MTC-GAN Bearing Fault Diagnosis for Small Samples and Variable Operating Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Construction of Vibration Images
2.2. Local Binary Mode
2.3. Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
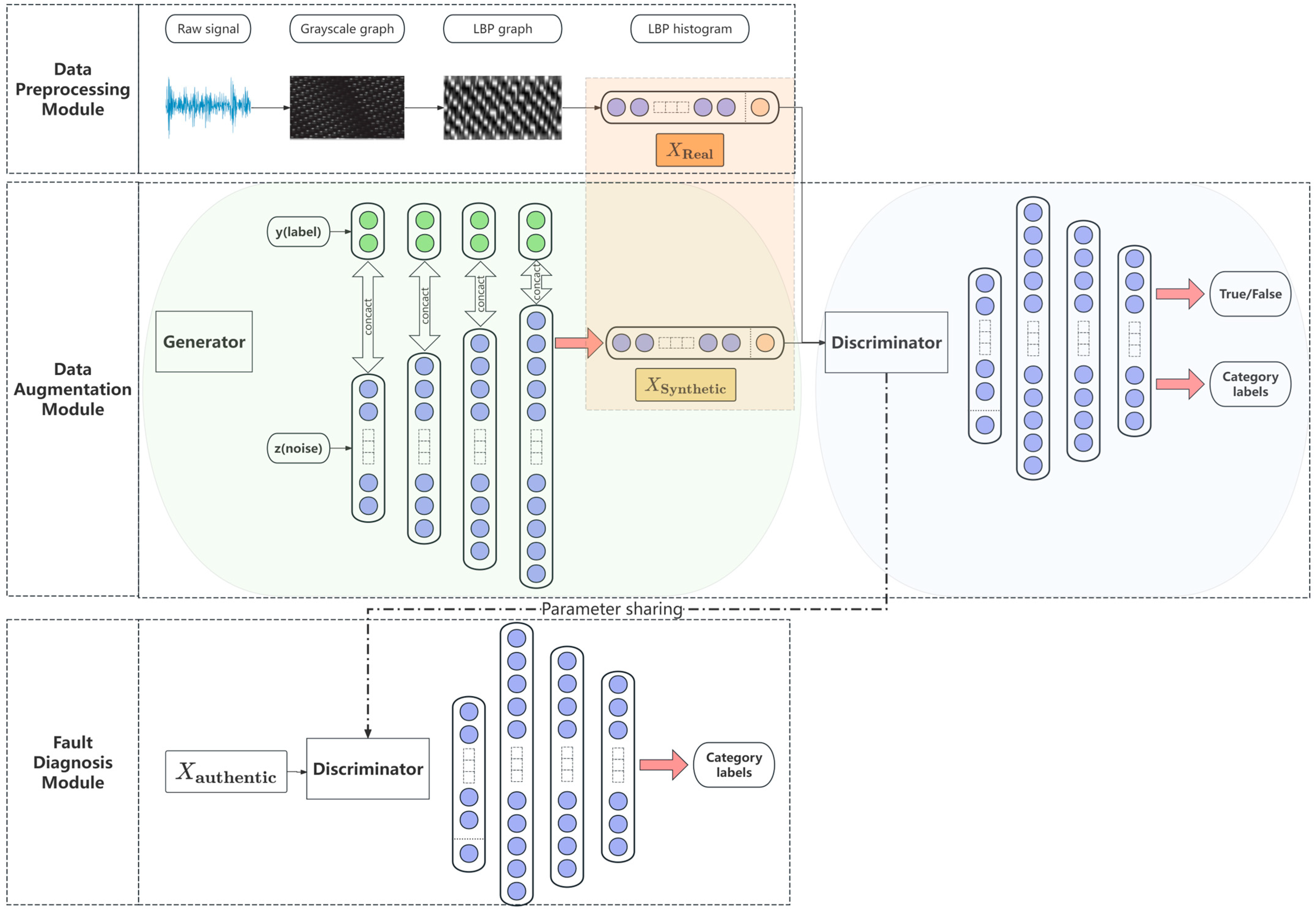
3. MTC-GAN Model Structure Design
3.1. Generator Structure
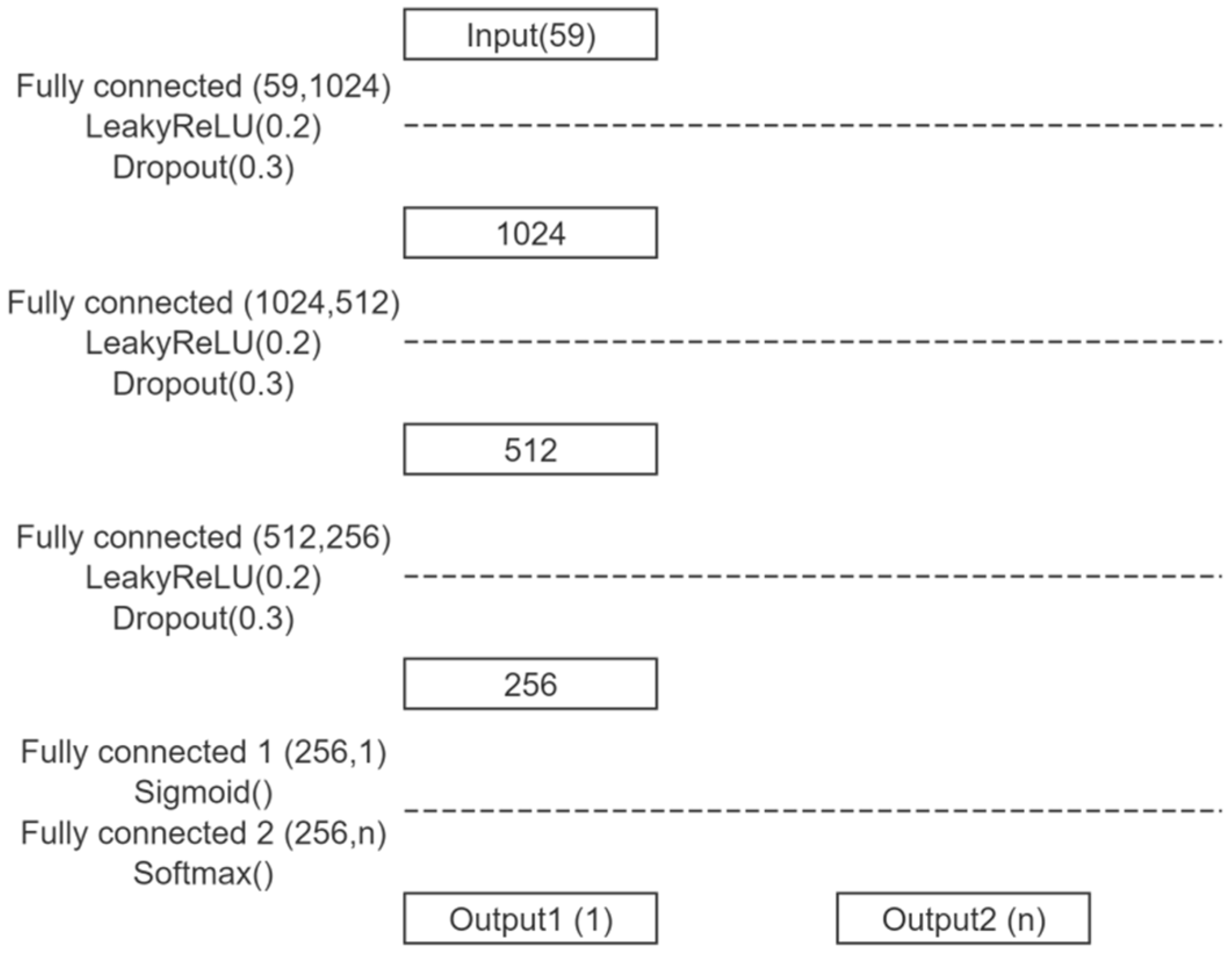
3.2. Discriminator Structure
3.3. Model Training and Loss Function
3.4. Modelling Structure
4. Experimental Validation
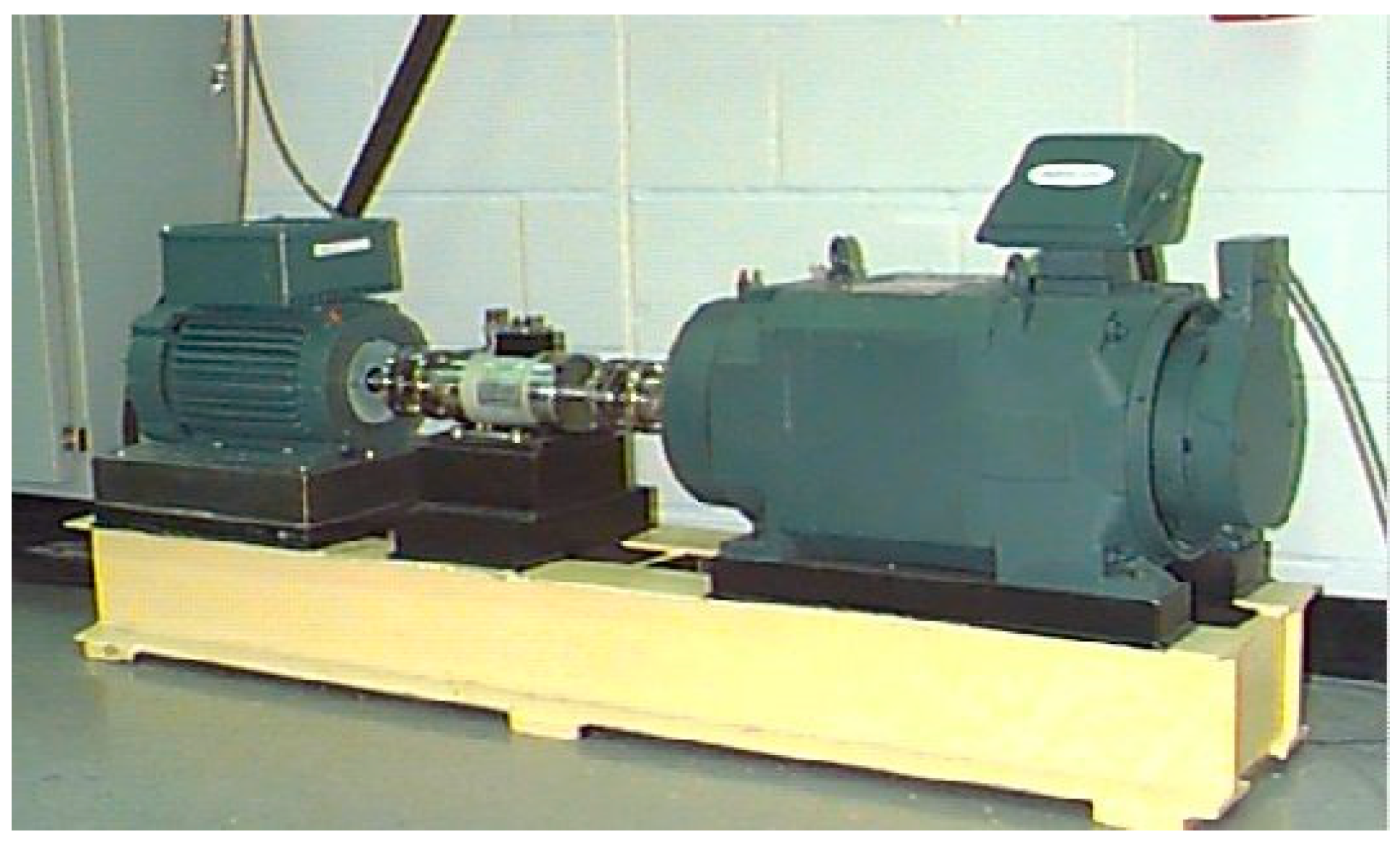
4.1. Data Sets
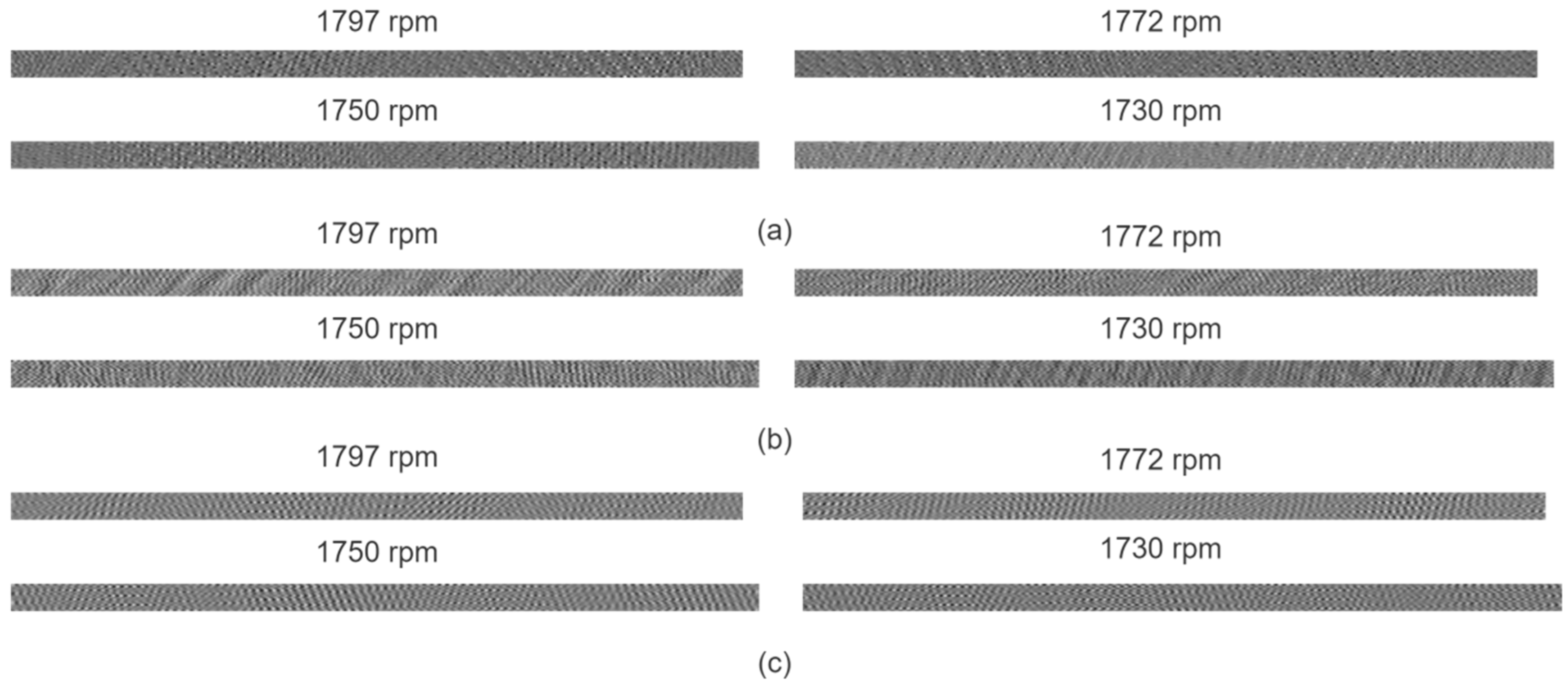
4.2. Image Construction
4.3. Fault Signature Construction
4.4. Model Testing
4.5. Comparative Experiments
4.5.1. Single-Condition Comparison Experiment
4.5.2. Varying-Condition Comparison Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, Q.; Jiang, X.; Du, G.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Z. Smart Multichannel Mode Extraction for Enhanced Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 189, 110107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaleshtori, A.E.; Aghaie, A. A