Abstract
The aim of this work was to perform a simulation analysis of the dynamics of a freight wagon with a variant vibration damping: dry friction and viscous damping. The following mathematical models of the damping characteristics are presented: the Maxwell model and the Kolsch model. The differences among the types of damping were first analyzed based on the dynamic responses of the 1 DOF model. Simulation studies were then carried out in a VI-Rail environment with the use of S-curved track models comprising short straight sections connecting the curves. The track models differed in the values of curve radii, cant, and length, which made it possible to run at different speeds. The multibody model of the vehicle represents a typical two-axle freight wagon. The dynamics of the wagon model were investigated for two states: empty and laden. Standard kinematic and dynamic values were compared in order to investigate if the nature of the damping has a significant impact on the dynamic properties of a freight wagon. The analysis of the simulation study showed that replacing dry friction damping with the viscous one can generally reduce forces acting on the wheel–rail contact, which, in turn, can be related to improving the running behavior of wagons while reducing the negative impact on the track.
1. Introduction
The suspension damping of freight wagons is achieved in the majority of bogie and two-axle wagon types by dry friction. This solution has been used practically since the early days of railway development and was also the basis for two-axle passenger coaches. Over time, viscous damping, provided by hydraulic dampers, became widely installed in passenger rolling stock, while dry-friction damping remained the domain of freight rolling stock and some special-purpose vehicles. It should be noted that dry friction is practically always present in the suspension and can be an additional, undesirable factor that affects the assumed damping characteristics. The additional damping force in the form of dry friction can be contributed to by, for example, the joints of the links, spring elements, and other interacting surfaces.
Design solutions of friction dampers show differences between different types of wagons and bogies. In the oldest solutions of the single-axle running gear of the two-axle freight wagons with horn guides, the damping of vertical vibrations was mainly realized by dry friction developed on the contact surface of the leaf springs. Also contributing to the damping of vertical vibrations in this type of running system are the sliders, bolted to the vertical walls of the axleboxes, which interact with the sliding liners of the guides. However, contact between the sliding surfaces also occurs when the longitudinal play is exhausted due to longitudinal displacements of the wheelset. A more recent, UIC-standardized solution, the so-called UIC double-link suspension, uses parabolic or trapezoidal leaf springs attached via double links to the vehicle frame. As in the classical solution, vertical vibrations are mainly damped by dry friction between the leaf springs, while displacements in the longitudinal direction are damped by dry friction developed in the link pin–end bearings pairs and lateral displacements by friction in the link–end bearings [1]. The damping of lateral and longitudinal displacements only occurs when a certain threshold force is exceeded, since for small amplitude movements the joints experience pure rolling [2]. The UIC double-link suspension model is depicted in Figure 1.
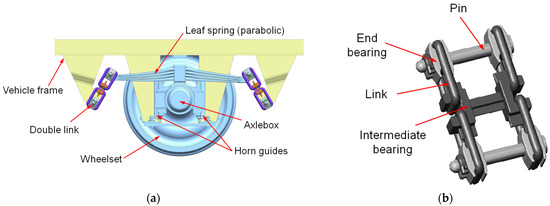
Figure 1.
UIC double-link suspension of a single-axle running gear. (a) Running gear model; (b) Diagram of a double-link connecting parabolic springs to a vehicle frame.
Vertical vibration damping by dry friction between leaf springs and other suspension elements (e.g., links and pins) is also used in two-axle freight wagon bogies—e.g., in DB 665 (standardized by UIC), presented in Figure 2, or Polish 1XT. The leaf springs in these bogies are installed in primary suspension.
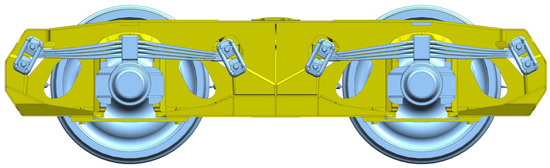
Figure 2.
DB 665 bogie with parabolic springs.
For the Y25 bogie family, the implementation of the primary suspension damper has taken a more complex form—the friction damper force depends on the load on the external (tare) spring. The friction damper consists of a pusher pressed by a spring holder against a friction plate fixed on the outer side of the axlebox. The spring holder is the upper spring seat on one side of the axlebox and is connected to the bogie via a Lenoir link positioned at an angle. As a result of the inclined position, the link exerts an angle-directed force (acting along the link) on a pin located in the spring holder. In this pin, there is a vertical component of the force, balancing part of the vertical load of the bogie, and a longitudinal component, pressing the spring holder against the pusher. The longitudinal component is responsible for the pressure on the pusher and increases with the wagon load (progressive characteristic) [3]. The Y25 bogie model and its friction damper are illustrated in Figure 3.
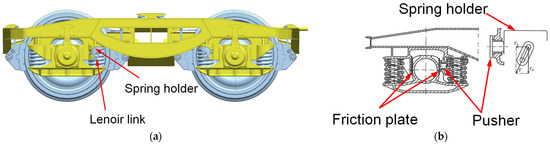
Figure 3.
Y25 bogie with parabolic springs: (a) Running gear model; (b) Diagram of the friction damper with Lenoir link (adapted from [4]).
A three-piece bogie (Figure 4), used predominantly in USA, Russia, China, and Australia, as well as other countries, has only a secondary suspension (between a bogie and a vehicle body) with wedge friction dampers. This bogie exists in two variations: with constant or with variable damping force. In the variable damping force variant, the friction wedge and the bolster are mounted on the separate springs, while in the constant damping force, the wedge is attached to the same springs as the bolster [5].
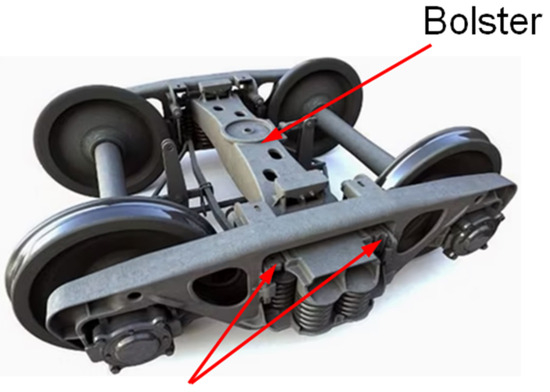
Figure 4.
