A Key Node Mining Method Based on K-Shell and Neighborhood Information
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- KCH adopts a hybrid approach to integrating both global and local information. The KCH method enhances the traditional K-shell approach by incorporating comprehensive network information. It combines structural hole data and the local clustering coefficient—an essential node attribute—with local topological structure information.
- (2)
- The experimental results on connectivity, monotonicity, and null models across ten networks demonstrate that KCH outperforms other K-shell variant methods and non-K-shell variant methods such as collective influence (CI), SC, hierarchical K-shell (HKS). The KCH shows superior accuracy, monotonicity, and universality, effectively identifying the influence of a node within the network.
2. Related Works
2.1. Local Indices
2.2. Global Indices
2.3. Hybrid Methods
3. Proposed Methods
3.1. Baseline Methods
3.1.1. Collective Influence (CI)
3.1.2. Social Capital (SC)
3.1.3. Hierarchical K-Shell (HKS)
3.1.4. K-Shell (KS)
3.1.5. Closeness Centrality (CC)
3.1.6. Extended Coreness Centrality (CNC+)
3.2. KCH Methods
3.2.1. Clustering Coefficient
3.2.2. Structural Hole
3.2.3. KCH
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Metrics
4.2.1. Robustness Metrics
4.2.2. Monotonicity
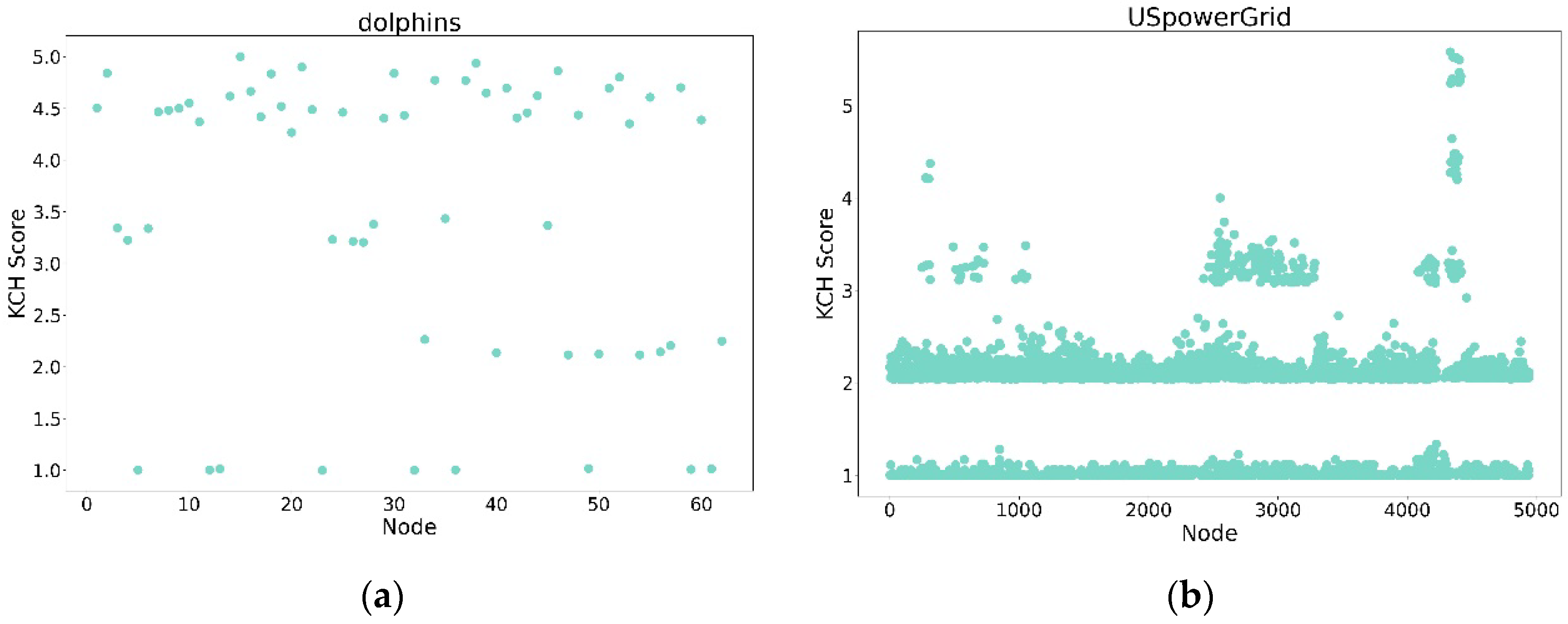
4.3. Performance of KCH
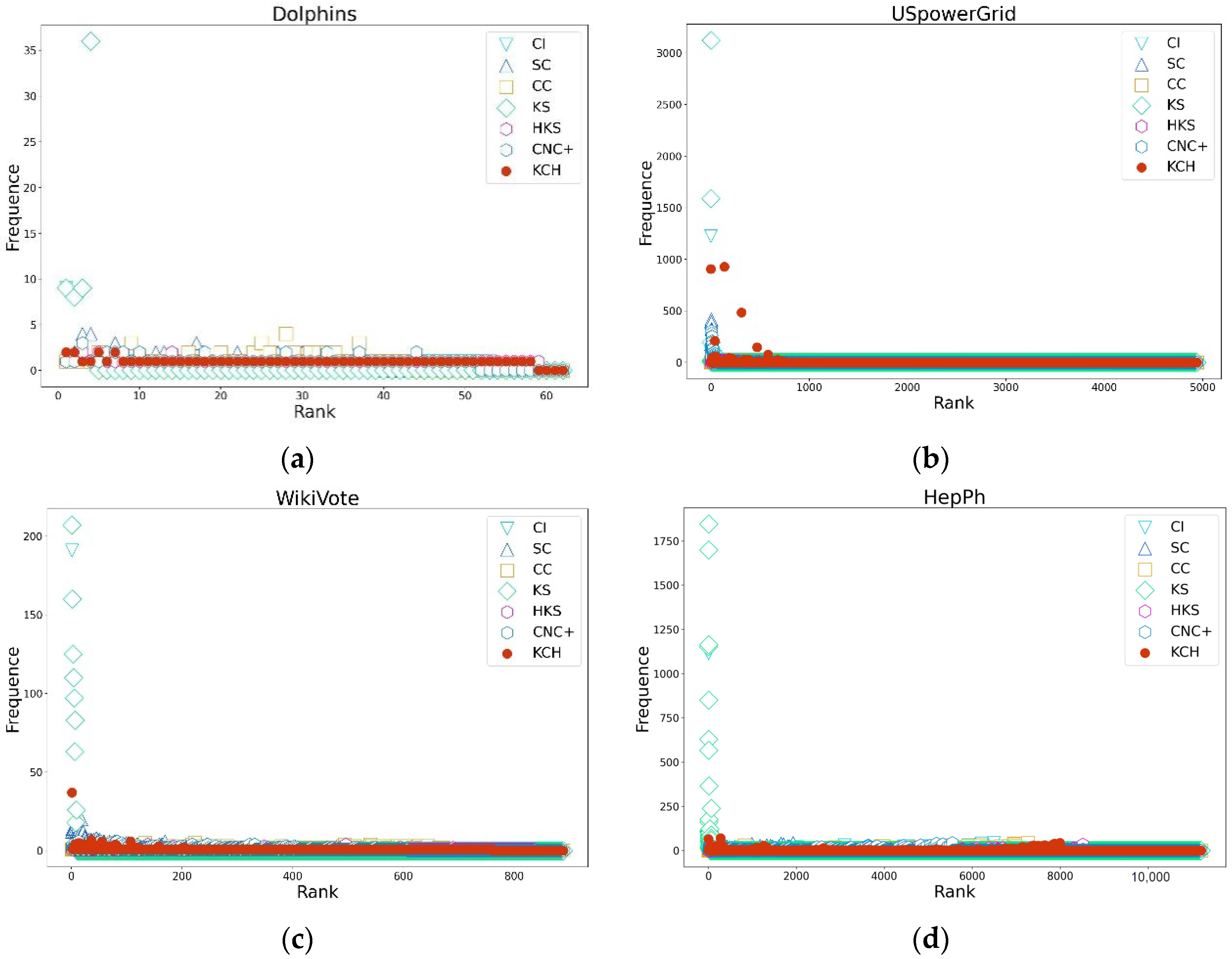
4.3.1. Connectivity Analysis
4.3.2. Monotonicity Analysis
4.3.3. Correlation Analysis
4.3.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Full name |
| DC | Degree centrality |
| SC | Social capital |
| SLC | Semi-local centrality |
| ERM | Entropy-based ranking measure |
| CC | Closeness centrality |
| BC | Betweenness centrality |
| KS | K-shell |
| CNC+ | Extended neighborhood coreness centrality |
| CN | Classified neighbors |
| KSIF | KS-IF |
| MDD | Mixed degree decomposition |
| CI | Collective influence |
| HKS | Hierarchical K-shell |
| LSC | Local structural centrality |
