Research on the Implementation Effect of Incentive Policies for Prefabricated Buildings Based on System Dynamics: A Chinese Empirical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on PBIP
2.2. The Application of SD in the Research of Policy Implementation Effect
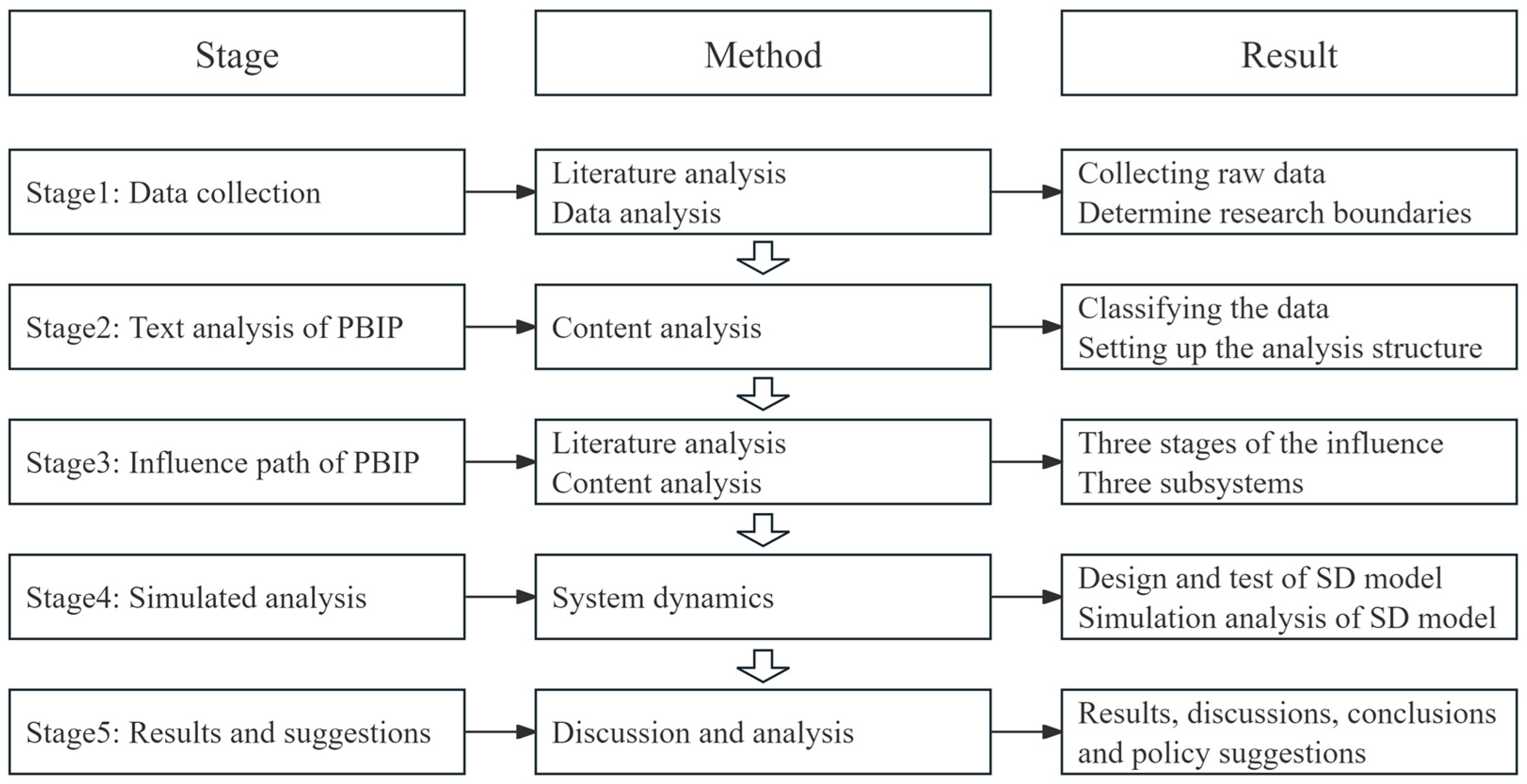
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Research Design
3.3. Combing and Induction of PBIP
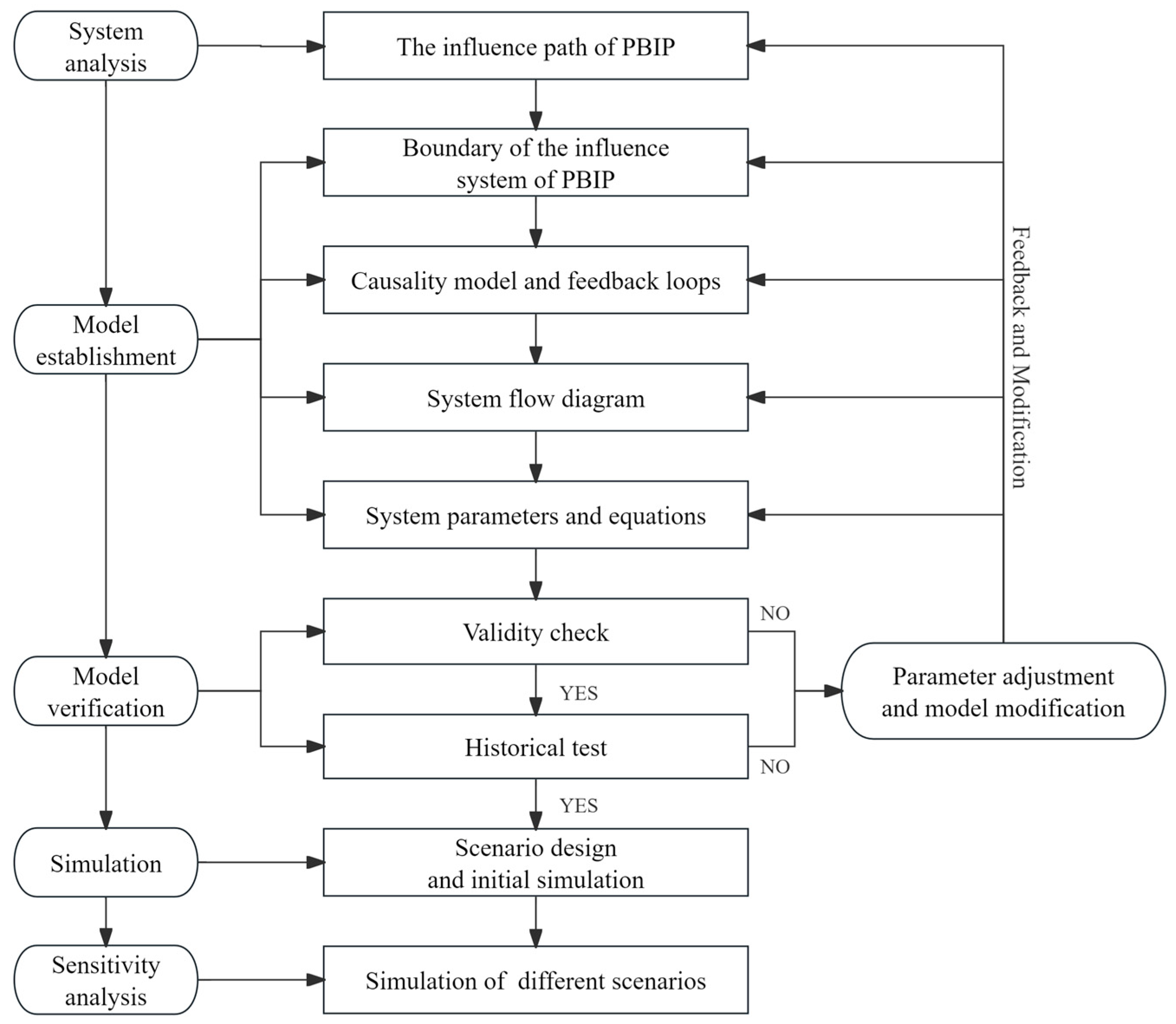
3.4. Model Analysis
3.4.1. Causality and Feedback Loop
3.4.2. Model Assumptions and System Flow Diagram
3.4.3. Equation Design and Parameter Interpretation
3.5. Model Checking
4. Results
4.1. Sensitivity Analysis
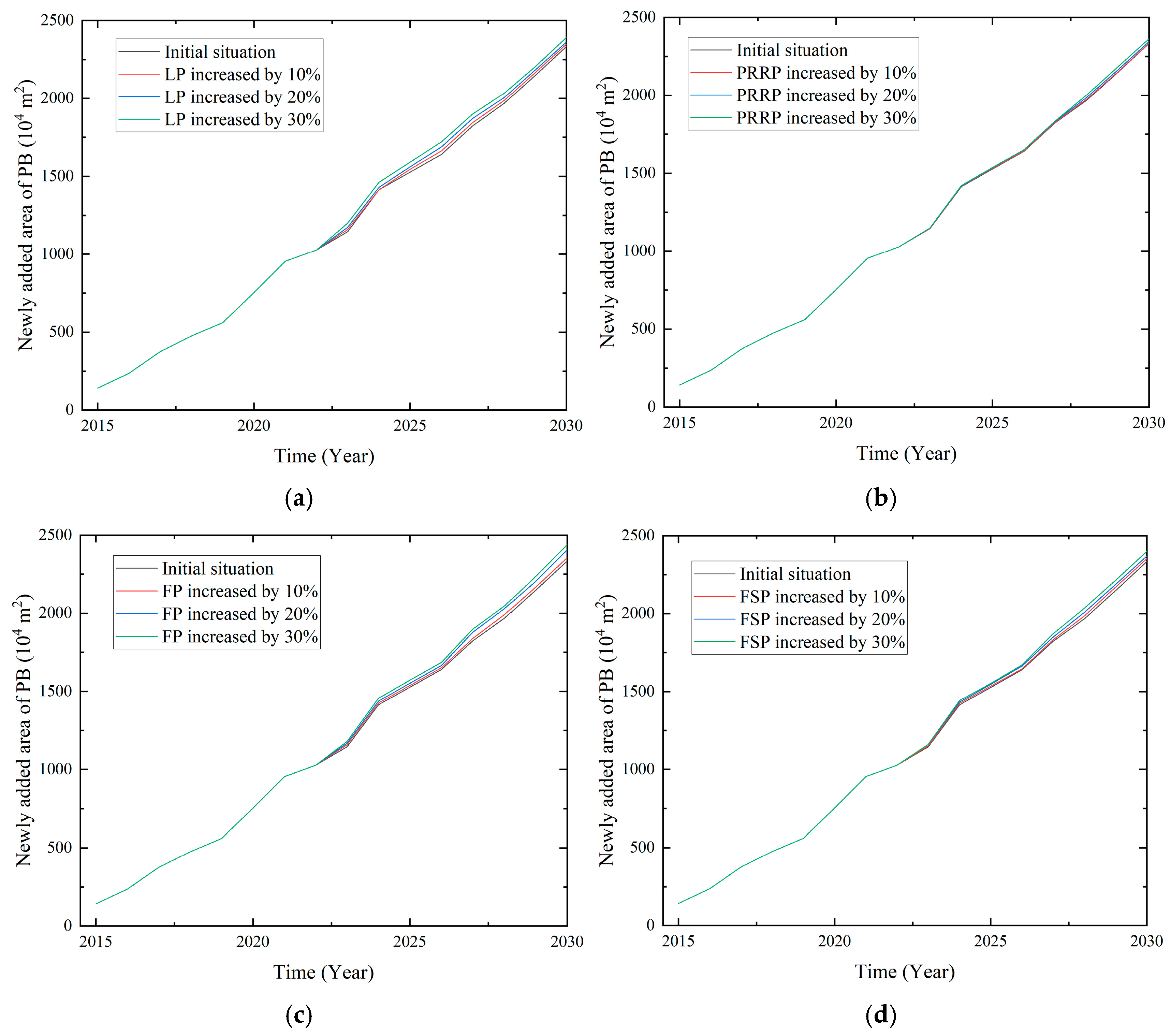
4.1.1. The Newly Added Area of PBs
4.1.2. The Supply of PB
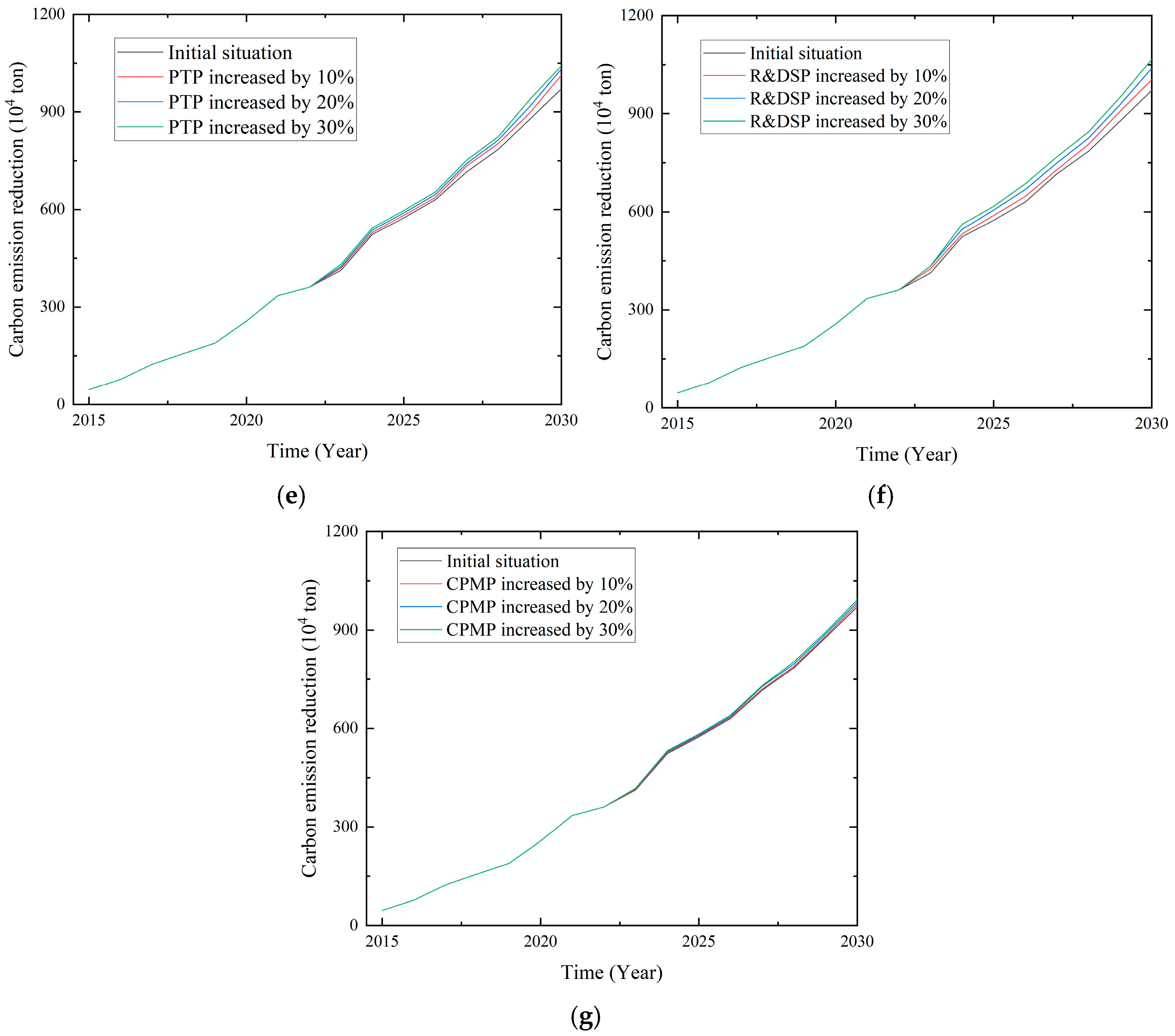
4.1.3. Carbon Emission Reduction
4.1.4. Statistical Analysis of the Simulation Results
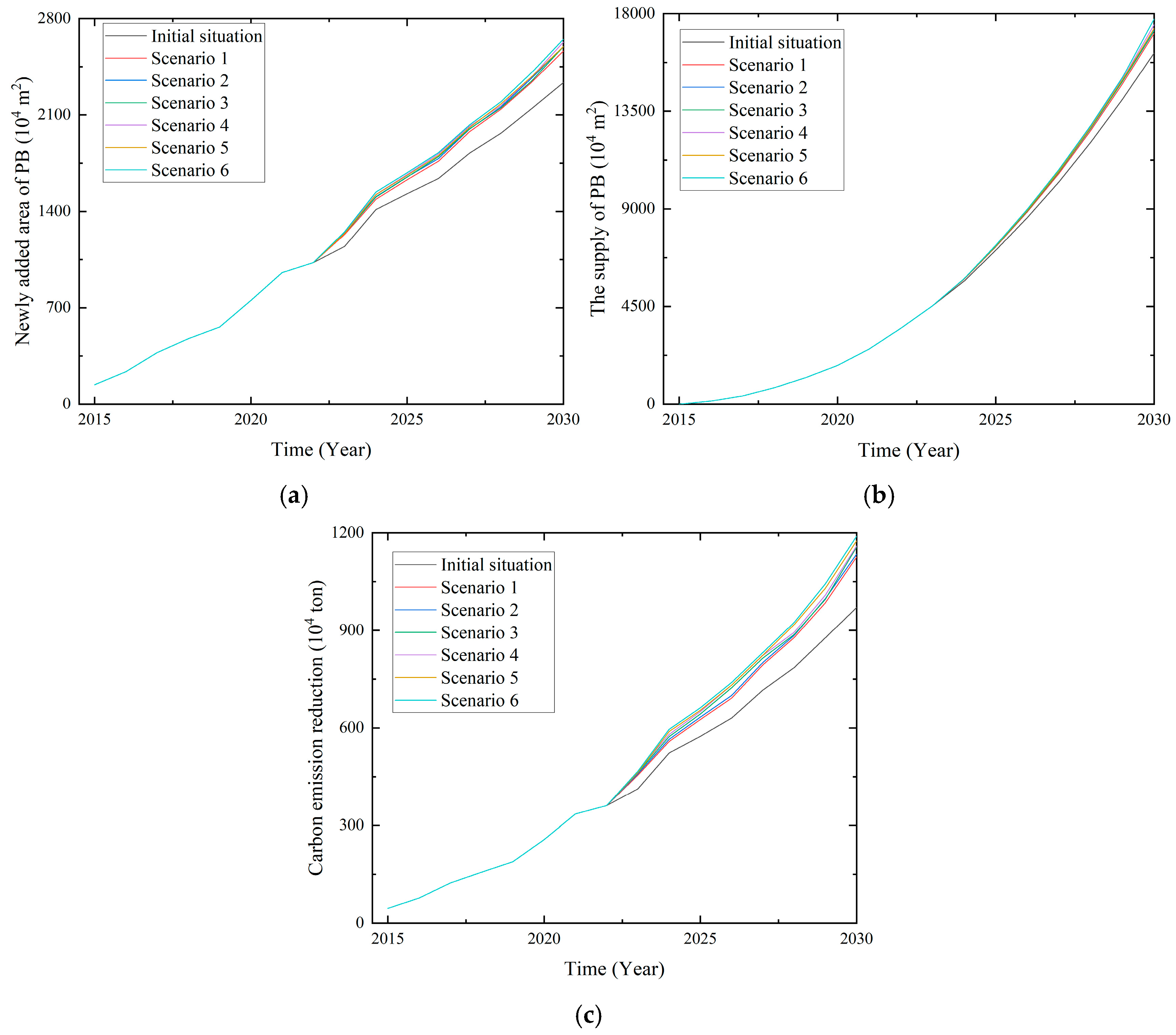
4.2. Comprehensive Simulation Analysis
4.2.1. Comprehensive Simulation Scenario Setting
4.2.2. Analysis of Comprehensive Simulation Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
6.1. Implications
6.2. Limitations and Further Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PBs | Prefabricated buildings |
| PBIPs | Incentive policies for prefabricated buildings |
| LP | Land policy |
| PRRP | Plot ratio reward policy |
| FP | Fund policy |
| FSP | Financial support policy |
| PTP | Preferential tax policy |
| R&DSP | Research and development support policy |
| CPMP | Construction process management policy |
Appendix A
| Types of Variables | Number | Variables | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| State variable | 1 | The supply of PBs | 104 m2 |
| 2 | The demand for PBs | ||
| Rate variable | 3 | The newly added area of PBs | 104 m2 |
| 4 | Increased market demand | ||
| Auxiliary variable | 5 | Land transfer price | Yuan |
| 6 | Land transfer area | 104 m2 | |
| 7 | Newly added total building area | 104 m2 | |
| 8 | Output value of PBs | 108 Yuan | |
| 9 | Carbon emission reduction | 104 tons | |
| 10 | GDP | 108 Yuan | |
| 11 | Per capita GDP | 104 Yuan | |
| 12 | Supply and demand ratio | % | |
| 13 | The selling price of PBs | Yuan | |
| 14 | Permanent population | 104 persons | |
| 15 | Per capita disposable income | Yuan | |
| 16 | Technical level growth rate | % | |
| 17 | The benefits of PBs | Yuan | |
| 18 | LP | Dmnl | |
| 19 | PRRP | ||
| 20 | FP | ||
| 21 | FSP | ||
| 22 | PTP | ||
| 23 | R&DSP | ||
| 24 | CPMP | ||
| 25 | Supply and demand ratio influence factors | ||
| 26 | The quality of PBs | ||
| 27 | Consumers’ purchase intention | ||
| 28 | Increase in the purchase of PBs | ||
| 29 | The influence coefficient of FP on cost savings for construction enterprises | ||
| 30 | The influence coefficient of CPMP on cost savings for construction enterprises | ||
| 31 | Cost savings for construction enterprise | ||
| 32 | The influence coefficient of LP on cost savings for development enterprises | ||
| 33 | The influence coefficient of LP on degree of support for the development of PBs | ||
| 34 | The influence coefficient of FP on cost savings for development enterprises | ||
| 35 | The influence coefficient of PRRP on cost savings for development enterprises | ||
| 36 | Cost savings for development enterprises | ||
| 37 | Cost incentives for the development of PBs | ||
| 38 | The willingness of development enterprises to build PBs | ||
| 39 | The influence coefficient of R&DSP on the technical level of PBs | ||
| 40 | The influence coefficient of PTP on the technical level of PBs | ||
| 41 | The influence coefficient of PTP on cost savings for prefabricated component supplier | ||
| 42 | The influence coefficient of FSP on cost savings for development enterprises | ||
| 43 | The influence coefficient of the quality of PBs on consumers’ purchase intention | ||
| 44 | The influence coefficient of FSP on consumers’ purchase intention | ||
