Abstract
Selenium (Se) is essential for various metabolic and physiological functions in the human body. However, the mechanisms of Se cycling in soils, particularly under different parent materials and land uses, remain understudied. This study investigates the spatial distribution and influencing factors of total Se in surface soils derived from limestone and sandstone in paddy and dryland systems in a Se-rich karst region of Southwest China. The mean Se content was 0.5 mg/kg, with 100% of samples exceeding national and global background levels, confirming Zheng’an County as a newly recognized Se-rich area. Soil Se concentrations, along with environmental variables such as soil organic matter (SOM), pH, elevation, slope, and trace elements (V, Cr, and Zn), were analyzed. One-way ANOVA revealed significant differences in Se content between parent materials and land-use types. Stepwise multiple regression identified SOM as the strongest predictor of Se, while Spearman correlation showed significant associations with topographic and chemical factors. These findings highlight the complex interactions between geology, land use, and topography in Se dynamics. Given the global distribution of karst landscapes, this research provides valuable insights into Se behavior in similar environments worldwide, with implications for land management and nutritional security.
1. Introduction
Selenium (Se), a metalloid first discovered by Swedish chemist Berzelius in 1817, shares many chemical properties with sulfur [1]. As an essential trace element, Se plays a crucial role in numerous physiological and metabolic functions in humans and animals. It contributes to cancer prevention, antioxidative defense, immune system regulation, endocrine health, and the detoxification of toxic elements such as arsenic, mercury, and chromium [2,3,4]. However, Se exhibits a narrow range between deficiency and toxicity. While insufficient intake can lead to disorders such as Keshan disease and Kashin–Beck disease, excessive intake may cause selenosis and other health issues, including skin lesions and neurological damage [5]. To manage this delicate balance, the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Chinese Nutrition Society recommend a daily Se intake of 40–400 μg [6].
Soil is the primary source of Se in the human diet, as it enters the food chain through plant uptake [7,8,9,10]. However, the distribution of Se in the Earth’s crust is highly heterogeneous [11,12] (Ma Jingxuan et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2018), leading to significant spatial variability in soil Se concentrations. Globally, soil Se levels are generally low, typically ranging from 0.01 to 2.00 mg·kg−1, with an average of approximately 0.40 mg·kg−1, and high-altitude areas tend to exhibit relatively higher Se concentrations [13]. This heterogeneity is influenced by multiple environmental factors, including parent material, land use, topography, and soil physicochemical properties. As a result, understanding the environmental controls on soil Se distribution has become a globally relevant scientific challenge.
Among these factors, parent rock is a fundamental determinant of soil Se content, as it serves as the primary geogenic source [6,14]. Different lithologies influence soil formation processes and elemental concentrations due to varying mineral compositions and weathering rates [15,16]. For example, carbonate rocks and sandstones weather at different rates, leading to distinct trace element profiles in derived soils [17]. Notably, Se-rich black shales from the Permian Gufeng Formation in Enshi, Hubei Province, have produced some of the highest recorded Se concentrations in soils, earning the region the title of “Se Capital of the World” [14]. Similar patterns have been observed in Ziyang County, Shaanxi Province, where Se levels in soils reach up to 279 mg/kg due to black shale weathering [18]. This underscores the fundamental role of parent rock in the geochemical cycling of Se and other elements.
In addition to geogenic sources, land use plays a critical role in modifying soil properties and influencing the mobility and bioavailability of Se [19,20,21,22]. Land use affects soil organic matter, pH, redox potential, and microbial activity, all of which are key factors in Se transformation and retention [23,24]. While numerous studies have examined the impact of land use on macronutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus [25,26], relatively fewer have focused on trace elements like Se [27,28,29,30]. Moreover, existing findings are often inconsistent. For instance, Se levels in dryland soils have been reported to be higher than in paddy soils in parts of Guizhou [31,32], whereas opposite trends have been observed in nearby regions [33]. Similarly, comparisons between agricultural and forest soils have yielded contradictory results [34,35,36,37], suggesting that other interacting variables, such as parent material and topography, may play significant roles.
Despite growing interest in the environmental behavior of Se, research on its cycling in karst landscapes remains limited, especially from a global perspective. Karst regions—formed by the dissolution of carbonate rocks—cover approximately 15% of the Earth’s land surface and support nearly 25% of the global population. These landscapes are particularly sensitive to environmental changes due to their thin soils, complex hydrology, and heterogeneous lithology. Yet, studies on Se dynamics in karst agroecosystems remain scarce [38] (Hu et al., 2024), leaving a critical knowledge gap in both geochemical and land management research. To address this gap, this study focuses on Zheng’an County in northern Guizhou Province, Southwest China. The area is characterized by a typical karst terrain, diverse parent materials (limestone and sandstone), and a mosaic of land use types (paddy fields, drylands, and forests). Recent surveys have identified extensive Se-rich farmlands in the region, with soil Se concentrations consistently exceeding national background values. These characteristics make Zheng’an an ideal natural laboratory for investigating the interactions among geology, land use, and topography in shaping soil Se distribution. The specific objectives of this study are as follows:
(1) Map the spatial distribution of total Se in surface soils of Zheng’an using inverse distance weighting (IDW) interpolation;
(2) Compare Se concentrations in soils derived from different parent rocks (limestone vs. sandstone);
(3) Assess the combined impact of parent material and land use on soil Se content;
(4) Explore how micro-scale factors (e.g., SOM, pH, and trace elements) and macro-scale variables (e.g., elevation and slope) interact within a unified analytical framework to influence Se accumulation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Zheng’an County (28°08′16″–28°50′59″ N, 107°04′23″–107°42′12″ E) is located in the northeastern region of Zunyi City, Guizhou Province, in southwestern China (Figure 1). The area experiences a subtropical monsoon climate, with average annual temperatures ranging from 5.1 °C to 26.6 °C and annual precipitation ranging from 772.2 mm to 1327.4 mm. The topography is diverse, with elevations ranging from 448 m to 1838 m. The eastern region is characterized by mid-altitude tablelands, the central region by low mountains and hilly terrain, and the western region by typical mid-altitude gorges. The exposed strata comprise Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Permian, Triassic, and Quaternary systems, featuring lithologies such as limestone, dolomite, sandstone, mudstone, and shale. Limestone and sandstone are the primary parent materials for soil formation, leading to the development of calcareous and yellow soils.
