Abstract
Thin-layer covers easily crack under traffic load, shortening their service life. Incorporating fiber materials into the mix can enhance crack resistance thanks to their abundance, affordability, and flexibility. However, different types of fibers have different performances in bitumen and mixtures due to different material properties. To explore this problem, basalt fiber, polypropylene fiber, and glass fiber were selected in this paper. The surface characteristics, internal structure, and adsorption capacity of oily substances were observed via scanning electron microscopy and oil absorption rate testing. The effects of fibers on the high-temperature and low-temperature properties of styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer-modified bitumen were investigated using the dynamic shear rheometer and the force ductility method. Ultimately, through indirect tensile testing and semi-circular bending tests, and the introduction of the toughness index and fracture toughness, a comprehensive evaluation was conducted on how varying fiber types and content affect the crack resistance and toughness of bitumen mixtures. The results show that the density and dispersion of the bundle fibers are the key to the oil absorption capacity under similar internal and external structural conditions. The oil absorption rate of polypropylene fiber is the best, reaching 5.423. Fiber incorporation can significantly improve the high-temperature rheological properties of bitumen. At 4% dosage, G*/sinδ increased by about 107.04% on average at 76 °C. At low temperatures, the increase in fiber content leads to a decrease in bitumen elasticity, and the influence of glass fiber is more obvious. The area of toughness did not reach 2000 N·mm at 4% dosage. After adding fibers, the toughness index and fracture toughness of the mixture increased by more than 2% and 35%, respectively. The maximum increases in fracture energy and crack initiation energy of the mixture are 14.29% and 47.29%, respectively. It shows that the fiber enhances the toughness, crack resistance, and crack propagation resistance of the mixture. The research results can provide some reference for the application of fiber-reinforced bitumen mixtures.
1. Introduction
As reported in the statistical bulletin detailing advancements in the transportation sector, China’s expressway network expanded to an impressive 122,300 km by the close of 2023 [1]. This places the nation at the forefront globally in terms of highway mileage. As the longevity of current roadways continues to rise, road maintenance technology is also evolving. One prevalent technique in road upkeep is the application of thin overlays, which can be directly laid over the existing pavement without the need for milling, leading to considerable savings in both construction expenses and operational complexity [2,3]. However, because of their inherent structural properties, thin overlays are susceptible to cracking under traffic stress, which ultimately shortens their lifespan [4,5]. Consequently, improving their resistance to cracking is important to enhancing the durability and effectiveness of these thin-layer applications.
Researchers have enhanced the bitumen mixture to slow the onset of cracking issues, prolong the maintenance intervals of the pavement, lower upkeep expenses, and ensure reliable, long-term performance of the bitumen surface [6,7]. Simultaneously, investigators utilize numerical models such as the cohesive zone model and the phase field method to explore and evaluate the fracture mechanics and damage evolution in altered bitumen mixtures [8,9]. Currently, the predominant approaches for improving crack resistance and toughness in bitumen mixtures involve both chemical and physical modifications.
Chemical techniques primarily enhance bitumen by incorporating substances such as epoxy resin, activated rubber powder, polyurethane, and various other polymers. Shi et al. [10] used crumb rubber (CR) to toughen epoxy bitumen mixture. CR particles enhance the toughness of epoxy bitumen mixtures, and the mixtures with less CR are susceptible to sudden fractures due to brittle coarse aggregates. Wu et al. [11] examined the impact of three different polymers—high-viscosity modifier (HVM), high-modulus modifier (HMM), and anti-rutting agent (ARA)—on the toughness of mixtures. Each mixture’s toughness was assessed through fracture energy (Gf) and the flexibility index (FI). Following HMM modification, the bitumen exhibited enhanced viscosity, and the blend displayed optimal toughness. Huang et al. [12] incorporated waste tire rubber (WTR), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer (SBS) into bitumen. Subsequent testing revealed that the inclusion of HDPE boosted both the hardness and modulus of the bitumen binder, leading to a notable enhancement in the fatigue performance of the bitumen mix. Additionally, the synergy of WTR, HDPE, and SBS improved the bond and cohesion between the binder and the aggregate particles, further improving the mixture’s resistance to cracking. These polymers interact with the bitumen, resulting in the formation of a three-dimensional cross-linked network structure [13,14,15]. This structure restricts the mobility of unbound bitumen, increases its viscosity, and effectively bolsters the crack resistance of the bitumen mixture [16]. Nevertheless, in real-world scenarios, it has been observed that as the strength of the altered bitumen mixture rises, it becomes more susceptible to brittle failure [17]. To tackle this issue, researchers have incorporated toughening agents and various modifiers to enhance composite materials, striving to strike a balance between crack resistance and the toughness of the blend. Nevertheless, the expense associated with composite modification is considerable, the procedures tend to be quite complex, and the modified components are often susceptible to environmental influences, which can diminish their effectiveness [18,19].
Physical modification focuses on improving the strength and modulus of the mixture by integrating nanoparticles or fiber materials, ultimately enhancing the crack resistance of bitumen pavements [20,21,22]. Nanoparticles can be effortlessly integrated with bitumen, due to their expansive specific surface area and exceptionally high surface energy [23]. Shafabakhsh et al. [24] investigated how ferric oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles influence the crack resistance of bitumen mixtures. Their findings indicate that the addition of just 1% of these nanoparticles considerably enhances the mixture’s fracture toughness. Zhang et al. [25] investigated how various sizes of nano-zinc oxide (ZnO) influence the low-temperature crack resistance of SBS bitumen mixtures. Their findings revealed that the effectiveness of nano-ZnO in enhancing crack resistance diminishes as the particle size increases. In essence, smaller particles yield higher surface energy, resulting in better performance in crack resistance at low temperatures. This characteristic significantly enhances the bonding quality at the interface between the aggregate and bitumen, while also boosting the mixture’s resistance to cracking. Jia et al. [26] investigated how bamboo fiber influences the mechanical characteristics of SBS bitumen binder and its mixtures. Their findings indicate that the inclusion of bamboo fiber enhances the flexibility of bitumen at low temperatures and bolsters the mixture’s resistance to cracking. Wei et al. [27] discovered that incorporating glass fiber into the epoxy bitumen mixture led to a notable 33.7% increase in both flexural and tensile strength. Ren et al. [28] revealed that using treated basalt fiber significantly boosts the bonding at the interface of the fiber and bitumen, thus enhancing the crack resistance of the fiber–bitumen blend. Therefore, fiber exhibits remarkable oil absorption capabilities and can be fully combined with bitumen, which greatly improves the mixture’s structural stability [29]. Additionally, fiber is cost effective and boasts exceptional flexibility. When incorporated into the mix, it not only provides a reinforcing effect but also enhances the mixture’s crack resistance and reduces the likelihood of crack propagation. Furthermore, fibers strategically placed at potential crack sites help diminish the formation of micro-cracks, thereby increasing the toughness of the mixture and extending the lifespan of the pavement [30,31]. The typical forms of fiber can be categorized as either bundled or flocculent, with bundled fibers being more commonly utilized due to their superior strength [32].