Novel Bearing Fault Diagnosis Approach Using the Gaussian Mixture Model and the Weighted Principal Component Analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 242, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Ma, N.; Ji, W.; Ng, S.-K. Open Set Bearing Fault Diagnosis with Domain Adaptive Adversarial Network under Varying Conditions. Actuators 2024, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ahmed, H.; Chen, X.; Yan, R.; Nandi, A.K. Improved Adversarial Transfer Network for Bearing Fault Diagnosis under Variable Working Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourari, A.W.; Soualhi, A.; Benkedjouh, T. Advancing Bearing Fault Diagnosis under Variable Working Conditions: A CEEMDAN-SBS Approach with Vibro-Electric Signal Integration. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 132, 2753–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, L.; Qin, Y. A Semi-Supervised Approach to Bearing Fault Diagnosis under Variable Conditions towards Imbalanced Unlabeled Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Sun, Y. Research on Bearing Variable Condition Fault Diagnosis Based on RDADNN. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2023, 23, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. A Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on Conditional Depth Convolution Countermeasure Generation Networks under Small Samples. Sensors 2022, 22, 5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Wang, W.; Wen, J.; Li, Y. Semi-Supervised Adversarial Transfer Networks for Cross-Domain Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearings. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maggio, L.G.; Brusa, E.; Delprete, C. Zero-Shot Generative AI for Rotating Machinery Fault Diagnosis: Synthesising Highly Realistic Training Data via Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Chen, X.; Gühmann, C.; Yan, J. Improvement of Generative Adversarial Network and Its Application in Bearing Fault Diagnosis: A Review. Lubricants 2023, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H. Adversarial Image Perturbations with Distortions Weighted by Color on Deep Neural Networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 13779–13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, S. Dual-Mode Method for Generating Adversarial Examples to Attack Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Gühmann, C. CNN Parameter Design Based on Fault Signal Analysis and Its Application in Bearing Fault Diagnosis. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 55, 101877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Kim, J.-M. Automated Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using 2D Analysis of Vibration Acceleration Signals under Variable Speed Conditions. Shock. Vib. 2016, 8729572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 2, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. Comput. Sci. 2014, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


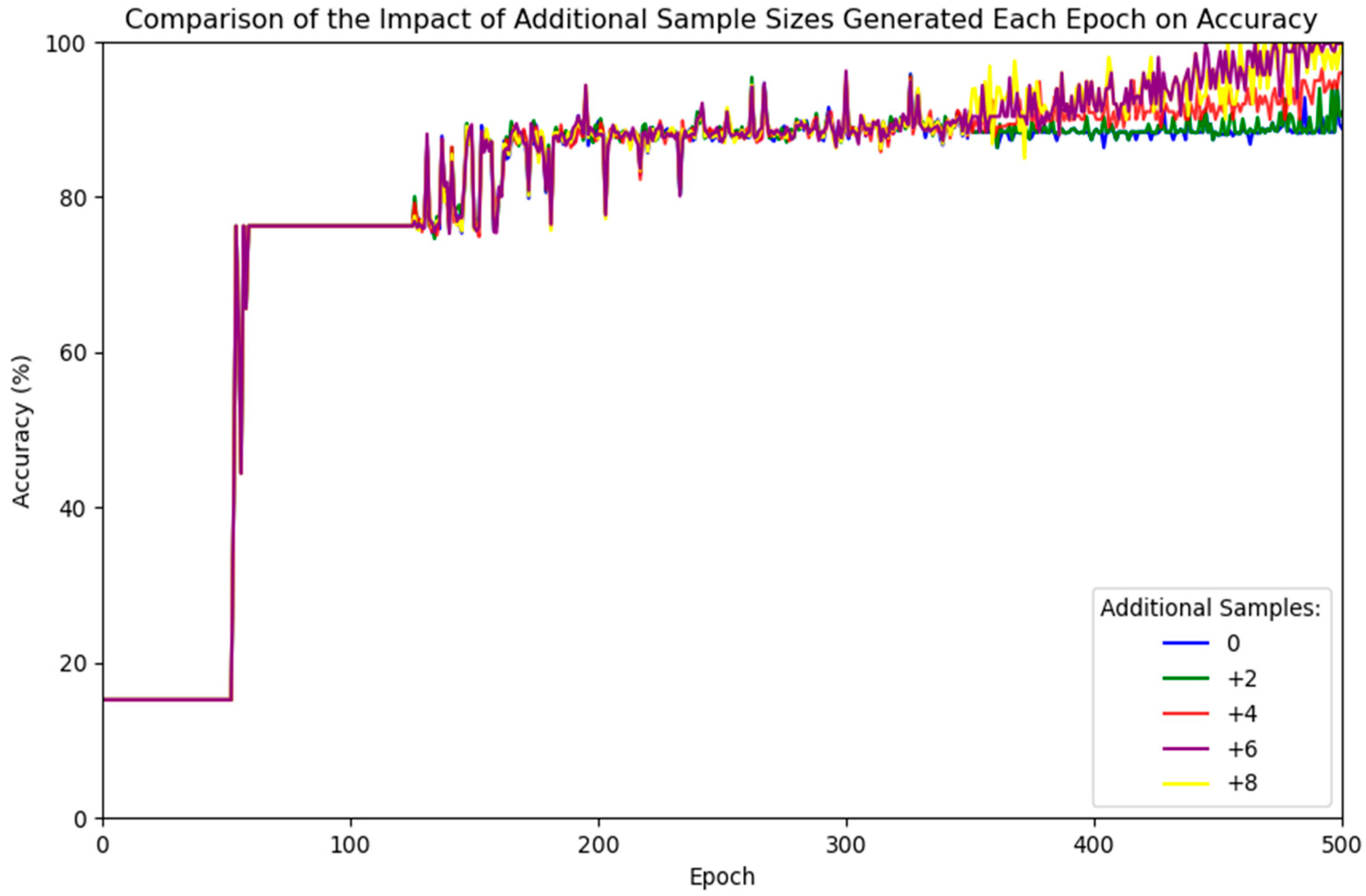
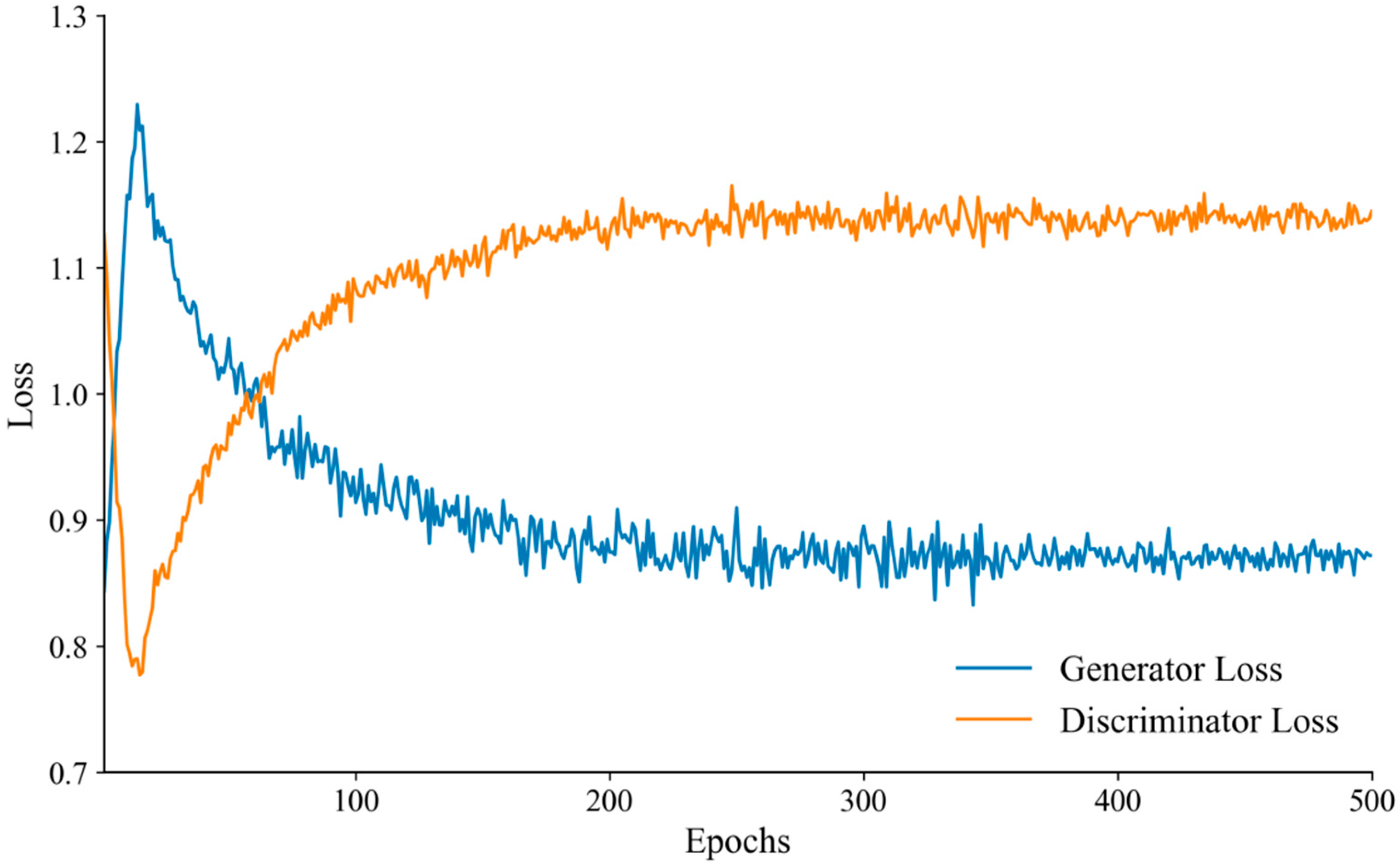
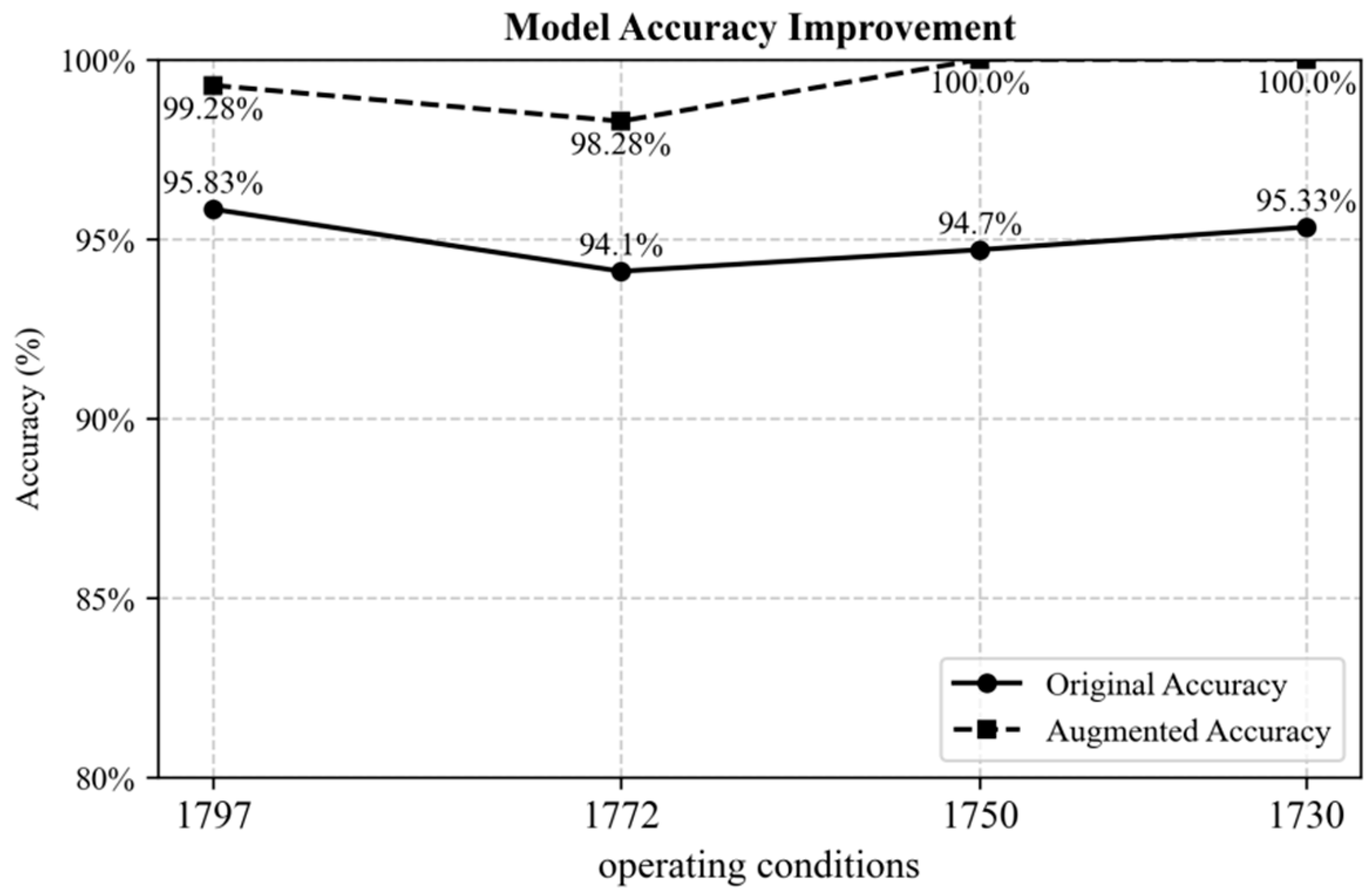
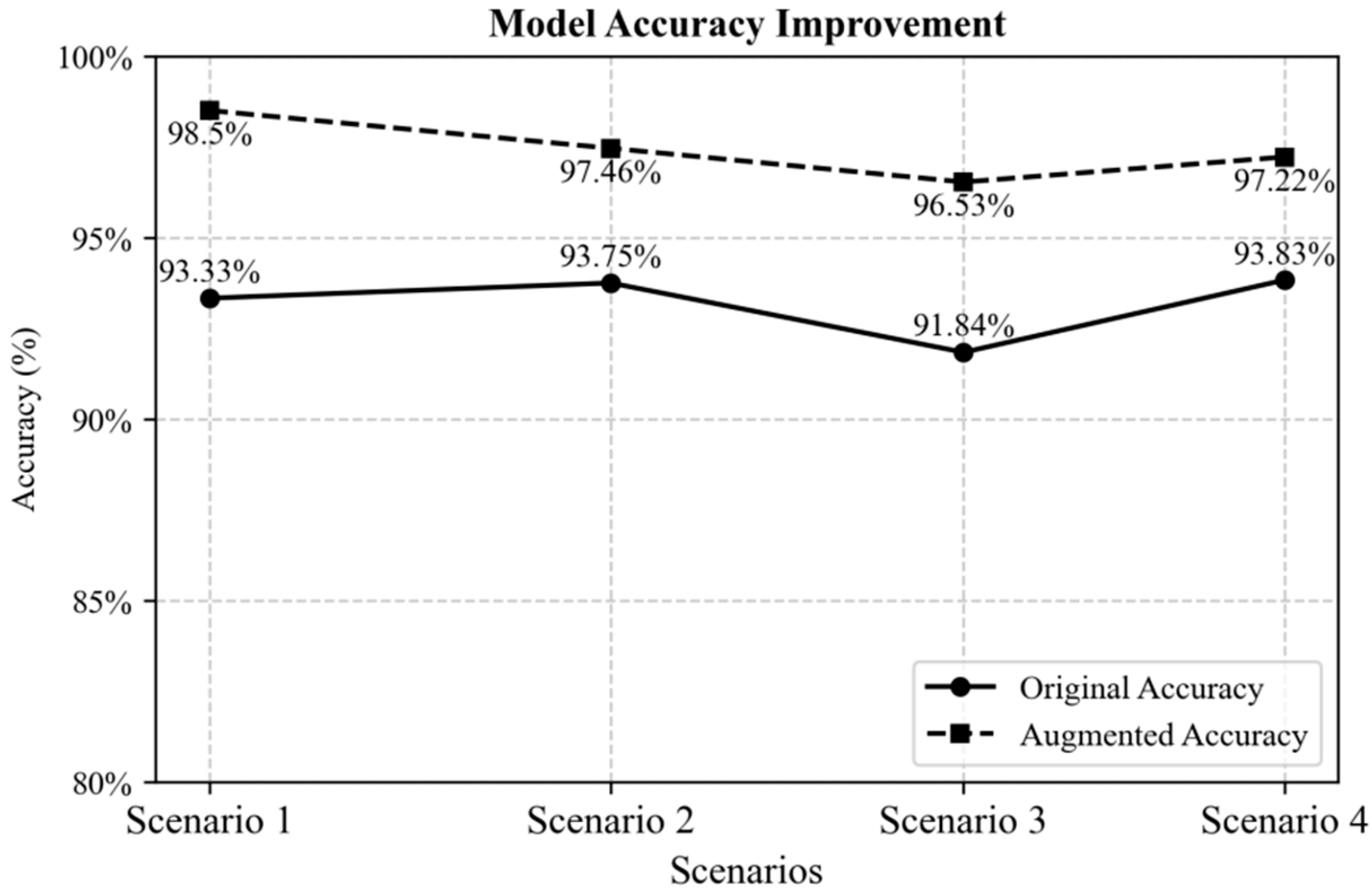

| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Model | JEM SKF 6205-2RS (SKF, Gothenburg, Sweden) |
