The Rheology, Texture, and Molecular Dynamics of Plant-Based Hot Dogs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sausage Analogs
2.3. Nutritional Value of PBSs
2.4. Texture Analysis of PBSs
2.5. Rheological Analyses of Batters and Sausage Analogs
2.6. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF NMR) of Batters and Sausage Analogs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Chemical Characteristics
3.2. Textural Properties of PBSs
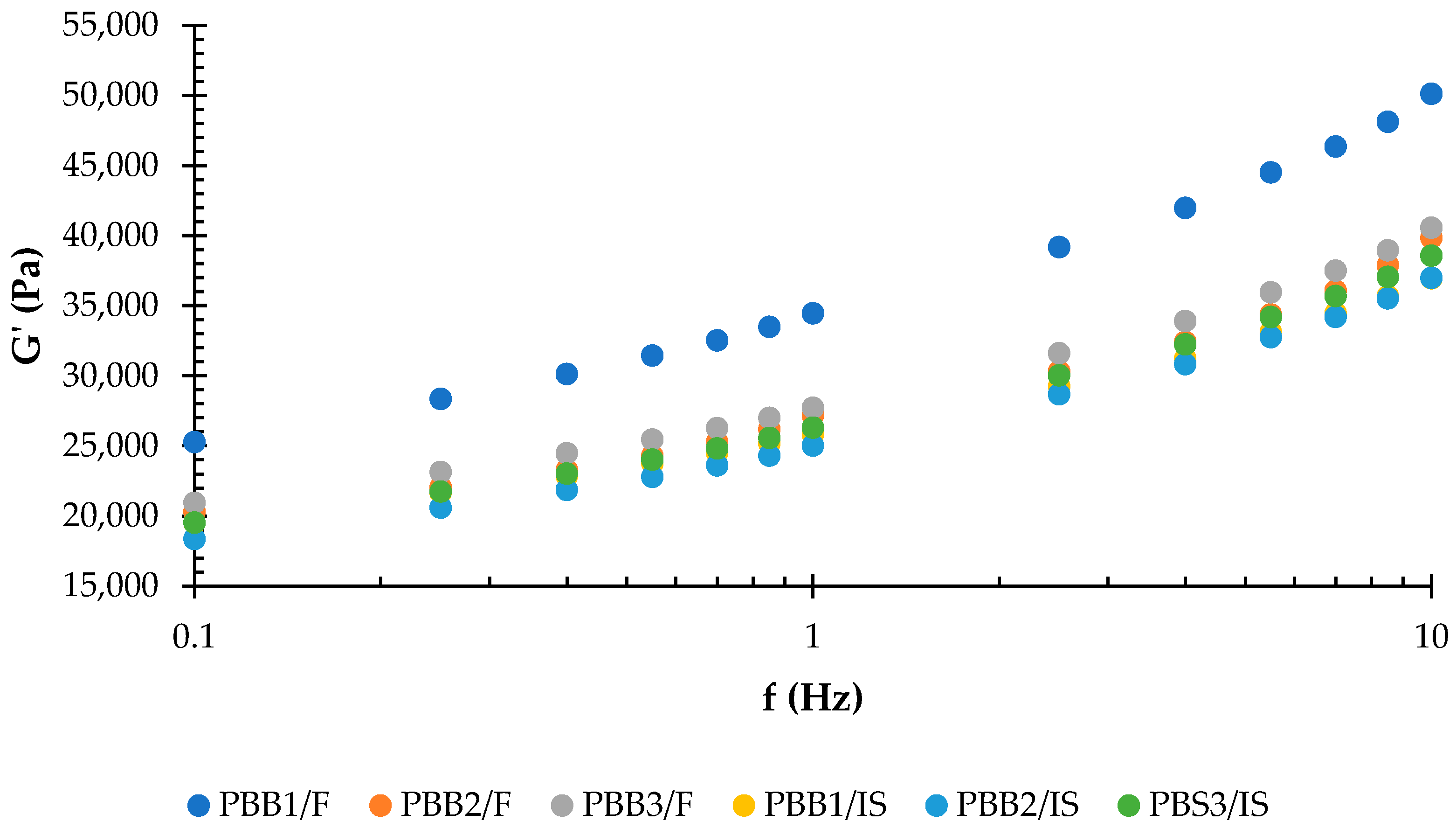
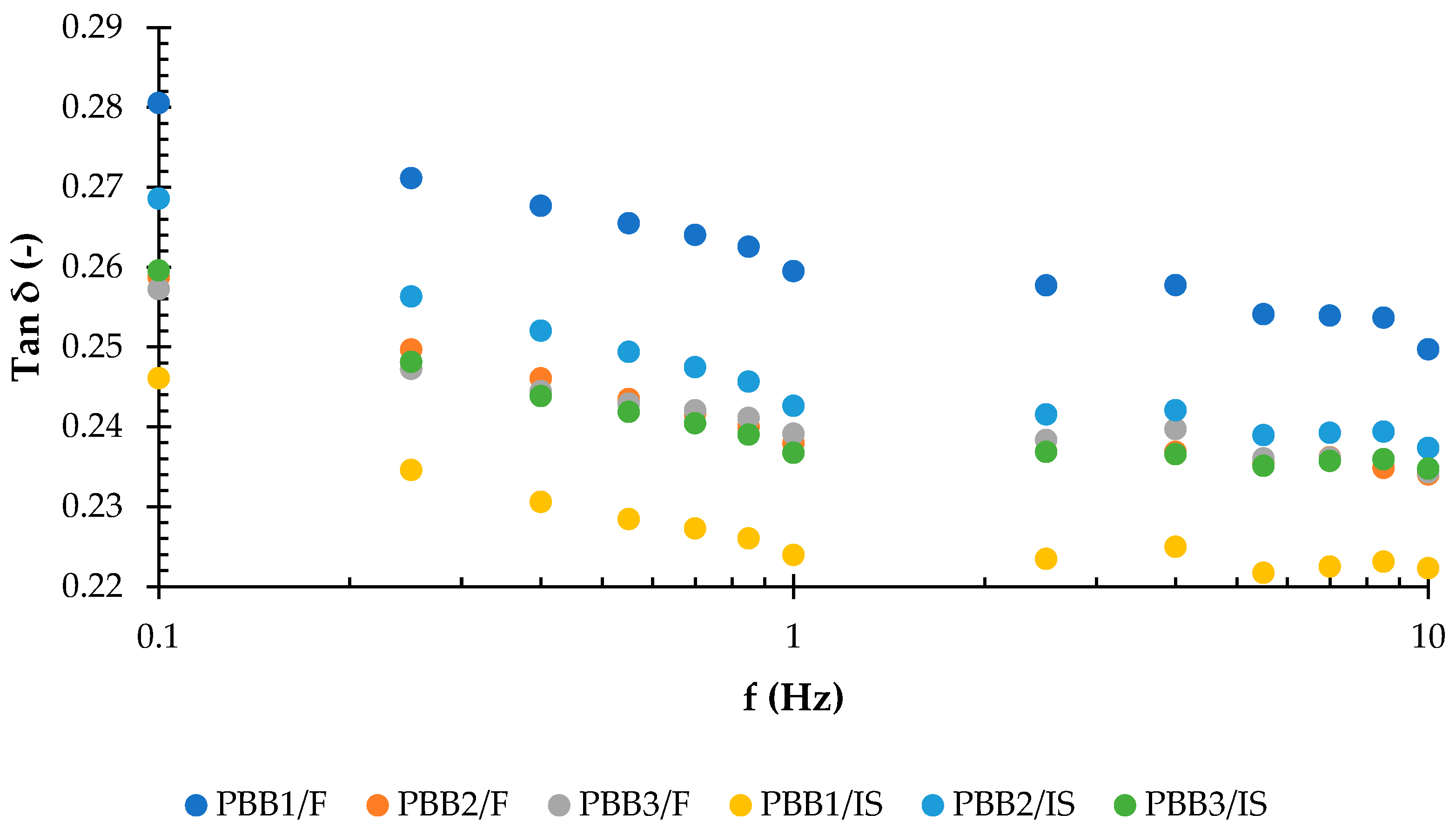
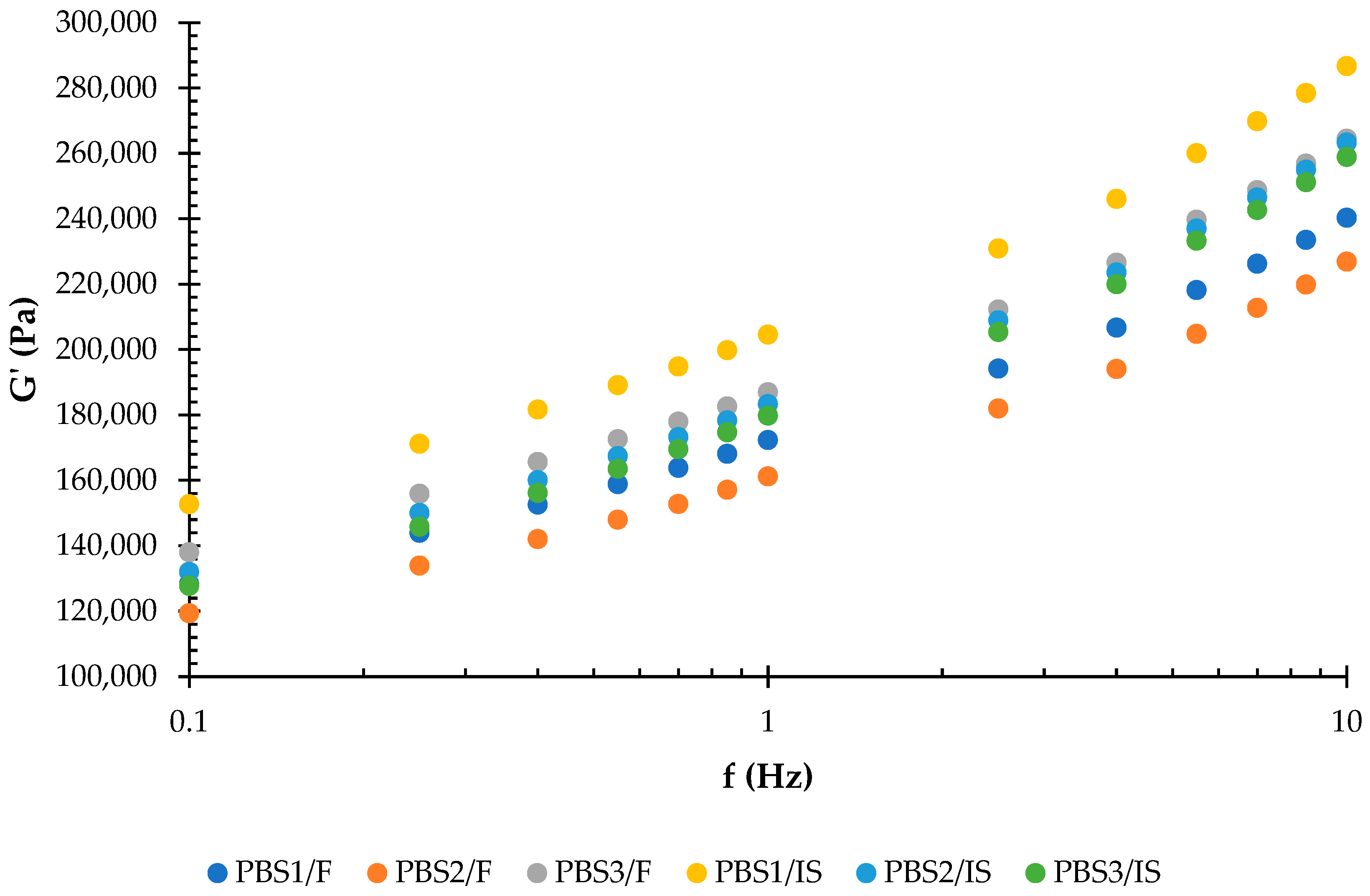
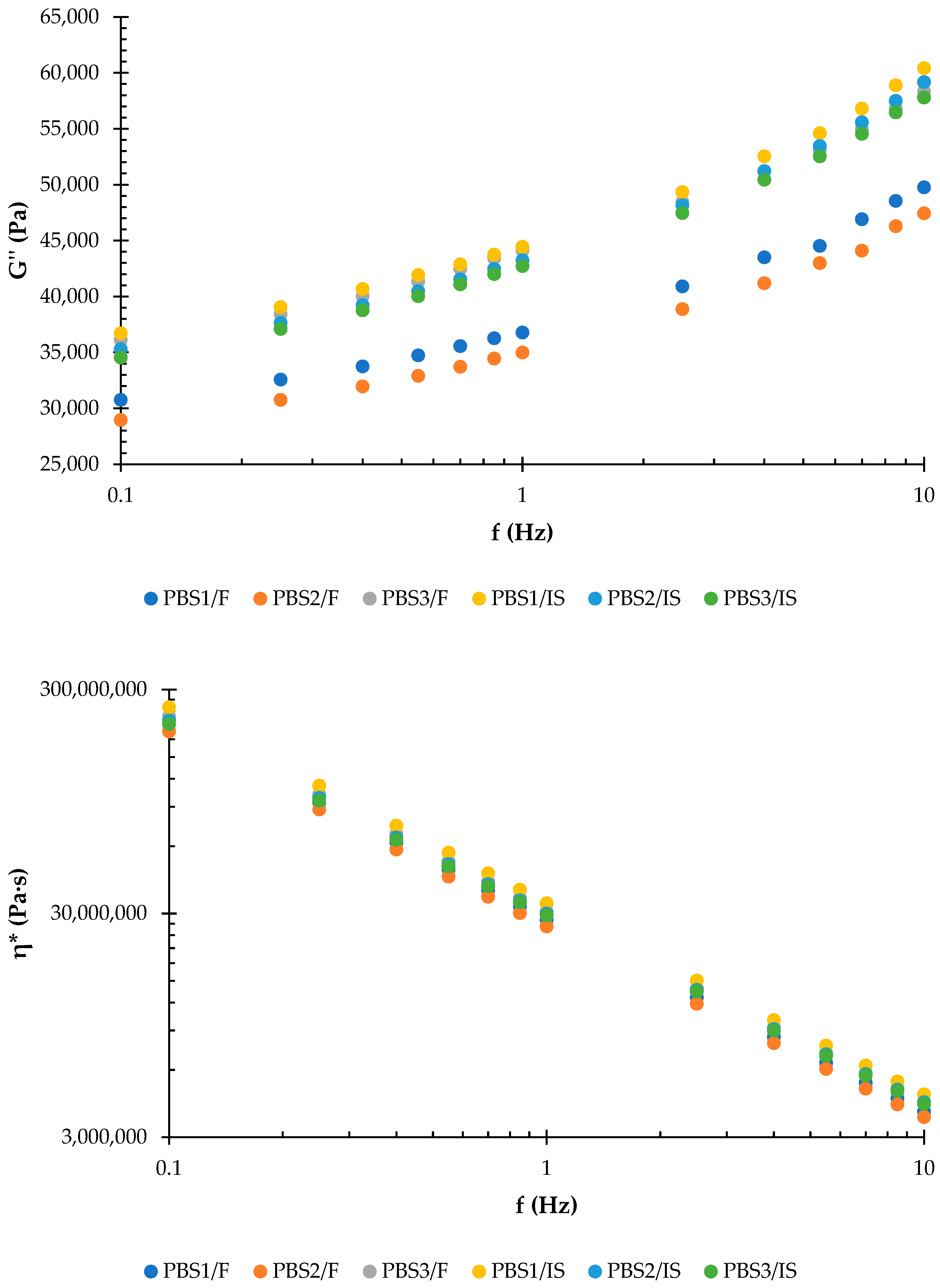
3.3. Rheological Properties of PBBs and PBSs
3.4. Molecular Properties of PBBs and PBSs
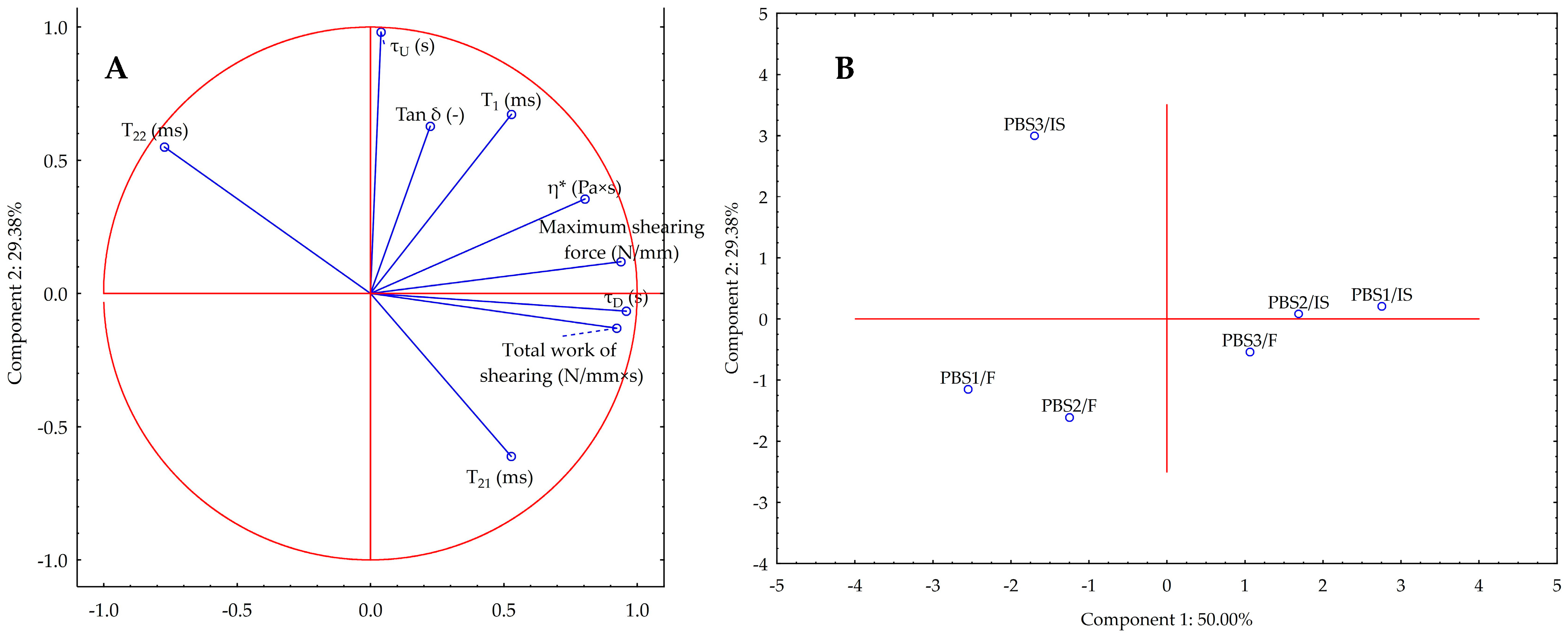
3.5. Statistical Considerations on the Properties of PBBs
4. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
6. Patent
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Contini, C.; Boncinelli, F.; Marone, E.; Scozzafava, G.; Casini, L. Drivers of plant-based convenience foods consumption: Results of a multicomponent extension of the theory of planned behaviour. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 84, 103931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybicka, I.; Bohdan, K.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł. Meat alternatives—Market and cunsumption. In Sustainable Food. Production and Consumption Perspectives; Pawlak-Lemańska, K., Borusiak, B., Sikorska, E., Eds.; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Ekonomicznego w Poznaniu: Poznań, Poland, 2024; pp. 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreman, L.; Nommensen, P.; Pennings, B.; Laus, M.C. Comprehensive overview of the quality of plant- and animal-sourced proteins based on the digestible indispensable amino acid score. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5379–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesogan, A.T.; Havelaar, A.H.; McKune, S.L.; Eilittä, M.; Dahl, G.E. Animal source foods: Sustainability problem or malnutrition and sustainability solution? Perspective matters. Glob. Food Sec. 2020, 25, 100325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskin, E.; Cianciosi, D.; Gulec, S.; Tomas, M.; Capanoglu, E. Iron Absorption: Factors, Limitations, and Improvement Methods. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 20441–20456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, A.; Naik, R. The Impact of a Vegan Diet on Many Aspects of Health: The Overlooked Side of Veganism. Cureus 2023, 15, e35148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galchenko, A.; Gapparova, K.; Sidorova, E. The influence of vegetarian and vegan diets on the state of bone mineral density in humans. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Keppler, J.K.; van der Goot, A.J. Functionality of Ingredients and Additives in Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, K.; Ashfaq, A.; Ahmad, A.; Anjum, Z.; Yousuf, O. A critical review focusing the effect of ingredients on the textural properties of plant-based meat products. J. Texture Stud. 2023, 54, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z. Soy protein isolates: A review of their composition, aggregation, and gelation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1940–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maningat, C.C.; Jeradechachai, T.; Buttshaw, M.R. Textured wheat and pea proteins for meat alternative applications. Cereal Chem. 2022, 99, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacka, M.; Trusinska, M.; Chraniuk, P.; Drudi, F.; Lukasiewicz, J.; Nguyen, N.P.; Przybyszewska, A.; Pobiega, K.; Tappi, S.; Tylewicz, U.; et al. Developments in Plant Proteins Production for Meat and Fish Analogues. Molecules 2023, 28, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kumar, R.; Sabapathy, S.N.; Bawa, A.S. Functional and Edible Uses of Soy Protein Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dou, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. The development history and recent updates on soy protein-based meat alternatives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hong, S.; Li, Y. Pea protein composition, functionality, modification, and food applications: A review. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2022, 101, 71–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Xiong, Y.L. Plant protein-based alternatives of reconstructed meat: Science, technology, and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galves, C.; Galli, G.; Kurozawa, L. Potato protein: Current review of structure, technological properties, and potential application on spray drying microencapsulation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 6564–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Olejnik, A.; Świtek, S.; Bzducha-Wróbel, A.; Kubiak, P.; Kujawska, M.; Lewandowicz, G. Bioactive compounds of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) juice: From industry waste to food and medical applications. CRC. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2022, 41, 52–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-W.; Han, C.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Hsu, F.-L.; Hou, W.-C. Patatin, the Tuber Storage Protein of Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.), Exhibits Antioxidant Activity In Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4389–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Olejnik, A.; Białas, W.; Rybicka, I.; Zielińska-Dawidziak, M.; Siger, A.; Kubiak, P.; Lewandowicz, G. The Nutritional Value and Biological Activity of Concentrated Protein Fraction of Potato Juice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenbeck, I.; Graf, A.M.; Leuthold, M.; Pastor, A.; Beutel, S.; Scheper, T. Purification of high value proteins from particle containing potato fruit juice via direct capture membrane adsorption chromatography. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 168, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeżowski, P.; Polcyn, K.; Tomkowiak, A.; Rybicka, I.; Radzikowska, D. Technological and antioxidant properties of proteins obtained from waste potato juice. Open Life Sci. 2020, 15, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miedzianka, J.; Pęksa, A.; Aniołowska, M. Properties of acetylated potato protein preparations. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszkiewicz, T.; Florek, M.; Wodzak, M.; Kubiak, D.; Burczyk, E. Comparison of the Quality of Selected Meat Products and Their Plant-Based Analogs. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2023, 73, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Hairi, A.N.; Taufik, A.M.; Zainal Abidin, S.A.S. Product innovation: Palm oil fat in plant-based meat. In Innovation of Food Products in Halal Supply Chain Worldwide; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijaard, E.; Brooks, T.M.; Carlson, K.M.; Slade, E.M.; Garcia-Ulloa, J.; Gaveau, D.L.A.; Lee, J.S.H.; Santika, T.; Juffe-Bignoli, D.; Struebig, M.J.; et al. The environmental impacts of palm oil in context. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, M.; Costa, A.; Pozza, M.; Goi, A.; Manuelian, C.L. Detailed characterization of plant-based burgers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreher, J.; König, M.; Herrmann, K.; Terjung, N.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J. Varying the amount of solid fat in animal fat mimetics for plant-based salami analogues influences texture, appearance and sensory characteristics. LWT 2021, 143, 111140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Lee, Y.; Han, S.O.; Hyeon, J.E. Advancements in Sustainable Plant-Based Alternatives: Exploring Proteins, Fats, and Manufacturing Challenges in Alternative Meat Production. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO and FAO Joint Consultation: Fats and Oils in Human Nutrition. Nutr. Rev. 2009, 53, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.C.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. Achieving optimal essential fatty acid status in vegetarians: Current knowledge and practical implications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 640S–646S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmiecik, D.; Fedko, M.; Siger, A.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł. Nutritional Quality and Oxidative Stability during Thermal Processing of Cold-Pressed Oil Blends with 5:1 Ratio of ω6/ω3 Fatty Acids. Foods 2022, 11, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K. Omega-6 (n-6) and omega-3 (n-3) fatty acids in tilapia and human health: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. Evolutionary Aspects of Diet: The Omega-6/Omega-3 Ratio and the Brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innis, S.M. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Biochemistry: Perspectives from Human Nutrition. Mil. Med. 2014, 179, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmadfa, I.; Kornsteiner, M. Fats and Fatty Acid Requirements for Adults. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 55, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska-Dawidziak, M.; Twardowski, T. Preparation with Higher Plant Ferritin Content and Other Forms of Iron, Process for Preparation and the Use Thereof. Polish Patent No. PL218747, 30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Świątek, M.; Antosik, A.; Kochanowska, D.; Jeżowski, P.; Smarzyński, K.; Tomczak, A.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł. The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron. Open Life Sci. 2023, 18, 20220805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzoobi, M.; Talebanfar, S.; Eskandari, M.H.; Farahnaky, A. Improving the quality of meat-free sausages using κ-carrageenan, konjac mannan and xanthan gum. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P. Plant-Based Protein Flavor Maskers and Enhancers. In Flavor-Associated Applications in Health and Wellness Food Products; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatansever, S.; Chen, B.; Hall, C. Plant protein flavor chemistry fundamentals and techniques to mitigate undesirable flavors. Sustain. Food Proteins 2024, 2, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarska, K.; Taylor, M.; Piyasiri, U.; Frank, D. Flavor and Metabolite Profiles of Meat, Meat Substitutes, and Traditional Plant-Based High-Protein Food Products Available in Australia. Foods 2021, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Zannou, O.; Karim, I.; Kasmiati; Awad, N.M.H.; Gołaszewski, J.; Heinz, V.; Smetana, S. Avoiding Food Neophobia and Increasing Consumer Acceptance of New Food Trends—A Decade of Research. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, M.; Hartmann, C. Consumer acceptance of novel food technologies. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, D.; Li, Y.; Alavi, S. Chemical and physicochemical features of common plant proteins and their extrudates for use in plant-based meat. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 131, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.R.; Stephani, R.; Perrone, Í.T.; de Carvalho, A.F. Plant-based proteins: A review of factors modifying the protein structure and affecting emulsifying properties. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Mehany, T.; Xie, W.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.; Peng, X. Use of food carbohydrates towards the innovation of plant-based meat analogs. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Grossmann, L. The science of plant-based foods: Constructing next-generation meat, fish, milk, and egg analogs. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4049–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Białas, W.; Kowalczewski, P.; Lewandowicz, G.; Olejnik, A.; Siger, A.; Dwiecki, K. Method for Obtaining a Pro-Healthy Protein Preparation. Patent No. PL240850, 13 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczewski, P.; Smarzyński, K.; Lesiecki, M.; Kmiecik, D.; Zielińska-Dawidziak, M.; Drabińska, N. Plant-Based Analogue of Hot Dog Sausage and Method of Producing a Plant-Based Analogue of Hot Dog Sausage. Polish Patent Aplication No. P.445946, 30 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 1871:2009; Food and Feed Products—General Guidelines for the Determination of Nitrogen by the Kjeldahl Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- AOAC. AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, 21st ed.; AOAC international: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- AACC. AACCI 32-07.01 Soluble, Insoluble, and Total Dietary Fiber in Foods and Food Products. In AACC International Approved Methods; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. 44-19.01 Moisture--air-oven method, drying at 135 degrees. In AACC International Approved Methods; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 763:2003; Fruit and Vegetable Products—Determination of Ash Insoluble in Hydrochloric Acid. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Lewandowicz, G.G.; Krzywdzińska-Bartkowiak, M.; Piątek, M.; Baranowska, H.M.; Białas, W.; Jeziorna, M.; Kubiak, P. Finely comminuted frankfurters fortified with potato juice—Quality and structure. J. Food Eng. 2015, 167, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeżowski, P.; Menzel, J.; Baranowska, H.M.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł. Microwaved-Assisted Synthesis of Starch-Based Biopolymer Membranes for Novel Green Electrochemical Energy Storage Devices. Materials 2023, 16, 7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosio, E.; Gianferri, R.R. Low-resolution NMR—An analytical tool in foods characterization and traceability. In Basic NMR in Foods Characterization; Brosio, E., Ed.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2009; pp. 9–37. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, H.Y.; Purcell, E.M. Effects of Diffusion on Free Precession in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Experiments. Phys. Rev. 1954, 94, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiboom, S.; Gill, D. Modified Spin-Echo Method for Measuring Nuclear Relaxation Times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1958, 29, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małyszek, Z.; Lewandowicz, J.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Walkowiak, K.