Incorporating fiber is a key strategy for enhancing the crack resistance of bitumen mixtures. Various fiber types exhibit distinct impacts on bitumen and mixture, driven by their unique material characteristics. However, existing researchers focus on the influence of fiber on bitumen mixtures, and there are few studies on fiber itself and its interaction with bitumen. Moreover, Gf or tensile strength is a single index to evaluate the toughness of the mixture. Based on this, we studied three types of bundled fibers: polypropylene, glass, and basalt, while also taking into account the thickness of a thin overlay using the SMA-10-type grading. The study examined both the properties of the fiber and its impact on the crack resistance and toughness of SBS-modified bitumen and bitumen mixtures. The oil absorption rate serves as a metric to assess how effectively fibers bind with oily materials. The G*/sinδ and the area of toughness provide insights into how fibers impact bitumen under high- and low-temperature conditions. The influence of fiber type and content on the toughness of the mixture was observed from the change in the toughness index and fracture toughness of the mixture. The effect of fiber on the mechanical properties of the mixture can be observed from the perspective of fracture energy and crack initiation energy. A wealth of evaluation indicators was selected in order to evaluate the effect of fiber toughening from multiple angles. This provides a theoretical basis for improving the performance of thin-layer bitumen mixtures.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Road petroleum bitumen adopts finished SBS-modified bitumen. Both coarse and fine aggregates are diabase, produced in Baise, Guangxi. The ore powder is made of ground limestone as filler. The bitumen–aggregate ratio of the SMA-10 mixture is 5.98%, and its gradation range requirements are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Mixture aggregate gradation range requirements.
Three kinds of fiber bundles were selected as the research objects, namely basalt fiber, polypropylene fiber, and glass fiber. In prior research and engineering applications, fibers with diameters of 3 mm, 6 mm, and 9 mm have been utilized quite often. However, when it comes to enhancing the toughness of the composite, the 3 mm fibers have proven to be somewhat lacking. The 9 mm fibers are quite difficult to disperse due to their bulkier size, which ultimately prevents the establishment of a robust spatial network within the bitumen mortar. Therefore, 6 mm was selected as the test size [33,34,35]. According to DB45/T 2531-2022 [36], the content of polymer fiber should be 0.2–0.4% of the quality of the bitumen mixture, which is adjusted according to the technical performance of the mixture. When the bitumen–aggregate ratio is 5.98%, the fiber content accounts for 3.5–7% of the bitumen. Due to the high content of bundled fiber, it is more likely to agglomerate and result in the loss of low-temperature performance of the mixture [37,38,39,40,41]. Therefore, this paper used 0%, 2%, and 4% three dosage tests. (In the following, the samples with different fiber contents of 2% and 4% are abbreviated as basalt fiber: B-2, B-4; polypropylene fiber: P-2, P-4; glass fiber: G-2, G-4). The details of fiber indicators are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Fiber performance index.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
Fibers exhibiting a rougher surface texture, greater internal voids, and lower density typically possess a larger specific surface area, which translates to an enhanced capacity for oil absorption [42,43]. This characteristic allows for a more effective integration with bitumen. The microscopic characteristics of different fibers were observed via Germany ZEISS Sigma 300 scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Since the fiber material lacks electrical conductivity, it is necessary to spray the sample with gold.
2.2.2. Oil Absorption Rate Test
The capacity of the fiber to bond with bitumen can be evaluated through its oil absorption characteristics, which serve as an important benchmark. The examination was conducted using JT/T 533-2020 [44]. The oil absorption capacity of various fibers was quantitatively assessed using the WXXYL-1 oil absorption rate tester, developed by Hunan Wangxuan Technology Co., Ltd., (Changsha, China). The calculation of fiber oil absorption rate is shown in Equation (1):
where ρ is the fiber oil absorption rate (It shows that the proportion of oil absorbed by the fiber to the mass of the fiber itself is in the form of multiples), my is the mass of the sieve and the sample after the shock (g), ms is the mass of the test sieve (g), and m is the mass of dry fiber (g).
2.2.3. The Dynamic Shear Rheometer
According to AASHTO T 315-20 [45], the fiber bitumen mortar was tested by the dynamic shear rheometer (DSR) test. Testing was conducted at a frequency of 10 rad/s ± 0.1 rad/s, with temperature scans performed at 58 °C, 64 °C, 70 °C, and 76 °C. According to the Superpave specification, the rutting factor G*/sinδ is used to characterize the high-temperature performance of bitumen binder. The impact of various fiber types and their quantities on the high-temperature rheological properties of the bitumen mortar were investigated.
2.2.4. The Force–Ductility Method
In line with NB/SH/T 0184-2010 [46], the test for the force–ductility method (FDT) of bitumen materials was conducted. The force–ductility behavior of fiber-reinforced bitumen was documented, allowing for a comparison with the standard curve associated with SBS bitumen. To assess how fibers affect bitumen, the areas of viscosity toughness, denoted as S, and yield strain energy, indicated as E, were computed. The relevant formulas for these calculations are provided in Equations (2) and (3):
where S is the area of toughness (N·mm), D is the ductility (mm), and F is the force (N);
where E is the yield strain energy (J), Fmax is the peak force (N), and Dmax is the elongation (mm) corresponding to the peak force.
The typical force–ductility curve of SBS bitumen is shown in Figure 1. The curve is divided into four stages. In the OA-elastic stage, the force rises rapidly to Fmax, and the bitumen mainly shows its viscosity. In the AB-yield stage, the force fluctuates slightly. In the BC-stress relaxation stage, the internal damage accumulates and the tensile force decreases sharply. In the DC-creep stage, the polymer in the modified bitumen gradually changes from a disordered state to an orderly arrangement, and the bitumen strength increases slightly in this process.
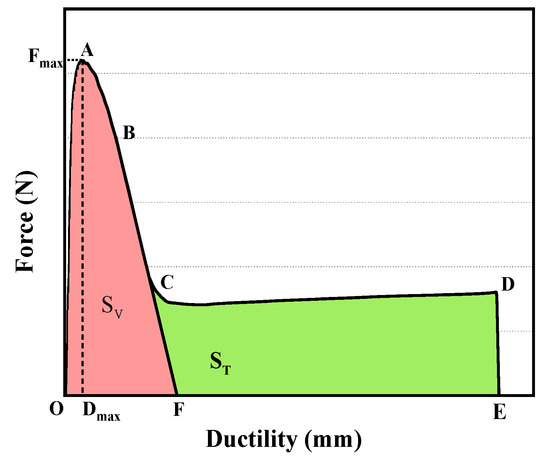
Figure 1.