| Location | Driver end |
| Outside diameter | 2.0472 inches |
| Inside diameter | 0.9843 inches |
| Thickness | 0.5906 inches |
| Ball diameter | 0.3126 inches |
| Pitch diameter | 1.537 inches |
| Fault Type | Fault Location | Fault Diameter (Inches) | Fault Depth (Inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inner raceway fault (IRF) | Inner raceway | 0.007 | 0.011 |
| Outer raceway fault (ORF) | Outer raceway | 0.007 | 0.011 |
| Ball fault(BF) | Ball | 0.007 | 0.011 |
| Normal | Nil | Nil | Nil |
| FCF (Hz) | Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | |
| 107.36 | 214.72 | 322.08 | 429.44 | 536.80 | |
| 162.19 | 324.38 | 486.57 | 648.76 | 810.95 | |
| 141.17 | 282.34 | 423.51 | 564.68 | 705.85 | |
| Datasets | Fault Type | Shaft Speed (rpm) | Motor Load (hp) | Number of Cycles | Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Inner raceway | 1797 | 0 | ~302 | 20 |
| Outer raceway | 1797 | 0 | ~304 | 60 | |
| Ball | 1797 | 0 | ~305 | 20 | |
| Normal | 1797 | 0 | ~608 | 40 | |
| 2 | Inner raceway | 1772 | 1 | ~300 | 19 |
| Outer raceway | 1772 | 1 | ~301 | 58 | |
