G&G Attack: General and Geometry-Aware Adversarial Attack on the Point Cloud
Abstract
1. Introduction
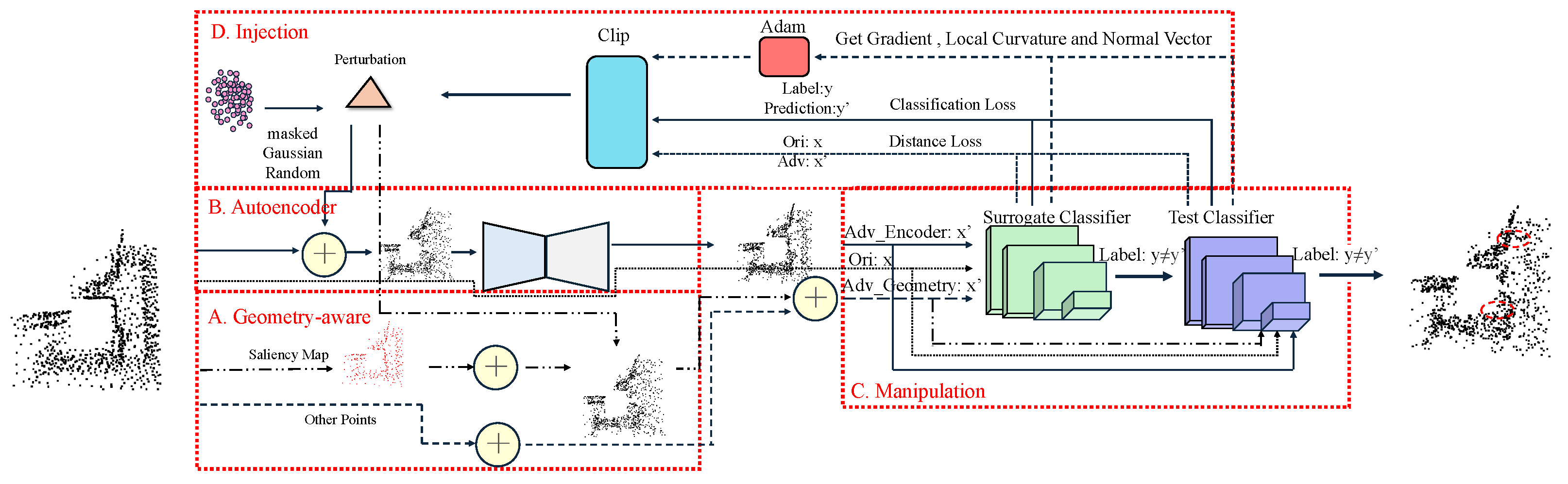
- To solve the problem of limited generalization and black-box attacks, an autoencoder is employed for 3D point cloud reconstruction. To mitigate the potential impact of benign surfaces caused by resampling on the effectiveness of attacks, an autoencoder is introduced to generate adversarial surfaces, which modify the density structure and local contextual features of the surface [31], resulting in generated adversarial point clouds that are smooth and uniform. We project the perturbation variables onto the input point cloud and account for classification and distance losses effectively. After multiple reconstructions, we successfully deceive the surrogate model.
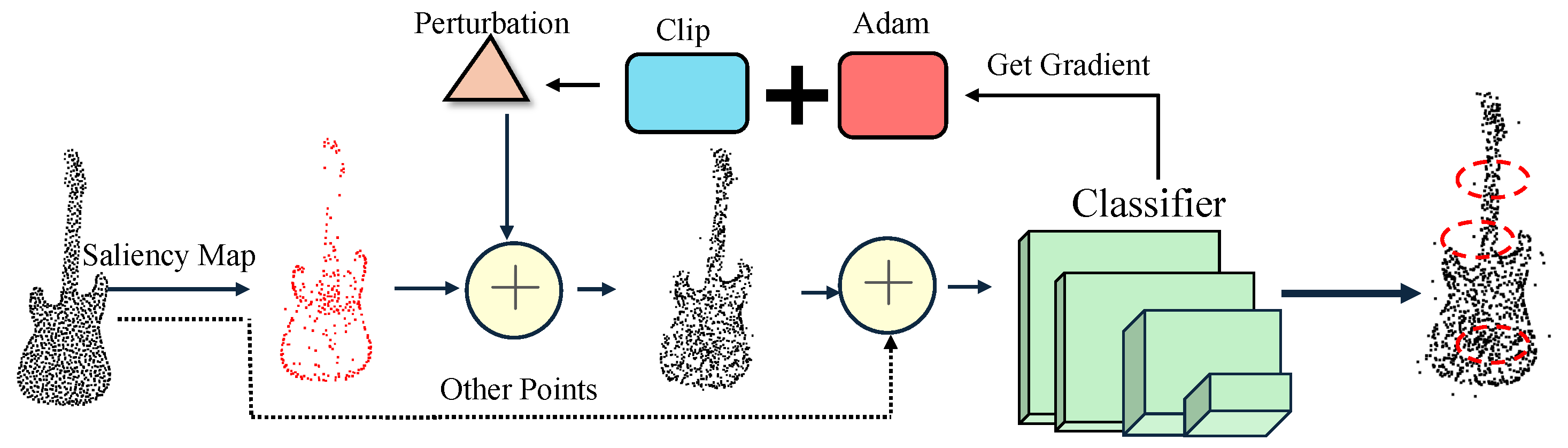
- Point cloud sensitivity maps are used to implement adaptive geometry-aware attacks. We introduce tangents, curvature, and integrated gradients (IGs) [32,33] to evaluate each point’s feature confidence in the classification results. We adaptively select the optimal attack direction and step size in the orthogonal search subspace. To address the problem of disturbance dimension explosion, global reconstruction and local interference are integrated.
- Through comprehensive experiments, we convincingly showcase the superiority of our method over existing approaches, boasting high attack success rates, robust generalization capabilities, and minimal perceptibility. In PointNet++ robustness testing, our method achieved an impressive ASR of 79.57%, a transferability rate of 79.2%, and an adversarial distance of .
