Biological and Behavioural Effects of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure: An In Vivo Study in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drosophila Stocks
2.2. BPA Treatment
2.3. Longevity Assay
2.4. Prolificacy Assay
2.5. Behavioural Assay
2.6. Genotoxicity Evaluation
2.6.1. SMART w/w+ Assay
2.6.2. Comet Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
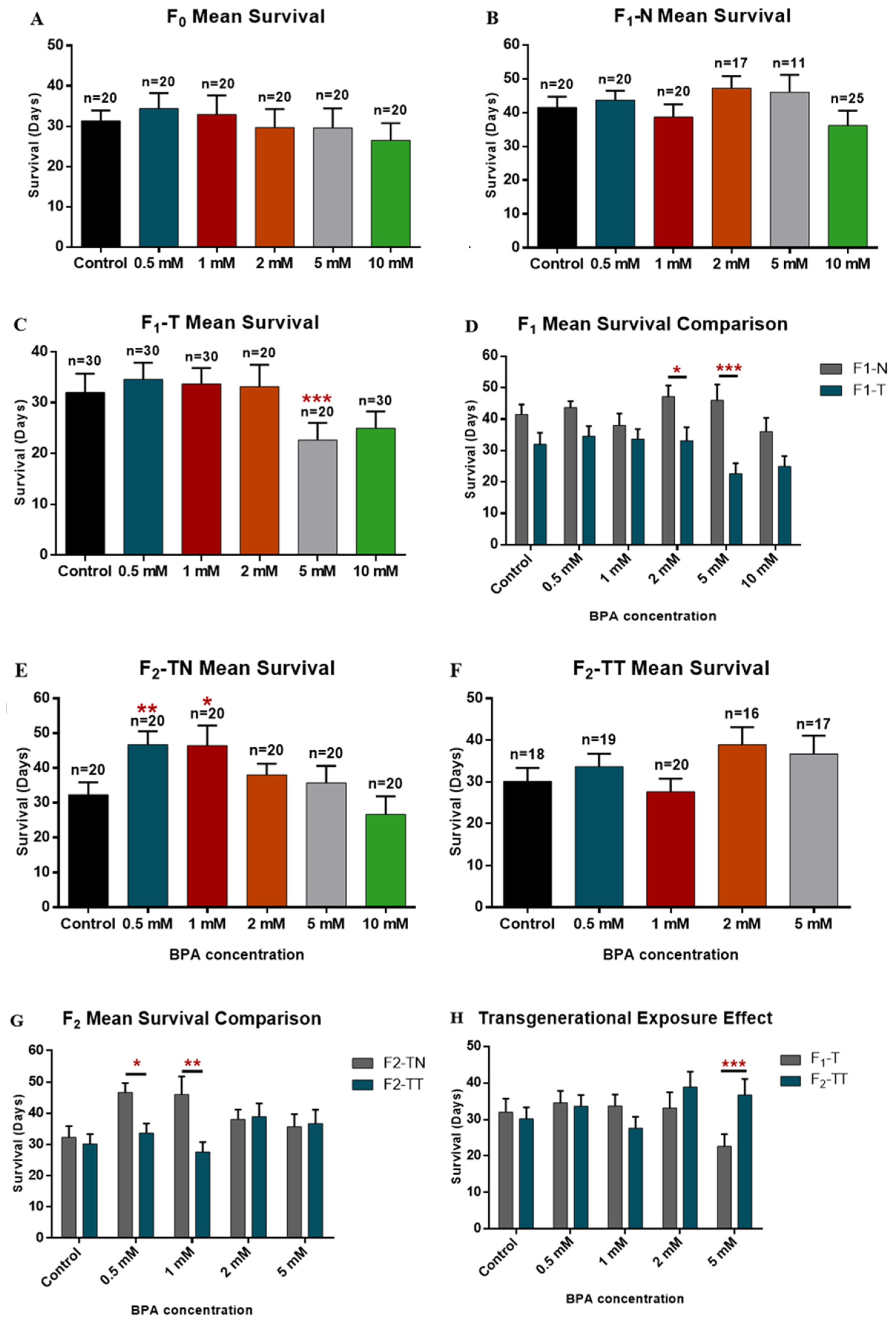
3.1. Effect on Longevity
3.2. Effect on Prolificacy
3.3. Effects on Behaviour
3.4. Genotoxic Effect
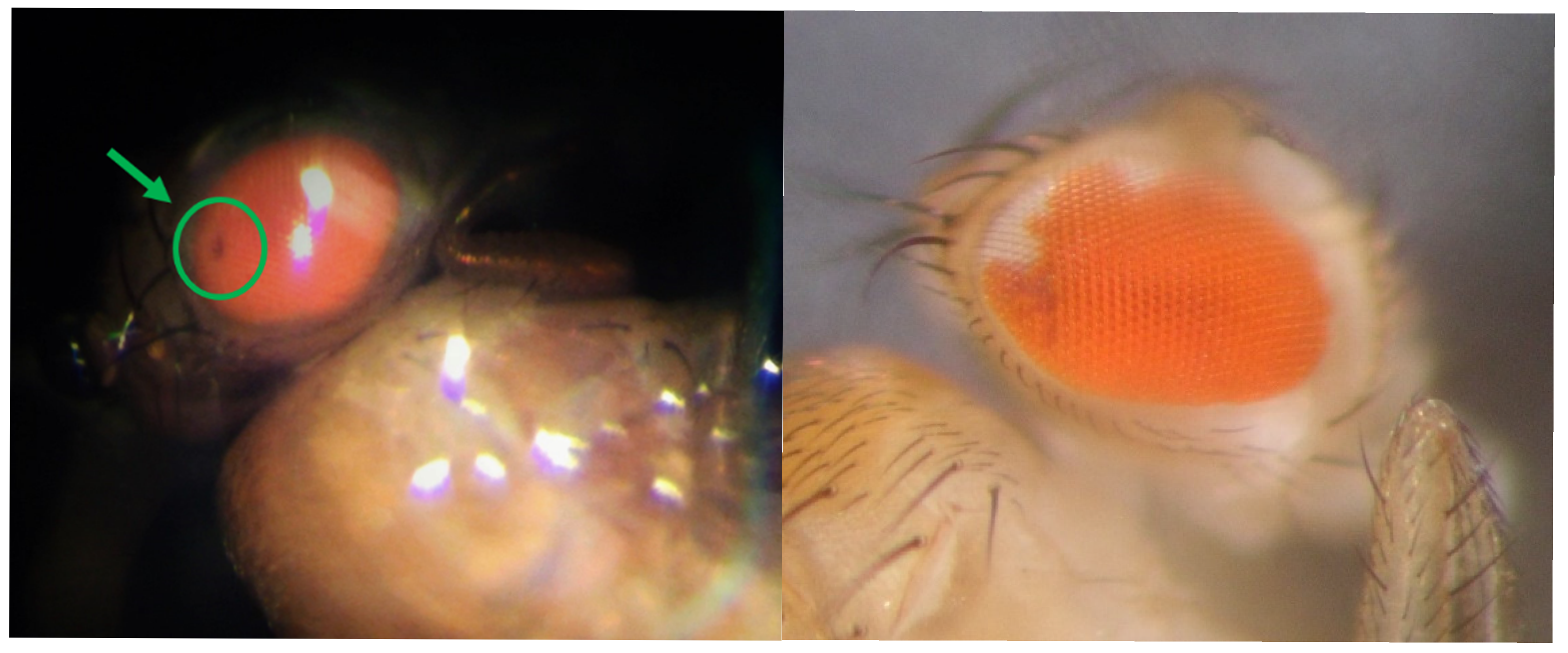
3.4.1. SMART Assay
3.4.2. Comet Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| EFSA | European Food Safety Authority |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| SMART | Somatic mutation and recombination test |
| EDC | Endocrine-disrupting chemicals |
| LOH | Loss of heterozygosity |
| OASIS | Online Application for Survival Analysis |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| CSTEE | Scientific Committee on Toxicity, Ecotoxicity and the Environment |
| BisGMA | Bisphenol A-glycidyl methacrylate |
| LOAEL | Lowest-observed-adverse-effect level |
| ADHD | Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| NMDRC | Non-monotonic dose–response curve |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Varghese, S.V.; Hall, J.M. Bisphenol A substitutes and obesity: A review of the epidemiology and pathophysiology. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1155694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, V.V.; Morozova, T.V.; Kushnir, M.V.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Kryvetskyi, V.V.; Kryvetska, I.I.; Kryvetskyi, I.V.; Biryuk, I.G.; Sykyrytska, T.B.; Ivanushko, Y.G.; et al. The Theoretical Description for Bisphenol S and Bisphenol AF Cathodic Determination by Bivalent Chromium, Intercalated into Conducting Polymeric Material. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2025, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.H.; Rasheed, S.; Rehman, K.; Imran, M.; Assiri, M.A. Toxicological evaluation of bisphenol analogues: Preventive measures and therapeutic interventions. RSC Adv. 2023, 31, 21613–21628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumu, K.; Vorst, K.; Curtzwiler, G. Endocrine modulating chemicals in food packaging: A review of phthalates and bisphenols. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 1337–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili Sadrabad, E.; Hashemi, S.A.; Nadjarzadeh, A.; Askari, E.; Akrami Mohajeri, F.; Ramroudi, F. Bisphenol A release from food and beverage containers—A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 3718–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, F.M.; Iribarne-Durán, L.M.; Artacho-Cordón, F. Human Exposure to Bisphenols, Parabens, and Benzophenones, and Its Relationship with the Inflammatory Response: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybczyńska-Tkaczyk, K.; Skóra, B.; Szychowski, K.A. Toxicity of bisphenol A (BPA) and its derivatives in diverse biological models with the assessment of molecular mechanisms of toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 75126–75140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, R.; Delgado-Marín, M.; Cook-Calvete, A.; González-Cucharero, C.; Alcharani, N.; Jiménez-Guirado, B.; Hernandez, I.; Ramirez-Carracedo, R.; Tesoro, L.; Botana, L.; et al. New environmental factors related to diabetes risk in humans: Emerging bisphenols used in synthesis of plastics. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasiman, R.; Nor, N.M.; Eshak, Z.; Mutalip, S.S.M.; Suwandi, N.R.; Bidin, H.; Abas, R. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Diphenol Analogs on Embryonic Development and Cytoskeletal Organization of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2023, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes and Processing Aids (CEP); Lambré, C.; Barat Baviera, J.M.; Bolognesi, C.; Chesson, A.