A three-piece bogie [4].
Suspension friction dampers, regardless of the technical solution, have common advantages, namely: simplicity of design and fabrication, low cost, and easy maintenance. However, at the same time, they have significant disadvantages, such as suboptimal damping in the partially laden condition, the difficulties in controlling friction to the desired design values, and changes in friction coefficient due to contaminations and wear of the friction surfaces [6]. These negative factors, together with the need to reduce the impact of freight wagons on the track and increasing transport of goods by rail [7,8], are prompting the search for other solutions that provide adequate running behavior while keeping the bogie design complexity low [9,10,11]. One potential improvement to the running gear of freight wagons could be replacing dry friction damping with viscous damping. As an example of the use of viscous damping in a freight wagon, reference can be made to the historical series of experimental HSFV wagons [12] and the TF 25 bogies (Figure 5) that are currently in service in the UK [13].
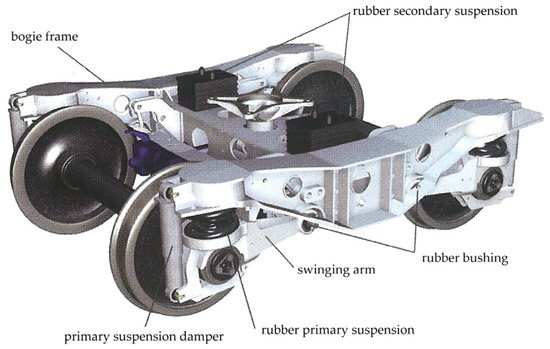
Figure 5.
TF 25 bogie [4].
Due to the literature gap concerning the comparison of the running behavior of freight wagons with variant damping (dry friction or viscous), this paper presents a comparative analysis of the results of simulation tests carried out according to the proposed scenarios.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. The multibody simulation model of the wagon is described in Section 2. The implemented mathematical damping models are introduced in Section 3. Simulation study conditions, analysis of the results, and discussion are included in Section 4. Section 5 closes with a conclusion and outlook.
2. Wagon Model
The impact of the nature of suspension damping on vehicle dynamics was investigated using a model of a two-axle wagon with geometric and mass-inertia parameters typical of a two-axle coal wagon. The rationale for choosing a two-axle wagon for the study was to reduce potential factors that could affect the running dynamics of the wagon, such as body–bogie yaw torque, or the coupling of bogie and body vibrations. The multibody wagon model, being implemented in the VI-Rail MD 2010 13.0 software (based on the Adams MD 2010 environment [14,15]), is relatively simple and does not take into account the suspension kinematics, with leaf springs and links (or double links) forming the technical pendulum [16], as found in the standard designs of two-axle freight wagons. Thus, there are no constraints in the suspension system due to the specifics of the suspension design; only spring and damping elements. Two wagon loading conditions were assumed for the tests: empty with a static axle load of 56 kN and laden with a static axle load of 219 kN.
The physical model of the wagon is depicted in Figure 6 and its main parameters are shown in Table 1—values referring to the laden wagon are placed in parenthesis.
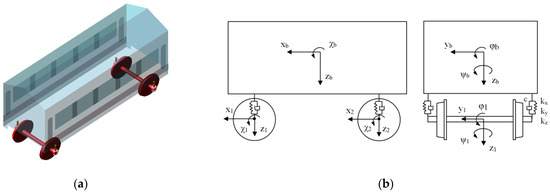
Figure 6.
Physical model of the wagon: (a) Simulation model in VI-Rail MD 2010 13.0 software; (b) Diagram of the wagon model.

Table 1.
Parameters of the two-axle freight wagon model.
The Differential Algebraic Equations (DAEs) describing the dynamics of the individual mass elements of the model are generated automatically in the Adams environment (Hexagon, formerly MSC Software) based on the Euler–Lagrange formalism. The general form of the equations is given by:
where q—column matrix of n generalized coordinates of the rigid bodies; L—Lagrangian (the difference in kinetic and potential energies: L = T − V); Φq—Jacobian matrix of constraints; λ—vector of Lagrange multipliers; Q—vector of external forces.
In order to solve (integrate) DAE in Adams, the default GSTIFF solver with I3 formulation was employed, and its error control is on the displacement states. GSTIFF is the integrator of variable-order, variable-step, multi-step, and its maximum integration order is six. However, the results of simulations are generated with a constant time step. The potential forces due to gravity are included in the vector of external forces Q in Adams solver. The wheel–rail creep forces are computed using the built-in procedure derived from the Kalker’s FASTSIM algorithm. This wheel–rail contact model represents a common way to calculate wheel–rail forces by means of a simulation approach [17,18,19,20,21]. At each simulation step, contact kinematics, required for creep force calculation, are computed using actual wheel and rail profiles. The implemented procedure allows for the analysis of the multipoint wheel–rail contact.
3. Vibration Damping Models
The section includes a description of the viscous friction based on the Maxwell model and the dry friction model developed by Kolsch. Mathematical descriptions are included.
3.1. Viscous Friction—The Maxwell Model
The Maxwell model is, along with the Kelvin–Voigt model, the basic mathematical description of the viscoelastic behavior of a solid material. It consists of a spring and a damper connected in series [22]. In this model, the spring represents the Young’s modulus and the damper the viscosity of the material. It allows for modeling stress relaxation. One can divide the total strain into one for the spring (ε1) and one for the dashpot (ε2) [23]. The standard form of the Maxwell model’s constitutive equation is (2):
where σ—stress, —stress rate, ε—strain, —strain rate, η—viscosity, E—Young modulus.
