Abstract
This study investigates the performance of different maximum power point tracking (MPPT) methods in a photovoltaic (PV) energy system, focusing on Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), reinforcement learning (RL), and conventional MPPT approaches. The primary objective is to evaluate the efficiency of these methods in maximizing PV energy production under varying environmental conditions, while also analyzing their impact on battery state-of-charge (SOC) and load management. The system is modeled using MATLAB, incorporating real-world climate data from Ankara, including monthly solar irradiance, temperature, and sunlight hours. The ANN-based MPPT employs a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) to improve PV efficiency, while the RL-based MPPT utilizes Q-learning to optimize energy production. A conventional MPPT method serves as a baseline for comparison. Simulations are conducted on an hourly and monthly basis, considering a 7.5 kW PV system with a 20 kWh battery system. The results indicate that both ANN and RL methods outperform the conventional MPPT in terms of annual energy production, with RL achieving the highest efficiency gains. Additionally, the ANN and RL methods demonstrate improved battery SOC management, reducing energy losses. The study concludes that advanced MPPT techniques, particularly RL, offer significant potential for enhancing PV system performance, making them viable solutions for renewable energy optimization.
1. Introduction
The global transition toward renewable energy sources has accelerated in recent years due to the increasing demand for sustainable energy and the urgent need to mitigate climate change. Among renewable energy technologies, photovoltaic (PV) systems have emerged as a leading solution due to their scalability, environmental benefits, and decreasing costs [1,2,3]. PV systems convert solar energy into electricity using semiconductor materials, making them a clean and abundant energy source. However, the intermittent nature of solar energy, influenced by factors such as solar irradiance, temperature, and weather conditions, poses challenges to the efficiency and reliability of PV systems [4,5,6].
The efficiency of a PV system is influenced by several factors, including solar irradiance, temperature, shading, and the electrical characteristics of the load. To maximize energy production, PV systems must operate at their maximum power point (MPP), which varies with environmental conditions [7,8]. To address this challenge, maximum power point tracking (MPPT) methods have been developed to maximize the energy output of PV systems by dynamically adjusting their operating points under varying environmental or load conditions [9]. MPPT algorithms can be broadly classified into conventional methods, Artificial Neural Network (ANN)-based methods, and machine learning (ML)-based methods.
The Perturb and Observe (P and O) method perturbs the operating point of the PV system and observes the resulting change in power. If the power increases, the perturbation continues in the same direction; otherwise, the direction is reversed [7]. While P and O is simple and effective, it may fail to track the MPP accurately under rapidly changing conditions [10]. The Incremental Conductance (IC) method calculates the derivative of the power with respect to voltage to determine the direction of the MPP. It offers better accuracy than P and O but requires more computational resources [11]. The Constant Voltage (CV) method assumes that the MPP occurs at a fixed voltage, typically around 70–80% of the open-circuit voltage. While this method is easy to implement, it is less accurate and may not adapt well to varying conditions [12].
Conventional MPPT methods, such as P and O and IC, have been widely used due to their simplicity, ease of implementation, and effectiveness under steady-state conditions. However, these methods often struggle to adapt to rapidly changing environmental conditions. They also have limitations when it comes to handling the nonlinear and time-varying characteristics of PV systems. This has led to the development of advanced MPPT methods based on ML and artificial intelligence (AI). Recent advancements in AI and ML have introduced novel approaches, such as ANN and reinforcement learning (RL), which offer improved adaptability and efficiency in MPPT applications [13].
Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) uses fuzzy logic rules to determine the optimal operating point of the PV system. It is robust and adaptive but requires careful tuning of the membership functions and rules [14]. ANNs are computational models inspired by the structure and function of biological neural networks. They are capable of learning complex patterns and relationships from data, making them suitable for MPPT applications in PV systems [15]. ANN-based MPPT methods typically involve training a neural network to perform the MPPT based on input features such as solar irradiance, temperature, and load conditions. Several studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of ANN-based MPPT methods. For instance, ref. [16] proposed an ANN-based MPPT algorithm that achieved higher accuracy and faster convergence compared to traditional methods. Similarly, ref. [17] developed a hybrid ANN–Fuzzy MPPT method that combined the adaptability of ANN with the robustness of fuzzy logic, resulting in improved performance under dynamic conditions. Advantages of ANN-based MPPT methods include their ability to handle nonlinearities, adapt to changing conditions, and improve the overall efficiency of PV systems. However, their implementation requires sufficient training data, computational resources, and careful tuning of the network architecture [18].
RL is a machine learning paradigm that enables an agent to learn optimal actions through interaction with its environment. In the context of MPPT, the RL agent learns to adjust the operating point of the PV system to maximize energy output. RL-based MPPT methods are particularly effective in handling dynamic and uncertain environments, as they do not rely on predefined models or assumptions [19]. Recent studies have highlighted the potential of RL-based MPPT methods. For instance, ref. [20] proposed a Q-learning-based MPPT algorithm that outperformed traditional methods in terms of tracking accuracy and energy efficiency. Another study [21] employed a deep reinforcement learning approach, which utilized a deep neural network to approximate the Q-function, enabling the agent to handle high-dimensional state spaces and complex PV system dynamics. Key advantages of RL-based MPPT methods include their adaptability, model-free nature, and ability to optimize long-term performance. However, their implementation can be computationally intensive and may require careful design of the reward function and exploration strategy [22]. The performance of MPPT methods can be evaluated based on different criteria such as tracking accuracy, convergence speed, computational complexity, and adaptability to changing conditions, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summarizes the key characteristics of the different MPPT methods.
The integration of advanced MPPT methods, such as ANN and RL, has significantly improved the performance of PV systems by addressing the limitations of traditional approaches [12]. ANN-based methods excel in handling nonlinearities and adapting to changing conditions, while RL-based methods offer unparalleled adaptability and long-term optimization [23,24]. However, the implementation of these methods requires careful consideration of computational resources, training data, and system design. In real environments, data quality can decrease significantly due to factors such as variable weather conditions, sensor failures, and photovoltaic panel aging. This can negatively affect both the performance of MPPT algorithms and the accuracy of AI-based models [25].