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Crebelli, R.; Gott, D.M.; Grob, K.; Lampi, E.; et al. Re-evaluation of the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e06857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hasan, H.; Hafizuddin Muhammad, M.; Kurniawan, S.; Buhari, J.; Abuyezad, O.H. Managing. Managing Bisphenol A Contamination: Advances in Removal Technologies and Future Prospects. Water 2023, 15, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Omeljaniuk, W.J.; Niklinski, J. Bisphenol A—What Do We Know? A Global or Local Approach at the Public Health Risk Level. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, I.; Russo, G.; Grumetto, L. Bisphenol A and Its Analogues: From Their Occurrence in Foodstuffs Marketed in Europe to Improved Monitoring Strategies—A Review of Published Literature from 2018 to 2023. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 2441–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.E.; Ford, E.A.; Roman, S.D.; Bromfield, E.G.; Nixon, B.; Pringle, K.G.; Sutherland, J.M. Impact of Bisphenol A and its Alternatives on Oocyte Health: A Scoping Review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2024, 30, 653–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razia, S.; Hadibarata, T.; Lau, S.Y. A Review on Biodegradation of Bisphenol A (BPA) with Bacteria and Fungi Under Laboratory Conditions. Int. Biodeteriorat. Biodegrad. 2024, 195, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaborowska, M.; Wyszkowska, J.; Borowik, A.; Kucharski, J. Bisphenols—A Threat to the Natural Environment. Materials 2023, 16, 6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Kang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Ma, B.; Zhang, S.; Lu, G. Exploring the Distribution and Fate of Bisphenol A in an Aquatic Microcosm, Combined with a Multimedia Model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 290, 117752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolella, G.; Fabbricino, M.; Lcasci, A.; Sirakov, M.; Pontoni, L. Fate of Bisphenol A in Marine Environment: A Critical Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.; Mishra, V.K. Impact of Bisphenol A in the Environment and its Removal Through Biological Agents: A Review. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2024, 34, e22246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, H.-T.; Au, C.-K.; Chan, W. Bisphenol A in Disposable Face Masks: A Novel Human Exposure Pathway and Impact on the Aquatic Environment. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2025, 38, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter Stein, T. Does Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure Cause Human Diseases? Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejaredar, M.; Lee, Y.; Roberts, J.D.; Sauve, R.; Dewey, D. Bisphenol A Exposure and Children’s Behavior: A Systematic Review. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, F.M.; Tariq, T.; Fatima, B.; Sahar, A.; Tariq, F.; Munir, S.; Khan, S.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Sameen, A.; Zeng, X.-A.; et al. An Insight into Bisphenol A, Food Exposure and Its Adverse Effects on Health: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1047827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- vom Saal, F.S.; Vandenberg, L. Update on the Health Effectsof Bisphenol A:Overwhelming Evidence of Harm. Endocrinology 2020, 162, bqaa171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.A.; Severo, M.; Correia, D.; Carvalho, C.; Magalhães, V.; Vileia, S.; Cunha, S.; Casal, S.; Lopes, C.; Lopes, C.; et al. Methodological Approaches for the Assessment of Bisphenol A Exposure. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opinion of the SCTEE on the Risk Assessment of Bisphenol A, Human Health Part. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/committees/sct/documents/out156_en.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Kamrin, M.A.; Bisphenol, A. A Scientific Evaluation. MedGenMed 2004, 6, 7. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1435609/ (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Marçal, R.; Pacheco, M.G.; Guilherme, S. Unveiling the Nexus between Parental Exposure to Toxicants and Heritable Spermiotoxicity—Is Life History a Shield or a Shadow? Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 95, 103955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efthimiou, I.; Vlastos, D.; Ioannidou, C.; Tsilimigka, F.; Drosopoulou, E.; Mavragani-Tsipidou, P.; Potsi, F.; Gournis, D.; Antonopoulou, M. Assessment of the genotoxic potential of three novel composite nanomaterials using human lymphocytes and the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster as model systems. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Cruz, L.F.; Ponciano-Gómez, A.; Torres-Gregorio, J.T.; Ramírez-Cruz, B.G.; Vázquez-Gómez, B.; Hernández-Portilla, L.B.; Flores-Ortiz, C.M.; Dueñas-García, I.E.; Heres-Pulido, M.E.; Castañeda-Partida, L.; et al. Zearalenone Does Not Show Genotoxic Effects in the Drosophila melanogaster Wing Spot Test, but It Induces Oxidative Imbalance, Development, and Fecundity Alterations. Toxins 2023, 15, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turna Demir, F. Protective Effect of Resveratrol Against Genotoxicity Induced by Nano and Bulk Hydroxyapatite in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2022, 85, 850–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna Romano, N.; Marchetti, M.; Marangoni, A.; Leo, L.; Retrosi, D.; Rosato, E.; Fanti, L. Neuronal Progenitors Suffer Genotoxic Stress in the Drosophila Clock Mutant per. Cells 2024, 13, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.; LeBlanc, G. Endocrine Disruption in Invertebrates: A Survey of Research Progress. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13365–13369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orchard, I.; Lange, A.B. The neuroendocrine and endocrine systems in insect—Historical perspective and overview. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2024, 580, 112108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morthorst, J.E.; Holbech, H.; de Crozé, N.; Matthiessen, P.; LeBlanc, G.A. Thyroid-like hormone signaling in invertebrates and its potential role in initial screening of thyroid hormone system disrupting chemicals. Int. Environ. Ass. Manag. 2023, 19, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knigge, T.; LeBlanc, G.; Ford, A.T. A Crab Is Not a Fish: Unique Aspects of the Crustacean Endocrine System and Considerations for Endocrine Toxicology. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 587608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, M.; Dungey, S.; Lillicrap, A.; Thompson, H.; Weltje, L.; Wheeler, J.R.; Lagadic, L. Commentary: Assessing the endocrine disrupting effects of chemicals on invertebrates in the European Union. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreevidya, C.P.; Manoj Kumar, T.M.; Balakrishnan, S.; Kunjiraman, S.; Sarasan, M.; Magnuson, J.T. Puthumana Establishment of a cell culture from Daphnia magna as an in vitro model for (eco)toxicology assays: Case study using Bisphenol A as a representative cytotoxic and endocrine disrupting chemical. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 278, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, M.F.; Villar-Argaiz, M.; Vela Soria, F.; Zambrano, A.F.; Medina-Sánchez, A.; Carrillo, P. Thresholds and interactive effects of BPA-gradient and temperature on life history traits of Daphnia magna. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 355, 124186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Chen, C.; Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X. Developmental and Reproductive Impacts of Four Bisphenols in Daphnia magna. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Pereira, E.A.; Labine, L.M.; Kleywegt, S.; Jobst, K.J.