The use of a spring and a damper series configuration in the Maxwell model extends beyond the analysis of the behavior of viscoelastic materials. As with the Kelvin–Voigt model used in vehicle dynamics generally to model two separate suspension elements, namely a spring and a damper working in parallel and simultaneously, the Maxwell’s series configuration is employed to represent the operation of a hydraulic damper only. In this model, a series spring relates to the mounting elements and also takes into account the effect of oil compressibility [24], so this model allows for a more accurate representation of the operation of an actual hydraulic damper. Hence, the EN 13802 standard applicable to railway suspension hydraulic dampers [25] requires providing parameters of the Maxwell model: dynamic stiffness (3) and dynamic damping rate (4), both depending on the phase shift, which is typically greater than in the Kelvin–Voigt model.
where F0—damper force amplitude at sinusoidal motion, d0—damper displacement amplitude at sinusoidal motion, Φ—force-displacement phase shift at sinusoidal motion, f—excitation frequency.
A scheme of the Maxwell model, relating to the suspension damper, is shown in Figure 7.
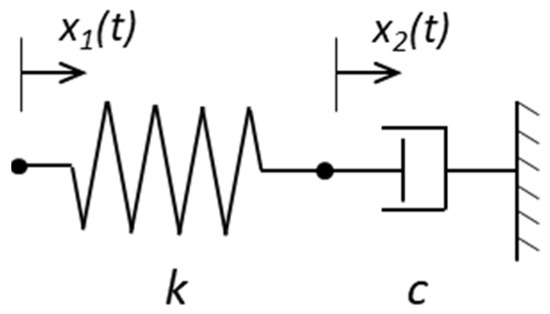
Figure 7.
The Maxwell model of a suspension damper.
The equation of motion of a dashpot rod of mass m, stiffness k, and damping constant c is expressed in the following form [26]:
Neglecting mass of the piston and rearranging:
Assuming harmonic input x1 of amplitude A, the solution of the equation for a zero initial condition is:
The damping force in Maxwell’s model can be calculated by differentiating expression (7) and multiplying it by the damping constant c. The characteristics of the viscous damping force in the Maxwell model are shown in Figure 8 for different values of the series stiffness k. An increase in stiffness k translates into a greater dashpot rod displacement and an increase in damping force. This implies a larger area under the curve, i.e., more energy is dissipated.
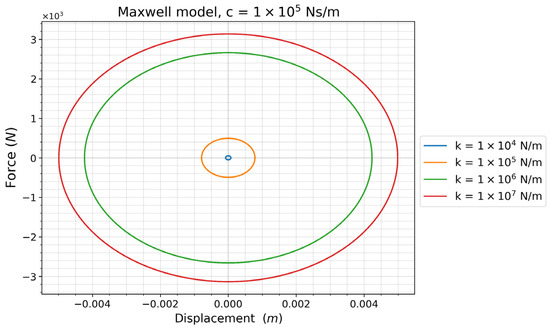
Figure 8.
Characteristics of the Maxwell model with constant damping c and for different stiffness k values, an excitation frequency f = 1 Hz, and an amplitude A = 0.005 m.
3.2. Dry Friction—The Kolsch Model
The dry friction model of suspension damping elements, implemented in VI-Rail software, is based on the model of structural members exhibiting static hysteresis, developed by Kolsch. Hysteresis is a known phenomenon occurring during a spring and damper operation, and it is usually included in models [24,26]. This model can also be used to reproduce the behavior of friction elements such as wedges, leaf, springs, and rubber components. The original form of the mathematical model includes ordinary differential equations—the constitutive equations of i = 1 … n, connected in parallel, n-forces Ki, essential for energy dissipation [27]. The Ki forces are state variables, called ‘hidden variables’, and cannot be directly measured in the process of model identification in contrast to the total force F to which Ki contributes. Since the forces Ki are originally associated with the structural damping of structural members exhibiting hysteresis, in this study, in order to model the dry friction damping element of suspension, only one K term is adopted in the Kolsch model. In this regard, it is no longer intended to reflect internal damping but the damping force generated in the interface of contacting suspension elements’ surfaces, and thus, it is henceforth denoted as friction force Ff. Adapted to the rail vehicle suspension, the Kolsch’s model consists of a series connection of a spring (with stiffness k1) and a friction component (with the hold force H). These are parallel-connected by another spring with stiffness k0, representing the main spring suspension element (Figure 9).
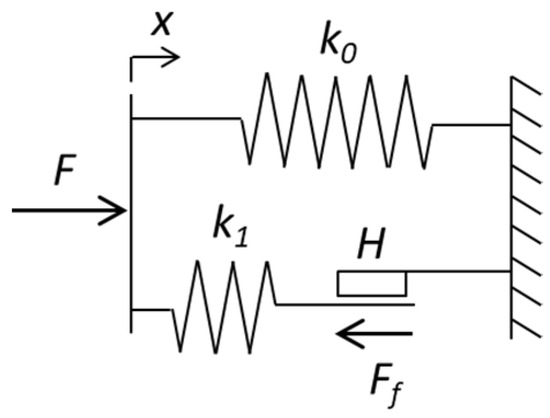
Figure 9.
The Kolsch dry friction model.
As long as the force in the spring k1 does not reach the hold force H, the system behaves like a spring with an equivalent stiffness . When the force in the spring k1 exceeds the hold force H, the friction element will start to slip, generating a friction force Ff. The hold force H is defined as (8):
where µ—coefficient of friction, Fpre—preload friction force, Ff—friction force in the friction element.
The friction force in the Kolsch model is described by expression (9):
where m—an exponent of the transition; α, β—constants; A(x)—a parameter depending on spring deflection.
The total force F in the suspension with the friction element is the sum of spring k0 force and force in the friction element (10):
Due to the lack of the Kolsch model parameter values obtained experimentally, the parameters implicitly implemented in the simulation software were used. These parameters are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Parameters of the friction damper—the Kolsch model.
The friction and total force characteristics of the Kolsch model, with the parameters presented in Table 2, are shown in Figure 10. The friction force characteristic is not ideally rectangular, but it is slightly sloping, reproducing elastic micro-deformation by spring k1. If the stiffness of this spring is reduced, the skewness of the hysteresis loop increases. When the stiffness k1 is infinite, then the loop will have a rectangular shape. The characteristics of the total suspension force exhibit a noticeable force–displacement relationship, increasing monotonically (spring k0), while forming a hysteresis loop as a result of spring k1 and the friction force element.
