Adaptive Frame Sampling and Feature Alignment for Multi-Frame Infrared Small Target Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose an adaptive frame sampling method based on mutual information for multi-frame infrared small target detection, to overcome the shortcomings of the fixed strategy frame sampling method.
- A multi-frame infrared small target detection model is proposed, which incorporates feature alignment by placing the registration operation at the feature map level. The model is trained in an end-to-end fashion, overcoming the limitations of manual registration in the preprocessing stage in terms of robustness.
- A comprehensive set of experiments were conducted on a mobile infrared small target dataset to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The results provide strong evidence supporting the efficacy of the proposed approach.
2. Related Work
2.1. Infrared Small Target Detection Based on a Single Frame
2.2. Infrared Small Target Detection Based on Multiple Frames
3. Our Method
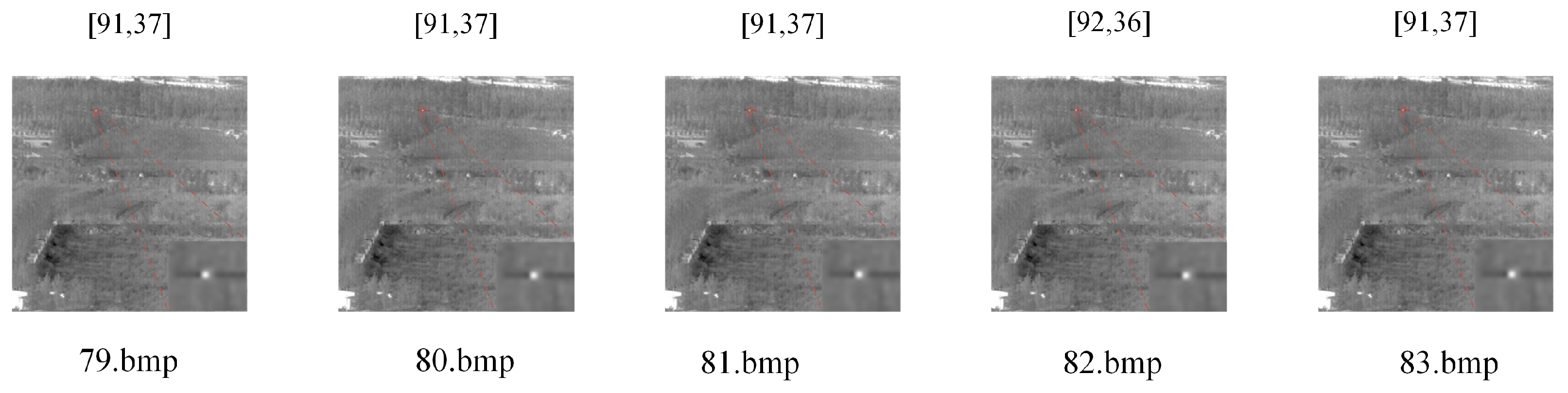
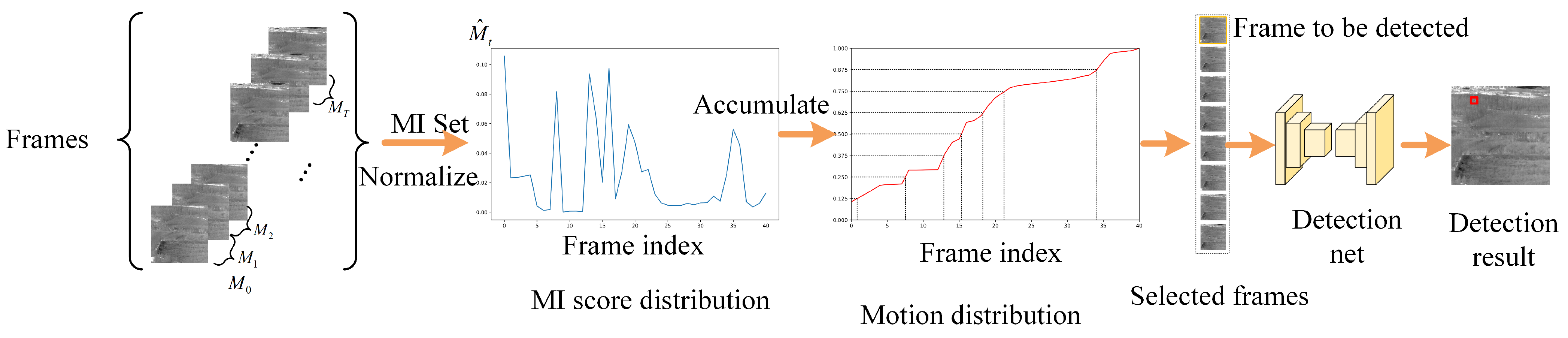
3.1. Adaptive Frame Sampling
3.1.1. Mutual Information
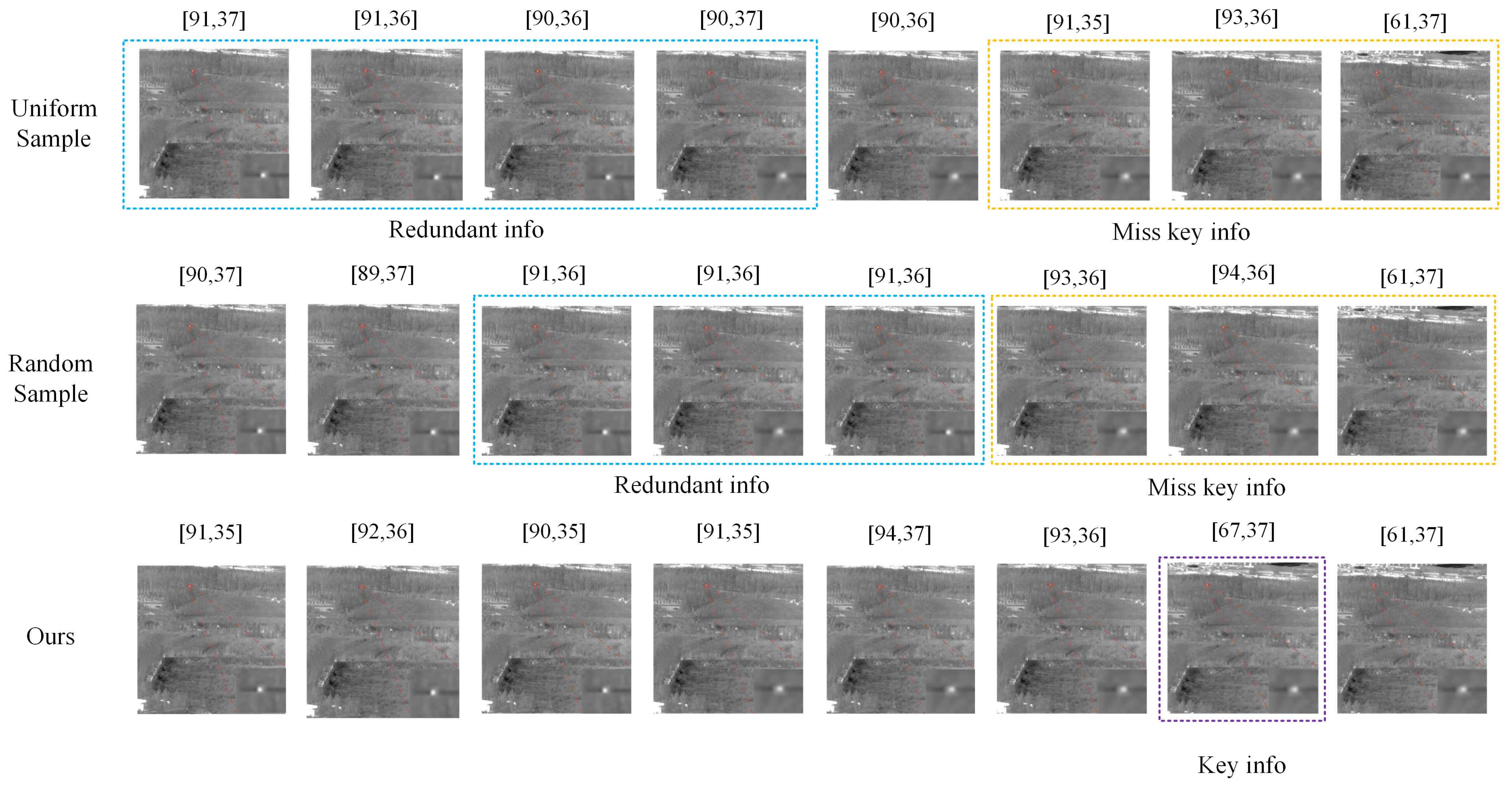
3.1.2. Adaptive Frame Sampling Based on Mutual Information
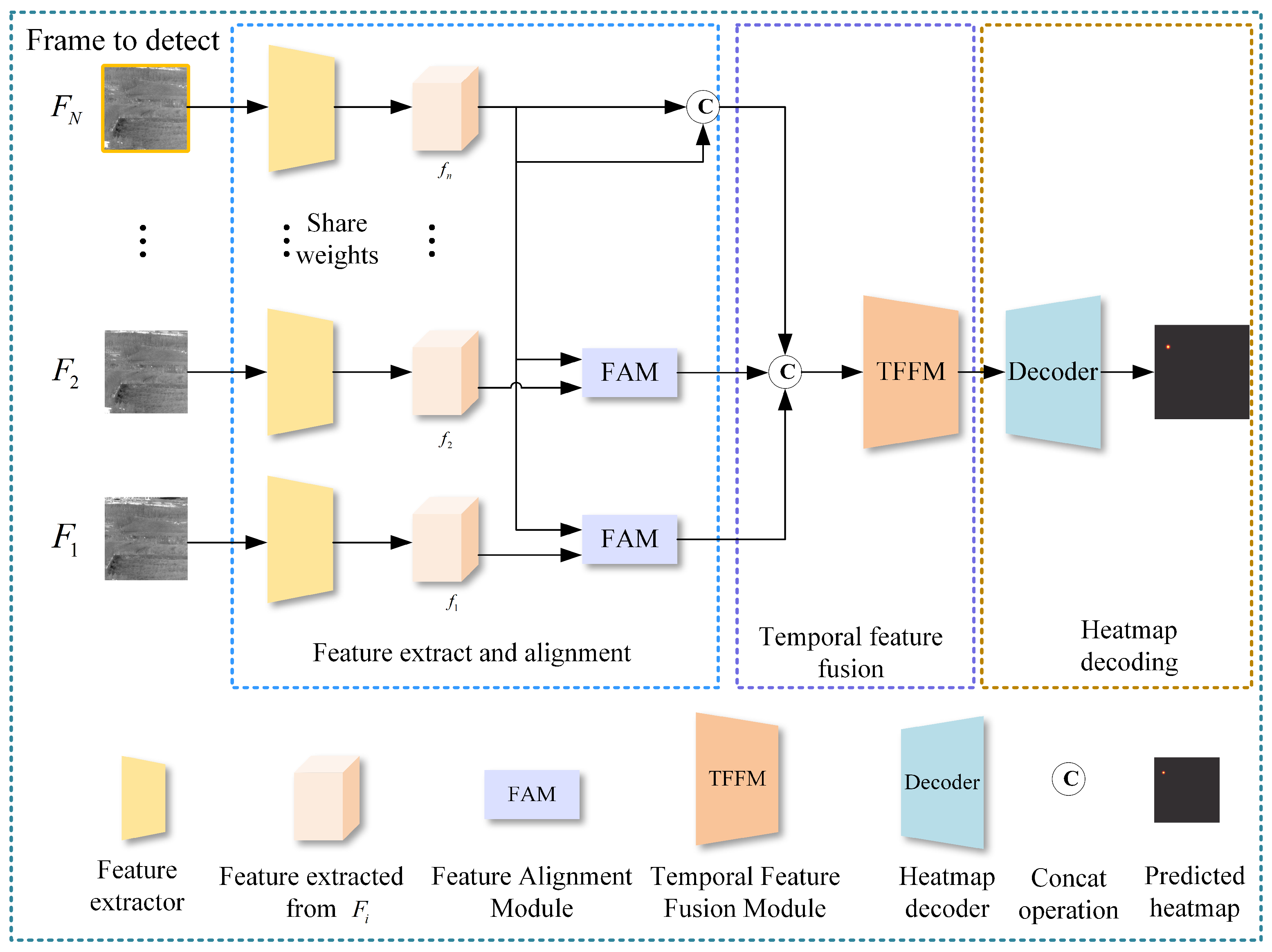
3.2. Network Architecture
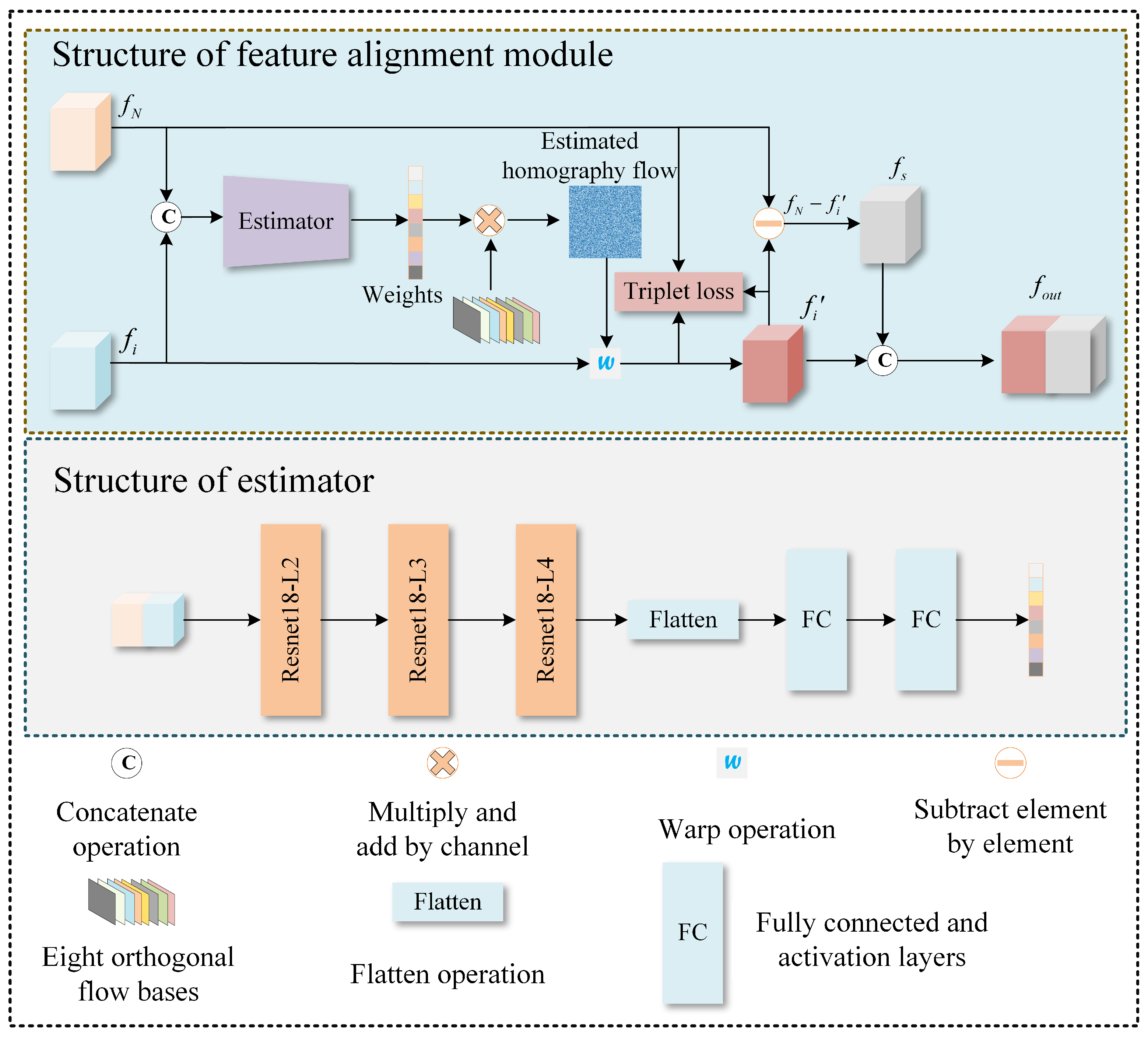
3.2.1. Feature Extraction and Alignment Module
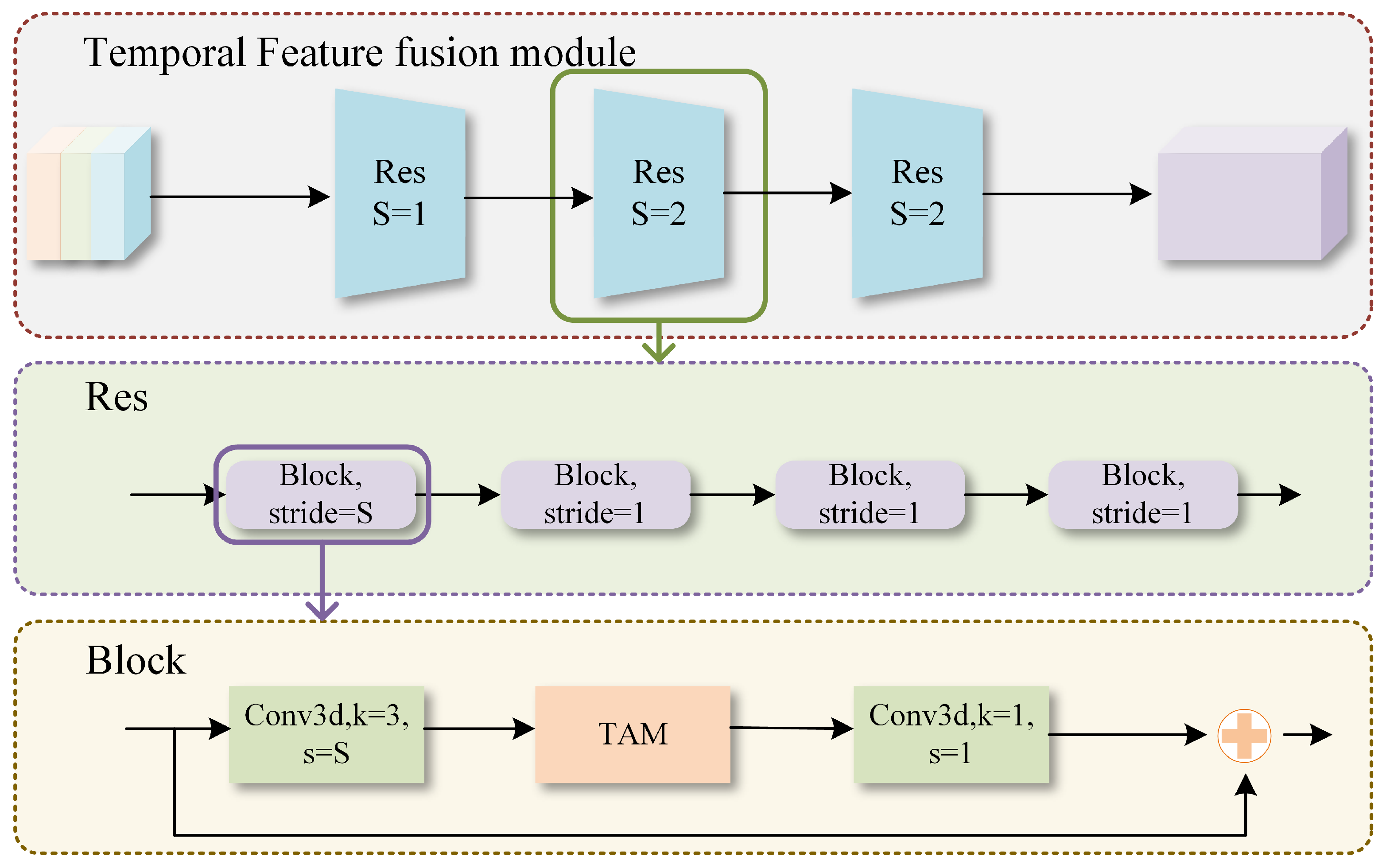
3.2.2. Temporal Feature Fusion Module
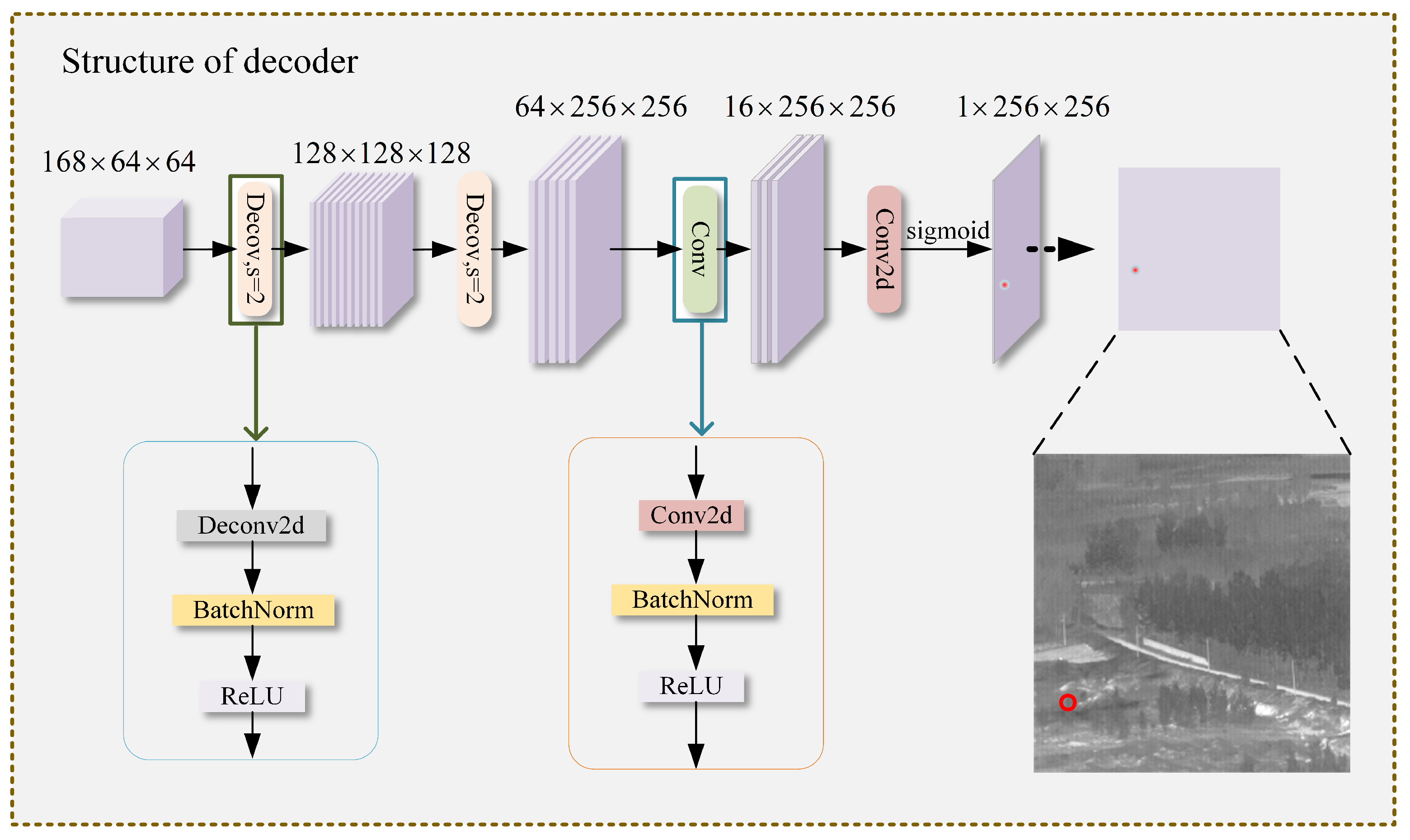
3.2.3. Decoding Module
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Experimental Results
4.4.1. Comparisons with Other Methods
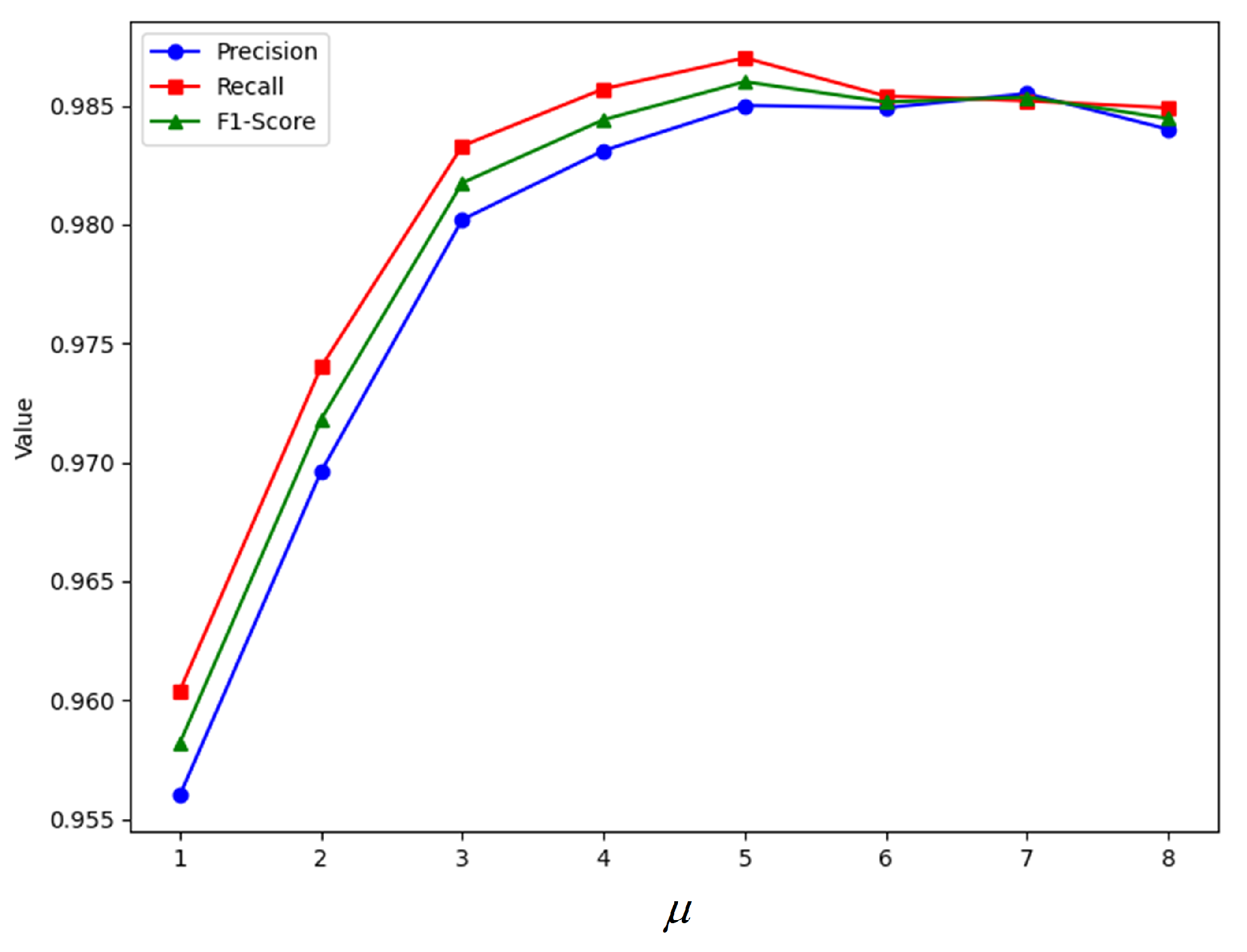
4.4.2. Ablation Experiment
