Estrone Degradation in Soil as Affected by Three Soil Groups
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Estrone Treatment
2.2.2. Pot Experiment
2.3. Analytical Procedures
2.3.1. Enzymatic Activity
2.3.2. LC/MS Analysis
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
| Soils | Cambisol | Fluvisol | Chernozem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | 49°33′15″ N | 50°09′50″ N | 50°07′40″ N |
| Longitude | 15°21′02″ E | 15°09′24″ E | 14°22′33″ E |
| Site | Humpolec | Patek | Suchdol |
| texture | sandy loam | silty clay | loamy |
| pH | 6.5 | 7.5 | 7.0 |
| WHC 1 | 14.77 | 13.71 | 14.78 |
| C (mg·kg−1) | 20,512 | 76,509 | 28,304 |
| N (mg·kg−1) | 2055 | 2882 | 2333 |
| C/N ratio | 10 | 26 | 12 |
| C/H ratio | 2 | 12 | 4 |
| K (mg·kg−1) 2 | 140 | 390 | 340 |
| P (mg·kg−1) 2 | 60 | 30 | 40 |
| Ca (mg·kg−1) 2 | 1540 | 26,290 | 6480 |
| Mg (mg·kg−1) 2 | 160 | 370 | 220 |
| Mn (mg·kg−1) 2 | 80 | 30 | 160 |
| S (mg·kg−1) 2 | 60 | 150 | 80 |
| Zn (mg·kg−1) 2 | 2.88 | 4.02 | 5.66 |
| Fe (mg·kg−1) 2 | 26 | 28 | 6 |
| Cu (mg·kg−1) 2 | 2.68 | 0.91 | 3.81 |
| Cr (mg·kg−1) 2 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
3.1. Soil Characteristics
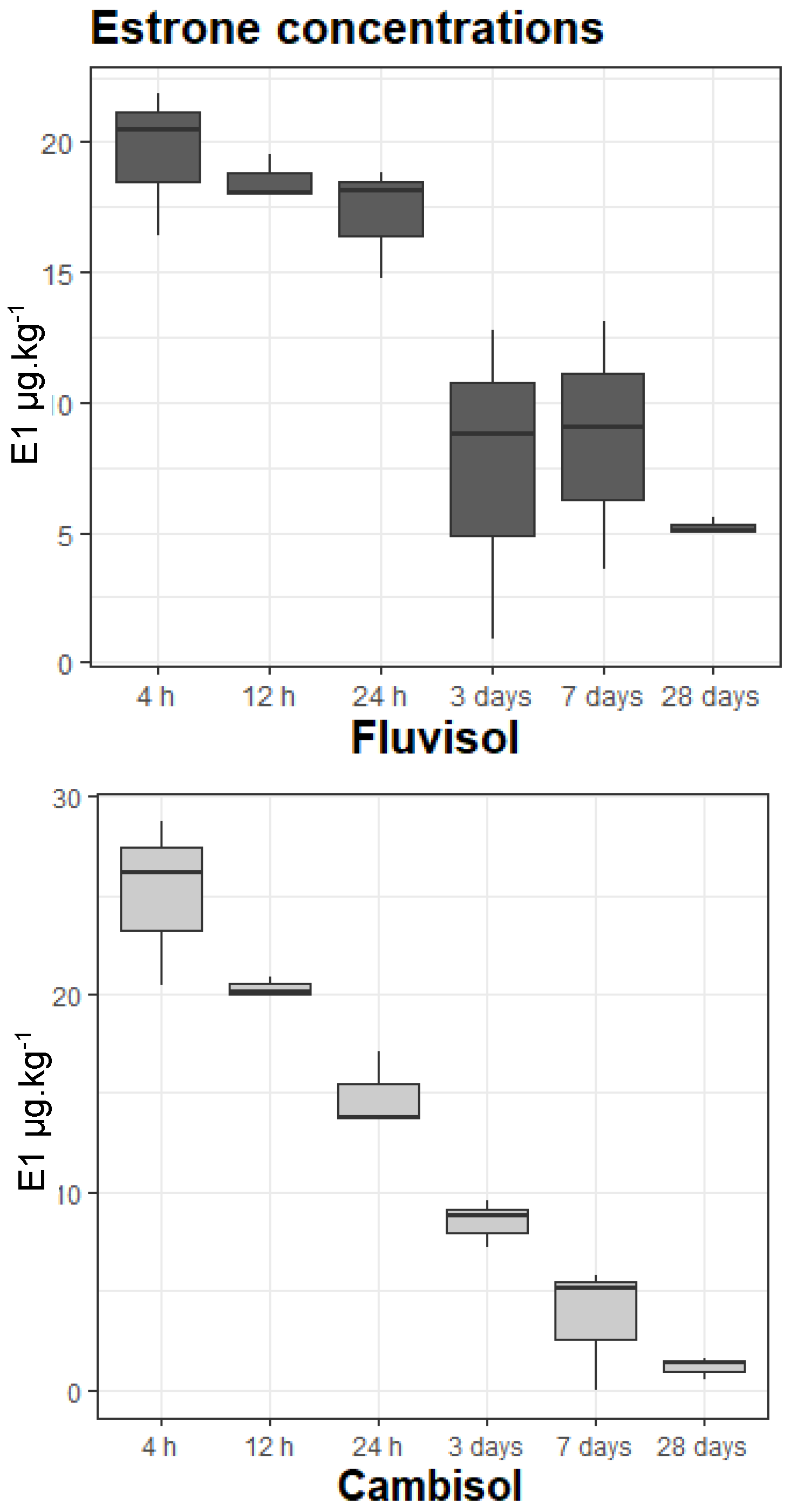
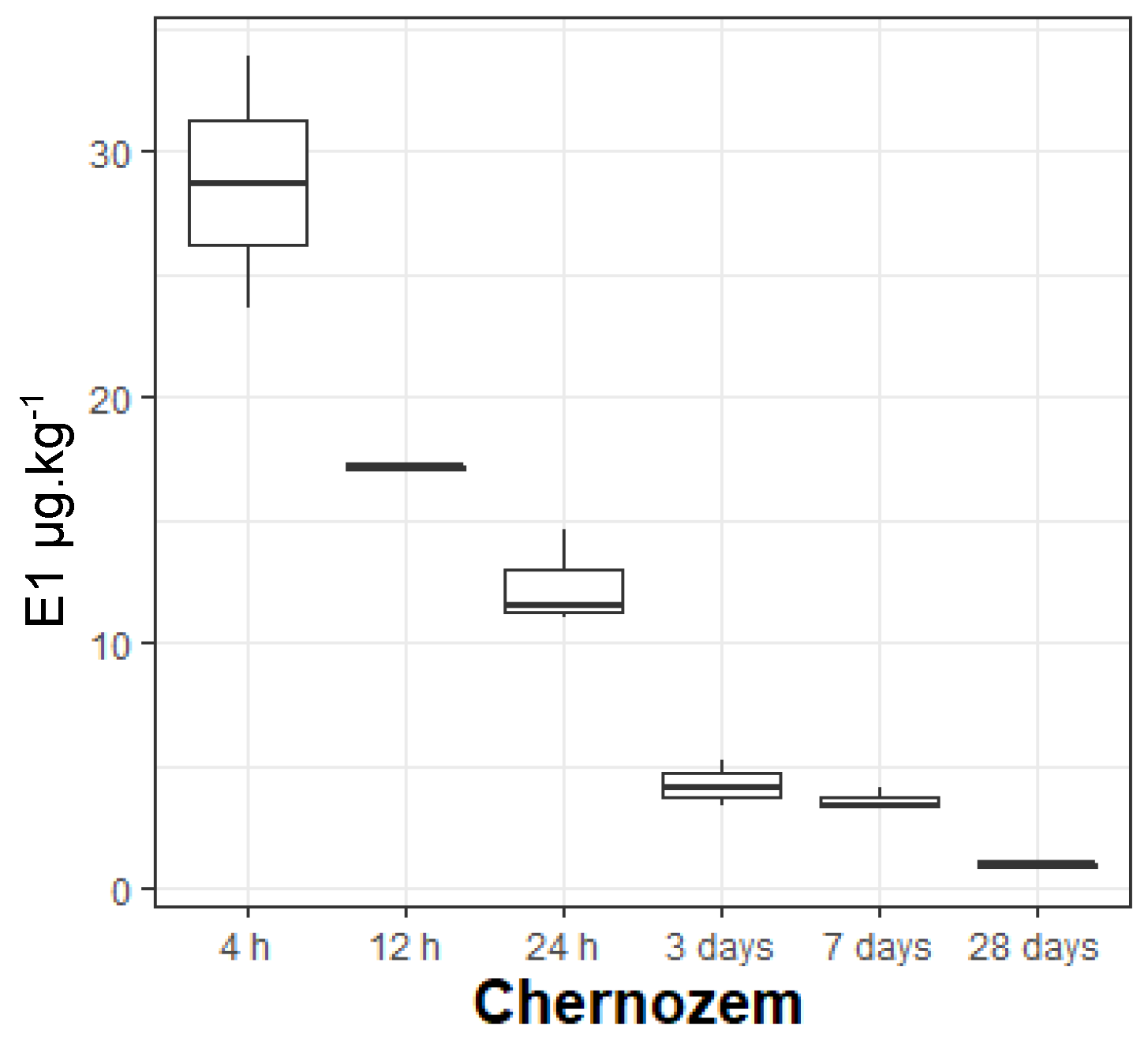
3.2. Estrone Concentrations
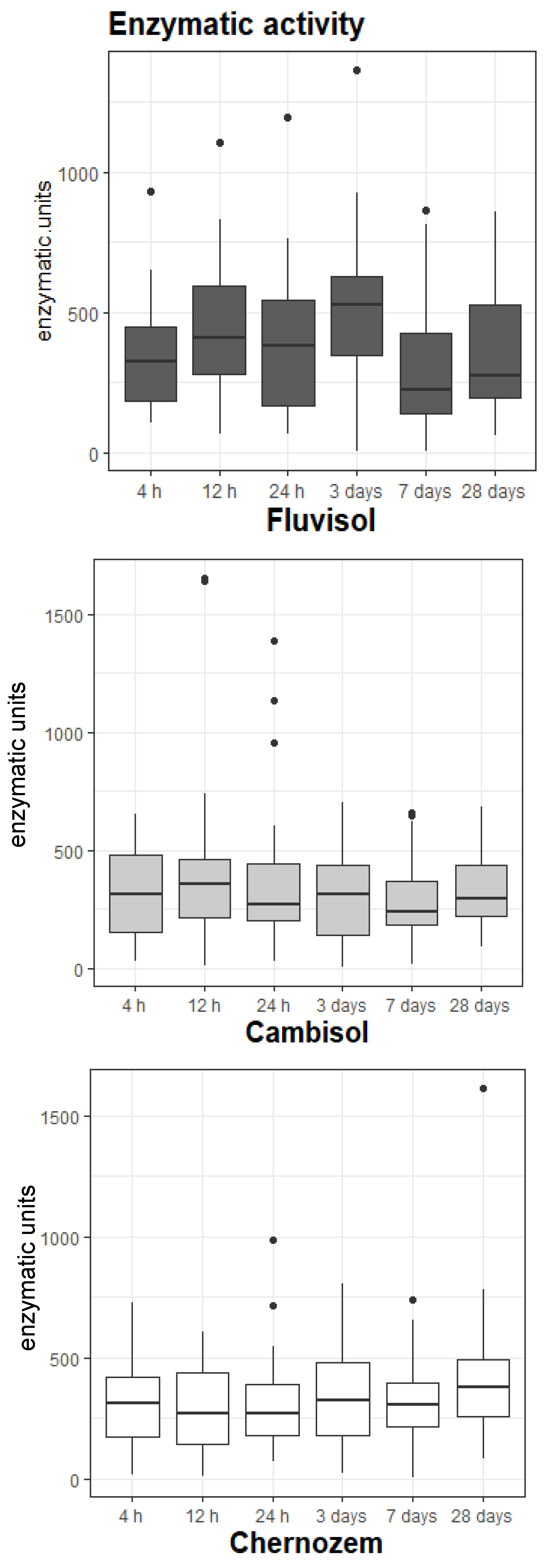
3.3. Enzymatic Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdellah, Y.A.Y.; Zang, H.; Li, C. Steroidal estrogens during composting of animal manure: Persistence, degradation, and fate, a Review. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2020, 231, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Snow, D.D.; Damon-Powell, T.; Miesbach, D. Occurrence of steroid hormones and antibiotics in shallow groundwater impacted by livestock waste control facilities. J. Cont. Hydrol. 2011, 123, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, H.E.; Sassman, S.A.; Jenkinson, B.; Lee, L.S.; Jafvert, C.T. Comparison of export dynamics of nutrients and animal-borne estrogens from a tile-drained Midwestern agroecosystem. Water Res. 2015, 72, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barel-Cohen, K.; Shore, L.S.; Shemesh, M.; Wenzel, A.; Mueller, J.; Kronfeld-Schor, N. Monitoring of natural and synthetic hormones in a polluted river. J. Environ. Manag. 2006, 78, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutaswiriya, N.; Homklin, S.; Kreetachat, T.; Vaithanomsat, P.; Kreetachat, N. Monitoring estrogen and androgen residues from livestock farms in Phayao Lake, Thailand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Inamdar, S.; Tso, J.; Aga, D.S.; Sims, J.T. Free and conjugated estrogen exports in surface-runoff from poultry litter–amended soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.G.; Kookana, R.S.; Kumar, A.; Mortimer, M. Occurrence and implications of estrogens and xenoestrogens in sewage effluents and receiving waters from South East Queensland. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5147–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciślak, M.; Kruszelnicka, I.; Zembrzuska, J.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D. Estrogen pollution of the European aquatic environment: A critical review. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, Y.F.; Praveena, S.M. Sources, mechanisms, and fate of steroid estrogens in wastewater treatment plants: A mini review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdulska, A.; Kowalik, R. Estrogen removal from wastewater. Struct. Environ. 2020, 12, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mina, O.; Gall, H.E.; Elliott, H.A.; Watson, J.E.; Mashtare, M.L.; Langkilde, T.; Harper, J.P.; Boyer, E.W. Estrogen occurrence and persistence in vernal pools impacted by wastewater irrigation practices. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combalbert, S.; Hernandez-Raquet, G. Occurrence, fate, and biodegradation of estrogens in sewage and manure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpe, B.; Marschner, B. Long-term sewage sludge application and wastewater irrigation on the mineralization and sorption of 17β-estradiol and testosterone in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 374, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Y.; Liang, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Shi, W.J.; Liu, S.S.; Hu, L.X.; Xie, L.; Ying, G.G. Swine farm wastewater discharge causes masculinization of western mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis). Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.D.; Jones, D.L. Biodegradation of estrone and 17 β-estradiol in grassland soils amended with animal wastes. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2803–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, I.E.; Morra, M.J. Environmental transport of endogenous dairy manure estrogens. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2017, 52, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yates, S.R. Degradation and metabolite formation of estrogen conjugates in an agricultural soil. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, H.; Kan, J.; Li, J.; Huang, T.; Xiong, G.; Hu, Z. A novel 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in Rhodococcus sp. P14 for transforming 17β-estradiol to estrone. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 276, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobling, S.; Reynolds, T.; White, R.; Parker, M.G.; Sumpter, J.P. A variety of environmentally persistent chemicals, including some phthalate plasticizers, are weakly estrogenic. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.A.H.; Lambert, J.G.D.; Vethaak, A.D.; Goos, H.J.T. Environmental pollution caused elevated concentrations of oestradiol and vitellogenin in the female flounder, Platichthys flesus (L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 1997, 39, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Louvado, A.; Esteves, V.I.