Weather conditions such as partial shading, rain, snow, and dust cause sudden changes in solar radiation and temperature data. These changes can cause noise and deviations in sensor measurements [26]. Sensor failures can produce incorrect or incomplete data, leading to the model making incorrect decisions. Panel aging leads to a decrease in efficiency over time, causing models trained on past data to no longer accurately reflect the current conditions [27]. Such data quality problems reduce the generalization ability and reliability of the model, especially in data-driven methods such as ANN and RL. In addition, the system’s energy production estimate and MPPT performance may decrease. To solve these problems, regular maintenance and calibration of the sensors in the system should be performed, and anomaly detection and data cleaning algorithms should be applied. Models should be retrained periodically with current and diverse data, and physical changes such as panel aging should be taken into account in the training of the model. These measures will increase the reliability and efficiency of the system by reducing the negative effects of data quality degradation in a real-world environment [28,29].
For traditional methods, finding the MPPT of photovoltaic systems under partial shading conditions is quite challenging because multiple local maxima occur. There are many studies in the literature which consider partial shading conditions. In one study, a memetic reinforcement learning-based MPPT algorithm was developed, and high tracking accuracy was achieved under partial shading [30]. In another study, the MPPT performance was enhanced by a dynamic leader-based collective intelligence approach and fast and stable tracking was achieved [31]. In addition, it was shown in another study that the global maximum could be effectively found under partial shading conditions using a biologically inspired memetic salp swarm algorithm [32]. These advanced methods significantly increase the efficiency of PV systems. MPPT techniques based on deep learning (DL)-RL and ANN-MLP quickly adapt to environmental changes under partial shading conditions, find the global maximum power point more effectively and increase system efficiency. This results in higher energy production and more stable system performance compared to traditional methods.
In the study, ANN, RL, and conventional MPPT methods are designed and compared and their efficiency is analyzed in a system including PVs, energy storage, and load. The system is modeled using MATLAB, incorporating real-world climate data from Ankara, including monthly solar irradiance, temperature, and sunlight hours. The ANN-based MPPT uses a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) to increase PV efficiency, whereas the RL-based MPPT optimizes energy production by Q-learning. The baseline for comparison is a traditional MPPT approach. A 7.5 kW PV system with a 20 kWh battery system is the subject of hourly and monthly simulations.
2. Designed Photovoltaic System
The designed system is a PV energy generation and battery-based energy storage system tailored for the climatic conditions of Ankara, Turkey. Ankara’s geographical location, characterized by a continental climate with significant seasonal variations in solar irradiance and temperature, makes it an ideal case study for evaluating the performance of advanced MPPT methods. The system integrates a PV array, a battery energy storage system (BESS), and a load, with advanced control algorithms to optimize energy generation, storage, and utilization. The primary objective of the system is to maximize energy efficiency while ensuring reliable power delivery to the load.
The system is designed to operate autonomously, leveraging three MPPT methods: ANN-based MPPT, RL-based MPPT, and a conventional MPPT method for comparison. The system’s performance is evaluated on an hourly and monthly basis, considering real-world environmental data from Ankara, including solar irradiance, temperature, and sunlight hours.
The block diagram of the designed system is shown in Figure 1. It illustrates the interaction between the PV system, BESS, the load, and the control algorithms. The system designed in MATLAB consists of three main components: PV array, BESS, and load. Each component is described in detail below, along with the parameters used in the design.
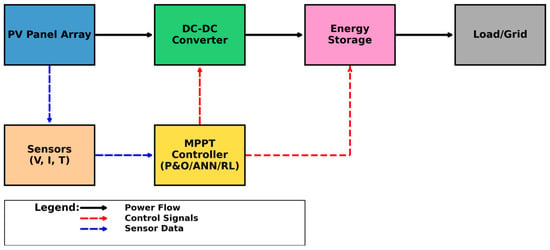
Figure 1.
Block diagram of the designed PV System.
2.1. Photovoltaic System
The PV array is the primary energy generation unit of the system. It consists of 30 solar panels, each with a rated power of 250 W, resulting in a total installed capacity of 7.5 kW. The PV array is designed to operate under varying environmental conditions, with its performance influenced by solar irradiance, temperature, and shading. The specifications of the PV system are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Parameters of the PV array.
Thirty photovoltaic panels are connected in series in the system. A basic diagram of the connection between these panels is presented in Figure 2.
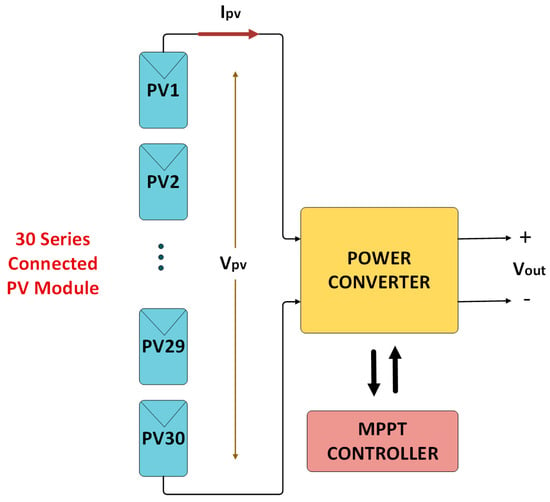
Figure 2.
The connection diagram of photovoltaic panels.
The PV array’s output is modeled using the single diode model, which accounts for the nonlinear relationship between voltage, current, and power. The system dynamically adjusts the operating point of the PV array to ensure it operates at its MPP under varying conditions.
2.2. Battery Energy Storage System (BESS)
The BESS is designed to store excess energy generated by the PV array during peak sunlight hours and supply power to the load during periods of low solar irradiance or at night. The battery system is critical for ensuring the reliability and stability of the system. The specification of the BESS is given in Table 3.