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J. Metabolomics Reveals That Bisphenol Pollutants Impair Protein Synthesis-Related Pathways in Daphnia magna. Metabolites 2021, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. Aquatic toxicity and ecological risk of bisphenol B, and comparison with those of bisphenol A. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assessm. Int. J. 2024, 30, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franko, N.; Kodila, A.; Dolenc, M.S. Adverse Outcomes of the Newly Emerging Bisphenol A Substitutes. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, C.; Johnson, E.; Tupikova, A.; Anderson, J.; Tinsley, B.; Newman, J.; Alfareh, A.; Davis, A.; Rodriguez, L.; Visger, C.; et al. Bisphenol A Affects Neurodevelopmental Gene Expression, Cognitive Function and Synaptic Morphology in Drosophila melanogaster. NeuroToxicity 2022, 89, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueña-Moreno, J.; Mora, A.; Kumar, M.; Meng, X.-Z.; Mahlknecht, J. Worldwide Risk Assessment of Phthalates and Bisphenol A in Humans: The Need for Updating Guidelines. Envir. Int. 2023, 181, 108294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, G.; Yazdanfar, N.; Shariatifar, N.; Molaee-Aghaee, E.; Sadighara, P. Health Risk Assessment and Determination of Bisphenol A and Aflatoxin M1 in Infant Formula. BMC Nutr. 2025, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, P.A. Elementary Atlas of Drosophila melanogaster Mutations. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2022, 45, e20220211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Squalli, E.; Caron, M.; Loppin, B. The White Gene as a Transgenesis Marker for the Cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. G3 2024, 14, jkae235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hong, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Yan, S.; Li, Z.; Zha, J. Comprehensive assessment of the safety of bisphenol A and its analogs based on multi-toxicity tests in vitro. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 486, 136983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendra, M.; Stampar, M.; Fras, K.; Novoa, B.; Figueras, A.; Zegura, B. Adverse (geno)toxic effects of bisphenol A and its analogues in hepatic 3D cell model. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Naz, S.; Ma, Y.; Han, S.K.; Choi, Y.; Nam, H.G.; Lee, S.-J. An Overview of Comet Assay Application for Detecting DNA Damage in Aquatic Animals. Agriculture 2023, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, M.A.; Rosan, C.A.; Laslo, V.; Agud, E.; Purcarea, C.; Vicas, S.I. The Comet Assay as a Sustainable Method for Evaluating the Genotoxicity Caused by the Soluble Fraction Derived from Sewage Sludge on Diverse Cell Types, Including Lymphocytes, Coelomocytes and Allium cepa L. Cells. Sustainability 2024, 16, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, R.; Gaivão, I.; Aguado, L.; Espina, M.; García, J.; Martínez-Camblor, P.; Sierra, L.M. The Comet Assay in Drosophila: A Tool to Study Interactions between DNA Repair Systems in DNA Damage Responses In Vivo and Ex Vivo. Cells 2023, 12, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustyniak, M.; Gladysz, M.; Dziewiecka, M. The Comet assay in insects—Status, prospects and benefits for science. Mut. Res. Rev. Mut. Res. 2016, 767, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaivão, I.; Sierra, L.M.Z. Drosophila comet assay: Insights, uses and future perspectives. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 00304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Nam, H.-J.; Seo, M.; Han, S.K.; Choi, Y.; Nam, H.G.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, S. OASIS: Online Application for the Survival Analysis of Lifespan Assays Performed in Aging Research. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Macro, J.; Huggins, B.J.; Mishra, D.; Martin, D.; Kannan, K. Rogina Extended lifespan in female Drosophila melanogaster through late-life calorie restriction. GeroScience 2024, 46, 4017–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, B.J.; Hoffmann, J.M. Microbiome Transplants May Not Improve Health and Longevity in Drosophila melanogaster. Biol. Open 2025, 14, bio061745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, T.N.; Schonherz, A.A.; Rohde, P.D.; Sorensen, J.G.; Loeschke, V. Selection for stress tolerance and longevity in Drosophila melanogaster have strong impacts on microbiome profiles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, O.L.; Villa, J.A.; Kamalakkannan, A.; James, E.; Hoffman, J.; Lyu, Y. Stochasticity in dietary restriction-mediated lifespan outcomes in Drosophila. GeroScience 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Albassam, M. Analysis and Allocation of Cancer-Related Genes Using Vague DNA Sequence Data. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 858005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M. “Statistical significance” and other important considerations in genotoxicity safety testing. Mut. Res. Gen. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2023, 888, 503627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Core, A.C.; La Merrill, M.A.; Partisaul, H.; Sargis, R.M. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Threats to Human Health. Pesticides, Plastics, Forever Chemicals and Beyond; Endocrine Society and IPEN: Austin, TX, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Reincke, M.; Arlt, W.; Damdimopoulou, P.; Kohrle, J.; Bertherat, J. Endocrine disrupting chemicals are a threat to hormone health: A commentary on behalf of the ESE. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 187–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Liu, P.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J. The adverse role of endocrine disrupting chemicals in the reproductive system. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1324993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, W.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ding, J.; Han, Y.; Zhang, H. Paternal exposures to endocrine-disrupting chemicals induce intergenerational epigenetic influences on offspring: A review. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Ramirez, S.A.; Ho, S.-M.; Leung, Y.K. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: A Looming Threat to Current and Future Generations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, K.R.; Gajanayakage, R.H.; Connolly, C.; Blache, D. Ancestral lineages of dietary exposure to an endocrine disrupting chemical drive distinct forms of transgenerational subfertility in an insect model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Gerona, R.G.; Kannan, K.; Taylor, J.A.; van Breemen, R.B.; Dickenson, C.A.; Liao, C.; Yuan, Y.; Newbold, R.R.; Padmanabhan, V.; et al. A round robin approach to the analysis of bisphenol a (BPA) in human blood samples. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Cui, C.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, K. The chronic toxicity of bisphenol A to Caenorhabditis elegans after long-term exposure at environmentally relevant concentrations. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlı, E.; Ünlü, H. Developmental and Reproductive Effects of Bisphenol A Bpa in Drosophila Melanogaster. Hacet. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 40, 61–68. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/hjbc/issue/61880/926040 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Weiner, A.K.; Ramirez, A.; Zintel, T.; Rose, R.W.; Wolff, E.; Parker, A.L.; Bennett, K.; Johndreau, K.; Rachfalski, C.; Zhou, J.; et al. Bisphenol A Affects Larval Growth and Advances the Onset Metamorphosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 101, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvan, K.; Padmavathy, P.; Velu, R.; Robinson, J.; Samraj, A.; Ranjeet, K. Evidence of microplastics in the polychaete worm (capitellids—Capitella capitata) (Fabricicus, 1780) along Thoothukudi region. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlmann, J.; Schulte-Oehlmann, U.; Bachmann, J.; Jeyashakila, R.; Aanand, S.; Kutty, R. Bisphenol A Induces Superfeminization in the Ramshorn Snail Marisa cornuarietis (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia) at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos Musachio, E.A.; Machado Araújo, S.; Cardoso Bartolotto, V.A.; de Freitas Couto, S.; Dahleh, M.M.M.; Poetini, M.R.; Jardim, E.F.; Barreto Meichtry, L.; Ramborgher, B.P.; Roehrs, R.; et al. Bisphenol A exposure is involved in the development of Parkinson like disease in Drosophila melanogaster. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Simon, A.F.; Chauhan, V.; Chauhan, A. Effect of bisphenol A on Drosophila melanogaster behavior—A new model for the studies on neurodevelopmental disorders. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 284, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.; Cui, M.; Zhou, D.; Pan, X.; Xie, Y.; Wu, X.; Liang, X.L.; Zhang, H.; Song, W. Adulthood bisphenol A exposure induces anxiety in male mice via downregulation of alpha-1D adrenergic receptor in paraventricular thalamus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrado, A.C.; Salaverry, L.S.; Macchi, R.; Bessone, M.L.; Mangone, F.M.; Castro, M.; Canellada, A.M.; Rey-Roldan, E. Immunomodulatory effect of dopamine in human keratinocytes and macrophages under chronical bisphenol—A exposure conditions. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimal, A.; Hooversmith, J.M.; Al Hamsi, M.H.; Holmes, P.V.; MohanKumar, P.S.; MohanKumar, S.M.J. Prenatal Exposure to Bisphenol A and/or Diethylhexyl Phthalate Impacts Brain Monoamine Levels in Rat Offspring. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 1036–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewar, S.; Auinger, P.; Braun, J.M.; Lamphear, B.; Yolton, K.; Epstein, J.N.; Ehrlich, S.; Froehlich, T. Association of Bisphenol A exposure and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in a national sample of U.S. children. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogocka, M.; Lewusz-Butkiewicz, K.; Marek, E.; Mazurek/Mochol, M.; Lagocka, R. The toxicity of Bis-GMA, a basic monomer of the dental composite’s organic matrix—A narrative review. Pomeran J. Life Sci. 2023, 69, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Folgar, R.; Sabroso, C.; Cañas-Portilla, A.I.; Torres-Ruiz, M.; Gonzalez-Caballero, M.C.; Dorado, H.; Velasco, I.; Morelas, M. DNA damage and molecular level effects induced by polystyrene (PS) nanoplastics (NPs) after Chironomus riparius (Diptera) larvae. Chemosphere 2024, 346, 140552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karzi, V.; Ozcagli, E.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Vakonaki, E.; Fragkiadoulaki, I.; Kalliantasi, A.; Chalkiadaki, C.; Alegakis, A.; Stivaktakis, P.; Karzi, A.; et al. DNA Damage Estimation after Chronic and Combined Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors: An In Vivo Real-Life Risk Simulation Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.; de la Fuente, M.; Folgar, R.M. BPA and its analogues (BPS and BPF) modify the expression of genes involved in the endocrine pathway and apoptosis and a multi drug resistance gene of the aquatic midge Chironomus riparius (Diptera). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Wen, D.; Mu, R. Exposure to Bisphenol A Induced Oxidative Stress, Cell Death and Impaired Epithelial Homeostasis in the Adult Drosophila melanogaster Midgut. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 248, 114285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesanoye, O.A.; Abolaji, O.A.; Faloye, T.R.; Olaoye, H.O.; Adedara, A.O. Luteolin/Supplemented Diets Ameliorates Bisphenol A-Induced Toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 142, 111478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Mahendran, T.S.; Meenakshisundaram, A.; Christopher, R.V.; Dan, P.; Sundararajan, V.; Jana, N.; Venkatasubbu, D.; Mohideen, S.S. Role of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Improving Oxidative Stress and Developmental Delays in Drosophila melanogaster as an In Vivo Model for Bisphenol A Toxicity. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Musachio, E.A.; de Freitas Couto, S.; Rosula Poetini, M.; Christopher, R.V.; Dan, P.; Sundararajan, V.; Jana, N.; Venkatasubbu, D.; Mohideen, S.S. Bisphenol A Exposure During the Embryonic Period: Insights into Dopamine Relationship and Behavioral Disorders in Drosophila melanogaster. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, U.; Tinsley, B.; Sen, Y.; Stein, J.; Palacios, Y.; Ceballos, A.; Welch, C.; Nzenkue, K.; Penn, A.; Murphy, L.; et al. Exposure to Bisphenol A Differentially Impacts Neurodevelopment and Behavior in Drosophila Melanogaster from Distinct Genetic Backgrounds. Neurotoxicology 2021, 82, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.; Pallab, P.; Das, D.; Ghosh, S. Endocrine-Disrupting Plasticizer Bisphenol A Exposure Causes Changes in Behavioral Attributes in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 2020, 12, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhan, M.J.; Kharomah, S.; Kharomah, S.; Zahrah, N.A.; Maghfiroh, H.; Fahmi, M.I.N.; Zubaidah, S.; Fauzi, A. Negative Geotaxis Assay in Three Drosophila Strains Consuming Bisphenol A: Duration and Number of Climbing Successes. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 1439, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishburn, J.L.A.; Larson, H.L.; Nguyen, A.; Welch, C.; Moore, T.; Penn, A.; Newman, J.; Mangino, A.; Widman, E.; Ghobashy, R.; et al. Bisphenol F Affects Neurodevelopmental Gene Expression, Mushroom Body Development and Behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Neurotoxicology Teratol. 2024, 102, 107331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, O.; Aquilino, M.; Sanchez-Arguello, P.; Planello, R. The BPA-substitute Bisphenol S Alters the Transcription of Gene Related to Endocrine Stress Response and Biotransformation Pathways in the Aquatic Midge Chironomus Riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Sun, M. Developmental Neurotoxic Effects of Bisphenol A and its Derivatives in Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 260, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, A.T.; Lemos, B. Interaction between Bisphenol A and Dietary Sugar Affects Global Gene Transcription in Drosophila melanogaster. Genom. Data 2022, 2, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, L.; Saini, S.; Thakur, R.S.; Dhowdhuri, D.K.; Gautam, N.K. Single and Combined Effect of Bisphenol A with High Sucrose Diet on the Diabetic and Renal Tubular Dysfunction Phenotypes in Drosophila melanogaster. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 96, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maczka, W.; Grabarczyk, M.; Winska, K. Can Antioxidants Reduce the Toxicity of Bisphenol? Antioxidants 2022, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirasanagandla, S.R.; Al-Huseini, I.; Sakr, H.; Moqadass, M.; Das, S.; Juliana, N.; Abu, I.F. Natural Products in Mitigation of Bisphenol A Toxicity: Future Therapeutic Use. Molecules 2022, 27, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Condition | Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fisher’s Exact Test | |||||
| Maximal Longevity at 25% | Maximal Longevity at 50% | Maximal Longevity at 75% | Maximal Longevity at 90% | ||
| F0 | Control vs. 0.5 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Control vs. 1 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 2 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 5 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 10 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| F1-N | Control vs. 0.5 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Control vs. 1 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 2 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 5 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 10 mM | * | ns | ns | ns | |
