Characterization of the Prepared CaO-Based Sorbents for Hydrogen Production through Ethanol Steam Reforming
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sorbents Preparation
2.3. Determination of the Calcination Temperature
2.4. Sorbents Characterization
2.4.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
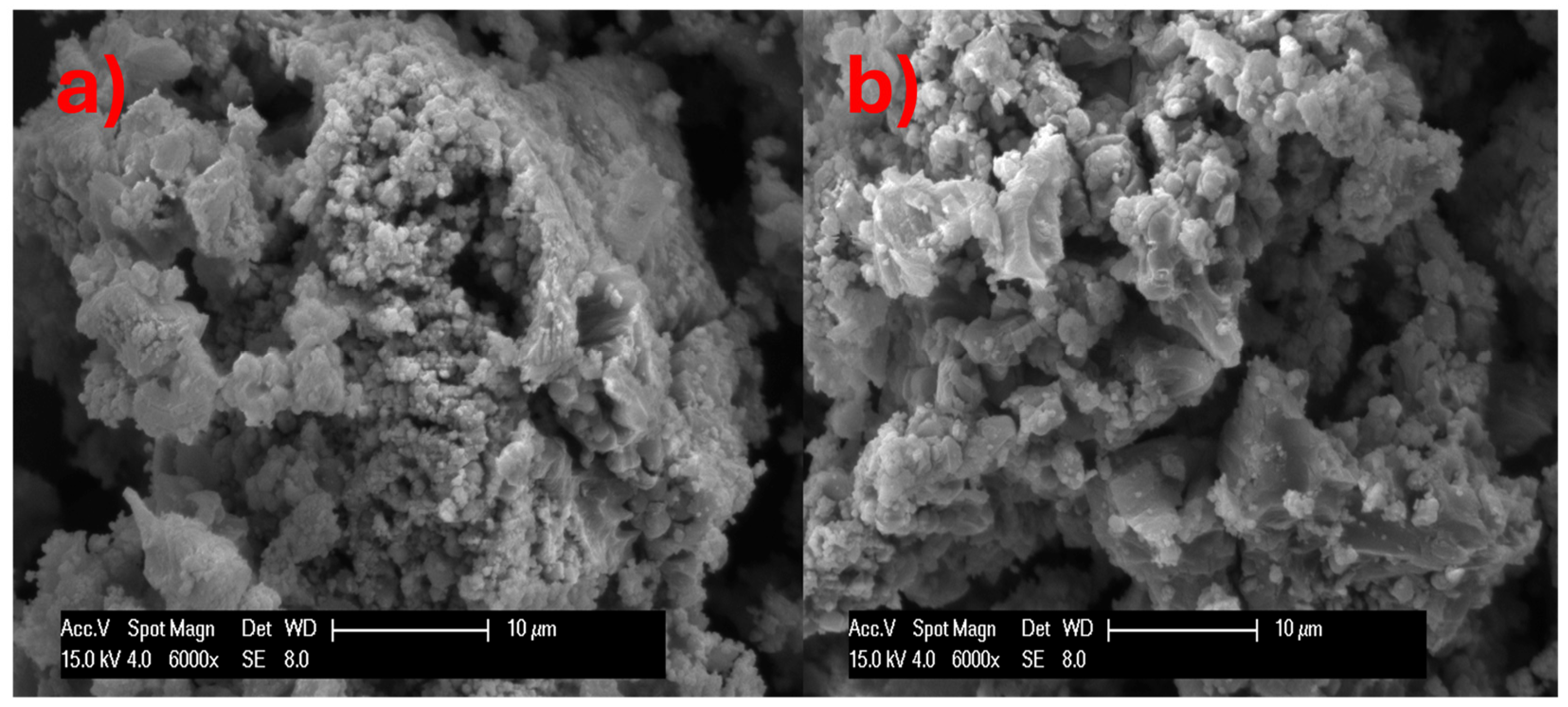
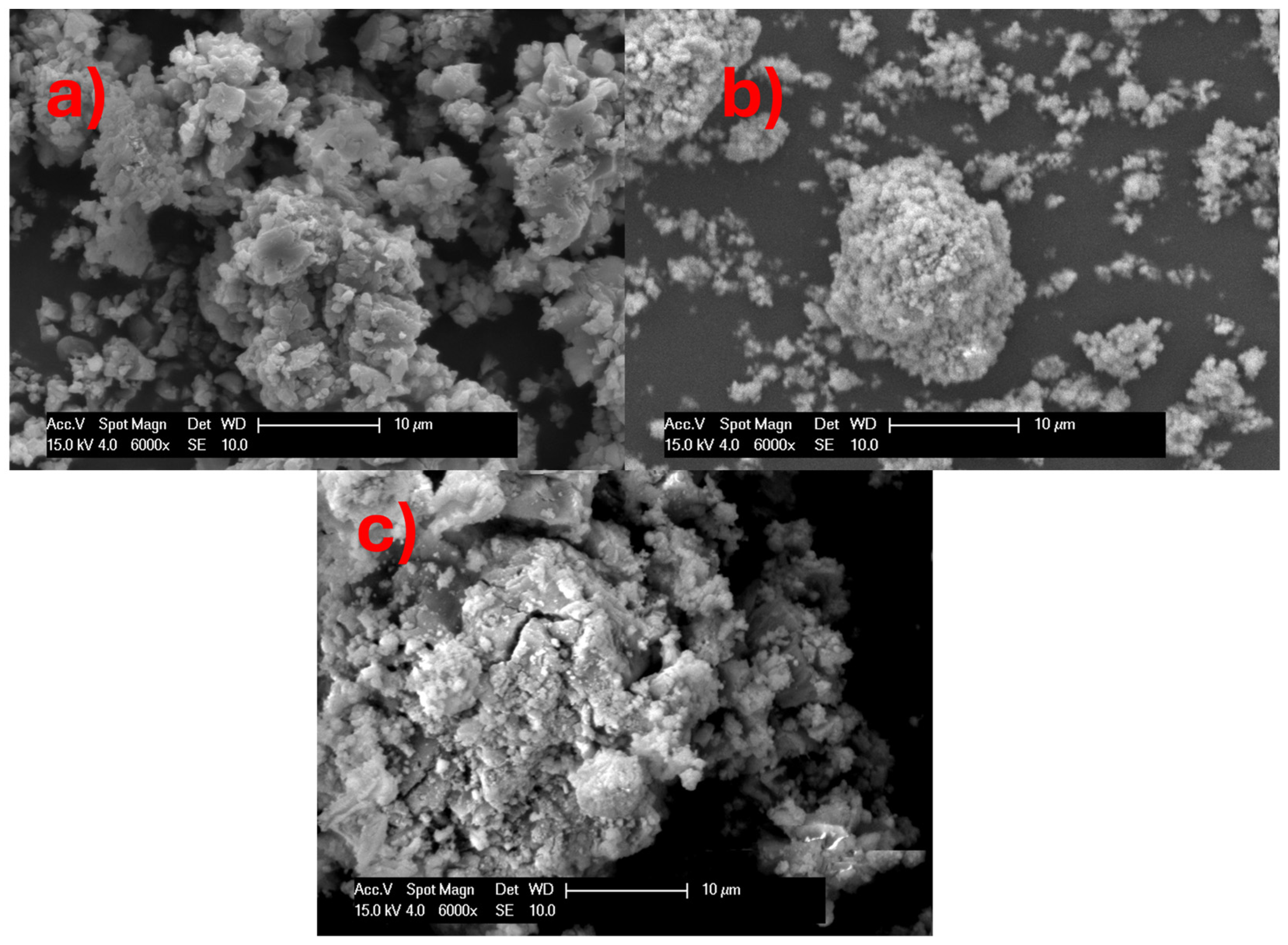
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.3. Surface Area Test (BET)
2.4.4. Porosity Test
2.5. Carbonation Test and Carbonation/De-Carbonation Multi-Cycle Test
- : is the initial sorbent weight,
- : is the sorbent weight at time ,
- is the final weight.
3. Results and Discussion
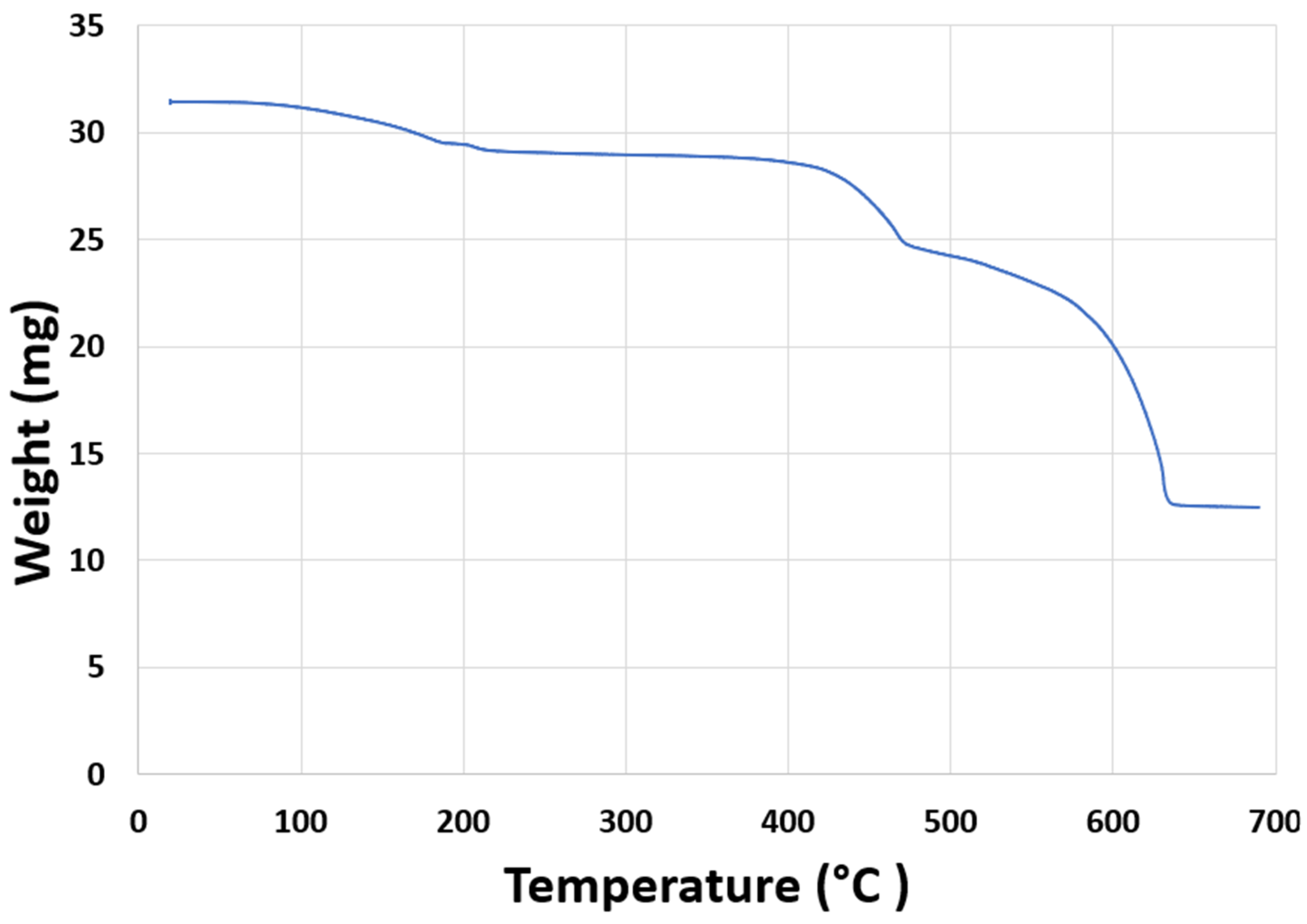
3.1. Determination of the Calcination Temperature
3.2. Carbonation Test
3.3. Sorbent Characterization
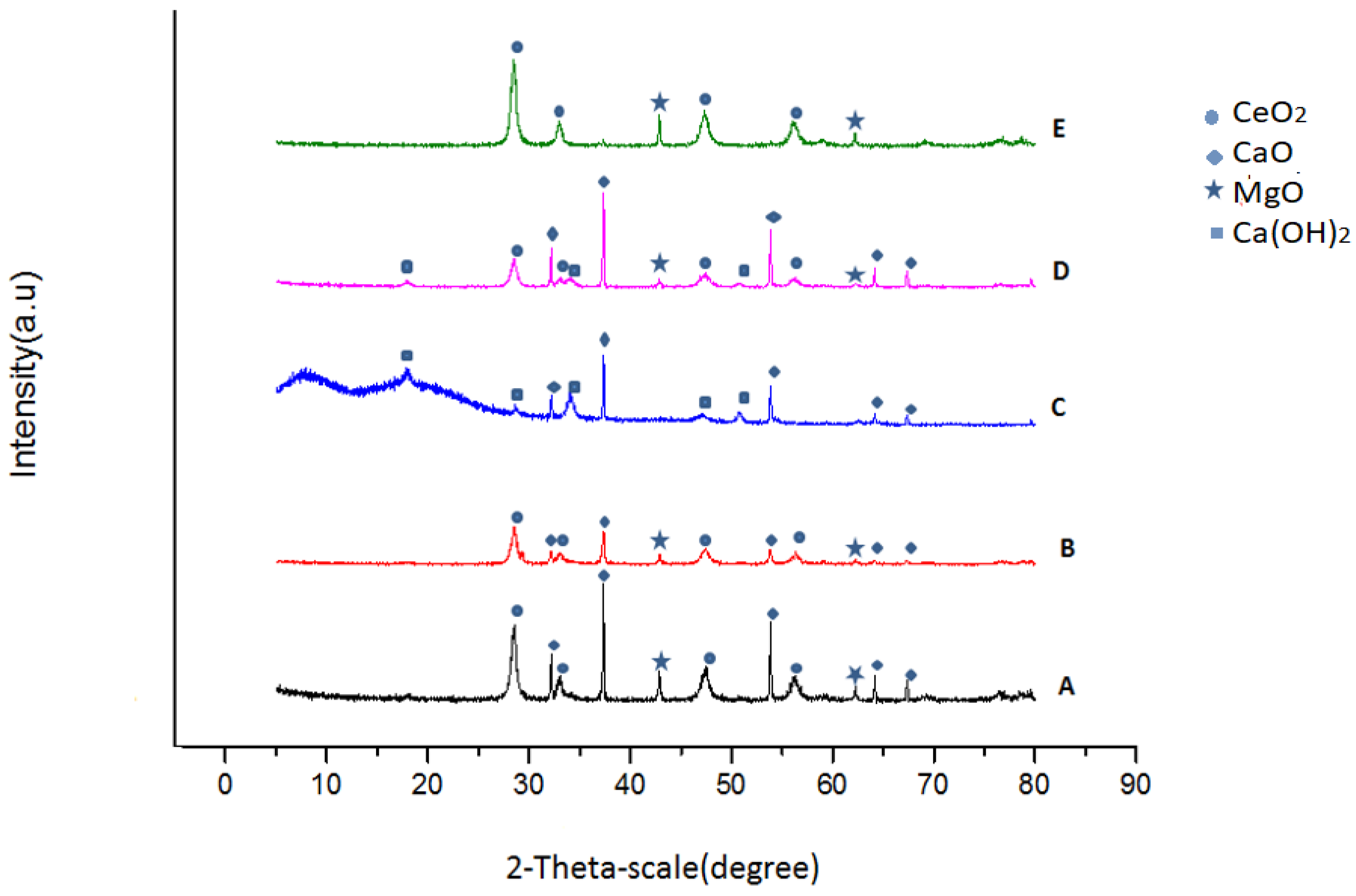
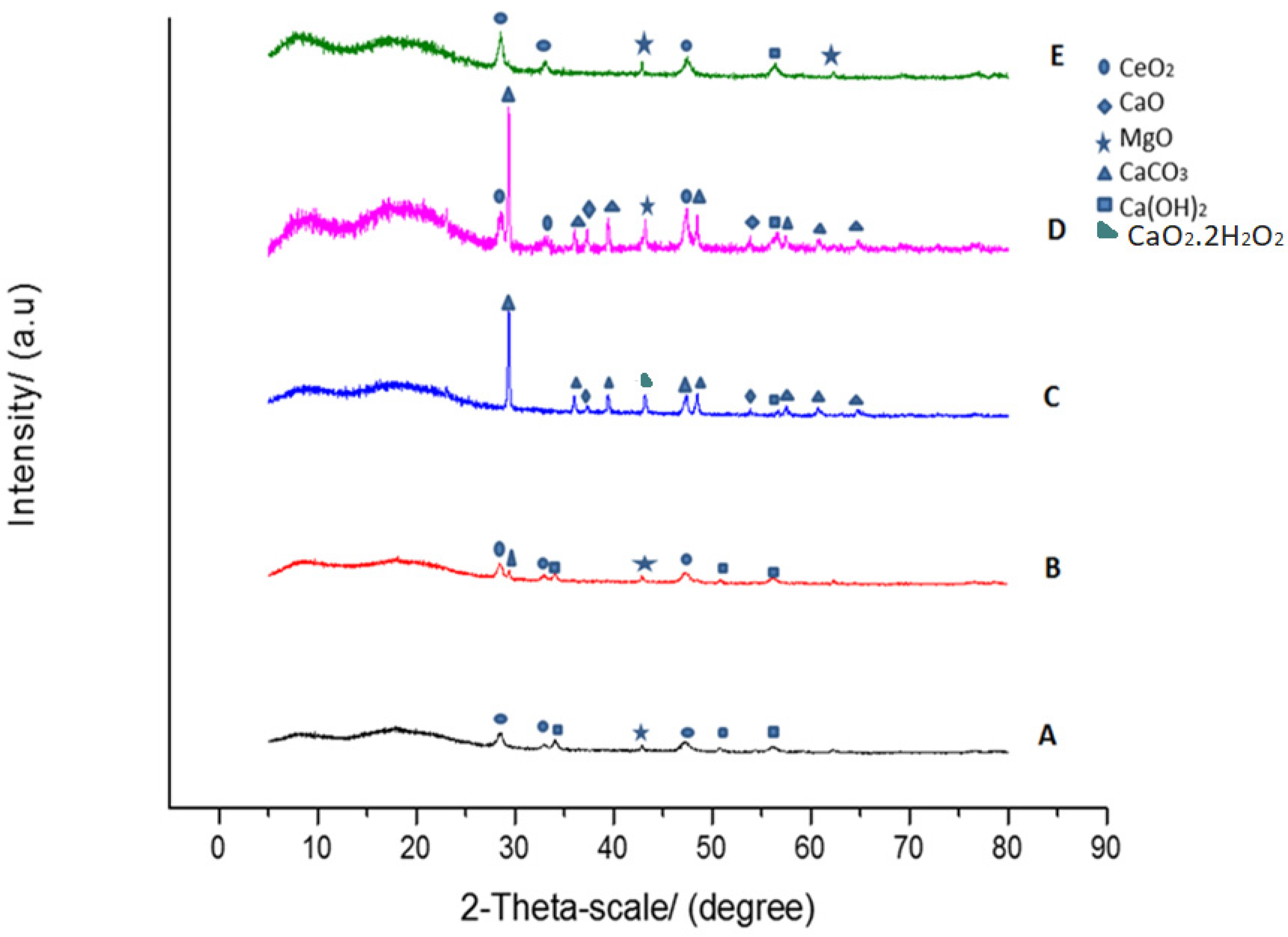
3.3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
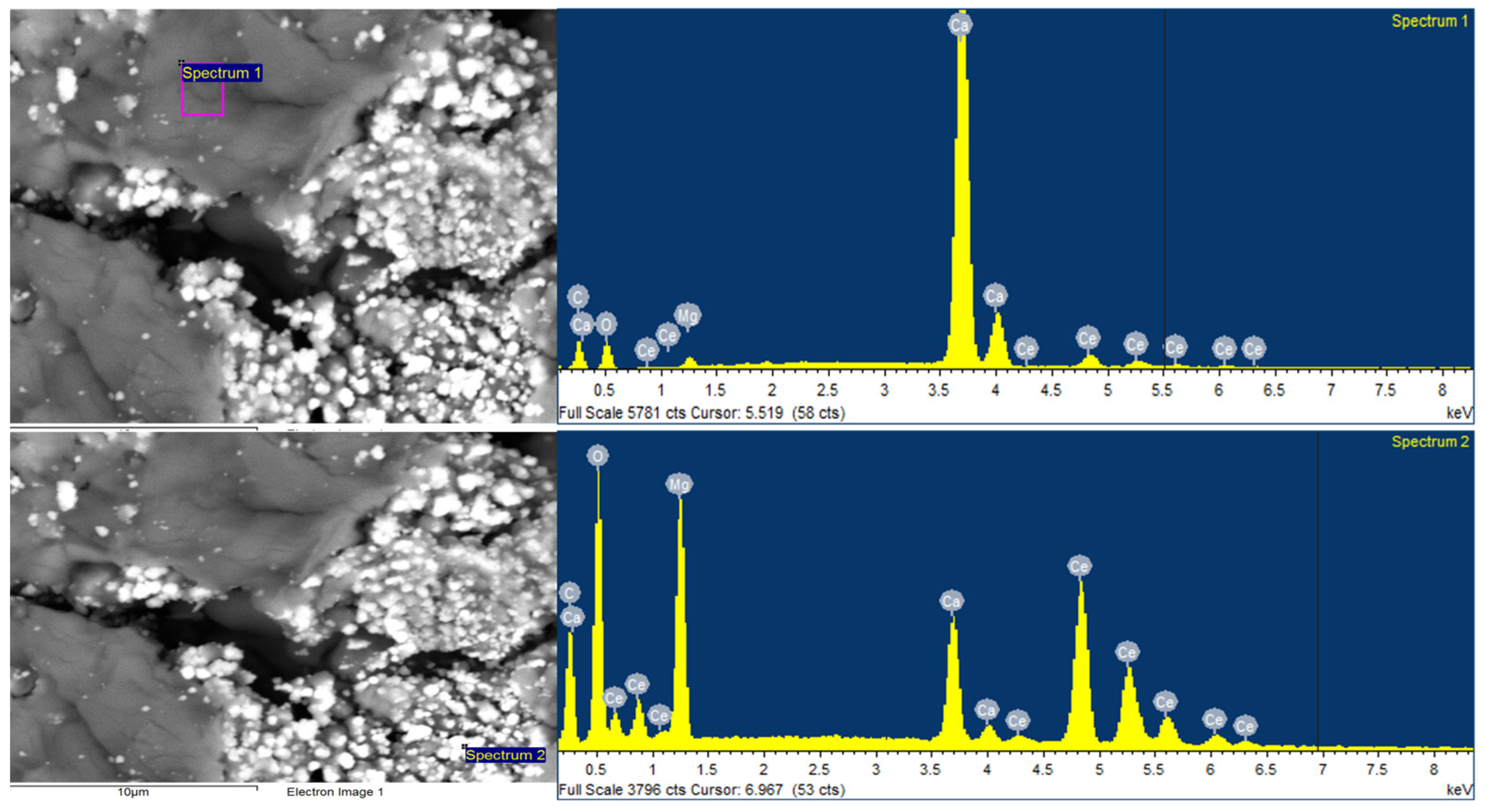
3.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
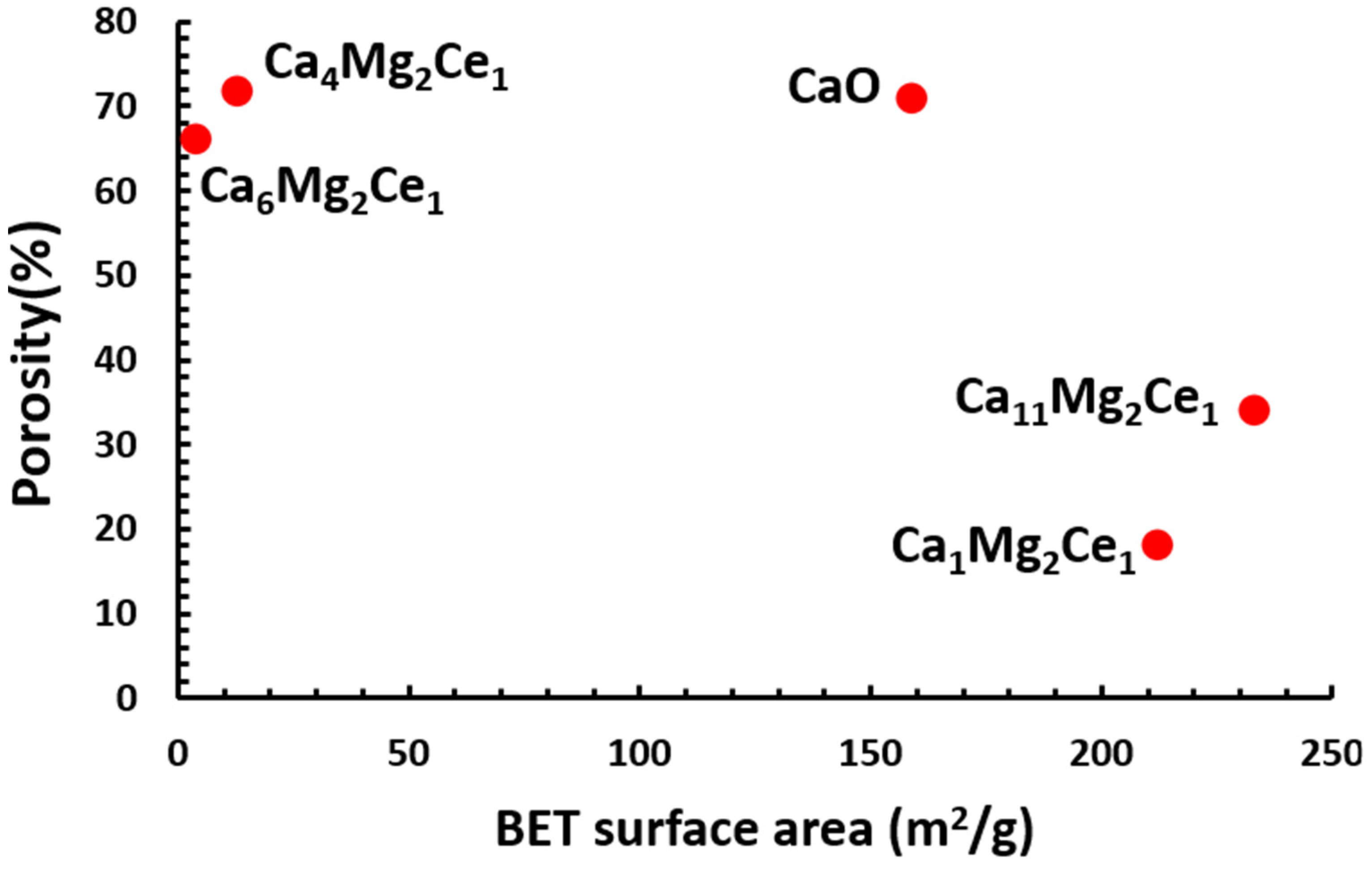
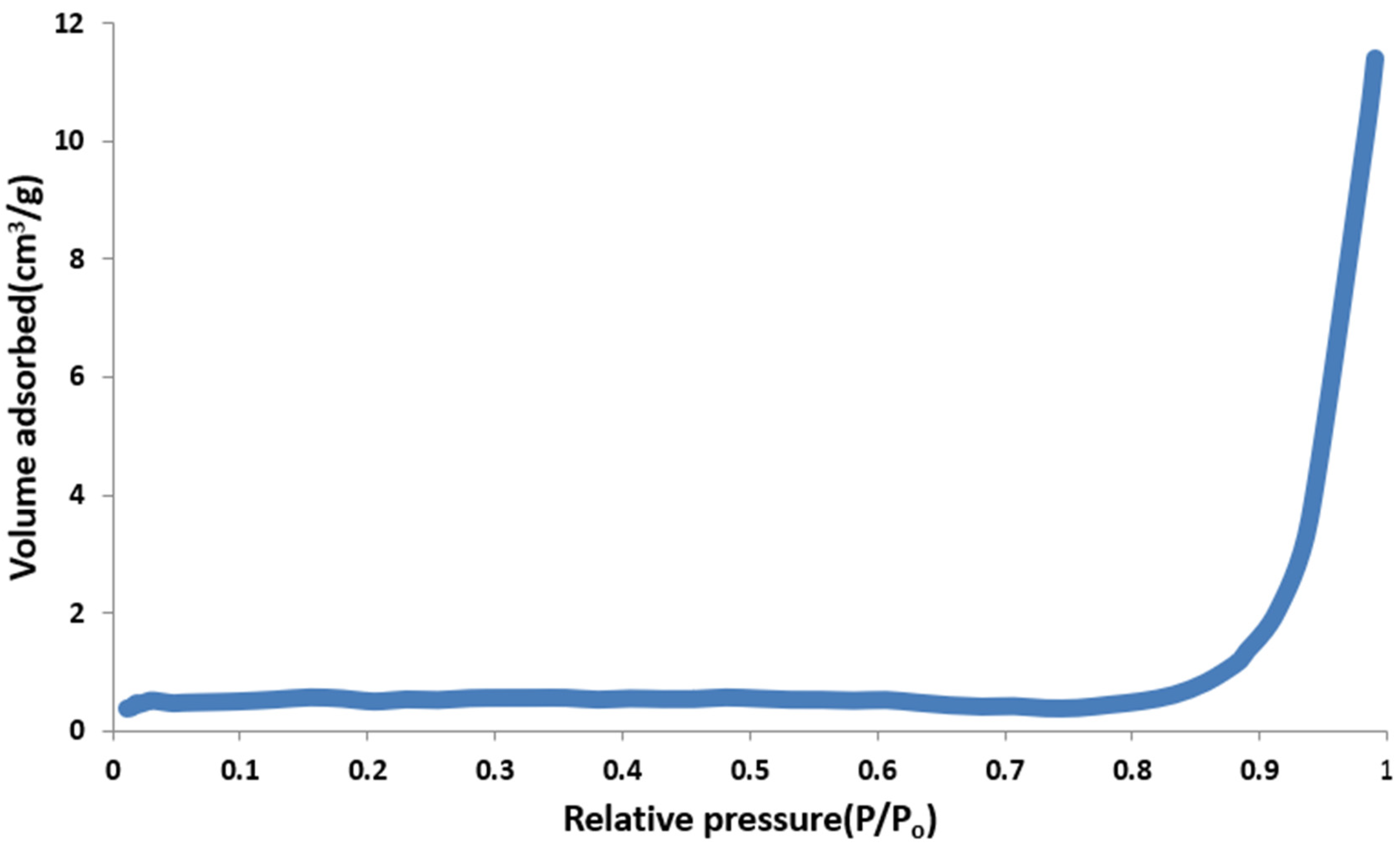
3.3.3. Measurement of Surface Area and Porosity
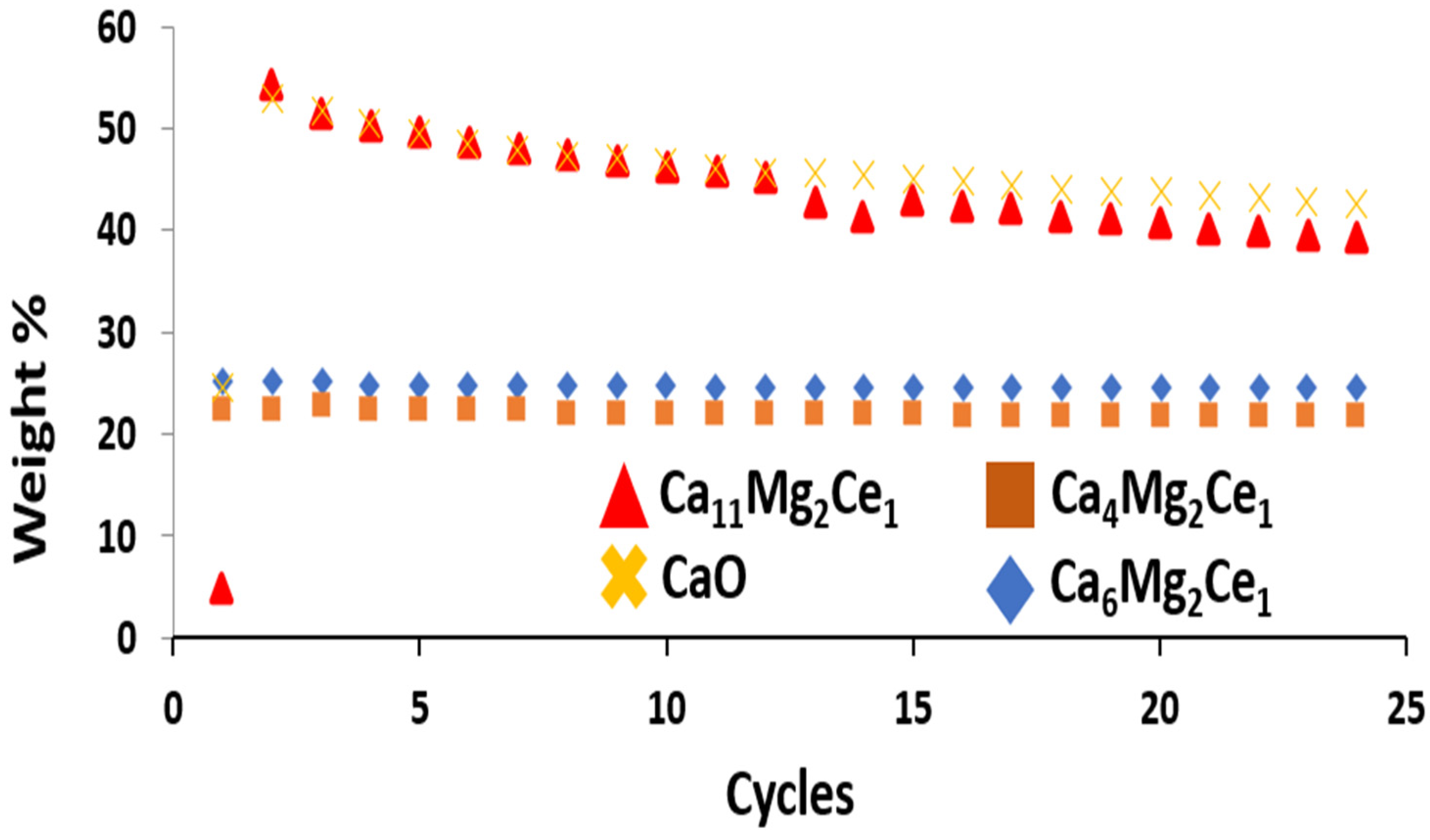