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Baranowska, H.M. Water Behavior of Emulsions Stabilized by Modified Potato Starch. Polymers 2021, 13, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloembergen, N.; Purcell, E.M.; Pound, R.V. Relaxation Effects in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Absorption. Phys. Rev. 1948, 73, 679–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Anjaneyulu, A.S.R.; Gadekar, Y.P.; Singh, R.P.; Pragati, H. Effect of full-fat soy paste and textured soy granules on quality and shelf-life of goat meat nuggets in frozen storage. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, M.C. Texture, Viscosity, and Food. In Food Texture and Viscosity; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, E.; Dolata, W.; Baranowska, H.M.; Rezler, R.; Niedbała, D. Quality of chopped sausages with additives produced under large-scale production conditions. Fleischwirtschaft 2009, 3, 52–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kamani, M.H.; Meera, M.S.; Bhaskar, N.; Modi, V.K. Partial and total replacement of meat by plant-based proteins in chicken sausage: Evaluation of mechanical, physico-chemical and sensory characteristics. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raouche, S.; Dobenesque, M.; Bot, A.; Lagaude, A.; Marchesseau, S. Casein micelles as a vehicle for iron fortification of foods. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, D.; Christopher, J.; Hegenauer, J.; Saltman, P. Effect of milk and casein on the absorption of supplemental iron in the mouse and chick. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1975, 28, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastorino, A.J.; Ricks, N.P.; Hansen, C.L.; McMahon, D.J. Effect of Calcium and Water Injection on Structure-Function Relationships of Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novaković, S.; Tomašević, I. A comparison between Warner-Bratzler shear force measurement and texture profile analysis of meat and meat products: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 85, 012063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raak, N.; Dürrschmid, K.; Rohm, H. Textural Characteristics of German Foods. In Textural Characteristics of World Foods; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dransfield, E. The taste of fat. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Healthier lipid formulation approaches in meat-based functional foods. Technological options for replacement of meat fats by non-meat fats. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulis, R.J.; Mckeith, F.K.; Brewer, M.S. Physical and sensory characteristics of commercially available frankfurters. J. Food Qual. 1994, 17, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.H.; Brown, R.D. Relaxation of solvent protons by paramagnetic ions and its dependence on magnetic field and chemical environment: Implications for NMR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 1984, 1, 478–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, G.; Ravera, E.; Calderone, V.; Botta, M.; Fragai, M.; Parigi, G.; Luchinat, C. Revisiting paramagnetic relaxation enhancements in slowly rotating systems: How long is the long range? Magn. Reson. 