Table 3.
Parameters of the battery.
The battery’s charging and discharging processes are managed by advanced control algorithms to minimize energy losses and prolong the battery’s lifespan. The state of charge (SOC) is continuously monitored and updated based on the net energy flow in the system.
2.3. Load
The load represents the energy demand of the system, which is assumed to be constant at 2 kW throughout the simulation. This simplification allows for a focused analysis of the energy generation and storage dynamics. The details of the load are given in Table 4.

Table 4.
Parameters of the load.
The load is connected to the system through a power management unit, which ensures that the energy demand is met either by the PV array or the battery, depending on the availability of solar energy.
2.4. Environmental Data
The designed system includes real-world environmental data for Ankara province using PVGIS (Photovoltaic Geographic Information System) monthly averages of solar irradiation, temperature and sunlight hours. These parameters are critical for accurately modeling the performance of the PV array and optimizing the MPPT algorithms. Table 5 below summarizes the monthly averages of these environmental parameters.

Table 5.
Environmental parameters.
Table 5.
Environmental parameters.
| Month | Solar Irradiance (kWh/m2/day) | Temperature (°C) | Sunlight Hours (hours/day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 1.9 | 0.3 | 3.1 |
| February | 2.7 | 2.1 | 4.2 |
| March | 4.0 | 6.7 | 6.1 |
| April | 5.4 | 12.1 | 8.1 |
| May | 6.5 | 17.2 | 10.0 |
| June | 7.3 | 21.5 | 11.0 |
| July | 7.5 | 23.5 | 11.2 |
| August | 6.8 | 23.0 | 10.5 |
| September | 5.4 | 18.5 | 8.5 |
| October | 3.8 | 12.5 | 6.2 |
| November | 2.4 | 6.0 | 4.0 |
| December | 1.8 | 1.0 | 3.1 |
- Solar Irradiance:
- ○
- Solar irradiance directly impacts the energy generation capacity of PV panels.
- ○
- In Ankara, solar irradiance is lowest during the winter months (1.8–1.9 kWh/m2/day in December and January) and peaks during the summer months (7.3–7.5 kWh/m2/day in June and July).
- Temperature:
- ○
- The efficiency of PV cells is temperature-dependent, with higher temperatures typically reducing performance.
- ○
- In Ankara, temperatures range from an average of 0.3 °C in January to 23.5 °C in July.
- Sunlight Hours:
- ○
- Daily sunlight hours determine the duration of energy generation by PV systems.
- ○
- In Ankara, sunlight hours are shortest in winter (3.1 h/day in December and January) and longest in summer (11.0–11.2 h/day in June and July).
2.5. Operation of the System
The operation of the system is governed by the interaction between the PV array, the battery system, and the load, with the MPPT algorithms playing a central role in optimizing energy generation. The system operates via the following steps.
2.5.1. Energy Generation
The PV array generates electricity based on the available solar irradiance and temperature. The output power of the PV array is calculated using the following equation:
where Vmmp and Immp are the voltage and current at the MPP, respectively. The MPPT unit continuously adjusts the operating point of the PV array to maximize Ppv.
2.5.2. Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
The MPPT unit employs three different algorithms to optimize the energy output of the PV array:
ANN-Based MPPT: Based on input characteristics like temperature, load power, and solar irradiation, the ANN model forecasts the MPP. The operating point of the PV array is modified based on the anticipated MPP.
RL-Based MPPT: The RL agent learns the optimal operating point through interaction with the environment. The Q-learning algorithm is used to update the Q-table based on the reward received for each action.
Conventional MPPT: The P and O method is used as a baseline for comparison. The operating point is perturbed, and the resulting change in power is observed to determine the direction of the next perturbation, where VMPP and IMPP are the voltage and current at the MPP, respectively. The MPPT unit continuously adjusts the operating point of the PV array to maximize PPV.
2.5.3. Energy Storage Management
The SOC manager monitors the state of charge of the battery and determines whether the battery should be charged or discharged. The following conditions are considered:
- Charging: if PPV > Pload, the excess energy is used to charge the battery, provided the SOC is below the maximum limit.
- Discharging: if PPV < Pload, the battery supplies the deficit, provided the SOC is above the minimum limit.
The SOC is updated by using Equation (2):
where is the net power flow, is the battery efficiency, and is the battery capacity.
2.5.4. Load Management
The power flow controller ensures that the load demand is met at all times. The following scenarios are considered:
Surplus energy: if PPV > Pload, the excess energy is stored in the battery or exported to the grid (if applicable).
Deficit energy: if PPV < Pload, the deficit is supplied by the battery.
No solar energy: during nighttime or periods of low irradiance, the battery is the sole source of power for the load.
2.5.5. Performance Evaluation
The system’s performance is evaluated based on the following metrics:
Energy efficiency: the ratio of useful energy output to the total energy input.
Battery utilization: the percentage of time the battery operates within its optimal SOC range.
MPPT accuracy: the ability of the MPPT algorithms to track the true MPP under varying conditions.
Load reliability: the percentage of time for which the load demand is fully met.
The designed system integrates advanced MPPT algorithms, a robust energy storage system, and a reliable load management strategy to optimize energy generation and utilization in Ankara’s climatic conditions. The system’s modular design and adaptability make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from residential to industrial energy systems.
3. Detailed Analysis of Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Methods
The optimization of energy production in PV systems is critical for enhancing system efficiency and minimizing energy losses. In this context, MPPT algorithms are developed to ensure that PV panels operate at their MPP. This section provides a detailed analysis of the three MPPT methods used in the designed system: ANN-based, RL-based, and conventional MPPT. A summary of the inputs and layers used for MPPT systems is presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Summary of inputs and layers.
The three MPPT methods used in the MATLAB-designed system have distinct characteristics and advantages:
- ANN-based MPPT method: Provides high accuracy and adaptability but requires a time-intensive training process.
