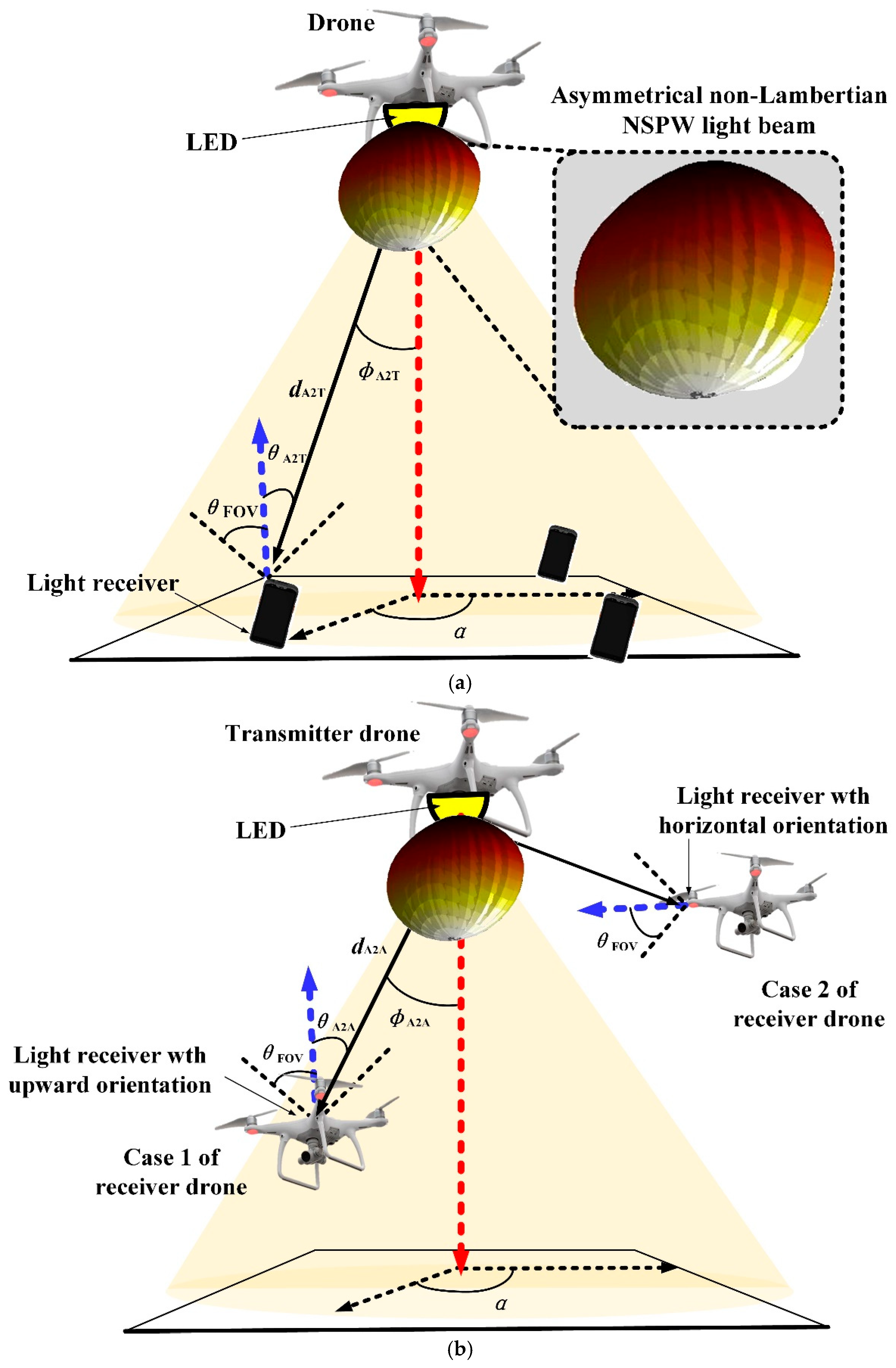
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Target area size (W × L) | 5 × 5 m2 |
| Total available signal power of transmitter | 1 W |
| Number of transmitters | 1 |
| Location of transmitter | (2.5, 2.5, 3) m |
| LED Lambertian semiangle | 60° |
| Receiver field of view | 90° |
| Height of receiving plane | 0.85 m |
| Physical area of PD | 1.0 cm2 |
| Responsively of PD | 0.8 A/W |
| Concentrator refractive index | 1.5 |
| Optical filter gain | 1 |
| Signal bandwidth | 10 MHz |
| VLC noise power density | 1 × 10−22 A2/Hz |
| Parameters [33] | Key Application Domains | |
|---|---|---|
| Emission intensity of Z-Power LED beam: |
| |
| Emission intensity of asymmetric NSPW LED beam: |
| |
| Radial Shift Amplitude (m) | Energy Efficiency of Lambertian Drone VLC (Bits/J/Hz) | Energy Efficiency of Z-Power Non-Lambertian Drone VLC (Bits/J/Hz) | Energy Efficiency of NSPW Non-Lambertian Drone VLC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wide Cross Section (Bits/J/Hz) | Narrow Cross Section (Bits/J/Hz) | |||
| −2.5 | 11.69 | 10.51 | 12.77 | 9.80 |
| 0 | 16.63 | 13.40 | 18.87 | 18.87 |
| 2.5 | 11.69 | 10.51 | 12.77 | 9.80 |
| Position of Receiver | Energy Efficiency of Lambertian Drone VLC (Bits/J/Hz) | Energy Efficiency of Z-Power Non-Lambertian Drone VLC (Bits/J/Hz) | Energy Efficiency of NSPW Non-Lambertian Drone VLC (Bits/J/Hz) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receiver Altitude of 0 m | Receiver Altitude of 2.95 m | Receiver Altitude of 0 m | Receiver Altitude of 2.95 m | Receiver Altitude of 0 m | Receiver Altitude of 2.95 m | ||
| Side position | Upward orientation | 13.04 | 0.002 | 11.31 | 4.99 | 11.53 (side position), 14.40 (side position 2) | 0.00 (side position), 0.046 (side position 2) |
| Horizontal orientation | 12.82 | 6.40 | 11.11 | 15.64 | 11.32 (side position), 14.19 (side position 2) | 1.76 (side position), 8.68 (side position 2) | |
| Corner position | Upward orientation | 10.83 | 0.00 | 10.00 | 2.00 | 9.64 | 0.00 |
| Horizontal orientation | 11.62 | 3.40 | 10.79 | 13.60 | 10.43 | 0.55 | |
| Performance Metric | Lambertian Drone VLC | Z-Power Non-Lambertian Drone VLC | NSPW Non-Lambertian Drone VLC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emitted Power of 100 mW | Emitted Power of 1000 mW | Emitted Power of 100 mW | Emitted Power of 1000 mW | Emitted Power of 100 mW | Emitted Power of 1000 mW | ||