| 45 | The influence coefficient of benefits on the development of PBs | ||
| 46 | The influence coefficient of FSP on degree of support for the development of PBs | ||
| 47 | The influence coefficient of CPMP on degree of support for the development of PBs | ||
| 48 | The influence coefficient of CPMP on cost savings for prefabricated component supplier | ||
| 49 | Degree of support for the development of PBs | ||
| 50 | Cost savings for prefabricated component supplier |
| Variables | Equations |
|---|---|
| The demand for PBs | INTEG (Increased market demand, 0), the initial value is 0. |
| Newly added area of PBs | Newly added total building area × The willingness of development enterprises to build PBs |
| Increased market demand | Consumers’ purchase intention × (0.057 × The selling price of PBs + 0.49 × Per capita disposable income + 0.56 × Permanent population) × 0.2 + Carbon emission reduction × 0.8 |
| Land transfer area | WITH LOOKUP{[(2015,0)-(2030,9110)],(2015,425),(2016,396),(2017,410),(2018,530),(2019,535),(2020,704),(2021,843),(2022,955),(2023,1020),(2024,1260),(2025,1310),(2026,1352),(2027,1450),(2028,1494),(2029,1508),(2030,1521)} |
| Newly added total building area | 450.578 + Land transfer price × 0.139 + Land transfer area × 1.023 |
| Output value of PBs | Newly added area of PBs × The selling price of PBs/10000 |
| Carbon emission reduction | 0.26 × (1 + 0.8 × The technical level of PBs) × Newly added area of PBs |
| GDP | (Output value of PBs × 0.804) + 4879.48 |
| Per capita GDP | GDP/Permanent population |
| Supply and demand ratio | The supply of PBs/The demand for PBs |
| Supply and demand ratio influence factors | 1.55 × Supply and demand ratio |
| The selling price of PBs | Supply and demand ratio influence factors × 10,000 |
| Permanent population | WITH LOOKUP{[(2015,800)-(2030,900)],(2015,829.1),(2016,829.2),(2017,829.4),(2018,831.6),(2019,832.2),(2020,832.8),(2021,833.7),(2022,834.6),(2023,835.5),(2024,836.6),(2025,837.2),(2026,838.1),(2027,838.9),(2028,839.8),(2029,840.6),(2030,841.5)} |
| Per capita disposable income | Per capita GDP × 0.615 |
| The quality of PBs | The technical level of PBs × 0.85 |
| Consumers’ purchase intention | The influence coefficient of FSP on consumers’ purchase intention × 0.5 + The influence coefficient of the quality of PBs on consumers’ purchase intention × 0.5 |
| Increase in the purchase of PBs | Consumers’ purchase intention × The supply of PBs |
| The benefits of PBs | Increase in the purchase of PBs × The selling price of PBs |
| The influence coefficient of FP on cost savings for construction enterprises | IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.1,0.09, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.15,0.13, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.2,0.156, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.25, 0.178, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.3,0.212, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.35,0.2416, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.4,0.26, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.45,0.29, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.5,0.32, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.55,0.36, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.6,0.395, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.65,0.425, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.7,0.458, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.75,0.534, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.8,0.574, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.85, 0.62, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.88,0.66, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.9,0.69, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.95, 0.72, IF THEN ELSE(FP ≤ 0.98, 0.75,0.79)))))))))))))))))))) |