- RL-based MPPT method: Continuously learns and adapts to environmental changes but has a slower initial learning phase.
- Conventional MPPT method: Simple and cost-effective but less effective under rapidly changing conditions. It does not have any adaptation ability.
Each method is tailored to optimize the energy generation of PV systems under different scenarios, contributing to the overall efficiency and reliability of the system. The characteristics, algorithms, working principles, and design details of each method are explained below.
3.1. ANN (Artificial Neural Network)-Based MPPT Method
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are machine learning methods inspired by the working principles of the human brain. ANN-based MPPT algorithms are used to adapt to the complex and dynamic nature of PV systems. This method learns the relationship between environmental variables (e.g., solar irradiance and temperature) and the output power of the PV system to predict the maximum power point.
- Advantages:
- ○
- Highly accurate predictions.
- ○
- Excellent adaptability to environmental changes.
- Disadvantages:
- ○
- The training process is time-consuming.
- ○
- The performance depends on the quality of the training dataset.
3.1.1. Algorithm and Working Principle
The ANN-based MPPT algorithm uses a multi-layer perceptron (MLP) architecture. The structure includes the following:
- Input Layer: Takes environmental and system parameters as inputs, such as the following:
- ○
- Solar irradiance.
- ○
- Temperature.
- ○
- Load power.
- Hidden Layers: Processes input data through weights and activation functions. These layers learn the nonlinear relationships in the system.
- Output Layer: predicts the voltage or current at the MPP.
The ANN is trained using historical data, and the learning process minimizes the error function to optimize the model. Once trained, the ANN can predict the maximum power point under various environmental conditions.
3.1.2. Design Details
The design of the ANN-based MPPT algorithm is structured to effectively model the nonlinear and dynamic behavior of PV systems. The following subsections detail the architectural and operational aspects of the neural network used for MPPT.
- Inputs
The input layer of the ANN is designed to receive real-time and relevant environmental and system parameters that directly influence the PV system’s output. These inputs include the following:
Solar irradiance: This parameter represents the intensity of sunlight on the surface of the PV panels, typically measured in W/m2. It is a primary factor affecting the power generation capability of the PV system.
Temperature: The ambient temperature, usually measured in degrees Celsius, impacts the efficiency and output characteristics of PV modules. Higher temperatures generally reduce the voltage output of PV cells.
Load power: This is the instantaneous power demand from the load connected to the PV system. Including load power as an input allows the ANN to consider the system’s operational context when predicting the MPP.
All input data are normalized before being fed into the network to ensure stable and efficient training.
- Hidden Layers
The hidden layer is the core computational component of the ANN, which is responsible for learning the complex, nonlinear relationships between the input variables and the MPP.
Number of layers: The network utilizes a single hidden layer, which is sufficient for capturing the essential nonlinearities in most MPPT applications.
Number of neurons: The hidden layer consists of 10 neurons. This number is chosen as a balance between model complexity and computational efficiency, ensuring that the network can learn intricate patterns without overfitting.
Activation function: Each neuron in the hidden layer uses a sigmoid activation function. The sigmoid function introduces nonlinearity and allows the network to model complex relationships between inputs and outputs.
- Training Process
The effectiveness of the ANN-based MPPT algorithm depends heavily on the quality of the training process.
Training data: The network is trained using a comprehensive dataset that includes historical records of solar irradiance, temperature, and load power, along with the corresponding MPPs. The dataset should cover a wide range of environmental conditions to ensure robust generalization.
Error function: The Mean Squared Error (MSE) is used as the loss function during training, defined as Equation (3):
where yi is the actual value and yi′ is the predicted value.
Optimization: The network’s weights are updated using the backpropagation algorithm, which computes the gradient of the error function with respect to each weight and adjusts them to minimize the overall error. An appropriate learning rate is selected to ensure convergence without overshooting.
- Implementation Considerations
Data preprocessing: input data normalization and, if necessary, feature scaling are performed to improve training stability and convergence speed.
Overfitting prevention: techniques such as early stopping or regularization may be employed to prevent overfitting, especially if the training dataset is limited.
Deployment: once trained, the ANN model is embedded into the MPPT controller, where it processes real-time sensor data and outputs the optimal operating point for the PV system.
This detailed design ensures that the ANN-based MPPT algorithm can adapt to varying environmental conditions and provide accurate, real-time predictions for maximum power extraction from PV systems.
3.2. RL (Reinforcement Learning)-Based MPPT Method
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a machine learning method in which an agent (controller) learns from its interactions with the environment. RL-based MPPT algorithms are used to discover and maintain the MPP of PV systems. This method continuously optimizes itself based on environmental conditions.
- Advantages:
- ○
- Rapid adaptation to environmental changes.
- ○
- Continuous learning capability.
- Disadvantages:
- ○
- A slow learning process at the beginning.
- ○
- The reward function must be carefully designed.
3.2.1. Algorithm and Working Principle
The RL-based MPPT algorithm typically uses the Q-learning method. The main steps are as follows:
State: represents the current state of the PV system (e.g., solar irradiance and temperature).
Action: represents the decision to adjust the operating point of the PV system (e.g., voltage or current adjustment).
Reward: a positive reward is given when the maximum power point is approached.
Q-value update: The agent updates the Q values according to the reward and the new state, as in Equation (4):
where α is the learning rate, r is the reward, γ is the discount factor, s is the current state, a is the current action, s′ is the next state, and a′ is a possible next action.
The RL algorithm selects the best action based on the Q-values and ensures that the PV system operates at the maximum power point.
3.2.2. Design Details
The Q-learning-based MPPT algorithm is designed to enable the PV system to autonomously learn the optimal operating strategy for maximum power extraction under varying environmental conditions. The following sections elaborate on the key components and operational details of the Q-learning approach.