The typical force–ductility curve of SBS bitumen.
2.2.5. Indirect Tensile Testing
For the indirect tensile testing (IDT) method from standard JTG E20-2011 (T 0716-2011) [47], various fiber-reinforced bitumen mixtures were subjected to indirect tensile tests. The tests were conducted with a loading rate of 50 mm/min at a temperature of 15 °C, and a Poisson’s ratio (μ) of 0.3 was maintained throughout. From these tests, the stress–horizontal strain curve for the bitumen mixtures was derived, allowing for the calculation of the splitting tensile strength (RT), Gf, and initiation energy (Gif). The stress–strain curve of the compressive cracking of the specimen can be divided into two parts: the pre-peak and the post-peak of the stress value. The pre-peak is the stage of resistance to cracking deformation, and the post-peak is the stage of resistance to crack propagation. Gf is the total area under the stress–strain curve of the whole cracking process of the specimen, indicating the work done by the mixture from the beginning of compression to the whole process of breaking. Gif is the crack initiation work per unit area of the failure section. In order to facilitate the analysis, the load and horizontal deformation are standardized. By dividing the peak load and the corresponding horizontal deformation, respectively, the standardized load–horizontal deformation curve is obtained. All the deformation curves have a unified peak ‘1’. The post-peak curves of different mixtures can be compared longitudinally. The rate of decline is slow, indicating that the anti-deformation ability of the mixture is stronger [48]. In order to quantitatively analyze the ability of the material to absorb energy during the failure process, this paper introduces the dimensionless toughness index TFAC. TFAC can be used to analyze the strength and deformation capacity of reinforced soil [49,50]. TFAC characterizes the ability of the mixture to absorb energy by calculating the area of the normalized curve from a point after the peak to the peak. TFAC and horizontal deformation are detailed in Equations (4) and (5):
where TFAC is the toughness index of bitumen mixture, Xp is the horizontal strain (mm) at the peak stress, Ap is the area under the normalized curve before the peak stress, XX/Xp is normalized horizontal strain, AX/Xp is the area under the pre-normalized curve, Y is the total vertical change (mm) of the specimen corresponding to the maximum failure load, and X is the total change in the horizontal direction of the specimen corresponding to the maximum failure load (mm).
2.2.6. The Semi-Circular Bending Test
The medium-temperature semi-circular bending test (SCB), as outlined in AASHTO TP 124-16 [51], was employed to assess the properties of the bitumen mixture at ambient temperature. This process involved measuring the Gf, along with introducing parameters such as fracture toughness (KIC), FI, and toughness index (TI) [52]. A thorough analysis was conducted to evaluate the impact of fiber reinforcement on the toughness of the mixture. The test was carried out at a loading rate of 50 mm/min and a temperature of 25 °C.
where KIC is fracture toughness (MPa·m0.5), σ0 is the stress corresponding to the peak load (MPa), F is the maximum load (kN), and YI(0.8) is the standard dimension gravitational intensity factor.
where FI is a dimensionless flexible index, Gf is fracture energy (J/m2), A is the unit scaling factor (taken as 0.01), and m is the slope of the post-peak inflection point of the curve.
where TI is a dimensionless toughness index, Gf,Post-peak is the post-peak fracture energy (J/m2), Δmdp is the displacement (m) at 50% of the peak load after the peak, and ΔPmax is the displacement at the peak load (m).
The overall flow of this study is referred to in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Research methodology flowchart.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fiber Performance Analysis
3.1.1. Microscopic Morphology
The fiber was tested using SEM, and the outcomes are presented in Figure 3.
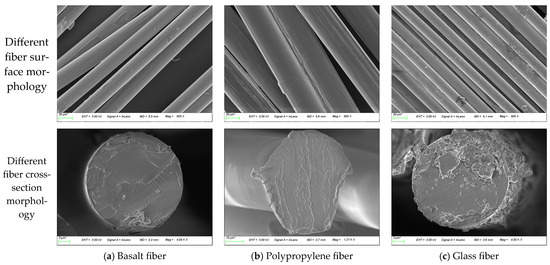
Figure 3.
Fiber surface and interface.
The three fibers are bundled, with a smooth surface, less texture, and uniform thickness. This means that the apparent structure has little effect on the binding ability of the three fibers to oily substances. Among them, the diameter of polypropylene fiber is the largest, about 40 μm, and the diameter of glass fiber is the smallest, about 20 μm. Polypropylene fiber has a low density and large monomer diameter. When compared to other fibers of equal quality, polypropylene fiber offers an increased surface area when integrated with bitumen, which restricts the mobility of free bitumen. This characteristic enhances the structural integrity of the mixture and boosts its resistance to cracking.
There are significant differences in the cross-sectional state of the three fibers. The cross-sectional shape of basalt fiber and glass fiber is a regular circle, but there are many fine chips in the cross-section of glass fiber, which may be produced during the processing of fiber. The cross-section of polypropylene fiber is deformed and irregular, which may be caused by the soft texture of polypropylene fiber.
3.1.2. Fiber Adsorption Properties
The oil absorption rate test was conducted to assess the capacity of the three fibers to absorb oil, with the findings displayed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Test results of fiber oil absorption rate.
The adsorption properties of the three fiber materials showed significant differences. Polypropylene fiber has the best adsorption performance, and its oil absorption rate is as high as 5.423. The oil absorption capacity of glass fiber is less than half that of polypropylene fiber, whereas basalt fiber’s absorption rate is merely one-fifth of that of polypropylene, standing at just 0.879. This difference may be related to the density characteristics of fiber materials. The density of polypropylene fiber is only 0.9 g/cm3–0.92 g/cm3, which is about one-third of the density of the other two fibers. In contrast to the other two types of fibers, polypropylene fiber boasts a greater surface area per unit weight, allowing it to absorb a larger quantity of oily substances [53]. While basalt and glass fibers share a comparable density of approximately 2.7 g/cm3, their oil absorption rates differ markedly. This disparity arises from the inadequate dispersion of basalt fibers, which prevents the monofilament fibers from making complete contact with oily materials, thus restricting their absorption capacity [54]. Fibers that exhibit superior dispersion create a more intricate network within the bitumen. When the bitumen is subjected to load, the fiber can transfer and disperse stress in multiple directions. This process mitigates the negative impacts of vehicular loads, bolsters the bitumen’s resistance to cracking, and ultimately enhances the longevity of the roadway [55,56].