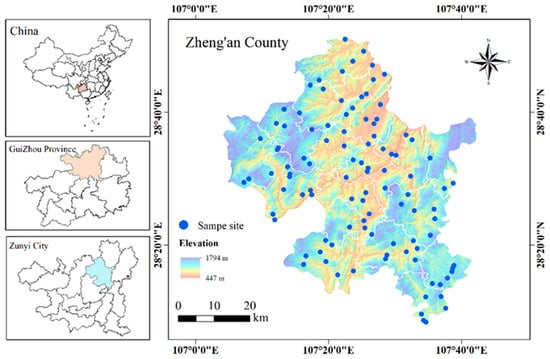
Figure 1.
Study area and distribution of sampling sites.
2.2. Sample Collection
Field sampling was conducted from May to July 2023. Sampling locations were selected based on the types of parent materials (limestone and sandstone) and land use types (drylands and paddy fields, respectively). A total of 80 soil samples were collected from a depth of 0–20 cm across the study area to ensure adequate spatial coverage and statistical robustness. The sample size was determined based on previous studies in similar karst regions and a preliminary statistical power analysis. These references indicated that 80 samples would provide sufficient statistical power for multiple regression analyses involving five to seven predictor variables. Of these, 38 samples were from limestone-derived soils (including both paddy fields and drylands), while 42 samples were from sandstone-derived soils with similar land use types. During the sampling period, paddy fields were cultivated with rice, while drylands were planted with maize. To ensure representativeness, three subsamples were collected from each location, thoroughly mixed to form a composite sample, and then reduced to over 1 kg using the quartering method. The composite samples were stored in clean polyethylene bags. The soil samples were air-dried at room temperature, manually cleaned of roots and stones, and then sieved through a 2 mm mesh. The sieved (<2 mm) soil was used to analyze pH, particle size distribution, and other physicochemical properties. To determine total Se, SOM, and concentrations of vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), and zinc (Zn), a portion of the sieved soil (<2 mm) was further ground and passed through a 0.15 mm mesh.
2.3. Chemical Analysis
The total Se concentration was determined in accordance with the National Environmental Protection Standard of China (HJ 680-2013), incorporating the revised procedures proposed by Zhao et al. [39]. It should be noted that this study measured only total Se concentrations. While total Se provides an overview of its distribution in soils, it does not reflect the bioavailable forms relevant to plant uptake and ecological risk. This limitation will be addressed in future research.
For cold digestion, 5 mg of soil was mixed with 8 mL of a nitric acid–hydrochloric acid solution (1:3, v/v) and left to stand at room temperature overnight. Subsequent digestion was performed following the heating program outlined in Table 1 and the parameters listed in Table 2. The digested solution was then filtered and diluted to 50 mL with deionized water using a volumetric flask. Next, 10 mL of the diluted solution was mixed with 10 mL of hydrochloric acid in a 50 mL volumetric flask. After standing at room temperature for 30 min, the mixture was diluted to volume with deionized water for analysis. The total Se content was determined using a hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometer (AFS-8220; Jitian Instruments Co., Ltd., Beijing, China).

Table 1.
Microwave digestion heating program.

Table 2.
Atomic fluorescence spectrophotometer instrument parameters.
Soil pH was measured using a water-to-soil suspension at a ratio of 1:2.5, following the Chinese National Environmental Protection Standard (HJ 962-2018), with a water quality analyzer (YSI ProPlus, YSI, Yellow Springs, OH, USA). SOM was determined by the loss-on-ignition method in accordance with HJ 658-2013. Prior to total organic carbon (TOC) analysis, samples were acidified to remove inorganic carbon, and TOC was quantified using a TOC analyzer (Vario TOC cube, Elementar, Langenselbold, Germany). Concentrations of vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), zinc (Zn), and other trace metals were determined following the Chinese National Standard HJ 1315-2023. Sample digestion was conducted using microwave-assisted aqua regia (HCl:HNO3 = 3:1, v/v), with the addition of hydrofluoric and perchloric acids. The digested solutions were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES 5100, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Quality control was ensured through the use of reagent blanks, duplicate samples, and certified reference materials (GBW07405), with recovery rates ranging from 90% to 110% and relative standard deviations (RSDs) below 5%.
2.4. Calculation of Topographic Parameters
Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data were utilized to evaluate the influence of topographic factors on soil Se concentrations. The DEM, obtained from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) at a spatial resolution of 30 m, was processed using ArcGIS to extract elevation, slope, and aspect. Notably, the DEM used to calculate the Stream Power Index (SPI) and Topographic Wetness Index (TWI) also had a 30 m resolution, which may not sufficiently capture microtopographic variability within small catchments. This limitation could introduce uncertainty in the estimation of hydrological indices and their association with soil Se concentrations.
Topography plays a vital role in soil formation by regulating both surface and subsurface water flow patterns. These hydrological processes vary spatially and are influenced by topographic attributes such as upslope contributing area and slope gradient. As slope steepness increases, soil moisture content generally decreases due to reduced water retention capacity, and the upslope contributing area per unit contour length also tends to decline. To quantify the spatial distribution of soil moisture, Beven and Kirkby [40], followed by Moore et al. [41], introduced the Topographic Wetness Index (TWI), which integrates the upslope contributing area per unit contour length and the local slope gradient:
In this context, α represents the area contributing per unit contour length, while β denotes the slope gradient at a specific location. Using a depression-free DEM, the flow direction is determined by identifying the steepest downslope path for each grid cell [42]. The contributing area is subsequently calculated based on the flow direction.
The SPI serves as an indicator of water flow erosion potential, assuming that discharge is directly proportional to the contributing area. Higher SPI values indicate more concentrated runoff, which can lead to soil erosion [43]. Moore et al. [44] proposed the following formula:
SPI = α⋅tanβ
Here, α denotes the upslope area contributing per unit contour length, and β denotes the slope gradient at a specific point.