2021, 2, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, F.M.; Martin, S.J.; McBrierty, V.J. Dynamics of water molecules in polymers. J. Mol. Liq. 1996, 69, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, A.; Dwiecki, K.; Kubiak, P.; Baranowska, H.M.; Lewandowicz, G. Polymer-Solvent Interactions in Modified Starches Pastes–Electrokinetic, Dynamic Light Scattering, Rheological and Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Approach. Polymers 2022, 14, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, E.G.; Domenici, V.; Florek-Wojciechowska, M.; Gradišek, A.; Kruk, D.; Maltar-Strmečki, N.; Oztop, M.; Ozvural, E.B.; Rollet, A.-L. Field-dependent NMR relaxometry for Food Science: Applications and perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ingredient [%] | PBS1/F | PBS2/F | PBS3/F | PBS1/IS | PBS2/IS | PBS3/IS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrated protein base | 58.4 | 58.4 | 58.4 | 58.4 | 58.4 | 58.4 |
| Oil blend | 15.9 | 15.9 | 15.9 | 15.9 | 15.9 | 15.9 |
| Methylcellulose | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Sausage aroma | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Smoke aroma | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Inactivated yeast | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.9 |
| Dried beetroot juice | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Salt | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Carrageenan | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Dry protein mix | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.5 |
| Sprouts containing ferritin | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Iron (II) sulfate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.007 |
| Ice water | 11.1 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 11.093 | 11.093 | 11.093 |
| Parameter | Unit | Sample | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS1/F | PBS2/F | PBS3/F | PBS1/IS | PBS2/IS | PBS3/IS | ||
| Protein content | g/100 g | 21.7 ± 1.0 | 20.7 ± 0.5 | 21.3 ± 0.6 | 19.9 ± 0.9 | 21.6 ± 1.4 | 21.2 ± 0.8 |
| Fat content | g/100 g | 15.8 ± 0.3 | 16.3 ± 0.1 | 16.8 ± 0.3 | 16.2 ± 0.3 | 16.4 ± 0.4 | 16.5 ± 0.5 |
| Fiber content | g/100 g | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 6.8 ± 0.1 | 6.8 ± 0.1 | 4.9 ± 0.3 | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 5.1 ± 0.6 |
| Carbohydrates content | g/100 g | 9.9 ± 1.3 | 12.3 ± 0.8 | 11.0 ± 0.7 | 13.2 ± 1.3 | 12.0 ± 1.8 | 8.4 ± 1.0 |
| Mineral content | g/100 g | 4.2 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 4.2 ± 0.0 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.4 | 4.1 ± 0.3 |
| Energy value | kcal/100 g | 297.3 ± 1.9 | 317.0 ± 3.3 | 313.4 ± 1.5 | 308.5 ± 2.2 | 302.7 ± 2.9 | 296.1 ± 1.4 |