2. Related Work
2.1. Point Cloud Classification
2.2. 3D Point Cloud Adversarial Attacks
3. Methods
3.1. 3D Point Cloud
3.2. Geometry-Aware
3.3. Autoencoder
3.3.1. The Curve Aggregation Strategy
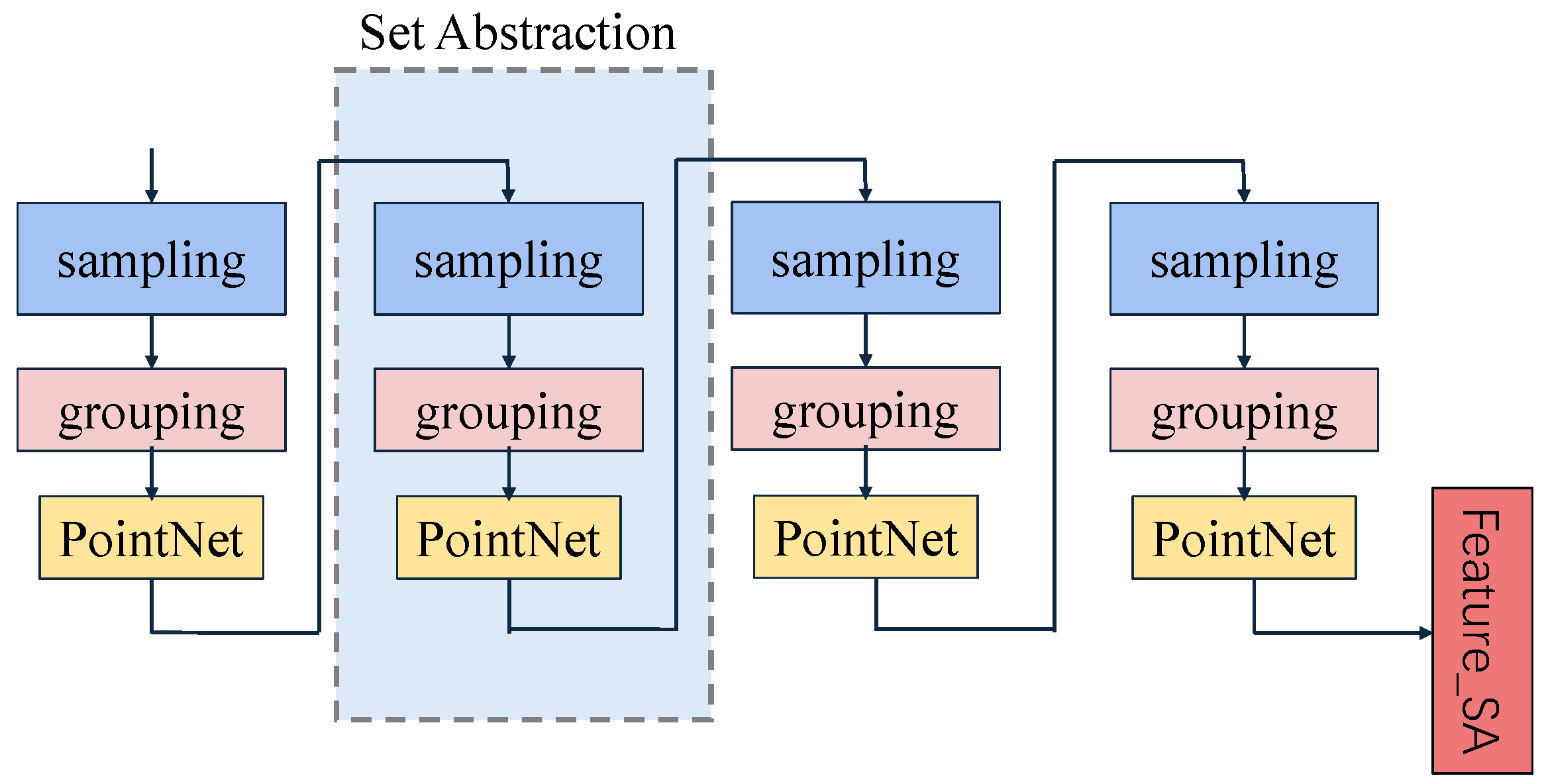
3.3.2. Set Abstraction
3.3.3. Attention Mechanism Fusion
3.4. Manipulation
3.5. Injection
4. Experiments Settings and Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Main Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Imperceptibility
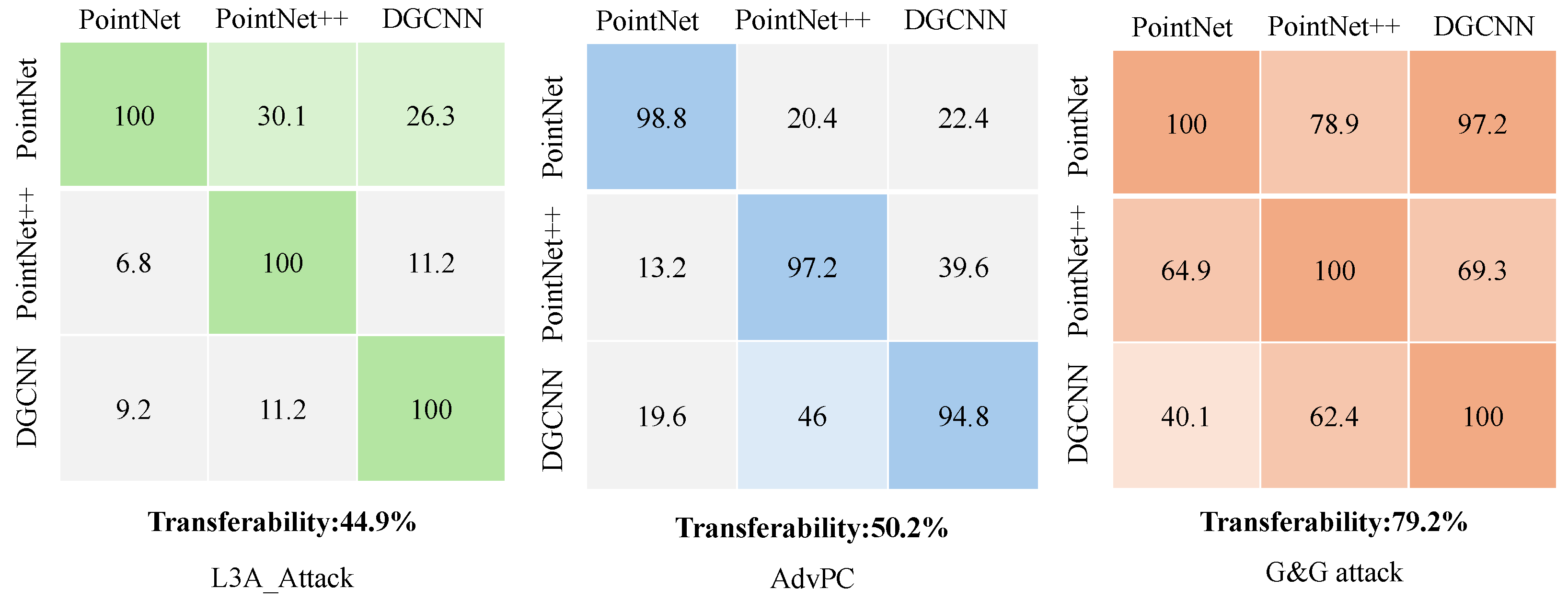
5.2. Transferability
5.3. Ablation Study
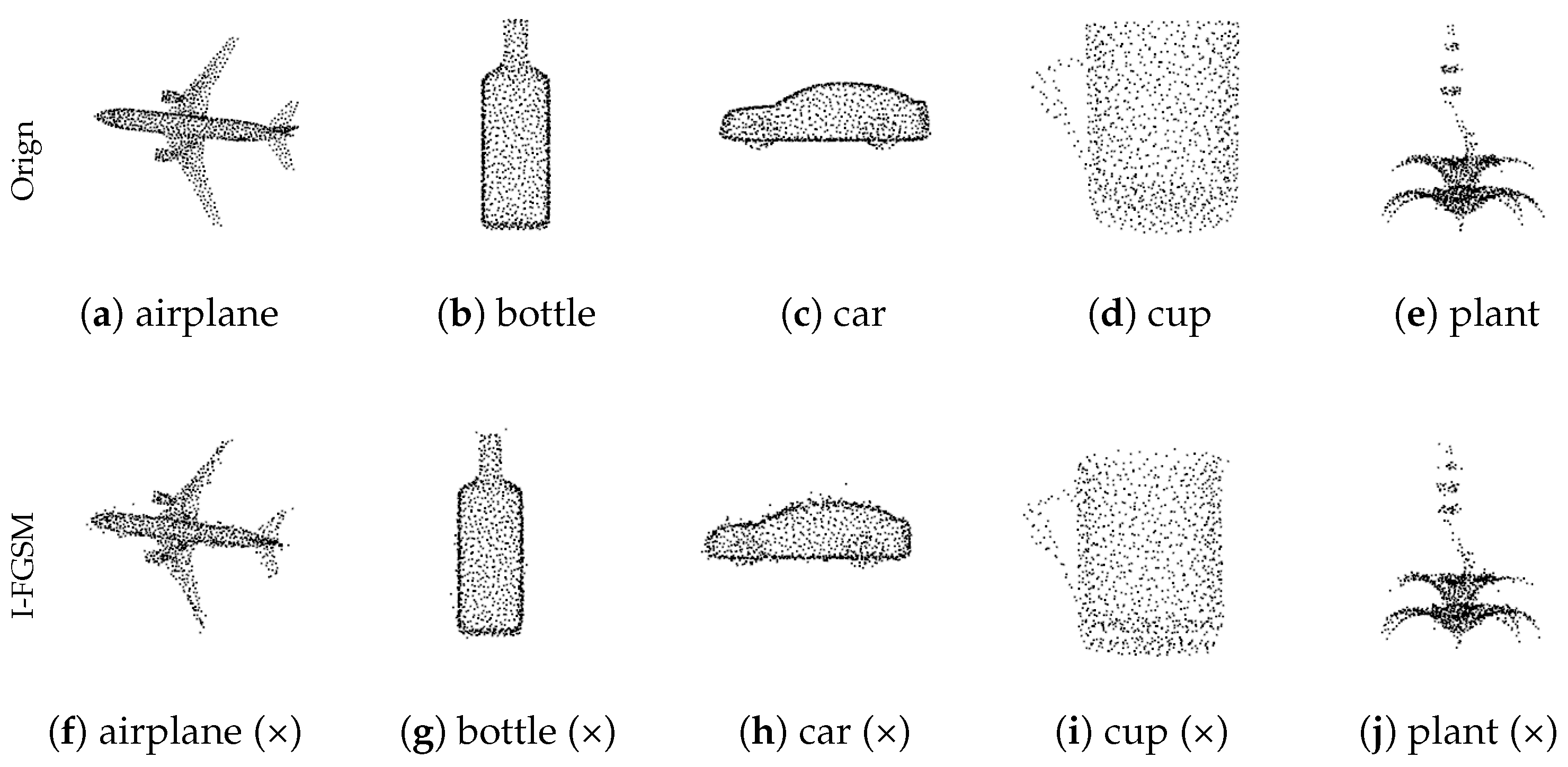
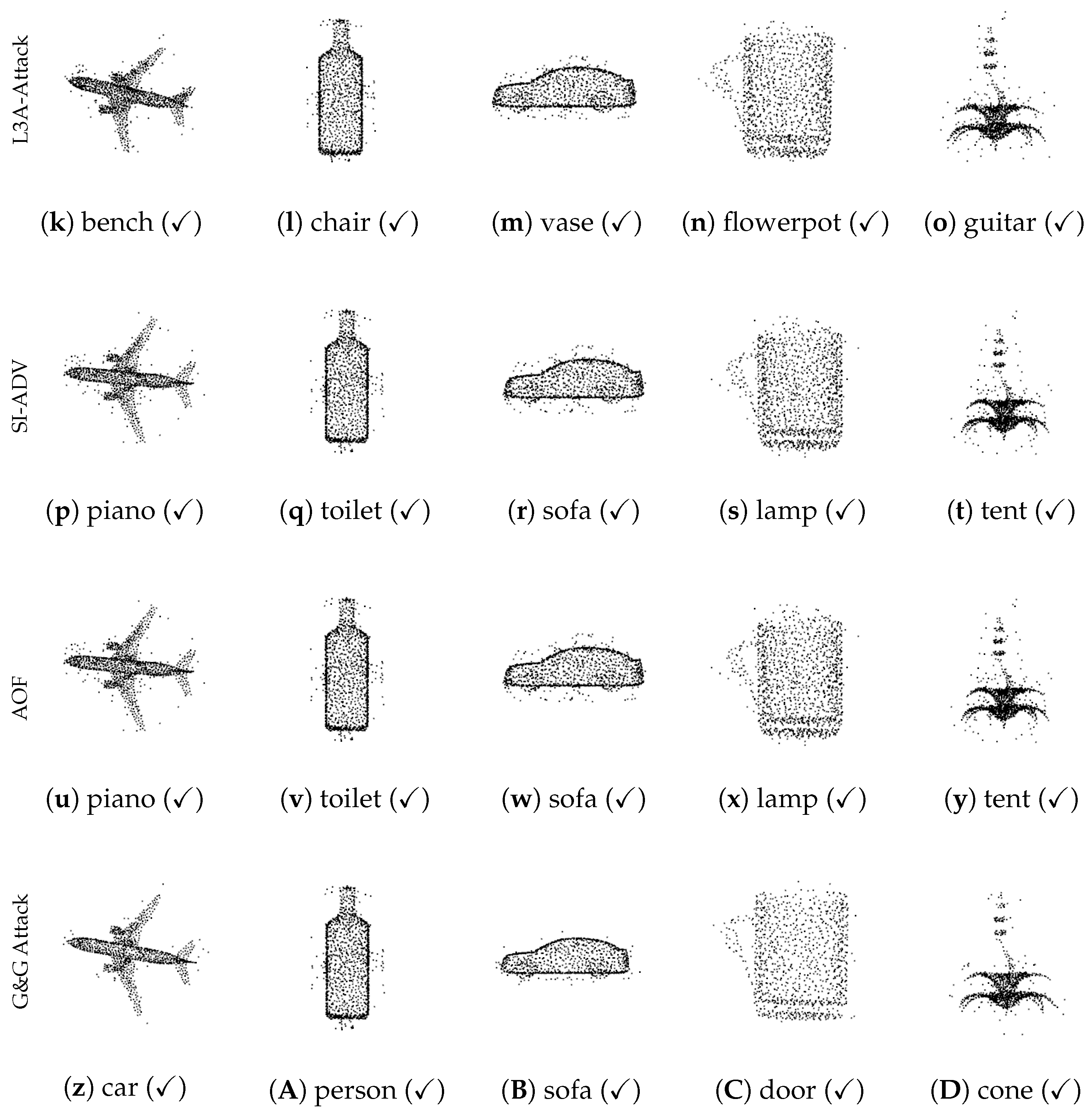
5.4. Visualization of Adversarial Samples
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOR | statistical outlier removal |
| DupNet | denoiser and upsampler network |
| FPS | farthest point sampling |
| KNN | k-nearest neighbor |
| ASR | attack success rate |
| CD | Chamfer Distance |
| HD | Hausdorff Distance |
| DGCNN | dynamic graph convolution neural network |
| AOF | adversarial attacks with attacking on frequency |
| PCT | point cloud transformer |
References
- Huang, C.Q.; Jiang, F.; Huang, Q.H.; Wang, X.Z.; Han, Z.M.; Huang, W.Y. Dual-Graph Attention Convolution Network for 3-D Point Cloud Classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 35, 4813–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, S.; Fairhurst, G.; Verdicchio, F. WiSE–a satellite-based system for remote monitoring. Int. J. Satell. Commun. Netw. 2017, 35, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Huq, K.M.S. LFT-Net: Local Feature Transformer Network for Point Clouds Analysis. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, C. Multi-Task Y-Shaped Graph Neural Network for Point Cloud Learning in Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 9568–9579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Koh, C.K.; George Lee, C.S. A 3-D-Point-Cloud System for Human-Pose Estimation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2014, 44, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Shlens, J.; Szegedy, C. Explaining and Harnessing Adversarial Examples. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6572. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Bruna, J.; Erhan, D.; Goodfellow, I.; Fergus, R. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1312.6199. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, W.; Yi, X.; Tang, Y. Deep CNN-based Visual Target Tracking System Relying on Monocular Image Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eykholt, K.; Evtimov, I.; Fernandes, E.; Li, B.; Rahmati, A.; Xiao, C.; Prakash, A.; Kohno, T.; Song, D. Robust Physical-World Attacks on Deep Learning Visual Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Komkov, S.; Petiushko, A. AdvHat: Real-World Adversarial Attack on ArcFace Face ID System. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakin, A.; Goodfellow, I.J.; Bengio, S. Adversarial examples in the physical world. In Artificial Intelligence Safety and Security; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Papernot, N.; McDaniel, P.; Goodfellow, I.; Jha, S.; Celik, Z.B.; Swami, A. Practical black-box attacks against machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM on Asia Conference on computer and Communications Security, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2–6 April 2017; pp. 506–519. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, A.; Engstrom, L.; Athalye, A.; Lin, J. Black-box adversarial attacks with limited queries and information. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 2137–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Liao, F.; Pang, T.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; Hu, X.; Li, J. Boosting Adversarial Attacks With Momentum. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, K.; Chen, C.P.; Jia, K. Geometry-aware generation of adversarial point clouds. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 2984–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Shi, Y.; Lou, T.; Peng, W.; He, X.; Zhu, P.; Gu, Z.; Tian, Z. Rethinking Perturbation Directions for Imperceptible Adversarial Attacks on Point Clouds. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 5158–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Qiu, C.; Liu, F.; Pan, Z. Point Cloud Upsampling via Perturbation Learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 4661–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madry, A.; Makelov, A.; Schmidt, L.; Tsipras, D.; Vladu, A. Towards Deep Learning Models Resistant to Adversarial Attacks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1706.06083. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, R.; Ni, B.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q. Adversarial Attack and Defense on Point Sets. arXiv 2021, arXiv:1902.10899. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Dong, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N. Shape-Invariant 3D Adversarial Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 15335–15344. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, R.B.; Marton, Z.C.; Blodow, N.; Holzbach, A.; Beetz, M. Model-based and learned semantic object labeling in 3D point cloud maps of kitchen environments. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St Louis, MO, USA, 11–15 October 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 3601–3608. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Yu, R.; Su, H. Extending Adversarial Attacks and Defenses to Deep 3D Point Cloud Classifiers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 2279–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, A.; Rojas, S.; Thabet, A.; Ghanem, B. Advpc: Transferable adversarial perturbations on 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XII 16. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 241–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Chen, C.; Yuan, J.; Li, B.; Ren, K. PointCloud Saliency Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J. Boosting 3d adversarial attacks with attacking on frequency. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 50974–50984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel Liu, R.Y.; Su, H. Adversarial Shape Perturbations on 3D Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the ECCV 2020 Workshops, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.; Qi, C.R.; Li, B. Generating 3D Adversarial Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Gardner, J.; You, Y.; Wilson, A.G.; Weinberger, K. Simple black-box adversarial attacks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 2484–2493. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, X.; Ni, B.; Zhao, C. Learning black-box attackers with transferable priors and query feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 12288–12299. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lim, A.; Zhou, J.T. Pointba: Towards backdoor attacks in 3d point cloud. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 16492–16501. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, B.; Ouyang, B.; Zhu, J.; Kuang, M.; Wang, H.; Meng, Y. The art of defense: Letting networks fool the attacker. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 12, 3267–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Cai, W. Walk in the cloud: Learning curves for point clouds shape analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 915–924. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. A point set generation network for 3d object reconstruction from a single image. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sheshappanavar, S.V.; Kambhamettu, C. SimpleView++: Neighborhood Views for Point Cloud Classification. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), Virtual, 2–4 August 2022; pp. 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Newry, UK, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Cai, J.X.; Liu, Z.N.; Mu, T.J.; Martin, R.R.; Hu, S.M. Pct: Point cloud transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2021, 7, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc. (NeurIPS): La Jolla, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr, P.H.; Koltun, V. Point transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 16259–16268. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Hua, B.S.; Nguyen, T.; Yeung, S.K. Minimal Adversarial Examples for Deep Learning on 3D Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 7797–7806. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Meng, W.; Wu, B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X. Efficient joint gradient based attack against sor defense for 3d point cloud classification. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 1819–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Carlini, N.; Wagner, D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (sp), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 39–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, C.; Wang, G. Robust Structured Declarative Classifiers for 3D Point Clouds: Defending Adversarial Attacks With Implicit Gradients. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 15294–15304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.; Kuang, M.; Yuan, X. Improving transferability of 3D adversarial attacks with scale and shear transformations. Inf. Sci. 2024, 662, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Kailkhura, B.; Yu, Z.; Xiao, C.; Mao, Z.M. Benchmarking Robustness of 3D Point Cloud Recognition Against Common Corruptions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.12296. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. VoxelNet: End-to-End Learning for Point Cloud Based 3D Object Detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.06396. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Han, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Q. Query-efficient black-box adversarial attack with customized iteration and sampling. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 2226–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.C.; Ting, P.; Chen, P.Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Yi, J.; Hsieh, C.J.; Cheng, S.M. Autozoom: Autoencoder-based zeroth order optimization method for attacking black-box neural networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Voluem 33, pp. 742–749. [Google Scholar]