The precision of the extracted elevation, slope, aspect, TWI, and SPI is affected by the DEM resolution, with an error of 0.9 km2 in this study.
2.5. Quality Control
Quality control in this study was ensured through the use of reagent blanks, certified soil reference materials (GBW07410, provided by the National Research Center for Certified Reference Materials, Beijing, China), and duplicate samples analyzed alongside the soil samples. The certified reference materials included GSS-2A, GSS-3A, and GSS-5A, with certified Se concentrations and associated uncertainties of 0.26 ± 0.03 μg/g, 0.12 ± 0.03 μg/g, and 0.75 ± 0.12 μg/g, respectively. The average recovery rate for Se was 107%, indicating acceptable analytical accuracy.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Prior to data analysis, the assumptions of normality, multicollinearity, homoscedasticity, and independence of residuals were evaluated to ensure the validity of the subsequent statistical models. When the assumption of normality was violated, Spearman’s rank correlation analysis was employed to examine the relationships between Se content and other variables. A two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to evaluate the effects of parent material, land use, and their interaction on total Se content. To validate the inverse distance weighting (IDW) interpolation method, leave-one-out cross-validation was performed, with ordinary kriging used as a benchmark for comparison. The root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE) were calculated to assess the predictive accuracy of the interpolation methods. The results showed that IDW performed comparably to kriging, supporting its applicability in this study.
All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics 27.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) under an academic license. Spatial mapping of Se concentrations and topographic features was conducted using ArcGIS 10.8 (Esri Inc., Redlands, CA, USA), while statistical graphs were generated with OriginPro 2021 (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA). All software used in this study was licensed to China University of Geosciences (Wuhan, China).
3. Result
3.1. Total Se in Soil and Soil Physicochemical Properties
The total Se concentration in cropland soils ranged from 0.25 to 1.60 mg/kg, with a mean value of 0.50 mg/kg and a coefficient of variation (CV) of 0.43 (Table 3). The average Se content exceeded both the Chinese soil background value of 0.29 mg/kg [35] and the global average of 0.40 mg/kg [45]. According to the classification standards for total Se in surface soils in China [12], Se levels are categorized into five classes: deficient (<0.125 mg/kg), marginal (0.125–0.175 mg/kg), moderate (0.175–0.400 mg/kg), sufficient (0.400–3.000 mg/kg), and excessive (>3.000 mg/kg). All samples in this study fell within the moderate or higher categories, with 64% classified as “sufficient”, indicating that Zheng’an County can be considered a Se-rich region.

Table 3.
Summary of mean values for total Se and influencing factors.
The CV of 0.43 suggests considerable spatial variability in total Se distribution across the study area. The observed differences in Se concentrations among sampling sites may be attributed to variations in parent material, land use types, or their combined effects. Soil pH values ranged from 4.84 to 8.16, with an average of 6.05, indicating that most soils in the area are acidic (Table 3). SOM content varied between 14.5 and 50.9 g/kg, with an average of 27.59 g/kg, reflecting relatively high SOM levels in the region.
Figure 2 illustrates the spatial distribution patterns of total Se, soil pH, and SOM, all of which exhibit pronounced spatial variability across the study area. As shown in the figure, total Se concentrations were relatively high in the eastern part of Banzhu Town and the central region of Xiaoya Town in Zheng’an County, with values exceeding 1.1 mg/kg. In contrast, lower Se concentrations formed a belt-like pattern extending from north to south, closely mirroring the spatial distribution of SOM. Alkaline soils were mainly concentrated in the northeastern part of Anchang Town, whereas the rest of the region was predominantly characterized by acidic soils.
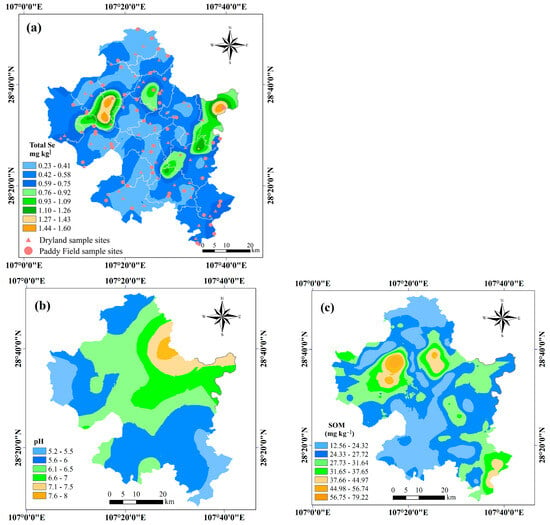
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution maps of (a) soil total Se, (b) pH, and (c) SOM.
3.2. Topographic Parameters
In addition to parent material, climate, anthropogenic activities, and time, topography plays a critical role in soil formation processes. Topographic variables are also essential indicators for terrain classification, among which surface curvature and slope are fundamental. The TWI and the SPI are commonly used to represent soil moisture status and the erosive potential of surface runoff, respectively, thereby emphasizing the influence of topography on the hydrological characteristics of the study area. In this study, elevation, slope, SPI, and TWI were employed to characterize the topographic attributes of the region.
Based on the classification of China’s basic landform types proposed by Li Bingyuan et al. [46], elevation in the study area was divided into three categories: 200–500 m (low-relief mountainous areas), 500–1000 m (medium-relief mountainous areas), and 1000–2500 m (high-relief mountainous areas). Similarly, slope was classified into three groups: less than 5° (gentle slopes), 5–15° (moderate slopes), and greater than 15° (steep slopes). As there are no standardized classification criteria for the TWI and SPI, the natural breaks (Jenks) classification method was applied. Figure 3 displays the spatial distribution maps of elevation, slope, SPI, and TWI across the study area.
