Comparing Fine-Tuning and Prompt Engineering for Multi-Class Classification in Hospitality Review Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Theoretical Background
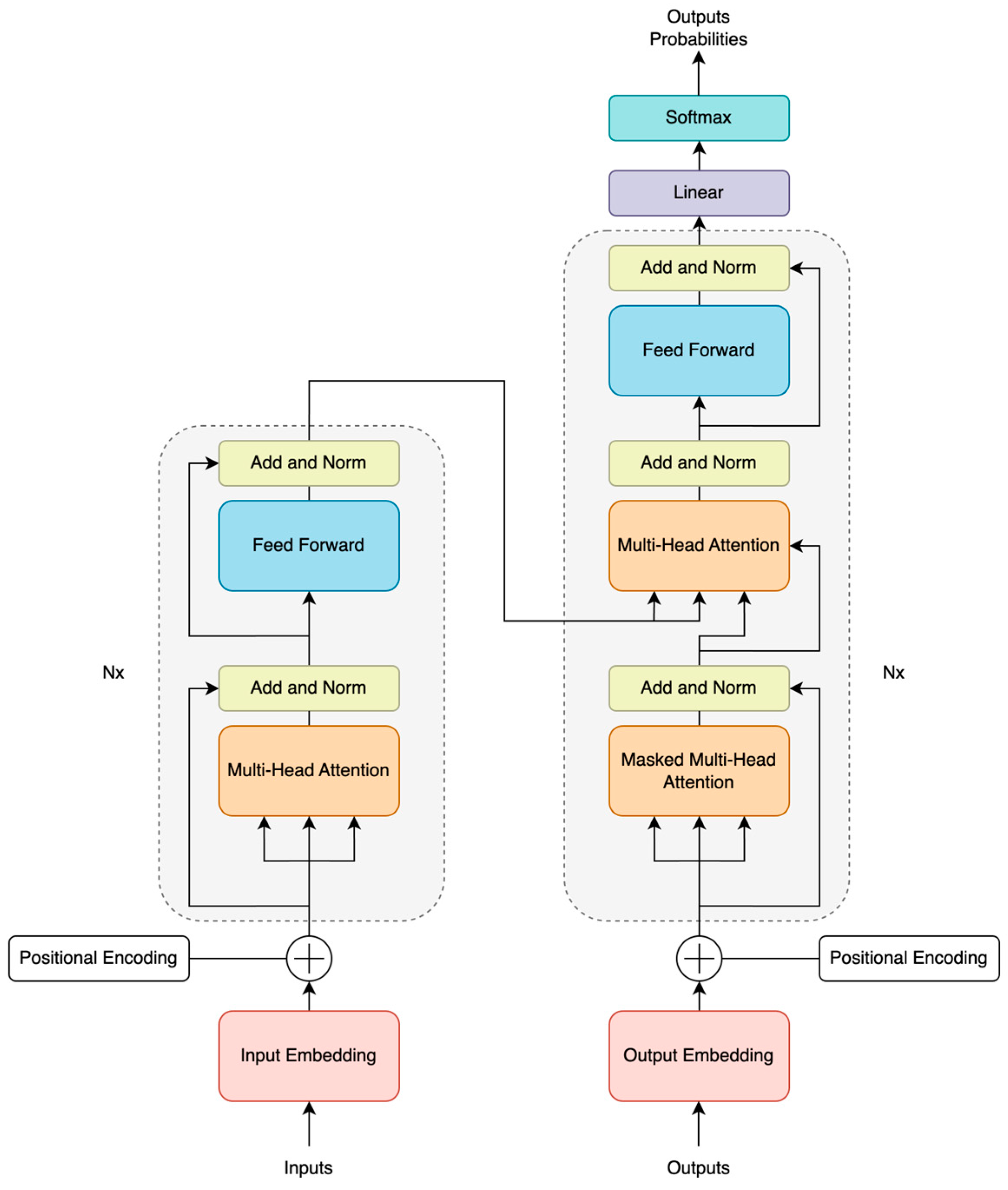
3.1. Overview of Transformer Architecture
3.2. Transformers-Based Models
4. Research Methodology
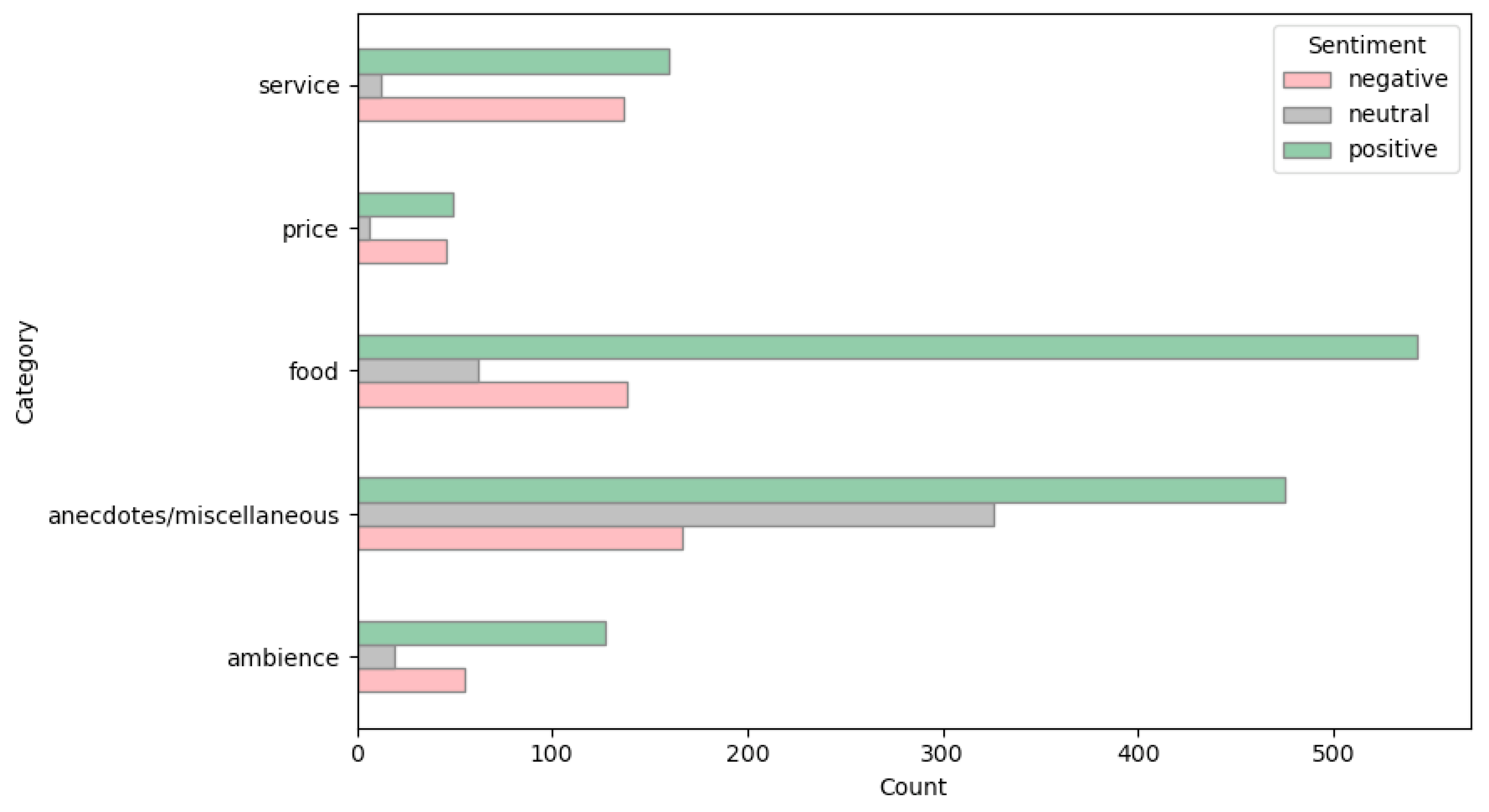
4.1. Selection and Description of the Dataset
4.2. Data Preprocessing and Preparation
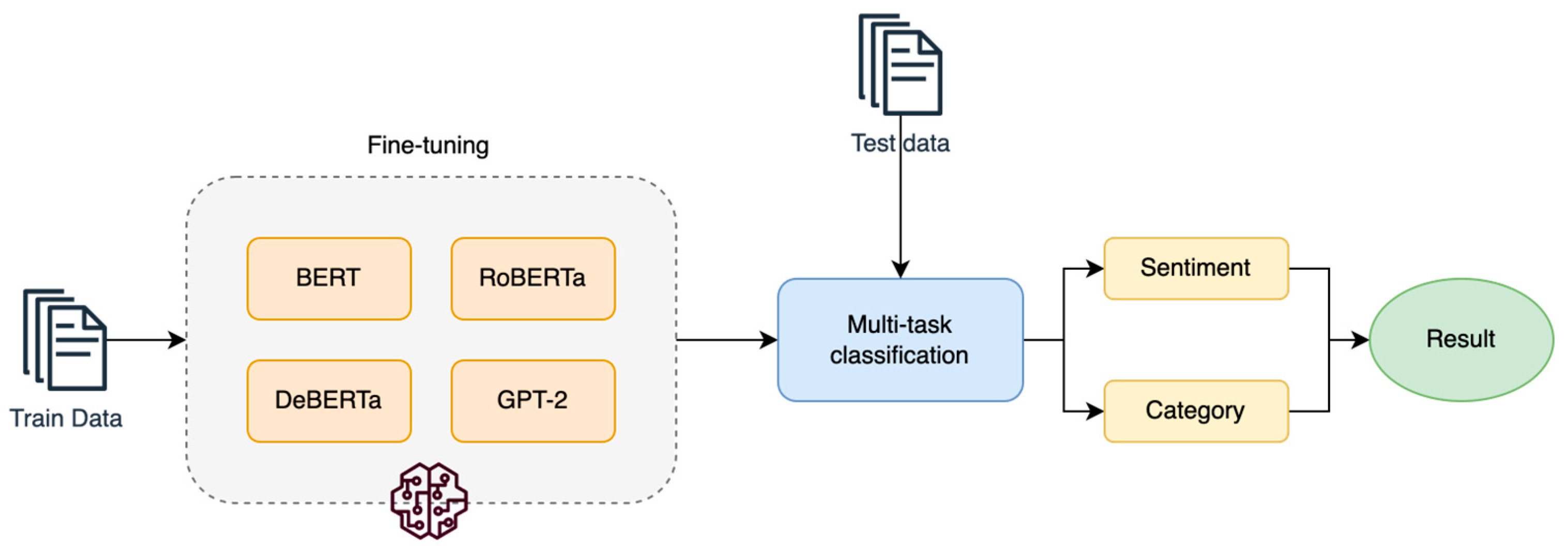
4.3. System Architecture Design
5. Experimental Procedure and Results
5.1. Parameters and Fine-Tuning Strategy
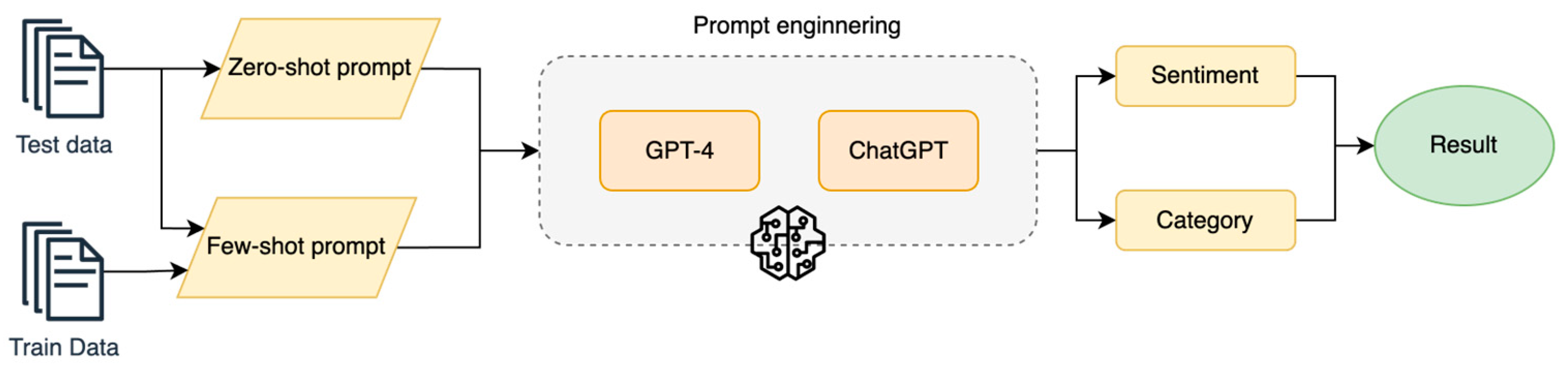
5.2. Prompt Engineering for LLMs
“Please perform multi-task and multi-class text classification on the following review to one of the categories: ambience, anecdotes/miscellaneous, food, price, service, and one of the sentiments: negative, neutral, positive. A few examples are provided below where this classification is done correctly.”
5.3. Comparison and Evaluation of Models
5.4. Discussion of Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bompotas, A.I.; Ilias, A.; Kanavos, C.; Makris, G.; Rompolas, P.; Savvopoulos, A. A Sentiment-Based Hotel Review Summarization Using Machine Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 16th IFIP WG 12.5 International Conference, AIAI 2020, Neos Marmaras, Greece, 5–7 June 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, A.; Umer, M.; Mushtaq, M.F.; Medaglia, C.; Siddiqui, H.U.R.; Mehmood, A.; Choi, G.S. Extensive hotel reviews classification using long short-term memory. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 9375–9385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, X. Sentiment analysis of hotel online reviews using the BERT model and ERNIE model—Data from China. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0275382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, D. Transformers for Natural Language Processing Build Innovative Deep Neural Network Architectures for NLP with Python, Pytorch, TensorFlow, BERT, RoBERTa, and More; Packt Publishing, Limited: Birmingham, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Čumlievski, N.; Brkić Bakarić, M.; Matetić, M. A Smart Tourism Case Study: Classification of Accommodation Using Machine Learning Models Based on Accommodation Characteristics and Online Guest Reviews. Electronics 2022, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Garain, A.; Sarkar, R. An ensemble-based hotel recommender system using sentiment analysis and aspect categorization of hotel reviews. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2021, 98, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ibánez, M.; Casánez-Ventura, A.; Castejón-Mateos, F.; Cuenca-Jiménez, P.M. A review on sentiment analysis from social media platforms. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 223, 119862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.Q.; Vu, T.; Nguyen, A.T. BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.10200. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Kheiri, K.; Karimi, H. SentimentGPT: Exploiting GPT for Advanced Sentiment Analysis and its Departure from Current Machine Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.10234. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Ding, Z.; Feng, Y.; Xia, R. Is ChatGPT a Good Sentiment Analyzer? A Preliminary Study. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.04339. [Google Scholar]
- Kublik, S.; Saboo, S. Building Innovative NLP Products Using Large Language Models; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, K.; Ji, C.; Yan, Q.; He, L.; et al. A Comprehensive Survey on Pretrained Foundation Models: A History from BERT to ChatGPT. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.09419. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Qiu, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X. How to Fine-Tune BERT for Text Classification? arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.05583. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Han, T.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Tian, J.; He, H.; Li, A.; He, M.; Liu, Z.; et al. Summary of ChatGPT-Related Research and Perspective Towards the Future of Large Language Models. Meta-Radiol. 