3.4. Sorbent Behavior in Carbonation/De-Carbonation Multi-Cycle Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, Y.; Yang, H.; Cheng, J.; Hu, J.; Tian, G.; Yu, X. Preparation of hydrogen from metals and water without CO2 emissions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 38134–38154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khzouz, M.; Gkanas, E.I.; Du, S.; Wood, J. Catalytic performance of Ni-Cu/Al2O3 for effective syngas production by methanol steam reforming. Fuel 2018, 232, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazali, N. Emerging technologies by hydrogen: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 18753–18771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khzouz, M.; Gkanas, E. Experimental and numerical study of low temperature methane steam reforming for hydrogen production. Catalysts 2017, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchaki-Penchah, H.; Bahn, O.; Bashiri, H.; Bedard, S.; Bernier, E.; Elliot, T.; Hammache, A.; Vaillancourt, K.; Levasseur, A. The role of hydrogen in a net-zero emission economy under alternative policy scenarios. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 49, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkanas, E.I.; Steriotis, T.A.; Stubos, A.K.; Myler, P.; Makridis, S. A complete transport validated model on a zeolite membrane for carbon dioxide permeance and capture. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 74, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khzouz, M.; Gkanas, E.I.; Shao, J.; Sher, F.; Beherskyi, D.; El-Kharouf, A.; Qubeissi, M. Life cycle costing analysis: Tools and applications for determining hydrogen production cost for fuel cell vehicle technology. Energies 2020, 13, 3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRENA. World Energy Transition Outlook, 2022; IRENA: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Khzouz, M.; Gkanas, E.I.; Girella, A.; Statheros, T.; Milanese, C. Sustainable hydrogen production via LiH hydrolysis for unmanned air vehicle (UAV) applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 5384–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.; Durrant, P.; Kochhar, K. Reaching Zero with Renewables: Capturing Carbon; IRENA: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2021; Volume 108. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, T.H.; Chaghouri, M.; Cesário, M.R.; Tidahy, H.L.; Gennequin, C.; Macedo, D.A.; Abi-Aad, E. The role of CO2 sorbents materials in SESMR for hydrogen production. In Heterogeneous Catalysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 141–174. [Google Scholar]