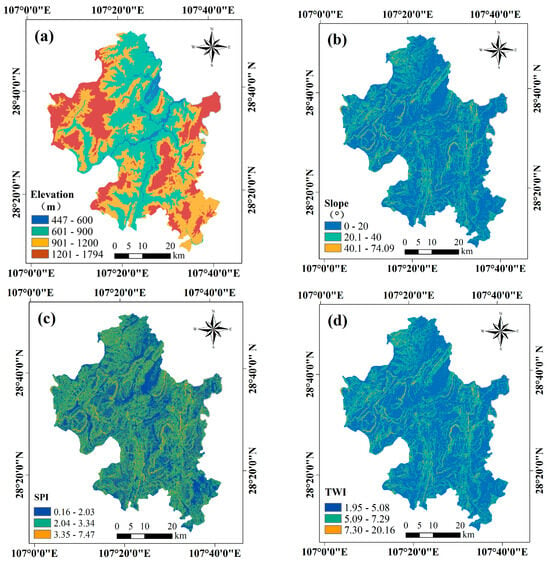
Figure 3.
Maps showing the spatial distribution of (a) elevation, (b) slope, (c) Stream Power Index (SPI), and (d) Topographic Wetness Index (TWI).
Figure 3 illustrates the overall topographic pattern of Zheng’an County, which can be divided into three major geomorphological regions: eastern, central, and western. The eastern and western regions are predominantly characterized by medium-relief mountainous terrain, featuring deeply incised river valleys and primarily unidirectionally inclined mountain slopes. In contrast, the central region mainly consists of low mountains and hills, with rivers forming “U”-shaped valleys, accompanied by well-developed floodplains and river terraces. The spatial distributions of slope, SPI, and TWI are complex and interwoven throughout the study area. As shown in Table 3, the average slope is 15.55°, placing the region within the steep slope category, although areas of gentle slopes are also present. Variations in slope exert a significant influence on the region’s hydrological conditions, and the spatial patterns of SPI and TWI are similarly affected by slope gradients.
4. Discussion
4.1. Differences in Soil Se Content Across Parent Rock Types and Land Use Categories
The lithological distribution of Zheng’an County is shown in Figure 4. Figure 5 demonstrates that total Se content differs significantly between soils derived from limestone and sandstone (p < 0.05), and exhibits a marginally significant difference between paddy fields and drylands (p < 0.1). Within limestone-derived soils, total Se content varies significantly across land use types, with drylands exhibiting higher Se concentrations than paddy fields. In contrast, no significant difference is observed between land use types within sandstone-derived soils, indicating an interaction effect between parent material and land use. On average, total Se content in limestone regions is approximately 17% higher than in sandstone regions. Moreover, within limestone areas, Se content in drylands is, on average, 42% higher than in paddy fields. This disparity is primarily attributed to prolonged waterlogging in paddy fields, which accelerates the decomposition of organic matter. Consequently, organically bound Se is transformed into more bioavailable forms, such as fulvic acid-bound Se, which are readily absorbed by crops, leading to Se depletion in the soil [47]. Additionally, Se losses through leaching and percolation under flooded conditions further contribute to Se depletion in paddy soils [48].
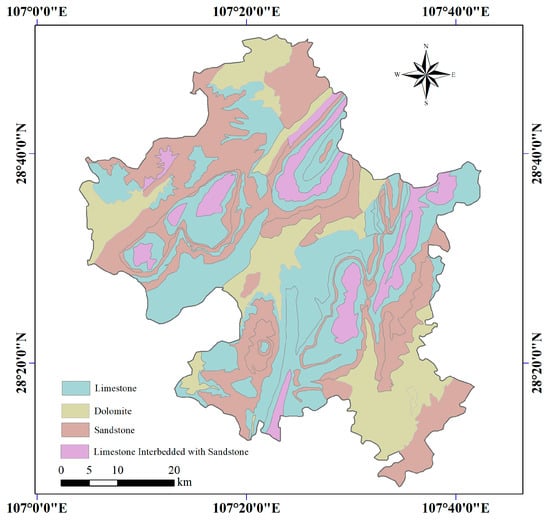
Figure 4.
Lithological distribution map of Zheng’an County.
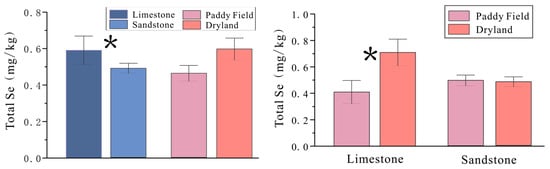
Figure 5.
Comparative analysis of total Se content differences based on land use and lithology. * indicates a significant difference.
The bars represent the mean ± standard error (n = 20). An asterisk (*) denotes a statistically significant difference at p < 0.05 between limestone- and sandstone-derived soils, as well as between paddy fields and drylands.
In soils derived from limestone, V and SOM are the strongest predictors of total Se content, jointly explaining 86% of its variation (Table 4). This suggests a strong association between Se and elements such as V and zinc (Zn), consistent with the findings of Lin et al. [49]. Both V and Zn are partially indicative of clay mineral content, with V exhibiting a higher adsorption capacity for Se compared to Zn. Among the topographic variables, elevation shows a relatively weak influence on total Se content, with a correlation coefficient of 0.141.

Table 4.
Stepwise multiple linear regression analysis of influencing factors on soil total Se under different land uses and parent rock controls.
In sandstone-derived soils, SOM emerges as the primary explanatory variable, accounting for 62.4% of the variation in total Se content. A similar pattern is observed in dryland soils within limestone regions, where SOM explains 80% of the variation, indicating a stronger influence. In contrast, in paddy soils derived from limestone, SOM alone accounts for 75% of the variation in total Se content, suggesting that organic matter plays a dominant role in Se retention under flooded conditions.
The analysis of Figure 5 reveals significant variations in total Se content between soils derived from different parent materials, whereas no substantial differences are observed among different land-use types. This indicates that parent material exerts a stronger influence on Se concentrations than land use. In limestone regions, dryland soils exhibit markedly higher Se levels than paddy soils, while overall Se concentrations are substantially lower in sandstone-derived soils. Notably, the elevated Se levels in limestone areas are primarily attributable to Se-enriched dryland soils. In contrast, Se concentrations in paddy soils from limestone regions are even lower than those in both paddy and dryland soils from sandstone regions. These distribution patterns may be shaped by additional factors, such as topography and soil physicochemical properties, that interact with both land use and parent material to influence total Se content.