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, Â. Biodegradation of 17β-estradiol by bacteria isolated from deep sea sediments in aerobic and anaerobic media. J. Hazard. Mat. 2017, 323, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.P.; Roh, H.; Chu, K.H. 17β-Estradiol-Degrading Bacteria Isolated from Activated Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratush, A.; Yang, Q.; Peng, T.; Huang, T.; Hu, Z. Identification of non-accumulating intermediate compounds during estrone (E1) metabolism by a newly isolated microbial strain BH2-1 from mangrove sediments of the South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5097–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, S.; Yamamura, A.; Tanaka, S.; Shi, J.; Nishikawa, M.; Nakashimada, Y.; Hosomi, M. Pathway of 17β-estradiol degradation by Nitrosomonas europaea and reduction in 17β-estradiol-derived estrogenic activity. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2011, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Nandakumar, R.; Madayiputhiya, N.; Li, X. Proteomic Analysis of 17β-Estradiol Degradation by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5947–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Yu, C.P.; Lee, T.H.; Goh, K.S.; Chu, K.H.; Wang, P.H.; Ismail, W.; Shih, C.J.; Chiang, Y.R. Biochemical mechanisms and catabolic enzymes involved in bacterial estrogen degradation pathways. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Tao, S.; Xing, B. Sorption Mechanisms of Phenanthrene, Lindane, and Atrazine with Various Humic Acid Fractions from a Single Soil Sample. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xiao, B.; Huang, W.; Peng, P. Sorption of steroid estrogens to soils and sediments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2004, 23, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, E.; Farenhorst, A.; Zvomuya, F.; Gaultier, J.; Rank, N.; Goddard, T.; Sheedy, C. Sorption of four estrogens by surface soils from 41 cultivated fields in Alberta, Canada. Geoderma 2010, 155, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlich, A. Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: A modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 1984, 15, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashtare, M.L.; Green, D.A.; Lee, L.S. Biotransformation of 17α- and 17β-estradiol in aerobic soils. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Persistence and impact of steroidal estrogens on the environment and their laccase-assisted removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa, Y.; Yamaki, R.; Hirai, H.; Kawai, S.; Nishida, T. Removal of estrogenic activity of natural steroidal hormone estrone by ligninolytic enzymes from white rot fungi. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štursová, M.; Baldrian, P. Effects of soil properties and management on the activity of soil organic matter transforming enzymes and the quantification of soil-bound and free activity. Plant Soil. 2011, 338, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, F.X.M.; Šimůnek, J.; Lee, J.; Larsen, G.L.; Hakk, H. Sorption, mobility, and transformation of estrogenic hormones in natural soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, F.G.; Leeds-Harrison, P.B.; Brown, C.D.; van Beinum, W. Determination of time-dependent partition coefficients for several pesticides using diffusion theory. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Jung, C.; Han, J.; Her, N.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Son, A.; Yoon, Y. Sorptive removal of selected emerging contaminants using biochar in aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng.Chem. 2016, 36, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Cao, N.; Sun, D.; Yang, Y. The response of steroid estrogens bioavailability to various sorption mechanisms by soil organic matter extracted with sequential alkaline-extraction method from an agriculture soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Pardue, J.H.; Moe, W.M.; Kim, D.J. Effect of sorption and desorption-resistance on biodegradation of chlorobenzene in two wetland soils. J. Hazard. Mat. 2009, 161, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flogeac, K.; Guillon, E.; Aplincourt, M. Adsorption of several metal ions onto a model soil sample: Equilibrium and EPR studies. J. Coll. Interf. Sci. 2005, 286, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kommalapati, R.R.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Pardue, J.H.; Constant, W.D. Rate-Limited Desorption of Volatile Organic Compounds from Soils and Implications for the Remediation of a Louisiana Superfund Site. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2002, 75, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neale, P.A.; Escher, B.I.; Schäfer, A.I. Quantification of solute–solute interactions using negligible-depletion solid-phase microextraction: Measuring the affinity of estradiol to bulk organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2886–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, R.G. Comparison of the behavior of soluble organic and inorganic nutrients in forest soils. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2000, 138, 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, E.; Senesi, N. Fate of anthropogenic organic pollutants in soils with emphasis on adsorption/desorption processes of endocrine disruptor compounds. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drahorad, S.L.; Jehn, F.U.; Ellerbrock, R.H.; Siemens, J.; Felix-Henningsen, P. Soil organic matter content and its aliphatic character define the hydrophobicity of biocrusts in different successional stages. Ecohydrology 2020, 13, e2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán–Álvarez, J.C.; Prado, B.; Ferroud, A.; Juayerk, N.; Jiménez-Cisneros, B. Sorption, desorption and displacement of ibuprofen, estrone, and 17β estradiol in wastewater irrigated and rainfed agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Xing, B.; Liu, W.; Tao, S.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Dai, H.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y. Two-compartment sorption of phenanthrene on eight soils with various organic carbon contents. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2006, 41, 1333–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takigami, H.; Taniguchi, N.; Shimizu, Y. Sorption and desorption of 17β-estradiol to natural sediment. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, H.; Haapakangas, H.; van Beelen, P. Effects of antibiotics on soil microorganisms: Time and nutrients influence pollution-induced community tolerance. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Enzymatic Activity | |
|---|---|
| soils comparison | p-values |
| equality of variance ANOVA Post hoc pairwise comparison Fluvisol-Cambisol Fluvisol-Chernozem Cambisol-Chernozem | Brown–Forsythe test 0.00466543 Kruskal–Wallis 0.01272 Wilcoxon test with Bonferroni corrections 0.045 0.023 1.000 |
| Estrone | |
| soils comparison | p-values |
| soils, individually—0 to 28 days Fluvisol Cambisol Chernozem soils, together—equality of variance 0 and 28 days 0 days 28 days ANOVA 0 days 28 days Post hoc pairwise comparison 0 days Fluvisol-Cambisol Fluvisol-Chernozem Cambisol-Chernozem 28 days Fluvisol-Cambisol Fluvisol-Chernozem Cambisol-Chernozem | Friedman test 0.0262 0.0142 0.0121 Brown–Forsythe test 0.9438856 0.1035599 0.001856509 One-way ANOVA 0.0914 1.2 × 10−5 Tukey HSD 0.3101227 0.0804346 0.5635242 0.0000253 0.0000186 0.7627496 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumitriu, A.C.; Szakova, J.; Cemperova, S. Estrone Degradation in Soil as Affected by Three Soil Groups. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5703. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105703
Dumitriu AC, Szakova J, Cemperova S. Estrone Degradation in Soil as Affected by Three Soil Groups. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5703. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105703
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumitriu, Alexandra Cristina, Jirina Szakova, and Sara Cemperova. 2025. "Estrone Degradation in Soil as Affected by Three Soil Groups" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5703. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105703
APA StyleDumitriu, A. C., Szakova, J., & Cemperova, S. (2025). Estrone Degradation in Soil as Affected by Three Soil Groups. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5703. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105703






