Chemicals from Brominated Flame Retardants: Analytical Methods, Occurrence, Transport and Risks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analytical Methods for the Detection of BFRs in Environmental and Biological Samples
2.1. Sample Collection and Extraction Methods
2.1.1. Biotic Samples
Humans and Animal Tissues
Serum and Urine Samples
Food and Feed
2.1.2. Abiotics Samples
Water Samples
Soil Samples, Sediment, Sewage Sludge and Biosolids
Food Contact Articles
Dust Samples
Air Samples
2.2. Clean-Up Methods
2.3. Analytical Instruments
3. Distribution of BFRs in Different Matrices
3.1. Surface Sediment
3.2. Biota
3.2.1. Water
3.2.2. Food
3.2.3. Air and Dust
3.2.4. Soil
3.2.5. Human Sample
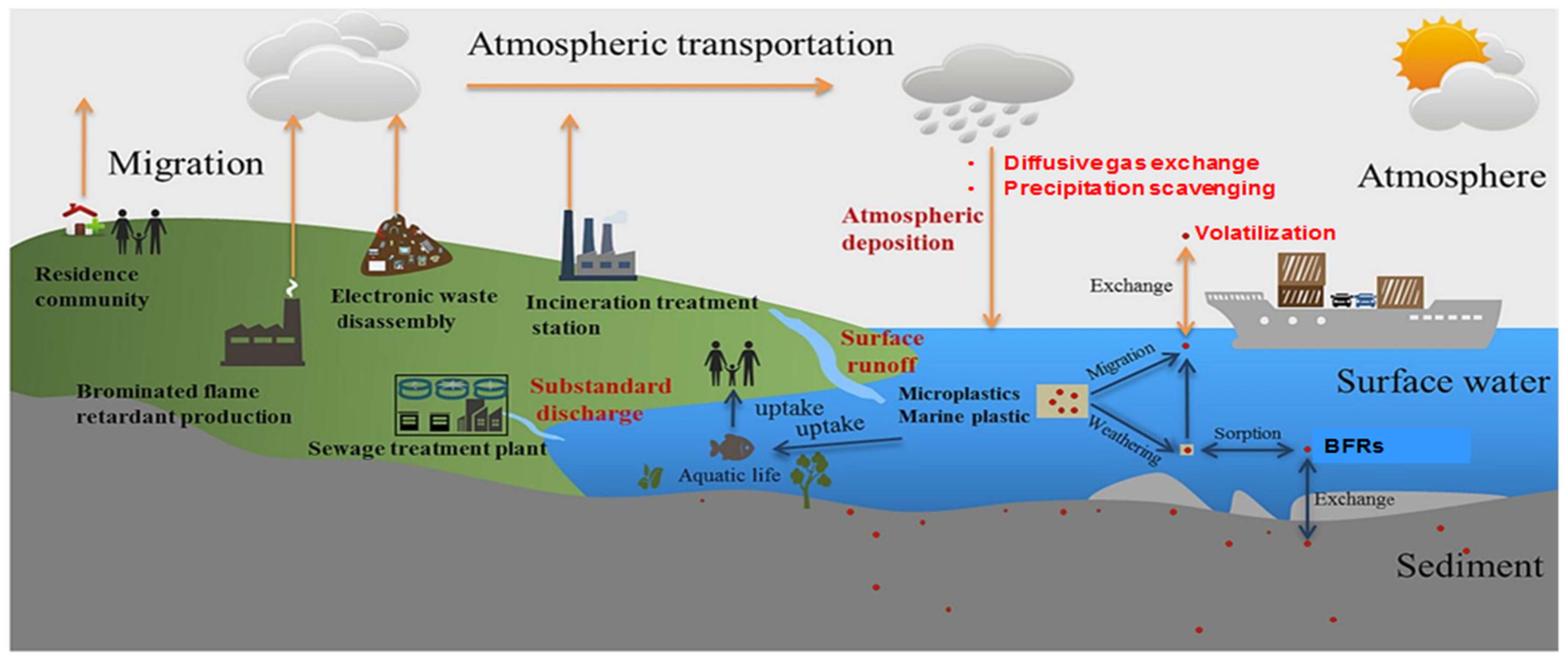
4. Transport Mechanisms of BFRs
4.1. Atmospheric Dispersion and Deposition Dynamics
4.2. Water Transport and Fate Processes
4.3. Soil Sorption and Fate Processes
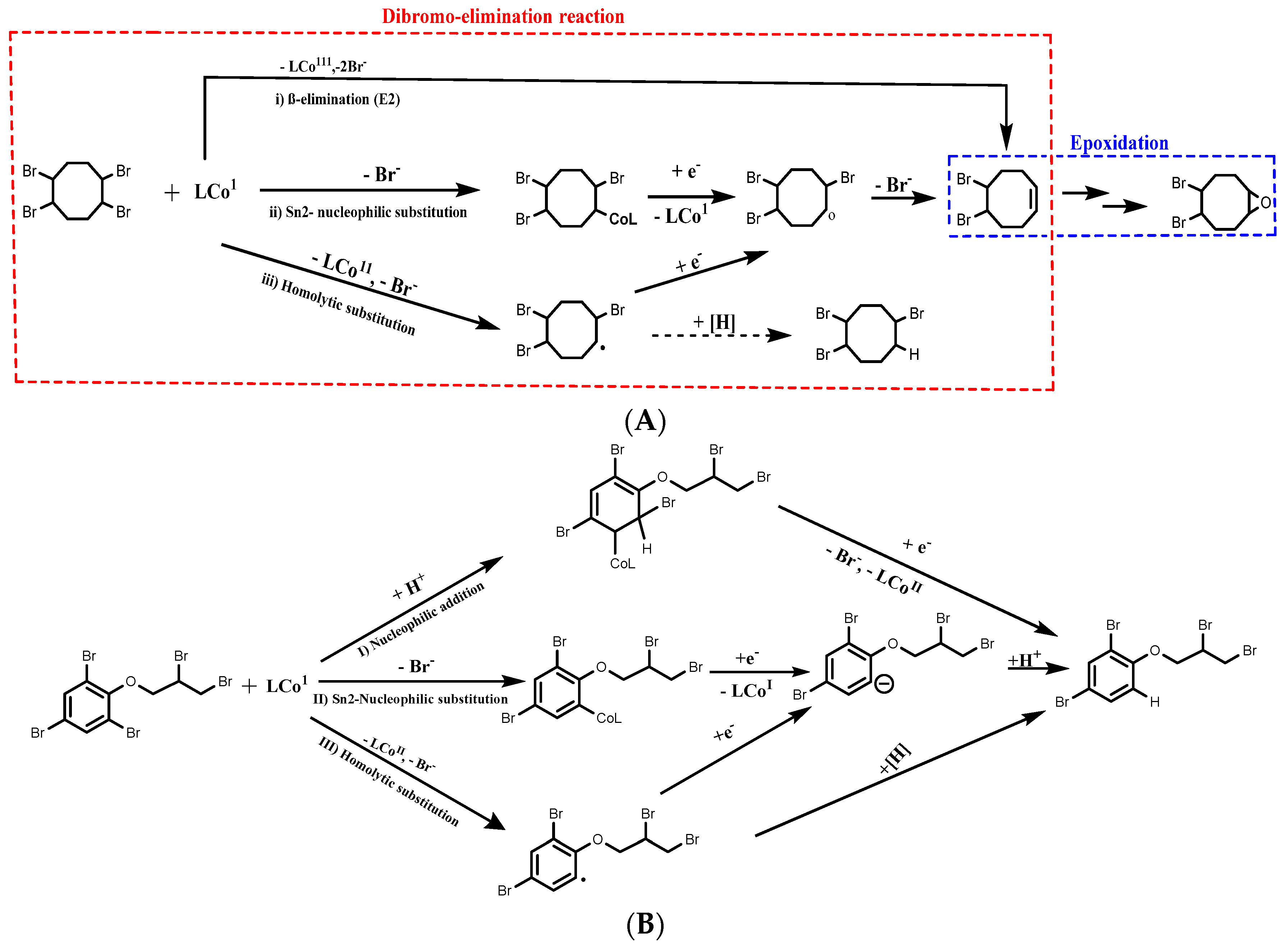
4.3.1. BFRs Transformation in Soil
4.3.2. Plant Uptake of BFRs in Soil
5. Risks Associated with BFRs and Associated Chemicals
5.1. Categorization of BFRs
- Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs)
- Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD)
- Tetrabromobisphenol (TBBPA)
- Polybrominated Biphenyls (PBBs)
- Novel Brominated Fire Retardants
5.2. Health Effects of BFR and Chemical Exposure: Developmental, Neurological, and Endocrine Disruption Risks
5.3. Environmental Hazards of BFRs and Associated Chemicals
5.4. Regulatory Frameworks and Risk Mitigation Strategies for BFR and Chemical Management
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Future Perspectives
- Enhanced Analytical Techniques: The continued development of more sensitive and selective analytical methods is crucial. This includes improving detection limits, increasing the accuracy of quantification, and expanding the range of detectable BFRs in complex matrices.
- Comprehensive Monitoring Programs: Establishing robust, large-scale monitoring programs to track the occurrence and distribution of BFRs across different environmental and biological media. This will provide a clearer picture of their global impact and aid in risk assessment.
- Mechanistic Studies: Further research into the mechanisms of BFR toxicity is needed. Understanding how BFRs interact with biological systems at the molecular level will help elucidate their health effects and support the development of mitigation strategies.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Strengthening regulatory frameworks to manage the production, use, and disposal of BFRs. This includes phasing out the most hazardous BFRs, promoting safer alternatives, and enforcing stricter environmental and health standards.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vuong, A.M.; Yolton, K.; Cecil, K.M.; Braun, J.M.; Lanphear, B.P.; Chen, A. Flame retardants and neurodevelopment: An updated review of epidemiological literature. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2020, 7, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TSE. Flammschutz Online—The Flame Retardants Market. Townsend Solutions Estimate. 2023. Available online: https://web.archive.org/web/20160304070150/http://www.flameretardants-online.com/web/en/106/7ae3d32234954e28e661e506e284da7f.htm (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Dagani, M.J.; Barda, H.J.; Benya, T.J.; Sanders, D.C. Bromine Compounds. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Scientific opinion on emerging and novel brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in food. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, Å.A.; Rydén, R.J.; Law, J.; de Boer, A.; Covaci, M.; Alaee, L.; Birnbaum, M.; Petreas, M.; Rose, S.; Sakai, N.; et al. A novel abbreviation standard for organobromine, organochlorine and organophosphorus flame retardants and some characteristics of the chemicals. Environ. Int. 2012, 49, 57–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Legacy and emerging brominated flame retardants in China: A review on food and human milk contamination, human dietary exposure and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 522–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, P.; Ruan, Z.; Sun, X.; Rao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Su, X. Novel brominated flame retardant (NBFR) concentrations and spatial distributions in global fishmeal. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Brominated Flame Retardants. 2024. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/brominated-flame-retardants#:~=Brominated%20flame%20retardants%20(BFRs)%20are,textiles%20and%20electrical%2Felectronic%20equipment (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Jarosiewicz, M.; Miłowska, K.; Krokosz, A.; Bukowska, B. Evaluation of the Effect of Selected Brominated Flame Retardants on Human Serum Albumin and Human Erythrocyte Membrane Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuiderveen, E.; Slootweg, J.C.; de Boer, J. Novel brominated flame retardants—A review of their occurrence in indoor air, dust, consumer goods and food. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, B.; Yakubu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Issaka, E.; Zhang, Y.; Adams, M. A Review on Tetrabromobisphenol A: Human Biomonitoring, Toxicity, Detection and Treatment in the Environment. Molecules 2023, 28, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeke, E.S.; Huang, B.; Mao, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhengjia, Z.; Qian, X.; Feng, W. Review of the environmental occurrence, analytical techniques, degradation and toxicity of TBBPA and its derivatives. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-F.; Liu, S.; Tian, F.; Chen, H.-G.; Xu, X.-R. Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecanes in sediments from fishing ports along the coast of South China: Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; Cui, J.; Yu, Y.; Ma, S.J. Identification and occurrence of TBBPA and its debromination and O-methylation transformation products in sediment, fish and whelks from a typical e-waste dismantling site. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ding, P.; Chen, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Hu, G. Brominated flame retardants in surface sediment from Western Guangdong, South China: Occurrence, distribution and toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 145, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Elwafa, A. Advances in instrumental analysis of brominated flame retardants: Current status and future perspectives. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 651834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durães, N.; Novo, L.A.; Candeias, C.; Da Silva, E.F. Distribution, transport and fate of pollutants. In Soil Pollution; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 29–57. [Google Scholar]