4.2. Influence of Soil Physicochemical Properties on Total Se in Soils Derived from Different Parent Rocks
A Spearman correlation analysis, accompanied by a heatmap visualization (Figure 6), was conducted to investigate the relationships between total Se content and various soil physicochemical properties. This approach enabled a comprehensive assessment of the factors influencing Se distribution. The results revealed that in limestone-dominated regions, no significant correlation was observed between soil pH and total Se content. In contrast, a strong negative correlation was found in sandstone-dominated areas (r = −0.47, p = 0.01), indicating that higher pH levels are associated with lower Se concentrations.
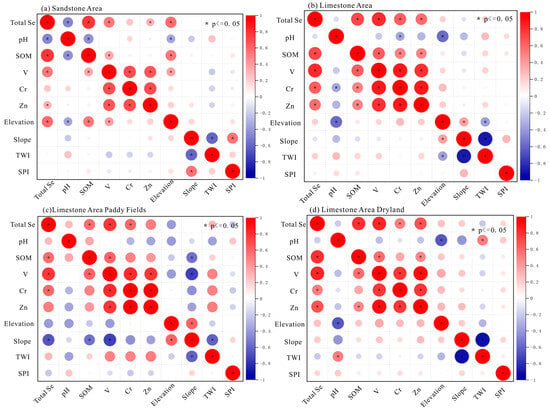
Figure 6.
Heatmap showing the correlations between Se concentration and key influencing factors. * indicates a significant difference.
In limestone regions (Figure 6b), the absence of a significant relationship between pH and total Se may be attributed to the dominant influence of other factors, such as SOM and mineral components, which possess a strong capacity to adsorb Se. Similar findings were reported by Xi Yaowei and Yin Quanming [50], who suggested that external inputs of Se into the soil may mitigate the inhibitory effect of pH on Se accumulation.
In general, soil pH exhibits a negative correlation with total Se content. As pH increases, the positive charge on hydroxides and clay minerals decreases, thereby reducing their capacity to adsorb Se [51,52]. Another possible explanation is that lower pH levels suppress microbial activity, which in turn slows the decomposition of SOM and alters Se dynamics [27,53,54]. The negative correlation observed between pH and total Se in sandstone-derived soils aligns with this general trend, likely due to the relatively low adsorption capacity of these soils. Furthermore, the humid climate and high rainfall in Southwest China may exacerbate Se loss through leaching, thereby contributing to the overall decline in total Se content.
Numerous studies have reported positive correlations between Se and both SOM and pH levels [55,56,57]. The findings of the present study are consistent with this trend (Figure 6a,b), showing that total Se is significantly positively correlated with SOM in both sandstone- and limestone-dominated areas (r = 0.715 and r = 0.472, p = 0.01, respectively). This relationship may be attributed to the formation of ternary complexes involving Se, SOM, and mineral elements such as V, Cr, and Zn, which can reduce Se leaching and enhance its retention in soils [58,59,60].
In addition, SOM plays a crucial role in Se redox transformations by promoting the development of anaerobic microsites within soil aggregates, thereby facilitating the reduction and immobilization of Se [61,62,63]. Moreover, SOM increases the number of available adsorption sites for Se, enabling its direct binding to soil particles [62,63,64]. The observed correlations between Se and mineral elements such as V, Cr, and Mn in this study further support the ternary complexation mechanism.
4.3. Influence of Soil Physicochemical Properties on Total Se in Soils Under Different Land Uses in Limestone Regions
As shown in the heatmaps in Figure 6c,d, no significant relationship is observed between soil pH and total Se content in either paddy fields or drylands. This result is consistent with the pattern observed in sandstone-dominated regions, as opposed to limestone-dominated areas. These findings suggest that land use type does not significantly influence the role of pH in regulating soil Se content.
In contrast, a comparison of the heatmaps in Figure 6a,b indicates that parent material plays a critical role in modulating total Se content through its influence on soil pH. It is hypothesized that parent material not only serves as the primary source of Se in soils but also strongly affects the physicochemical properties of the overlying soil, thereby shaping Se dynamics [65,66].
In limestone regions, SOM is significantly correlated with total Se content in both paddy and dryland soils, with correlation coefficients of r = 0.878 and r = 0.900 (p = 0.01), respectively. These strong correlations underscore the critical role of SOM in influencing total Se concentrations. Compared to previously reported correlation coefficients for SOM in limestone regions, the observed values represent increases of 0.163 and 0.185, corresponding to relative increases of 22.8% and 25.8%, respectively. This suggests that land use positively influences SOM accumulation, thereby enhancing total Se content in soils.
This phenomenon is likely attributable to the substantial impact of anthropogenic activities, which can alter key soil properties such as clay content, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and pH. These changes promote the accumulation of organic matter, which in turn facilitates Se enrichment in soils [67].
4.4. Influence of Topographic Factors on Total Se Under Different Parent Materials and Land Uses in Limestone Regions
As shown in Figure 6a,b, in limestone regions, soil Se content shows no significant correlation with any topographic factors. In contrast, in sandstone regions, soil Se content exhibits a significant positive correlation with elevation, consistent with previous findings [12,68]. The elevated Se concentrations at higher altitudes can be attributed to several factors beyond reduced anthropogenic disturbance. These include lower temperatures that slow the decomposition of soil organic matter, reduced Se mobility and transformation rates, decreased leaching losses, and diminished plant uptake of Se. Moreover, parent material plays a critical role in modulating these processes, thereby establishing an indirect link between elevation and soil Se content.
As illustrated in Figure 6c,d, in limestone regions, the total Se content in paddy soils exhibits a significant negative correlation with slope, whereas no significant relationship is observed between total Se content in dryland soils and topographic factors. Slope is a key factor influencing soil erosion and leaching processes, with steeper gradients typically associated with more severe soil loss (Yan et al., 2008) [69]. This not only alters the transport mechanisms of Se but also indirectly affects its spatial distribution through the redistribution of trace elements within the soil profile [12].
The study area, characterized by mountainous terrain, is particularly susceptible to intense soil erosion and nutrient depletion due to its complex topography. As shown in Figure 6, SOM content decreases with increasing slope, further exacerbating Se loss. These findings highlight the critical role of slope in regulating soil Se dynamics, particularly in paddy fields, where the combined effects of waterlogging, erosion, and topographic variability are more pronounced.