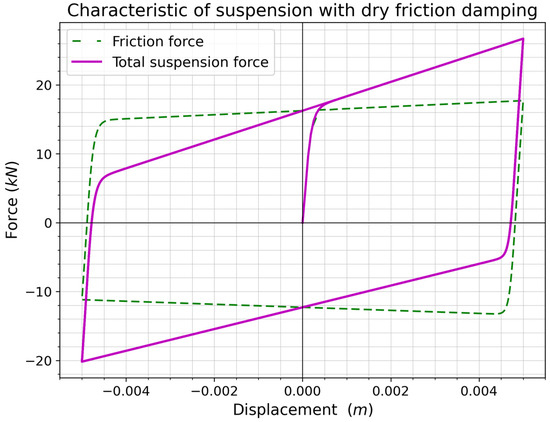
Figure 10.
Characteristics of the Kolsch friction damper model, excitation frequency f = 1 Hz, and amplitude A = 0.005 m.
Figure 5 compares the damping of the vertical free vibration of a 1DOF quarter of a wagon body with viscous damping using Maxwell’s model with an infinitely stiff spring (Maxwell model reduced to a dashpot) and dry friction damping (Kolsch model). The vibration amplitudes for both damping models show significant differences. Dry friction damping is characterized by larger amplitudes, but the vanishing of vibrations occurs at practically the same instant as in the case of viscous damping. Dry friction damping exhibits the disadvantage of varying the equilibrium position with respect to the initial (zero) position at each half of the vibration cycle. This phenomenon is evident in both the time waveform (Figure 11a) and the phase portrait (Figure 11b).
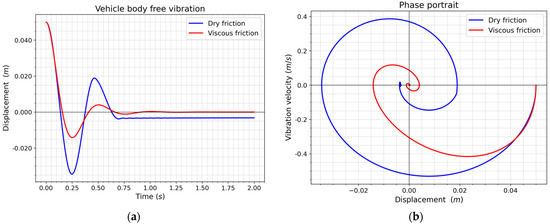
Figure 11.
Comparison of vertical vibrations of a vehicle model body with dry friction and viscous damping: (a) Vehicle body free vibration; (b) Phase portrait.
4. Simulation Study
The research was performed by means of simulation computations. There were defined specific conditions for simulations. All details about the simulation study and the achieved results are described in this section.
4.1. Conditions of the Study
The study on the influence of the nature of damping on the dynamics of a rail vehicle was carried out on two S-curved track models, differing in length, radius values, and superelevation:
- The first track: R = 150 m, cant h = 0 mm, total length = 220 m;
- The second track: R = 320 m, cant h = 110 mm, total length = 950 m.
Plan views of the simulated tracks are presented in Figure 12.
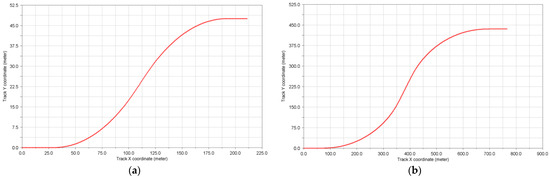
Figure 12.
Plan view of the simulated S-curved tracks: (a) the first track: R = 150 m, length = 220 m; (b) the second track: R = 320 m, length = 950 m.
Geometric irregularities were implemented in both tracks, generated from the power spectral densities for the vertical (Szz) and lateral (Syy) directions [28], according to Formulas (11) and (12):
where = 0.8246 rad/m, = 0.0206 rad/m, Av = 1.08 × 10−6 m rad, AA = 6.1 × 10−7 m rad. The values were adopted from ORE B 176 for a high level of irregularities [29].
Track irregularities belong to very important input parameters for a model. They influence the rail vehicle dynamics and its resulting dynamic response [30,31,32]. Based on the height of the irregularities and their standard deviation, a qualitative classification of the track geometric quality can be made. The height of the irregularities for the modeled tracks corresponds to the good maintenance condition (QN1) for tracks with a permissible speed ≤ 80 km/h according to the UIC 518 leaflet [33]. In turn, in terms of the standard deviation of the irregularities, the track is classified as a track of medium maintenance condition (QN2). The values of statistical measures describing irregularities for a track of geometric quality QN1 are smaller than for QN2. The values of irregularities’ measures based on UIC 518 for a given track geometric quality and the values of irregularities’ measures implemented in the simulation model are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The values of statistical measures of irregularities for a track with permissible speed v ≤ 80 km/h. Adapted from [33].
In rail vehicle dynamics simulation, the track is often modeled as flexible [34]; however, for the purpose of this study, the tracks were assumed to be rigid in order to reduce the number of potential variables affecting the vehicle’s dynamic responses.
The vehicle speed on the first track was v = 50 km/h, while on the second track, with a larger radius of the curves, it was v = 80 km/h. Due to the high running speed in relation to the radius of the curves, the test scenario using the first track may correspond to a vehicle emergency (e.g., due to a faulty brake system) or driver error. The assumed geometrical parameters of the first track and the assumed running speed result in an unsustainable lateral acceleration of ay = 1.29 m/s2 and a cant deficiency of CD = 197 mm, which significantly exceed the permissible values used on railway lines worldwide. The second track, on the other hand, was designed such that for a running speed of v = 80 km/h, the unbalanced lateral acceleration ay = 0.79 m/s2, while the cant deficiency CD = 121 mm. The acceleration values were obtained using a simple point-mass vehicle model of mass m running on a slope (Figure 13).
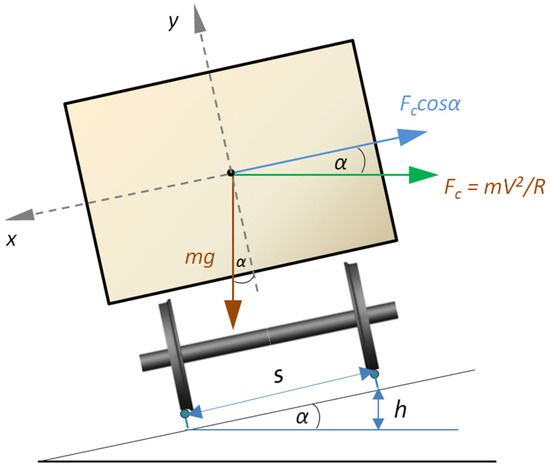
Figure 13.