| Achievable rate (Bits/Hz) | Receiver altitude of 0.85 m | 6.38 | 13.03 | 4.67 | 11.31 | 4.89 (side position), 7.76 (side position 2) | 11.53 (side position), 14.40 (side position 2) |
| Receiver altitude of 2.5 m | 2.09 | 8.69 | 4.67 | 11.31 | 0.0066 (side position), 1.22 (side position 2) | 3.27 (side position), 7.71 (side position 2) | |
| Energy efficiency (Bits/J/Hz) | Receiver altitude of 0.85 m | 63.83 | 13.03 | 46.71 | 11.31 | 48.86 (side position), 77.56 (side position 2) | 11.53 (side position), 14.40 (side position 2) |
| Receiver altitude of 2.5 m | 20.89 | 8.69 | 46.67 | 11.31 | 3.27 (side position), 12.16 (side position 2) | 0.066 (side position), 7.71 (side position 2) | |
| Side Position | Corner Position | Side Position 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receiver Altitude of 0.85 m | Receiver Altitude of 2.5 m | Receiver Altitude of 0.85 m | Receiver Altitude of 2.5 m | Receiver Altitude of 0.85 m | Receiver Altitude of 2.5 m | |
| Maximum energy efficiency (Bits/J/Hz) | 14.40 | 7.71 | 11.67 | 3.72 | 14.40 | 7.71 |
| Azimuth rotation of maximum energy efficiency (°) | 90 | 90 | 50 | 50 | 0 | 0 |
| Minimum energy efficiency (Bits/J/Hz) | 11.53 | 3.27 | 8.70 | 0.12 | 11.53 | 3.27 |
| Azimuth rotation of minimum energy efficiency (°) | 0 | 0 | 140 | 140 | 90 | 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, J.; I, C.-L.; Wang, J.; Yang, H. Performance Comparison of Lambertian and Non-Lambertian Drone Visible Light Communications for 6G Aerial Vehicular Networks. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115835
Ding J, I C-L, Wang J, Yang H. Performance Comparison of Lambertian and Non-Lambertian Drone Visible Light Communications for 6G Aerial Vehicular Networks. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(11):5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115835
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Jupeng, Chih-Lin I, Jintao Wang, and Hui Yang. 2025. "Performance Comparison of Lambertian and Non-Lambertian Drone Visible Light Communications for 6G Aerial Vehicular Networks" Applied Sciences 15, no. 11: 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115835
APA StyleDing, J., I, C.-L., Wang, J., & Yang, H. (2025). Performance Comparison of Lambertian and Non-Lambertian Drone Visible Light Communications for 6G Aerial Vehicular Networks. Applied Sciences, 15(11), 5835. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15115835








