Organochlorine Contaminants in Maize Fertilized with Meat and Bone Meal Derived from Animal By-Products
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Materials and Methods
2.1. Site and Experimental Design
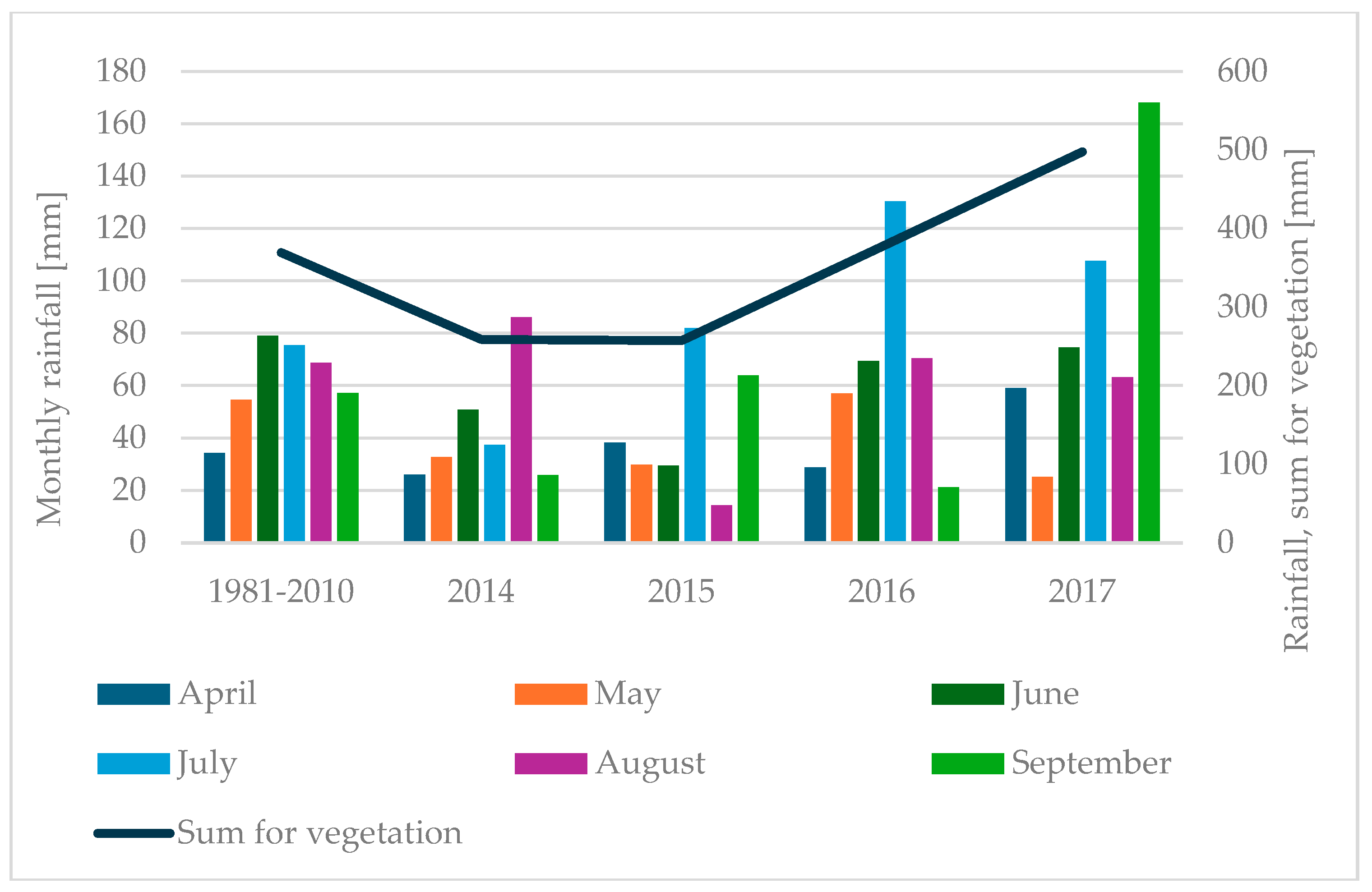
2.2. Plant Growth and Weather Conditions
2.3. Determination of Grain Yield and Grain Lipid Content
2.4. Determination of Organic Pollutants in Meat and Bone Meal, Soil, and Grain
2.5. Determination of Soil Organic Carbon
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
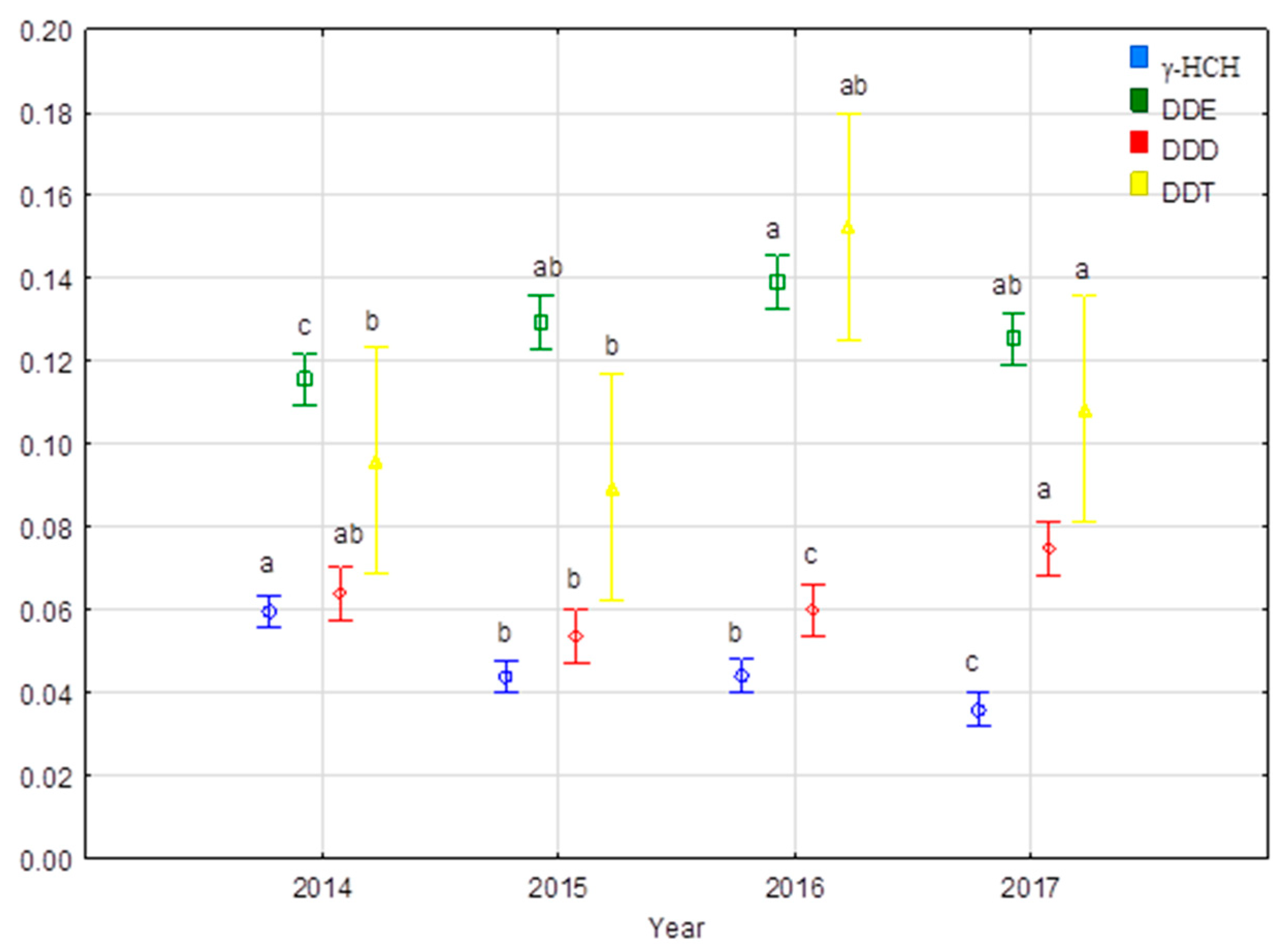
3.1. Residual Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides in Meat and Bone Meal
3.2. Soil Organic Carbon (Corg)
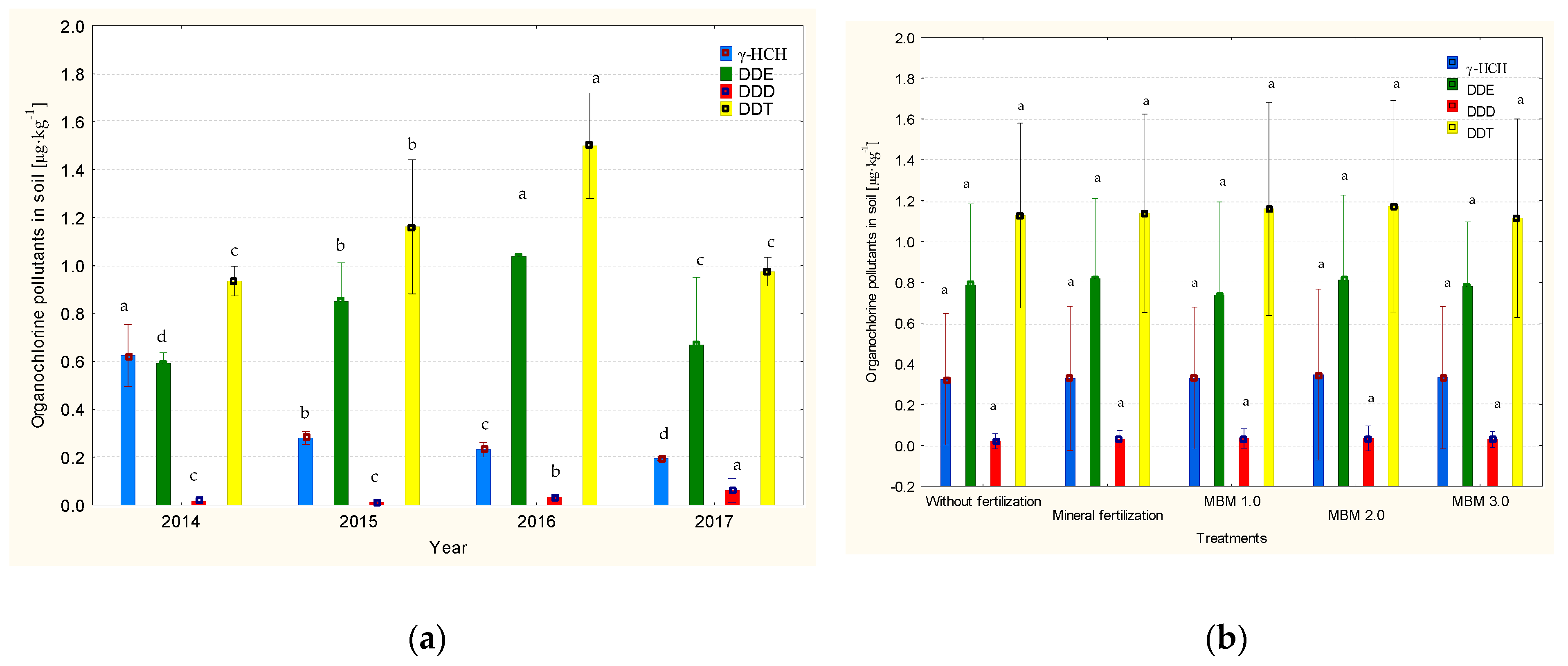
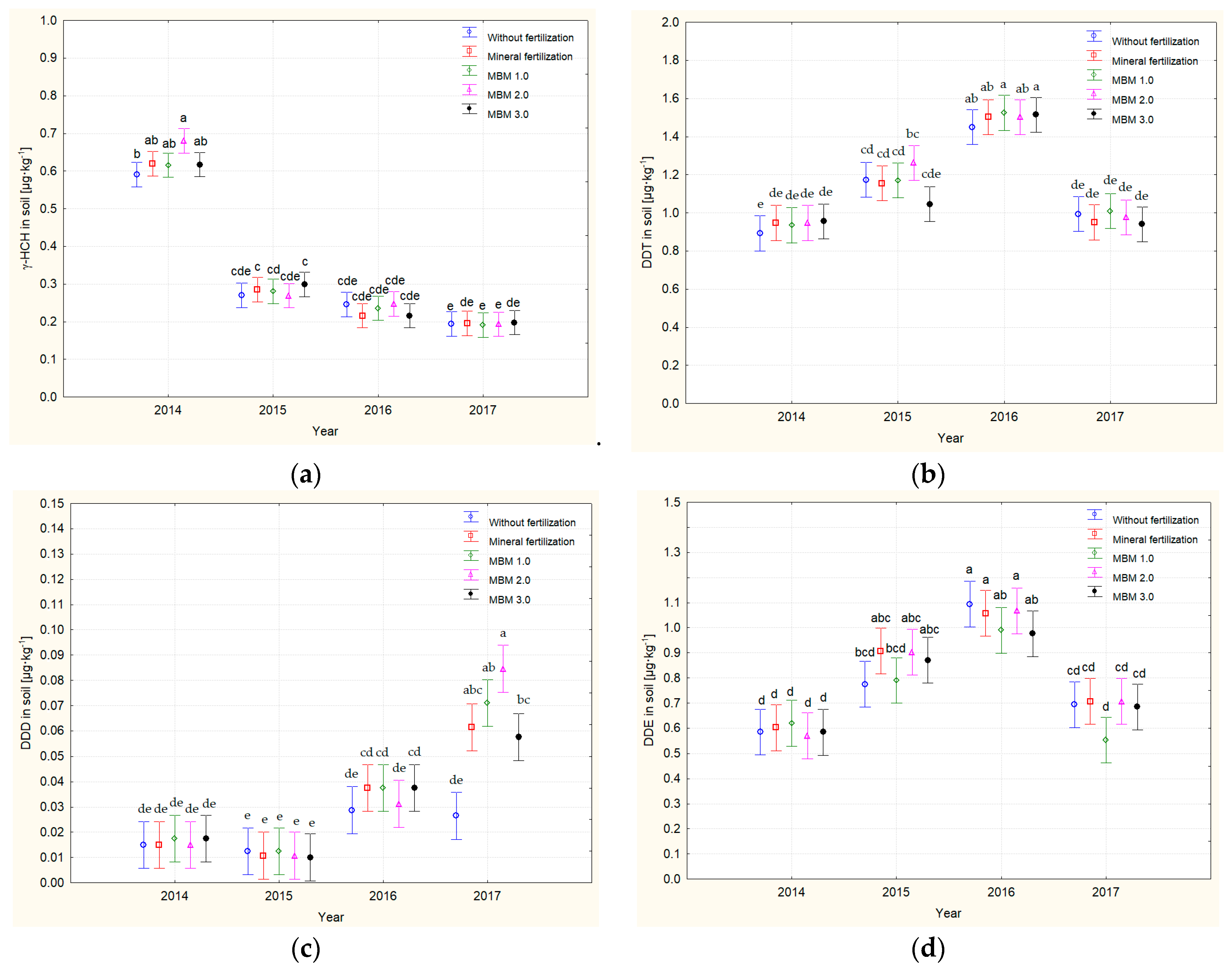
3.3. Residual Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides in Soil
3.4. Grain Yield and Grain Lipid Content
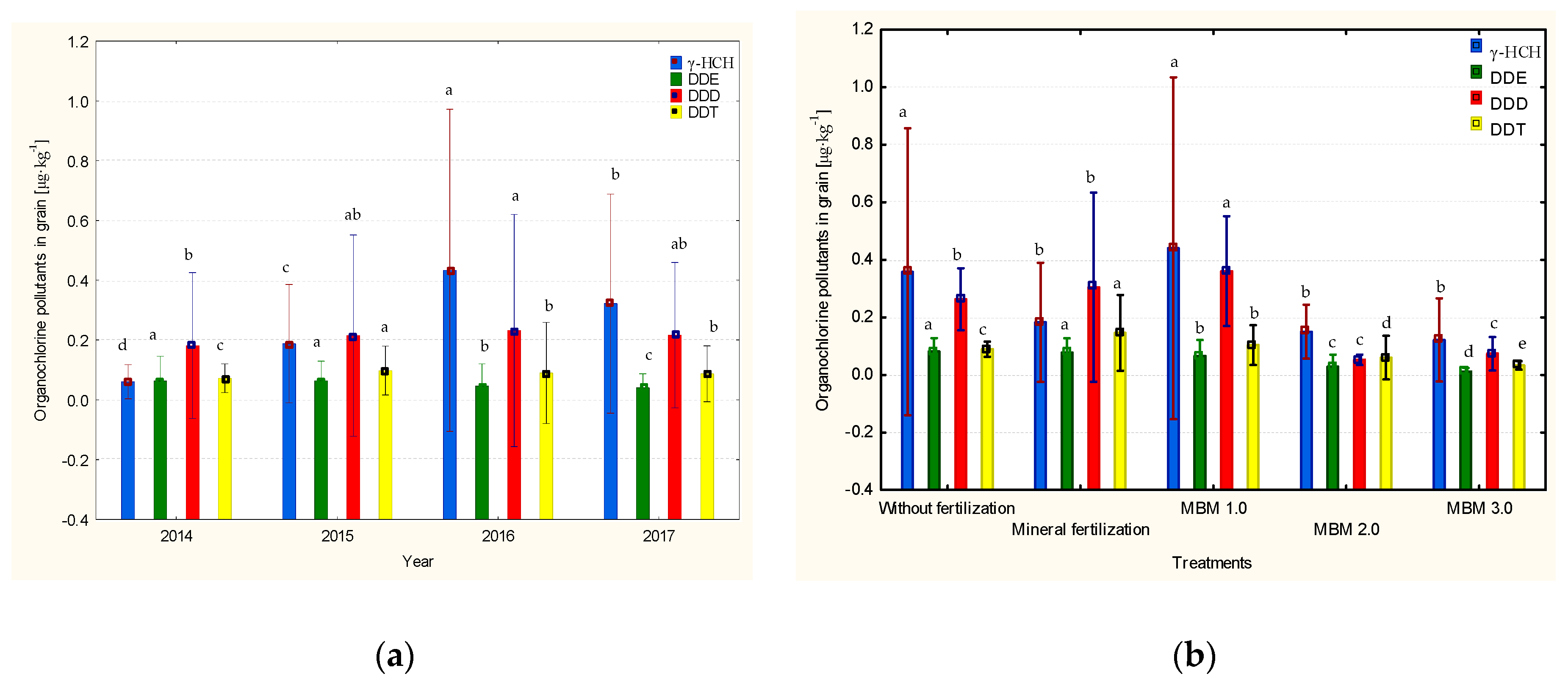
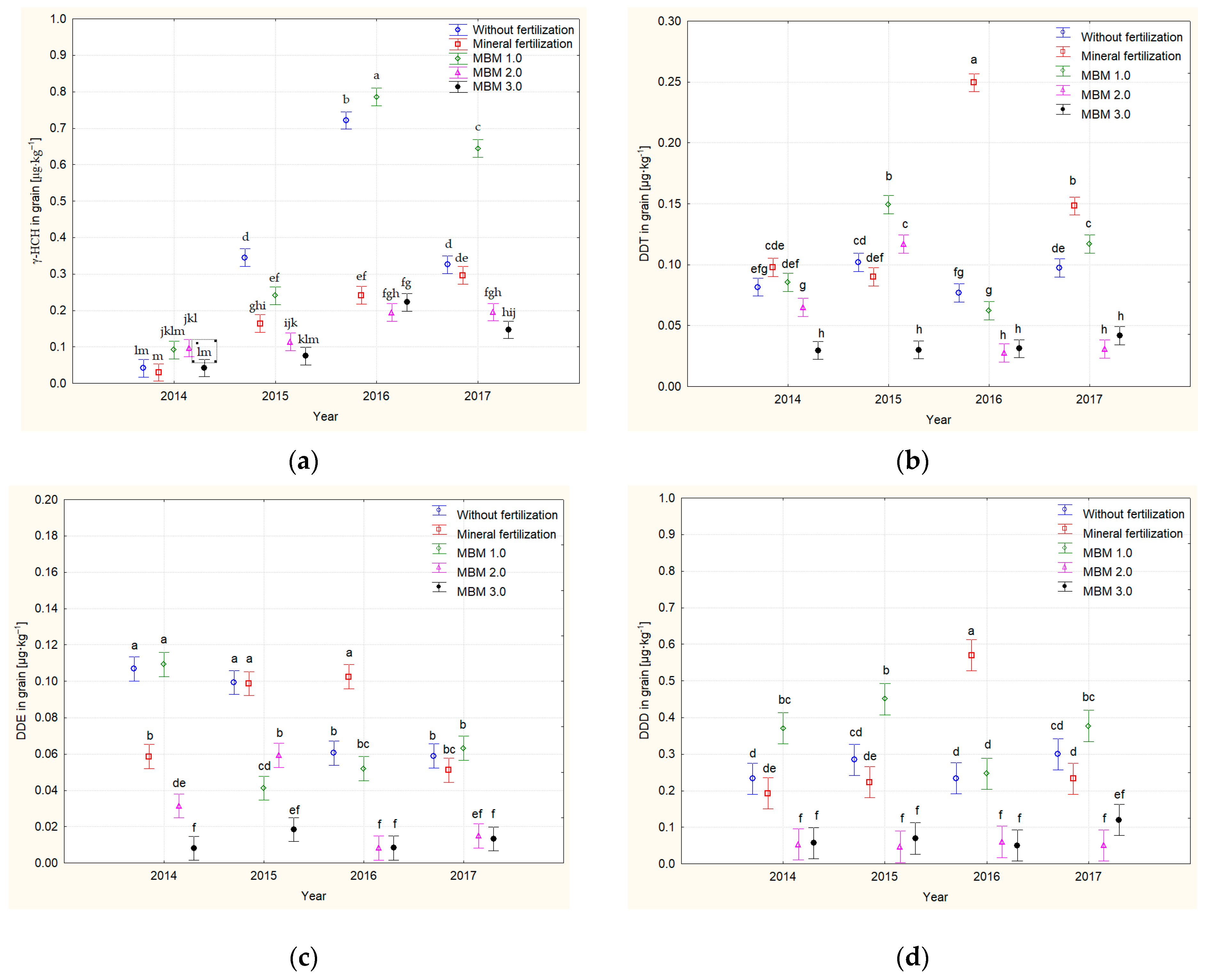
3.5. Residual Levels of Organochlorine Pesticides in Grain
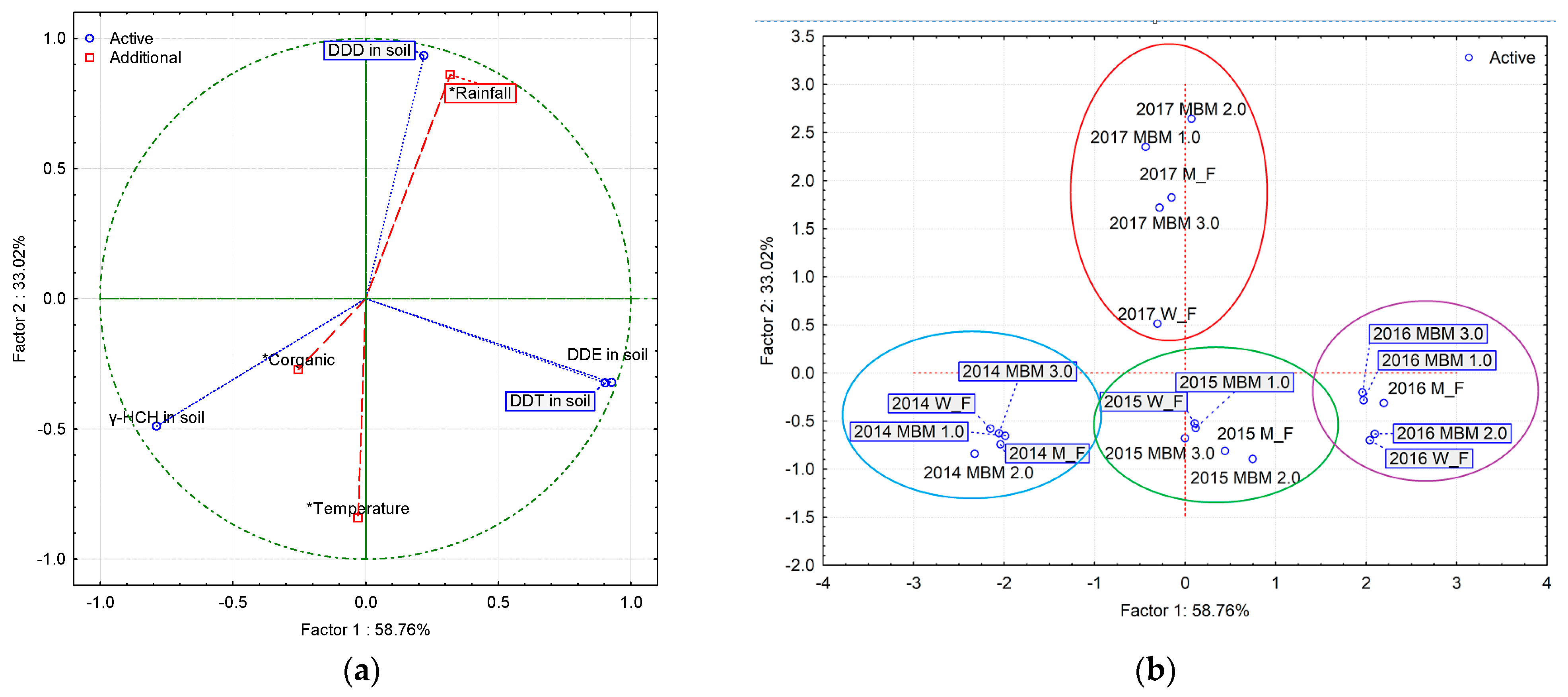
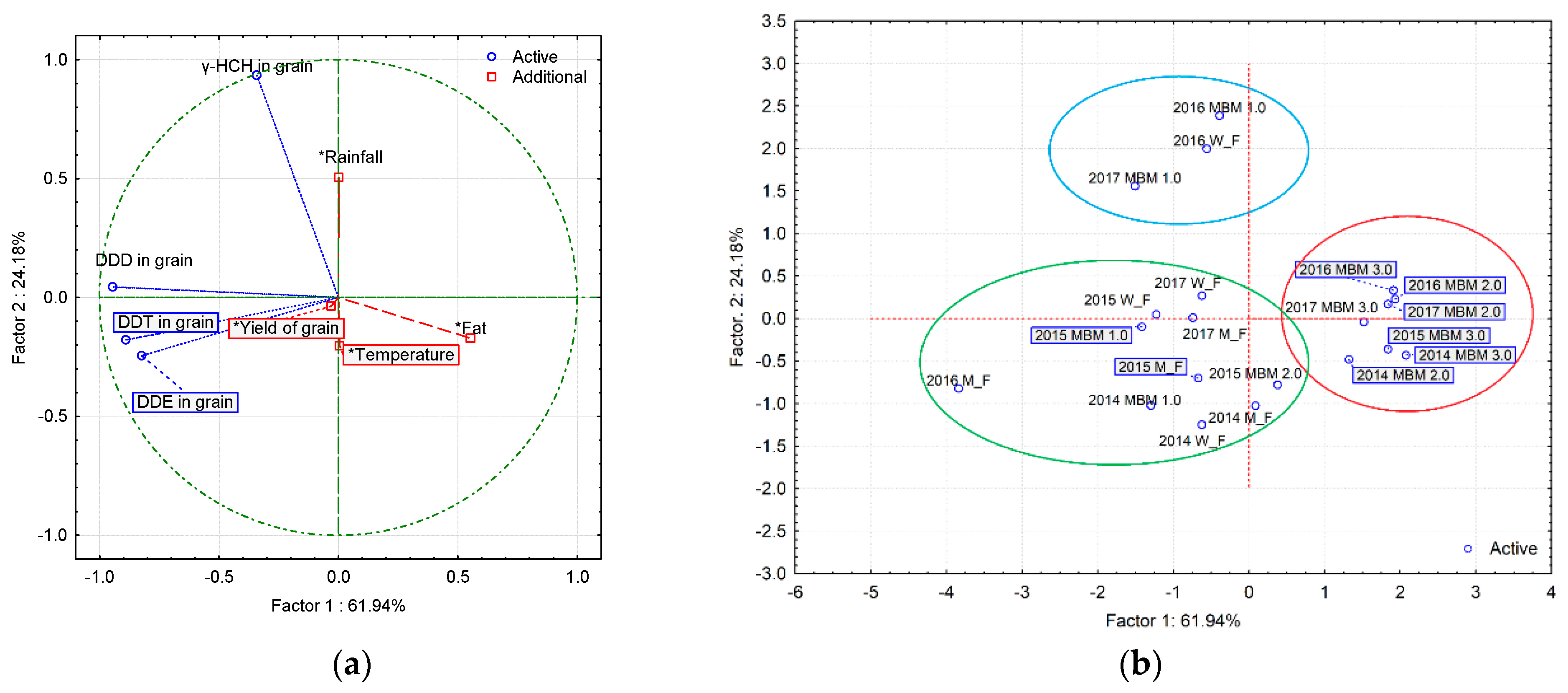
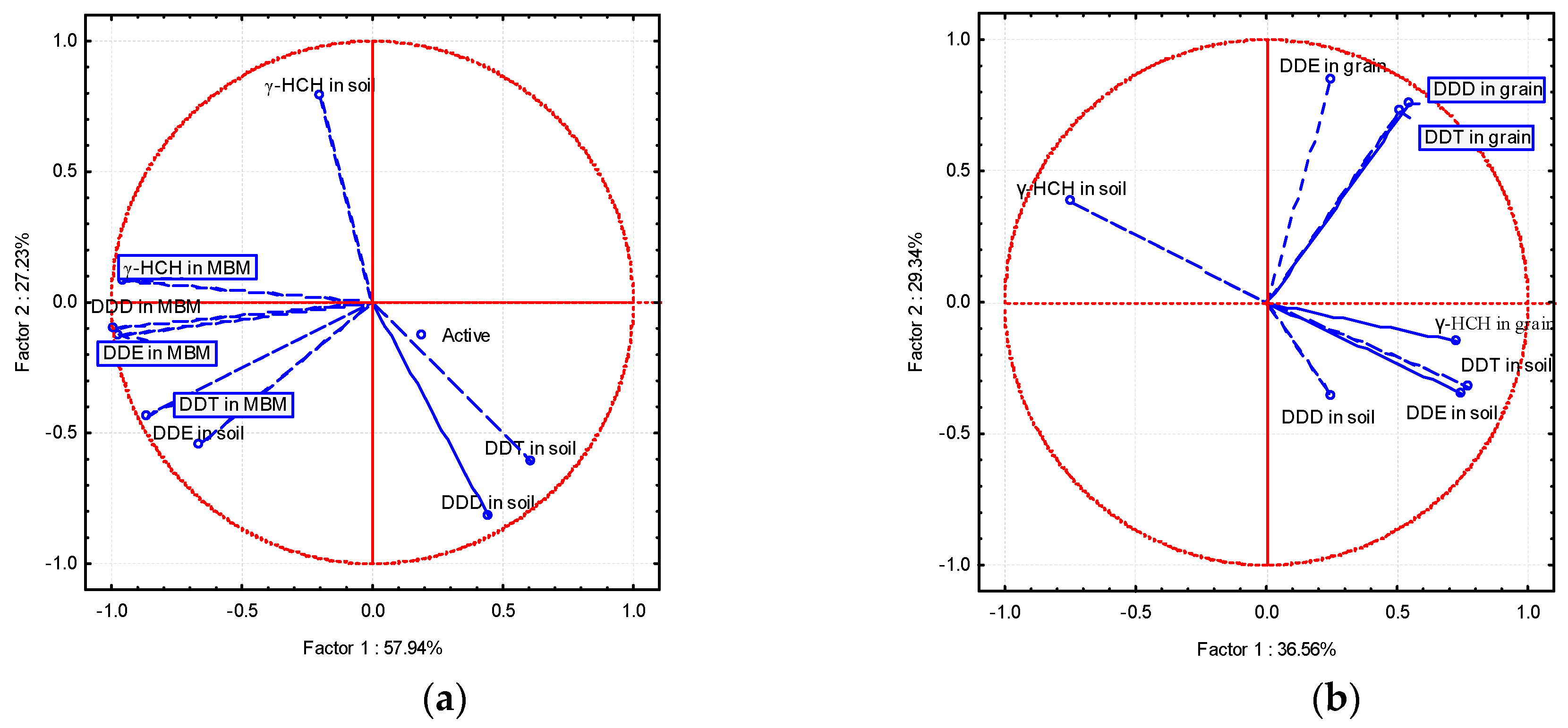
3.6. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalyabina, V.P.; Esimbekova, E.N.; Kopylova, K.V.; Kratasyuk, V.A. Pesticides: Formulants, distribution pathways and effects on human health—A review. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamalesh, T.; Kumar, P.S.; Rangasamy, G. An insights of organochlorine pesticides categories, properties, eco-toxicity and new developments in bioremediation process. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.; Megha, P.; Sreedev, P. Organochlorine pesticides, their toxic effects on living organisms and their fate in the environment. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2016, 9, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanetou, E.N.; Karasali, H. A comprehensive review of organochlorine pesticide monitoring in agricultural soils: The silent threat of a conventional agricultural past. Agriculture 2022, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheriff, I.; Debela, S.A.; Mans-Davies, A. The listing of new persistent organic pollutants in the stockholm convention: Its burden on developing countries. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 130, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliszewska-Kordybach, B.; Smreczak, B.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A. Evaluation of the Status of Contamination of Arable Soils in Poland with DDT and HCH Residues; National and Regional Scales. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, R.; Sharpanabharathi, N.; Prusty, B.A.K.; Azeez, P.A.; Kurakalva, R.M. Organochlorine pesticide residues in plants and their possible ecotoxicological and agri food impacts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qian, Y.; Jia, Q.; Weng, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Qiu, J. A national-scale distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in cropland soils and major types of food crops in China: Co-occurrence and associated risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, F.P. Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wen, D.; Qin, C.; Qian, Y.; Fu, R.; Lin, S. Physical, chemical, biological, and synergistic technologies for remediation of pesticide-contaminated Soil. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 262, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.F.A.; Ikenaka, Y.; Yohannes, Y.B.; Darwish, W.S.; Eldaly, E.A.; Morshdy, A.E.M.; Nakayama, S.M.M.; Mizukawa, H.; Ishizuka, M. Distribution and health risk assessment of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) residue in edible cattle tissues from northeastern part of Egypt: High accumulation level of OCPs in tongue. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Pan, X.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y. Soil aggregate-associated distribution of DDTs and HCHs in farmland and bareland soils in the Danjiangkou Reservoir Area of China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odewale, G.O.; Sosan, M.B.; Oyekunle, J.A.O.; Adeleye, A.O. Human health risk assessment of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables in Nigeria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 33133–33145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łozowicka, B.; Kaczyński, P.; Wolejko, E.; Piekutin, J.; Sagitov, A.; Toleubayev, K.; Isenova, G.; Abzeitova, E. Evaluation of organochlorine pesticide residues in soil and plants from East Europe and Central Asia. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebsa, G.; Gizaw, B.; Admassie, M.; Degu, T.; Alemu, T. The role and mechanisms of microbes in dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) and its residues bioremediation. Biotechnol. Rep. 2024, 42, e00835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijgen, J.; de Borst, B.; Weber, R.; Stobiecki, T.; Forter, M. HCH and lindane contaminated sites: European and global need for a permanent solution for a long-time neglected issue. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolankowska, E.; Wojtkowiak, K.; Stępień, A.; Choszcz, D.J.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R. Micronutrients and organochlorine pesticide residues in the grain of ancient wheat species from organic farms. Przemysł Chem. 2024, 103, 79–85. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermer, S.; Yalcin, M.; Turgut, C. The uptake modeling of DDT and its degradation products (o, p′-DDE and p, p′-DDE) from soil. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ren, C.; Xie, Y.W.; Zhang, X.W.; Sojinu, S.O.; Chen, T.H.; Wang, J.Z. Residues of organophosphorus insecticides in sediment around a highly eutrophic lake, Eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Pannu, R. Perspectives of lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane) biodegradation from the environment: A review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2018, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Smreczak, B.; Siebielec, G. Assessment of pesticide residue content in Polish agricultural soils. Molecules 2020, 25, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Du, Y.; Yin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, B.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Kong, F.; Su, L.; et al. Response of microbial communities to different organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) contamination levels in contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbe, C.C.; Oyetibo, G.O.; Ilor, M.O. Ecological impact of organochlorine pesticides consortium on autochthonous microbial community in agricultural soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Syed, J.H.; Malik, R.N.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Jones, K.C. Organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in South Asian region: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, G.; Anawar, H.M.; Takuwa, D.T.; Chibua, I.T.; Singh, G.S.; Sichilongo, K. Environmental assessment of fate, transport and persistent behavior of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethanes and hexachlorocyclohexanes in land and water ecosystems. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 2741–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odukkathil, G.; Vasudevan, N. Toxicity and bioremediation of pesticides in agricultural soil. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. 2013, 12, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chang, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, B.; Weng, L.; Li, Y. Comparative study on the pollution status of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) and bacterial community diversity and structure between plastic shed and open-field soils from northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 139620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantachote, D.; Naidu, R.; Williams, B.; McClure, N.; Megharaj, M.; Singleton, I. Bioremediation of DDT-contaminated soil: Enhancement by seaweed addition. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.; Tao, S.; Liu, Y.; Shi, K.L. Sequestration of organochlorine pesticides in soils of distinct organic carbon content. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Ramanayaka, S.; Bolan, N.; Ok, Y.S. The role of soils in the disposition, sequestration and decontamination of environmental contaminants. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2021, 376, 20200177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrema, E.J.; Rubino, F.M.; Brambilla, G.; Moretto, A.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Colosio, C. Persistent organochlorinated pesticides and mechanisms of their toxicity. Toxicology 2013, 307, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, G.; Acquaah, S.O. Levels of organochlorine pesticides residues in meat. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 4, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Mo, W.Y.; Man, Y.B.; Nie, X.P.; Li, K.B.; Wong, M.H. Replacing fish meal by food waste in feed pellets to culture lower trophic level fish containing acceptable levels of organochlorine pesticides: Health risk assessments. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, A.; Wojtkowiak, K.; Grzywińska-Rąpca, M.; Pawluczuk, J. Meat processing waste as a source of nutrients and its effect on the physicochemical properties of soil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Załuszniewska, A.; Nogalska, A. The effect of meat and bone meal (MBM) on phosphorus (P) content and uptake by crops, and soil available P balance in a six-year field experiment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piash, M.I.; Uemura, K.; Itoh, T.; Iwabuchi, K. Meat and bone meal biochar can effectively reduce chemical fertilizer requirements for crop production and impart competitive advantages to soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Siddiqui, M.S.I.; Islam, M.T.; Islam, M.R.; Chowdhury, E.H. Usage of meat and bone meal in animal, poultry and fish feeds: A survey and risk analysis for the occurrence of bovine spongiform encephalopathy in Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, N.M.; Hamasalim, H.J.; Mohammed, H.N.; Arkwazee, H.A. Effects of pesticide residues in animal by-products relating to public health. J. Appl. Vet. Sci. 2023, 8, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Niu, B.; Hu, Y.; Luo, T.; Zhang, G. Warming and increased precipitation indirectly affect the composition and turnover of labile-fraction soil organic matter by directly affecting vegetation and microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 714, 136787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, Y.; Lin, D.; Hou, M.; Li, X.; Hu, D.; Wang, Z. Transformation of soil organic matter subjected to environmental disturbance and preservation of organic matter bound to soil minerals: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, S.; Rasool, T.; Gani, K.M. A review of interactions of pesticides within various interfaces of intrinsic and organic residue amended soil environment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krełowska-Kułas, N. Analysis of Food Products Quality; PWE: Warszawa, Poland, 1993. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Ludwicki, J.; Góralczyk, K.; Czaja, K.; Struciński, P. Determination of Residues of Organochlorine Insecticides and Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Foodstuffs by Gas Chromatography; Wydawnictwo Metodyczne PZH: Warszawa, Poland, 1996. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Gąsior, J.; Kaniuczek, J.; Hajduk, E.; Właśniewski, S.; Nazarkiewicz, M.; Bilek, M. Methods of testing physical properties of soils. Acta Carp. 2013, 6, 1–54. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Fenner, K.; Canonica, S.; Wackett, L.P.; Elsner, M. Evaluating pesticide degradation in the environment: Blind spots and emerging opportunities. Science 2013, 341, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukalska-Jaruga, A.; Bejger, R.; Smreczak, B.; Podlasiński, M. Sorption of organic contaminants by stable organic matter fraction in soil. Molecules 2023, 28, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, W.; Qin, N.; He, Q.S.; Kong, X.Z.; Tao, S.; Xu, F.L. Distributions, sources, and ecological risks of DDT-related contaminants in water, suspended particulate matter, and sediments from Haihe Plain, Northern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 1777–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Die, Q.; Tian, Y.; Liu, F.; He, J.; Huang, Q. Organochlorine pesticides in soil, air, and vegetation at and around a contaminated site in southwestern China: Concentration, transmission, and risk evaluation. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koblizkova, M.; Ruzickova, P.; Cupr, P.; Komprda, J.; Holoubek, I.; Klánová, J. Soil burdens of persistent organic pollutants: Their levels, fate, and risks. Part IV. Quantification of volatilization fluxes of organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls from contaminated soil surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3588–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiantas, P.; Karasali, H.; Pavlidis, G.; Kavasilis, S.; Doula, M. The status of organochlorine pesticide contamination in Greek agricultural soils: The ghost of traditional agricultural history. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 117654–117675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namiki, S.; Otani, T.; Seike, N. Fate and plant uptake of persistent organic pollutants in soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Paulose, S.V.; Cyril, N.; Santhosh, S.K.; Varghese, A.; Nelson, A.B.; Kunjankutty, S.V.; Kasu, S. Organochlorine pesticides in the soils of Cardamom Hill Reserve (CHR), Kerala, India: Geo spatial distribution, ecological and human health risk assessment. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, W.; Yuan, H.; Zhou, S.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.F. Spatial distribution of hexachlorocyclohexanes in agricultural soils in Zhejiang Province, China, and correlations with elevation and temperature. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6303–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Xu, C.; Zhu, S.; Bao, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, J.; Liu, W. Enantiomer signature and carbon isotope evidence for the migration and transformation of DDTs in arable soils across China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Chen, Z.; Ahrens, L.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.F. Concentrations of DDTs and enantiomeric fractions of chiral DDTs in agricultural soils from Zhejiang Province, China, and correlations with total organic carbon and pH. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8294–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Huo, L.; Zhang, R.; Gu, X.; Chen, G.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, W.; Hui, K.; Jiang, Y. Effect of soil-groundwater system on migration and transformation of organochlorine pesticides: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogalska, A.; Załuszniewska, A. The effect of meat and bone meal (MBM) on crop yields, nitrogen content and uptake, and soil mineral nitrogen balance. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, A.; Wojtkowiak, K.; Kolankowska, E. Use of meat industry waste in the form of meat-and-bone meal in fertilising maize (Zea mays L.) for grain. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Hua, Y.; Sinkkonen, A.; Romantschuk, M.; Lv, Y.; Wu, Q.; Hui, N. Meat and bone meal stimulates microbial diversity and suppresses plant pathogens in asparagus straw composting. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 953783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirás-Avalos, J.M.; Salvador, R.; Guillén, M.; Dechmi, F.; Quílez, D. Effects of irrigation with HCH-contaminated water on crop performance and HCH accumulation in plant and soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo-Ibarra, K.C.; Daesslé, L.W.; Macías-Zamora, J.V.; Ramírez-Álvarez, N. Persistent organic pollutants associated to water fluxes and sedimentary processes in the Colorado River delta, Baja California, México. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairul, U.T.; Idris, N.I.M.; Shah, R.M.; Nawi, I.H.M.; Soh, N.C. Evaluation of Minerals Composition in Fish Bone Meal as Organic Fertilizer Development for Sustainable Environment. Curr. World Environ. 