- Inputs (State)
The state space of the Q-learning agent is defined by the environmental variables that significantly affect the PV system’s performance:
Solar irradiance: This parameter quantifies the intensity of sunlight incident on the PV panels, typically measured in W/m2. It is a primary factor influencing the power output of the PV system.
Temperature: The ambient temperature, measured in degrees Celsius, impacts the efficiency and voltage characteristics of the PV modules. Both irradiance and temperature are discretized into finite levels to form a manageable state space for the Q-learning algorithm.
The combination of these two parameters at any given time represents the current state of the PV system.
- Action Space
The action space defines the set of possible actions the agent can take to adjust the operating point of the PV system:
Voltage or current adjustments: At each decision step, the agent can choose to increase, decrease, or maintain the operating voltage (or current) of the PV array. These discrete actions allow the agent to explore different operating points and move towards the MPP.
The granularity of the action space (i.e., the step size for voltage or current adjustments) is chosen to balance the trade-off between search resolution and computational complexity.
- Q-Table
The Q-table is the core data structure in the Q-learning algorithm:
State-action value storage: the Q-table is a two-dimensional matrix where each entry Q(s,a) represents the expected cumulative reward for taking action a in state s.
Dynamic updates: After each action, the Q-value for the corresponding state–action pair is updated using the Q-learning update rule. Equation (4) is used for this. Over time, the Q-table converges to represent the optimal policy for selecting actions that maximize the long-term reward (i.e., power output).
- Reward Function
The reward function guides the learning process by providing feedback on the effectiveness of each action:
Positive rewards: The agent receives a positive reward when its action results in an increase in the output power, indicating movement towards the MPP.
Negative or zero rewards: If the action leads to a decrease or no change in power output, the reward is negative or zero, discouraging the agent from repeating such actions.
- Implementation Considerations
State and action discretization: Both the state and action spaces are discretized to ensure the Q-table remains computationally manageable. The number of discrete levels is chosen based on the desired balance between accuracy and memory requirements.
Exploration vs. exploitation: An exploration strategy, such as epsilon-greedy, is used to balance the trade-off between exploring new actions and exploiting known high-reward actions.
Initialization: the Q-table is typically initialized with zeros or small random values, allowing the agent to learn optimal values through interaction with the environment.
Convergence: the learning rate and discount factor are carefully selected to ensure stable and efficient convergence of the Q-values.
This detailed design enables the Q-learning-based MPPT algorithm to adaptively and autonomously optimize the operating point of the PV system, ensuring maximum power extraction under dynamic environmental conditions.
3.3. Conventional MPPT Method
Conventional MPPT methods have been used in PV systems for many years as simple and effective algorithms. These methods optimize the operating point of the PV system based on direct measurements of environmental conditions.
- Advantages:
- ○
- Simple and cost-effective.
- ○
- Low hardware requirements.
- Disadvantages:
- ○
- May become unstable under rapidly changing environmental conditions.
- ○
- Can miss the MPP.
- ○
- A trade-off between the tracking speed and steady-state oscillation is required.
3.3.1. Algorithm and Working Principle
The conventional MPPT method used in the design is the Perturb and Observe (P and O) algorithm.
3.3.2. Design Details
The P and O algorithm is a traditional method for MPPT that is widely used in PV systems due to its simplicity and ease of implementation. The following sections provide a detailed explanation of the design and operational principles of the P and O algorithm.
- Inputs
The P and O algorithm relies on real-time electrical measurements from the PV system to determine the current operating point and to guide the search for the MPP.
Voltage: The output voltage (V) of the PV array is measured at each sampling interval. This value is essential for calculating the instantaneous power and for determining the effect of perturbations.
Current: The output current (I) of the PV array is also measured at each step. Together with the voltage, it allows for the calculation of the output power (P = V × I).
These measurements are typically obtained using voltage and current sensors connected to the PV system.
- Algorithm Steps
The core operation of the P and O algorithm involves iterative adjustments to the operating point of the PV system and observation of the resulting changes in output power.
Perturbation: at each iteration, the algorithm perturbs (i.e., slightly increases or decreases) the operating voltage (or current) of the PV array. The size of the perturbation step is a design parameter and affects the speed and accuracy of tracking.
Observation: after each perturbation, the algorithm measures the new output power and compares it to the previous value.
Decision logic: if the output power increases as a result of the perturbation, the algorithm continues to perturb the operating point in the same direction (i.e., further increase or decrease).
If the output power decreases, the direction of the perturbation is reversed for the next step.
Iteration: This process is repeated continuously, causing the operating point to oscillate around the maximum power point. The algorithm dynamically adapts to changes in environmental conditions (such as irradiance and temperature) by continuously seeking the new MPP.
- Implementation Considerations
Step size selection: The magnitude of the perturbation step is critical. A large step size can lead to faster tracking but causes larger oscillations around the MPP, reducing efficiency. A small step size minimizes oscillations but slows down the tracking response.
Sampling rate: The frequency at which voltage and current are sampled and the algorithm is executed should be chosen to balance responsiveness and computational load.
Steady-state oscillation: The P and O algorithm inherently causes the operating point to oscillate around the MPP, which can result in minor power losses. Advanced versions of the algorithm may include adaptive step sizes or filtering techniques to minimize these losses.
Environmental adaptation: The algorithm is capable of tracking the MPP under slowly varying environmental conditions. However, under rapidly changing irradiance or temperature, the algorithm may temporarily lose track of the true MPP.
The P and O algorithm’s design is based on a simple feedback mechanism that requires only voltage and current measurements. Its straightforward implementation and low computational requirements make it suitable for real-time MPPT in PV systems, especially where cost and simplicity are prioritized. However, its performance can be affected by the choice of step size and the rate of environmental changes.