- Blamey, J.; Anthony, E.; Wang, J.; Fennell, P. The calcium looping cycle for large-scale CO2 capture. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 260–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, J.C.; Anthony, E.J.; Lu, D.Y.; Salvador, C.; Alvarez, D. Capture of CO2 from combustion gases in a fluidized bed of CaO. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, B.; Wang, C.; Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, B.; Yang, M.; Xu, Y. Solid sorbents for in-situ CO2 removal during sorption-enhanced steam reforming process: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 53, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Yi, K. Effects of preparation method on cyclic stability and CO2 absorption capacity of synthetic CaO–MgO absorbent for sorption-enhanced hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katheria, S.; Gupta, A.; Deo, G.; Kunzru, D. Effect of calcination temperature on stability and activity of Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst for steam reforming of methane at high pressure condition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 14123–14132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Wang, Y.; Xing, S.; Pang, C.; Hao, Y.; Song, C.; Liu, Q. Progress in reducing calcination reaction temperature of Calcium-Looping CO2 capture technology: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criado, Y.A.; Alonso, M.; Abanades, J. Kinetics of the CaO/Ca(OH)2 hydration/dehydration reaction for thermochemical energy storage applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 12594–12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, K.; Kaneeda, M.; Nakamura, H. Development of Novel CeO2-based CO2 adsorbent and analysis on its CO2 adsorption and desorption mechanism. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 2481–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qi, Y.; Xie, M.; Cheng, Z.; Yuan, W. Synthesis of CaO-based sorbents through incorporation of alumina/aluminate and their CO2 capture performance. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 74, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Han, L.; Wu, Y.; Rong, N.; Xin, C.; Wang, Z.; Ding, H.; Qi, Z. Synthesis of a composite Fe–CaO-based sorbent/catalyst by mechanical mixing for CO2 capture and H2 production: An examination on CaO carbonation and tar reforming