| LGC | Local-and-global centrality |
| IKS | Improved K-shell |
| KSGC | K-shell based on gravity centrality |
| LGM | Local version of GM |
| KS+ | Extended K-shell hybrid method |
| SH | Structural holes |
| LSH | Semi-local centrality and structural holes |
| MLC | Modified local centrality |
| CPU | Central processing unit |
Appendix A


Appendix B
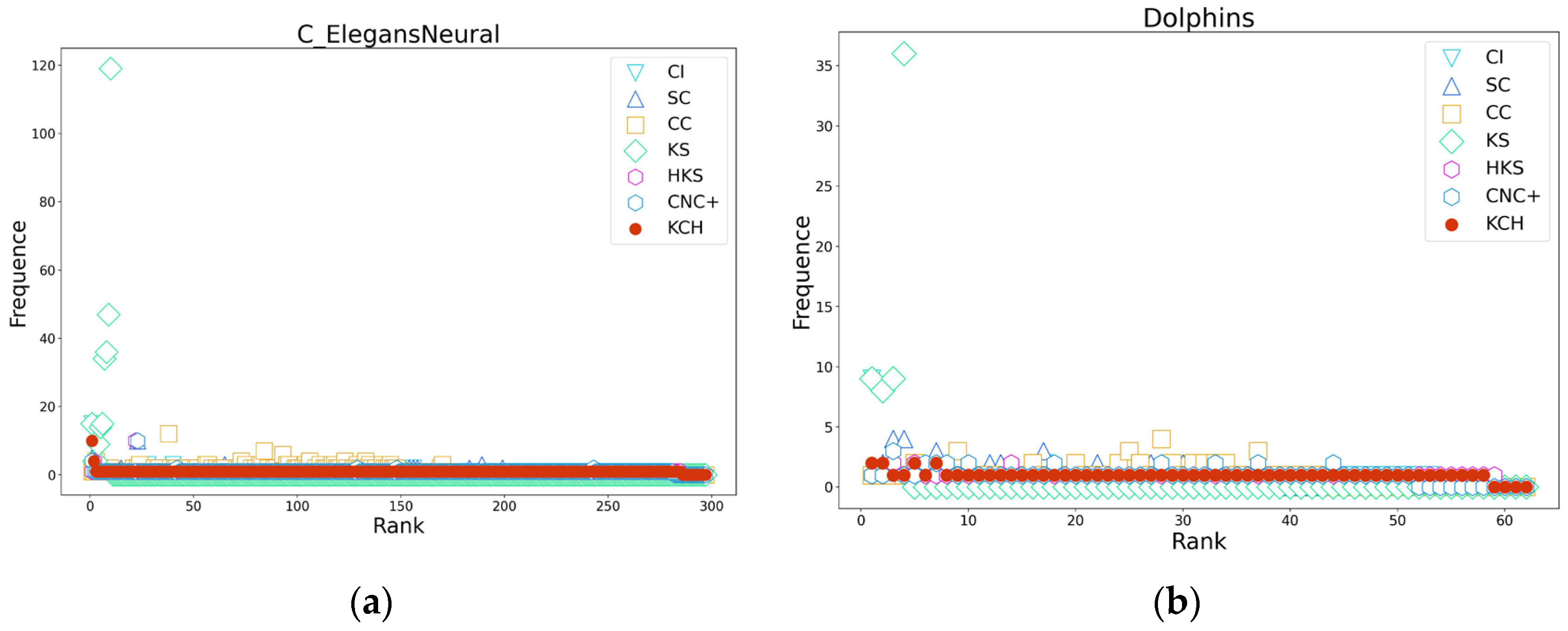

Appendix C


Appendix D
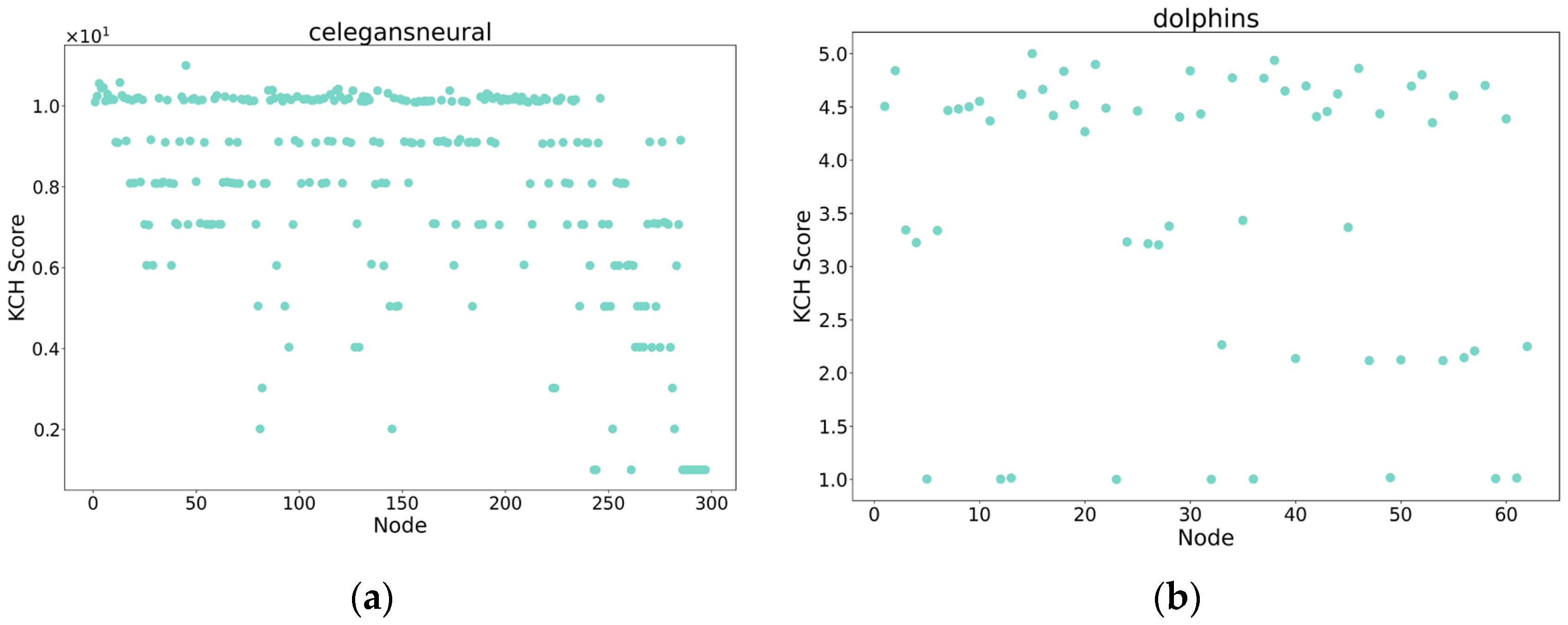

References
- Li, M.; Liu, R.-R.; Lü, L.; Hu, M.-B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.-C. Percolation on Complex Networks: Theory and Application. Phys. Rep. 2021, 907, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Chen, D.-B. Spreading Predictability in Complex Networks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, T. Identifying Significant Edges via Neighborhood Information. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 548, 123877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S.; Wen, J.; Zhao, N. Identifying Key Spreaders in Complex Networks Based on Local Clustering Coefficient and Structural Hole Information. New J. Phys. 2023, 25, 123005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, S.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Estimating the Relative Importance of Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Network Embedding and Gravity Model. J. King Saud. Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 101758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, N. Relatively Important Nodes Mining Algorithm Based on Community Detection and Biased Random Walk with Restart. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2022, 607, 128219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabasi, A.-L. Statistical Mechanics of Complex Networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2001, 74, 47–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.