- Brendel, W.; Rauber, J.; Bethge, M. Decision-based adversarial attacks: Reliable attacks against black-box machine learning models. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.04248. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Su, H.; Wu, B.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, J. Efficient decision-based black-box adversarial attacks on face recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7714–7722. [Google Scholar]
- Sundararajan, M.; Taly, A.; Yan, Q. Axiomatic attribution for deep networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, A.A.; Hanbury, A. Metrics for evaluating 3D medical image segmentation: Analysis, selection, and tool. BMC Med Imaging 2015, 15, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederik, P.K.; Jimmy, B. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Song, S.; Khosla, A.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L.; Tang, X.; Xiao, J. 3d shapenets: A deep representation for volumetric shapes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1912–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M. Local aggressive adversarial attacks on 3d point cloud. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 17–19 November 2021; PMLR: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. (tog) 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bu, R.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Di, X.; Chen, B. Pointcnn: Convolution on x-transformed points. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation, Inc. (NeurIPS): La Jolla, CA, USA, 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, W.; Fang, H.; Zhou, W.; Yu, N. Dup-net: Denoiser and upsampler network for 3d adversarial point clouds defense. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 1961–1970. [Google Scholar]

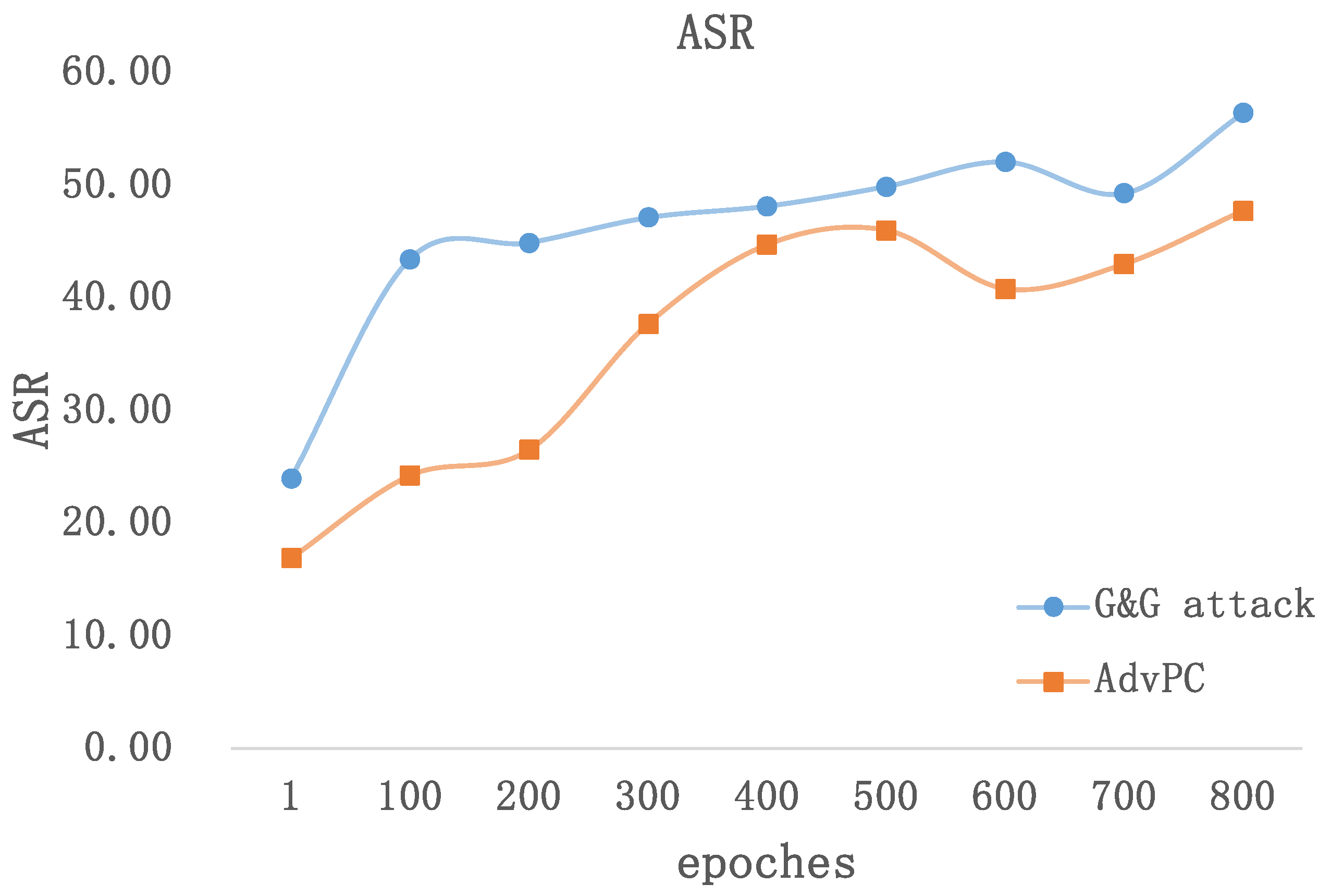
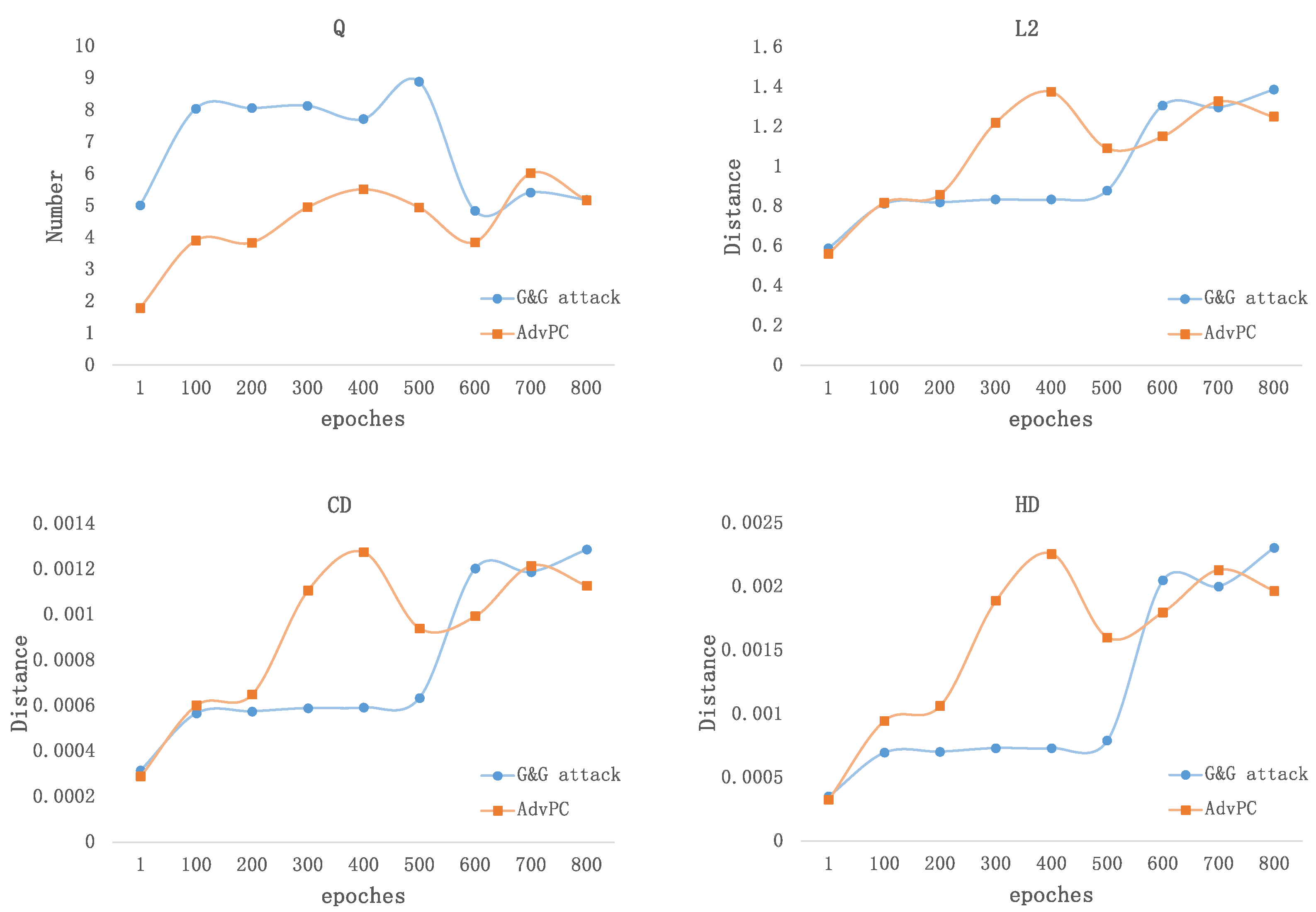
| Target Model | Attack | ASR | CD | HD | L2 | AT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet++ | PGD | 42.34% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 1.32729 |
| I-FGSM | 9.64% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20468 | 1.81929 | |
| SIADV | 52.07% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 1.81142 | |
| Saliency Map | 13.29% | 0.00493 | 0.11499 | None | 3.43626 | |
| Add | 8.63% | 0.00012 | 0.00457 | 0.25674 | 4.56375 | |
| AOF | 73.74% | 0.00708 | 0.02498 | 3.13824 | 39.04768 | |
| L3A-attack | 30.06% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 1.24706 | |
| G&G Attack | 78.971% | 0.00127 | 0.00942 | 0.88586 | 11.17533 | |
| DGCNN | PGD | 61.95% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 0.76333 |
| I-FGSM | 13.37% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20467 | 0.67050 | |
| SIADV | 41.41% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 1.85480 | |
| Saliency Map | 24.47% | 0.00495 | 0.11492 | None | 4.04345 | |