| Cost savings for development enterprises | 0.4 × The influence coefficient of FP on cost savings for development enterprises + 0.2 × The influence coefficient of FSP on cost savings for development enterprises + 0.3 × The influence coefficient of LP on cost savings for development enterprises + 0.1 × The influence coefficient of PRRP on cost savings for development enterprises |
| Cost incentives for the development of PBs | 0.2 × Cost savings for construction enterprise + 0.2 × Cost savings for prefabricated component supplier + 0.6 × Cost savings for development enterprises |
| Cost savings for prefabricated component supplier | The influence coefficient of CPMP on cost savings for prefabricated component supplier × 0.4 + The influence coefficient of PTP on cost savings for prefabricated component supplier × 0.6 |
References
- Huang, L.Z.; Krigsvoll, G.; Johansen, F.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhang, X.L. Carbon emission of global construction sector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1906–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebaibi, N.; Boutouil, M. Reducing energy consumption of prefabricated building elements and lowering the environmental impact of concrete. Eng. Struct. 2020, 213, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Gao, Y.; Meng, X.X.; Liu, X.L.; Feng, Y.C. Assessing the air pollution abatement effect of prefabricated buildings in China. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Abidi, K.M.A.; Ofori, G.; Zakaria, S.A.S.; Aziz, A.R.A. Using Prefabricated Building to Address Housing Needs in Libya: A Study based on Local Expert Perspectives. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 8289–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.Q.; Wei, Y.H.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.T.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, L.P.; Huang, J.L.; Kang, X.F. Evolutionary Game Simulation on Government Incentive Strategies of Prefabricated Construction: A System Dynamics Approach. Complexity 2020, 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Yan, X.Y.; Piroozfar, P. An overall review of research on prefabricated construction supply chain management. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 5160–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Dong, X.C.; Jiang, Q.Z.; Dong, K.Y.; Liu, G.X. What is the probability of achieving the carbon dioxide emission targets of the Paris Agreement? Evidence from the top ten emitters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Xue, X.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Xue, W.R.; Tan, Y.T. A systematic overview of prefabricated construction policies in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.D.; Guo, C.B.; Li, L.H. Evaluating the Effect of Prefabricated Building Incentive Policies Using Structural Equation Modeling: A Chinese Empirical Study. Buildings 2024, 14, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.K.; Xue, H.; Han, R.; Zhang, S.J.; Sun, Z.; Song, Y.R. Policies of Improving Developers? Willingness to Implement Prefabricated Building: A Case Study from China. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2023, 29, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.; Froese, T.M. Analysis of Costs and Benefits of Panelized and Modular Prefabricated Homes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Design, Engineering and Construction (ICSDEC), Tempe, AZ, USA, 18–20 May 2016; pp. 1291–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Pujadas-Gispert, E.; Sanjuan-Delmás, D.; Josa, A. Environmental analysis of building shallow foundations: The influence of prefabrication, typology, and structural design codes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Y.; Qin, Y.J.; Fang, S.Z. Impacts of Consumers and Real Estate Enterprises on the Implementation of Prefabrication in Residential Buildings: The Moderating Role of Incentive Policies. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewerin, S.; Beland, D.; Cashore, B. Designing policy for the long term: Agency, policy feedback and policy change. Policy Sci. 2020, 53, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.P.; Luo, L.R.; Wu, Z.Z.; Fei, J.B.; Antwi-Afari, M.F.; Yu, T. An Investigation of the Effectiveness of Prefabrication Incentive Policies in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, G.C.; Vicente, R.; Azenha, M.; Ferreira, T.M. A systematic review of Prefabricated Enclosure Wall Panel Systems: Focus on technology driven for performance requirements. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, R. Industrialized Housing Construction—The UK Experience. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Building Technology (ABT 2002), Hong Kong, China, 4–6 December 2002; pp. 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.N.; Xue, X.L.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.W. Mapping the dynamics of China’s prefabricated building policies from 1956 to 2019: A bibliometric analysis. Build. Res. Inf. 2021, 49, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zayed, T.; Niu, Y.M. Comparative analysis of modular construction practices in mainland China, Hong Kong and Singapore. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.L.; Xie, K.X.; Liu, H.Q.; Rameezdeen, R.; Wen, T. A bibliometric and content analysis of policy instruments on facilitating the development of prefabricated construction in China. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 3976–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Xu, X.B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.P.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, J. Impact of Consumer Preference on the Decision-Making of Prefabricated Building Developers. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2022, 28, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Gong, Z.Q.; Li, N.; Liu, C.K. Policy Framework for Prefabricated Buildings in Underdeveloped Areas: Enlightenment from the Comparative Analysis of Three Types of Regions in China. Buildings 2023, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Wang, C.J.; Li, W.L. Research on Incentive Policy Evaluation of Prefabricated Buildings Based on Grey Relational Analysis. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Xue, X. Evaluation of Construction Industrialization Policy Based on PMC Index Model. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Construction and Real Estate Management, Charleston, SC, USA, 9–10 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, J.R.; Lei, X.; Yang, B.Z. Effect and Mechanism of China’s Prefabricated Building Policies to Promote Patent Output with Carbon-Neutrality as a Target. J. Green Build. 2024, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qin, Y.J.; Zhou, J.Y. Incentive policies for prefabrication implementation of real estate enterprises: An evolutionary game theory-based analysis. Energy Policy 2021, 156, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Y.; Wang, J.W.; Ye, M.W.; Zhao, S.M.; Si, X. A Study on the Incentive Policy of China’s Prefabricated Residential Buildings Based on Evolutionary Game Theory. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.B.; Zhao, C.Y.; Kleit, A.N. The impact of the under enforcement of RPS in China: An evolutionary approach. Energy Policy 2019, 135, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selya, A.S. Reducing the smoking-related health burden in the USA through diversion to electronic cigarettes: A system dynamics simulation study. Harm Reduct. J. 2021, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 13 May 2020).