2023, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandiran, S. Getting Started with Google BERT: Build and Train State-of-the-Art Natural Language Processing Models Using BERT; Packt Publishing, Limited: Birmingham, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. Available online: https://gluebenchmark.com/leaderboard (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13461. [Google Scholar]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: Smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/codelucas/newspaper (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.02155. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, G.; Dalsgaard, J.A.; Pera, A.; Aiello, L.M. Is a prompt and a few samples all you need? Using GPT-4 for data augmentation in low-resource classification tasks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.13861. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, J. Inside Open Assistant: The Open Source Platform for Light, High-Performance LLMs. Towards AI. Available online: https://pub.towardsai.net/inside-open-assistant-the-open-source-platform-for-light-high-performance-llms-fed9e1ebc7c6 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Pujari, S.C.; Friedrich, A.; Strötgen, J. A Multi-Task Approach to Neural Multi-Label Hierarchical Patent Classification using Transformers. In Advances in Information Retrieval; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 12656, pp. 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Ba, H.; Huynh, V.N. Measuring hotel review sentiment: An aspect-based sentiment analysis approach. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godnov, U.; Redek, T. Good food, clean rooms and friendly staff: Implications of user-generated content for Slovenian skiing, sea and spa hotels’ management. Management 2018, 23, 29–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Kim, J. A bert-based multi-criteria recommender system for hotel promotion management. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontiki, M.; Galanis, D.; Pavlopoulos, J.; Papageorgiou, H.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Manandhar, S. SemEval-2014 Task 4: Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval 2014), Dublin, Ireland; 2014; pp. 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Chatdesk. Grouphug. GitHub. Available online: https://github.com/chatdesk/grouphug (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.-S.; Yang, Y. Generation-driven Contrastive Self-training for Zero-shot Text Classification with Instruction-tuned GPT. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.11872. [Google Scholar]
| Hyperparameter | BERT | RoBERTa | DeBERTa | GPT-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epochs | 18 | 15 | 12 | 15 |
| Learning rate | 0.00004035 | 0.00005921 | 0.00004325 | 0.00004012 |
| Train batch size | 50 | 42 | 60 | 24 |
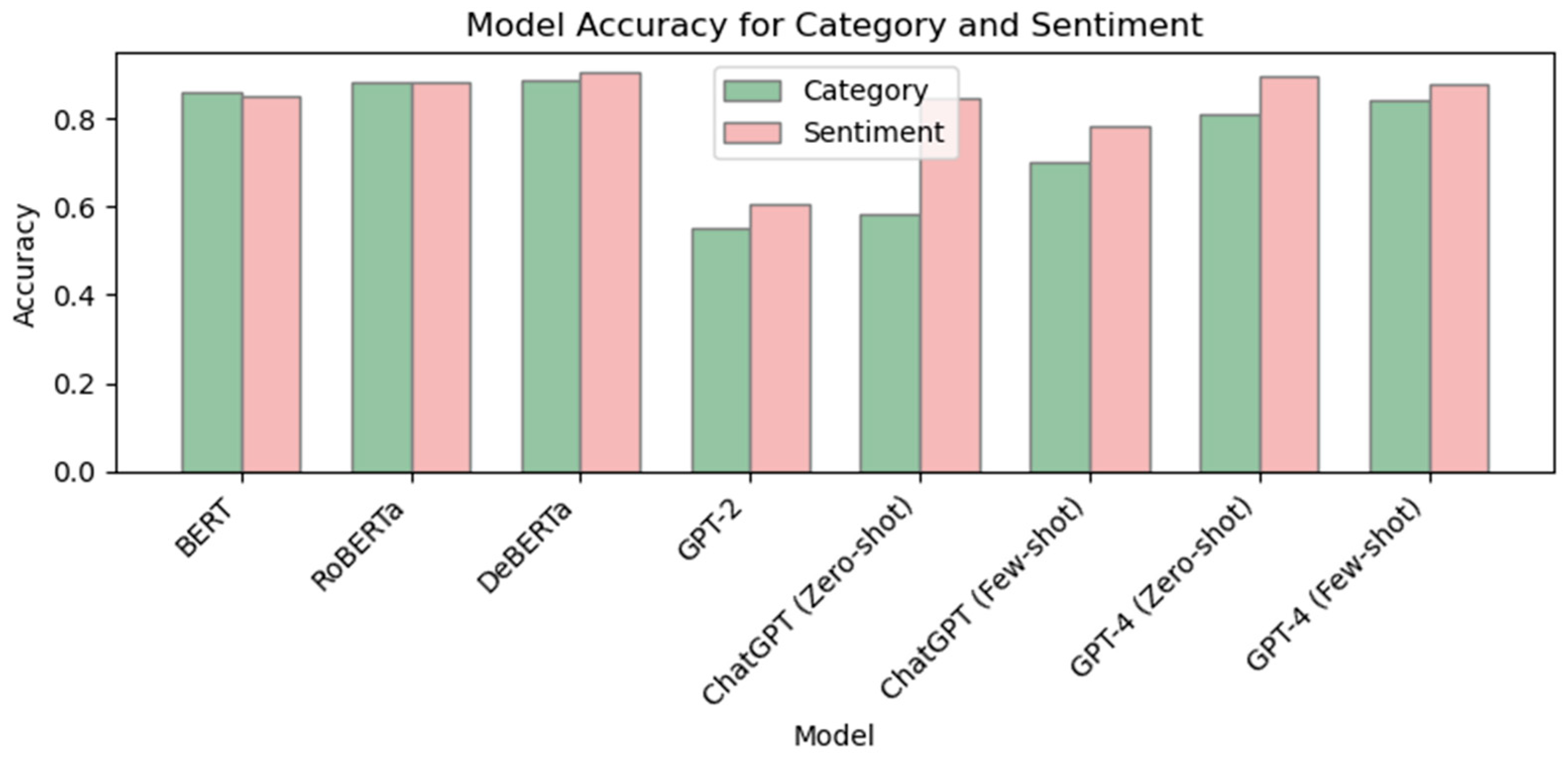
| Model | Accuracy | F1 | Time | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Sentiment | Category | Sentiment | ||
| BERT | 0.860 | 0.849 | 0.861 | 0.835 | 7.34 s |
| RoBERTa | 0.883 | 0.881 | 0.884 | 0.880 | 7.32 s |
| DeBERTa | 0.886 | 0.903 | 0.886 | 0.902 | 7.28 s |