| F1-T | Control vs. 0.5 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Control vs. 1 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 2 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 5 mM | ns | * | *** | ns | |
| Control vs. 10 mM | ns | ns | *** | ns | |
| F2-TN | Control vs. 0.5 mM | ns | ** | ns | ns |
| Control vs. 1 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 2 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 5 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 10 mM | *** | ns | ns | ns | |
| F2-TT | Control vs. 0.5 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Control vs. 1 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 2 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 5 mM | ns | * | ns | ns | |
| Control vs. 10 mM | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Condition | Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fisher’s Exact Test | |||||
| Maximal Longevity at 25% | Maximal Longevity at 50% | Maximal Longevity at 75% | Maximal Longevity at 90% | ||
| F1-N vs. F1-T | Control F1-N vs. Control F1-T | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| 0.5 mM F1-N vs. 0.5 mM F1-T | * | ns | ns | ns | |
| 1 mM F1-N vs. 1 mM F1-T | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| 2 mM F1-N vs. 2 mM F1-T | * | ns | ns | ns | |
| 5 mM F1-N vs. 5 mM F1-T | * | * | *** | ns | |
| 10 mM F1-N vs. 10 mM F1-T | *** | ns | ** | ns | |
| F2-TN vs. F2-TT | Control F2-TN vs. Control F2-TT | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| 0.5 mM F2-TN vs. 0.5 mM F2-TT | ns | *** | ns | ns | |
| 1 mM F2-TN vs. 1 mM F2-TT | ns | * | * | ns | |
| 2 mM F2-TN vs. 2 mM F2-TT | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| 5 mM F2-TN vs. 5 mM F2-TT | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| F1-T vs. F2-TT | Control F1-T vs. Control F2-TT | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| 0.5 mM F1-T vs. 0.5 mM F2-TT | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| 1 mM F1-T vs. 1 mM F2-TT | ns | * | * | ns | |
| 2 mM F1-T vs. 2 mM F2-TT | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| 5 mM F1-T vs. 5 mM F2-TT | ns | *** | ** | ns | |
| BPA Concentration | Observed Spots/Analyzed Eyes (n) | Number of Spots per 100 Eyes (%) | Results Obtained by X2 Test for Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 22/748 | 2.941 | |
| 1 mM | 25/710 | 3.521 | i |
| 10 mM | 19/364 | 5.220 | - |
| 20 mM | 45/810 | 5.556 | w+ |
| 50 mM | 31/732 | 4.235 | i |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaivão, I.; Santos, R.A.; Morozova, T.V.; Tkach, V.V. Biological and Behavioural Effects of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure: An In Vivo Study in Drosophila melanogaster. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5588. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105588
Gaivão I, Santos RA, Morozova TV, Tkach VV. Biological and Behavioural Effects of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure: An In Vivo Study in Drosophila melanogaster. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(10):5588. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105588
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaivão, Isabel, Rita António Santos, Tetiana V. Morozova, and Volodymyr V. Tkach. 2025. "Biological and Behavioural Effects of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure: An In Vivo Study in Drosophila melanogaster" Applied Sciences 15, no. 10: 5588. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105588
APA StyleGaivão, I., Santos, R. A., Morozova, T. V., & Tkach, V. V. (2025). Biological and Behavioural Effects of Bisphenol A (BPA) Exposure: An In Vivo Study in Drosophila melanogaster. Applied Sciences, 15(10), 5588. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15105588