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Geng, Y.; Wang, Q. Policy Trends and Policy Analysis for the Industrialization of the Construction Industry: A Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Construction and Real Estate Management, Charleston, SC, USA, 9–10 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Egmond, C.; Jonkers, R.; Kok, G. A strategy to encourage housing associations to invest in energy conservation. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 2374–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhardt, D.A.; Manley, K. Adoption of prefabricated housing-the role of country context. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 22, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Han, Q.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.C. Adoptions of prefabrication in residential sector in China: Agent-based policy option exploration. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 1697–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.L.; Liu, L.C.; Wen, T. Evaluation of Policies on the Development of Prefabricated Construction in China: An Importance-Performance Analysis. J. Green Build. 2022, 17, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tian, X.L. Prefabrication policies and the performance of construction industry in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Yi, X.; Li, S.S.; Qiu, H. Evolutionary game of government safety supervision for prefabricated building construction using system dynamics. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2023, 30, 2947–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.B.; Liu, H.D. Research on Behavior Incentives of Prefabricated Building Component Manufacturers. Information 2021, 12, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.H.; Song, S.Y.; Zhuang, W.L. Behavioral Strategies between Government and Real Estate Developers on Prefabricated Buildings Based on Triangular Fuzzy Matrix Game. Buildings 2022, 12, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Wang, C.; Kassem, M.A.; Bimenyimana, S. Fairness Theory-Driven Incentive Model for Prefabricated Building Development. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 13487–13498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.X.; Yao, J.T.; Tong, R.P. The impact of behavior safety management system on coal mine work safety: A system dynamics model of quadripartite evolutionary game. Resour. Policy 2023, 82, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.X.; Qi, Y.; Chen, J.Y. Research on the Development Policy of Prefabricated Building based on asymmetric Evolutionary Game. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Civil Engineering, Environment Resources and Energy Materials, Changsha, China, 18–20 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, K.C.; Li, X.D.; Cao, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.H. Prefabricated Housing Subsidy Analysis in China Based on an Evolutionary Game Model. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2021, 27, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Wang, J.W.; Liu, D.H.; Huangfu, Y.R.; Guo, F.; Liu, Y.P. The Influence of Government’s Economic Management Strategies on the Prefabricated Buildings Promoting Policies: Analysis of Quadripartite Evolutionary Game. Buildings 2021, 11, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Shen, G.F.; Luo, L.Z.; Zhou, X. Influence of policies on stakeholders to drive the success of modular integrated construction in Hong Kong. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2024, 32, 2814–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.K.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.J.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.L.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.L. Natural language processing for smart construction: Current status and future directions. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, M.A.; Rasti-Barzoki, M.; Safarzadeh, S. A hybrid evolutionary game-theoretic and system dynamics approach for analysis of implementation strategies of green technological innovation under government intervention. Technol. Soc. 2022, 70, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, M.P.; Tustanovski, E.; Ip, A.W.H.; Yung, K.L.; Roblek, V. System dynamics models for the simulation of sustainable urban development A review and analysis and the stakeholder perspective. Kybernetes 2020, 49, 460–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lin, B.R.; Zhou, H.; Wu, X.Y.; Little, J.C. CO2 emissions from urban buildings at the city scale: System dynamic projections and potential mitigation policies. Appl. Energy 2020, 277, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesterager, J.P.; Frederiksen, P.; Kristensen, S.B.P.; Vadineanu, A.; Gaube, V.; Geamana, N.A.; Pavlis, V.; Terkenli, T.S.; Bucur, M.M.; van der Sluis, T.; et al. Dynamics in national agri-environmental policy implementation under changing EU policy priorities: Does one size fit all? Land Use Policy 2016, 57, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, F.; Barisa, A.; Dzene, I.; Blumberga, A.; Blumberga, D. Implementation of different policy strategies promoting the use of wood fuel in the Latvian district heating system: Impact evaluation through a system dynamic model. Energy 2014, 76, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansah, J.P.; Matchar, D.B.; Malhotra, R.; Love, S.R.; Liu, C.; Do, Y. Projecting the effects of long-term care policy on the labor market participation of primary informal family caregivers of elderly with disability: Insights from a dynamic simulation model. BMC Geriatr. 2016, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.J.; Qian, Q.K.; Straub, A.; Visscher, H. Stakeholder Perceptions of Transaction Costs in Prefabricated Housing Projects in China. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Letter from the General Office of the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development on the Recognition of the First Batch of Demonstration Cities and Industrial Bases for Prefabricated Buildings. 2017. Available online: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/zc/wjk/art/2017/art_17339_233987.html (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Office of the People’s Gorvernment of Shenyang City. Notice of the Office of the People’s Government of Shenyang City on Printing and Distributing the Work Plan for Vigorously Developing Prefabricated Buildings in Shenyang City. 2021. Available online: https://www.shenyang.gov.cn/zwgk/zcwj/zfwj/szfbgtwj1/202112/t20211201_1700616.html (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Gao, Y. Research on the Development of National Demonstration Cities for Prefabricated Buildings—Shenyang. 2020. Available online: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/339681342 (accessed on 8 February 2025).
- Li, L.H.; Shi, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, R.Y.; Guo, C.B. Simulation of Carbon Emission Reduction in Power Construction Projects Using System Dynamics: A Chinese Empirical Study. Buildings 2023, 13, 3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, Z.F.; Li, L.; Gao, Y.L. Constraints on the Promotion of Prefabricated Construction in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, C.H.; Park, S.H. Changes in renovation policies in the era of sustainability. Energy Build. 2012, 47, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Hong, J.K.; Fan, C.; Xu, X.X.; Shen, G.Q. Schedule delay analysis of prefabricated housing production: A hybrid dynamic approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, P.-H.; Chen, C.-T. Evolutionary game analysis of government and enterprises during promotion process of prefabricated construction. J. Interdiscip. Math. 2017, 20, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.K.; Shen, G.Q.P.; Li, Z.D.; Zhang, B.Y.; Zhang, W.Q. Barriers to promoting prefabricated construction in China: A cost-benefit analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Mao, C.; Hou, L.; Wu, C.K.; Tan, J.J. A SWOT analysis for promoting off-site construction under the backdrop of China’s new urbanisation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 173, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, M. Coordination of Prefabricated Construction Supply Chain under Cap-and-Trade Policy Considering Consumer Environmental Awareness. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