- Brits, M.; De Vos, J.; Weiss, J.M.; Rohwer, E.R.; De Boer, J. Critical review of the analysis of brominated flame retardants and their environmental levels in Africa. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajeb, P.; Castano, A.; Cequier, E.; Covaci, A.; López, M.E.; Antuna, A.G.; Vorkamp, K. Critical review of analytical methods for the determination of flame retardants in human matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1193, 338828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas, M.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. An overview of analytical methods for enantiomeric determination of chiral pollutants in environmental samples and biota. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredsdorff, L.; Olesen, P.T.; Beltoft, V.M.; Sharma, A.K.; Hansen, M.; Nørby, K.; Ekstrøm, J. Identifying and collecting relevant literature related to the toxicity of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), tetrabromobisphenol a (TBBPA) and brominated phenols. EFSA Support. Publ. 2023, 20, 8014E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, S.; Baini, M.; Martellini, T.; Bissoli, M.; Galli, M.; Concato, M.; Cincinelli, A. Novel ultrasound assisted extraction and d-SPE clean-up for the analysis of multiple legacy and emerging organic contaminants in edible fish. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoršćak, M.; Jagić, K.; Besednik, L.; Šimić, I.; Klinčić, D. First application of microwave-assisted extraction in the analysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human milk. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, L.G.; De Oliveira-Ferreira, N.; Torres, J.P.M.; Azevedo, A.F.; Meirelles, A.C.O.; Flach, L.; Eljarrat, E. Brominated flame retardants and natural organobrominated compounds in a vulnerable delphinid species along the Brazilian coast. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoloni, T.; Stramenga, A.; Stecconi, T. Single sample preparation for brominated flame retardants in fish and shellfish with dual detection: GC-MS/MS (PBDEs) and LC-MS/MS (HBCDs). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, S.C.; Vorkamp, K.; Nielsen, J.B.; Sørensen, L.S.; Knudsen, L.E.; Frederiksen, M. Novel and legacy brominated flame retardants in human breast milk and house dust from Denmark. J. Environ. Expo. Assess. 2024, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, G.; Meng, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, G. Novel biomonitoring method for determining five classes of Legacy and alternative flame retardants in human serum samples. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 131, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, J.; González-Mariño, I.; Pavón, J.L.P. In-situ acetylation followed by liquid-liquid extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for the determination of bromophenols in urine. Talanta 2024, 275, 126146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillol, C.; Oleko, A.; Saoudi, A.; Zeghnoun, A.; Balicco, A.; Gane, J.; Denys, S. Exposure of the French population to bisphenols, phthalates, parabens, glycol ethers, brominated flame retardants, and perfluorinated compounds in 2014–2016: Results from the Esteban study. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmiełowska, M.; Zabiegała, B. Current trends in analytical strategies for determination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in samples with different matrix compositions–Part 1: Screening of new developments in sample preparation. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 115255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G.; Zhu, J.; Takser, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Bellenger, J.P. Complementarity of plasma and stool for the characterization of children’s exposure to halogenated flame retardants: Update on analytical methods and application to a Canadian cohort. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qing, J.; Meng, T.; Jiao, Y.; Chen, M.; Wen, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ding, L. Determination of Brominated Flame Retardants in Biological Samples by Nitrogen Doped Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced Hollow Fibers Liquid-phase Microextraction Coupled with High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Zggx 2023, 42, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Tobiishi, K.; Hori, T.; Tsutsumi, T.; Akiyama, H.; Matsui, T. Simultaneous determination of hexabromocyclododecanes, polybrominated diphenyl ethers, and dechlorane-related compounds in boxed sushi meals using a developed analytical method. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2023, 29, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Bu, T.; Li, T.; Bao, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Jin, J. Concentration, distribution and biomagnification of novel brominated flame retardant in grassland food chain and sheep from Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, V.C.; Domingues, V.F.; Nunes, M.S.; Matos, R.; Kuźniarska-Biernacka, I.; Fernandes, D.M.; Delerue-Matos, C. Graphene-type materials for the dispersive solid-phase extraction step in the QuEChERS method for the extraction of brominated flame retardants from capsicum cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 3898–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Deng, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. A pretreatment method combined matrix solid-phase dispersion with dispersive liquid–liquid micro–extraction for polybrominated diphenyl ethers in vegetables through quantitation of gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS). RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 15772–15782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lörchner, D.; Tang, D.; Mauch, T.; Jung, C.; Hofmann, A.; Kroh, L.W. Development and validation of a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for simultaneous analysis of triazine-based brominated flame retardants in environmental samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, V.C.; Freitas, M.; Pacheco, J.G.; Domingues, V.F.; Delerue-Matos, C. Evaluation of the QuEChERS and magnetic micro dispersive solid-phase extraction of brominated flame retardants in red fruits with determination by GC/MS. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Stubbings, W.A.; Jin, J.; Cline-Cole, R.; Abdallah, M.A.; Harrad, S. Impact of Legislation on Brominated Flame Retardant Concentrations in UK Indoor and Outdoor Environments: Evidence for Declining Indoor Emissions of Some Legacy BFRs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 4237–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Stubbings, W.A.; Cline-Cole, R.; Abdallah, M.A.E.; Harrad, S. Rising concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Nigerian foodstuffs despite global restrictions. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Han, W.; Lou, T.T.; Ma, L.L.; Xiao, Y.B.; Xu, Z.; Ding, L. An iron-based metal–organic framework as a novel dispersive solid-phase extraction sorbent for the efficient adsorption of tetrabromobisphenol A from environmental water samples. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, F.; Li, J.; Liu, R. Determination of tetrabromobisphenol A and its brominated derivatives in water, sediment and soil by high performance liquid chromatography–tandem Mass spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 2023, 39, 1875–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Hu, W.; Jia, C.; Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Cai, Y.; Han, Y. Rapid screening of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in water by solid-phase microextraction coupled with ultrahigh-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Gan, Z.; Su, S.; Ding, S.; Hou, L. Distribution and leaching behavior of organophosphorus and brominated flame retardants in soil in Chengdu. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Meng, W.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, P.; Jiang, G. Concentrations and distribution of novel brominated flame retardants in the atmosphere and soil of Ny-Ålesund and London Island, Svalbard, Arctic. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, T.J.; Kolobaric, A.; Lee, E.; Clarke, B.O. Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in Western Australian biosolids and implications for land application. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lestido-Cardama, A.; Paseiro-Cerrato, R.; Ackerman, L.K.; Sendón, R.; de Quirós, A.R.B. Determination of BFRs in food contact articles: An analytical approach using DART-HRMS, XFR and HPLC-MS/MS. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Xu, M.; Hu, P.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z. Distribution of flame retardants among indoor dust, airborne particles and vapour phase from Beijing: Spatial–temporal variation and human exposure characteristics. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.Q.; Li, Y.f.; Liu, L.Y. Occurrence and partitioning of brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in indoor air and dust: A 15-month case study in a test home. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35126–35136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachterle, M.L.; Lowe, L.E.; Butler, C.R.; Schoffstall, A.M.; Owens, J.E. Micro-extraction method for the analysis of flame retardants in dust collected from air filters from HVAC systems. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Du, R.; Fan, Y.; Wei, P.; Liu, X. Gas-particle partition and size-segregated distribution of flame retardants in indoor and outdoor air: Reevaluation on the role of fine particles in human exposure. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Lai, C.; Xu, F.; Huang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, H. A review of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and novel brominated flame retardants in Chinese aquatic environment: Source, occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esplugas, R.; Rovira, J.; Mari, M.; Fernández-Arribas, J.; Eljarrat, E.; Domingo, J.L.; Schuhmacher, M. Emerging and legacy flame retardants in indoor air and dust samples of Tarragona Province (Catalonia, Spain). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tana, V.M.; Shane, R.; Lisa, B.; Alice, D.; Daryl, M.; Paul, H.; Hayley, H. Temporal Trends of Legacy and Current-Use Halogenated Flame Retardants in Lake Ontario in Relation to Atmospheric Loadings, Sources, and Environmental Fate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 14396–14406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.R.; Liu, M.Y.; Hu, J.J.; Song, A.M.; Peng, P.A.; Ying, G.G.; Chen, T. Occurrence and carcinogenic potential of airborne PBDD/Fs and PCDD/Fs around a large-scale municipal solid waste incinerator: A long-term passive air sampling study. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Li, J.; Xiao, Z.; Shi, Z. Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane isomers in breast milk from the general population in Beijing, China: Contamination levels, temporal trends, nursing infant’s daily intake, and risk assessment. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Xie, J.; Xie, C.; Hu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Luo, X. Tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecanes in sediments and biota from two typical mangrove wetlands of South China: Distribution, bioaccumulation and biomagnification. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 141695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Zhou, S.; Tan, J.; Lu, C.; Fu, M.; Peng, C. Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in sediment from a typical e-waste dismantling region in Southern China: Occurrence, spatial distribution, composition profiles, and ecological risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Wang, J.; Cui, W.; Zhu, L. Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of TBBPA in seawater and zooplankton in northern sea areas, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 4759–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, L.T.; Laurich, B.; Hebert, C.E.; Drake, C.; Letcher, R. Tetrabromobisphenol-A-bis (dibromopropyl ether) flame retardant in eggs, regurgitates, and feces of herring gulls from multiple North American Great Lakes locations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9564–9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, X.; Yang, S.J.I. Contamination level, distribution characteristics, and ecotoxicity of tetrabromobisphenol a in water and sediment from Weihe River Basin, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aixue, Z.; Pengyan, L.; Yichao, G.; Muyuan, L.; Jianbing, S.; Guisui, L. Residual levels and risk assessment of tetrabromobisphenol A in Baiyang Lake and Fuhe river, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200, 110770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Tang, J. Legacy and novel halogenated flame retardants in seawater and atmosphere of the Bohai Sea: Spatial trends, seasonal variations, and influencing factors. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Guo, M.; Xu, H.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L.; Yao, C. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of alkylphenols, bisphenol A, and tetrabromobisphenol A in surface water, suspended particulate matter, and sediment in Taihu Lake and its tributaries. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wei, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, B.; Yang, C.; Yang, J. Phototransformation of tetrabromobisphenol A in saline water under simulated sunlight irradiation. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 1, 132697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loosmore, G.A.; Cederwall, R.T. Precipitation scavenging of atmospheric aerosols for emergency response applications: Testing an updated model with new real-time data. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, I.; Anderson, W.; Crowley, D.; Daly, S.; Evans, R.; Fernandes, A.; Tlustos, C. Brominated and fluorinated organic pollutants in the breast milk of first-time Irish mothers: Is there a relationship to levels in food? Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; Lee, S.; Lim, J.E.; Moon, H.B. Legacy and novel flame retardants in water and sediment from highly industrialized bays of Korea: Occurrence, source tracking, decadal time trend, and ecological risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Jung-Hwan, K. Persistence and bioaccumulation potential of alternative brominated flame retardants. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2020, 88, 191–214. [Google Scholar]
- Yulong, M.; William, A.; Stubbings, M.; Abou-Elwafa, A.; Reginald, C.; Stuart, H. Temporal trends in concentrations of brominated flame retardants in UK foodstuffs suggest active impacts of global phase-out of PBDEs and HBCDD. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.F.; He, M.J.; Yang, Z.H.; Wei, S.Q. Occurrence of tetrabromobisphenol a (TBBPA) and hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in soil and road dust in Chongqing, western China, with emphasis on diastereoisomer profiles, particle size distribution, and human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Yue, C.; Tang, J.; Lin, M.; Zhuo, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; An, T. Occurrence and distribution of typical semi-volatile organic chemicals (SVOCs) in paired indoor and outdoor atmospheric fine particle samples from cities in southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Sellström, U.; de Wit, C.A. Organohalogenated flame retardants and organophosphate esters in office air and dust from Sweden. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, D.J.; Kim, M.K.; Zoh, K.D. Distribution of brominated flame retardants and phthalate esters in house dust in Korea. Environ. Eng. Res. 2018, 23, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Xiaoli, W.; Lin, F.; Shuhan, G.; Xinqi, W.; Chong, W.; Li, L.; Hang, L.; Yun, C.; Mengmeng, L.; et al. Levels, distribution, childhood exposure assessment, and influencing factors of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in household dust from nine cities in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.W.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Hwang, S.M.; Choi, S.D. Spatial distribution, source identification, and anthropogenic effects of brominated flame retardants in nationwide soil collected from South Korea. Environ Pollut. 2021, 272, 116026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inthavong, C.; Hommet, F.; Bordet, F.; Rigourd, V.; Guérin, T.; Dragacci, S. Simultaneous liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis of brominated flame retardants (tetrabromobisphenol A and hexabromocyclododecane diastereoisomers) in French breast milk. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Luo, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, M.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Mei, S.; Zhang, G. Levels and profiles of persistent organic pollutants in breast milk in China and their potential health risks to breastfed infants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barghi, M.; Shin, E.S.; Choi, S.D.; Behrooz, R.D.; Chang, Y.S. HBCD and TBBPA in human scalp hair: Evidence of internal exposure. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Several typical endocrine-disrupting chemicals in human urine from the general population in China: Regional and demographic-related differences in exposure risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorothea, F.K.; Rawn, C.C.; Cathie, M.; Wing-Fung, S.; François, B.; Tye, E. Arbuckle. Novel halogenated flame retardants in Canadian human milk from the MIREC study (2008–2011). Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Lu, C.; Peng, C.; Zhang, W.; Lin, K.; Zhou, B. Characteristics of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in water and sediment surrounding two e-waste dismantling regions in Taizhou, eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Ruan, M.M.P.; Tsui, Q.; Wang, J. Occurrence and spatial distribution of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in seawater and sediment of the South China sea. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S. Releases of brominated flame retardants (BFRs) from microplastics in aqueous medium: Kinetics and molecular-size dependence of diffusion. Water Res. 2019, 151, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaniyan, O.O.; Adeniji, A.O.; Semerjian, L.; Okoh, A.I.; Okoh, O.O. Global Co-Occurrence of Trace Elements and Additive Legacy Brominated Flame Retardants in Aquatic Environment: A Cause for Concern. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 11, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, B.; Metian, M.; Oberhaensli, F.; Mourgkogiannis, N.; Karapanagioti, H.K.; Bersuder, P.; Tolosa, I. Extruded polystyrene microplastics as a source of brominated flame retardant additives in the marine environment: Long-term field and laboratory experiments. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H. A low-volume air sampling method for legacy and novel brominated flame retardants in indoor environment using a newly developed sorbent mixture. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 210, 111837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Wang, J. Persistent halogenated organic pollutants in surface water in a megacity: Distribution characteristics and ecological risks in Wuhan, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 77, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.S. Atmospheric transport and dispersion of air pollutants associated with vehicular emissions. In Air Pollution, the Automobile, and Public Health; Watson, A.Y., Bates, R.R., Kennedy, D., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Enyoh, C.E.; Verla, A.W.; Verla, E.N. Airborne microplastics: A review study on method for analysis, occurrence, movement and risks. Environ. Monit. Assess 2019, 191, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Shunthirasingham, C.; Lei, Y.D.; Zhan, F.; Li, Y.; Dalpé Castilloux, A.; Ben Chaaben, A.; Lu, Z.; Lee, K.; Gobas, F.A.P.C.; et al. The atmospheric fate of 1,2-dibromo-4-(1,2-dibromoethyl)cyclohexane (TBECH): Spatial patterns, seasonal variability, and deposition to Canadian coastal regions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 10191–10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, R.M.; van Drooge, B.L.; Fernández, P.; Grimalt, J.O. Passive water sampling and air-water diffusive exchange of long-range transported semi-volatile organic pollutants in high-mountain lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G. Accumulation and influencing factors of novel brominated flame retardants in soil and vegetation from Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, M.S.; Sellström, U. Precipitation scavenging of particle-bound contaminants—A case study of PCDD/Fs. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 6084–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Liu, D.; Yan, W. A Simple New Method for Calculating Precipitation Scavenging Effect on Particulate Matter: Based on Five-Year Data in Eastern China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santachiara, G.; Prodi, F.; Belosi, F. Atmospheric aerosol scavenging processes and the role of thermo- and diffusio-phoretic forces. Atmos. Res. 2013, 128, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elperin, T.; Fominykh, A.; Krasovitov, B. Precipitation scavenging of gaseous pollutants having arbitrary solubility in inhomogeneous atmosphere. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2015, 127, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.Y.; Park, R.J.; Kim, Y.P.; Woo, J.H. Effects of below-cloud scavenging on the regional aerosol budget in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 58, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, A. Emissions of selected brominated flame retardants from consumer materials: The effects of content, temperature, and timescale. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24201–24209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jia, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, S.; Li, Y. Bioaccumulation of novel brominated flame retardants in crucian carp (Carassius auratus): Implications for electronic waste recycling area monitoring. Environ. Res. 2023, 239 Pt 2, 117412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirtu, A.C.; Ionas, A.C.; Malarvannan, G.; Covaci, A. Transformation Products of Brominated Flame Retardants (BFRs). Transform. Prod. Emerg. Contam. Environ. 2014, 21, 545–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshansky, Y.; Polubesova, T.; Vetter, W.; Chefetz, B. Sorption–desorption behavior of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2375–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, P.; Johansson, N.; Viberg, H.; Fischer, C.; Fredriksson, A. Comparative developmental neurotoxicity of flame-retardants, polybrominated flame-retardants and organophosphorous compounds, in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 200, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Wang, L. Photochemical degradation of six polybrominated diphenyl ether congeners under ultraviolet irradiation in hexane. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Peng, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, X. Characterizing distributions, composition profiles, sources and potential health risk of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in the coastal sediments from East China Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyholm, J.R.; Lundberg, C.; Andersson, P.L. Biodegradation kinetics of selected brominated flame retardants in aerobic and anaerobic soil. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, H. Plant accumulation and transformation of brominated and organophosphate flame retardants: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggio, G.; Bonato, T.; Marangoni, S.; Bravin, M.N.; Fantinato, E.; Nigris, S.; Pivato, A.; Piazza, R. Uptake and translocation of brominated flame retardants in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum L.): Results from a standard soil-based biotest. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, L.S.; Staskal, D. Brominated flame retardants: Cause for concern? Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs). 2010. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/polybrominated-diphenyl-ethers-pbdes (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Covaci, A.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.; Ali, N.; Law, R.J.; Herzke, D.; de Wit, C.A. Novel brominated flame retardants: A review of their analysis, environmental fate and behaviour. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 532–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, A.M.; Pugh, R.S.; Moors, A.; Ellisor, M.B.; Porter, B.J.; Becker, P.R. Hexabromocyclododecane in white-sided dolphins: Temporal trend and stereoisomer distribution in tissues. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2650–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kato, Y.; Masuda, N.; Harada, K.H.; Koizumi, A.; Haraguchi, A. Contamination trends and factors affecting the transfer of hexabromocyclododecane diastereomers, tetrabromobisphenol A, and 2,4,6-tribromophenol to breast milk in Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, G.; Abdallah, M.A.E.; de Saa, E.V.; Harrad, S. Dermal bioaccessibility of flame retardants from indoor dust and the influence of topically applied cosmetics. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 27, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, C.A. An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 583–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.Y.; Kacew, S.; Dekant, W. Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA): Possible modes of action of toxicity and carcinogenicity in rodents. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, T.; Wei, Y.; Dang, D.; Huang, K.; Chen, X.; Yin, H.; Tao, X.; Lin, Z.; Dang, Z.; et al. Photocatalytic debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) on metal doped TiO2 nanocomposites: Mechanisms and pathways. Environ. Int. 2019, 127, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ling, S.; Guan, K.; Luo, X.; Chen, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, W.; Mai, B.; Zhou, B. Bioconcentration, biotransformation, and thyroid endocrine disruption of decabromodiphenyl ethane (Dbdpe), a novel brominated flame retardant, in zebrafish larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8437–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, D.; Jing, L.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Shi, Z. A comparison of the thyroid disruption induced by decabrominated diphenyl ethers (BDE-209) and decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, T.; Chu, J.; Qiu, Y.; Gong, H.; Li, R. Effects of tetrabromobisphenol A on maize (Zea mays L.) physiological indexes, soil enzyme activity, and soil microbial biomass. Ecotoxicology 2019, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q.; Su, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Li, C. Thermal catalytic degradation of α-HBCD, β-HBCD and γ-HBCD over Fe3O4 micro/nanomaterial: Kinetic behavior, product analysis and mechanism hypothesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, J.; Biemba, G.; Brooks, M.I.; Costello, J.; Ommerborn, M.; Bresnahan, M.; Flynn, D.; Simon, J.L. Children of female sex workers and drug users: A review of vulnerability, resilience and family-centred models of care. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2010, 13 (Suppl. 2), S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbstman, J.B.; Sjödin, A.; Kurzon, M.; Lederman, S.A.; Jones, R.S.; Rauh, V.; Needham, L.L.; Tang, D.; Niedzwiecki, M.; Wang, R.Y.; et al. Prenatal exposure to PBDEs and neurodevelopment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascon, M.; Fort, M.; Martinez, D.; Carsin, A.E.; Forns, J.; Grimalt, J.O. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in breast milk and neuropsychological development in infants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiteiro, J.; Mariana, M.; Cairrão, E. Health toxicity effects of brominated flame retardants: From environmental to human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turyk, M.; Anderson, H.; Knobeloch, L.; Imm, P.; Persky, V. Organochlorine Exposure and Incidence of Diabetes in a Cohort of Great Lakes Sport Fish Consumers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyche, J.L.; Rosseland, C.; Berge, G.; Polder, A. Human health risk associated with brominated flame-retardants (BFRs). Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harley, K.G.; Marks, A.R.; Chevrier, J.; Bradman, A.; Sjödin, A.; Eskenazi, B. PBDE concentrations in women’s serum and fecundability. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.A.; Chen, S.C.; Chang, C.M.; Koh, T.W.; Chang-Chien, G.P.; Ouyang, E. Concentrations of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in breast milk correlated to maternal age, education level, and occupational exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, G.A.; Sanders, J.M.; Birnbaum, L.S. Disposition of the emerging brominated flame retardant, 2-ethylhexyl 2, 3, 4, 5-tetrabromobenzoate, in female SD rats and male B6C3F1 mice: Effects of dose, route, and repeated administration. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 154, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.; Keshu, M.; Sillanpää, M.; Shanker, U. An updated review on environmental occurrence, scientific assessment and removal of brominated flame retardants by engineered nanomaterials. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