3.2. Performance Analysis of Fiber Bitumen Mortar
3.2.1. High-Temperature Rheological Property
The impact of fiber type and content on the high-temperature performance of SBS bitumen was examined using the DSR test. The findings from this test are depicted in Figure 4.
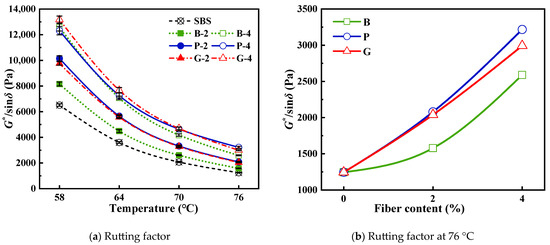
Figure 4.
DSR test results.
As the test temperature escalated from 58 °C to 76 °C, the G*/sinδ ratio for SBS bitumen mortar plummeted by an astonishing 80.89%. When the fiber content was bumped up to 2%, the G*/sinδ for various fiber-reinforced bitumen blends dropped by an average of 79.75%. And if the fiber content was doubled to 4%, the G*/sinδ of different fiber bitumen decreased by 76.85% on average. Despite the varying degrees of decrease, all bitumen types exhibited a downward trajectory. The rationale lies in the fact that as the bitumen is heated, the internal molecular friction diminishes, thereby enhancing the bitumen’s fluidity.
Different fibers have different effects on improving the high-temperature performance of bitumen due to the difference in oil absorption rate and dispersion. When the fiber content is 2%, the improvement effect of polypropylene fiber and glass fiber is better. When the content of is 4%, the G*/sinδ of both increases, but the improvement effect of polypropylene fiber is better. What plays a leading role is the dispersion of the fiber. The fiber with good dispersion can ensure that the fiber surface is in full contact with the bitumen and increase the oil absorption area. The fiber distribution is more disordered, and the stability of the three-bit network structure is better.
With the increase in fiber content, the high-temperature performance of bitumen is significantly improved. With the increase in fiber content, the G*/sinδ of bitumen increases step by step. For instance, consider the rutting factor measured at 76 °C. At a fiber content of 2%, the average increase in G*/sinδ hovers around 52.58%. When the fiber content is boosted to 4%, this average rise jumps to approximately 107.04%. This suggests that incorporating fiber enhances the anti-rutting properties of bitumen mortar. Two reasons can explain this observation. First, after the fiber is incorporated, the light components in the bitumen are adsorbed. The content of free bitumen in the mortar system is reduced, and the viscosity of SBS bitumen is improved. Secondly, the random distribution of fibers in bitumen forms a three-dimensional network structure, which produces internal friction resistance in bitumen. The movement of light components is limited, and the transformation of matrix structure of bitumen mortar from sol type to sol-gel type is promoted [57,58]. Increasing the fiber content can amplify these benefits, leading to even greater enhancement of the high-temperature performance and a reduction in the temperature sensitivity of the bitumen mortar. The anti-rutting performance of fiber-reinforced bitumen is improved.
3.2.2. The Force–Ductility Method
The 5 °C force–ductility test was conducted to examine how fibers affect the mechanical characteristics and low-temperature performance of bitumen. The findings of the test are presented in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
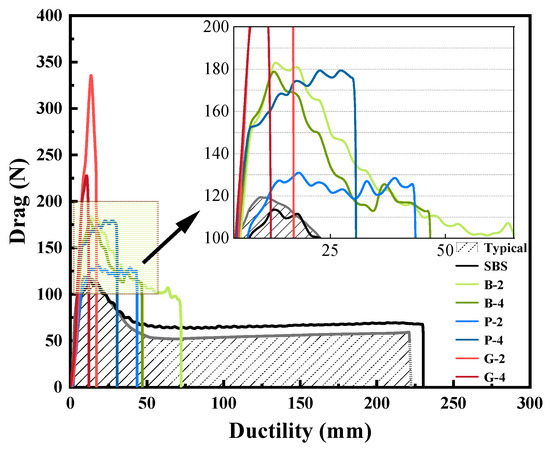
Figure 5.
Fiber-modified bitumen force–ductility curve.
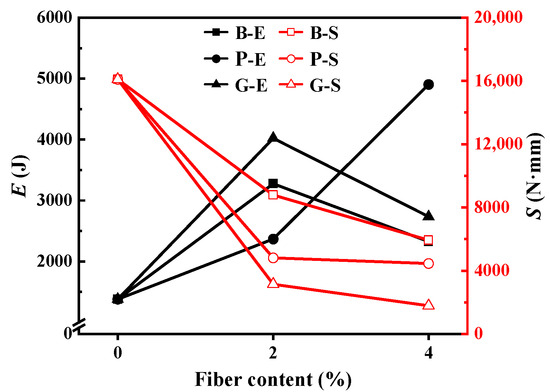
Figure 6.
Yield strain energy and toughness area (tensile work).
Incorporating fiber enhances the viscosity of SBS bitumen but may negatively impact its tensile characteristics at low temperatures. The pre-peak gradient of the force–ductility curve serves as an indicator of the bitumen’s viscosity. Compared with the typical curve, the pre-peak slope of the measured curve of the composite-modified bitumen increases, the curve fluctuates significantly after the peak, the tension decreases rapidly, and the creep stage disappears. The findings indicate that adding fiber enhances the viscosity of bitumen, while its brittleness increases in colder temperatures. As a result, the maximum tensile force of fiber-reinforced bitumen sees an increase, although its ductility diminishes. Throughout the testing, internal damage develops within the bitumen. Certain fibers at the fracture surface of the specimen experience a sequence of ’curved-straight-broken,’ while others are pulled out from the bitumen itself [59]. This intricate interaction results in noticeable fluctuations within the curve. After the peak tension, the polymer inside the bitumen cannot be changed from disordered to ordered, and the sample is destroyed, resulting in the disappearance of the SBS bitumen strength ‘not falling but rising’ stage, and the curve shows a cliff-like decline.