4. Simulation Results
The designed photovoltaic (PV) system was simulated using MATLAB to evaluate its performance under the climatic conditions of Ankara. The simulation was conducted on an hourly and monthly basis, incorporating real-world environmental data, including solar irradiance, temperature, and sunlight hours. The results were analyzed to compare the performance of three MPPT methods: ANN-based MPPT, RL-based MPPT, and the P and O MPPT method. The key metrics evaluated include PV energy production, battery SOC, and load reliability. This section presents the simulation results, accompanied by graphical representations, and provides detailed interpretations of each graph.
4.1. Battery State-of-Charge (SOC) Variation
Figure 3 illustrates the monthly variation in the battery’s SOC for the three MPPT methods: ANN-based MPPT, RL-based MPPT, and P and O MPPT method. The SOC is expressed as a percentage and plotted against the months of the year. It can be seen from the figure that the RL-based MPPT method demonstrates the most stable SOC profile throughout the year, maintaining the battery within the optimal SOC range (20% to 90%). This indicates that the RL algorithm effectively balances energy generation and consumption, minimizing energy losses and ensuring reliable battery operation. It is clear that the ANN-based MPPT method also performs well, with slight fluctuations in SOC during the winter months (e.g., December and January). These fluctuations are attributed to lower solar irradiance and shorter sunlight hours, which reduce PV energy production. The conventional MPPT method exhibits the most significant SOC variations, with the battery frequently approaching the minimum SOC limit during winter. This highlights the limitations of traditional methods in adapting to dynamic environmental conditions. The results suggest that advanced MPPT methods, particularly RL, are more effective at managing battery SOC, ensuring reliable energy storage and utilization.
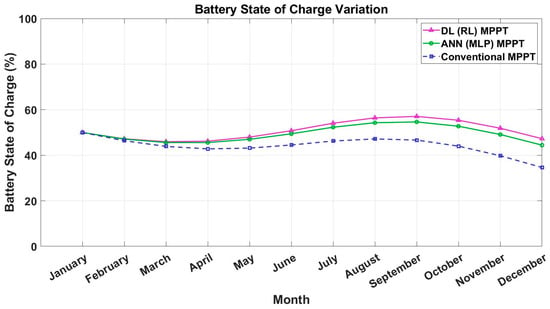
Figure 3.
Battery state-of-charge (SOC) variation.
4.2. Monthly PV Energy Production and Efficiency Gains
Figure 4 compares the monthly PV energy generation with three MPPT methods. The energy generation is expressed in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and plotted against the months of the year. It is seen that the RL-based MPPT method achieves the highest energy production across all months, with a noticeable advantage during the summer months (e.g., June, July, and August) when solar irradiance is at its peak. This demonstrates the RL algorithm’s ability to dynamically optimize the operating point of the PV array under varying conditions. The ANN-based MPPT method also performs well, with energy production values close to those of the RL method. However, slight underperformance is observed during the transition months (e.g., March and October), likely due to the ANN model’s reliance on training data, which may not fully capture transitional weather patterns. The conventional MPPT method generates the least energy, particularly during the winter months (e.g., December and January). This is attributed to its inability to accurately track the maximum power point (MPP) under rapidly changing conditions.
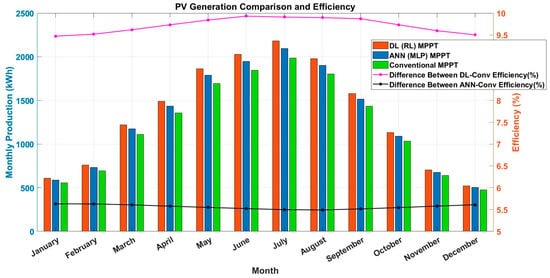
Figure 4.
Monthly PV energy generation and efficiency gains.
Figure 4 also compares the annual PV energy production for the three MPPT methods and presents the percentage efficiency gains of the RL and ANN methods over the traditional method. It is determined that the RL-based MPPT method achieves the highest annual energy production, followed closely by the ANN-based method. The traditional method produces the least energy, exhibiting a significant performance gap compared to the advanced methods. The efficiency gains of the RL method over the traditional method range from 10% to 15%, depending on the month, with the highest gains observed during the summer months. The ANN method achieves efficiency gains of 8% to 12%, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving energy production. The results confirm that advanced MPPT methods significantly enhance the efficiency of PV systems, with RL-based MPPT offering the greatest performance improvements.
4.3. Daily Power Profiles
Figure 5 and Figure 6 present the daily power profiles for a representative day in summer (1 July) and winter (1 December). The graphs show the PV energy generation, battery power, and load power for each hour of the day.
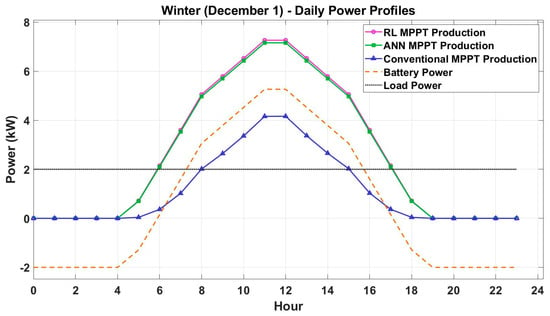
Figure 5.
Daily power profiles (summer—1 July).
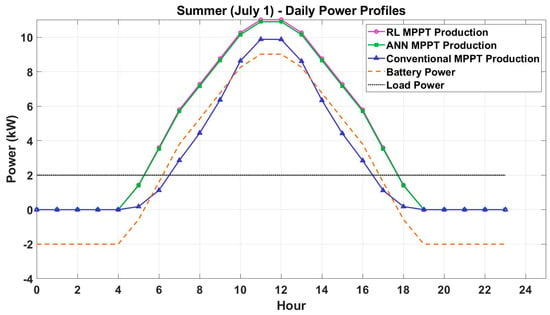
Figure 6.
Daily power profiles (winter—1 December).