| Sample | Maximum Shearing Force (N/mm) | Total Work of Shearing (N/mm∙s) |
|---|---|---|
| PBS1/F | 4.33 ± 0.19 c | 46.71 ± 2.88 c |
| PBS2/F | 4.68 ± 0.48 b | 51.61 ± 2.99 b |
| PBS3/F | 4.87 ± 0.32 a,b | 55.07 ± 4.78 a,b |
| PBS1/IS | 5.09 ± 0.33 a | 60.61 ± 2.64 a |
| PBS2/IS | 4.83 ± 0.17 b | 52.95 ± 4.84 b |
| PBS3/IS | 4.63 ± 0.27 b | 47.89 ± 2.75 c |
| Sample | T1 (ms) | T21 (ms) | T22 (ms) | τD (s) | τU (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batters | |||||
| PBB1/F | 128.3 ± 0.5 d | 32.4 ± 1.3 b | 83.1 ± 4.7 b | 5.02 × 10−9 | 1.38 × 10−8 |
| PBB2/F | 133.2 ± 0.7 c | 34.0 ± 1.7 b | 86.1 ± 6.2 b | 5.04 × 10−9 | 1.36 × 10−8 |
| PBB3/F | 130.7 ± 0.6 d | 38.0 ± 2.5 a | 78.3 ± 5.4 bc | 5.64 × 10−9 | 1.22 × 10−8 |
| PBB1/IS | 140.7 ± 0.7 b | 32.2 ± 1.4 b | 81.7 ± 5.2 bc | 5.89 × 10−9 | 1.30 × 10−8 |
| PBB2/IS | 147.3 ± 0.7 a | 37.2 ± 2.3 a | 75.8 ± 5.6 c | 6.86 × 10−9 | 1.38 × 10−8 |
| PBB3/IS | 140.6 ± 0.6 b | 30.7 ± 1.0 c | 95.1 ± 6.2 a | 4.68 × 10−9 | 1.55 × 10−8 |
| Sausages | |||||
| PBS1/F | 104.1 ± 0.6 d | 30.7 ± 1.4 b | 74.4 ± 3.4 a | 4.25 × 10−9 | 1.20 × 10−8 |
| PBS2/F | 109.1 ± 0.4 c | 33.5 ± 2.4 ab | 75.3 ± 6.0 a | 4.52 × 10−9 | 1.16 × 10−8 |
| PBS3/F | 107.5 ± 0.5 c | 31.6 ± 3.3 ab | 64.7 ± 6.6 b | 5.60 × 10−9 | 1.21 × 10−8 |
| PBS1/IS | 119.9 ± 0.4 b | 32.2 ± 2.8 ab | 65.7 ± 7.3 b | 5.90 × 10−9 | 1.29 × 10−8 |
| PBS2/IS | 123.3 ± 0.5 a | 35.2 ± 3.2 a | 69.0 ± 9.8 b | 6.18 × 10−9 | 1.24 × 10−8 |
| PBS3/IS | 120.5 ± 0.7 b | 28.1 ± 1.2 b | 85.4 ± 9.2 a | 4.31 × 10−9 | 1.40 × 10−8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Smarzyński, K.; Lewandowicz, J.; Jeżowski, P.; Ruszkowska, M.; Wróbel, M.M.; Kubiak, P.; Kačániová, M.; Baranowska, H.M. The Rheology, Texture, and Molecular Dynamics of Plant-Based Hot Dogs. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177653
Kowalczewski PŁ, Smarzyński K, Lewandowicz J, Jeżowski P, Ruszkowska M, Wróbel MM, Kubiak P, Kačániová M, Baranowska HM. The Rheology, Texture, and Molecular Dynamics of Plant-Based Hot Dogs. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(17):7653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177653
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalczewski, Przemysław Łukasz, Krzysztof Smarzyński, Jacek Lewandowicz, Paweł Jeżowski, Millena Ruszkowska, Martyna Maria Wróbel, Piotr Kubiak, Miroslava Kačániová, and Hanna Maria Baranowska. 2024. "The Rheology, Texture, and Molecular Dynamics of Plant-Based Hot Dogs" Applied Sciences 14, no. 17: 7653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177653
APA StyleKowalczewski, P. Ł., Smarzyński, K., Lewandowicz, J., Jeżowski, P., Ruszkowska, M., Wróbel, M. M., Kubiak, P., Kačániová, M., & Baranowska, H. M. (2024). The Rheology, Texture, and Molecular Dynamics of Plant-Based Hot Dogs. Applied Sciences, 14(17), 7653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14177653