| Add | 11.02% | 0.00012 | 0.00456 | 0.25669 | 4.69601 | |
| AOF | 83.55% | 0.00702 | 0.02507 | 3.12184 | 10.75699 | |
| L3A-attack | 36.30% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 0.54858 | |
| G&G Attack | 97.20% | 0.00136 | 0.00423 | 1.44489 | 10.04447 | |
| CurveNet | PGD | 40.44% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 1.12563 |
| I-FGSM | 12.97% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20466 | 1.14258 | |
| SIADV | 48.58% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 1.53974 | |
| Saliency Map | 19.21% | 0.00494 | 0.11536 | None | 2.66501 | |
| Add | 9.97% | 0.00012 | 0.00459 | 0.25670 | 3.27948 | |
| AOF | 75.12% | 0.00708 | 0.02513 | 3.13730 | 22.04874 | |
| L3A-attack | 30.11% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 1.06008 | |
| G&G Attack | 95.30% | 0.00141 | 0.00410 | 1.47170 | 9.67680 | |
| PointCNN | PGD | 31.60% | 0.00512 | 0.02054 | 2.56925 | 1.12270 |
| I-FGSM | 23.99% | 0.00009 | 0.00835 | 0.20464 | 1.22103 | |
| SIADV | 21.47% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 1.31106 | |
| Saliency Map | 36.55% | 0.00492 | 0.11484 | None | 2.08533 | |
| Add | 23.30% | 0.00012 | 0.00456 | 0.25681 | 3.46817 | |
| AOF | 49.76% | 0.00706 | 0.02498 | 3.13396 | 24.89447 | |
| L3A-attack | 23.91% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 1.48106 | |
| G&G Attack | 81.36% | 0.00149 | 0.00409 | 1.46869 | 13.32512 |
| Target Model | Attack | ASR | CD | HD | L2 | AT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet++ | PGD | 34.48% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 0.98669 |
| I-FGSM | 8.91% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20468 | 1.08552 | |
| SIADV | 13.33% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 2.35535 | |
| Saliency Map | 14.10% | 0.00493 | 0.11499 | None | 1.27082 | |
| Add | 9.93% | 0.00186 | 0.00903 | 1.46697 | 3.34064 | |
| AOF | 65.19% | 0.00708 | 0.02498 | 3.13824 | 10.16391 | |
| L3A-attack | 17.10% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 1.75391 | |
| G&G Attack | 69.25% | 0.00153 | 0.00389 | 1.48500 | 14.72075 | |
| DGCNN | PGD | 44.65% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 1.04294 |
| I-FGSM | 26.74% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20467 | 1.11005 | |
| SIADV | 16.86% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 1.54077 | |
| Saliency Map | 55.19% | 0.00495 | 0.11492 | None | 1.05804 | |
| Add | 32.01% | 0.00186 | 0.00902 | 1.46481 | 3.85096 | |
| AOF | 87.76% | 0.00702 | 0.02507 | 3.12184 | 34.62557 | |
| L3A-attack | 35.94% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 0.82829 | |
| G&G Attack | 94.77% | 0.00139 | 0.00359 | 1.45356 | 13.18447 | |
| CurveNet | PGD | 44.65% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 1.04294 |
| I-FGSM | 18.44% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20466 | 0.88368 | |
| SIADV | 14.10% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 1.91420 | |
| Saliency Map | 31.85% | 0.00492 | 0.11534 | None | 1.43144 | |
| Add | 18.68% | 0.00186 | 0.00902 | 1.46567 | 3.43966 | |
| AOF | 74.64% | 0.00708 | 0.02513 | 3.13730 | 13.58630 | |
| L3A-attack | 22.45% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 1.91566 | |
| G&G Attack | 87.84% | 0.00150 | 0.00376 | 1.50523 | 9.00795 | |
| PointCNN | PGD | 36.51% | 0.00512 | 0.02054 | 2.56925 | 1.61203 |