-L.; Albert, R. Emergence of Scaling in Random Networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, N.; Goswami, B.; Rheinwalt, A.; Bookhagen, B.; Hoskins, B.; Kurths, J. Complex Networks Reveal Global Pattern of Extreme-Rainfall Teleconnections. Nature 2019, 566, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, F. The Effective Enhancement of Information in 3D Small-World Networks of Biological Neuronal Cells. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2023, 9, 065019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, K. A Multidimensional Network Link Prediction Algorithm and Its Application for Predicting Social Relationships. J. Comput. Sci. 2021, 53, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Chen, D.; Ren, X.-L.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Zhou, T. Vital Nodes Identification in Complex Networks. Phys. Rep. 2016, 650, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ye, S.; Fiumara, G.; De Meo, P. Influence Nodes Identifying Method via Community-Based Backward Generating Network Framework. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 236–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Fan, N.; Hu, J. Modeling the Spread of Infectious Diseases through Influence Maximization. Optim. Lett. 2022, 16, 1563–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Shen, H.; Meng, Z.; Chang, H.; He, H. Community-Based Influence Maximization for Viral Marketing. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 2137–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Guo, J.; Huang, C.; Wu, W. Community-Based Rumor Blocking Maximization in Social Networks: Algorithms and Analysis. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2020, 840, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yin, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, N. Mining Algorithm of Relatively Important Nodes Based on Edge Importance Greedy Strategy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namtirtha, A.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, B. Weighted Kshell Degree Neighborhood: A New Method for Identifying the Influential Spreaders from a Variety of Complex Network Connectivity Structures. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2020, 139, 112859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, N.; Burt, R.S.; Minor, M.J. Applied Network Analysis: A Methodological Introduction. Proc. Can. J. Sociol./Cah. Can. Sociol. 1985, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Lü, L.; Mariani, M.S. Fast Influencers in Complex Networks. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2019, 74, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lü, L.; Shang, M.-S.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Zhou, T. Identifying Influential Nodes in Complex Networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2012, 391, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Stanley, H.E. The H-Index of a Network Node and Its Relation to Degree and Coreness. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareie, A.; Sheikhahmadi, A.; Fatemi, A. Influential Nodes Ranking in Complex Networks: An Entropy-Based Approach. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2017, 104, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabidussi, G. The Centrality Index of a Graph. Psychometrika 1966, 31, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in Social Networks Conceptual Clarification. Soc. Netw. 1978, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsak, M.; Gallos, L.K.; Havlin, S.; Liljeros, F.; Muchnik, L.; Stanley, H.E.; Makse, H.A. Identification of Influential Spreaders in Complex Networks. Nat. Phys. 2010, 6, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Kim, S. Identifying and Ranking Influential Spreaders in Complex Networks by Neighborhood Coreness. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 395, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Sun, S.; Xia, C. Identification of Influential Spreaders Based on Classified Neighbors in Real-World Complex Networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 320, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xi, J.; Du, C. Fast Ranking Influential Nodes in Complex Networks Using a K-Shell Iteration Factor. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2016, 461, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Zhang, C.-J. Ranking Spreaders by Decomposing Complex Networks. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective Dynamics of ‘Small-World’ Networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namtirtha, A.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, B. Identifying Influential Spreaders in Complex Networks Based on Kshell Hybrid Method. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 499, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, H.; Wen, J.; Li, J.; Jing, M.; Wang, J. Identifying Critical Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Neighborhood Information. New J. Phys. 2023, 25, 083020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Ma, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Xing, C. Ranking the Spreading Ability of Nodes in Complex Networks Based on Local Structure. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 403, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, J.; Burt, R.S. Structural Holes: The Social Structure of Competition. Econ. J. 1994, 104, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, T. Research status and prospect of structural holes identification in social networks. Mod. Comput. 2019, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.S. Structural Holes and Good Ideas. Am. J. Sociol. 2004, 110, 349–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batagelj, V.; Zaversnik, M. An O(m) Algorithm for Cores Decomposition of Networks. arXiv 2003, arXiv:cs/0310049. [Google Scholar]
- Brin, S.; Page, L. The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine. Comput. Netw. ISDN Syst. 1998, 30, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Wang, B.; Sheng, J.; Long, J.; Khan, N.; Sun, Z. Identifying Vital Nodes from Local and Global Perspectives in Complex Networks. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2021, 186, 115778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, Y. Identifying Influential Spreaders in Complex Networks Based on Improved K-Shell Method. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2020, 554, 124229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xiao, F. An Improved Gravity Model to Identify Influential Nodes in Complex Networks Based on K-Shell Method. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 227, 107198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. Research on Node Importance Measurement and Influence Blocking Maximization in Complex Networks. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T. Research on Influence Maximization Based on Semi-Local Centrality and Structural Holes. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, M. Research on Node Influence Measurement and k-Nodes Influence Maximization Problem in Social Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Morone, F.; Makse, H.A. Influence Maximization in Complex Networks through Optimal Percolation. Nature 2015, 524, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareie, A.; Sheikhahmadi, A. A Hierarchical Approach for Influential Node Ranking in Complex Social Networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 93, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Vega-Redondo, F. Structural Holes in Social Networks. J. Econ. Theory 2007, 137, 460–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.M.; Moreira, A.A.; Andrade, J.S.; Havlin, S.; Herrmann, H.J. Mitigation of Malicious Attacks on Networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3838–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J. Ranking Influential Spreaders Based on Both Node K-Shell and Structural Hole. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 260, 110163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Lü, L.; Shi, D.; Zhou, T. Characterizing Cycle Structure in Complex Networks. Commun. Phys. 2021, 4, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, P.; Hubble, C.; Krioukov, D. Orbis: Rescaling Degree