Effect of Different Laser Parameters on Surface Physical Characteristics and Corrosion Resistance of 20 Steel in Laser Cleaning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
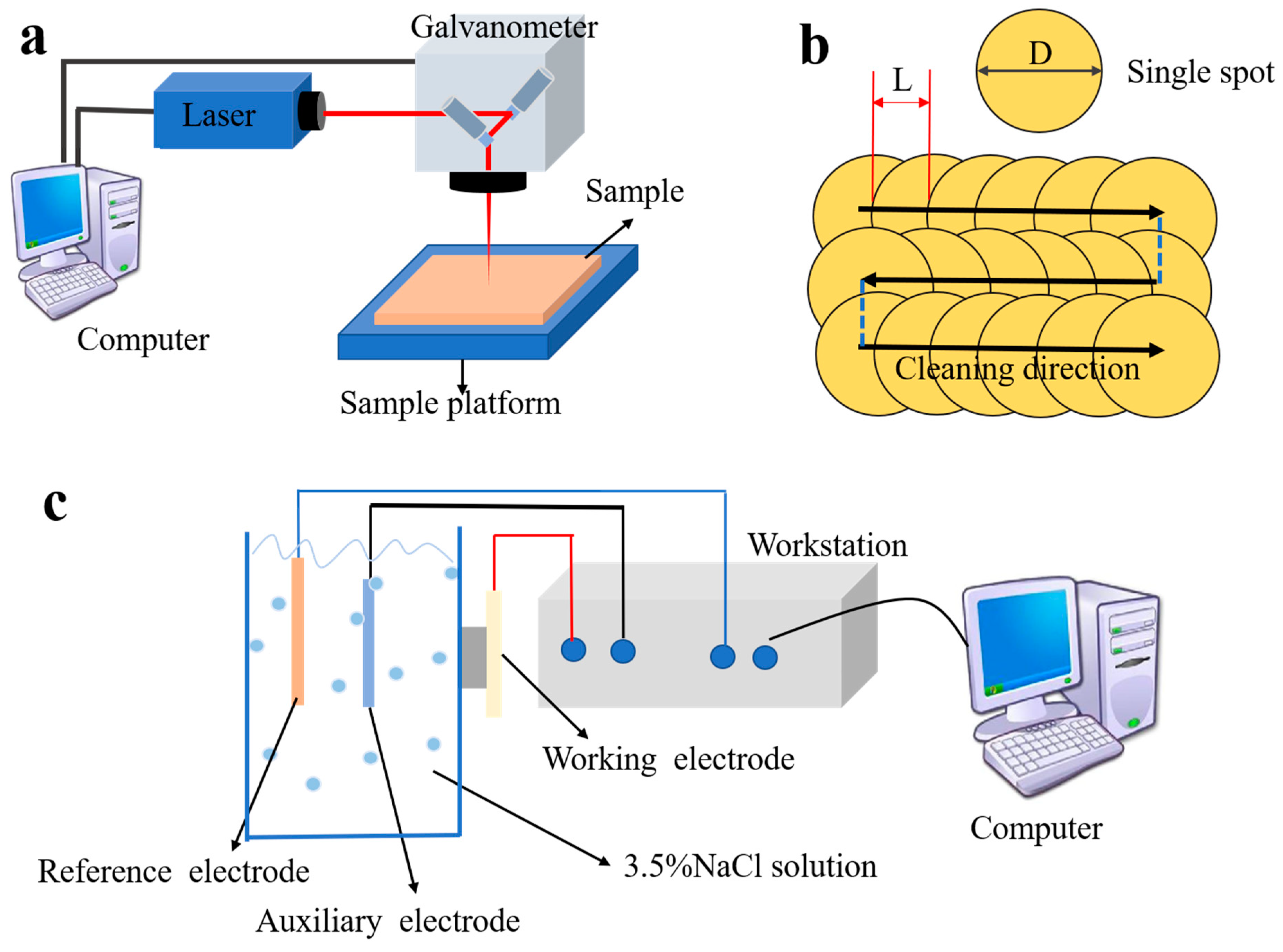
2.2. Laser-Cleaning Experiment
2.3. Surface Analysis
2.4. Electrochemical Experiments
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
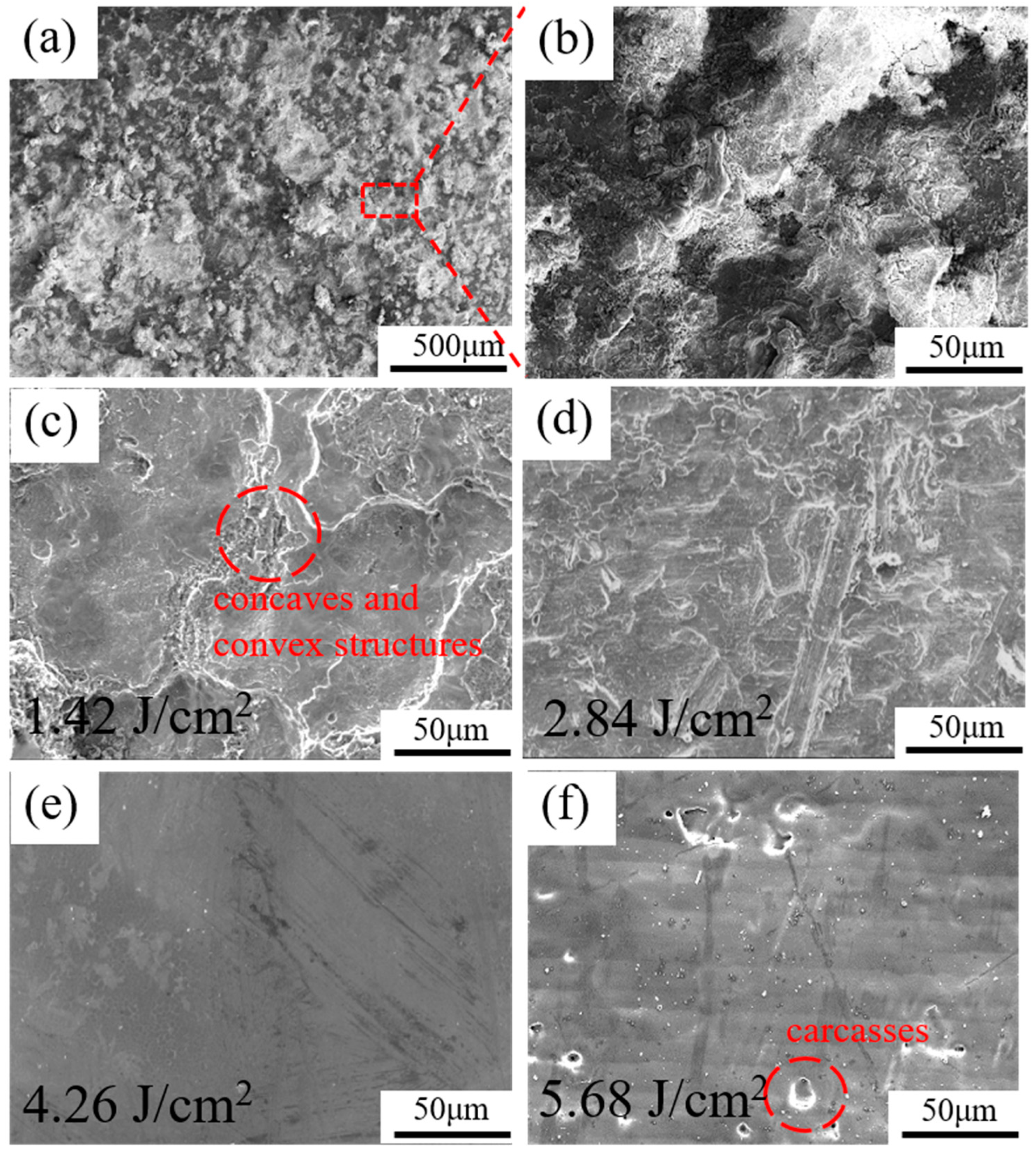
3.1. Microstructure Analysis
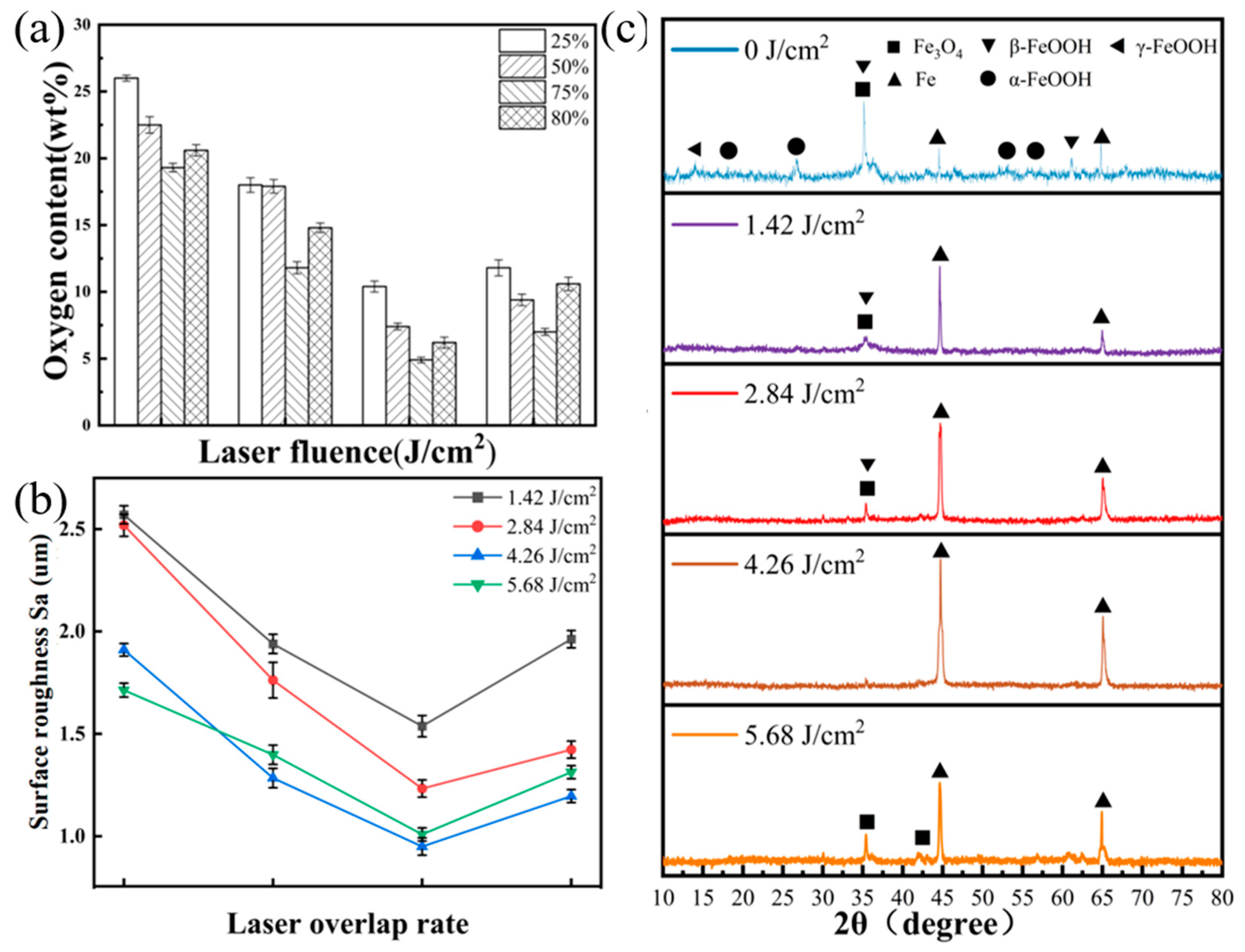
3.2. Surface Composition Analysis after Laser Cleaning
3.3. Microhardness Analysis
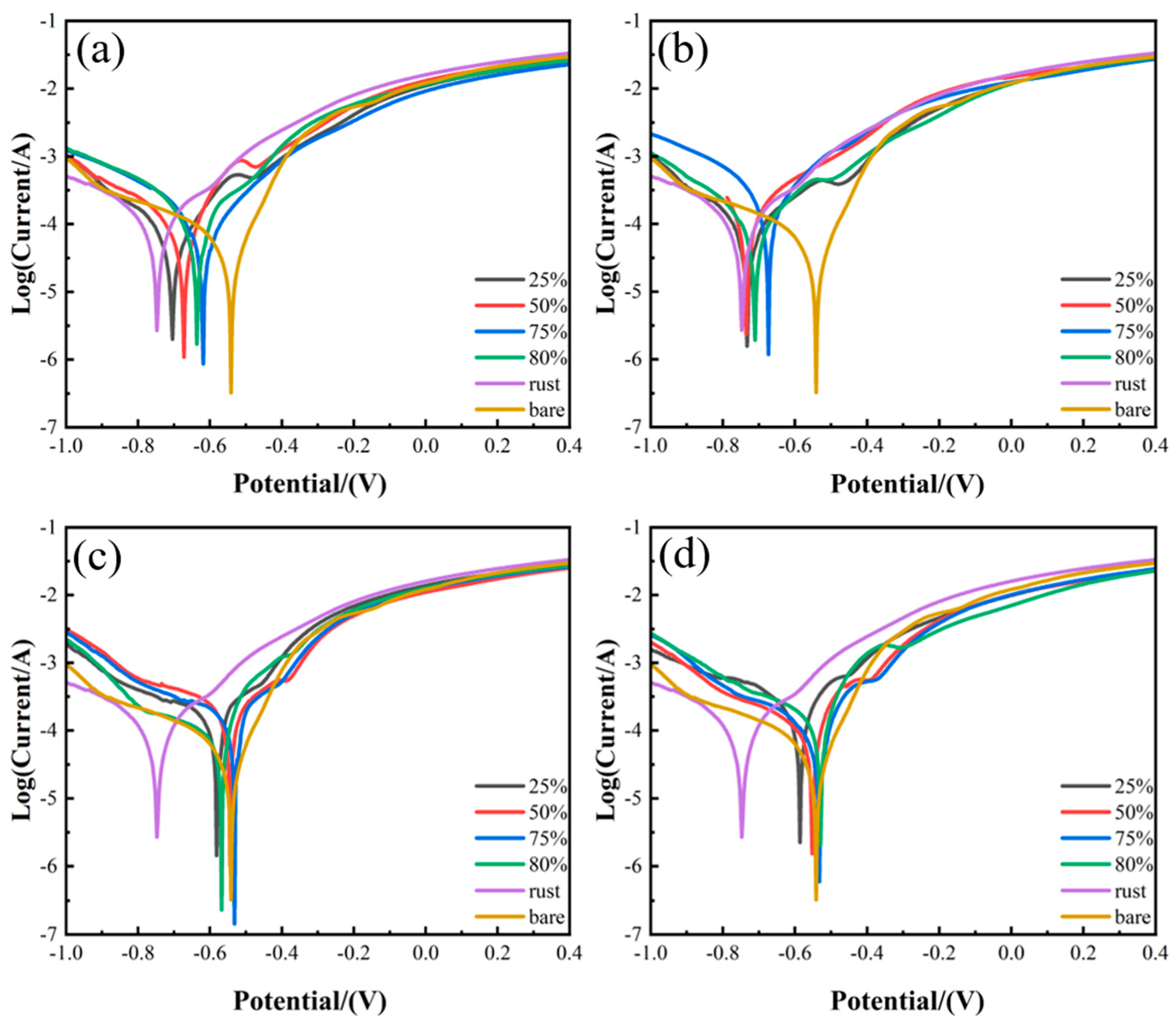
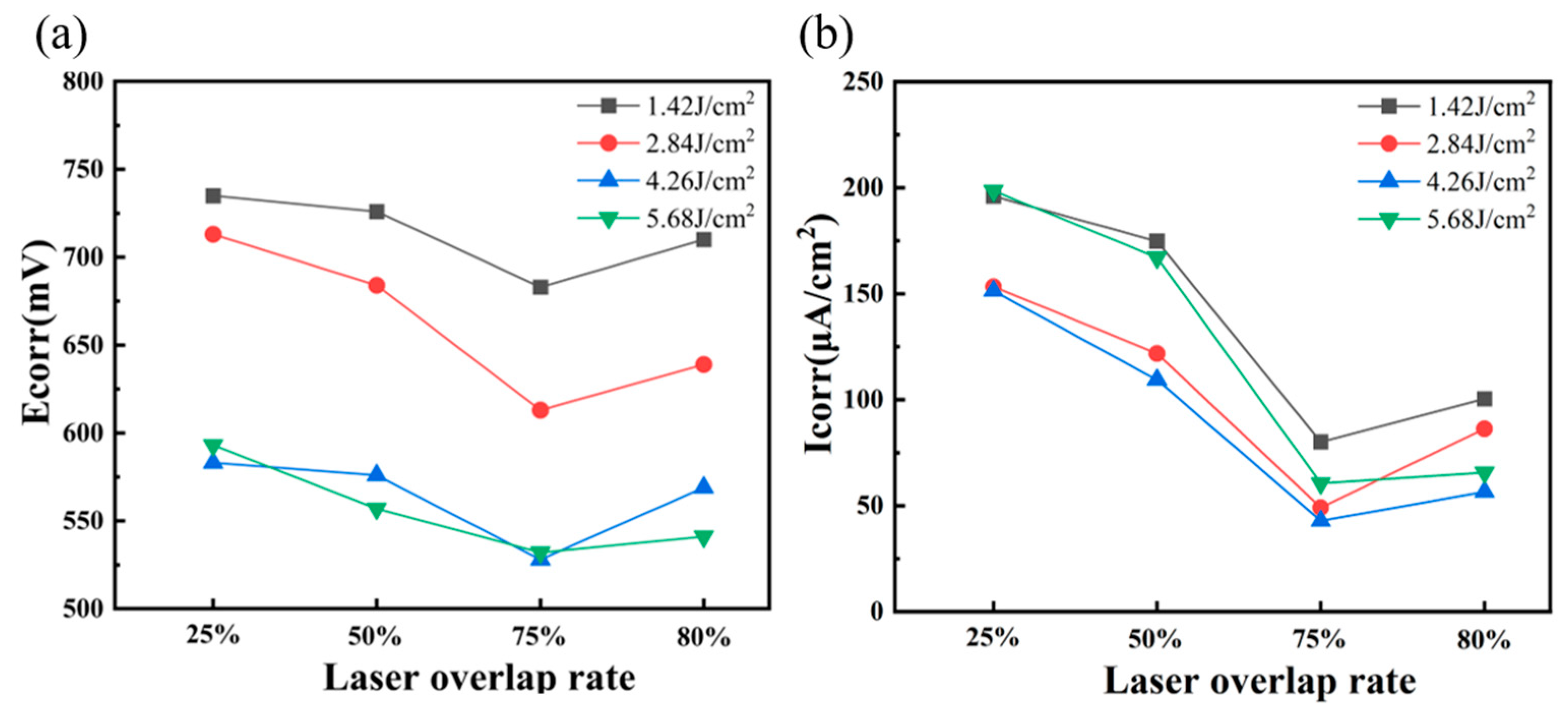
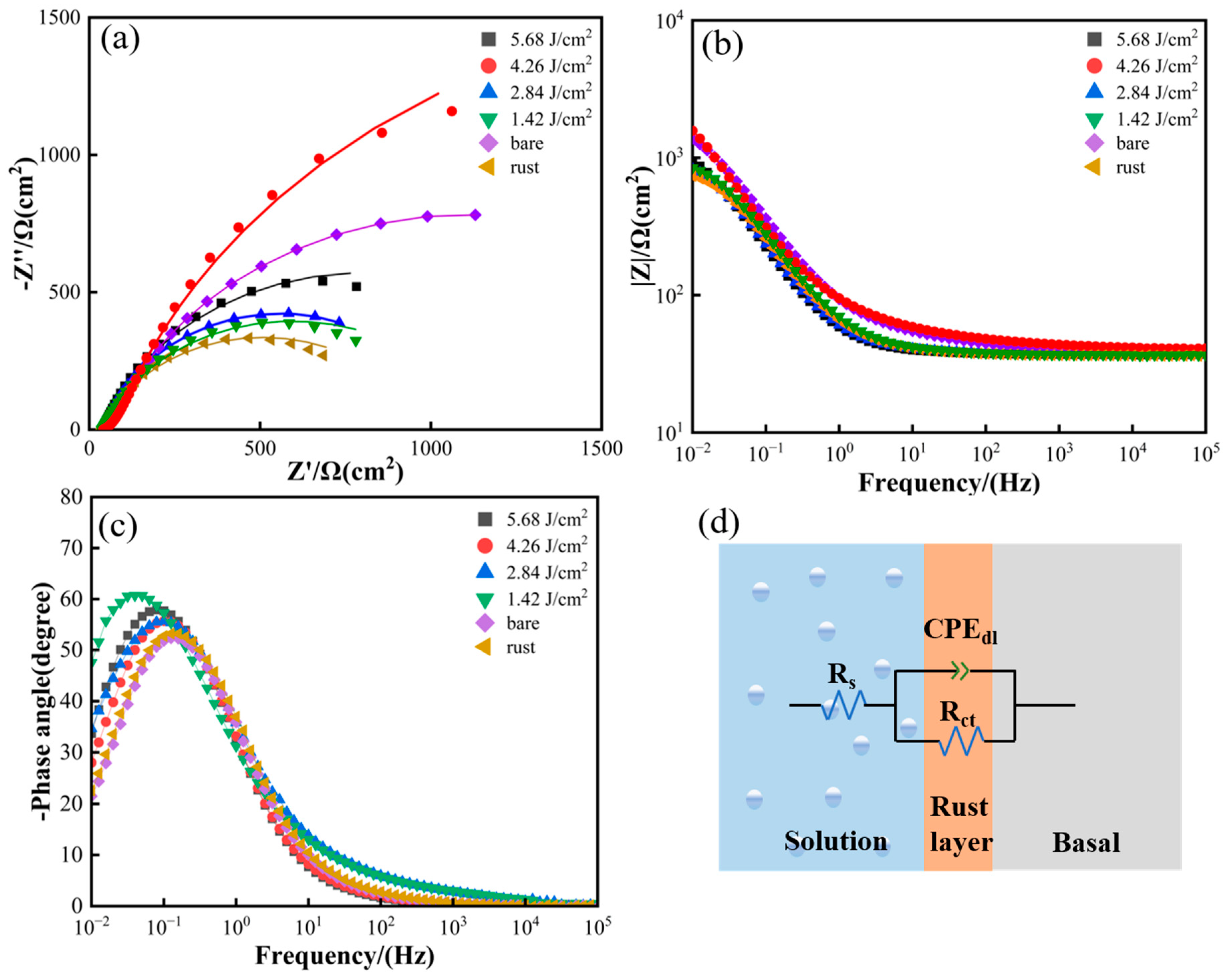
3.4. Corrosion Behavior Analysis
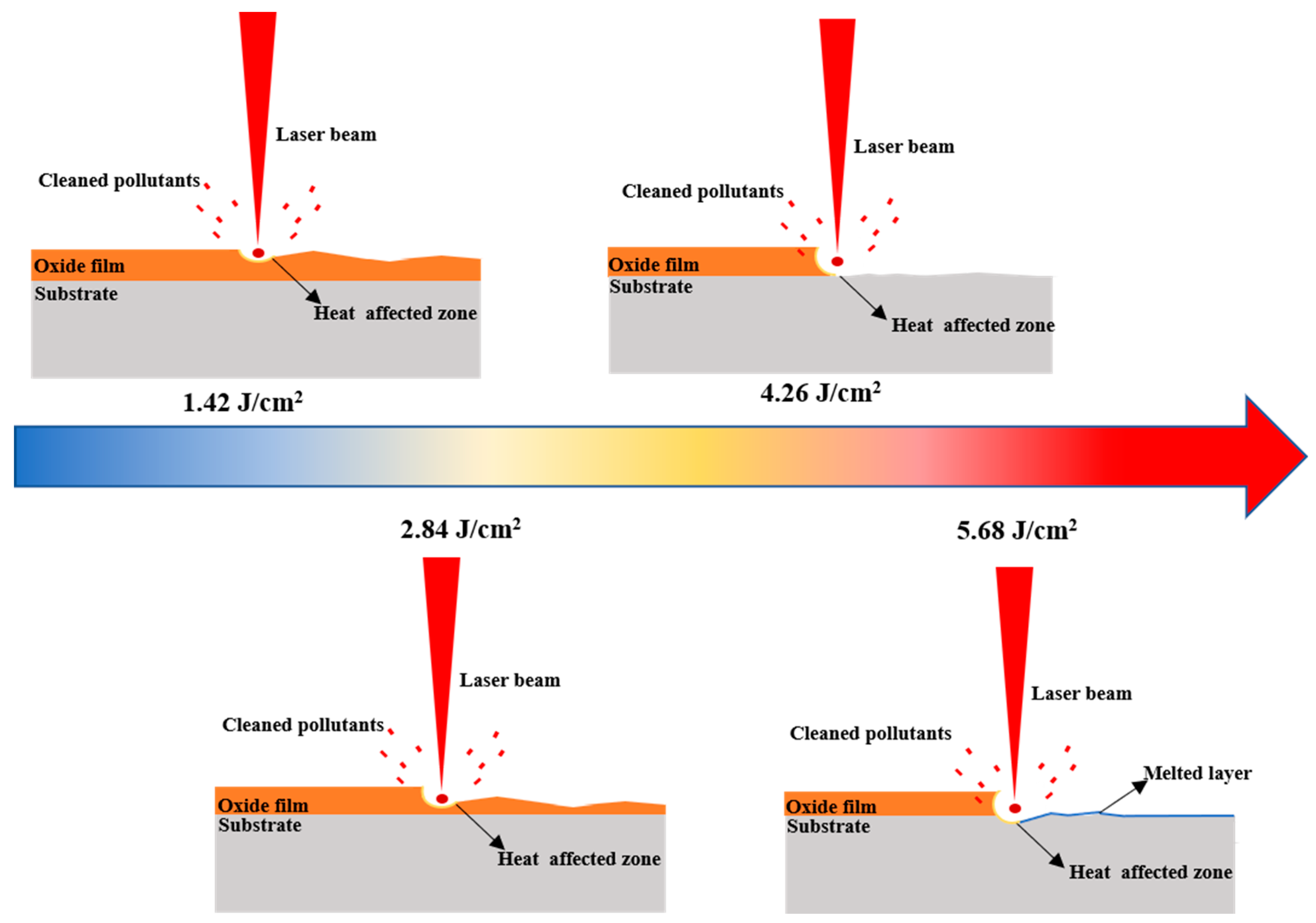
3.5. Rust Removal Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Through this study, at the laser energy density of 1.42–4.26 J/cm2, the removal of the rust layer on the surface of 20 steel is effective, especially at 4.26 J/cm2: the surface rust layer is basically removed without causing damage to the sample surface.
- (2)
- Infrared nanosecond pulsed laser can effectively remove the rust layer of 20 steel. The removal mechanism of the rust layer is mainly ablation. When the laser energy is higher than 4.26 J/cm2, the substrate absorbs too much laser energy and melts the substrate.