During the daytime in the summer months, the PV energy production follows a bell-shaped curve, peaking around noon when solar irradiance is highest. The RL-based MPPT method achieves the highest peak power, followed by the ANN-based and traditional methods. The battery power profile indicates that the battery is charged during the morning and early afternoon, when PV production exceeds the load demand. The RL and ANN methods ensure efficient charging, while the conventional method results in slower charging rates. In addition, the load power remains constant throughout the day, with the excess PV energy stored in the battery for use during nighttime.
During the day in winter, PV energy production is significantly lower due to reduced solar irradiance and shorter sunlight hours. The RL-based MPPT method still achieves the highest energy generation, demonstrating its adaptability to low-irradiance conditions. The battery power profile shows that the battery is discharged throughout most of the day to meet the load demand, as PV production is insufficient. The RL and ANN methods minimize battery discharge losses, while the conventional method results in deeper discharges, potentially reducing battery lifespan. The daily power profiles highlight the importance of advanced MPPT methods in optimizing energy generation and storage under both summer and winter conditions.
4.4. PV Energy Production Comparison and Efficiency Gains
Figure 2 and Table 7 compare the annual PV energy production for the three MPPT methods and presents the percentage efficiency gains of the RL and ANN methods over the conventional method.

Table 7.
Summary of inputs and layers.
It is seen that the RL-based MPPT method achieves the highest annual energy production, followed closely by the ANN-based method. The conventional method produces the least energy, with a significant performance gap compared to the advanced methods. The efficiency gains of the RL method over the traditional method range from 9% to 10%, depending on the month, with the highest gains observed during the summer months. The ANN method achieves efficiency gains of 5% to 6%, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving energy production. The obtained results confirm that advanced MPPT methods significantly enhance the efficiency of PV systems, with RL-based MPPT offering the greatest performance improvements.
4.5. Load Reliability
Figure 7 illustrates the percentage of time for which the load demand is fully met for each MPPT method. The load reliability is expressed as a percentage and plotted against the months of the year.
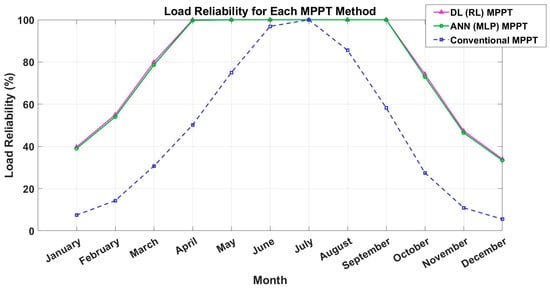
Figure 7.
Load reliability.
The RL-based MPPT method achieves 100% load reliability throughout the year, ensuring that the load demand is always met, even during periods of low solar irradiance. The ANN-based MPPT method also performs well, with load reliability exceeding 95% in all months. Minor reliability issues are observed during the winter months, likely due to reduced PV energy production. However, the conventional MPPT method exhibits the lowest load reliability, particularly during the winter months, when the battery frequently reaches its minimum SOC limit. The results demonstrate the critical role of advanced MPPT methods in ensuring reliable power delivery to the load, particularly under challenging environmental conditions.
The obtained simulation results provide valuable insights into the performance of the designed PV system and the effectiveness of the three MPPT methods. The key findings can be summarized as follows:
- i.
- Energy production: The RL-based MPPT method consistently outperforms the ANN-based and traditional methods in terms of PV energy production, achieving the highest efficiency gains.
- ii.
- Battery management: The RL and ANN methods effectively manage the battery SOC, minimizing energy losses and prolonging battery lifespan. The conventional method exhibits significant limitations in this regard.
- iii.
- Load reliability: The RL-based MPPT method ensures 100% load reliability, highlighting its potential for real-world applications in which an uninterrupted power supply is critical.
- iv.
- Adaptability: The advanced MPPT methods demonstrate superior adaptability to varying environmental conditions, with the RL method excelling in both summer and winter scenarios.
5. Conclusions
This study presents the design, simulation, and performance evaluation of a photovoltaic (PV) energy system tailored for the climatic conditions of Ankara, Turkey. The system integrates advanced MPPT methods, including ANN-based MPPT, RL-based MPPT, and a conventional MPPT method, to optimize energy generation and storage. The results demonstrate the significant advantages of advanced MPPT methods over conventional approaches in terms of energy efficiency, battery management, and load reliability. RL-based MPPT method emerged as the most effective approach, achieving the highest energy production and ensuring 100% load reliability throughout the year. Its ability to dynamically adapt to varying environmental conditions, such as changes in solar irradiance and temperature, highlights its potential for real-world applications. The ANN-based MPPT method also performed well, offering substantial efficiency gains and reliable battery management, though it exhibited minor limitations during transitional weather conditions. In contrast, the conventional MPPT method, while it is simple and widely used, showed significant performance gaps, particularly during winter months when solar energy availability is limited.
The integration of a BESS further enhanced the system’s reliability by mitigating the mismatch between energy generation and consumption. The advanced MPPT methods effectively managed the battery’s SOC, minimizing energy losses and prolonging battery lifespan. These findings underscore the importance of combining advanced control algorithms with energy storage systems to maximize the efficiency and reliability of PV systems.
Despite the promising results, several areas for improvement and future research have been identified. One of the key challenges in implementing advanced MPPT methods, such as RL and ANN, is their computational complexity and reliance on extensive training data. Future studies should focus on developing lightweight and computationally efficient algorithms that can be deployed on low-cost microcontrollers. Additionally, hybrid MPPT methods that combine the strengths of RL, ANN, and traditional approaches could be explored to further enhance system performance under diverse conditions. Another important area for future research is the integration of the PV system with emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart grids. IoT-enabled sensors and communication networks can provide real-time environmental data, enabling more accurate and adaptive control of the system. Smart grid integration can facilitate energy trading and grid support services, further increasing the economic and environmental benefits of PV systems.