performance. J. Energy Inst. 2023, 109, 101256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Memon, M.Z.; Seelro, M.A.; Fu, W.; Gao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ji, G. A review of CO2 sorbents for promoting hydrogen production in the sorption-enhanced steam reforming process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 23358–23379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manovic, V.; Anthony, E. Long-term behavior of CaO-based pellets supported by calcium aluminate cements in a long series of CO2 capture cycles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 8906–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Peng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, P.; Yu, J. Preparation of CaO–Al2O3 sorbent and CO2 capture performance at high temperature. Fuel 2013, 111, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Beum, T.; Yang, J.; Kim, J. Properties of Ca-base CO2 sorbent using Ca(OH)2 as precursor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 7896–7899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Tahmasebpoor, M.; Mousavi, S.B.; Pevida, C.J. CO2 capture activity of a novel CaO adsorbent stabilized with (ZrO2+ Al2O3+ CeO2)-based additive under mild and realistic calcium looping conditions. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 53, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, S. Efficient MgO-doped CaO sorbent pellets for high temperature CO2 capture. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Molar Ratio |
|---|---|
| Ca4Mg2Ce1 | 3.7:1.7:1 |
| Ca6Mg2Ce1 | 5.5:1.7:1 |
| Ca3Mg2Ce1 | 2.8:1.7:1 |
| Ca2Mg2Ce1 | 1.8:1.7:1 |
| Ca1Mg2Ce1 | 0.6:1.7:1 |
| Ca7Mg2Ce1 | 7.4:1.7:1 |
| Ca11Mg2Ce1 | 11.0:1.7:1 |
| Ca3Mg2Ce1 | 2.6:1.7: 1 |
| CaO | 100 |
| Sample | CO2 Uptake in Weight/% | CO2 Uptake in/Molar (*) % |
|---|---|---|
| Ca4Mg2Ce1 | 25 | 66 |
| Ca6Mg2Ce1 | 29 | 66 |
| Ca3Mg2Ce1 | 10 | 33 |
| Ca2Mg2Ce1 | 16 | 42 |
| Ca1Mg2Ce1 | 7 | 69 |
| Ca7Mg2Ce1 | 6 | 12 |
| Ca11Mg2Ce1 | 17 | 30 |
| CaO | 14 | 18 |
| Sample | CaO Percentage in Sample /wt.% | CO2 Uptake by Weight (wt CO2/wt CaxMgyCez) /wt.% | CO2 Uptake by Weight (wt CO2/wt CaO) /wt.% | CO2 Uptake by Moles * (CO2 Moles/CaO Moles) /mol.% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca4Mg2Ce1 | 46 | 25 | 52 | 66 |
| Ca6Mg2Ce1 | 56 | 29 | 52 | 66 |
| CaO | 100 | 14 | 14 | 18 |
| Ca11Mg2Ce1 | 72 | 17 | 24 | 30 |
| Ca1Mg2Ce1 | 13 | 7 | 54 | 69 |