- (3)
- Compared with the traditional cleaning method, when the laser energy density is 4.26 J/cm2, with a spot overlap rate of 75%, laser cleaning not only does not reduce the corrosion resistance of 20-gauge steel but also improves the corrosion resistance of the original 20-gauge steel 1.218 times.
- (4)
- The morphological evolution of the sample surface after laser ablation at high energy density with different spot overlap rates is discussed; the key lies in the different cooling times of the molten material at different laser-scanning speeds at high energies, which leads to different distributions of the molten material flow around. This evolution provides a reference for the subsequent topographic changes of laser-cleaned substrates.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhandari, J.; Khan, F.; Abbassi, R.; Garaniya, V.; Ojeda, R. Modelling of pitting corrosion in marine and offshore steel structures—A technical review. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2015, 37, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, M.; Chico, B.; Díaz, I.; Cano, H.; de la Fuente, D. Atmospheric corrosion data of weathering steels. A review. Corros. Sci. 2013, 77, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, V.; Dionísio, A.; Pozo-Antonio, J.S.; Rivas, T.; Ramil, A. Mechanical and laser cleaning of spray graffiti paints on a granite subjected to a SO2-rich atmosphere. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol Pozo, A.A.; Bustos Bustos, E.; Monroy-Guzman, F. Decontamination of radioactive metal surfaces by electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 361, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Si, R.; Dai, Q.; You, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. A critical review of corrosion development and rust removal techniques on the structural/environmental performance of corroded steel bridges. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 126–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetser, S.E.; Cloete, T.E. Biofouling and Biocorrosion in Industrial Water Systems. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 31, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obot, I.B.; Meroufel, A.; Onyeachu, I.B.; Alenazi, A.; Sorour, A.A. Corrosion inhibitors for acid cleaning of desalination heat exchangers: Progress, challenges and future perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 111760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufus, A.L.; Velmurugan, S.; Sathyaseelan, V.S.; Narasimhan, S.V. Comparative study of nitrilo triacetic acid (NTA) and EDTA as formulation constituents for the chemical decontamination of primary coolant systems of nuclear power plants. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2004, 44, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Jia, X.; Hong, M.; Ren, Y.; Ma, M. A novel de-rusting method with molten salt precleaning and laser cleaning for the recycling of steel parts. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Yan, D.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S. Influence of laser beam incidence angle on laser lap welding quality of galvanized steels. Opt. Commun. 2017, 402, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siano, S.; Salimbeni, R. Advances in Laser Cleaning of Artwork and Objects of Historical Interest: The Optimized Pulse Duration Approach. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hua, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Shen, C.; Cheng, J. Investigation on mechanism of oxide removal and plasma behavior during laser cleaning on aluminum alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, Y. Investigation of the Surface Integrity of Q345 Steel After Nd:YAG Laser Cleaning of Oxidized Mining Parts. Coatings 2020, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y. An environmentally friendly laser cleaning method to remove oceanic micro-biofoulings from AH36 steel substrate and corrosion protection. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 127961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.H.; Narayanan, V.; Singh, R.K.; Marla, D.; Kondo, Y. Laser cleaning for rust removal on mild steel: An experimental study on surface characteristics. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 221, 01007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Mativenga, P.; Goffin, N.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Mirhosseini, N.; Jones, L.; Woolley, E.; Li, L. Energy consumption and performance optimisation of laser cleaning for coating removal. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2022, 37, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; Galtieri, G.; Borsellino, C.; Di Bella, G.; Proverbio, E. Durability of hybrid clinch-bonded steel/aluminum joints in salt spray environment. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 3137–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Qi, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L. Thermodynamic simulation, surface morphology and bending property of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite material subjected to laser cleaning. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, G.; Shan, Z. Effect of single pulsed picosecond and 100 nanosecond laser cleaning on surface morphology and welding quality of aluminium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 127, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, S.; Cheng, W.; Ren, Y.; Wen, D. Corrosion and wear performance of aircraft skin after laser cleaning. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 132, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yang, X.; Dong, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Gu, X. Layer-by-layer investigation of the multilayer corrosion products for different Ni content weathering steel via a novel Pull-off testing. Corros. Sci. 2022, 195, 109988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Dong, J.H. Study on the rusting evolution and the performance of resisting to atmospheric corrosion for Mn-Cu steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2010, 46, 1365–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, C.; Shan, D.; Guo, B. Removal mechanism of blue paint on aluminum alloy substrate during surface cleaning using nanosecond pulsed laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMangour, B.; Grzesiak, D.; Cheng, J.; Ertas, Y. Thermal behavior of the molten pool, microstructural evolution, and tribological performance during selective laser melting of TiC/316L stainless steel nanocomposites: Experimental and simulation methods. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 257, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | Ni | Cr | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass faction | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.35 | 0.035 | 0.30 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Specimen | Rs (Ω cm2) | CPEdl | Rct (Ω cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rust | 36.98 | 0.78771 | 943.4 |
| 1.42 J/cm2 | 37.43 | 0.78488 | 1114 |
| 2.84 J/cm2 | 37.78 | 0.80803 | 1178 |
| 4.26 J/cm2 | 37.61 | 0.81421 | 4116 |
| 5.68 J/cm2 | 37.45 | 0.81096 | 1544 |
| Bare | 37.46 | 0.69734 | 3379 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, C.; Yang, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Deng, L.; Fang, L.; Li, C. Effect of Different Laser Parameters on Surface Physical Characteristics and Corrosion Resistance of 20 Steel in Laser Cleaning. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052058
He C, Yang C, Yang H, Wang J, Liu J, Deng L, Fang L, Li C. Effect of Different Laser Parameters on Surface Physical Characteristics and Corrosion Resistance of 20 Steel in Laser Cleaning. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(5):2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052058
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Chengzhi, Can Yang, Huan Yang, Jiayan Wang, Jiani Liu, Leimin Deng, Licun Fang, and Chunbo Li. 2024. "Effect of Different Laser Parameters on Surface Physical Characteristics and Corrosion Resistance of 20 Steel in Laser Cleaning" Applied Sciences 14, no. 5: 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052058
APA StyleHe, C., Yang, C., Yang, H., Wang, J., Liu, J., Deng, L., Fang, L., & Li, C. (2024). Effect of Different Laser Parameters on Surface Physical Characteristics and Corrosion Resistance of 20 Steel in Laser Cleaning. Applied Sciences, 14(5), 2058. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14052058