2024, 19, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macavei, M.G.; Gheorghe, V.C.; Ionescu, G.; Volceanov, A.; Pătrașcu, R.; Mărculescu, C.; Magdziarz, A. Thermochemical conversion of animal-derived waste: A mini-review with a focus on chicken bone waste. Processes 2024, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashmakov, D.I.; Lukatkin, A.S.; Miliauskiene, J.; Samuoliene, G.; Duchovskiene, L.; Stępień, A.; Duchovskis, P. Effects of pre-sowing treatment with synthetic and natural plant growth regulators on the response of maize (Zea mays L.) to lead stress. J. Elem. 2021, 26, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation, 1259. Commission Regulation (EU) no. 1259/2011 of 2 December 2011 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as Regards Maximum Levels for Dioxins, Dioxin-like PCBs and Non Dioxin-like PCBs in Foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Union. 320, 18–23. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:320:0018:0023:EN:PDF (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Qu, C.; Albanese, S.; Chen, W.; Lima, A.; Doherty, A.L.; Piccolo, A.; Arienzo, M.; Qi, S.; De Vivo, B. The status of organochlorine pesticide contamination in the soils of the Campanian Plain, southern Italy, and correlations with soil properties and cancer risk. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Li, L.; Wania, F.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, B.; Chen, Y.; Qi, S. Do dissipation and transformation of γ-HCH and p, p’-DDT in soil respond to a proxy for climate change? Insights from a field study on the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitton, F.M.; Miglioranza, K.S.; Gonzalez, M.; Shimabukuro, V.M.; Monserrat, J.M. Assessment of tolerance and efficiency of crop species in the phytoremediation of DDT polluted soils. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ling, W.; Lin, C. Effects of different treatments on soil-borne DDT and HCH dynamics and plant uptake. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2011, 46, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Corganic | N | P | K | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MBM * | Kmineral | ||||
| Without fertilization | 0.0 | - | - | - | - |
| Mineral fertilization | 0.0 | 133.0 | 79.6 | - | 83.1 |
| MBM * 1.0 t ha−1 | 666.9 | 61.0 | 31.1 | 4.0 | 79.1 |
| MBM 2.0 t ha−1 | 1333.8 | 122.0 | 62.2 | 8.0 | 75.1 |
| MBM 3.0 t ha−1 | 2000.7 | 183.0 | 93.3 | 12.0 | 71.1 |
| Year | Without Fertilization | Mineral Fertilization | MBM * 1.0 t ha−1 | MBM 2.0 t ha−1 | MBM 3.0 t ha−1 | Av. for Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 11.68 ± 0.29 cde | 12.30 ± 0.18 bcd | 12.85 ± 0.41 ab | 12.35 ± 0.10 abcd | 12.75 ± 0.12 abc | 12.39 ± 0.14 A |
| 2015 | 11.20 ± 0.11 def | 12.53 ± 0.35 abc | 13.30 ± 0.09 ab | 12.70 ± 0.09 abc | 13.48 ± 0.19 a | 12.64 ± 0.20 A |
