Transcranial Doppler-Based Neurofeedback to Improve Hemispheric Lateralization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
- A transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound to measure the cerebral blood velocity in the left and right middle cerebral arteries (MCAs), and the two signals are made available as analog output;
- The signals are digitally sampled (100 Hz) by an Arduino component and transmitted to a PC;
- A lateralization index is then calculated and used to provide real-time visual feedback to the user, as described below.
2.2. Feedback
2.3. Task
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.4.1. Session: Training and Test
2.4.2. Questionnaire
2.5. Data Analysis and Statistics
2.5.1. Assessment of the Differentiation of Responses to Left/Right Tasks
2.5.2. Classification
Binary Classification (Single Threshold)
Three-Class Classification (Two Threshold)
3. Results
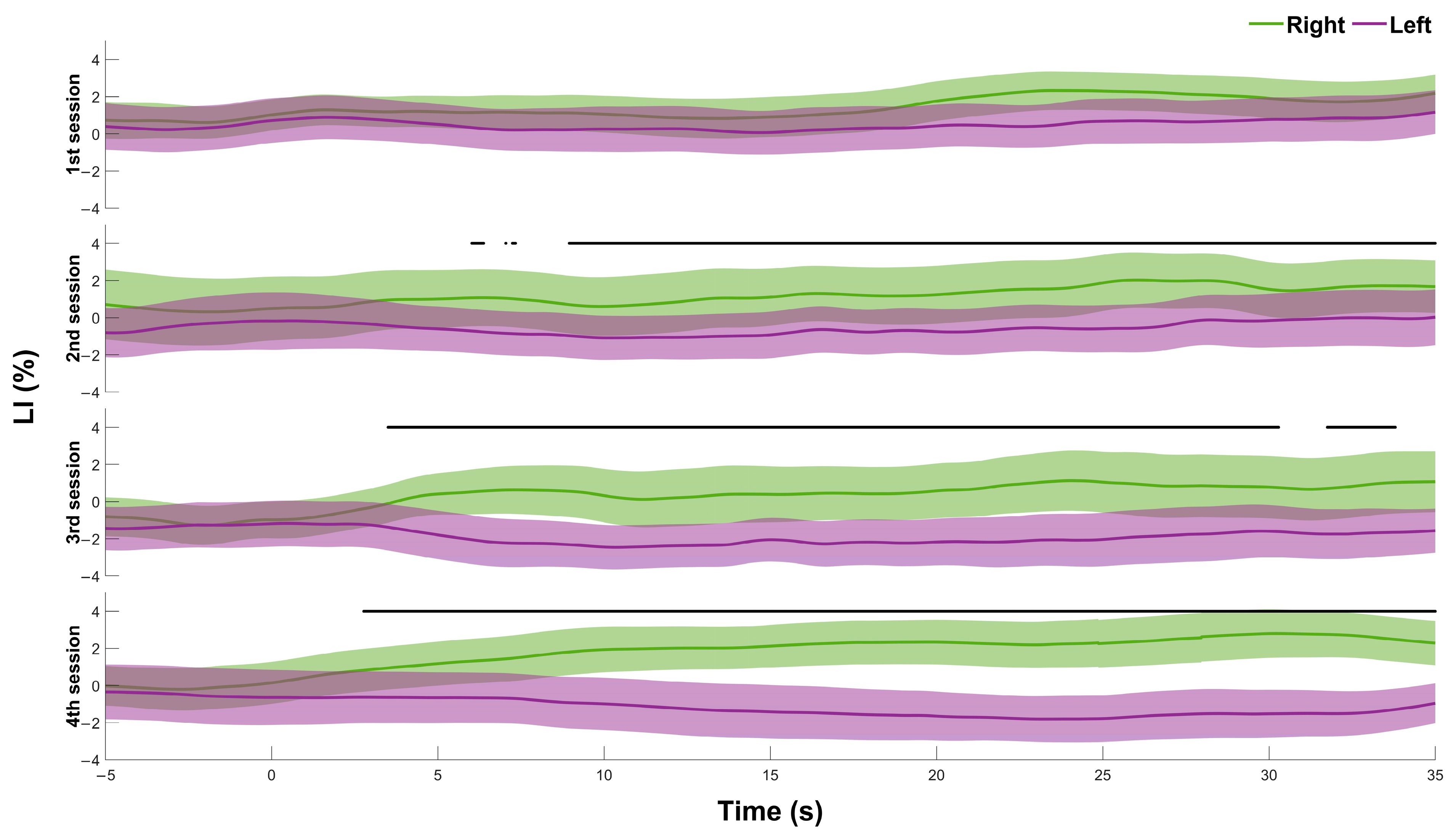
3.1. Differentiation of Responses to Left/Right Tasks
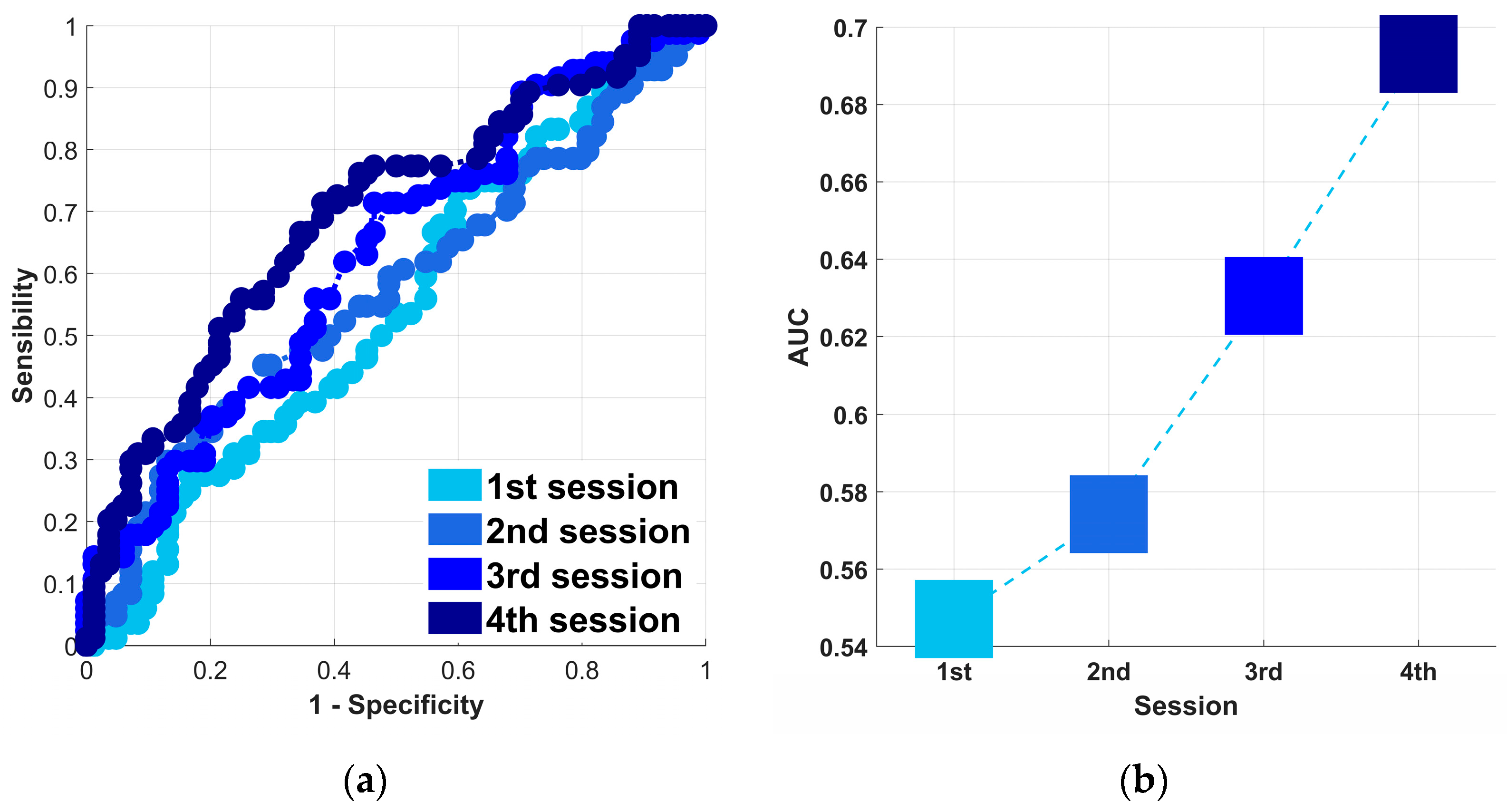
3.2. Binary Classification
3.3. Three-Class Classification
3.4. Results from the Questionnaire
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Limitation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCI | brain–computer interface |
| EEG | electroencephalogram |
| fMRI | functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| fNIRS | functional near-Infrared spectroscopy |
| fTCD | functional transcranial Doppler ultrasound |
| MCA | middle cerebral artery |
| LI | lateralization index |
| CBFV | cerebral blood flow velocity |
| ITR | information transfer rate |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | area under curve |
References
- Rogers, L.J. A Matter of Degree: Strength of Brain Asymmetry and Behaviour. Symmetry 2017, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolis, V.R.; Corbetta, M.; Thiebaut de Schotten, M. The Architecture of Functional Lateralisation and Its Relationship to Callosal Connectivity in the Human Brain. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y. Brain Plasticity and Rehabilitation in Stroke Patients. J. Nippon. Med. Sch. 2015, 82, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomeo, P.; Thiebaut de Schotten, M. Let Thy Left Brain Know What Thy Right Brain Doeth: Inter-Hemispheric Compensation of Functional Deficits After Brain Damage. Neuropsychologia 2016, 93, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqadah, A.; Hsieh, Y.-W.; Morrissey, Z.D.; Chuang, C.-F. Asymmetric Development of the Nervous System. Dev. Dyn. 2018, 247, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocklenburg, S.; Mundorf, A.; Gerrits, R.; Karlsson, E.M.; Papadatou-Pastou, M.; Vingerhoets, G. Clinical Implications of Brain Asymmetries. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, D.V.M. Cerebral Asymmetry and Language Development: Cause, Correlate, or Consequence? Science 2013, 340, 1230531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, M.; Dellatolas, G.; Bancaud, J.; Talairach, J. Hemispheric Lateralization of Motor and Speech Functions After Early Brain Lesion: Study of 73 Epileptic Patients with Intracarotid Amytal Test. Neuropsychologia 1988, 26, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, B.M.; Nigogosyan, Z.; Walton, L.M.; Song, J.; Nair, V.A.; Grogan, S.W.; Tyler, M.E.; Edwards, D.F.; Caldera, K.; Sattin, J.A.; et al. Changes in Functional Brain Organization and Behavioral Correlations after Rehabilitative Therapy Using a Brain-Computer Interface. Front. Neuroeng. 