Simplified model of a rail vehicle running on a canted track.
By applying D’Alembert principle to the x-axis, the following relation is obtained (13):
Expressing sinα using track cant (14):
where h—track cant, s—lateral distance between contact points, s = 1.5 m for standard-gauge track.
However, if the forces in (11) are not in equilibrium (e.g., insufficient track superelevation for a given vehicle’s running speed), a vehicle experiences an unbalanced ay acceleration whose value should not exceed the limit value alim. Assuming that the x component of inertial force is greater than the x component of a vehicle’s weight and the root term equals 1 (in fact near 1, since usually [35]), the equation for the unbalanced acceleration due to cant deficiency is (15):
The simulations were run with solver settings given in Table 4. The sampling frequency in the first scenario was c.a. 117 Hz, with a time step of 0.0085 s, and in the second one, the values were 100 Hz and 0.01 s, respectively.

Table 4.
Solver settings for simulation scenarios.
Since the aim of the study was to investigate differences in the dynamic responses of the wagon model due to the character of damping, while the accurate modeling of a specific damper was out of scope of this study, the series stiffness k1 in the Maxwell model was assumed to be infinite. This fact entailed reduction of the Maxwell model to adashpot for the wagon model with viscous damping in suspension.
In the course of the simulation studies, the dynamic quantities—lateral and vertical forces—were recorded, which are related to both running safety and the impact of the vehicle on the track [36,37,38]. For the quantitative assessment of the obtained signals, the normative parameters used to assess running characteristics in the rail vehicle approval process were used, namely the median and percentile—0.15% and 99.85%. As the test sections of the track are relatively short and the track consists of reverse curves, the recorded signals will have similar median values. For this purpose, a measure of dispersion—standard deviation—was introduced to allow for greater distinguishability of qualitatively similar signals.
4.2. Result of the Simulation Study
The vertical forces on the left wheel of the first (front) wheelset, for the two loading conditions of the wagon, are shown in Figure 14 and in Figure 15 for the changes in the forces on the right wheel during running in the first track.
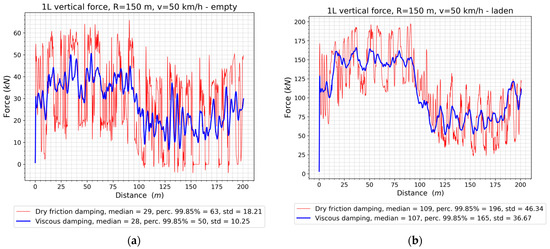
Figure 14.
The vertical forces of the left wheel of the first wheelset: (a) The empty wagon; (b) The laden wagon.
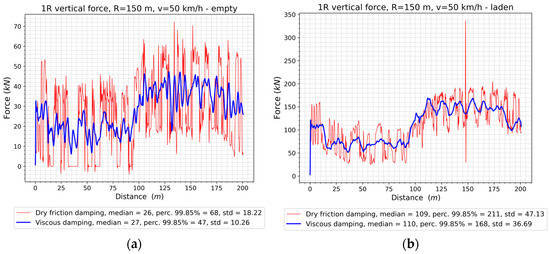
Figure 15.
The vertical forces of the right wheel of the first wheelset: (a) The empty wagon; (b) The laden wagon.
An increase in the value of vertical forces depending on the load mass is an obvious, expected result. The effect of using viscous damping instead of dry friction damping is the reduction of the impact of the vehicle on the track in the vertical direction. Both the 99.85% percentile values and the standard deviation of the vertical force on wheels of the first wheelset are significantly lower. The same observations are also valid for the recorded forces in the right wheel contact of the first wheelset (Figure 15).
The sum of the lateral forces is the quantity used to assess the running characteristics of rail vehicles in the acceptance process according to EN-14363 [39]. The values of the sum of lateral forces recorded in the first track for the first wheelset are shown in Figure 16, and for the second wheelset in Figure 17. Changes in the value of the sum of lateral forces are characterized by a greater spread of values when the damping is a dry friction force (larger standard deviation). The extreme values, defined by the percentiles, are more favorable for the model with viscous damping. These conclusions are also valid for the second wheel set and the empty wagon (Figure 17a).
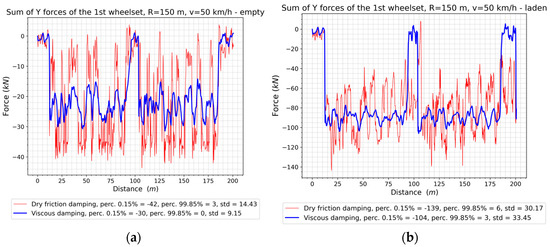
Figure 16.
Sum of lateral forces of the first wheelset: (a) The empty wagon; (b) The laden wagon.
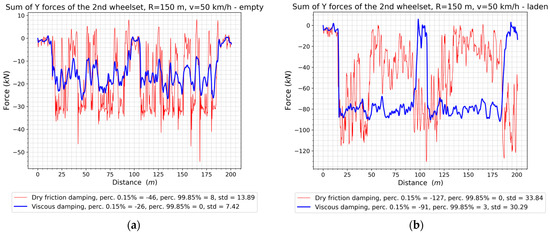
Figure 17.
The sum of lateral forces of the second wheelset: (a) The empty wagon; (b) The laden wagon.