In conclusion, this study highlights the potential of advanced MPPT methods, particularly RL and ANN, to revolutionize the performance of PV systems. By addressing the challenges and exploring the opportunities outlined above, future research can pave the way for more efficient, reliable, and sustainable renewable energy solutions.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Esram, T.; Chapman, P.L. Comparison of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking techniques. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2007, 22, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyimaya, S.E.; Altin, N. Review of energy management systems in microgrids. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, M.; Leon, J.I.; Abu-Rub, H. Photovoltaic energy systems. In Power Electronics in Renewable Energy Systems and Smart Grid: Technology and Applications; Wiley-IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 347–389. [Google Scholar]
- Altin, N.; Eyimaya, S.E. A combined energy management algorithm for wind turbine/battery hybrid system. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 4430–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Agarwal, V. Maximum power point tracking scheme for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Mohanty, A.; Mohapatra, A.G.; Gantayat, A.; Kumar, S. Soft Computing Techniques in Solar PV Energy Systems. In Soft Computing in Renewable Energy Technologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Belghiti, H.; Kandoussi, K.; Chellakhi, A.; Mchaouar, Y.; El Otmani, R.; Sadek, E.M. Performance optimization of photovoltaic system under real climatic conditions using a novel MPPT approach. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2024, 46, 2474–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anssari, O.M.H.; Badamchizadeh, M.; Ghaemi, S. Designing of a PSO-based adaptive SMC with a Multilevel Inverter for MPPT of PV systems under rapidly changing weather conditions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 41421–41435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artetxe, E.; Uralde, J.; Barambones, O.; Calvo, I.; Martin, I. Maximum power point tracker controller for solar photovoltaic based on reinforcement learning agent with a digital twin. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, M.; El-Mohandes, M.T.; Goda, M. An improved perturb-and-observe based MPPT method for PV systems under varying irradiation levels. Sol. Energy 2018, 171, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh Ahmadi, S.H.; Karami, M.; Gholami, M.; Mirzaei, R. Improving MPPT performance in PV systems based on integrating the incremental conductance and particle swarm optimization methods. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2022, 46, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasheen, M.; Rahman, A.K.A.; Abdel-Salam, M.; Ookawara, S. Performance enhancement of constant voltage based MPPT for photovoltaic applications using genetic algorithm. Energy Procedia 2016, 100, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, D.; Sain, C.; Biswas, P.K.; Sanjeevikumar, P.; Khan, B. Overview of solar photovoltaic MPPT methods: A state of the art on conventional and artificial intelligence control techniques. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2024, 2024, 8363342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altin, N. Interval type-2 fuzzy logic controller based maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic systems. Adv. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2013, 13, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Baul, A.; Sarker, G.C.; Sadhu, P.K.; Hodges, D.R. A comprehensive review of the application of machine learning in fabrication and implementation of photovoltaic systems. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 77750–77778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Duan, S.; Liu, F.; Liu, B.; Kang, Y. A variable step size INC MPPT method for PV systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2622–2628. [Google Scholar]
- Koutroulis, E.; Kalaitzakis, K.; Voulgaris, N.C. Development of a microcontroller-based, photovoltaic maximum power point tracking control system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2001, 16, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, A.P.; Rowe, R.C.; York, P.; Brown, M. Optimisation of the predictive ability of artificial neural network (ANN) models: A comparison of three ANN programs and four classes of training algorithm. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 25, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltawil, M.A.; Zhao, Z. MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 25, 793–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, H.; Eltamaly, A.M. A comprehensive comparison of different MPPT techniques for photovoltaic systems. Sol. Energy 2015, 112, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, F.P. Adaptive perturb and observe MPPT technique for grid-connected photovoltaic inverters. Procedia Eng. 2011, 23, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarzaman, N.A.; Tan, C.W. A comprehensive review of maximum power point tracking algorithms for photovoltaic systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 37, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolrasol, M.G.M.; Hussain, S.M.S.; Ustun, T.S.; Sarker, M.R.; Hannan, M.A.; Mohamed, R.; Ali, J.A.; Mekhilef, S.; Milad, A. Artificial neural networks based optimization techniques: A review. Electronics 2021, 10, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M. Deep Reinforcement learning for resilient power and energy systems: Progress, prospects, and future avenues. Electricity 2023, 4, 336–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dubey, A.K.; Segovia Ramírez, I.; Muñoz del Río, A.; García Márquez, F.P. Artificial intelligence techniques for the photovoltaic system: A systematic review and analysis for evaluation and benchmarking. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2024, 31, 4429–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barutcu, I.C.; Sharma, G.; Gandhi, R.V.; Jadoun, V.K.; Garg, A. Investigations on solar PV integration and associated power quality challenges in distribution systems through the application of MCS and GA. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2024, 71, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Al Mansur, A.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Rahman, S.; Ashique, R.H.; Houran, M.A.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Hossain, E. Investigation of degradation of solar photovoltaics: A review of aging factors, impacts, and future directions toward sustainable energy management. Energies 2023, 16, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledmaoui, Y.; El Maghraoui, A.; El Aroussi, M.; Saadane, R.; Chehri, A.; Chebak, A. PV solar anomaly detection using low-cost data logger and ANN algorithm. Telecommun. Comput. Electron. Control. 2024, 23, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangis, D.; Livera, A.; Tziolis, G.; Makrides, G.; Kyprianou, A.; Georghiou, G.E. Trend-Based Predictive Maintenance and Fault Detection Analytics for Photovoltaic Power Plants. Sol. RRL 2024, 8, 2400473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, S.; He, T.; Yang, B.; Yu, T.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Sun, L. Memetic reinforcement learning based maximum power point tracking design for PV systems under partial shading condition. Energy 2019, 174, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yu, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Shu, H.; Sang, Y.; Jiang, L. Dynamic leader based collective intelligence for maximum power point tracking of PV systems affected by partial shading condition. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 179, 286–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, X.; Shu, H.; Yu, T.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Sun, L. Novel bio-inspired memetic salp swarm algorithm and application to MPPT for PV systems considering partial shading condition. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 1203–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).