| Sample | CaO Crystallite Size/nm | Ca(OH)2 Crystallite Size/nm | MgO Crystallite Size/nm | CeO2 Crystallite Size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca4Mg2Ce1 | 219 | N/A | 55 | 15 |
| Ca6Mg2Ce1 | 408 | 126 | 62 | 14 |
| Ca11Mg2Ce1 | 107 | 17 | 55 | 12 |
| Ca1Mg2Ce1 | 60 | N/A | 61 | 15 |
| CaO | 116 | 24 | N/A | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elfaki, H.; Khzouz, M.; Gkanas, E.I.; Walker, G. Characterization of the Prepared CaO-Based Sorbents for Hydrogen Production through Ethanol Steam Reforming. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146304
Elfaki H, Khzouz M, Gkanas EI, Walker G. Characterization of the Prepared CaO-Based Sorbents for Hydrogen Production through Ethanol Steam Reforming. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146304
Chicago/Turabian StyleElfaki, Hind, Martin Khzouz, Evangelos I. Gkanas, and Gavin Walker. 2024. "Characterization of the Prepared CaO-Based Sorbents for Hydrogen Production through Ethanol Steam Reforming" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146304
APA StyleElfaki, H., Khzouz, M., Gkanas, E. I., & Walker, G. (2024). Characterization of the Prepared CaO-Based Sorbents for Hydrogen Production through Ethanol Steam Reforming. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146304