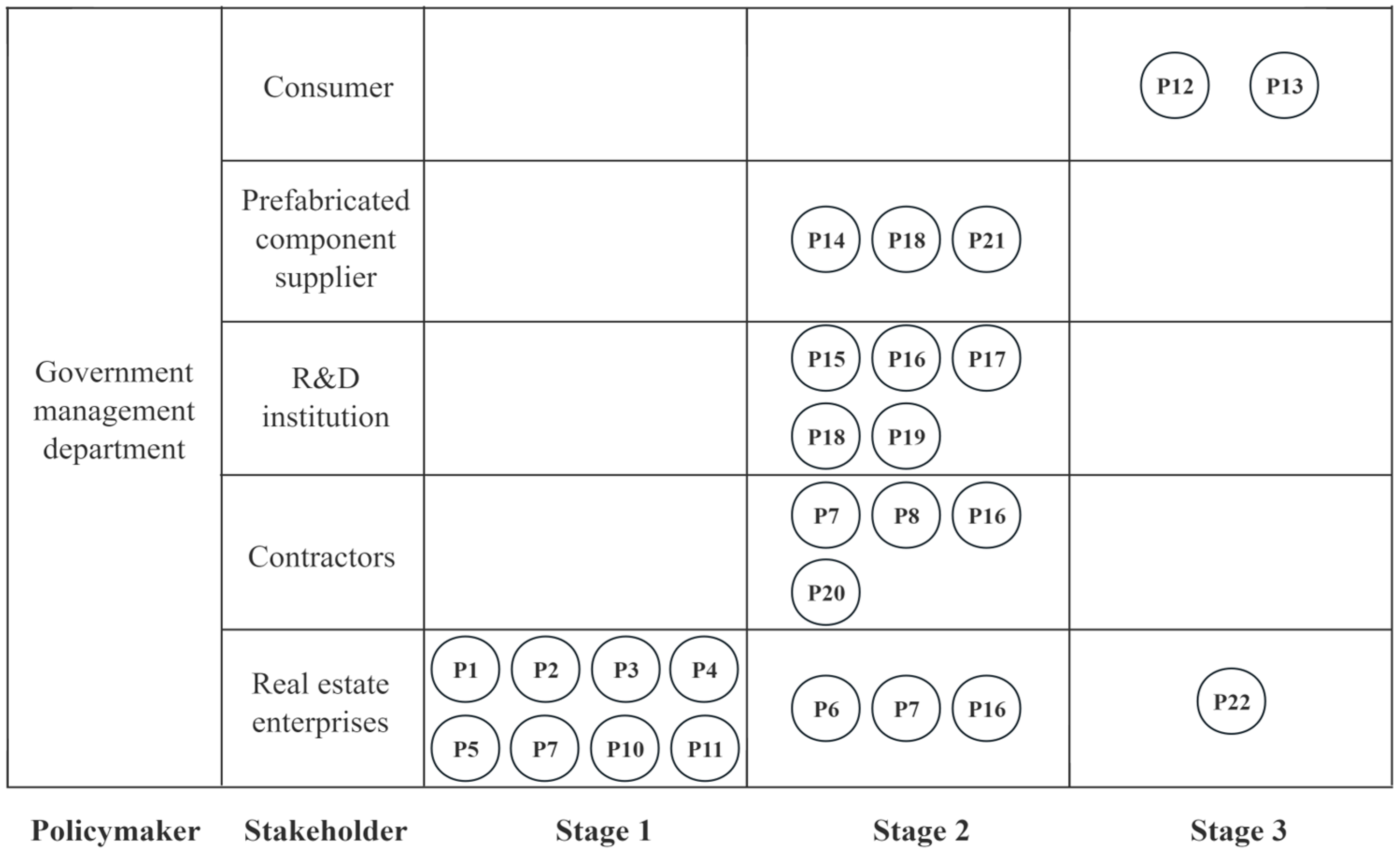
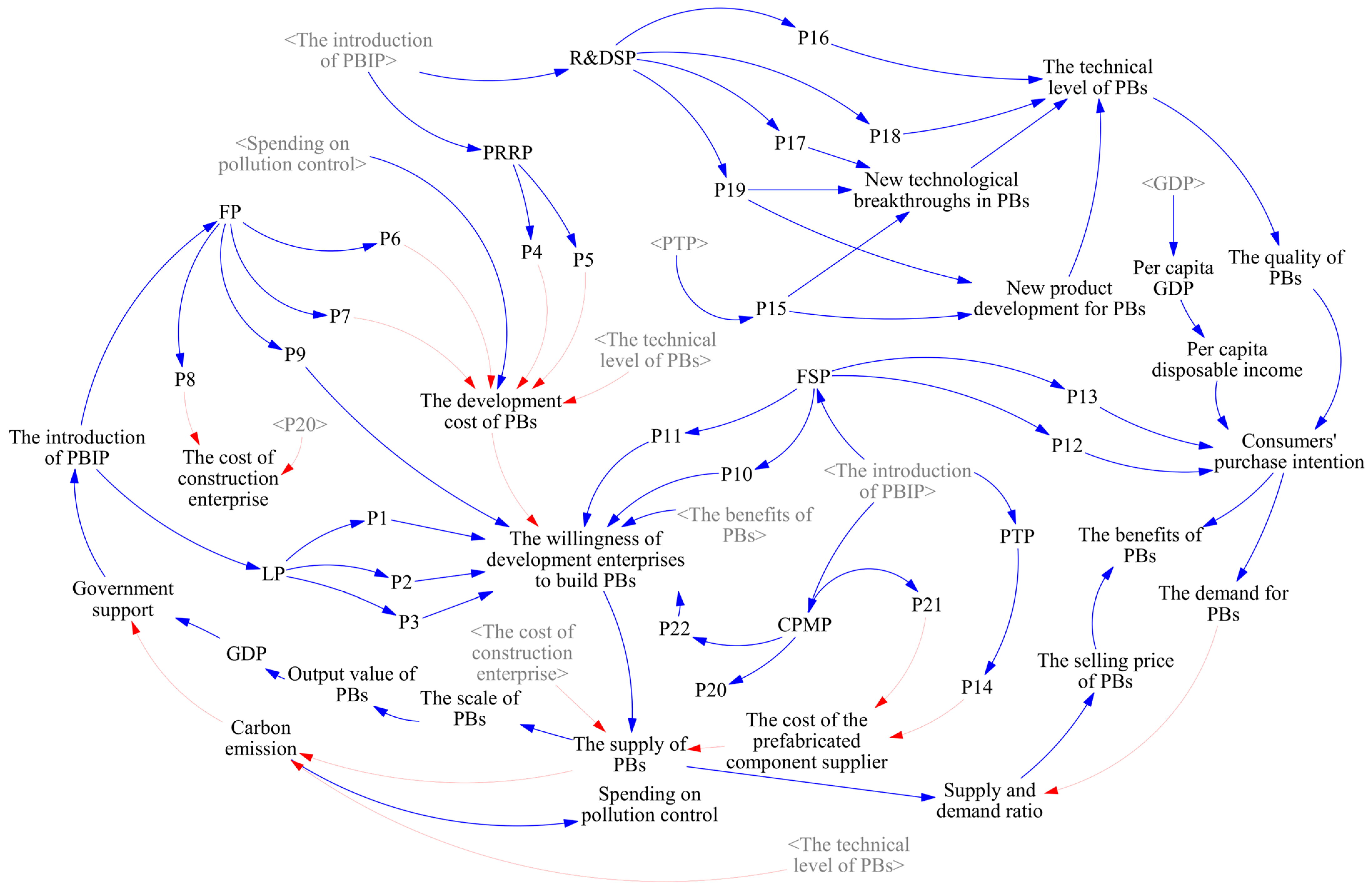




| Policies | The Specific Contents of the Policy | Stage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| LP | Provide priority land for PB. (P1) | √ | × | × |
| Reduce the land transfer conditions of PB. (P2) | √ | × | × | |
| Land transfer fees can be paid in installments. (P3) | √ | × | × | |
| PRRP | The prefabricated area of the exterior wall is not included in the plot ratio calculation. (P4) | √ | × | × |
| Reward PBs with a plot ratio of no more than 3%. (P5) | √ | × | × | |
| FP | Grant financial subsidies to eligible PB projects. (P6) | × | √ | √ |
| Provide financial subsidies to PB-related enterprises. (P7) | √ | √ | √ | |
| Qualified PB projects may not pay waste discharge fees. (P8) | × | √ | × | |
| Give priority to returning PBs’ wall reform fund. (P9) | × | × | √ | |
| FSP | Give priority to lending to PB-related enterprises. (P10) | √ | × | × |
| Discount interest on loans to PB-related enterprises. (P11) | √ | × | × | |
| Give priority to lending to consumers who buy PBs. (P12) | × | × | √ | |
| The down payment ratio was reduced to 20%. (P13) | × | × | √ | |
| PTP | VAT refund for prefabricated components. (P14) | × | √ | × |
| R&D expenses of PB technology are not subject to tax. (P15) | × | √ | × | |
| R&DSP | The government promotes the preparation of PB technical standards. (P16) | × | √ | × |
| Set up a government fund to support the R&D of PBs. (P17) | × | √ | × | |
| Support technology transformation of PBs. (P18) | × | √ | × | |
| Building the Key Laboratory of PB Technology. (P19) | × | √ | × | |
| CPMP | Hydropower projects enter the construction site in advance. (P20) | × | √ | × |
| Approval process for reducing transportation of large prefabricated components. (P21) | × | √ | × | |
| Provide a fast track for PB sales approval. (P22) | × | × | √ | |
| Year | Simulation Value (108 yuan) | Actual Value (108 yuan) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 5056.52 | 5242.9 | 3.55% |
| 2016 | 5376.82 | 5288.9 | −1.66% |
| 2017 | 5702.54 | 5549.3 | −2.76% |
| 2018 | 6021.35 | 6101.9 | 1.32% |
| 2019 | 6407.26 | 6464.5 | 0.89% |
| 2020 | 6815.22 | 6571.5 | −3.71% |
| 2021 | 7264.72 | 7249.7 | −0.21% |
| 2022 | 7519.71 | 7695.8 | 2.29% |
| Variables | Policies | Rate of Increase | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Confidence Interval (95%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The newly added area of PB (104 m2) | Initial value | 1749.58 | 130.65 | [1493.51, 2005.65] | |
| LP | +10% | 1765.53 | 131.38 | [1508.02, 2023.03] | |
| PRRP | 1752.41 | 130.69 | [1496.25, 2008.56] | ||
| FP | 1765.10 | 131.91 | [1506.55, 2023.64] | ||
| FSP | 1762.06 | 132.28 | [1502.80, 2021.32] | ||
| PTP | 1771.04 | 135.03 | [1506.38, 2035.69] | ||
| R&DSP | 1768.08 | 131.90 | [1509.54, 2026.61] | ||
| CPMP | 1759.37 | 131.48 | [1501.66, 2017.07] | ||
| LP | +20% | 1784.04 | 131.52 | [1526.25, 2041.82] | |
| PRRP | 1758.99 | 131.96 | [1500.35, 2017.63] | ||
| FP | 1792.03 | 136.75 | [1523.99, 2060.07] | ||
| FSP | 1776.88 | 133.57 | [1515.09, 2038.67] | ||
| PTP | 1785.05 | 136.56 | [1517.39, 2052.71] | ||
| R&DSP | 1788.05 | 133.52 | [1526.35, 2049.76] | ||
| CPMP | 1772.28 | 132.84 | [1511.92, 2032.63] | ||
| LP | +30% | 1812.28 | 131.00 | [1555.51, 2069.05] | |
| PRRP | 1767.12 | 134.37 | [1503.76, 2030.48] | ||
| FP | 1813.26 | 138.76 | [1541.29, 2085.22] | ||
| FSP | 1792.98 | 137.10 | [1524.26, 2061.69] | ||
| PTP | 1801.76 | 138.36 | [1530.57, 2072.94] | ||
| R&DSP | 1797.33 | 133.64 | [1535.41, 2059.26] | ||
| CPMP | 1783.12 | 134.81 | [1518.90, 2047.34] | ||
| The supply of PB (104 m2) | Initial value | 9803.54 | 1356.91 | [7143.98, 12,463.09] | |
| LP | +10% | 9861.29 | 1373.35 | [7169.53, 12,553.05] | |
| PRRP | 9812.71 | 1359.38 | [7148.33, 12,477.09] | ||
| FP | 9864.44 | 1376.10 | [7167.28, 12,561.59] | ||
