Natural Phenolic Acids as Effective Bulk Oil Antioxidants: Oxidative Stability Modeling Using Olive Kernel Oil as a Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Olive Kernel Oil (OKO)
2.3. OKO Enrichment with Antioxidants
2.4. Rancimat Test
2.5. Accelerated Oxidation Treatment
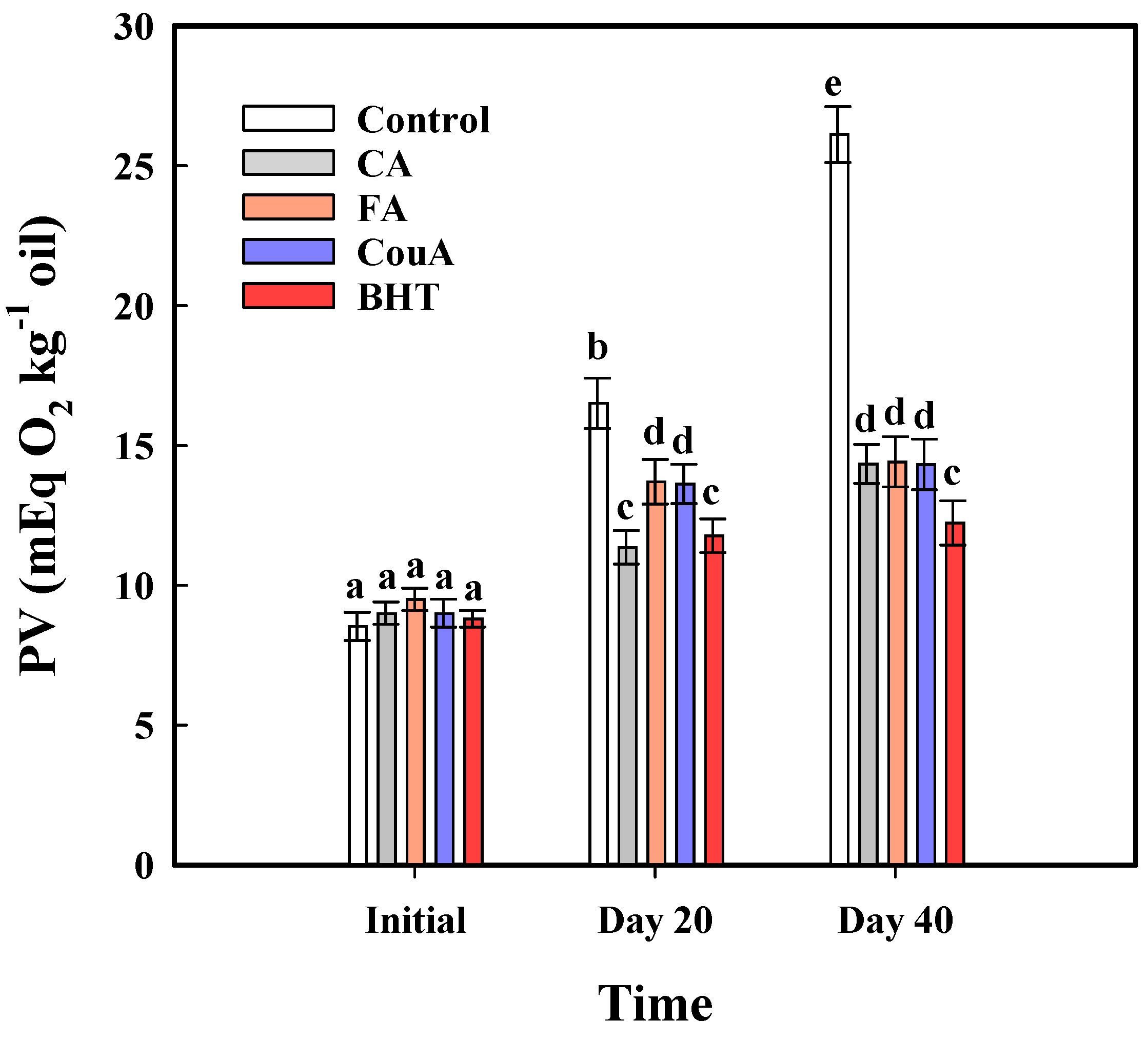
2.6. Peroxide Value (PV) Determination
2.7. Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS) Determination
2.8. Determination of the Antiradical Activity
2.9. Data Processing and Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Investigation Based on the Model DPPH• Radical
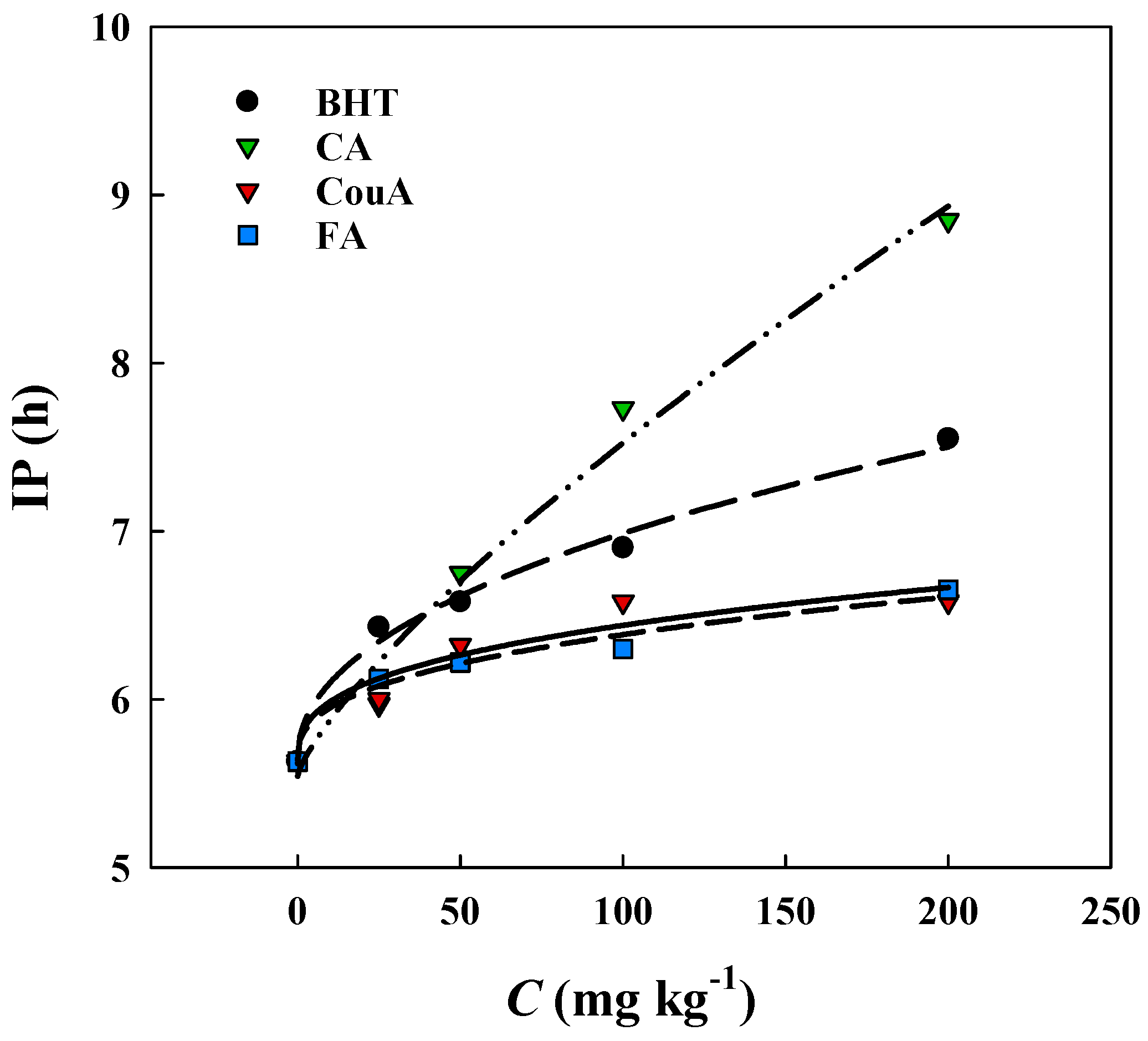
3.2. Rancimat Trials—Concentration-Dependent Effects in a Lipid Matrix (Olive Kernel Oil)
3.3. Accelerated Storage Trials
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Long, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G. Food additives: From functions to analytical methods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8497–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novais, C.; Molina, A.K.; Abreu, R.M.; Santo-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.; Pereira, C.; Barros, L. Natural food colorants and preservatives: A review, a demand, and a challenge. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2789–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Nam, K.; Ahn, D.U. Analytical methods for lipid oxidation and antioxidant capacity in food systems. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Chang, C.; Hong, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. Phenolic compounds as stabilizers of oils and antioxidative mechanisms under frying conditions: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, M.; Rodriguez-Alcalá, L.M.; Gomes, A.M.; Pintado, M. Vegetable oils oxidation: Mechanisms, consequences and protective strategies. Food Rev. Inter. 2023, 39, 4180–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, A.; Hu, S.; Ares, I.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.-R.; Wang, X.; Martínez, M.; Anadón, A.; Martínez, M.-A. Synthetic phenolic antioxidants: Metabolism, hazards and mechanism of action. Food Chem. 2021, 353, 129488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Mabury, S.A. Synthetic phenolic antioxidants: A review of environmental occurrence, fate, human exposure, and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11706–11719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xiong, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Analysis, occurrence, toxicity and environmental health risks of synthetic phenolic antioxidants: A review. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, F.; Cossignani, L. An overview of natural extracts with antioxidant activity for the improvement of the oxidative stability and shelf life of edible oils. Processes 2020, 8, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Belur, P.D.; Iyyaswami, R. Use of antioxidants for enhancing oxidative stability of bulk edible oils: A review. Inter. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrebień-Filisińska, A. Application of natural antioxidants in the oxidative stabilization of fish oils: A mini-review. J. Food Proc. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A. Concept, mechanism, and applications of phenolic antioxidants in foods. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, I.; Decker, E.A. Underlying mechanisms of synergistic antioxidant interactions during lipid oxidation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 133, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, X. Antioxidant properties of lipid concomitants in edible oils: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makris, D.P.; Boskou, D. Plant-derived antioxidants as food additives. Plants Source Nat. Antioxid. 2014, 398, 169–190. [Google Scholar]
- Makris, D.P. High-performance green extraction of natural products. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, S.; Soltanipour, F.; Ferrari, G.; Pataro, G.; Donsì, F. Emerging green techniques for the extraction of antioxidants from agri-food by-products as promising ingredients for the food industry. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.A.; Zhou, H.; Aui, A.; Wright, M.M.; Wen, Z.; Brown, R.C. A lignin-first strategy to recover hydroxycinnamic acids and improve cellulosic ethanol production from corn stover. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 138, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, E.S.; Palaiogiannis, D.; Lalas, S.I.; Mitlianga, P.; Makris, D.P. Polyphenol release from wheat bran using ethanol-based organosolv treatment and acid/alkaline catalysis: Process modeling based on severity and response surface optimization. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Hayashi, T.; Namiki, M. Effect of ascorbic acid on lipid autoxidation in a model food system. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Undeland, I.; Ekstrand, B.; Lingnert, H. Lipid oxidation in herring (Clupea harengus) light muscle, dark muscle, and skin, stored separately or as intact fillets. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Andersen, M.L.; Skibsted, L.H. Interactions between tocopherols, tocotrienols and carotenoids during autoxidation of mixed palm olein and fish oil. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.-E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefalas, P.; Kallithraka, S.; Parejo, I.; Makris, D.P. Note: A comparative study on the in vitro antiradical activity and hydroxyl free radical scavenging activity in aged red wines. Food Sci. Technol. Inter. 2003, 9, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goupy, P.; Dufour, C.; Loonis, M.; Dangles, O. Quantitative kinetic analysis of hydrogen transfer reactions from dietary polyphenols to the DPPH radical. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Niki, E. Stoichiometric and kinetic studies on Ginkgo biloba extract and related antioxidants. Lipids 1998, 33, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaño, D.; Fernández-Pachón, M.S.; Moyá, M.L.; Troncoso, A.; García-Parrilla, M. Radical scavenging ability of polyphenolic compounds towards DPPH free radical. Talanta 2007, 71, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangles, O.; Fargeix, G.; Dufour, C. One-electron oxidation of quercetin and quercetin derivatives in protic and non protic media. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1999, 2, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.C.; Daquino, C.; Geraci, C. Electron-transfer reaction of cinnamic acids and their methyl esters with the DPPH• radical in alcoholic solutions. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, L.; Imperiale, S.; Ding, Y.; Scampicchio, M.; Morozova, K. A novel stoichio-kinetic model for the DPPH• assay: The importance of the side reaction and application to complex mixtures. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.C. Use and Abuse of the DPPH• Radical. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8765–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cos, P.; Rajan, P.; Vedernikova, I.; Calomme, M.; Pieters, L.; Vlietinck, A.J.; Augustyns, K.; Haemers, A.; Berghe, D.V. In vitro antioxidant profile of phenolic acid derivatives. Free Rad. Res. 2002, 36, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, E.O.; Oh, J.H.; Yoon, K.S.; Parris, N.; Hicks, K.B.; Moreau, R.A. Antioxidant and antimelanogenic activities of polyamine conjugates from corn bran and related hydroxycinnamic acids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3920–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołosiak, R.; Drużyńska, B.; Derewiaka, D.; Piecyk, M.; Majewska, E.; Ciecierska, M.; Worobiej, E.; Pakosz, P. Verification of the conditions for determination of antioxidant activity by ABTS and DPPH assays—A practical approach. Molecules 2021, 27, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.; Gaspar, A.; Garrido, E.M.; Garrido, J.; Borges, F. Hydroxycinnamic acid antioxidants: An electrochemical overview. BioMed Res. Inter. 2013, 2013, 251754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Ojha, H.; Chaudhury, N.K. Estimation of antiradical properties of antioxidants using DPPH assay: A critical review and results. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuzaki, H.; Hisamoto, M.; Hirose, K.; Akiyama, K.; Taniguchi, H. Antioxidant properties of ferulic acid and its related compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, A.-D.M.; Durand, E.; Laguerre, M.; Bayrasy, C.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P.; Jacobsen, C. Antioxidant properties and efficacies of synthesized alkyl caffeates, ferulates, and coumarates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12553–12562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Abraham, T.E.; Zakaria, Z.A. Reactivity of phenolic compounds towards free radicals under in vitro conditions. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5790–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csepregi, K.; Neugart, S.; Schreiner, M.; Hideg, É. Comparative evaluation of total antioxidant capacities of plant polyphenols. Molecules 2016, 21, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleva, O.; Torkova, A.; Nikolaev, I.; Khrameeva, E.; Fedorova, T.; Tsentalovich, M.; Amarowicz, R. Evaluation of the antiradical properties of phenolic acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 16351–16380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinova, E.M.; Yanishlieva, N.V. Effect of lipid unsaturation on the antioxidative activity of some phenolic acids. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1994, 71, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziedzic, S.Z.; Hudson, B.J. Phenolic acids and related compounds as antioxidants for edible oils. Food Chem. 1984, 14, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, J.; Karasawa, H.; Arai, H.; Nagao, A.; Suzuki, T.; Takama, K. Peroxyl radical scavenging activity of caffeic acid and its related phenolic compounds in solution. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993, 57, 1204–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; Min, D.B. Mechanisms of antioxidants in the oxidation of foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2009, 8, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.; Dufour, C.; Mora, N.; Dangles, O. Antioxidant activity of olive phenols: Mechanistic investigation and characterization of oxidation products by mass spectrometry. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natella, F.; Nardini, M.; Di Felice, M.; Scaccini, C. Benzoic and cinnamic acid derivatives as antioxidants: Structure− activity relation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamać, M.; Kosińska, A.; Pegg, R.B. Comparison of radical-scavenging activities for selected phenolic acids. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2005, 55, 165–170. [Google Scholar]



| Antioxidant | nt | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| BHT | 0.31 | 160.6 |
| CA | 2.63 | 20.0 |
| FA | 1.10 | 47.8 |
| CouA | 0.28 | 187.7 |
| Antioxidant | R2 | k | a |
|---|---|---|---|
| BHT | 0.99 | 0.155 | 0.469 |
| Caffeic acid | 0.98 | 0.056 | 0.774 |
| Ferulic acid | 0.91 | 0.164 | 0.349 |
| p-Coumaric acid | 0.96 | 0.132 | 0.378 |
| Antioxidant | Equation | R2 | Slope |
|---|---|---|---|
| BHT | Rm = 0.128C + 1.089 | 0.9981 | 0.128 |
| Caffeic acid | Rm = 0.104C + 2.026 | 0.9999 | 0.104 |
| Ferulic acid | Rm = 0.150C + 0.373 | 0.9999 | 0.150 |
| p-Coumaric acid | Rm = 0.148C + 0.656 | 0.9990 | 0.148 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trajkovska, M.; Derwiche, F.; Grigorakis, S.; Makris, D.P. Natural Phenolic Acids as Effective Bulk Oil Antioxidants: Oxidative Stability Modeling Using Olive Kernel Oil as a Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6508. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156508
Trajkovska M, Derwiche F, Grigorakis S, Makris DP. Natural Phenolic Acids as Effective Bulk Oil Antioxidants: Oxidative Stability Modeling Using Olive Kernel Oil as a Case Study. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(15):6508. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156508
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrajkovska, Martina, Feyrouz Derwiche, Spyros Grigorakis, and Dimitris P. Makris. 2024. "Natural Phenolic Acids as Effective Bulk Oil Antioxidants: Oxidative Stability Modeling Using Olive Kernel Oil as a Case Study" Applied Sciences 14, no. 15: 6508. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156508
APA StyleTrajkovska, M., Derwiche, F., Grigorakis, S., & Makris, D. P. (2024). Natural Phenolic Acids as Effective Bulk Oil Antioxidants: Oxidative Stability Modeling Using Olive Kernel Oil as a Case Study. Applied Sciences, 14(15), 6508. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156508