The additional load on the wagon causes an increase in the dispersion of the sum of the guiding forces (standard deviation), which, for the first (Figure 16b) and second wheelsets (Figure 17b), can be the result of a significant reduction in the sum of the forces on the track section connecting the reverse curves and on the final track section. In curves, however, the first wheelset sustained much smaller variations in force values when the damping was viscous, as well as smaller values of percentile 0.15%, indicating smaller, in absolute terms, lateral forces. On the other hand, the sum of the lateral forces of the second wheelset reached higher, in absolute terms, values of percentiles for the model with dry friction. The wagon model with viscous damping is characterized by qualitatively similar runs of the sum of the guiding forces on the first and second wheelsets, in contrast to the model with dry friction, whose sum of the transverse forces of the second wheelset in the loaded state differs from the other plots for dry friction dampers. In general, it can be concluded that the variation in the sum of the lateral forces is greater in the case of dry friction damping.
In order to statistically capture the obtained results, percentage changes in the percentile values and RMS values of forces in contact with the rail wheel were calculated using Formula (16):
Percentage changes in the values of vertical forces are shown in Figure 18. The percentile 99.85% values of the vertical forces of both wheels of the first wheelset were lower in each case analyzed for the wagon model with viscous damping—the reduction in values ranged from 15% to 31%. Conversely, the RMS values for only the laden vehicle running on the second track were only increased by 1% relative to dry friction damping. The percentage changes for the left and right wheels are equal. In general, it can be concluded that, for the adopted tracks and running speeds, the implementation of viscous damping can contribute to a reduced vertical impact on the track.
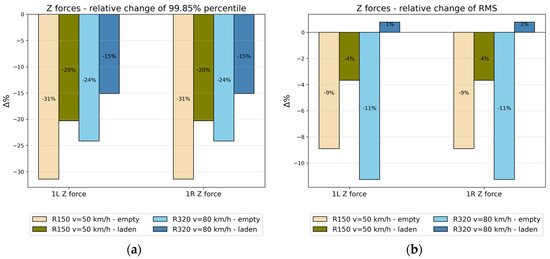
Figure 18.
Vertical forces of a left and right wheel of the first wheelset: (a) Relative changes of the 99.85% percentile; (b) The RMS value.
The percentage changes in the sum of the lateral forces are shown in Figure 19. In addition to the RMS values, percentile 0.15% was chosen for the analysis due to the fact that the extreme values of the sum of the lateral forces are negative. The use of viscous damping resulted in a reduction in the absolute value of the forces (percentile 0.15%), by up to 70% for the front wheelset and 44% for the rear wheelset when the laden wagon was running on the second track. This is particularly favorable given the greater impact of a laden vehicle on the track. A reduction in the extreme values of the sum of lateral forces occurred in all study scenarios. Considering the RMS value, it can generally be seen that viscous damping has a reducing effect on the averaged values of the sum of the lateral forces. Also in this case, a 70% reduction in values was achieved for the front wheelset of the laden wagon moving on the second track, but on the rear wheelset, the reduction in lateral forces was only 6%. The increase in RMS value relates only to the run of a laden wagon on the first track and is 24%.
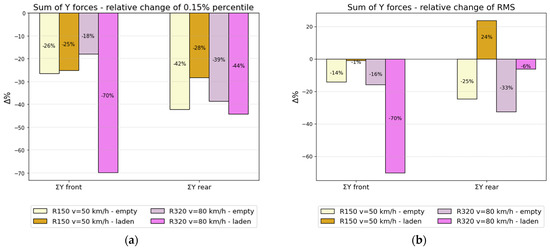
Figure 19.
A sum of guiding forces: (a) Relative changes of the 99.85% percentile; (b) The RMS values.
In order to explain the adverse increase in the sum of the guiding forces on the second wheelset during running of a laden wagon on the first track, the lateral displacements of the wheelsets can be investigated for this purpose (Figure 20), as well as their angles of attack (Figure 21). This allows for the alignment of the wheelsets with respect to the track to be clarified, which has a significant effect on the generated forces in wheel–rail contact. The rear wheelset of the empty model follows the curvature of the track, regardless of the damping used (Figure 20a). The plot of angle of attack is qualitatively similar for the same model, indicating an incomplete radial alignment of the wheelset in the track (Figure 21a). As a result of the increased weight of the wagon, the wheelset of the friction damped wagon changes to the opposite lateral shift from about halfway through the first curve. Disregarding the straight section between the curves, the wheelset is displaced in the opposite direction to that of an empty wagon and opposite to that of a wagon with viscous damping (Figure 20b). With the exception of a short section of tangent track connecting the reverse curves, where the value of angles of attack reached as much as 1.5°, for the remainder of the section, the angles of attack were smaller than for the empty wagon and for the wagon with viscous damping. The laden wagon with friction dampers ran at a near-zero angle of attack for certain sections of the track, thus reducing its interaction with the track. This phenomenon can explain the 24% increase in the RMS value of the sum of lateral forces on the wheelset of the laden wagon model with viscous damping.
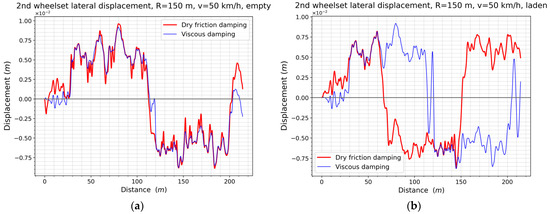
Figure 20.
Lateral displacement of the second wheelset in the first simulation track: (a) The empty wagon; (b) The laden wagon.
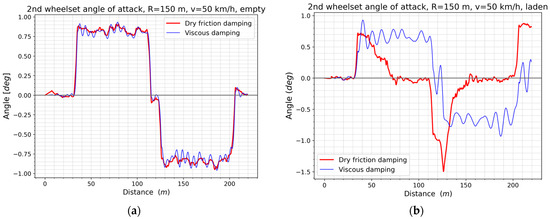
Figure 21.
Angles of attack of the second wheelset in the first simulation track: (a) The empty wagon; (b) The laden wagon.
Qualitatively and quantitatively, the plots of angle of attack of the rear wheelset for the wagon with viscous damping without load and with load were similar.