The inclusion of fiber enhances the mechanical characteristics of SBS bitumen at low temperatures while also diminishing its elasticity. Specifically, this results in a notable increase in the E of SBS bitumen, alongside a gradual reduction in its S. When the fiber content was 2%, the E of B-2, P-2, and G-2 increased by 138%, 72%, and 192% respectively, while the S decreased by 45%, 70%, and 80% respectively. The above phenomena indicate that bitumen needs to do more work in the yield stage, but its overall tensile work decreases significantly with the decrease in ductility. The reason is that after adding fibers, the unbroken fibers in the tensile process can connect the broken ends of the specimen, and the structural bitumen increases, so the fracture of the specimen needs to be stronger [60]. As the fiber concentration rose to 4%, the enhancements in E for B-4, P-4, and G-4 were striking, climbing by 69%, 256%, and 98%, respectively, when juxtaposed with SBS bitumen. Notably, only polypropylene fiber played a continuous role in the improvement. The S of B-4, P-4, and G-4 decreased by 63%, 72%, and 89%, respectively, compared with SBS bitumen. Compared with S at 2% content, the decrease for P-4 was the smallest, only 7%. The fiber dispersion is not good, and the agglomeration is easily destroyed. Under low dosage, agglomeration appears less, and its disadvantage is not significant. With the increase in fiber content, agglomeration hinders the formation of network structure, and the disadvantages become more prominent. It shows an increase in brittleness in the test. And the reduction in free bitumen will increase the viscosity. Under the two effects, the breaking process is greatly shortened, and the tensile force in a short time is significantly improved. The dispersion of basalt fiber and glass fiber is poor, and the content increases, and the agglomeration has a significant effect on it. This causes E to decrease. As the fiber content rises from 2% to 4%, polypropylene fibers exhibit better integration with the bitumen due to their greater oil absorption capability, resulting in the lowest rate of change in S for SBS bitumen.
3.3. Performance Analysis of Fiber Bitumen Mixture
3.3.1. Indirect Tensile Testing
Through IDT, the influence of different fiber types and content on the crack resistance of the mixture was explored. The test results are shown in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9.
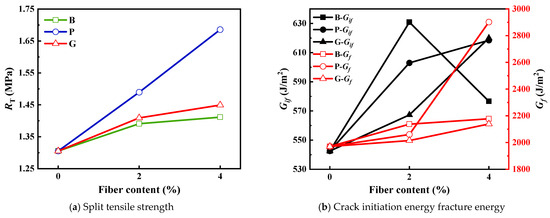
Figure 7.
Some results of IDT.
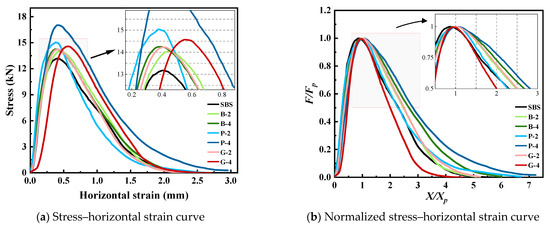
Figure 8.
Stress–horizontal strain curves before and after normalization.
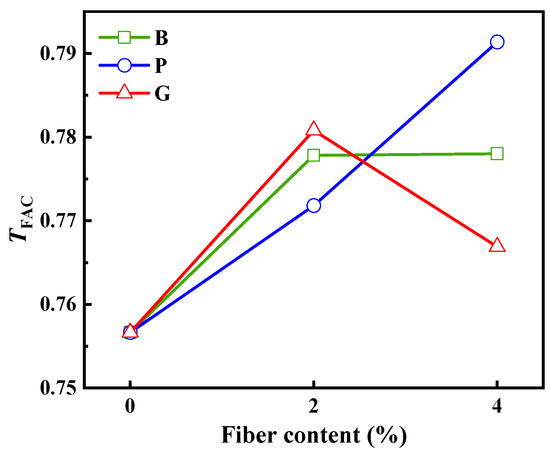
Figure 9.
Toughness index.
The fiber content is positively correlated with the RT of the mixture, and the gain effect of different types of fibers is different. At a fiber concentration of 2%, the RT for samples B-2, P-2, and G-2 rose by 6.55%, 14.1%, and 7.96%, respectively. When the fiber content was elevated to 4%, the RT values for B-4, P-4, and G-4 experienced increases of 8.13%, 29.14%, and 10.53%, respectively. The improvement effect of polypropylene fiber is particularly significant. This is because the stability of the mixture skeleton is enhanced after the fiber is incorporated. Fiber can absorb bitumen, which boosts the structural bitumen ratio and strengthens the adhesion between bitumen and aggregate [61]. As the amount of fiber rises, this benefit becomes more pronounced. Especially when the content of polypropylene fiber reaches 4%, the anti-deformation effect of the mixture is significantly improved, and the increase in RT is about three times that of the other two fibers. Polypropylene fiber has good dispersion performance and can build a more complex network structure in the mixed material, thereby significantly improving the overall effect. It can be speculated that if the fiber content exceeds 4%, its dispersibility may be affected. The force applied to the specimen cannot be effectively dispersed, thereby weakening some of the crack resistance. The benefits of adding fiber may show a decreasing trend. Therefore, in practical applications, ensuring dispersion is one of the keys to maximizing the benefits of fiber modification.
Incorporating fiber into the mixture can boost both the Gif and Gif, ultimately strengthening its resistance to cracking and the progression of cracks. When the fiber content was 2%, the Gif of B-2, P-2, and G-2 increased by 16.29%, 11.14%, and 4.57%, respectively, and the Gf increased by 8.5%, 4.56%, and 2.28%, respectively. At a fiber concentration of 4%, the Gif of B-4, P-4, and G-4 increased by 6.29%, 14%, and 14.29%, respectively, and the Gf increased by 10.54%, 47.29%, and 8.58%, respectively. Basalt fiber shows the most significant enhancement at lower quantities, whereas polypropylene fiber provides the most balanced overall improvement. This can be attributed to the fact that basalt fiber boasts superior tensile strength, despite its less effective dispersion. As a result, the agglomeration is not significant at low dosages, and the improvement effect is better. At high dosages, the agglomeration phenomenon is aggravated and the performance is decreased. The incorporation of polypropylene fiber into bitumen proves to be more efficient thanks to its outstanding ability to disperse and absorb oil. This significantly enhances the bonding characteristics at the interface of the mixture, particularly when used in higher concentrations.
Upon examining the stress–horizontal strain curve, it is evident that the horizontal strain that aligns with the maximum stress of various specimens typically hovers around 0.5 mm. In order to carry out quantitative analysis and unified evaluation, a unified standard was adopted when calculating the toughness index of the mixture. After the stress reaches the peak value, when the stress decreases to 50% of the peak value, the corresponding normalized horizontal deformation is XX/Xp, and the area under the normalized curve is AX/Xp. The toughness of the mixture was assessed by calculating the proportion of the area beneath the 50% normalized curve, following the peak, to the normalized horizontal strain of the section.