| Ball | 1772 | 1 | ~298 | 19 | |
| Normal | 1772 | 1 | ~1190 | 80 | |
| 3 | Inner raceway | 1750 | 2 | ~296 | 19 |
| Outer raceway | 1750 | 2 | ~295 | 58 | |
| Ball | 1750 | 2 | ~294 | 19 | |
| Normal | 1750 | 2 | ~1177 | 79 | |
| 4 | Inner raceway | 1730 | 3 | ~293 | 19 |
| Outer raceway | 1730 | 3 | ~293 | 58 | |
| Ball | 1730 | 3 | ~290 | 20 | |
| Normal | 1730 | 3 | ~1615 | 78 |
| Hyperparameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Generator Learning Rate | 0.0002 |
| Discriminator Learning Rate | 0.0002 |
| Batch Size | 4 |
| Number of Epochs | 500 |
| Noise Dimension | 100 |
| Training Datasets (Number of Training Samples) | Testing Datasets (Number of Test Samples) | Classification Accuracy (%) | Average Classification Accuracy (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Fault (BF) | Inner Race Fault (IRF) | Outer Race Fault (ORF) | Normal | |||
| Dataset 1797 (15) | Dataset 1797 (125) | 94.72 | 92.76 | 95.84 | 100.00 | 95.83 |
| Dataset 1772 (15) | Dataset 1772 (162) | 92.28 | 91.33 | 94.23 | 98.56 | 94.10 |