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y. A kernel-based nonparametric regression method for clutter removal in infrared small-target detection applications. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2010, 7, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, Z.; Kong, D.; He, Y. Infrared dim and small target detection based on stable multisubspace learning in heterogeneous scene. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5481–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Tang, Z.; Long, G.; Yu, Q. Real-time visual enhancement for infrared small dim targets in video. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 83, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Peng, Z.; Wu, H.; He, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, C. Infrared small target detection via self-regularized weighted sparse model. Neurocomputing 2021, 420, 124–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dai, K.; Bai, K. Single frame infrared image small target detection via patch similarity propagation based background estimation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 106, 103197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Qi, J.; Shao, G.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, P. Low-rank approximation and multiple sparse constraint modeling for infrared low-flying fixed-wing UAV detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4150–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Li, J.; Peng, Z. The design of top-hat morphological filter and application to infrared target detection. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2006, 48, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.H.; Chuang, J.H.; Liu, T.L. Regularized background adaptation: A novel learning rate control scheme for Gaussian mixture modeling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 20, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Chen, G. Analysis of selection of structural element in mathematical morphology with application to infrared point target detection. In Proceedings of the Infrared Materials, Devices, and Applications, Beijing, China, 11–15 November 2007; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008; Volume 6835, pp. 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Kerekes, R.; Kumar, B.V. Enhanced video-based target detection using multi-frame correlation filtering. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2009, 45, 289–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.Y.; Sun, S.L.; Lin, C.Q.; Liu, G.R. Space moving target detection and tracking method in complex background. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 91, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Hu, M.; Shen, X.; Liu, Z.; Ji, X. Multiple frames based infrared small target detection method using CNN. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Algorithms, Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Sanya, China, 22–24 December 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, M.; Chen, S.; Deng, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y. A spatial-temporal feature-based detection framework for infrared dim small target. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 3000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Mo, B.; Zhou, J. Boost infrared moving aircraft detection performance by using fast homography estimation and dual input object detection network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Meng, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hauptmann, A.G. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 4996–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, B.; Fan, F.; Liang, K.; Fang, Y. A robust infrared small target detection algorithm based on human visual system. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; You, X.; Li, H. Multiscale patch-based contrast measure for small infrared target detection. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 58, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Sun, X.; Liu, M.; Ye, C.; Zhou, X. Infrared small-target detection using multiscale gray difference weighted image entropy. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y. Infrared small target and background separation via column-wise weighted robust principal component analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2016, 77, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Yang, J.; Jiang, S.; Wei, C. Target detection algorithm based on two layers human visual system. Algorithms 2015, 8, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Du, H.y.; Zhao, Y.j.; Dong, L.q.; Hui, M.; Wang, S. Image small target detection based on deep learning with SNR controlled sample generation. Curr. Trends Comput. Sci. Mech. Autom. 2017, 1, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Shi, M.; Li, H. Infrared dim and small target detection based on two-stage U-skip context aggregation network with a missed-detection-and-false-alarm combination loss. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 35383–35404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Du, S.; Liu, C.; Cao, Z. Interior attention-aware network for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5002013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, M.; An, W.; Guo, Y. Dense nested attention network for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 32, 1745–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; An, G. Infrared moving targets detection based on optical flow estimation. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology, Harbin, China, 24–26 December 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 2452–2455. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, W. Sparse representation based infrared small target detection via an online-learned double sparse background dictionary. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 99, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, T.; Shao, S.; Zhang, E.; Lin, G. Infrared moving small-target detection via spatiotemporal consistency of trajectory points. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tao, B.; Kong, X.; Peng, Z. Infrared small target detection using nonoverlapping patch spatial–temporal tensor factorization with capped nuclear norm regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5001417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.; Gribben, D. Practical approaches to target detection in long range and low quality infrared videos. Signal Image Process. Int. J. (SIPIJ) 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.; Gribben, D.; Budavari, B. Target Detection and Classification Performance Enhancement Using Superresolution Infrared Videos. Signal Image Process. Int. J. (SIPIJ) 2021, 12, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Sheng, W.; Liu, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, S. Local motion and contrast priors driven deep network for infrared small target superresolution. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 5480–5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Cui, W.; Yan, P. Infrared image small-target detection based on improved FCOS and spatio-temporal features. Electronics 2022, 11, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wei, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Lin, H.; Nie, H.; Deng, X. CenterADNet: Infrared Video Target Detection Based on Central Point Regression. Sensors 2024, 24, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, F.; Collignon, A.; Vandermeulen, D.; Marchal, G.; Suetens, P. Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1997, 16, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, Y.; Tong, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, G. Mgsampler: An explainable sampling strategy for video action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1513–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Andrew, G.; Menglong, Z. Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications, mobilenets. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, M.; Lu, Y.; Ye, N.; Lin, C.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, S. Unsupervised homography estimation with coplanarity-aware gan. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–24 June 2022; pp. 17663–17672. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Hara, K.; Kataoka, H.; Satoh, Y. Learning spatio-temporal features with 3d residual networks for action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3154–3160. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Lu, T. Tam: Temporal adaptive module for video recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 13708–13718. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, S.; Jia, L.; Ye, N.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J. Content-aware unsupervised deep homography estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Part I 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 653–669. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, B.; Song, Z.; Fan, H.; Zhong, P.; Hu, W.; Zhang, X.; Ling, J.; Su, H.; Jin, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A dataset for infrared detection and tracking of dim-small aircraft targets under ground/air background. China Sci. Data 2020, 5, 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Liang, K.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, L. Infrared small target detection utilizing the multiscale relative local contrast measure. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.l.; Wen, C.l.; Bao, Z.j.; Liu, M.q. Detecting slowly moving infrared targets using temporal filtering and association strategy. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2016, 17, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Yao, S.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Cui, W. Real-time detection and tracking of infrared small targets based on grid fast density peaks searching and improved KCF. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Input Size | Operator | Exp Size | Output Channels | SE | NL | Stride |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conv2d,3 | - | 16 | - | HS | 1 | |
| Bneck,3 | 16 | 16 | True | RE | 2 | |
| Bneck,3 | 72 | 24 | False | RE | 1 | |
| Bneck,3 | 88 | 24 | False | RE | 1 | |
| Bneck,5 | 96 | 40 | True | HS | 2 | |
| Bneck,5 | 240 | 40 | True | HS | 1 | |
| Bneck,5 | 240 | 40 | True | HS | 1 | |
| CCA | - | 40 | - | - | - |
| Data Segment | Frames | Average SCR | SCR Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data1 | 399 | 9.72 | 0.033 |
| Data2 | 599 | 4.34 | 0.220 |
| Data3 | 100 | 2.17 | 0.908 |
| Data4 | 399 | 3.75 | 3.646 |
| Data5 | 3000 | 5.45 | 1.285 |
| Data6 | 399 | 5.11 | 1.571 |
| Data7 | 399 | 6.33 | 20.316 |
| Data8 | 399 | 6.07 | 0.159 |
| Data9 | 399 | 6.29 | 17.086 |
| Data10 | 401 | 0.38 | 0.031 |
| Data11 | 745 | 2.88 | 2.148 |
| Data12 | 1500 | 5.20 | 2.226 |
| Data13 | 763 | 1.98 | 0.886 |
| Data14 | 1426 | 1.51 | 1.538 |
| Data15 | 751 | 3.42 | 0.965 |
| Data16 | 499 | 2.98 | 0.674 |
| Data17 | 500 | 1.09 | 0.353 |
| Data18 | 500 | 3.32 | 0.165 |
| Data19 | 1599 | 3.84 | 0.886 |
| Data20 | 400 | 3.01 | 1.485 |
| Data21 | 500 | 0.42 | 0.092 |
| Data22 | 500 | 2.20 | 0.150 |
| Method | Data5 | Data6 | Data15 | Data19 | Data20 | Data22 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| MPCM | 68.58 | 47.99 | 62.25 | 52.35 | 35.05 | 31.96 | 84.16 | 25.33 | 76.11 | 38.28 | 39.54 | 34.49 |
| RLCM | 69.56 | 4.77 | 45.40 | 4.88 | 39.50 | 4.54 | 81.39 | 4.12 | 81.90 | 4.13 | 40.39 | 5.13 |
| STLCF | 65.74 | 3.92 | 73.59 | 3.94 | 57.39 | 3.95 | 60.83 | 3.85 | 67.24 | 3.87 | 82.70 | 3.91 |
| MMTF | 33.26 | 4.19 | 56.15 | 4.02 | 47.84 | 4.09 | 24.73 | 3.95 | 40.12 | 3.93 | 35.99 | 3.98 |
| Ours | 99.8 | 0.33 | 100 | 0 | 99.6 | 4.72 | 97.94 | 2.2 | 95.5 | 4.97 | 96.6 | 0 |
| Method | Data8 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| Yan et al. [48] | 98.12 | 14.35 | 91.46 |
| Ours | 97.80 | 1.2 | 98.30 |
| Method | Data2 | Data8 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| Yao et al. [32] | 98.9 | 99.6 | 99.2 | 98.4 | 99.2 | 98.8 |
| Ours | 99.3 | 99.5 | 99.4 | 100 | 99.0 | 99.5 |