The addition of fiber notably enhances the TFAC of the bitumen mixture. When a 2% dosage is applied, the TFAC of B-2, P-2, and G-2 increased by 2.8%, 2%, and 3.19%, respectively, and the differences among the three were small. When the content increased to 4%, the TFAC of B-4, P-4, and G-4 increased by 2.82%, 4.59%, and 1.36%, respectively. The definition of TFAC is closely related to the post-peak behavior of the indirect tensile test curve. As illustrated in Figure 8b, the slope of P-4 post-peak curve is the smallest, which signifies that incorporating polypropylene fiber at a 4% concentration leads to the most substantial enhancement in the toughness of the bitumen mixture. The slope of G-4 is the smallest. Incorporating 4% glass fiber into the bitumen mixture enhances its initial crack resistance; it falls short in sustaining resistance against persistent cracking, leading to lackluster overall toughness. Fibers enhance the mixture’s resistance to cracking through mechanisms such as lapping, reinforcement, and load transfer. However, fiber agglomeration and uneven dispersion weaken its positive role in the mixture, thereby reducing crack resistance and toughness. The various types and amounts of fiber play an important role in influencing how bitumen mixtures perform during different stages of cracking. Basalt fiber and glass fiber can effectively resist the propagation of small cracks in the early stage of crack resistance due to their high monofilament tensile strength. Polypropylene fiber, with its excellent flexibility and elasticity, is more conducive to delaying the further expansion of cracks, showing the potential to improve toughness in bitumen mixtures [62].
3.3.2. The Semi-Circular Bending Test
The SCB test was employed to explore how various fiber types and their respective concentrations influence the crack resistance and toughness of the mixture. The progression of cracking is illustrated in Figure 10, while the results from the tests are presented in Figure 11 and Figure 12.
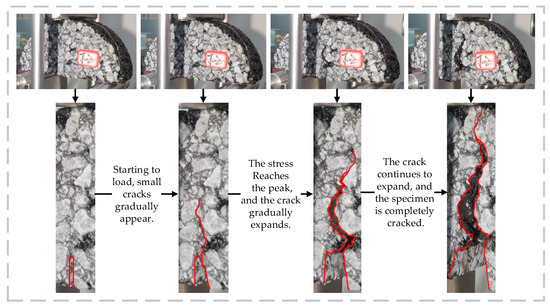
Figure 10.
Cracking process of SCB specimen.
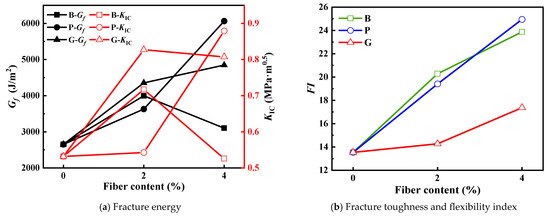
Figure 11.
Some results of SCB test.
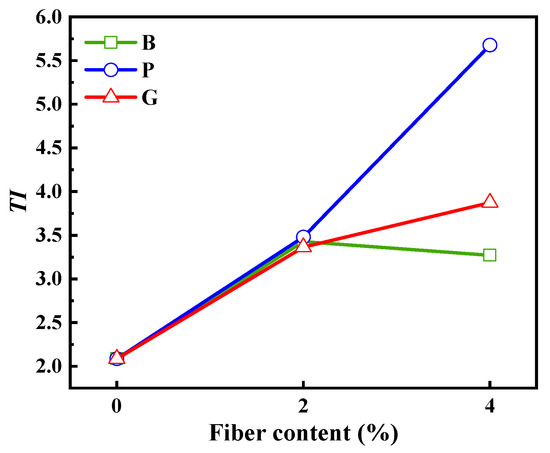
Figure 12.
Toughness index.
Introducing fiber into the bitumen mixture notably enhances both its Gf and KIC properties. At a 2% concentration, the Gf values for B-2, P-2, and G-2 saw remarkable increases of 51%, 37%, and 64%, respectively, with glass fiber demonstrating the most impressive results. At a fiber concentration of 4%, the Gf for B-4, P-4, and G-4 rose by 67%, 78%, and just 11%, respectively. The lifting effect of polypropylene fiber is the best, and basalt fiber has a downward trend. The trend of KIC is similar to that of Gf. The KIC improvement for P-2 is not as good as that for B-2 and G-2. At a fiber concentration of 4%, the KIC of P-4 increased significantly, while the KIC of B-2 and G-2 decreased. The value of B-2 is even slightly lower than that of the undoped fiber mixture, which may be caused by test deviation. The incorporation of fibers effectively enhances the crack resistance and toughness of the mixture and enhances its ability to resist crack propagation. The reason is that, in addition to the ‘reinforcement’ effect of fiber, the fiber adsorbs the light components in the bitumen, weakens the lubrication effect of the bitumen, and then improves the interface strength between the bitumen and the aggregate [63,64]. The ability of the mixture to withstand the moving load of the vehicle is enhanced. It is worth noting that too high a dosage may also have adverse effects.
The FI of the bitumen mixtures rises as the fiber content increases. At 2% dosage, the FI values for B-2, P-2, and G-2 showed rises of 49.86%, 43.39%, and 5.44%, respectively. Both basalt and polypropylene fibers exhibited substantial benefits. At 4% dosage, the FI for B-4, P-4, and G-4 experienced increases of 76.34%, 84.32%, and 28.32%, respectively, with polypropylene fiber demonstrating the most significant improvement. It is worth noting that the changing trend for FI is not always synchronized with Gf and KIC. FI is not only based on Gf, but also integrates the peak change rate of the stress–strain curve after fracture. This index serves as a thorough representation of the material’s toughness and its ability to absorb energy. It offers a fresh lens through which to assess the fiber modifications in bitumen mixtures, enabling a more holistic evaluation of how fibers impact the performance of these mixtures.
The inclusion of fiber markedly enhances the TI of the bitumen blend, while also improving the material’s resistance to cracking and overall durability. At the dosage of 2%, the TI of the three fiber mixtures was improved compared with that before incorporation, and the difference was small, but the polypropylene fiber still showed the best improvement effect. At the dosage of 4%, the TI for both P-4 and G-4 saw increases of 63% and 15%, respectively. Conversely, the TI for B-4 dipped by 5%, yet it remained above the baseline value of the undoped fiber. Polypropylene fiber significantly enhances the overall toughness of the mixture. Incorporating fiber into the bitumen blend can certainly boost its resistance to cracking and improve its toughness. Nonetheless, it is essential to consider the appropriate fiber dosage with great care. For fibers with high tensile strength but weak bonding ability with bitumen, excessive content may lead to curling and agglomeration of fibers in the mixture. This diminishes the strengthening benefits of fiber, potentially impacting the bond between bitumen and aggregate, and ultimately compromising the overall structural integrity of the mixture. On the contrary, for fibers with relatively low tensile strength but strong binding capacity with bitumen and good dispersion, it may be more appropriate to increase their content [65]. Under the condition of the same amount of bitumen, this kind of fiber can be combined with more bitumen, showing a more significant effect. Thus, the variety and composition of fiber, along with its relationship with bitumen, are important elements for enhancing the performance of the bitumen blend. A thorough consideration of these aspects is essential to attain optimal modification results.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, the performance of the fiber itself and the effect of the fiber on the crack resistance and toughening efficiency of SBS-modified bitumen and bitumen mixture were studied. The conclusions are as follows.