| FSP | 9836.69 | 1365.82 | [7159.68, 12,513.70] | ||
| PTP | 9885.67 | 1388.56 | [7164.10, 12,607.24] | ||
| R&DSP | 9866.01 | 1374.86 | [7171.30, 12,560.73] | ||
| CPMP | 9845.10 | 1371.44 | [7157.07, 12,533.12] | ||
| LP | +20% | 9919.24 | 1388.23 | [7198.31, 12,640.16] | |
| PRRP | 9827.34 | 1364.49 | [7152.94, 12,501.74] | ||
| FP | 9992.90 | 1420.41 | [7208.90, 12,776.90] | ||
| FSP | 9884.81 | 1380.19 | [7179.64, 12,589.99] | ||
| PTP | 9931.02 | 1402.43 | [7182.26, 12,679.78] | ||
| R&DSP | 9932.31 | 1393.57 | [7200.90, 12,663.71] | ||
| CPMP | 9873.77 | 1377.12 | [7174.61, 12,572.93] | ||
| LP | +30% | 10,031.20 | 1416.00 | [7255.83, 12,806.57] | |
| PRRP | 9868.70 | 1381.34 | [7161.28, 12,576.11] | ||
| FP | 10,112.83 | 1454.86 | [7261.30, 12,964.35] | ||
| FSP | 9955.75 | 1403.34 | [7205.21, 12,706.30] | ||
| PTP | 9980.49 | 1417.48 | [7202.24, 12,758.75] | ||
| R&DSP | 9985.59 | 1413.82 | [7214.50, 12,756.68] | ||
| CPMP | 9894.03 | 1382.30 | [7184.73, 12,603.32] | ||
| Carbon emission reduction (104 ton) | Initial value | 685.98 | 61.90 | [564.66, 807.29] | |
| LP | +10% | 693.51 | 62.53 | [570.96, 816.06] | |
| PRRP | 687.07 | 61.92 | [565.71, 808.43] | ||
| FP | 692.06 | 62.50 | [569.57, 814.56] | ||
| FSP | 690.28 | 62.33 | [568.10, 812.45] | ||
| PTP | 701.75 | 65.42 | [573.53, 829.96] | ||
| R&DSP | 704.92 | 64.41 | [578.67, 831.17] | ||
| CPMP | 689.82 | 62.29 | [567.72, 811.91] | ||
| LP | +20% | 701.54 | 63.09 | [577.88, 825.20] | |
| PRRP | 688.79 | 62.17 | [566.94, 810.64] | ||
| FP | 702.77 | 64.56 | [576.23, 829.31] | ||
| FSP | 696.09 | 62.89 | [572.84, 819.35] | ||
| PTP | 712.43 | 67.09 | [580.93, 843.94] | ||
| R&DSP | 724.14 | 66.67 | [593.47, 854.81] | ||
| CPMP | 694.90 | 62.90 | [571.62, 818.18] | ||
| LP | +30% | 714.09 | 63.66 | [589.31, 838.86] | |
| PRRP | 691.39 | 63.00 | [567.90, 814.88] | ||
| FP | 712.99 | 66.23 | [583.19, 842.79] | ||
| FSP | 701.39 | 63.95 | [576.04, 826.73] | ||
| PTP | 722.55 | 68.04 | [589.18, 855.91] | ||
| R&DSP | 740.72 | 69.19 | [605.10, 876.33] | ||
| CPMP | 699.21 | 63.72 | [574.31, 824.11] | ||
| Scenario | LP | PRRP | FP | FSP | PTP | R&DSP | CPMP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑20% | ↑30% | ↑10% | ↑10% | ↑30% |
| Scenario 2 | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑10% | ↑10% | ↑30% |
| Scenario 3 | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑20% | ↑30% | ↑10% | ↑20% | ↑30% |
| Scenario 4 | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑10% | ↑20% | ↑30% |
| Scenario 5 | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑20% | ↑30% | ↑10% | ↑30% | ↑30% |
| Scenario 6 | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑30% | ↑10% | ↑30% | ↑30% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.; Yan, W.; Guo, Z. Research on the Implementation Effect of Incentive Policies for Prefabricated Buildings Based on System Dynamics: A Chinese Empirical Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5627. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105627
Guo C, Yan W, Guo Z. Research on the Implementation Effect of Incentive Policies for Prefabricated Buildings Based on System Dynamics: A Chinese Empirical Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5627. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105627
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Chunbing, Weidong Yan, and Zhenxu Guo. 2025. "Research on the Implementation Effect of Incentive Policies for Prefabricated Buildings Based on System Dynamics: A Chinese Empirical Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5627. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105627
APA StyleGuo, C., Yan, W., & Guo, Z. (2025). Research on the Implementation Effect of Incentive Policies for Prefabricated Buildings Based on System Dynamics: A Chinese Empirical Study. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5627. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105627