| 2016 | 11.10 ± 0.35 ef | 10.30 ± 0.17 f | 10.63 ± 0.21 ef | 12.50 ± 0.04 abc | 13.03 ± 0.18 ab | 11.51 ± 0.26 B |
| 2017 | 10.95 ± 0.32 ef | 10.85 ± 0.23 ef | 10.58 ± 0.17 ef | 12.63 ± 0.14 abc | 12.65 ± 0.22 abc | 11.53 ± 0.23 B |
| Av. for Year | 11.23 ± 0.15 C | 11.49 ± 0.27 C | 11.84 ± 0.34 B | 12.54 ± 0.06 A | 12.98 ± 0.11 A |
| Year | Without Fertilization | Mineral Fertilization | MBM * 1.0 t ha−1 | MBM 2.0 t ha−1 | MBM 3.0 t ha−1 | Av. for Freatments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain yield (t ha−1) | ||||||
| 2014 | 4.75 ± 0.30 b | 4.06 ± 0.23 bcd | 3.98 ± 0.11 bcd | 3.83 ± 0.23 bcd | 2.74 ± 0.33 de | 3.87 ± 0.18 B |
| 2015 | 2.42 ± 0.16 e | 3.41 ± 0.41 bcde | 2.80 ± 0.22 cde | 3.03 ± 0.12 cde | 2.91 ± 0.29 cde | 2.91 ± 0.13 C |
| 2016 | 3.96 ± 0.22 bcd | 7.97 ± 0.30 a | 4.64 ± 0.47 b | 7.11 ± 0.39 a | 6.87 ± 0.14 a | 6.11 ± 0.38 A |
| 2017 | 1.12 ± 0.08 f | 3.87 ± 0.26 bcd | 3.05 ± 0.34 cde | 4.28 ± 0.04 bc | 4.21 ± 0.16 bc | 3.06 ± 0.28 C |
| Av. for Year | 3.06 ± 0.37 D | 4.83 ± 0.49 A | 3.62 ± 0.24 C | 4.56 ± 0.41 AB | 4.18 ± 0.44 B | |
| Lipid content (%) | ||||||
| 2014 | 5.80 ± 0.01 cd | 5.12 ± 0.01 cde | 9.39 ± 0.01 a | 4.00 ± 0.01 fgh | 9.12 ± 0.27 ab | 6.68 ± 0.50 A |
| 2015 | 3.71 ± 0.06 fghi | 2.79 ± 0.01 ij | 2.83 ± 0.01 ij | 2.26 ± 0.01 j | 5.52 ± 0.06 cd | 3.41 ± 0.26 C |
| 2016 | 3.60 ± 0.09 ghi | 2.27 ± 0.13 j | 4.39 ± 0.86 efg | 8.08 ± 0.05 b | 5.86 ± 0.13 c | 4.84 ± 0.48 B |
| 2017 | 3.42 ± 0.10 ghi | 2.91 ± 0.07 hij | 2.90 ± 0.04 hij | 8.52 ± 0.02 ab | 4.76 ± 0.04 def | 4.49 ± 0.49 B |
| Av. for Year | 4.13 ± 0.25 D | 3.27 ± 0.28 E | 4.88 ± 0.72 C | 5.71 ± 0.69 B | 6.31 ± 0.44 A | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stępień, A.; Wojtkowiak, K.; Kolankowska, E.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R. Organochlorine Contaminants in Maize Fertilized with Meat and Bone Meal Derived from Animal By-Products. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105620
Stępień A, Wojtkowiak K, Kolankowska E, Pietrzak-Fiećko R. Organochlorine Contaminants in Maize Fertilized with Meat and Bone Meal Derived from Animal By-Products. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105620
Chicago/Turabian StyleStępień, Arkadiusz, Katarzyna Wojtkowiak, Ewelina Kolankowska, and Renata Pietrzak-Fiećko. 2025. "Organochlorine Contaminants in Maize Fertilized with Meat and Bone Meal Derived from Animal By-Products" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105620
APA StyleStępień, A., Wojtkowiak, K., Kolankowska, E., & Pietrzak-Fiećko, R. (2025). Organochlorine Contaminants in Maize Fertilized with Meat and Bone Meal Derived from Animal By-Products. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105620