- (1)
- The microscopic surface morphology of the three fibers is bundle-like and the interior is a solid structure. The oil absorption rate of polypropylene fiber is high, reaching 5.423. It shows that the dispersion and density of bundled fibers with similar morphology will have a significant impact on the oil absorption rate.
- (2)
- The addition of fiber can effectively improve the high-temperature rheological properties of SBS bitumen, but the elasticity at low temperatures is reduced. When the fiber content reaches 4%, the G*/sinδ of SBS bitumen increases by about 107.04% on average, while S decreases by 89%. This means that the combination of fiber and free bitumen has a double-sided effect on the binder.
- (3)
- The incorporation of fiber significantly improves the crack resistance and toughness of bitumen mixtures, and the improvement effect of 4% polypropylene fiber is the most significant. According to the results of IDT, RT and TFAC of P-4 increased by 29.14% and 4.59%, respectively. The SCB test showed that the Gf and FI of P-4 increased by 78% and 84.32%, respectively. These findings underscore the importance of fiber dispersion in achieving a uniform distribution within the mixture, which subsequently influences the effectiveness of the fiber network structure and its bridging properties.
In choosing fibers to enhance the mixture’s crack resistance, it is necessary to consider the double-sided effect caused by the type and content of the fibers. In subsequent studies, we will explore the effects of more factors on the crack resistance of fiber mixtures and study the effects of these choices on practical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.W.; methodology, J.M.; investigation, Y.H. and P.L.; data curation, W.W. and C.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2021YFB2601000), a Guangxi Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2023AA14005), and the Guangxi Key Research and Development Program (No. AB21220070).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Yanlong Han was employed by the company Jiangxi Transportation Engineering Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Statistical Bulletin of Transportation Industry Development in 2023. Available online: https://xxgk.mot.gov.cn/2020/jigou/zhghs/202406/t20240614_4142419.html (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, H.; Yang, F. Anti-reflective crack performance of high viscosity and high elasticity asphalt mixture for ultra-thin wear layer. J. Shenzhen Univ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 40, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YU, J.; Chen, F.; Peng, X.; Lu, G.; Deng, K.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Mo, G.; Lu, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. High-toughness, ultra-thin friction course for the channel on the Zhuhai artificial island of the Hong Kong Zhuhai-Macao Bridge. J. Tsinghua Univ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.G.; Kang, A.H.; Wu, B.W.; Luo, C.F. Influence of basalt fiber on performance of thin overlayer asphalt mixtures based on multiple experimental methods. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Luo, S.; Quan, X.; Wei, X.H.; Yang, X.; Li, Q. Laboratory evaluation of performance of porous ultra-thin overlay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China’s Subgrade Engineering Research.2021. China J. Highw. Transp. 2021, 34, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Ma, B.A.; Chen, S.S.; Wei, K.; Kang, X.X. Properties of epoxy-resin binders and feasibility of their application in pavement mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maio, U.; Greco, F.; Lonetti, P.; Pranno, A. A combined ALE-cohesive fracture approach for the arbitrary crack growth analysis. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2024, 301, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, P.K.; Niordson, C.F.; Martínez-Pañeda, E. An assessment of phase field fracture: Crack initiation and growth. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2021, 379, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.G.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.P.; Liu, S.; Liu, P.F.; Yang, J.; Huang, W. Analysis of crumb rubber content influence on damage evolution and pattern recognition of rubberised epoxy asphalt mixture using acoustic emission techniques. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2024, 25, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.W.; Luo, C.F.; Pei, Z.H.; Xia, J.; Chen, C.C.; Kang, A.H. Effect of Different Polymer Modifiers on the Long-Term Rutting and Cracking Resistance of Asphalt Mixtures. Materials 2021, 14, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.X.; Yan, K.Z.; Wang, M.; Shi, K.X.; Li, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.H. Performance evaluation of SBS-modified asphalt mixtures incorporating waste tire rubber and HDPE. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 430, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, T.; Wei, D.; Li, B. Evaluation of Road Performance of Activated Rubber Powder Composite Modified Asphalt Mixture. J. Build. Mater. 2024, 27, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.D.; Wu, C.L.; Cheng, Y.C.; Wang, H.T.; Liang, J.X.; Zhao, W.S. Synergistic effect of waste rubber powder on low-temperature toughness and high-temperature rheological properties of SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, X.C.; Lv, S.T.; Zhang, Y.N.; He, W.; Yu, F. Research on performance and mechanism of terminal blend/grafting activated crumb rubber composite modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shan, M.Y.; Li, C. The cracking characteristics of the polymer-modified asphalt mixture before and after aging based on the digital image correlation technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.Y.; Zhang, F.F.; Wu, H.; Zhao, P.C. Effect of Graphene Oxide on the Low-Temperature Crack Resistance of Polyurethane-SBS-Modified Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures. Polymers 2022, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, M.; Dai, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H. Study on Performance of Fiber-toughened Waterborne Epoxy Emulsified Asphalt Mixture. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2024, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, X.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Ge, D.D.; Wang, S.F.; Ding, Z.Y.; Lv, S.T. Microbial treatment of waste crumb rubber: Reducing energy consumption and harmful emissions during asphalt production process. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 464, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbarma, K.; Debnath, B.; Sarkar, P.P. A comprehensive review on the usage of nanomaterials in asphalt mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucho, J.; Picado-Santos, L.; Neves, J.; Capitas, S. A Review of Nanomaterials’ Effect on Mechanical Performance and Aging of Asphalt Mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Parry, T.; Thom, N.; Grenfell, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of fibre reinforced asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 240, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, A.; Shafiei, M.; Kazemzadeh, Y.; Escrochi, M.; Riazi, M. Asphaltene prevention and treatment by using nanomaterial: A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 382, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafabakhsh, G.; Sadeghnejad, M.; Hejazi, S.K.; Shirazi, A. Evaluation the Rheological Behavior of Asphalt Binder, Fracture Resistance and Moisture Susceptibility of Asphalt Mixtures: Before and After Adding Nano Fe2O3. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Gao, Y.; Guo, G.H.; Zhao, B.J.; Yu, J.Y. Effects of ZnO particle size on properties of asphalt and asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.C.; Sheng, Y.P.; Lv, H.L.; Kim, Y.R.; Zhao, X.R.; Meng, J.D.; Xiong, R. Effects of bamboo fiber on the mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 289, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.T.; Mao, X.; Xu, W.; Xi, C.C.; Yan, S.J.; Sun, T.W.; Hu, X.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chi, F.X. Experimental Research on the Effect of Fiberglass on the Performance of Epoxy Asphalt Concrete. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.Y.; Luo, W.R.; Su, S.N.; Wang, Z.L.; Kong, L.; Ai, C.F. Study on crack resistance of basalt fiber reinforced asphalt mixture modified by titanate coupling agent based on digital image correlation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 437, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, M.; Ujhelyiova, A.; Ryba, J.; Hricova, M.; Kovar, V. Sorption Capabilities of Polypropylene/Modified Polypropylene Fibers. Preprints 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.W.; Pei, Z.H.; Xiao, P.; Lou, K.K.; Wu, X. Influence of fiber-asphalt interface property on crack resistance of asphalt mixture. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Kang, A.H.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of Cracking Resistance of SMA-13 Hot Recycling Asphalt Mixtures Reinforced by Basalt Fiber. Materials 2024, 17, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.X.; Jiao, Y.B.; Chen, X.H. Reinforcement evaluation of different fibers on fracture resistance of asphalt mixture based on acoustic emission technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.C.; Li, R.; Lu, S.H.; Bi, Y.Q.; He, H.Q. Evaluation of the Effect of Fiber Type, Length, and Content on Asphalt Properties and Asphalt Mixture Performance. Materials 2020, 13, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, M.H.; Kang, A.H.; Wu, Z.G.; Kou, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, P. Effect of fiber characteristic parameters on the synergistic action and mechanism of basalt fiber asphalt mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.S.; Cheng, Y.C.; Tan, G.J. Design Optimization of SBS-Modified Asphalt Mixture Reinforced with Eco-Friendly Basalt Fiber Based on Response Surface Methodology. Materials 2018, 11, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DB45/T 2531-2022; Technical Specification for Ultra-Thin Wear Layer of Hot Mix Asphalt Mixture for Expressway. Market Supervision Administration of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region: Nanning, China, 2022.