Given that Pearson and Spearman correlation analyses primarily capture linear or monotonic relationships and may fail to detect more complex nonlinear associations between variables, we further analyzed the mean soil Se content across different intervals of topographic factors (Figure 7). SOM, previously identified as a key influencing factor, was also included in this analysis. As illustrated in Figure 7, the relationship between total Se content and topographic factors is not strictly monotonic. Instead, a nonlinear pattern is observed, characterized by an initial decrease in Se content followed by a subsequent increase. This trend aligns with earlier findings, in which elevation and slope exhibited positive and negative correlations with soil Se content, respectively, as reflected in the patterns shown in Figure 7.
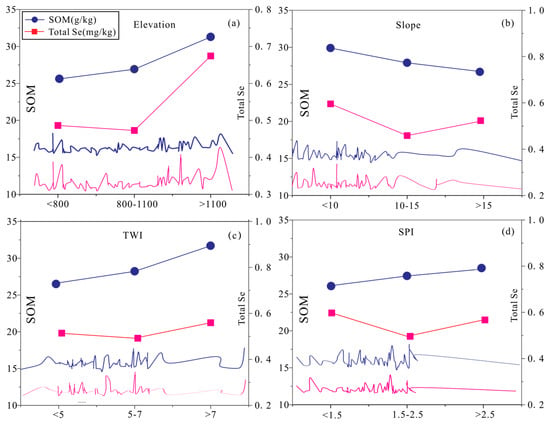
Figure 7.
Average content of soil total Se and SOM at different (a) elevations, (b) slopes, (c) TWI and (d) SPI values.
Two widely used indices for assessing the influence of topography on surface runoff are the TWI and the SPI. Lower TWI values generally indicate drier soil conditions, whereas higher SPI values correspond to areas with greater runoff potential and, consequently, wetter soils. Both indices are commonly employed as proxies for soil moisture status. As shown in Figure 6, when the TWI exceeds 7, both total Se and SOM contents are relatively high. Similarly, the highest concentrations of Se and SOM are observed when the SPI is less than 1.5. However, this positive association does not persist across all SPI intervals. Notably, a marked decline in total Se content occurs when SPI values range between 1.5 and 2.5, despite SOM levels remaining relatively high. This discrepancy may be attributed to the effects of runoff-induced soil erosion, which likely outweigh the capacity of SOM to adsorb and retain Se. Under such conditions, the rate of Se loss due to erosion may surpass its retention by SOM, resulting in a net decrease in total Se content.
The polyline represents the mean variation trends of total soil Se and SOM across different intervals of topographic factors, while the curve illustrates the continuous change trends of total Se and SOM with increasing values of the topographic variables.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the spatial distribution and influencing factors of Se in soils of a Se-rich karst region in Zheng’an County, Guizhou Province. By comparing soils derived from two parent materials (limestone and sandstone) under different land-use types (paddy fields and drylands), we found that Se content is significantly enriched across the region, with all samples exceeding the national and global background values. Notably, Se was more concentrated in the eastern part of Banzhu Township and central Xiaoya Township.
Parent material and land use jointly influenced Se distribution, with limestone-derived soils generally exhibiting higher Se levels. SOM emerged as the most consistent predictor of total Se content across different settings, likely due to its role in Se adsorption and redox stabilization. Although pH was not directly correlated with Se content, it may exert an indirect influence through its interaction with parent material and SOM.
At the macro scale, topographic factors such as elevation and slope showed significant correlations with Se content in specific subregions. Elevation influenced Se indirectly by affecting SOM accumulation through climatic and biological processes, while slope affected Se distribution by altering erosion and leaching dynamics.
These findings highlight the complex interplay between geological and ecological factors in shaping Se dynamics in karst landscapes. The results provide a scientific basis for improving land management and soil nutrient conservation in Se-rich regions. However, this study is limited by its focus on total Se rather than bioavailable forms. Future research should incorporate Se speciation, plant uptake, and seasonal dynamics to better understand Se cycling and its implications for food security and human health.
Author Contributions
J.B.: Supervision, Writing—Review and Editing, Conceptualization, and Investigation. C.X.: Methodology, Writing—Original Draft, Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, and Visualization. X.X.: Investigation, Writing—Review and Editing, Funding acquisition, and Project administration. Z.H.: Software and Data Curation. J.Z.: Software, Resources, Visualization, and Data Curation. C.Y.: Investigation, Writing—Review and Editing, Y.H.: Software, Resources, Visualization, and Data Curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Guizhou Province (ZK-2022-227), the Geological Mineral Exploration and Development Fund of Guizhou Province (QDKKH2021-15), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41907177), and the Open Research Program of the Groundwater Remediation Technology Transformation Pilot Base of Hubei Province (GRTT202003).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Requests should be directed to Jianwei Bu (jwbu@cug.edu.cn).
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the 106 Geological Brigade of the Guizhou Provincial Bureau of Geology and Minerals for their support in gathering geological and geochemical data, as well as aiding in field surveys and sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors affirm that there are no financial or personal conflicts of interest that could have influenced the results presented in this paper.