Correlations to Generate Annotated Internet Topologies. In Proceedings of the 2007 Conference on Applications, Technologies, Architectures, and Protocols for Computer Communications, Kyoto, Japan, 27–31 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gjoka, M.; Kurant, M.; Markopoulou, A. 2.5K-Graphs: From Sampling to Generation. In Proceedings of the 2013 Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, Turin, Italy, 14–19 April 2013; pp. 1968–1976. [Google Scholar]
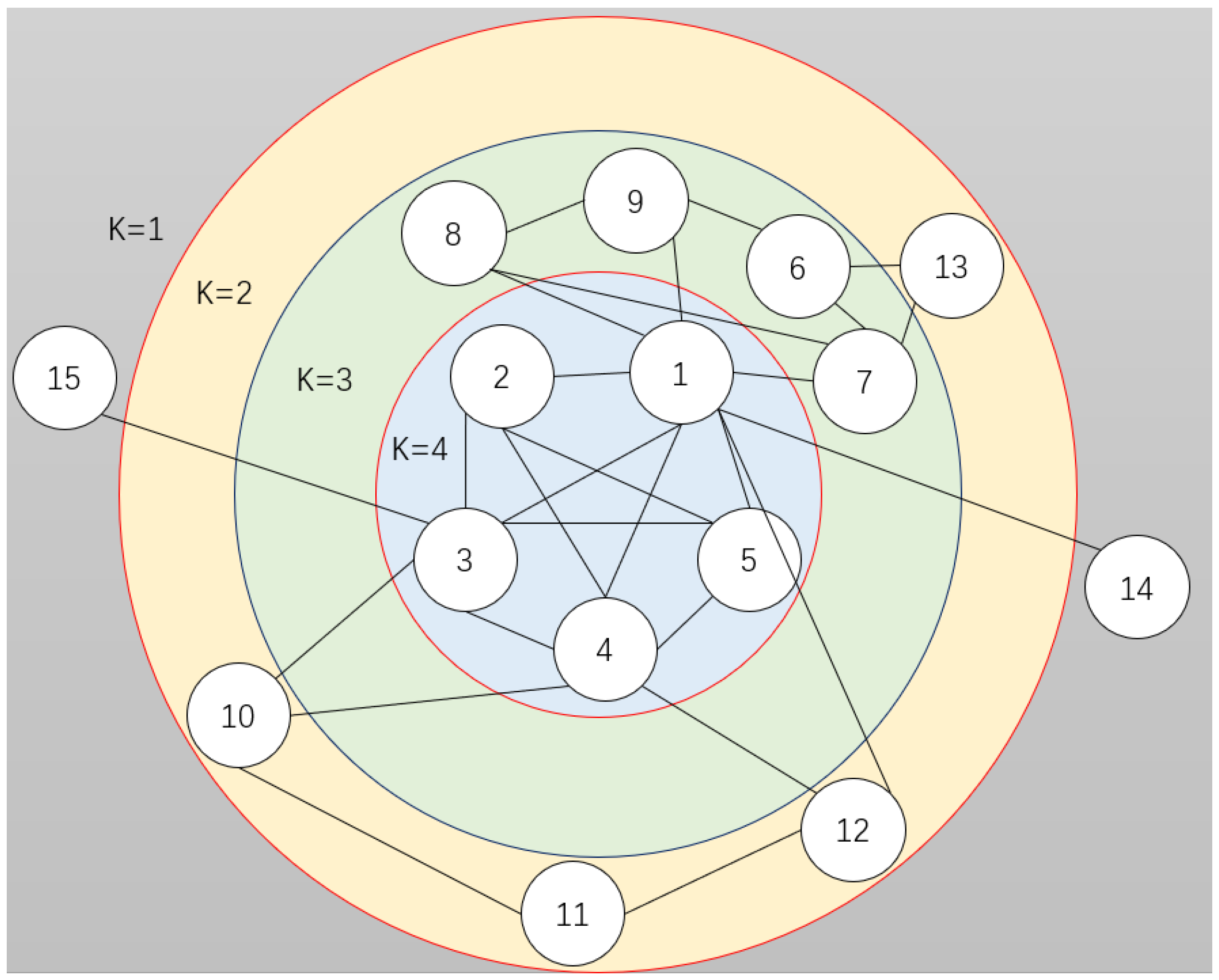



| Node | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| local clustering coefficient | 0.25 | 1 | 0.53 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| network constraint coefficient | 0.2496 | 0.5788 | 0.4179 | 0.5788 | 0.9999 | 0.5000 |
| Networks | N | E | <K> | Kmax | C | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windsurfer | 43 | 336 | 15.63 | 31 | 0.6534 | −0.147 |
| WikiVote | 889 | 2914 | 6.56 | 102 | 0.1528 | −0.0288 |
| USpowerGrid | 4941 | 6594 | 2.67 | 19 | 0.0801 | 0.0035 |
| Tribes | 16 | 58 | 7.25 | 10 | 0.5392 | 0.0499 |
| Seventh | 29 | 250 | 17.24 | 28 | 0.7767 | −0.1575 |
| Rhesus | 16 | 69 | 8.63 | 12 | 0.7085 | −0.1091 |
| HepPh | 11,204 | 117,619 | 19.00 | 491 | 0.6115 | 0.6323 |
| Health | 2539 | 10,455 | 8.24 | 27 | 0.1467 | 0.2513 |
| Dolphins | 62 | 159 | 5.13 | 12 | 0.259 | −0.0436 |
| C_ElegansNeural | 297 | 2148 | 14.46 | 134 | 0.2924 | −0.1632 |
| Networks | KCH | CI | SC | HKS | KS | CC | CNC+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windsurfer | 0.4170 | 0.4191 | 0.4240 | 0.4283 | 0.4294 | 0.4310 | 0.4240 |
| WikiVote | 0.2052 | 0.2188 | 0.2419 | 0.2799 | 0.2200 | 0.2954 | 0.2638 |
| USpowerGrid | 0.0826 | 0.0876 | 0.0915 | 0.1000 | 0.2113 | 0.1973 | 0.1179 |
| Tribes | 0.4219 | 0.4375 | 0.4375 | 0.4414 | 0.4375 | 0.4297 | 0.4375 |
| Seventh | 0.4578 | 0.4602 | 0.4661 | 0.4637 | 0.4649 | 0.4602 | 0.4661 |
| Rhesus | 0.4063 | 0.4141 | 0.4102 | 0.4141 | 0.4375 | 0.4141 | 0.4141 |
| HepPh | 0.2727 | 0.2693 | 0.2868 | 0.3323 | 0.2814 | 0.2851 | 0.3270 |