The vibration damping ability can be compared based on the power dissipated by individual dampers. The RMS values of the dissipated power for the wagon models tested on the first track are shown in Figure 22 and Figure 23. For an empty wagon, the RMS value of the dissipated power is several times higher when viscous damping is used. This difference increased considerably in the case of a laden wagon—in an extreme instance, there was even a difference of more than 20 times in the value of the dissipated power (Figure 22a, 1R wheel). When the laden wagon passed on the second track, the difference was on average 10 times in favor of the wagon with viscous damping (Figure 23a).
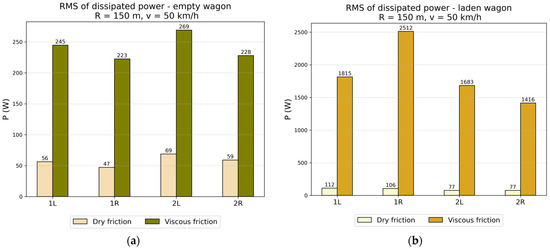
Figure 22.
RMS values of dissipated power by dry friction dampers and viscous dampers in the track with curves of R = 150 m, v = 50 km/h: (a) The empty wagon; (b) The laden wagon.
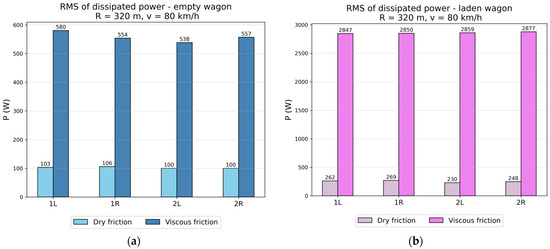
Figure 23.
RMS values of dissipated power by dry friction dampers and viscous dampers in the track with curves of R = 320 m, v = 80 km/h: (a) The empty wagon; (b) The laden wagon.
5. Conclusions
Improving the running behavior of freight wagons while reducing the negative impact on the track is in the interest of manufacturers and vehicle and infrastructure operators. With the tendency to increase axle loads and operating speeds, the specific solutions must be implemented to meet these requirements. One of the potential ways to improve the running behavior of the vehicle while reducing the impact on the track may be the introduction of viscous damping in the vehicle suspension. The analysis presented herein shows that it is possible to reduce the negative impact on the track by using hydraulic dampers. The model of a two-axle freight wagon was tested under conditions of significantly exceeding the permissible lateral acceleration for the adopted track, i.e., for conditions not occurring during normal operation. Maintaining running safety in such conditions is a particular challenge for the running gear. Given the design of the two-axle wagon—the large wheelbase compared to the bogie wagons and, thus, the positioning of the wheelsets at greater angles of attack—this task was made even more difficult. As indicated by the results of the conducted simulation tests, the use of viscous damping instead of dry friction damping in the wagon suspension may contribute to reducing the vertical and lateral impact of the vehicle on the track. In most cases, the reduction of the parameters (the measured values) ranged from 1% to even 70%. In a special case—a laden wagon running in the first track—a 24% increase in the sum of lateral forces on the second wheelset was obtained. The reason for this was the positioning of the wheelset in the track, which was even more favorable than for the empty wagon. In addition, the power values dissipated by viscous dampers are up to 20 times higher than those of standard friction dampers, which have an effect on the damping of vibrations.
A two-axle model was used in the analysis due to the lack of additional wheelset–bogie–carbody interactions. It should be noted that two-axle wagons have a marginal share in freight transport and have been practically completely replaced by four-axle wagons. Therefore, the assessment of the impact of viscous damping on the running behavior and track impact of the freight wagon should be further carried out on a four-axle freight wagon model.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app142210624/s1, The vehicle and the track models in the form of a database ‘Rail_Veh_Viscous_vs_Friction.cdb’ in the VI-Rail MD 2010 13.0 software have been provided with the description in the document ‘Description.docx’.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, simulation, data analysis, writing—original draft preparation, R.M.; simulation, data analysis, funding acquisition, editing, S.K.; literature review, simulation, J.S.; simulation, literature review, editing, supervision, J.D.; data curation, visualization, supervision, J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by a research grant in 2023 of the Scientific Council of the Discipline of Civil Engineering, Geodesy and Transport, grant number 504/04849/1160/43.072305, grant manager Seweryn Koziak, administrative support provided by the administrative services of Faculty of Transport, Warsaw University of Technology.
Data Availability Statement
Simulation models are contained within the Supplementary Material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Development of Functional Requirements for Sustainable and Attractive European Rail Freight. D4.1—State of the Art. FR8RAIL. 2017. Available online: https://projects.shift2rail.org/s2r_ip5_n.aspx?p=FR8RAIL (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Freight Train Derailment at Ely West Junction, 14 August 2017. Rail Accident Investigation Branch. 2018. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/report-092018-freight-train-derailment-at-ely-west-junction (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Gialleonardo, E.D.; Bruni, S.; True, H. Analysis of the Nonlinear Dynamics of a 2–Axle Freight Wagon in Curves. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2014, 52, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, P. Rail Vehicles II, 1st ed.; University of West Bohemia in Pilsen: Pilsen, Czech Republic, 2019; pp. 124–126. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Spiryagin, M.; Cole, C. Methodology to Optimize Wedge Suspensions of Three-Piece Bogies of Railway Vehicles. J. Vib. Control 2018, 24, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, A.; Boronenko, Y. The Anatomy of Railway Vehicle Running Gear. In Handbook of Railway Vehicle Dynamics, 1st ed.; Iwnicki, S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 39–81. [Google Scholar]