2014, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Murguialday, A.; Broetz, D.; Rea, M.; Läer, L.; Yilmaz, O.; Brasil, F.L.; Liberati, G.; Curado, M.R.; Garcia- Cossio, E.; Vyziotis, A.; et al. Brain-Machine Interface in Chronic Stroke Rehabilitation: A Controlled Study. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, M.E.; Carino-Escobar, R.I.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Hernandez-Arenas, C.; Ramirez-Nava, A.G.; Pacheco-Gallegos, M.d.R.; Valdés-Cristerna, R.; Cantillo-Negrete, J. Neuroplasticity Changes in Cortical Activity, Grey Matter, and White Matter of Stroke Patients After Upper Extremity Motor Rehabilitation via a Brain–Computer Interface Therapy Program. J. Neural Eng. 2025, 22, 026025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loriette, C.; Ziane, C.; Ben Hamed, S. Neurofeedback for Cognitive Enhancement and Intervention and Brain Plasticity. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, S.L.; Nagy, Z.; Skare, S.; Forsman, L.; Forssberg, H.; Ullén, F. Extensive Piano Practicing Has Regionally Specific Effects on White Matter Development. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1148–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orndorff-Plunkett, F.; Singh, F.; Aragón, O.R.; Pineda, J.A. Assessing the Effectiveness of Neurofeedback Training in the Context of Clinical and Social Neuroscience. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huster, R.J.; Mokom, Z.N.; Enriquez-Geppert, S.; Herrmann, C.S. Brain-Computer Interfaces for EEG Neurofeedback: Peculiarities and Solutions. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 91, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbaumer, N.; Ramos Murguialday, A.; Weber, C.; Montoya, P. Chapter 8 Neurofeedback and Brain–Computer Interface: Clinical Applications. In International Review of Neurobiology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 86, pp. 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Enriquez-Geppert, S.; Huster, R.J.; Herrmann, C.S. EEG-Neurofeedback as a Tool to Modulate Cognition and Behavior: A Review Tutorial. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruzelier, J.H. EEG-Neurofeedback for Optimising Performance. III: A Review of Methodological and Theoretical Considerations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 44, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, A.; Di Spiezio, A.; Speggiorin, M.; Zonta, M. Two Decades of Astrocytes in Neurovascular Coupling. Front. Netw. Physiol. 2023, 3, 1162757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rota, G.; Sitaram, R.; Veit, R.; Erb, M.; Weiskopf, N.; Dogil, G.; Birbaumer, N. Self-Regulation of Regional Cortical Activity Using Real-Time fMRI: The Right Inferior Frontal Gyrus and Linguistic Processing. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2008, 30, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, J.; Weingartner, J.H.; Bado, P.; Basilio, R.; Sato, J.R.; Melo, B.R.; Bramati, I.E.; de Oliveira-Souza, R.; Zahn, R. Voluntary Enhancement of Neural Signatures of Affiliative Emotion Using fMRI Neurofeedback. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, R.T.; MacPherson, A.; Lifshitz, M.; Roth, R.R.; Raz, A. Neurofeedback with fMRI: A Critical Systematic Review. NeuroImage 2018, 172, 786–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caria, A.; Veit, R.; Sitaram, R.; Lotze, M.; Weiskopf, N.; Grodd, W.; Birbaumer, N. Regulation of Anterior Insular Cortex Activity Using Real-Time fMRI. Neuroimage 2007, 35, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapborisuth, P.; Zhang, X.; Noah, A.; Hirsch, J. Neurofeedback-Based Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Upregulates Motor Cortex Activity in Imagined Motor Tasks. Neurophotonics 2017, 4, 021107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohl, S.H.; Mehler, D.M.A.; Lührs, M.; Thibault, R.T.; Konrad, K.; Sorger, B. The Potential of Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy-Based Neurofeedback—A Systematic Review and Recommendations for Best Practice. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Sigut, E.; Daws, R.; Payne, H.; Blott, J.; Marshall, C.; MacSweeney, M. Language Lateralization of Hearing Native Signers: A Functional Transcranial Doppler Sonography (fTCD) Study of Speech and Sign Production. Brain Lang. 2015, 151, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestrini, M.; Cupini, L.M.; Matteis, M.; Troisi, E.; Caltagirone, C. Bilateral Simultaneous Assessment of Cerebral Flow Velocity During Mental Activity. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1994, 14, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badcock, N.A.; Groen, M.A. What Can Functional Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography Tell Us About Spoken Language Understanding? Lang. Cogn. Neurosci. 2017, 32, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppe, M.; Knecht, S.; Papke, K.; Lohmann, H.; Fleischer, H.; Heindel, W.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Henningsen, H. Assessment of Hemispheric Language Lateralization: A Comparison Between fMRI and fTCD. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2000, 20, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deppe, M.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Knecht, S. The Investigation of Functional Brain Lateralization by Transcranial Doppler Sonography. NeuroImage 2004, 21, 1124–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Samadani, A.-A.; Guerguerian, A.-M.; Chau, T. An Online Three-Class Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Brain Computer Interface. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 107, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.L.; Oermann, E.K.; Opie, N.L.; Panov, F.; Oxley, T.; Yaeger, K. Sensor Modalities for Brain-Computer Interface Technology: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, E108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duschek, S.; Schuepbach, D.; Doll, A.; Werner, N.S.; Reyes del Paso, G.A. Self-Regulation of Cerebral Blood Flow by Means of Transcranial Doppler Sonography Biofeedback. Ann. Behav. Med. 2011, 41, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, B.; Rodríguez, A.; Lloréns-Bufort, E.; Tembl, J.; Muñoz, M.