| Health | 0.4195 | 0.4202 | 0.4281 | 0.4514 | 0.4437 | 0.4353 | 0.4376 |
| Dolphins | 0.2789 | 0.2882 | 0.3184 | 0.3387 | 0.2968 | 0.3699 | 0.3215 |
| C_ElegansNeural | 0.3464 | 0.3480 | 0.3869 | 0.3722 | 0.3902 | 0.3942 | 0.3869 |
| Networks | KCH | CI | SC | HKS | KS | CC | CNC+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windsurfer | 1.0000 | 0.9824 | 0.9956 | 1.0000 | 0.4269 | 0.9454 | 1.0000 |
| WikiVote | 0.9958 | 0.9100 | 0.9887 | 0.9997 | 0.7265 | 0.9988 | 0.9976 |
| USpowerGrid | 0.8417 | 0.8646 | 0.9048 | 0.9963 | 0.2460 | 0.9998 | 0.9419 |
| Tribes | 1.0000 | 0.8867 | 0.9834 | 1.0000 | 0.0156 | 0.7951 | 1.0000 |
| Seventh | 0.9951 | 0.8622 | 0.9902 | 1.0000 | 0.1365 | 0.8622 | 0.9951 |
| Rhesus | 1.0000 | 0.7656 | 0.9669 | 1.0000 | 0.3501 | 0.7656 | 1.0000 |
| HepPh | 0.9994 | 0.9798 | 0.9941 | 0.9998 | 0.8350 | 0.9995 | 0.9991 |
| Health | 0.9997 | 0.9982 | 0.9894 | 0.9999 | 0.5245 | 0.9994 | 0.9979 |
| Dolphins | 0.9958 | 0.9613 | 0.9675 | 0.9968 | 0.3769 | 0.9737 | 0.9873 |
| C_ElegansNeural | 0.9977 | 0.9949 | 0.9955 | 0.9977 | 0.6094 | 0.9893 | 0.9975 |
| Average | 0.9825 | 0.9206 | 0.9776 | 0.9990 | 0.4247 | 0.9329 | 0.9917 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, N.; Feng, Q.; Wang, H.; Jing, M.; Lin, Z.; Wang, J. A Key Node Mining Method Based on K-Shell and Neighborhood Information. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146012
Zhao N, Feng Q, Wang H, Jing M, Lin Z, Wang J. A Key Node Mining Method Based on K-Shell and Neighborhood Information. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146012
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Na, Qingchun Feng, Hao Wang, Ming Jing, Zhiyu Lin, and Jian Wang. 2024. "A Key Node Mining Method Based on K-Shell and Neighborhood Information" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146012
APA StyleZhao, N., Feng, Q., Wang, H., Jing, M., Lin, Z., & Wang, J. (2024). A Key Node Mining Method Based on K-Shell and Neighborhood Information. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146012