| Method | Input Size | Inference Time (s) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPCM | [256,256] | 0.5208 | 1.92 |
| RLCM | [256,256] | 4.1667 | 0.24 |
| STLCF | [256,256] | 1.3513 | 0.74 |
| MMTF | [256,256] | 0.6329 | 1.58 |
| Yan et al. [48] | [256,256] | 0.0596 | 16.78 |
| Yao et al. [32] | [256,256] | 0.0282 | 35.50 |
| Ours | [256,256] | 0.0269 | 37.14 |
| n | (%) | Flops (G) | Parameters (M) | Inference Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 98.6 | 43.17 | 4.62 | 0.0269 |
| 8 | 98.9 | 84.32 | 6.78 | 0.0423 |
| 16 | 99.0 | 178.73 | 9.43 | 0.1153 |
| Method | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Sampling | 95.6 | 96.04 | 95.82 | 96.04 | 4.39 |
| Random Sampling | 97.3 | 97.5 | 97.39 | 97.5 | 2.72 |
| Uniform Sampling | 97.4 | 97.7 | 97.5 | 97.7 | 2.61 |
| Adaptive Sampling | 98.5 | 98.74 | 98.61 | 98.7 | 1.52 |
| FAM | Feature Minus | Triplet Loss | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 93.9 | 94.7 | 94.3 | 94.7 | 6.06 |
| ✔ | ✗ | ✗ | 97.0 | 96.3 | 96.6 | 96.3 | 2.98 |
| ✔ | ✔ | ✗ | 97.1 | 97.9 | 97.5 | 97.9 | 2.87 |
| ✔ | ✗ | ✔ | 97.9 | 96.4 | 97.1 | 96.4 | 2.09 |
| ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | 98.5 | 98.7 | 98.6 | 98.7 | 1.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, C.; Zhao, H. Adaptive Frame Sampling and Feature Alignment for Multi-Frame Infrared Small Target Detection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146360
Yao C, Zhao H. Adaptive Frame Sampling and Feature Alignment for Multi-Frame Infrared Small Target Detection. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146360
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Chuanhong, and Haitao Zhao. 2024. "Adaptive Frame Sampling and Feature Alignment for Multi-Frame Infrared Small Target Detection" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146360
APA StyleYao, C., & Zhao, H. (2024). Adaptive Frame Sampling and Feature Alignment for Multi-Frame Infrared Small Target Detection. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146360