| I-FGSM | 30.67% | 0.00009 | 0.00835 | 0.20464 | 1.57526 | |
| SIADV | 20.75% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 1.83620 | |
| Saliency Map | 49.43% | 0.00492 | 0.11484 | None | 3.30967 | |
| Add | 27.76% | 0.00186 | 0.00903 | 1.46394 | 4.54837 | |
| AOF | 53.40% | 0.00706 | 0.02498 | 3.13396 | 13.46032 | |
| L3A-attack | 29.86% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 1.80675 | |
| G&G Attack | 90.52% | 0.00137 | 0.00345 | 1.43998 | 12.94643 |
| Target Model | Attack | ASR | CD | HD | L2 | AT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet++ | PGD | 42.75% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 2.00264 |
| I-FGSM | 12.36% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20470 | 1.94486 | |
| SIADV | 19.17% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 3.96888 | |
| Saliency Map | 19.17% | 0.00496 | 0.11553 | None | 2.15756 | |
| Add | 13.82% | 0.00186 | 0.00902 | 1.46693 | 5.04174 | |
| AOF | 55.68% | 0.00668 | 0.02393 | 2.99472 | 25.12229 | |
| L3A-attack | 19.73% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 3.01929 | |
| G&G Attack | 60.53% | 0.00182 | 0.00450 | 1.60559 | 7.46479 | |
| DGCNN | PGD | 83.47% | 0.00512 | 0.02054 | 2.56925 | 1.52712 |
| I-FGSM | 67.59% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20467 | 1.50940 | |
| SIADV | 52.15% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 3.86802 | |
| Saliency Map | 19.17% | 0.00496 | 0.11553 | None | 2.50536 | |
| Add | 74.07% | 0.00186 | 0.00901 | 1.46448 | 4.28733 | |
| AOF | 65.68% | 0.00668 | 0.02393 | 2.99472 | 25.12229 | |
| L3A-attack | 71.88% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 3.97484 | |
| G&G Attack | 83.83% | 0.00139 | 0.00356 | 1.45443 | 12.97936 | |
| CurveNet | PGD | 33.35% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 2.34982 |
| I-FGSM | 14.75% | 0.00009 | 0.00835 | 0.20467 | 2.19222 | |
| SIADV | 18.88% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 5.03818 | |
| Saliency Map | 26.13% | 0.00497 | 0.11533 | None | 3.34793 | |
| Add | 14.87% | 0.00186 | 0.00902 | 1.46607 | 6.76772 | |
| AOF | 63.21% | 0.00669 | 0.02393 | 2.99106 | 31.26717 | |
| L3A-attack | 20.46% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 4.01711 | |
| G&G Attack | 39.38% | 0.00153 | 0.00377 | 1.51820 | 10.31737 | |
| PointCNN | PGD | 82.94% | 0.00512 | 0.02053 | 2.56925 | 2.14265 |
| I-FGSM | 83.51% | 0.00009 | 0.00836 | 0.20471 | 18.71319 | |
| SIADV | 81.00% | 0.00180 | 0.06930 | 1.85480 | 4.65357 | |
| Saliency Map | 86.26% | 0.00493 | 0.11509 | None | 32.97012 | |
| Add | 83.95% | 0.00186 | 0.00901 | 1.46387 | 6.84810 | |
| AOF | 85.58% | 0.00671 | 0.02404 | 3.01063 | 19.06874 | |
| L3A-attack | 83.31% | 0.00076 | 0.01834 | 0.70428 | 6.19376 | |
| G&G Attack | 58.51% | 0.00018 | 0.00186 | 0.28452 | 10.43081 |
| Attack | PointNet++ | CurveNet | PointCNN | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASR | Q | CD | HD | ASR | Q | CD | HD | ASR | Q | CD | HD | |
| SimBA | 8.27% | 50.74 | 1.95 × 10−7 | 2.59 × 10−5 | 16.73% | 73.73 | 1.11 × 10−5 | 2.26 × 10−4 | 59.36% | 1558.16 | 1.03× 10−5 | 1.78 × 10−3 |
| SimBA++ | 8.14% | 50.74 | 4.62 × 10−7 | 1.73 × 10−5 | 16.33% | 48.53 | 4.04 × 10−6 | 6.92 × 10−5 | 58.27% | 1559.68 | 2.08 × 10−5 | 1.65 × 10−3 |