| GPT-2 | 0.552 | 0.608 | 0.507 | 0.537 | 8.07 s |
| ChatGPT (zero-shot) | 0.582 | 0.845 | 0.511 | 0.848 | 335.45 s |
| ChatGPT (few-shot) | 0.703 | 0.780 | 0.678 | 0.787 | 557.66 s |
| GPT-4 (zero-shot) | 0.810 | 0.894 | 0.818 | 0.892 | 545.57 s |
| GPT-4 (few-shot) | 0.840 | 0.879 | 0.842 | 0.883 | 507.02 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Botunac, I.; Brkić Bakarić, M.; Matetić, M. Comparing Fine-Tuning and Prompt Engineering for Multi-Class Classification in Hospitality Review Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6254. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146254
Botunac I, Brkić Bakarić M, Matetić M. Comparing Fine-Tuning and Prompt Engineering for Multi-Class Classification in Hospitality Review Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6254. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146254
Chicago/Turabian StyleBotunac, Ive, Marija Brkić Bakarić, and Maja Matetić. 2024. "Comparing Fine-Tuning and Prompt Engineering for Multi-Class Classification in Hospitality Review Analysis" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6254. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146254
APA StyleBotunac, I., Brkić Bakarić, M., & Matetić, M. (2024). Comparing Fine-Tuning and Prompt Engineering for Multi-Class Classification in Hospitality Review Analysis. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6254. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146254