Á.; Montoya, P.; Herrero-Bosch, V.; Monzo, J.M. Design and Validation of an FPGA-Based Configurable Transcranial Doppler Neurofeedback System for Chronic Pain Patients. Sensors 2018, 18, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbito, R.; Cinanni, A.; Bussi, L.; Guiot, C.; Roatta, S. A Neuro-Feedback Prototype Based on Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound for Brain Computer Interface Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, A.A.; Chan, F.H.; Zheng, M.M.Z.; Krassioukov, A.V.; Ainslie, P.N. Neurovascular Coupling in Humans: Physiology, Methodological Advances and Clinical Implications. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbito, R.; Guiot, C.; Roatta, S. Functional Transcranial Doppler (fTCD) Investigation of Brain Lateralization Following Visual Stimuli. In Proceedings of the 2023 45th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Sydney, Australia, 24–27 July 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Serrien, D.J.; O’Regan, L. Word Perception and Upper-Lower Visual Field Asymmetries. Brain Cogn. 2025, 186, 106294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-K.; Ryu, S.-J.; Hsu, P.-W. Interhemispheric Comparisons of Cerebral Blood Flow Velocity Changes During Mental Tasks with Transcranial Doppler Sonography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2009, 28, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, L.J. Brain Lateralization and Cognitive Capacity. Animals 2021, 11, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinet, A.S.M.; Panerai, R.B.; Robinson, T.G. Effects of Active, Passive and Motor Imagery Paradigms on Cerebral and Peripheral Hemodynamics in Older Volunteers: A Functional TCD Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermaier, B.; Neuper, C.; Guger, C.; Pfurtscheller, G. Information Transfer Rate in a Five-Classes Brain- Computer Interface. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2001, 9, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J. Contralateral focal increase of cerebral blood flow in man during arm work. Brain 1971, 94, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knecht, S.; Deppe, M.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Wirtz, M.; Lohmann, H.; Dräger, B.; Huber, T.; Henningsen, H. Reproducibility of Functional Transcranial Doppler Sonography in Determining Hemispheric Language Lateralization. Stroke 1998, 29, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Khalaf, A.; Sybeldon, M.; Sejdic, E.; Akcakaya, M. A Brain-Computer Interface Based on Functional Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound Using Wavelet Transform and Support Vector Machines. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 293, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Mamun, K.A.; Chau, T. Online Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonographic Control of an Onscreen Keyboard. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrden, A.J.B.; Kushki, A.; Sejdić, E.; Guerguerian, A.-M.; Chau, T. A Brain-Computer Interface Based on Bilateral Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, A.; Ahmed, E.; Islam, A.; Lu, J.; Sarkar, F.; Mamun, K.A. Decoding Human Brain States Using Transcranial Doppler Ultrasonography. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Communication Technology (ICEEICT), Savar, Bangladesh, 21–23 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, A.; Sejdic, E.; Akcakaya, M. A Novel Motor Imagery Hybrid Brain Computer Interface Using EEG and Functional Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 313, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faress, A.; Chau, T. Towards a Multimodal Brain–Computer Interface: Combining fNIRS and fTCD Measurements To Enable Higher Classification Accuracy. NeuroImage 2013, 77, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Yin, X.; Huang, J.; Jia, B.; Gan, L.; Yin, X.; Huang, J.; Jia, B. Transcranial Doppler Analysis Based on Computer and Artificial Intelligence for Acute Cerebrovascular Disease. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 1695–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Franc, S.; Herrera Altamira, G.; Guillen, M.; Butet, S.; Fleck, S.; Lécuyer, A.; Bougrain, L.; Bonan, I. Toward an Adapted Neurofeedback for Post-Stroke Motor Rehabilitation: State of the Art and Perspectives. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 917909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Left Hemispheres | Right Hemispheres |
|---|---|
| Word generation [30,38] | Spatial orientation [27] |
| Mental calculation [39] | Evoking strong emotions, listening to melodies, and meditation [40] |
| Movements of the right upper and lower limbs [41] | Motor movements of the left side of the body [41] |
| Session # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.60 | 0.65 |
| ITR (bit/min) | 0.00012 | 0.010 | 0.036 | 0.084 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabbito, R.; Ermini, L.; Guiot, C.; Roatta, S. Transcranial Doppler-Based Neurofeedback to Improve Hemispheric Lateralization. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5763. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105763
Rabbito R, Ermini L, Guiot C, Roatta S. Transcranial Doppler-Based Neurofeedback to Improve Hemispheric Lateralization. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5763. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105763
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabbito, Rosita, Leonardo Ermini, Caterina Guiot, and Silvestro Roatta. 2025. "Transcranial Doppler-Based Neurofeedback to Improve Hemispheric Lateralization" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5763. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105763
APA StyleRabbito, R., Ermini, L., Guiot, C., & Roatta, S. (2025). Transcranial Doppler-Based Neurofeedback to Improve Hemispheric Lateralization. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5763. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105763