| SI-ADV | 8.39% | 4.24 | 1.26 × 10−7 | 2.09 × 10−5 | 16.29% | 2.94 | 5.91 × 10−7 | 3.87 × 10−5 | 58.95% | 146.47 | 7.59 × 10−6 | 1.62 × 10−3 |
| G&G Attack | 78.97% | 34.41 | 1.27 × 10−3 | 9.42 × 10−3 | 95.30% | 9.66 | 1.41 × 10−3 | 4.10 × 10−3 | 81.36% | 8.28 | 1.49 × 10−3 | 4.09 × 10−3 |
| Target Model | Method | ASR | Q | CD | HD | L2 | AT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet++ | G&G attack | 78.97% | 34.41 | 0.00127 | 0.00942 | 0.88586 | 11.18 |
| w/o local geometry-aware attack | 61.51% | 2.93 | 0.00131 | 0.00243 | 1.40282 | 2.27 | |
| w/o autoencoder | 13.82% | 115.83 | 0.00097 | 0.00504 | 0.96031 | 33.01 | |
| DGCNN | G&G attack | 97.20% | 8.76 | 0.00136 | 0.04232 | 1.44489 | 10.04 |
| w/o local geometry-aware attack | 66.61% | 3.34 | 0.00129 | 0.00234 | 1.41377 | 0.24 | |
| w/o autoencoder | 33.87% | 88.26 | 0.00072 | 0.00390 | 0.72971 | 7.34 | |
| CurveNet | G&G attack | 95.30% | 9.66 | 0.00141 | 0.00410 | 1.47170 | 9.68 |
| w/o local geometry-aware attack | 63.05% | 3.03 | 0.00133 | 0.00244 | 1.44300 | 1.51 | |
| w/o autoencoder | 35.70% | 101.85 | 0.00085 | 0.00454 | 0.85685 | 23.90 | |
| PointCNN | G&G attack | 81.36% | 8.26 | 0.00149 | 0.00409 | 1.46869 | 13.33 |
| w/o local geometry-aware attack | 78.16% | 3.03 | 0.00142 | 0.00242 | 1.44440 | 0.44 | |
| w/o autoencoder | 57.74% | 116.18 | 0.00097 | 0.00502 | 0.96174 | 32.72 |
| Target Model | Attack | ASR | CD | HD | L2 | AT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet | Gauss Noise ( = 0, = 0.01) | 38.65% | 0.00142 | 0.07518 | 0.43488 | 21.68067 |
| Gauss Noise ( = 0, = 0.1) | 38.65% | 0.00142 | 0.07518 | 0.43488 | 15.85776 | |
| Random Noise ( = 0.5) | 38.81% | 0.00142 | 0.07518 | 0.43491 | 13.22587 | |
| Random Noise ( = 0.8) | 38.70% | 0.00142 | 0.0752 | 0.4349 | 12.17309 | |
| DGCNN | Gauss Noise ( = 0, = 0.01) | 58.87% | 0.00197 | 0.07824 | 0.43535 | 10.69092 |
| Gauss Noise ( = 0, = 0.1) | 58.87% | 0.00197 | 0.07824 | 0.43535 | 8.95007 | |
| Random Noise ( = 0.5) | 58.67% | 0.00198 | 0.07823 | 0.43536 | 11.80419 | |
| Random Noise ( = 0.8) | 58.87% | 0.00198 | 0.07824 | 0.43536 | 9.97715 | |
| CurveNet | Gauss Noise ( = 0, = 0.01) | 64.58% | 0.00191 | 0.07835 | 0.43522 | 24.13438 |
| Gauss Noise ( = 0, = 0.1) | 64.60% | 0.00191 | 0.07845 | 0.4356 | 23.58111 | |
| Random Noise ( = 0.5) | 64.71% | 0.00191 | 0.07837 | 0.43523 | 22.96008 | |
| Random Noise ( = 0.8) | 63.09% | 0.00192 | 0.07865 | 0.43735 | 20.45849 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, C.; Li, T. G&G Attack: General and Geometry-Aware Adversarial Attack on the Point Cloud. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010448
Chen G, Zhang Z, Peng Y, Li C, Li T. G&G Attack: General and Geometry-Aware Adversarial Attack on the Point Cloud. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(1):448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010448
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Geng, Zhiwen Zhang, Yuanxi Peng, Chunchao Li, and Teng Li. 2025. "G&G Attack: General and Geometry-Aware Adversarial Attack on the Point Cloud" Applied Sciences 15, no. 1: 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010448
APA StyleChen, G., Zhang, Z., Peng, Y., Li, C., & Li, T. (2025). G&G Attack: General and Geometry-Aware Adversarial Attack on the Point Cloud. Applied Sciences, 15(1), 448. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15010448