| Dataset 1750 (15) | Dataset 1750 (160) | 93.49 | 91.56 | 95.33 | 98.40 | 94.70 |
| Dataset 1730 (15) | Dataset 1730 (160) | 93.78 | 93.20 | 94.35 | 100 | 95.33 |
| Training Datasets (Number of Training Samples) | Testing Datasets (Number of Test Samples) | Classification Accuracy (%) | Average Classification Accuracy (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Fault (BF) | Inner Race Fault (IRF) | Outer Race Fault (ORF) | Normal | |||
| Dataset 1 (15) | Dataset 2, 3, 4 (527) | 90.13 | 92.28 | 92.83 | 99.48 | 93.33 |
| Dataset 2 (15) | Dataset 1, 3, 4 (490) | 90.89 | 92.44 | 92.06 | 99.61 | 93.75 |
| Dataset 3 (15) | Dataset 1, 2, 4 (492) | 92.80 | 88.91 | 94.20 | 98.53 | 91.84 |
| Dataset 4 (15) | Dataset 1, 2, 3 (492) | 93.34 | 86.50 | 96.20 | 99.28 | 93.83 |
| Model | Classification Accuracy (%) | Training Time (s) | Testing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 75.32 | 144 | 27 |
| CNN | 90.45 | 962 | 62 |
| LSTM | 92.87 | 1089 | 74 |
| Proposed Method | 99.28 | 182 | 35 |
| Model | Classification Accuracy (%) | Training Time (s) | Testing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 65.83 | 144 | 102 |
| CNN | 80.47 | 962 | 233 |
| LSTM | 83.64 | 1089 | 278 |
| DTL | 91.56 | 705 | 254 |
| DAN | 93.43 | 682 | 194 |
| Proposed Method | 98.50 | 182 | 131 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Wei, Y.; Gu, X. MTC-GAN Bearing Fault Diagnosis for Small Samples and Variable Operating Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198791
Li J, Wei Y, Gu X. MTC-GAN Bearing Fault Diagnosis for Small Samples and Variable Operating Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(19):8791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198791
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinghua, Yonghe Wei, and Xiaojiao Gu. 2024. "MTC-GAN Bearing Fault Diagnosis for Small Samples and Variable Operating Conditions" Applied Sciences 14, no. 19: 8791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198791
APA StyleLi, J., Wei, Y., & Gu, X. (2024). MTC-GAN Bearing Fault Diagnosis for Small Samples and Variable Operating Conditions. Applied Sciences, 14(19), 8791. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14198791