- Bizoń, K.; Chmielewska, A.; Chudzikiewicz, A.; Sładkowski, A.; Stelmach, A. Integrated research of multi-purpose stanchion baskets for transporting timber and containers. Transp. Probl. 2023, 18, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlici, J.; Lovska, A.; Pavliuchenkov, M. Study of the Dynamics and Strength of the Detachable Module for Long Cargoes under Asymmetric Loading Diagrams. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, S.; Gerlici, J.; Vatulia, G.; Lovska, A.; Rybin, A.; Kravchenko, O. Strength assessment of an improved design of a tank container under operating conditions. Commun. Sci. Lett. Univ. Žilina 2023, 25, B186–B193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatulia, G.; Lovska, A.; Pavliuchenkov, M.; Nerubatskyi, V.; Okorokov, A.; Hordiienko, D.; Vernigora, R.; Zhuravel, I. Determining patterns of vertical load on the prototype of a removable module for long-size cargoes. East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2022, 6, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovskaya, A.; Rybin, A. The study of dynamic load on a wagon platform at a shunting collision. East. Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2016, 3, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickens, A.H.; Gilchrist, A.O.; Hobbs, A.E.W. Suspension Design for High-Performance Two-Axle Freight Vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1969, 184, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwnicki, S.D.; Stichel, S.; Orlova, A.; Hecht, M. Dynamics of Railway Freight Vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2015, 53, 995–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakyt, G.; Abdullayev, S.; Suleyeva, N.; Yelshibekov, A.; Seidemetova, Z.; Sadvakassova, Z. Simulation of dynamic processes of interaction of car and railway track during train passage of curved sections of the track. Transp. Probl. 2020, 15, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusza, M.; Golofit-Stawinska, M.; Zboinski, K. The Nonlinear Lateral Stability of a Four-Axle Freight Car with Y25 Bogies and Measures to Improve Its Faults. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, V.M.G.; Correia, J.; Calçada, R.; Barbosa, R.S.; De Jesus, A.M.P. Fatigue in Trapezoidal Leaf Springs of Suspensions in Two-Axle Wagons—An Overview and Simulation. In Structural Integrity and Fatigue Failure Analysis; Lesiuk, G., Szata, M., Blazejewski, W., Jesus, A.M.P.D., Correia, J.A.F.O., Eds.; Structural Integrity; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 25, pp. 97–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov, E.; Semenov, S.; Sapronova, S.; Tkachenko, V. On the issue of wheel flange sliding along the rail. Lect. Notes Intell. Transp. Infrastruct. 2020, 1380, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, E.; Semenov, S.; Kliuiev, S.; Dižo, J.; Blatnický, M.; Gerlici, J.; Harušinec, J.; Kovtanets, M. Clarification of features of the wheel movement with a perspective constructive scheme on a rail. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, T.; Gerlici, J. Wheel/rail tangential contact stress evaluation by means of the modified strip method. Commun. Sci. Lett. Univ. Žilina 2014, 16, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, T.; Gerlici, J. Railway wheel and rail roughness analysis. Commun. Sci. Lett. Univ. Žilina 2009, 11, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, T.; Gerlici, J. Contact area and normal stress determination on railway wheel/rail contact. Komunikacie 2005, 7, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, D.; Barrera, O. Mechanics Constitutive Models for Viscoelastic Solid Materials: Development and a Critical Review. Adv. Appl. Mech. 2023, 56, 189–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.A. Mechanics Lecture Notes: An introduction to Solid Mechanics. Available online: http://homepages.engineering.auckland.ac.nz/~pkel015/SolidMechanicsBooks/index.html (accessed on 25 September 2024).
- Huang, C.; Zeng, J. Comparison of the Maxwell Model and a Simplified Physical Model for a Railway Yaw Damper in Damping Characteristics and Vehicle Stability Assessment. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. F J. Rail. Rapid Transit 2022, 236, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 13802:2013; Railway Applications—Suspension Components—Hydraulic dampers. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.
- Yang, D.; Chi, M.; Cai, W.; Wang, X. Study on Piecewise Linear Model of Anti-yaw Damper and Test Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Industrial Informatics and Computer Engineering Conference, Xi’an, China, 10–11 January 2015; pp. 1179–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Kolsch, H. On the Identification of Parameters for Structural Members Exhibiting Static Hysteresis. Mech. Res. Commun. 1994, 21, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitriu, M. Condition Monitoring of the Dampers in the Railway Vehicle Suspension Based on the Vibrations Response Analysis of the Bogie. Sensors 2022, 22, 3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ORE B 176; Vol. 1: Preliminary Studies and Specifications, Vol. 2: Specification for a Bogie with Improved Curving Characteristics, Vol. 3: Specifications for a Bogie with Improved Curving Characteristics For Body Tilt. Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1989.
- Jover, V.; Fischer, S. Statistical analysis of track geometry parameters on tramway line No. 1 in Budapest. Balt. J. Road Bridge Eng. 2022, 17, 75–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jover, V.; Gaspar, L.; Fischer, S. Investigation of tramway line no. 1, in Budapest, based on dynamic measurements. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2022, 19, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudzikiewicz, A.; Bogacz, R.; Kostrzewski, M. Using acceleration signals recorded on a railway vehicle wheelsets for rail track condition monitoring. In Proceedings of the 7th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring, EWSHM 2014, Nantes, France, 8–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UIC 518:2009; Testing and Approval of Railway Vehicles from the Point of View of Their Dynamic Behaviour—Safety—Track Fatigue—Running Behaviour. International Union of Railways: Paris, France, 2009.
- Dižo, J.; Blatnický, M.; Harušinec, J.; Suchánek, A. Assessment of Dynamics of a Rail Vehicle in Terms of Running Properties While Moving on a Real Track Model. Symmetry 2022, 14, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grulkowski, S.; Kędra, Z.; Koc, W.; Nowakowski, M.J. Railway Tracks, 1st ed.; Gdańsk University of Technology: Gdańsk, Poland, 2013; pp. 188–190. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kardas-Cinal, E. Statistical analysis of dynamical quantities related to running safety and ride comfort of a railway vehicle. Sci. J. Silesian Univ. Technol. Ser. Transp. 2020, 106, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Sysyn, M.; Liu, J. Influence of crossing wear on rolling contact fatigue damage of frog rail. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2024, 22, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozhenko, V.; Kovtanets, M.; Sergienko, O.; Prosvirova, O.; Kovtanets, T.; Boyko, G.; Semenov, S. Method for determining the linear velocity of a locomotive development. In Proceedings of the 25th International Scientific Conference Transport Means 2021, Kaunas, Lithuania, 6–8 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- EN 14363:2016; Railway Applications—Testing for the Acceptance of Running Characteristics of Railway Vehicles—Testing of Running Behaviour and Stationary Tests. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).