References
- Jiang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y. Advances in research on the mechanisms of selenium uptake, transformation, and physiological functions in plants. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 4067–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afton, S.E.; Catron, B.; Caruso, J.A. Elucidating the Selenium and Arsenic Metabolic Pathways Following Exposure to the Non-Hyperaccumulating Chlorophytum Comosum, Spider Plant. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, A.A.D.S.; Namorato, F.A.; Guilherme, L.R.G.; Silva, M.L.D.S.; Liu, J.; Li, L. Glutathione Is Involved in Selenium Detoxification and Suppresses the Selenate-Induced SULTR1;1 Gene Expression in Plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 213, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, D.; Peng, Q.; Cui, Z.; Huang, J.; Lin, Z. Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability: A review. Geoderma 2017, 295, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, K.; Van Cappellen, P.; Tong, L.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y. Loss of Selenium from Mollisol Paddy Wetlands of Cold Regions: Insights from Flow-through Reactor Experiments and Process-Based Modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 6228–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Zhang, H. Source Apportionment of Selenium and Influence Factors on Its Bioavailability in Intensively Managed Greenhouse Soil: A Case Study in the East Bank of the Dianchi Lake, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2019, 170, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, T. Selenium Transformation and Selenium-Rich Foods. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, S.; Li, B.; Long, J.; Fan, J.; Luo, K. Distribution Characteristics and Main Influencing Factors of Selenium in Surface Soil of Natural Selenium-Rich Area: A Case Study in Langao County, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Luo, D.; Ma, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Tian, X.; Nie, Y. Different Effects of Selenium Speciation on Selenium Absorption, Selenium Transformation and Cadmium Antagonism in Garlic. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. Food-Chain Selenium and Human Health: Emphasis on Intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cui, X.; Liang, Q.; Hu, W.; Huang, B. Characteristics and influencing factors of selenium content in soil and crops in a typical selenium-rich black soil area of Northeast China: A case study of Hailun City. Soils 2024, 56, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Kong, C. Effects of Topography and Soil Properties on Soil Selenium Distribution and Bioavailability (Phosphate Extraction): A Case Study in Yongjia County, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Guan, Q.; Kong, L.; Yang, R.; Wang, W.; Jin, Y.; Liu, X.; Qu, J. Overlooked Mechanism of Pb Immobilization on Montmorillonite Mediated by Dissolved Organic Matter in Manure Compost. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, B.; Xu, K.; Zheng, D.; Tian, J. Distribution of Se in the Rocks, Soil, Water and Crops in Enshi County, China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 122, 104707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Wilhelmy, M.; Klosterhuber, R.; Cocuzza, E.; Geitner, C.; Katzensteiner, K. A System for Classifying Subsolum Geological Substrates as a Basis for Describing Soil Formation. Catena 2021, 198, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.J. The Importance of Parent Material in Soil Classification: A Review in a Historical Context. Catena 2019, 182, 104131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Filippelli, G.M.; Ji, J.; Ji, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, T.; Wu, T.; Zhuo, X.; et al. Distribution and Secondary Enrichment of Heavy Metal Elements in Karstic Soils with High Geochemical Background in Guangxi, China. Chem. Geol. 2021, 567, 120081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunli, L.; Lirong, X.; Jian’an, T.; Douhu, W.; Lianhua, X. Selenium Source in the Selenosis Area of the Daba Region, South Qinling Mountain, China. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yu, Y.-J.; Sun, J.-E.; Zhang, J.-B.; Cai, Z.-C.; Guo, G.-X.; Zhong, W.-H. Parent Materials Have Stronger Effects than Land Use Types on Microbial Biomass, Activity and Diversity in Red Soil in Subtropical China. Pedobiologia 2015, 58, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, N.; Askin, T. Effects of Parent Material and Land Use on Soil Erodibility. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2003, 166, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.-L.; He, T.-B.; Liu, C.-Q.; Lu, X.-H. Effects of Land Use and Parent Materials on Trace Elements Accumulation in Topsoil. J. Environ. Qual. 2013, 42, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Quang, T.D.; Tran, T.A.T.; Zhou, F.; Yang, W.; Wang, M.; Song, W.; Liang, D. Effect of Selenium-Enriched Organic Material Amendment on Selenium Fraction Transformation and Bioavailability in Soil. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Lu, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, H.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Parent Material Modulates Land Use Effects on Soil Selenium Bioavailability in a Selenium-Enriched Region of Southwest China. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Niyogi, D.; Ojima, D. Changes in Land Use and Water Use and Their Consequences on Climate, Including Biogeochemical Cycles Preface. Glob. Planet. Change 2009, 67, IV. [Google Scholar]
- Cherubin, M.R.; Franco, A.L.C.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Karlen, D.L.; Pavinato, P.S.; Rodrigues, M.; Davies, C.A.; Cerri, C.C. Phosphorus Pools Responses to Land-Use Change for Sugarcane Expansion in Weathered Brazilian Soils. Geoderma 2016, 265, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potthast, K.; Hamer, U.; Makeschin, F. Land-Use Change in a Tropical Mountain Rainforest Region of Southern Ecuador Affects Soil Microorganisms and Nutrient Cycling. Biogeochemistry 2012, 111, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelov, G.; Anguelova, I. Assessment of Land-Use Effect on Trace Elements Concentrations in Soil Solution from Ultisols in North Florida. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 130, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Raknuzzaman, M. Trace Elements in Different Land Use Soils of Bangladesh and Potential Ecological Risk. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plak, A.; Bartminski, P. The Impact of Land Use on the Organic and Inorganic Selenium Content in Soils Developed from Loess. J. Elem. 2017, 22, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, J.; Mizuhara, S.; Yamada, H. Soluble Selenium Content of Agricultural Soils in Japan and Its Determining Factors with Reference to Soil Type, Land Use and Region. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2015, 61, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, B.; Hong, W.; Shen, X.; Han, Y. Characteristics of selenium content in arable land and study on selenium-rich crops in Dejiang County, Guizhou Province. Guizhou Geol. 2020, 37, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, W.; Mang, S.; Zhang, Q. Investigation and distribution characteristics of selenium-rich arable land in the agricultural demonstration zone of Libo County, Guizhou Province. West. Prospect. Eng. 2022, 34, 182–185+190. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Luo, Y.; Pu, Q.; Linghu, D.; Song, X. Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of selenium in arable soil in Zhenyuan County, Guizhou Province. Geoscience 2021, 35, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Luo, W.; Wu, G.; Xu, L.; Gao, J.; Kong, P.; Bi, X.; Cheng, Z. Spatial distribution of Se in soils from different land use types and its influencing factors within the Yanghe Watershed, China. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2015, 36, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.A.; Zhu, W.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Li, R.B.; Hou, S.F.; Wang, D.C.; Yang, L.S. Selenium in Soil and Endemic Diseases in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 284, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolu, J.; Thiry, Y.; Bueno, M.; Jolivet, C.; Potin-Gautier, M.; Le Hecho, I. Distribution and Speciation of Ambient Selenium in Contrasted Soils, from Mineral to Organic Rich. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, K.; Zhou, S.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Kong, J.; Shao, T.; Tao, X. Concentrations and Characteristics of Selenium in Soil Samples from Dashan Region, a Selenium-Enriched Area in China. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2015, 61, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Xiong, X.; Bu, J.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, J. Form, Bioavailability, and Influencing Factors of Soil Selenium in Subtropical Karst Regions of Southwest China. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L. Interference sources and elimination methods in the determination of selenium in soils and fluvial sediments by atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Rock Miner. Anal. 2019, 38, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BEVEN, K.J.; KIRKBY, M.J. A Physically Based, Variable Contributing Area Model of Basin Hydrology / Un Modèle à Base Physique de Zone d’appel Variable de l’hydrologie Du Bassin Versant. Hydrol. Sci. Bull. 1979, 24, 43–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.; Burch, G.; Mackenzie, D. Topographic Effects on the Distribution of Surface Soil-Water and the Location of Ephemeral Gullies. Trans. ASAE 1988, 31, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenson, S.; Domingue, J. Extracting Topographic Structure from Digital Elevation Data for Geographic Information-System Analysis. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1988, 54, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, S. Terrain Analysis: Principles and Applications. Environ. Plan. B-Plan. Des. 2002, 29, 152–153. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, I.; Grayson, R.; Ladson, A. Digital Terrain Modeling—A Review of Hydrological, Geomorphological, and Biological Applications. Hydrol. Process. 1991, 5, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordyce, F. Selenium Geochemistry and Health. Ambio 2007, 36, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Pan, B.; Han, J. A discussion on the basic types of terrestrial landforms in China and their classification criteria. Quat. Res. 2008, 28, 535–543. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, T.; Hou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in farmland soils of Hainan Island. Geoscience 2012, 26, 837–849. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Kamada, A.; Usuki, M.; Yanai, J. Total Selenium Content of Agricultural Soils in Japan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2009, 55, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G. Characteristics and genesis of selenium-rich cultivated soils in the Camellia oleifera demonstration zone of Yuping, Guizhou Province. Acta Geol. Sichuan 2022, 42, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, Y.; Yin, Q. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in surface cultivated soils in Jianhe County, Guizhou Province. Inn. Mong. Coal Econ. 2022, 14, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, K.S.; Dhillon, S.K. Adsorption-Desorption Reactions of Selenium in Some Soils of India. Geoderma 1999, 93, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.R.; Griffin, R.A. Effect of pH on Adsorption of Arsenic and Selenium from Landfill Leachate by Clay Minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1977, 41, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.; Domsch, K. The Metabolic Quotient for Co2 (Qco2) as a Specific Activity Parameter to Assess the Effects of Environmental-Conditions, Such as Ph, on the Microbial Biomass of Forest Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1993, 25, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Nilsson, S.I. Influence of pH and Temperature on Microbial Activity, Substrate Availability of Soil-Solution Bacteria and Leaching of Dissolved Organic Carbon in a Mor Humus. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerla, P.J.; Sharif, M.U.; Korom, S.F. Geochemical Processes Controlling the Spatial Distribution of Selenium in Soil and Water, West Central South Dakota, USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chang, S.X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X. Topography-Soil Relationships in a Hilly Evergreen Broadleaf Forest in Subtropical China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.-S.; Zhang, W.-C.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.-B. The Controlling Factors of Soil Selenium Content in a Selenium-Deficient Area in Southwest China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlet, L.; Scheinost, A.C.; Tournassat, C.; Greneche, J.M.; Géhin, A.; Fernández-Martı´nez, A.; Coudert, S.; Tisserand, D.; Brendle, J. Electron Transfer at the Mineral/Water Interface: Selenium Reduction by Ferrous Iron Sorbed on Clay. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2007, 71, 5731–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppin, F.; Chabroullet, C.; Martin-Garin, A. Selenite Interactions with Some Particulate Organic and Mineral Fractions Isolated from a Natural Grassland Soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 60, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, N.; Marmier, N.; Lomenech, C.; Giffaut, E.; Ehrhardt, J.-J. Competition between Selenium (IV) and Silicic Acid on the Hematite Surface. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tullo, P.; Pannier, F.; Thiry, Y.; Le Hecho, I.; Bueno, M. Field Study of Time-Dependent Selenium Partitioning in Soils Using Isotopically Enriched Stable Selenite Tracer. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floor, G.H.; Calabrese, S.; Roman-Ross, G.; D’Alessandro, W.; Aiuppa, A. Selenium Mobilization in Soils Due to Volcanic Derived Acid Rain: An Example from Mt Etna Volcano, Sicily. Chem. Geol. 2011, 289, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, L.H.E.; Vriens, B.; Jones, G.D.; Schneider, L.S.; Pilon-Smits, E.; Banuelos, G.S. Selenium Cycling Across Soil-Plant-Atmosphere Interfaces: A Critical Review. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4199–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, C.; Maes, A.; Vancluysen, J. The Interaction of Dissolved Boom Clay and Gorleben Humic Substances with Selenium Oxyanions (Selenite and Selenate). Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Eggen, O.A.; Jensen, H.; Stampolidis, A.; Bjerkgard, T.; Sandstad, J.S. Geochemistry of Soil in Relation to Air-Borne Geophysical Data and Bedrock Geology in Hattfjelldal, Northern Norway. Nor. J. Geol. 2015, 95, 315–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vestin, J.L.K.; Nambu, K.; van Hees, P.A.W.; Bylund, D.; Lundstrom, U.S. The Influence of Alkaline and Non-Alkaline Parent Material on Soil Chemistry. Geoderma 2006, 135, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, G.; Zhang, M.; Zhan, L.; Liang, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Yong, T.; Tang, Z. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils of southern Jiangxi: A case study of the Qingtang–Meijiao area. Geoscience 2018, 32, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils of the low- to mid-mountain areas in Danzhai County. South. Land Resour. 2020, 2, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.X.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, X.T. Character and Trend of Soil Erosion in Black Soil North-Eastern China. Soil Water Conserv. China 2008, 12, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).