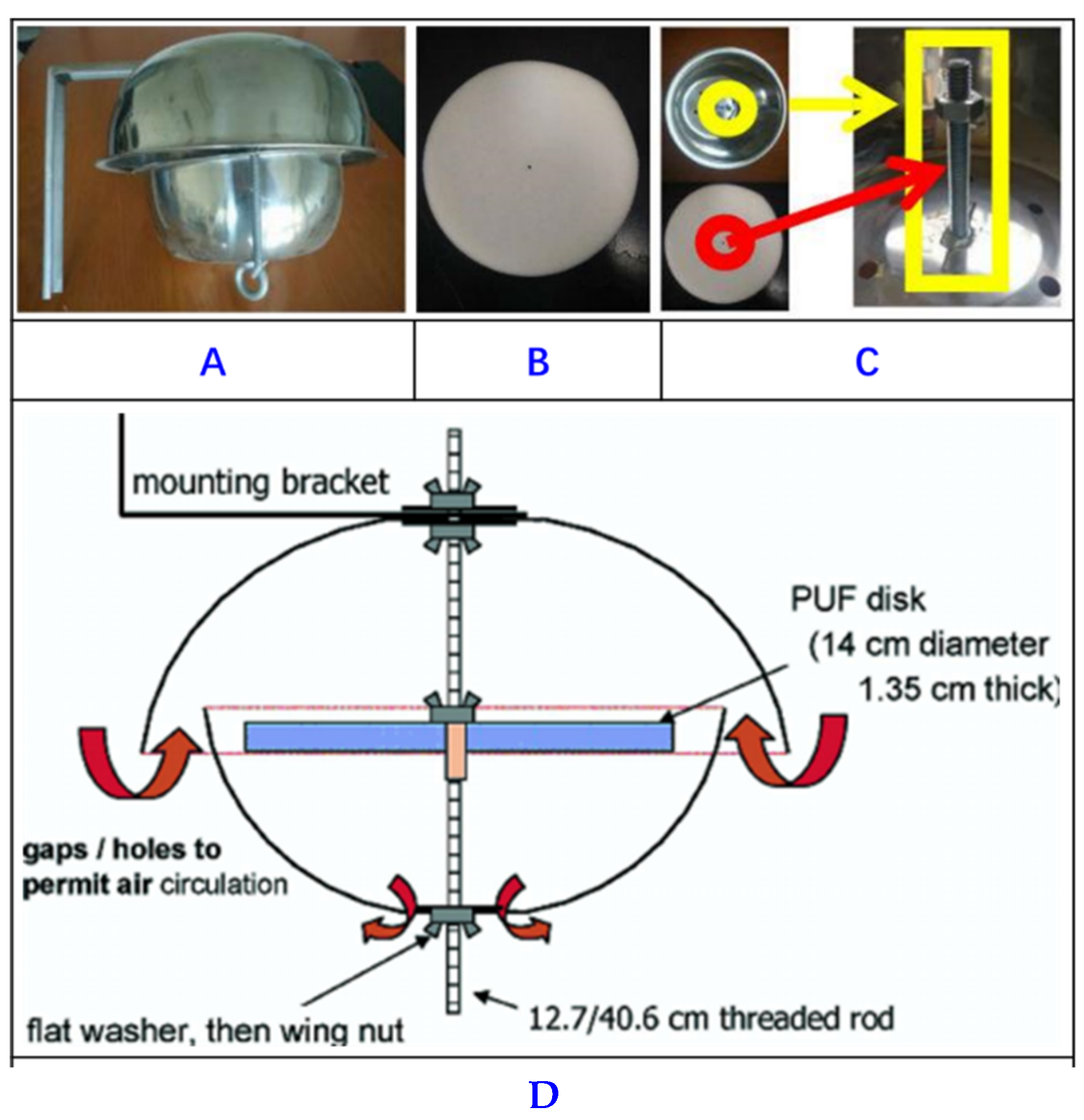

| BFRs | Sample Matrix | Pretreatment | Extraction | Clean-Up | Instrumental Analysis | Recovery (%) | Method LOQ (ng/g) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biotic Samples | ||||||||
| (PBDEs), and (HBCDD) | Food and feed | blended and sieved | hexane and acetone (3:1, v/v) accelerated solvent extractor 2 g of precleaned hydromatrix, 2 g of florisil, 3 g of alumina | in-cell clean-up (see pretreatment) | GCMS and LC-MS/MS | 31–135% | 0.042–2.0 | [39,40] |
| PBDEs | vegetables | matrix solid phase dispersion (MSPD) | dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction (DLLME) | GC-MS | 82.9–113.8% | 5.7–25.3 | [36] | |
| triazine-BFRs | fish (bream) and surface sediment samples | freeze-dried and sieved | pressurized liquid, solid-liquid, ultrasound-assisted, and Soxhlet extraction | SPE (modified multilayer silica gel) (sediment), GPC, Florisil columns (fish) | LC-MS/MS. | 98–114% | Varying values (0.4–80) | [37] |
| PBDE, and NBFRs | Capsicum | QuEChERS | graphene-type materials | GC-ECD/GC-MS/GC-MS/MS | 90–108% | 0.35–0.82 | [35] | |
| PBDEs | breast milk | manual breast milk pump, dried with diatomaceous earth | Soxhlet with hexane:acetone (4:1) | multilayer column including sulfuric acid-impregnated silica eluted with 250 mL hexane | GC-ECNI-MS | 52–120% | Not reported | [26] |
| HBCDDs and NBFRs | breast milk | Collected manual breast milk pump, dried with | Soxhlet extraction hexane:dichloromethane (1:1) | multilayer column including sulfuric acid-impregnated silica eluted with 250 mL hexane | GC-ECNI-MS LC-MS-MS | 52–120% | Not reported | [26] |
| PBDEs | breast milk | manual breast milk and freeze-dried | MAE | multilayer SPE column with 20 mL n-hexane:dichloromethane (4:1, v/v) elution solvent | GC-µECD or GC-MS/MS | 54–67% (GC-µECD) 77–103% (GC-MS/MS) | 0.01–0.13 | [23] |
| NBFRs, PBDEs, | fish muscles | Dorsal fillets | Soxhlet extraction or UAE | - multilayer silica gel column, acid silica, activated silica and anhydrous Na2 SO4−, hexane as elution solvent, in ultrapure nitrogen, - d-SPE | GC-MS | 116.1–83.6% | Not reported | [22] |
| PBDEs, MeO-BDEs | Dolphins | subcutaneous adipose tissue | ASE system; solvent: dichloromethane: n-hexane (1:1, v/v) | sulfuric acid; solid-phase extraction eluted with dichloromethane:n-hexane (2:1, v/v) and toluene | GC-NCI-MS | 90–120% | 0.58–12 | [24] |
| (PBDEs) and (HBCDs) | fish, shellfish and muscle | QuEChERS-like extraction | QuEChERS | GC-MS/MS, LC-MS/MS | 72–97% | - | [25] | |
| TBBPA and BDE209 | Serum and urine | HF-LPME | HF-LPME | HPLC | 84.5–114% | Serum (0.375–2.8 ng/mL), urine (1.25–9.4 ng/mL) | [32] | |
| Abiotic samples | ||||||||
| PBDEs | Dust | heated to 37 °C then dried with diatomaceous earth | Soxhlet with hexane:acetone (4:1) | column 2 g activated aluminum oxide, 2 g sulfuric acid impregnated silica, Na2 SO4 eluted with 60 mL hexane | GC-ECNI-MS LC-MS-MS | 68–116% | Not reported | [26] |
| HBCDDs and NBFRs | Dust | heated to 37 °C then dried with diatomaceous earth | Pressurized Liquid Extraction hexane:dichloromethane (1:1) | 2 g activated aluminum oxide, 2 g deactivated silica and some Na2 SO4 and eluted with 60 mL hexane:dichloromethane (1:1). Gel Permeation Chromatography | GC-ECNI-MS LC-MS-MS | 68–116% | - | [26] |
| PBDE and NBFR | Dust | PUF, pretreated vacuum cleaner, and sieved | - Soxhlet-extracted, acetone:hexane (1:1, v:v, 350 mL) for 24 h, - UAE | Isooctane, solvent-exchanged to isooctane with a gentle stream of nitrogen | GC-MS | 72.3–114% | - | [49] |
| TCPP, TDCPP, TPHP, T24DtBPP, TBBPA, and TriBBPA | Dust | HVAC air filters, dust sieved | - Micro-extraction - Solvent extraction using hexane/acetone - UAE | on line auto-sampler | GC/MS, LC/MS | 70–130% | 0.010–0.020 | [50] |
| TBBPA, tri-BBPA, di-BBPA, mono-BBPA, BPA | Water, soil and sediments | - Water was collected and filtered using GF/F filters - soil and sediment were dried, and sieved | SPE (water) ASE (soil and sediment) | nitrogen evaporator organic phase microporous filter membrane | HPLC–MS/MS | Water (80.28%) soil (79.40%) and sediments (75.65%) | 0.27~0.64 (ng·mL−1) | [42] |
| PBDEs | water | SPME | SPME | GC-MS/MS, UHRMS | 57.2–75.2% | 0.05–4.00 (ng/mL) | [43] | |
| (PBDEs; 28, 47, 99, 100, 153, 154, 183 and 209) NBFRs; (PBT), (PBEB), (HBB), (EH-TBB), (BTBPE) and (DBDPE)) | biosolids | glass vials with PTFE lined lids, acetone rinsed and baked in a muffle furnace at 550 °C for 16 h | selective pressurized liquid extraction (SPLE) (ASE) | chromatographic column, columns containing Florisil and acidified silica eluted with (50:50) hexane/DCM, reconstituted with iso-octane and toluene (80:20) | GC-MS/MS | 80–120% | 0.03–120 | [46] |
| 8 PBDEs, 3 HBCDDs, 5 NBFRs | Air sample | (PUF) and (GFFs) | UAE | SPE | HBCDDs (LC-MS/MS) PBDEs and NBFRs (GC-EI-MS-MS) | 41 and 119% | 2–86 (pg/m3) | [53] |
| PBDD/Fs and PCDD/Fs | Air sample | PUF | UAE extracted dichloromethane | acid silica gel bed, multi-layer silica column, and a Florisil column | GCMS | 38 and 128% | - | [54] |
| TBP, TBBPA and BDE-209 | FCA | cutting | Ultrasonic assisted extraction methanol-isopropanol | PTFE membrane filter | DART-HRMS, HPLC-MS/MS | 82–120% | 0.005–0.02 | [47] |
| Chemicals | Concentration | Occurrence | Country/Region | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Sediments | ||||
| Tetrabromobisphenol (TBBPA) | ND–12.591 µg/kg | surface sediment | Western Guangdong, China | [15] |
| 0.02–18.3 µg/kg | surface sediment | South China Coast | [13] | |
| 19.8–1.52 × 104 ng/g dw | A typical waste dismantling site | China | [14] | |
| 0.003–0.31 ng/g dw, not detected (ND) to 1.11 ng/g dry weight | Mangrove wetlands | South China | [57] | |
| 0.02–21.5 ng/g dw | Coast land | South China | [13] | |
| Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCDs): α-, β-, and γ-HBCD | ND–6.307 µg/kg | surface sediment | South China Coast | [15] |
| Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) | 0.345–401,000 ng/g dw | A typical e-waste dismantling region | China | [58] |
| 7 Novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) | 0.581–73,100 ng/g dw | A typical e-waste dismantling region | China | [58] |
| Biota | ||||
| Tetrabromobisphenol (TBBPA) | 0.56–22.1 ng/g ww | Biota species from two mangrove wetlands | South China | [57] |
| ND–9.83 µg/kg ww | Zooplankton samples | Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea, Northern China | [59] | |
| Tetrabromobisphenol-A-bis(2,3,-dibromopropyl ether) (TBBPA-BDBPE) | <LOD-42.8 ng/g ww | Herring gull egg pools | Laurentian Great lakes, North American | [60] |
| Water | ||||
| Tetrabromobisphenol (TBBPA) | ND–0.46 µg/L | surface seawater | Northern China | [61] |
| ND–12.279 ng/L | Weihe River Basin | China | [60] | |
| 18.5–82.6 ng/L | Baiyang Lake | China | [62] | |
| ND–32.3 ng/L | Surface water | Taihu Lake, China | [63] | |
| Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) | 0.00226–0.00751 ng/L | Bohai Sea | China | [63] |
| ND–71.77 ng/L | Surface water | Taizhou, China | [64] | |
| ND–4.28 ng/L | Sea | South China | [65] | |
| 0.723–3.796 ng/L | Dongjiang River | China | [66] | |
| Novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) | 0.0107–0.0104 ng/L | Bohai Sea | China | [64] |
| ND–3.34 ng/L | Surface water | Taizhou, China | [66] | |
| ND–7.63 ng/L | Sea | South China | [65] | |
| Decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) | 2010 (ND–35,000) ng/L | Lian River and Beigang River | Guiyu, South China | [66] |
| 9.5 (ND–120) ng/L | Taizhou | East China | [67] | |
| 7.28 (0.06–69.5) ng/L | Shihwa Lake | Republic of Korea | [68] | |
| 3.29 (0.22–37.6) ng/L | Ulsan/Onsan Bays | Republic of Korea | [69] | |
| 1,2-bis-(2,4,6-tribromophenoxy)ethane (BTBPE) | 830 (ND–36,800) ng/L | Lian River and Beigang River | Guiyu, South China | [58] |
| 0.043 (ND–0.60) ng/L | Taizhou | East China | [69] | |
| Food stuffs | ||||
| Novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs): 1,2-bis(2,4,6-tribromophenoxy) ethane (BTBPE or TBE), and bis(2-ethyl hexyl) tetrabromophthalate (BEH-TEBP or TBPH) | <0.42–170 ng/g lw | Food stuffs | UK | [70] |
| Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) | 0.13–36 ng/g lw | Food stuffs | UK | [70] |
| Air and dust | ||||
| Tetrabromobisphenol (TBBPA) | <LOD-74.1 ng/g dw | Soil and road dust | western China | [71] |
| ND–144 pg/m3 | Indoor dust | Sothern China | [72] | |
| ND–326 pg/m3 | Outdoor dust | Sothern China | [72] | |
| <0.1 pg/m3 | Office air and dust | Sweden | [73] | |
| 69 ng/g dw | House dust | Republic of Korea | [74] | |
| Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) | 490–89,000 ng/g | Indoor dust, indoor air, and outdoor air | Birmingham, UK | [72] |
| 94–227 ng/g | Household dust | China | [75] | |
| Hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) | 46–14,000 pg/m3 | Indoor and outdoor dust | Birmingham, UK | [64] |
| 1.06–14.1 µg/kg | Indoor dust, indoor and outdoor air | South China Coast | [13] | |
| Novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) | 22–11,000 pg/m3 | Indoor dust, indoor and outdoor air | Birmingham, UK | [64] |
| Soil | ||||
| Tetrabromobisphenol (TBBPA) | <LOD-33.8 ng/g dw | Soil | Chongqing, western China | [71] |
| 0.025–78.6 ng/g dw | Soil | Republic of Korea | [76] | |
| Human sample | ||||
| Tetrabromobisphenol (TBBPA) | <LOD-42 ng/g lw | Breast milk | Beijing, China | [56] |
| <LOD-15.1 ng/g lw | Breast milk | French | [77] | |
| 4.73 ng/g lw | Breast milk | China | [78] | |
| ND–1.08 ng/g | Hair | China | [79] | |
| 0.0793–1.15 µg/L | Urine | China | [80] | |
| Novel halogenated flame retardants (NHFRs) | Maximum 6930 pg g−1 lipid | Breast milk | Canada | [81] |
| methoxy-polybrominated diphenyl ethers (MeO-PBDEs) | Maximum 1600 pg g−1 lipid | Breast milk | Canada | [81] |
| Novel Bromine Fire Retardants | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 ethylhexyl-2,3,4,5 tetrabromobenzoate (EH-TBB) | Potentially an endocrine disruptor | [93] |
| 2 | Bis (2-ethylhexyl) tetrabromophthalate (BEH-TEBP) | Potentially an endocrine disruptor and very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects | [123] |
| 3 | Decabromodiphenyl ethane (DBDPE) | Potentially an endocrine disruptor and very toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects | [93] |
| 4 | 1,2-bis (2,4,6 tribromophenoxy) ethane (BTBPE) | Potentially an endocrine disruptor Suspected to be a carcinogen and mutagen | [93] |
| 5 | 1,2 bromo-4-(1,2 dibromoethyl)cyclohexane (DBE-DBCH) | Suspected to be a carcinogen and mutagen | [124] |
| 6 | Tetrabromobisphenol A Bis (2,3 dibromopropyl)ether (TBBPA-BDBPE) | Potentially bioaccumulate and toxic endocrine disruptor | [123] |
| 7 | Hexabromo benzene (HBB) | Suspected to be bio-accumulative | [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Enyoh, C.E.; Maduka, T.O.; Rana, M.S.; Osigwe, S.C.; Ihenetu, S.C.; Wang, Q. Chemicals from Brominated Flame Retardants: Analytical Methods, Occurrence, Transport and Risks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177892
Enyoh CE, Maduka TO, Rana MS, Osigwe SC, Ihenetu SC, Wang Q. Chemicals from Brominated Flame Retardants: Analytical Methods, Occurrence, Transport and Risks. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177892
Chicago/Turabian StyleEnyoh, Christian Ebere, Tochukwu Oluwatosin Maduka, Md. Sohel Rana, Sochi Chinaemerem Osigwe, Stanley Chukwuemeka Ihenetu, and Qingyue Wang. 2024. "Chemicals from Brominated Flame Retardants: Analytical Methods, Occurrence, Transport and Risks" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177892
APA StyleEnyoh, C. E., Maduka, T. O., Rana, M. S., Osigwe, S. C., Ihenetu, S. C., & Wang, Q. (2024). Chemicals from Brominated Flame Retardants: Analytical Methods, Occurrence, Transport and Risks. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7892. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177892