- Huang, Q.; Kang, X.G.; Chen, P.F.; Zhang, Z.J.; Yan, E.H.; Zang, Z.H.; Yan, H. Characterization of viscoelastic behavior of basalt fiber asphalt mixtures based on discrete and continuous spectrum models. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, Y.X.; Men, G.Y.; Xiao, P.; Tang, Q.; Han, F.Y.; Kang, A.H.; Wu, Z.G. Recent Advances in Basalt Fiber Reinforced Asphalt Mixture for Pavement Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Khater, A.; Yue, Y.C.; Abdelsalam, M.; Zhang, Z.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, J.N.; Iseley, D.T. The performance of asphalt mixtures modified with lignin fiber and glass fiber: A review Dong. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Aliha, M.R.M.; Moniri, A.; Saghafi, Y. Crack resistance of hot mix asphalt containing different percentages of reclaimed asphalt pavement and glass fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.F.; Zhang, K.; Xie, X.B.; Yao, X.G. Performance evaluation and material optimization of Micro-surfacing based on cracking and rutting resistance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ren, J.Q.; Cui, Y.H.; Shah, T.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhang, B.L. Length controllable tubular carbon nanofibers: Surface adjustment and oil adsorption performances. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 615, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Guan, C. Research on Basalt Fiber Oil/Asphalt Absorption Performance and Test Methods Suitable for Asphalt Mixture with Different Structures. Coatings 2024, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JT/T 533-2020; Fiber for Asphalt Pavements. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- AASHTO T 315-20; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR). AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- NB/SH/T 0184-2010; Specification on Technical Documentation for Construction Process of Petrochemical Construction Projects-Force Ductility Test of Bituminous Materials. National Energy Board: Beijing, China, 2010.
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Guo, N.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. Effect of fiber contents on toughness of polyester fiber asphalt concrete. J. Transp. Eng. 2006, 6, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhan, K.; Mashnad, M. Mechanical Stabilization of Cemented Soil–Fly Ash Mixtures with Recycled Plastic Strips. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhan, K.; Mashnad, M. Tensile Strength and Toughness of Soil–Cement–Fly-Ash Composite Reinforced with Recycled High-Density Polyethylene Strips. J. Environ. Eng. 2002, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO TP 124-16; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Fracture Potential of Asphalt Mixtures Using Semicircular Bend Geometry (SCB) at Intermediate Temperature. AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Feng, D.; Cui, S.; Yi, J.; Chen, Z.; Qin, W. Evaluation Index of Lowtemperature Asphalt Mixture PerformanceBased on Semicircular Bending Test. China J. Highw. Transp. 2020, 33, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.Y.; Chen, S.H.; Li, Y.; Pei, J.Z.; Zhang, J.P.; Wen, Y.; Li, R.; Cui, S.C. Effect of different fibers on the properties of asphalt mastics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.G.; Zhao, B.J.; Dai, T.T.; Li, G.Q.; Li, Y. Study on the dispersibility of modified basalt fiber and its influence on the mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Qin, X.; Chen, Q.; Ma, Q. Investigation of enhancing effect and mechanism of basalt fiber on toughness of asphalt material. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Lv, Y.; Xiao, P.; Ding, Z.; Yu, H. Toughness research and mechanism analysis of basalt fiber asphalt mixtures. J. Nanjing Univ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 39, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.W.; Pei, Z.H.; Luo, C.F.; Xia, J.; Chen, C.C.; Kang, A.H. Effect of different basalt fibers on the rheological behavior of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, H.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J.X.; Wang, T.L.; Peng, L.F. Modification and Enhancing Contribution of Fiber to Asphalt Binders and Their Corresponding Mixtures: A Study of Viscoelastic Properties. Materials 2023, 16, 5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Jiang, C.S.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, F.P.; Wang, J.G. Low temperature performance characteristics of polyethylene modified asphalts—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mallick, R.B.; Rahbar, N. Toughening mechanisms in polypropylene fiber-reinforced asphalt mastic at low temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiao, Y.B.; Liu, F.C.; Dong, Z.Z. Investigation of the low-temperature properties and cracking resistance of fiber-reinforced asphalt concrete using the DIC technique. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2020, 229, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.R.; Hu, Y.Y. Effect of aging on the low-temperature performance of fiber-reinforced asphalt mixtures. Aip Adv. 2023, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xiao, P.; Lou, K.K.; Wu, Y.H. Interfacial characteristics of fiber asphalt mastic and aggregates: Impact on mixture crack resistance performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.F.; Li, P.L.; Wei, X.F.; Sun, S.F.; Zhu, L.; Dong, C. Analysis of interface interaction of aggregate-asphalt system and its effect on shear-slip behavior of asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiloo, H.R.; Karimi, H.R.; Aliha, M.R.M.; Farahani, H.Z.; Salehi, S.M.; Hajiloo, M.; Haghighatpour, P.J. Crack resistance of fiber-reinforced asphalt mixtures: Effect of test specimen and test condition. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2022, 45, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).